(
A Case Study of Fourth Semester Students in English Teacher
Education Department of Sunan Ampel State Islamic University
)
THESIS
Submitted in partial fulfillment of requirement for the degree of Sarjana
Pendidikan (S.Pd) in Teaching English
By
Siti Maghfirotun Hasaniyah
D05212031
ENGLISH TEACHER EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF EDUCATION AND TEACHER TRAINING
SUNAN AMPEL STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
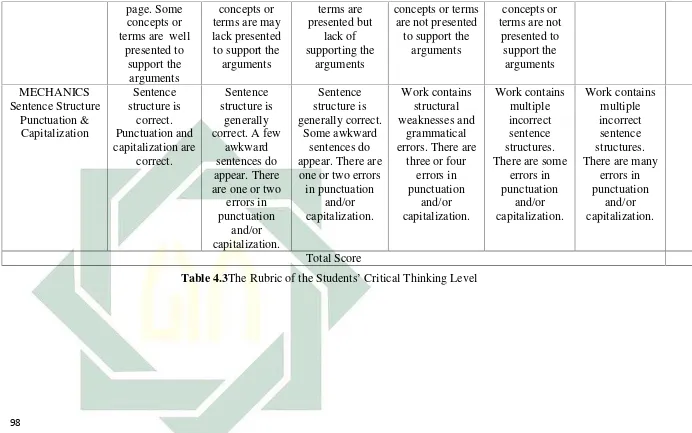
SURABAYA
v
Hasaniyah, Siti Maghfirotun (2017). An Analysis of The Students’ Critical Thinking in Writing Argumentative Essay (A Case Study Of Forth Semester Students In English Teacher Education Progam of Universitas Islam Negeri Sunan Ampel Surabaya, A Thesis English Teacher Education Department, Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teacher Training, Sunan Ampel State Islamic University. Advisor: Dr. Phil. Khoirun Niam
Key Word: Writing, Argumentative Essay, Critical Thinking Level, Critical Thinking Skill
This study was analyzed the students’ critical thinking in writing argumentative
essay in fourth semester students of English teacher education program at UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya. The focus is to know the students’ level and also the way they
apply the critical thinking in their writing. Based on the theory, there are six levels in critical thinking. Those are the unreflective, the challenge, beginning, practicing, advanced, and accomplished thinker. The researcher used qualitative as the design of her research. Data collection technique used in this research was questionnaire and documentation. The questionnaire was to know students’ ability in applying their critical thinking when writing argumentative essay. The documentation use to gain more information about students’ critical thinking and complete the information in the questionnaire test.
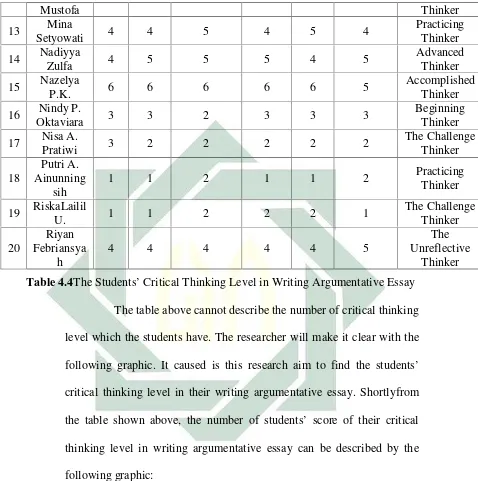
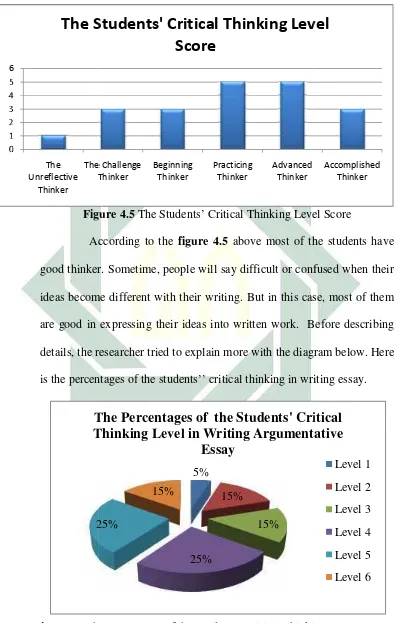
Based on theresult of study, the students’ ability in applying critical thinking is 29% in advanced thinker and practicing thinker, 20% in beginning thinker, 10% in accomplished thinker, 9% in the challenge thinker, and 1% in unreflective thinker,
and the students’ writing is 25% students in practicing and advanced thinker, 15% student in the challenge thinker, beginning thinker, and accomplished thinker, and 5% student in the unreflective thinker, and the last students’ achievement of critical
ADVISOR APPROVAL SHEET……… i
APROVAL SHEET ... ii
MOTTO ... iii
DEDICATION ... iv
ABSTARCT ... v
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... vi
PERNYATAAN KEASLIAN TULISAN ... viii
TABLE OF CONTENT ... ix
LIST OF TABLE ... xi
LIST OF FIGURE... xii
LIST OF APPENDIXES... xiii
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION A. Research Background ... 1
B. Research question ... 7
C. Objective of the Study ... 8
D. Significance of the Study ... 8
E. Scope Limit of the Study ... 8
F. Definition of Key Term ... 9
CHAPTER II: REVIEW RELATED LITERATURE A. Critical Thinking ... 11
1. Critical Thinking Definitions ... 11
2. The Basic Building Blocks of Critical Thinking... 13
3. The Process of Critical Thinking ... 18
4. Assessing Critical Thinking ... 21
5. Critical Thinking Level ... 27
B. Writing ... 39
2. The Criteria A Good Essay Argumentation ... 42
3. The Generic Structure of Argumentative essay ... 43
E. Previous Study ... 44
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODE A. Approach and Research Design ... 46
B. Research Subject ... 47
C. The Data and Sources of The Data ... 48
D. Data Collection Technique ... 49
E. Research Instruments ... 50
F. Research Procedure ... 56
G. The Data Analysis Technique ... 56
H. Research Validity ... 58
CHAPTER IV: FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION A. Findings... 59
B. Discussion ... 116
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A. Conclusion ... 122
B. Suggestion ... 123
This chapter discusses the area of the study that will be covered in some
headings (1) The Background of this Study, (2) Statements of the Problem, (3)
Objectives of this Study, (4) Significance of the Study, (5) Scope and Limitation, (6)
Definitions of Key Terms.
