ENGLISH DEPARTMENTS
STUDENTS’ PERSPECTIV
ES TOWARD THE
ROLE OF FIRST LANGUAGE IN THEIR GUIDED WRITING
THESIS
Submitted in Partial Fulfillment Of the Requirements for the Degree of
Sarjana Pendidikan
Finna Kristiningrum
112009047
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF LANGUAGE AND LITERATURE
SATYA WACANA CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY
ENGLISH DEPARTMENTS
STUDENTS’ PERSPECTIV
ES TOWARD
THE ROLE OF FIRST LANGUAGE IN THEIR GUIDED WRITING
THESIS
Submitted in Partial Fulfillment Of the Requirements for the Degree of
Sarjana Pendidikan
Finna Kristiningrum
112009047
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF LANGUAGE AND LITERATURE
SATYA WACANA CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY
COPYRIGHT STATEMENT
This thesis contains no such material as has been submitted for examination in any course or accepted for the fulfillment of any degree or diploma in any university. To the best of my knowledge and my belief, this contains no material previously published or written by any other person except where due reference is made in the text.
Copyright@ 2013 FinnaKristiningrum and Dra. Martha Nandari, M.A
All rights reserved. No part of this thesis may be reproduced by any means without the permission of at least one of the copyright owners or the English Department, Faculty of Language and Literature, SatyaWacana University, Salatiga.
TABLE OF CONTENTS B. First Language and Second Language Acquisition 5
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT STUDENTS’ PERSPECTIVES TOWARD THE ROLE caused errors in L2 learning. However, L1 use was still questionable whether beginner learners needed their L1 to support L2 learning. Inspired by the pros and cons, this
study was held to explore English Department students’ perspectives toward the role of
L1 in their guided writing. There were 15 English Department students of Satya Wacana University who have passed guided writing course. They were chosen randomly and they were interviewed using unstructured interview method. The finding
showed students’ positive responses toward L1 use. They used their L1 to generate
idea, help vocabulary learning, develop content on a certain topic, and improve the quality of writing creatively. Despite the positive roles, the students often made grammatical errors due to L1 use.
Keywords :first language, language transfer, positives roles, negative roles
INTRODUCTION
Reflecting on the complexity of L2 writing, as EFL beginner learners who set English as their foreign language in their environment, guided writing’s students may find many difficulties in the foreign language writing such as constructing grammar, getting some ideas, arranging well-formed paragraph, and so on. Therefore, they tend to transfer directly their first language to foreign language, whereas language transfer can cause positive and negative transfer (Xia, 2008).
Based on the writer’s experience in Guided writing class, the writer experienced
that foreign language writing was difficult. The writer often used L1 to compose the ideas before writing. At that time, the writer brainstormed ideas using Indonesian; my first language before writing in English. Even, the writer wrote the ideas in Indonesian first and then translated it to English. From that example, the role of first language was to help get the input when the writer thinks about some ideas before writing in L2. However, the writer was not aware that translating directly from first language caused an error. After the writer had been studying English structure in deep manner, the writer realized factors that caused error in L2 writing.
process. Knowing the fact that L1 gives significant influences to L2 writing, the writer is eager to reveal the validity of that theory in my study whether L1 gives the same effect on guided writing students.
However, the belief is that if the learners use their first language, it will be a hindrance in L2 learning due to transferring from the first language. This idea is strengthened by Krashen (1988) who claimed, “First language is several sources error in target language performance” (p.88). He means that the first language can cause
interference in L2 learning, especially when the learners translate directly from the first language to the target language. Because the target language pattern and the first language pattern are different, translating directly is not permitted. If the students still use their first language pattern in L2 writing, it means that they have not acquired the target language well.
Like what happened to guided writing students in English Department, they often make grammatical error such as the use of adjectives, preposition, tenses, and etc.This fact is strengthened by Nugrahaeni (2008) who conducted study about grammatical error analysis on guided writing students. She mentioned that one of major reasons why guided writing made error was that interferences from their first language. In fact, her participants had been studying English in a formal setting for about seven to eleven years. In this case, although they had studied English for a long time, they still made grammatical error. Thus, it can be assumed that they have not succeeded yet in learning L2.
writer who has lower proficiency in second language, because their first language would facilitate their learning. Similar to Brook (2001), Lay (1982) as stated in Jun (2008) believed that L1 facilitated their process thinking and writing in L2. L2 learners who have limited English should be encouraged to use their L1 to generate ideas. From
Brook’s and Lay’s statements, it seems that first language should be addressed for
lower language proficiency.