A. Research Background
In this era, critical thinking is important for learners to gain the
challenges of their life. It is not only in education, it is also useful in their social
life. Surely, teachers expected the students be able to think critically. This
cognitive thinking will require them to think critically for taking an idea from the
situation around. They have the basic skill involved critical thinking. It is like
working out whether they believe what they see and what they hear, taking steps
to find out whether something is likely to be true, and arguing our own case if
someone does not believe them. Another basic critical thinking skill that the
students have will help them to live with their society and get better chances in
many cases. Kanik argued that if students are to perform in a highly technical
society, they must be prepared with life-long learning and critical thinking skill is
necessary to obtain and process information in an ever changing world.1Surely,
1
FigenKanik. Doctoral Dissertation.An Assessment Of Teachers’ Conceptions Of Critical ThinkingAnd
the university will be more focused to increase the students that have ability in
this quality.
Essentially, the critical thinking has many purposes in gaining their
circumstances life. One of them will make the learners easier getting high
proficiency of their lesson. They will understand deeply about the lesson because
they create another process in their brain to make the information accepted or
understood by them. For example in every single lesson, when the teachers give
lesson to the students, they will accept and think deeply what is the important and
the purpose of the lesson. It will make them recognize one thing, that this lesson
give them information and new perception about something. If the students
assume this kind of information is good, they will process this continuously.
Conversely, they assume this kind of information is bad for them; it will process
in their thinking in another way.
Critical thinking plays important role in education process. Therefore
the teachers should care of this tool in order make the students easily in
understanding the lesson. Thus, the students’ cognitive thinking will process well
in their brain. This is in line with Wallace that critical thinking skills should be
embedded in the subject matter and woven into language education.2 Since the
critical thinking important for students, it acquire them to think naturally how the
2
information accepted by their brain. It proved by their work or exercise after
whether the students have good critical thinking or not.
At university level, critical thinking skill is essential abilities in using
intellectual tools by which one appropriately assesses thinking. In this case, by
utilizing critical thinking skills, students can use the intellectual tools that critical
thinking offers concepts and principles that enable them to analyze, assess, and
improve thinking. They will be able to work diligently to develop the intellectual
virtues of intellectual integrity, intellectual humility, intellectual civility,
intellectual empathy, intellectual sense of justice and confidence in reason. To
put it briefly, critical thinking skills are self-improvement in thinking through
intellectual tools that assess thinking.3
The critical thinking skill will help them directly in any circumstances
of information in their lesson caused by this cognitive thinking. One of the
important characteristic of critical thinking identified by many sources is
metacognition. Kurfiss argued that underlines three sides of critical thinking.
Those are declarative knowledge (the facts and concepts of the discipline or
field), procedural knowledge (how to reason, inquire, and present knowledge
about the discipline), and metacognition (being able to evaluate the outcomes of
the thinking process).4 Specifically, “Metacognition is being aware of one’s
3
The Critical Thinking Community. 2009.Defining Critical Thinking.
4
thinking as one performs specific tasks and then using this awareness to control
what one is doing”.5 Without this kind of intellectual skill, the view of students
about around them will be none. Occasionally, critical thinking influences people
to process the information that they get. How they can know whether the
information is right or not if cannot process the information in our cognitive
process about what happen around.
Thus, when they write the information in a paper, the critical thinking
skill persuades them to choose the information which they write on their paper.
There are many factors in building their argument in the writing work. The
important factor is covered by their social life. How the environment persuades
their brain to accept the information. It will process to be one of the important
things for them. When their environment is not supporting their brain to process
the information, it will make the teachers difficult to identify the ideas which
wrote by the students in their essay.
The concept of critical thinking increase more general questions about
the nature of knowledge and reasoning. On the one hand, thinking and reasoning
can be seen as a general cognitive processing ability that is readily transferable
across different topics and contexts.6 On the other hand, thinking and reasoning
5
T. A. Al-Sharadgah, Dr., Developing Critical Thinking Skills through Writing in an Internet-Based Environment. International Journal of Humanities and Social Science. Vol. 4 No.1 January 2014.
6
can be seen as highly used in knowledge and disciplinary contexts such that it is
only worthwhile assessing critical thinking as it relates to particular knowledge
areas. Those areas are history of life, definitions about something around,
problem of life, or anything around them.
Assessment of critical thinking at university normally occurs when an
academic analyses a student’s written work on a subject specific topic for
evidence of critical thinking. Occasionally, the teachers will know the students
thinking in their writing work. The teachers are often see written work as an
opportunity to show how much information they acquired about a particular
subject rather than as an opportunity to demonstrate critical thinking thought.
Moreover, it is often difficult for students to judge how much the evidence will
be given to critical thinking with internal or external factors that students have in
written work. This is in line with research from Anderson, Howe, Soden,
Halliday, and Low that specifically analyses students’ argument skills in essays
shows that they rarely use their knowledge in an evaluation or critical thinking
manner.7
Then, this case challenges the teachers as the one guider to make them
show up their skill of critical thinking. However, just because the students can
think critically this does not mean they do it in good way. This is to be expected,
7
as the teacher does not need to employ the same level of critical thinking for
everything they do because each student has different level in writing their
critical thinking on paper. It means there are some students feel difficult in
writing their essay because of many factors. The teachers could not expect all
students has same idea of the information that they have to describe. The
students’ ideas are also could not make the teachers judge the students. Due to
our mind has different cognitive processing or different skill in thinking. It
depends on the teachers’ explanation or the students’ cognitive level. It can also
come from their internal or external factors which makes them not confidence in
their written. Those causes become the teachers’ problem. In addition, the
students has different life that makes them cannot understand each other about
the thing that the teacher meant.
Irregularly, the students confused to describe something on the paper
that actually they have known. For example when the teachers ask to them to
describe the big problem of the university, this problem will make them confused
to choose the case due to many problems happen around which they trust and
entrust. They confused whether their written will be same idea with each other or
not. It means they have not sure with their own written work due to the
differences. They cannot imagine if what they though is negative as well as their
Furthermore, this argumentative essay becomes one text to be observed
due to those causes. Many teachers ask the students to write something with their
own idea without knowing any consequences. Some of teachers think that all
ideas are true but some of them say not. The same context will produce many
kind of information because of this critical thinking. The level of the cognitive
process in their writing will be seen clear enough. Additionally, teachers should
know what the students thinking same as what they are writing on their paper.
Therefore, this thesis will help the teachers. How the students write their
writing argumentative essay by understanding the factors and also those causes
of the students’ life. So based on those causes the researcher will help the
teachers and also reader by thesis entitled: “An Analysis of the Students’ Critical
Thinking in Writing Argumentative Essay of Fourth Semester Student of English
Teacher Training Department at SunanAmpel State Islamic University
Surabaya”.
B. Research Question
Based on the background of study above, this study intended to examine
the question “What is the students’ critical thinking level as appearin their
C. Objective of the Study
Referring to the research questions above, the objectives of this study
proposed research is to know what the students’ critical thinking level as appear
intheir argumentative essay.