Many studies have shown the pros and cons of first language use in L2 writing. The writer is interested in knowing whether the pros and cons of first language use are applicable to guided writing students in Satya Wacana Christian University or not. This study is aimed at investigating ED students’ perspectives toward the role of first language (Indonesian) in their guided writing class. The research question, “What are
ED students’ perspectives toward the role of first language in their guided writing?”
This study is worth studying because it provides more knowledge about first language use in guided writing process. The writer hopes for students who are going to enroll Guided Writing course anticipate the effect of L1 use, later they could reflect whether first language is beneficial or not in their writing process. Second, the study is crucial for the teacher to rethink the usage of first language in the classroom, especially when he/she explains specific terms/ an unfamiliar topic in English, in order to improve
the students’ performance in writing class. Furthermore, the result of the study will also
LITERATURE REVIEW
Definition of First Language and First Language Acquisition
According to Gass and Selinker (2008, p.7) first language is one’s native language. It refers to the language that the learners learn or use first time since they were children. First language is also known by mother tongue or primary language. The process of a child learns and masters his native language is called first language acquisition. For instance, how the children produce some words and then make it into a sentence. That language acquisition is not an instant process, but the language is learnt by a process of habit formation. The main components of habit formation are that the child will imitate the sound and practice to what they hear (Gass and Selinker, 2008, p. 90).
First Language and Second Language Acquisition
According to Nunan (2001), second language acquisition refers to the ways in which the learners acquire a second or foreign language. In other words, the learners learn a second or foreign language after their first language. There is an important relationship between first language and second language acquisition. The first language has functions as a tool to make the process of L2 acquisition easier (Urdaneta, 2011). The learners use their first language as the reference in L2 learning. Moreover, the learners learn how to form a sentence and how to speak from their native language. In conclusion, first language cannot be separated with L2 learning.
According to behaviorism principles, language transfer takes place from the first to the second language. Cook (1991) defines that language transfer is an effect of
the learners’ first language on L2 learning. The transfer can be a positive transfer and a
negative transfer. According to Cook (1991), “positive transfer is as the use of the rules that coincide in both L1 and L2”. Therefore, positive transfer may occur if the structure
of L1 and L2 are the same. For example, the Indonesian pattern (Santi makan hamburger) can be transferred directly into English (Santi eats hamburgers). According
to Nunan (2000), “negative transfer is as the use of first language rule in the learning
of L2 although such rules do not exist in the latter.” If the structure of L1 and L2 are not the same, it will cause an error. Negative transfer usually happens when the learners transfer every single word to the target language, because translating every single word in L2 may result in unintelligible sentences. Due to the differences structure between L1 and L2, it can be concluded that transferring native language gives benefit and drawback to L2 writing. Therefore, the students have to comprehend L2 structure well in order to avoid error.
Teaching writing
Hyland (2003) proposed some concepts in teaching writing for beginner learners of English. First, the teaching should focus on language structure. In this case learning how to write in a foreign language involves linguistic knowledge, vocabulary choices, syntactic patterns, and cohesive devices. He also emphasizes on language structure as the basis for writing teaching which covers typically four-stage processes as following:
2. Controlled writing : learners manipulate fixed patterns
3. Guided Writing : learners imitate model texts
4. Free writing : learners use the pattern they have to develop to write an essay,
letter. (p.22-23)
Second, teaching writing focuses on text functions. The aim of focusing on functions is to help the students to develop an effective paragraph by making topic sentence, supporting sentences, transitions and to developing another type of paragraphs. Teaching by focusing on text functions is preparing students to academic writing at college or university.
Third, teaching writing focuses on creative expression. This orientation takes more on the writer rather than the form. Hyland (2010) adds that creative expression in writing is like sharing personal meaning to the readers; whereas, the course of writing itself stresses the student to construct his or her own view on a topic. He believes that all the writers have a similar innate potential to express their own ideas creatively. In this case, guided writing students do not pay attention to grammar only, but they are given chance for writing to some feature such as style, clichés, and developing creative paragraph and so on.