D. Significance of the Study
This study is significant:
1. For the teachers: The result of the study can use by the teachers to know
the character of students’ writing and their level of critical thinking and
how to solve the students which have those differences.
2. For the students: The result gives them information to solve their problem
of their character of though and can help them easily in writing showing
their idea in writing.
3. For the readers: the result will give them further information about
students’ critical thinking and the factors in writing argumentative essay
about around.
E. Scope and Limitation
This study focuses on analyzing students’ critical thinking level in
students’ writing skill in argumentative essay. The subjects of the study are the
students in argumentative class of fourth semester in English Teacher Education
year 2016-2017. This study also aimed to know the factors and style of their
critical thinking in writing argumentative essay.
F. Definition of Key Terms
a. Writing
Writing is acombination of process and product of discovering ideas,
putting them on paper on paper and working with them until they are
presented in manner that is polished and comprehensible to readers.8
b. Argumentative essay
Argumentative essay is a genre of writing that requires the student to
investigate a topic; collect, generate, and evaluate evidence; and establish a
position on the topic in a concise manner.9
c. Critical thinking skill
Critical thinking is the intelligently self-controlled skill process of
actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing,
and evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation,
experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to belief and
action.10
8
caroline T. Linse, Practical English Language Teaching: Young Learners, (NY: McGraw Hill, 2006), p.98.
9Purdue Online Writing Lab. Online:https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/685/05/. Retrieved
on April 14th2017.
10H. Masduqi, 2006.Critical Thinking and Meaning.TEFLIN Journal, Vol. 22, No 2. Retrieved: 2 July
d. Critical thinking level
Critical thinking level is a position on a real or imaginary scale of
amount, quality, extent, or quantity where it measures the critical thinking or
an amount of critical thinking where the critical thinking has their own
position in building or creating something.11
11Linda E. & Richard P.,Critical Thinking: Concepts and Tools, (The Foundation for Critical Thinking,
In this chapter, the researcher explicates several theories through reviewing
some literatures related to this study. This theoretical construct deals with some main
areas: the definition of critical thinking, the concept map paragraph and essay, the
good criteria in writing argumentative essay. Furthermore, some previous studies
related to this current study are also discussed here.
A. Critical Thinking
1. Critical Thinking Definition
In university level critical thinking skills are essential abilities in
using intellectual tools by which one appropriately assesses thinking. By
utilizing critical thinking skills, students can use the intellectual tools that
critical thinking offers the concepts and principles that enable them to
analyze.
In the other hand Dewey introduced more recent effects in the critical
thinking show around life. He named critical thinking "reflective thinking"
and described it as "an active, persistent, and careful consideration of a belief
or supposed form of knowledge in the light of the grounds which support it
and the further conclusions to which it tends".1
1
Critical thinking is the intelligently self-controlled process of actively
and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and
evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation,
experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to belief and
action.2 The same line meaning described by Scriven and Richard that it
based on universal intellectual values that excel subject matter divisions:
clarity, accuracy, precision, consistency, relevance, sound evidence, good
reasons, depth, breadth, and fairness.✄
Linda and Richard argued that critical
thinking is the art of analyzing and evaluating thinking with a view to
improving it.4In short, critical thinking is that mode of thinking about any
subject, content, or problem in which the thinker improves the quality of his
or her thinking by skillfully taking charge of the structures inherent in
thinking and imposing intellectual standards upon them.
Another researcher S.P Norris in the Article of Synthesis of research
on Critical Thinking stated that there are nine definitions explained the
critical thinking based on many researches. Those are:5
a. Firstly,critical thinking is a complex of many considerations.
b. Secondly, Critical thinking is an educational idea;
☎
H. Masduqi, 2006.Critical Thinking and Meaning.TEFLIN Journal, Vol. 22, No 2. Retrieved: 2 July 2011. P.186
3
M. Scriven,&P. Richard, (1987).A Statement for the 8th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking and Education Reform,retrieved 13 June 2011.
✆
E.Linda. &P. Richard,Critical Thinking: Concepts and Tools, (The Foundation for Critical Thinking, 2006), 4thEdition. p.4
5
c. Thirdly, Critical thinking is not widespread. The way students in
measuring ability in recognizing assumptions or evaluation do not score
well. They frequently make simple judgmental errors on simple
problem.
d. Fourthly, Critical thinking is sensitive to context.
e. Fifthly, teachers should look for the reasoning behind students’
conclusion.
f. Sixthly, simple errors may signal errors in thinking at a deeper level.
g. Seventhly, having a critical spirit is as important as thinking critically.
h. Eighthly, to think critically one must have knowledge.
i. Ninthly, one is teachers do not know about great deal about the effects
of teaching critical thinking.
2. The Basic Building Blocks of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is self-directed, self-disciplined, self-monitored, and
self-corrective thinking. It requires rigorous standards of excellence and
mindful command of their use. It entails effective communication and
problem solving abilities and a commitment to overcome our native
egocentrism and sociocentrism.6
6E. Linda&P. Richard,Critical Thinking: Concepts and Tools, (The Foundation for Critical Thinking,
Linda & Richard argued that there are some elements of thought in
conception the critical thinking in our brain.7
Elements of thought
Figure2.1The Elements of Though
In another line argued that there are three basics to build the critical
thinking. Those are:8
a. Claims : A statement, true or false, that expresses an opinion or
belief.
b. Issues/question : What is raised when a claim is called into question
c. Argument : A two part structure of claims, one part of which (the
premise or premises) I given as a reason for thinking
the other part (the conclusion is true).
7Linda E. & Richard P.,Critical Thinking: Concepts and Tools, (The Foundation for Critical Thinking,
2006), 4thEdition. p.13 8
In the other hand, the same opinion stated by John and Geoff that the
word that is often used for a piece of reasoning is argument.9 The other
researcher said that arguments are using reasons to support a point of view,
so that known or unknown audiences may be persuaded to agree. An
argument may include disagreement, but it is more simply disagreement if it
is based on reasons.10
Another said Logicians two kind of good arguments: Deductive
argument and a good inductive argument.11 Focus on those arguments, it is
should know by people the distinction between the two is second nature to
the teachers of critical thinking, and it is easy for students and the teachers to
sometimes forget that it is new to many people. In addition, within the past
few pages we have already brought up several new ideas, including critical
thinking, claim, argument, premise, conclusion, issue and more.
a. Deductive Arguments
A good deductive argument is said to be valid. Which means it is not
possible for the premise to be true and the conclusion false.
Example 1 Premise: Rio Lives in Jakarta
Conclusion: Therefore, Rio lives in Indonesia (This is valid argument because it is not possible for Rio to live
in Jakarta and not live in Indonesia)
9J. Butterworth and G. Thwaites, 2011.Thinking Skills. Published: Cambridge University Press. p.7 10
S. Cottrell, 2005.Critical Thinking Skils; Developing an effective analysis and argument. Copyright Licensing Agency, 90 Tottenham Court Road, London W1T 4LP. Published by Palgrave Macmillan. P.52.
11
Example 2 Premise: Rio taller that his girlfriend and his girlfriend is taller than his sister.
Conclusion: Therefore, Rio taller than her sister (This is valid argument too because it is not possible for the
premise to be true and the conclusion to be false)
To put all this differently, the premises of good deductive argument,
assuming they are true prove or demonstrate the conclusion.
b. Inductive Arguments
A good inductive argument does not prove or demonstrate the
conclusion. They support it. It means that assuming they are true, they
raise the probability that the conclusion is true.
Example 1 Premise : Rio Lives in Jakarta
Conclusion : Therefore, Rio uses mosquito repellent.
(It means Rio living in Jakarta makes it probably that he uses mosquito repellent)
Example 1 Premise : People who live in Butte City already spend a lot of time in the sun
Conclusion : Therefore, a tanning salon will not do well there.
(The premise of this argument assuming it is true raises the
probability that the conclusion is true, thus it supports the conclusion)
The more support the premises of an argument provide for a conclusion,
the stronger the argument is said to be.
Stella argued that there are two key terms of argument in critical
thinking. Firstly is contributing arguments. It means individual reasons are
referred to as arguments or contributing arguments. Secondly is the overall
presents the authors’ position. The term line of reasoning is used to refer to a
set of reasons, or contributing arguments, structured to support the overall
argument.12
In the same line, Jim Wohlpart stated that the two features of critical
thinking. Those are:13
a. Overview of an argument:
1) Consciousness of point of view
2) Consciousness of intention and audience
3) Statement of central problem issue
4) Understanding keys ideas
b. Internal elements of an argument
1) Deduction: Consciousness of inferences and assumptions
2) Induction: analysis of information and proof
When you have believed in your writing, you will sure to build up the
writing using your idea of the information tough. Although the common
issue that comes to you is have two answers both true and false. From the
core critical thinking above can conclude that the process of critical thinking
begin form our assumptions about the information. All the complete
conceptualizing in our mind has becoming one circle rule.
12
Further, our thinking have virtues or traits in concepting the
information or the doamin of life. That is:14
The Virtues or Traits of Critical Thinking
Figure 2.2The Virtues or Traits of Critical Thinking
c. The Process of Critical Thinking
Dewey stated that there dimensions of critical thinking are emotional,
social, physical and cognitive.15 This current study focuses on cognitive
process of the students’ critical thinking in their writing argumentative essay.
Then, these Cognitive aspects can divide into five different categories:
Inference, Analysis, Evaluation, Conclusion and Induction. As a process,
critical thinking involves students in recognizing and researching the
14
Linda E. & Richard P.,Critical Thinking: Concepts and Tools, (The Foundation for Critical Thinking, 2006), 4thEdition. p.20
assumptions that undergird their thoughts and actions.16Critical thinking is,
in short, self-directed, self-disciplined, self-monitored, and self-corrective
thinking. It requires rigorous standards of excellence and mindfully
command of their use. It entails effective communication and problem
solving abilities and a commitment to overcome our native egocentrism and
sociocentrism.17
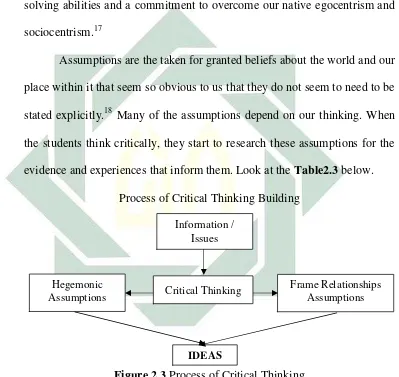
Assumptions are the taken for granted beliefs about the world and our
place within it that seem so obvious to us that they do not seem to need to be
stated explicitly.18 Many of the assumptions depend on our thinking. When
the students think critically, they start to research these assumptions for the
evidence and experiences that inform them. Look at theTable2.3below.
Process of Critical Thinking Building
Figure 2.3Process of Critical Thinking
16
S.D. Brookfield, Developing Critical Thinkers: Challenging Adults to Explore Alternative Ways of Thinking and Acting. San Fransisco: Jossey-Bass, 1987.
17
Linda E. & Richard P.,Critical Thinking: Concepts and Tools, (The Foundation for Critical Thinking, 2006), 4thEdition. P.4
18J. Butterworth and G. Thwaites, 2011.Thinking Skills. p.51
Hegemonic Assumptions
Frame Relationships Assumptions Information /
Issues
Critical Thinking
Based on theTableabove, the purpose of critical thinking tends to be
to scrutinize two particular and interrelated sets of assumptions.19
1) There are assumptions that frame how the students view power
relationships in our lives. Critical thinking entails adult understanding
that the flow of power is a permanent presence in our lives. In our
personal relationships, work activities, and political involvements,
power relations are omnipresent, though often submerged. Uncovering
and questioning these power relations so that people might redirect the
flow of power in a circular or democratic manner is important part of
critical thinking.
2) There are hegemonic assumptions that need to be uncovered.
Hegemonic assumptions are those that the students embrace eagerly
because people think they are in its best interests. Yet perversely these
assumptions actually work against us in the long term and serve the
purpose of those who do not have our best interests in our heart. The
term hegemony applies to the process whereby ideas, structures, and
actions come to be seen by the majority of people as wholly natural,
preordained, and working or their own good when in fact these ideas
constructed and transmitted by powerful minority interests to protect the
status quo that serves these interests so well.
19A. D. Rose, and M. A. Leahy. Assessng Adul Learning in Diverse Settings: Current Issues and
Critical
elements of reas
3)
4)
Figu
d. Assessing Critic
One of t
its assessment.
measurestudent
defined critica
taxonomy (1956
al thinkers routinely apply the intellectual standa
easoning in order to develop intellectual traits.
3)
4)
igure 2.4The Concept of Critical Thinking
itical Thinking
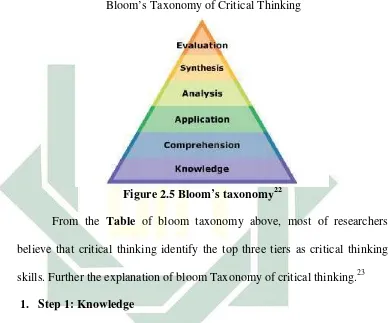
of the most intense discussions about critical thinki
nt. To be sure, standardized tests are available tha
udents’ability to reason in critical manner. Many res
cal thinking in terms of taxonomies, includi
1956). Choy and Cheah found that many believe
The Concept of Critical Thinking
tandards to the
hinking concerns
that purport to
researchers have
uding Bloom’s
three tiers to be
23Bruce R. Reichenbach,
ISBN:0073660272
o be critical thinking “analysis, synthesis, and
emons developed a study to assess students’ cri
ology course using Bloom’s taxonomy, particularl
tion, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation.21
Figure 2.5Bloom’s taxonomy22
the Table of bloom taxonomy above, most of
critical thinking identify the top three tiers as cri
r the explanation of bloom Taxonomy of critical thi
nowledge
of critical thinking, the basic level of acquisition
that you be able to identify what is being said:
h, (2008).Teacher Perceptions of Critical ThinkingAmong cation. International Journal of Teaching and Learning in H
emons, (2006).A New Method for Assessing Critical Th 6, 66-72.
’s Taxonomy.
23 , An Introduction of Critical Thinking, (Mc Graw
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Critical Thinking
issue, the thesis, and the main points.exhibits previously learned
material by recalling facts, terms, basic conceptsand answers. It is same
line by Barbara that Knoeledgw means exhibits previously learned
material by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts and answers.24
2. Step 2: Comprehension
Comprehension means understanding the material read, heard or seen. It
is also demonstrating understanding of facts and ideas by organizing,
comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptions and stating
main ideas.25In comprehending, you make the new knowledge that you
have acquired your own by relating it to what you already know. The
better you are involved with the information, the better you will
comprehend it. As always, the primary test of whether you have
comprehended something is whether you can put what you have read or
heard into your own words. Review some key words that help you
identify when comprehension is called for. Remember that
comprehending something implies that you can go beyond merely
parroting the material back but instead that you can give the material
your own significance.
24
Barbara Fowler, 1996,Bloom Taxonomy and Critical Thinking, Longview Community College.Inquires [email protected]
25A.E.Dreyfuss, J. Jordan, K. Rajaram, (2014) (2nd Ed.). The Work Matters: A guide for new
3. Step 3: Application
Application requires that you know what you have read, heard, or seen,
that you comprehend it, and that you carry out some task to apply what
you comprehend to an actual situation. Review the some tasks that
require application. It will solving the problems by applying acquired
knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way.26
4. Step 4: Analysis
Analysis involves breaking what you read or hear into its component
parts, in order to make clear how the ideas are ordered, related, or
connected to other ideas. Analysis deals with both form and content.
Review how critical thinkers analyze form. Review how critical thinkers
analyze content.
5. Step 5: Synthesis
Synthesis involves the ability to put together the parts you analyzed with
other information to create something original. Review some key words
that help you identify when synthesis is called for.
6. Step 6: Evaluation
Evaluation occurs once we have understood and analyzed what is said or
written and the reasons offered to support it. Then we can appraise this
information in order to decide whether you can give or withhold belief,
26A.E.Dreyfuss, J. Jordan, K. Rajaram, (2014) (2nd Ed.). The Work Matters: A guide for new
and whether or not to take a particular action. Review some key words
that help you identify when synthesis is called for. Never put evaluation
ahead of the other steps in critical thinking steps; otherwise, you will be
guilty of a "rush to judgement." When emotion substitutes for reasons,
evaluation incorrectly precedes analysis.
There are some terms within the definitions of critical thinking that
do not necessarily fit into Bloom’s taxonomy. One of these is creating or
constructing. In their re-creation, they placed “evaluating” with “creating” as
the top level, the skill that was considered to be the highest or most complex
cognitive task. Overbaugh and Schultz argued that the synonyms they used
for this skill were assembling, design, develop, formulate, and construct.
These tasks are similar to:27
a) Judging and evaluating
b) Creating an idea or opinion involves synthesizing information
c) Judging the information that has been collected
d) Forming an opinion based on that evidence.
However, constructing is a cognitive task that goes beyond judging or
evaluating something that is already there. It involves creating something
new.
D, Brookfield challenges the use of standardized assessments of
critical thinking adult learning influenced by the differences of student’s
27
critical thinking in learning. 28Stephen stated that learning to think critically
is an irreducibly social process. It happens best when people enlist the help
of other people to see our ideas and actions in new ways.29 In addition, if
critical thinking is certainly a social process, then it follows that its
assessment should also be a social process involving a multiplicity of
experiences, contributions, and perceptions. These cooperative approaches to
assessing critical thinking based on premised in three assumptions which it
should be subject to constant critical analysis.
a. Critical thinking can be assessed only in specific contexts. It means
studying the dimension of action what the students do as well as what
they say is crucial.
b. Critical thinking can often be best assessed by one’s peers, who function
as critical mirrors. Not only the teachers but also other learners can
provide valuable assessment of one’s developing capacity to question
hegemonic assumptions and imagine democratic alternatives.
c. Assessment of critical thinking should allow learners to document,
demonstrate, and justify their own engagement in critical thinking. In
viewing learning from other outside, the teachers may miss entirely the
critical dimensions of students’ though and practice.
28
J. Willey, & Sons, Inc. 2002.Assessing Adult Learning.Printed in the United States of America. 29
e. Critical Thinking Level
The critical thinking level that the researcher use is written by
Critical Thinking community. They are Linda Elder with Richard Paul. They
defined critical thinking as the ability and disposition to improve one’s
thinking by systematically subjecting it to intellectual self-assessment. On
this view they argued that persons are critical thinkers, in the fullest sense of
the term, only if they display this ability and disposition in all, or most, of
the dimensions of their lives. They exclude from their concept of the critical
thinker those who think critically in only one dimension of their lives. It
caused by the quality of one’s life is dependent upon high quality reasoning
in all domains of one’s life, not simply in one dimension. The stages are:30
a. The unreflective thinker
Defining features: largely unaware of the determining role that thinking
is playing in their lives. Unreflective thinkers lack the ability to
explicitly assess their thinking and improve it thereby.
Skill in Thinking: Unreflective thinkers may have developed a variety
of skills in thinking without being aware of them. Prejudices and
misconceptions often undermine the quality of thought of the
unreflective thinker.
30Linda E. & Richard P.,Critical Thinking: Concepts and Tools, (The Foundation for Critical Thinking,
Some Implications for Instruction: in the present mode of instruction
it is perfectly possible for students to graduate from high school, or even
college, and still be largely unreflective thinkers. Though all students
think, most students are largely unaware of how their thinking is
structured or how to assess or improve it. Thus when they experience
problems in thinking, they lack the skills to identify and “fix” these
problems. Most teachers do not seem to be aware of how unaware most
students are of their thinking. Little is being done at present to help
students "discover" their thinking. This emphasis needs shifting.
b. The Challenge Thinker
Defining Features:Thinkers move to the “challenged” stage when they
become initially aware of the determining role that thinking is playing in
their lives, and of the fact that problems in their thinking are causing
them serious and significant problems.
Principal Challenge: To become initially aware of the determining role
of thinking in one’s life and of basic problems that come from poor
thinking.
Knowledge of Thinking: Challenged thinkers, unlike unreflective
thinkers are becoming aware of thinking as such. They are becoming
aware, at some level, that high quality thinking requires deliberate
reflective thinking about thinking (in order to improve thinking). They
to identify many of these flaws. Challenged thinkers may develop an
initial awareness of thinking as involving concepts, assumptions,
inferences, implications, points of view, etc., and as involving standards
for the assessment of thinking: clarity, accuracy, precision, relevance,
logicalness, etc., though they have only an initial grasp of these
standards and what it would take to internalize them. Challenged
thinkers also develop some understanding of the role of self-deception
in thinking, though their understanding is limited. At this stage the
thinker develops some reflective awareness of how thinking operates for
good or ill.
Skill in Thinking: Most challenged thinkers have very limited skills in
thinking. However like unreflective thinkers, they may have developed a
variety of skills in thinking without being aware of them and these skills
may (ironically) serve as barriers to development. At this stage thinkers
with some implicit critical thinking abilities may more easily deceive
themselves into believing that their thinking is better than it actually is,
making it more difficult to recognize the problems inherent in poor
thinking. To accept the challenge at this level requires that thinkers gain
insight into the fact that whatever intellectual skills they have are
Relevant Intellectual Trait: The fundamental intellectual trait at this
stage is intellectual humility, in order to see that problems are inherent
in one’s thinking.
Some Implications for Instruction: The importance of challenging our
students in a supportive way to recognize both that they are thinkers and
that their thinking often goes awry. We must lead class discussions
about thinking. We must explicitly model thinking (e.g., thinking aloud
through a problem).
c. Beginning Thinker
Defining Feature: Those who move to the beginning thinker stage are
actively taking up the challenge to begin to take explicit command of
their thinking across multiple domains of their lives. Thinkers at this
stage recognize that they have basic problems in their thinking and make
initial attempts to better understand how they can take charge of and
improve it.
Principal Challenge:To begin to see the importance of developing as a
thinker and to begin to seek ways to develop as a thinker and to make an
intellectual commitment to that end.
Knowledge of Thinking: Beginning thinkers, unlike challenged
thinkers are becoming aware not only of thinking as such, but also of the
role in thinking of concepts, assumptions, inferences, implications,
of recognizing not only that there are standards for the assessment of
thinking: clarity, accuracy, precision, relevance, logicalness, etc., but
also that one needs to internalize them and thus begin using them
deliberately in thinking. They have a beginning understanding of the
role of egocentric thinking in human life.
Skill in Thinking: Beginning thinkers are able to appreciate a critique
of their powers of thought. Beginning thinkers have enough skill in
thinking to begin to monitor their own thoughts, though as “beginners”
they are sporadic in that monitoring. They are beginning to recognize
egocentric thinking in themselves and others.
Relevant Intellectual Traits: The key intellectual trait required at this
stage is some degree of intellectual humility in beginning to recognize
the problems inherent in thinking. In addition, thinkers must have some
degree of intellectual confidence in reason, a trait which provides the
impetus to take up the challenge and begin the process of active
development as critical thinkers, despite limited understanding of what
it means to do high quality reasoning.
Some Implications for Instruction: Once we have persuaded most of
our students that much of their thinking left to itself is flawed and that
they, like all of us, are capable of improving as thinkers, we must teach
in such a way as to help them to see that we all need to regularly
sporting analogies and analogies from other skill areas. Most students
already know that you can get good in a sport only if you regularly
practice.
d. Practicing Thinker
Defining Feature:Thinkers at this stage have a sense of the habits they
need to develop to take charge of their thinking. They not only
recognize that problems exist in their thinking, but they also recognize
the need to attack these problems globally and systematically. Based on
their sense of the need to practice regularly, they are actively analyzing
their thinking in a number of domains. However, since practicing
thinkers are only beginning to approach the improvement of their
thinking in a systematic way, they still have limited insight into deeper
levels of thought, and thus into deeper levels of the problems embedded
in thinking.
Principal Challenge: To begin to develop awareness of the need for
systematic practice in thinking.
Knowledge of Thinking: Practicing thinkers, unlike beginning thinkers
are becoming knowledgeable of what it would take to systematically
monitor the role in their thinking of concepts, assumptions, inferences,
implications, points of view, etc. Practicing thinkers are also becoming
knowledgeable of what it would take to regularly assess their thinking
thinkers recognize the need for systematical critical thinking and deep
internalization into habits. They clearly recognize the natural tendency
of the human mind to engage in egocentric thinking and self-deception.
Skill in Thinking: Practicing thinkers have enough skill in thinking to
critique their own plan for systematic practice, and to construct a
realistic critique of their powers of thought. Furthermore, practicing
thinkers have enough skill to begin to regularly monitor their own
thoughts. Thus they can effectively articulate the strengths and
weaknesses in their thinking. Practicing thinkers can often recognize
their own egocentric thinking as well as egocentric thinking on the part
of others. Furthermore practicing thinkers actively monitor their
thinking to eliminate egocentric thinking, although they are often
unsuccessful.
Relevant Intellectual Traits: The key intellectual trait required to
move to this stage is intellectual perseverance. This characteristic
provides the impetus for developing a realistic plan for systematic
practice (with a view to taking greater command of one’s thinking).
Furthermore, thinkers at this stage have the intellectual humility
required to realize that thinking in all the domains of their lives must be
subject to scrutiny, as they begin to approach the improvement of their
Some Implications for Instruction:Teachers must teach in such a way
that students come to understand the power in knowing that whenever
humans reason, they have no choice but to use certain predictable
structures of thought: that thinking is inevitably driven by the questions,
that we seek answers to questions for some purpose, that to answer
questions, we need information, that to use information we must
interpret it (i.e., by making inferences), and that our inferences, in turn,
are based on assumptions, and have implications, all of which involves
ideas or concepts within some point of view. We must teach in such a
way as to require students to regularly deal explicitly with these
structures (more on these structure presently).
e. The Advanced Thinker
Defining Feature: Thinkers at this stage have now established good
habits of thought which are “paying off.” Based on these habits,
advanced thinkers not only actively analyze their thinking in all the
significant domains of their lives, but also have significant insight into
problems at deeper levels of thought. While advanced thinkers are able
to think well across the important dimensions of their lives, they are not
yet able to think at a consistently high level across all of these
dimensions. Advanced thinkers have good general command over their
egocentric nature. They continually strive to be fair-minded. Of course,
Principal Challenge: To begin to develop depth of understanding not
only of the need for systematic practice in thinking, but also insight into
deep levels of problems in thought: consistent recognition, for example,
of egocentric and sociocentric thought in one’s thinking, ability to
identify areas of significant ignorance and prejudice, and ability to
actually develop new fundamental habits of thought based on deep
values to which one has committed oneself.
Knowledge of Thinking: Advanced thinkers are actively and
successfully engaged in systematically monitoring the role in their
thinking of concepts, assumptions, inferences, implications, points of
view, etc., and hence have excellent knowledge of that enterprise.
Advanced thinkers are also knowledgeable of what it takes to regularly
assess their thinking for clarity, accuracy, precision, relevance,
logicalness, etc. Advanced thinkers value the deep and systematic
internalization of critical thinking into their daily habits. Advanced
thinkers have keen insight into the role of egocentrism and
sociocentrism in thinking, as well as the relationship between thoughts,
feelings and desires.
Skill in Thinking:Advanced thinkers regularly critique their own plan
for systematic practice, and improve it thereby. Practicing thinkers
regularly monitor their own thoughts. They insightfully articulate the
knowledge of the qualities of their thinking. Advanced thinkers are
consistently able to identify when their thinking is driven by their native
egocentrism; and they effectively use a number of strategies to reduce
the power of their egocentric thoughts.
Relevant Intellectual Traits: The key intellectual trait required at this
stage is a high degree of intellectual humility in recognizing egocentric
and sociocentric thought in one’s life as well as areas of significant
ignorance and prejudice. In addition the thinker at this level needs: a)
the intellectual insight and perseverance to actually develop new
fundamental habits of thought based on deep values to which one has
committed oneself, b) the intellectual integrity to recognize areas of
inconsistency and contradiction in one’s life, c) the intellectual empathy
necessary to put oneself in the place of others in order to genuinely
understand them, d) the intellectual courage to face and fairly address
ideas, beliefs, or viewpoints toward which one has strong negative
emotions, e) the fair-mindedness necessary to approach all viewpoints
without prejudice, without reference to one’s own feelings or vested
interests. In the advanced thinker these traits are emerging, but may not
be manifested at the highest level or in the deepest dimensions of
f. The Accomplished Thinker
Defining Feature: Accomplished thinkers not only have systematically
taken charge of their thinking, but are also continually monitoring,
revising, and re-thinking strategies for continual improvement of their
thinking. They have deeply internalized the basic skills of thought, so
that critical thinking is, for them, both conscious and highly intuitive.
Principal Challenge: To make the highest levels of critical thinking
intuitive in every domain of one’s life, to internalize highly effective
critical thinking in an interdisciplinary and practical way.
Knowledge of Thinking: Accomplished thinkers are not only actively
and successfully engaged in systematically monitoring the role in their
thinking of concepts, assumptions, inferences, implications, points of
view, etc., but are also regularly improving that practice. Accomplished
thinkers have not only a high degree of knowledge of thinking, but a
high degree of practical insight as well. Accomplished thinkers
intuitively assess their thinking for clarity, accuracy, precision,
relevance, logicalness, etc.
Skill in Thinking: Accomplished thinkers regularly, effectively, and
insightfully critique their own use of thinking in their lives, and improve
it thereby. Accomplished thinkers consistently monitor their own
thoughts. They effectively and insightfully articulate the strengths and
of their thinking is outstanding. Although, as humans they know they
will always be fallible (because they must always battle their
egocentrism, to some extent), they consistently perform effectively in
every domain of their lives.
Relevant Intellectual Traits: Naturally inherent in master thinkers are
all the essential intellectual characteristics, deeply integrated.
Accomplished thinkers have a high degree of intellectual humility,
intellectual integrity, intellectual perseverance, intellectual courage,
intellectual empathy, intellectual autonomy, intellectual responsibility
and fair-mindedness. Egocentric and sociocentric thought is quite
uncommon in the accomplished thinker, especially with respect to
matters of importance. There is a high degree of integration of basic
values, beliefs, desires, emotions, and action.
Some implications for Instruction: For the foreseeable future the vast
majority of our students will never become accomplished thinkers any
more than most high school basketball players will develop the skills or
abilities of a professional basketball player or student writers the writing
skills of a published novelist. Nevertheless, it is important that they
learn what it would be to become an accomplished thinker. It is
important that they see it as a real possibility, if practicing skills of
thinking becomes a characteristic of how they use their minds day to
B. Writing
a) Writing Definitions
Writing is one of language skills and productive skill that be learnt by
students in school. Students will be able to express their ideas and feeling by
English writing. It can be used to maintain thoughts, ideas, and speech
sounds. Writing is a combination of process and product of discovering
ideas, putting them on paper and working with them until they are presented
in manner that is polished and comprehensible to readers.31 Thus, it is be
stated writing is one of language skills which combine to process and
productive skill that can be used preserve thought, ideas, and speech sounds.
C. Essay Writing
a) Definition of essay writing
Essay writing has different meaning of paragraph. It consists of more
paragraph and more clear explanation. This kind of text is one of the
student’s ideas to make their writing be more logical by readers. Setiawan
argued that essay writing is the expectation of the reader to write and extend
a topic more extensively or complex, it must convey it into essay form, in
which a kind of writing that consists of more than one paragraph.32There are
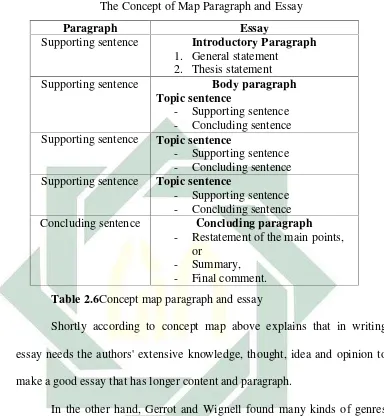
differences both of paragraph and essay writing. Look at table below.
31
Caroline, T. Linse,Practical English Language Teaching: Young Learners, (NY: McGraw Hill, 2006), p.98.
The Concept of Map Paragraph and Essay
Paragraph Essay
Supporting sentence Introductory Paragraph
1. General statement 2. Thesis statement
Supporting sentence Body paragraph
Topic sentence
- Supporting sentence - Concluding sentence Supporting sentence Topic sentence
- Supporting sentence - Concluding sentence Supporting sentence Topic sentence
- Supporting sentence - Concluding sentence Concluding sentence Concluding paragraph
- Restatement of the main points, or
- Summary, - Final comment.
Table 2.6Concept map paragraph and essay
Shortly according to concept map above explains that in writing
essay needs the authors' extensive knowledge, thought, idea and opinion to
make a good essay that has longer content and paragraph.
In the other hand, Gerrot and Wignell found many kinds of genres
(text type). They are: Those are spoof, recount, report, analytic exposition,
narrative, description, hortatory exposition, explanation, reviews, discussion,
procedure, news item.33
Another researcher said that there are three kind of writing such letter
writing, essay writing and creative writing. Then Alabi stated clear in her
33
book that in English language, there are four types. Those are narrative,
descriptive, expository and argumentative essays.34This study only concerns
of argumentative essay, in which college use. Further, only argumentative
writing focus of students logical thinking which makes them think critically
in their writing by expressing their idea, feeling, and though.
D. Argumentative essay
a) Definitions of argumentative essay
Argumentative essay is other types of essay writing and it is
concerned with the reasoning ability of the writer to present an issue
logically with an overriding view.35 In this kind of writing, the authors are
not only gives information but also present an argument with the PROS
(supporting ideas) and CONS (opposing ideas) of an argumentative issue.36
The argumentative essay is also called a genre of writing that requires the
student to investigate a topic; collect, generate, and evaluate evidence; and
establish a position on the topic in a concise manner.37 According to the
meanings above, it is stated that argumentative essay is an essay that requires
the writer or the author to convey their thinking in deep understanding and
extensive knowledge by considering the evidence or supporting ideas to
34
V.A.Alabi-Babatunde. The Use of English in Higher Education (Nigeria, Ilorin University Press, 1998), 172.
35V.A.Alabi-Babatunde.The Use of English in Higher Education. 175. 36
OyaOzagac,Argumentative Essay, ( www.buowl.boun.edu.tr, acessed on September 2004) 37
make the reader believe about the writers' argument. Therefore, in producing
a good argumentative essay the author must have extensive knowledge, good
ideas, deep thought and opinion about what they want to write.
b) The Criteria A Good Essay Argumentation
Recently, The Educational Testing Service revamped the infamous
Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT), which many universities use when
determining whether to admit an applicant. This change shows the
importance the educators place on the ability to write this type of essay. That
is because writing an argumentative essay is doing nothing other than
thinking critically and leaving a paper trail for others to follow. Occasionally
the teachers who have retired the students’ essay because they could not bear
to read another students’ essay. As a result, the students offer their two
moments’ substance here in hope of continuing to see familiar faces.
Generally, essay should have four components.38 Those are a
statement of the issue, a statement of one’s position on that issue, arguments
that support one’s position and rebuttals of arguments that support contrary
position. According Chris Endy there are three specific qualities in writing
good argumentation in essay. Those are Precision in argument and use of
terms, grounding in evidence, clarity and concision in prose.39
38
B.N. Moore & R. Parker, 2008. Critical Thinking-9thedition..p.87. 39
c) The Generic Structure of Argumentative essay
The students should master the generic structure of writing
argumentative essay before they are writing it. The structure of
argumentative essay follows some particular stages, the beginning, middle,
and the last part of the text. Each text has own generic structure. There are
three possible organization patterns.
The Concept Map Organization Pattern of Argumentative Essay
Figure 2.7Concept Map Organization Pattern of Argumentative Essay
Note: PROS is supporting ideas and CONS is opposing ideas
Pattern 1:
Thesis statement: PRO idea 1 PRO idea 2
CONS(s) + Refutation(s) Conclusion
Pattern 2:
Thesis statement:
CON(s) + Refutation(s) PRO idea 1
PRO idea 2 Conclusion
Pattern 3:
Thesis statement:
1. Previous Studies
This section discus about the previous study related to the researcher’s
topic “The Students’ Critical Thinking in Writing argumentative essay” and the
researcher will explain what the differences between study and the previous
study.
The first study by RirinKhoridah(2014) entitled “Efektifitas Model
Pembelajaran Critical Thinking
dalamMeningkatkanPemahamanSiswapadaBidangStudi PAI SMP Unggulan Al
FalahSiwalanpanjiBuduranSidoarjo”. Her research analyzed the
implementation of critical thinking method in learning, the strategies that used
to improve undersatdning, and the effectiveness critical thinking method in
improving students’ understanding.
The second study by NiswatulHasanah(2012) entitled
“EfektifitasPenerapan Model PembelajaranBerbasis Deep Dialogue/Critical
Thinking (DD/CT) TerhadapPrestasiBelajarSiswaKelas VIII B pada Mata
Pelajaran PAI di SMP Negeri 2 TanggulanginKabupatenSidoarjo”. She
analyzed the implementation of Deep Dialogue/ crtical thinking method in
learning. The purpose is improving students’ achievement using the method. It
proved that this study use new method in the class that did not use before.
The third study is written by Istiharoh (2015) entitled “The Students`
Ability to Think Critically on Critical Reading Class At English Teacher
State Islamic University SunanAmpel Surabaya 2015”. A thesis is in English
Education Department of Faculty of Education and Teacher Training. She is
the student from SunanAmpel State Islamic University Surabaya in 2015. The
result of the study is the students’ ability in their critical thinking developed
by the activity which created by the writer. Shortly, it is meant the writer
assumed the students in the reading class have less critical thinking ability
before. So that case, this writer tried to make the students engaged to think
critically in reading class.
This study concerned on how the students’ critical thinking level in
their writing of argumentative essay and their ability when writes the
argumentative essay using their own ideas or their own knowledge. The case
study is in the fourth semester where the argumentative essay tough by the
teacher. This study is on descriptive qualitative method to observe the factual
case in reality. For technical collecting data the researcher used instrument to
get the data they are questionnaire, and documentation that gave to 40students
as the sample from 87 students as population of fourth semester students of
This chapter will concern on the methodology and the procedure to develop
the study. On the research method, the researcher tries to conduct the validity and
reliability research by its method and its analysis. The subtitles of this chapter are
research design, subject of the study, the data and source of data, data collection
technique, research instruments, research procedure, data analysis technique and
research validity.
A. Approach and Research Design
The method of research is the common strategy that is used by research to
get and collect the data needed in order to answer the research
problems.1Considering the goal, this study is included as qualitative descriptive
design since it tries to describe a phenomenon of language behavior. In addition,
one of the characteristics of qualitative study is the natural setting since its goal is
to describe social phenomenon as it occurs naturally without manipulation.
The researcher tried to observe the research by defining the qualitative
research as the research that investigates the quality of relationships, activities,
situations, materials. It focuses on understanding the context and attempts to
explain the intentionality of behaviors.2
1
ArifFurqon.” PengantarPenelitianDalamPendidikan”. Translated from DonalAry. (Yogyakarta :PustakaPelajar, 2011), p.39.
2