The role of first language
first language influence appeared in word order error. Word order refers to the incorrect placement of words in a sentence. For example, “John wants to be a basketball player like Michael Jordan” instead of “John wants to be a player basketball like Michael
Jordan. “ The sentence John wants to be a “player basketball” is the result of
Indonesian direct translation; John ingin menjadi pemain bola basket seperti Michael Jordan. In addition, Ellis (1996) asserted that when L1 and L2 form share the same meaning but are expressed in different ways, an error is arisen because the learners transfer their L1 to L2. For example the word “di” in Indonesian is more or less share the same meaning as the word “at” in English. “I spent my vacation in selecta garden; the flower is beautiful in there”. The word “in” means disana; However in English
preposition “in” is not needed. Realizing the negative role of first language, the writer
wants to know whether guided writing students make errors and what kinds of errors that they often make.
Besides the negative effects of the L1 use, some study asserted that L1 gives positive effects in the target language. Nation (2001) developed four strands of first language use in learning L2. The four strands are:
1. Meaning focused on input
2. Meaning focused on output
3. Meaning focused on learning
4. Fluency development
Meaning focused on input and output means the learners have to know both on what to say and on how to say it. She gave an example of the effectiveness of discussion through the first language before performing in L2 writing. By doing the discussion, the learners gripped many ideas, so they could fully understand the content. For that reason, it is needed to investigate what kinds of ideas or topics that can stimulate guided writing students to develop content of writing.
The result was those who did preparation in first language performed better rather than those who did not. Meaning focused on learning emphasizes on conveying the meaning of unknown words. At this stage, the learners are persuaded to notice the strategies to learn L2 vocabulary which is related to L1. For example borrowing and loaning words from L2 to help the vocabulary learning is effective. Learning vocabulary could be done through reading, visual pictures, memorizing or L1 translation. The learners should have much vocabulary knowledge because lack of vocabulary leads to writing difficulty (Lee, 2003).
For example, they could remember the L1 stories or information which later be used for the L2 task.
THE STUDY
Context of the study
This study was conducted at Faculty of Language and Literature, Satya Wacana Christian University which is located in Salatiga, Central Java, Indonesia. The subjects of this study were English Department Students who have taken Guided Writing
course. Guided Writing’ students are beginner learners of English at the University
level who have passed Integrated Course which is a sort of basic English proficiency course.
Participants
The participants of this study were 15 students who have passed Guided Writing course in the second semester of academic year 2011/2012. Because they have passed that course, it was assumed that they had already had much knowledge and experience in guided writing tasks. The participants ranged in age from 17 to 18 years old. There were 14 females and 1 male in this study. The method used in selecting participants was random sampling.The participants would get an equal chance being included in the survey. All the participants were Indonesian students who set English as a foreign language because they rarely use English for their daily communication.
The writer used interview as the instrument for this study to get the data toward the
students’ perspective toward the role of first language (Indonesian) in their guided
writing. In order to know students’ perspective deeper, the semi-structure interview
was selected. It was because the writer could follow up the question, so the writer could get more information. There were 10 questions in the interview (which could be seen in appendix A and B). The interview atmosphere was warm and less formal. During the interview, the writer used Bahasa Indonesia. According to Husada (2007) conducting an interview with the participants’ native language would avoid problems in communications. The participants were interviewed on different days because not all the participants could be interviewed on the same day due to their schedule.
Data collection procedure
First, the writer made an appointment and then contacted the participants. Second, the writer gave the interview questions to each of participants 5 minutes earlier before the interview time. The reason the writer gave interview question earlier was to give them time to think first, so they would answer in detail during the interview. Third, all the participants were interviewed one by one. During the interview the writer took
notes for some important points from the participants’ response. The interviews took
around 10 – 15 minutes for each participant. Finally, all the students’ interviews were recorded, transcribed and then translated into English for data analysis. The writer used a clean transcription which focused only on the content of the interview.
responses. Second, the writer decided on theme or categories that emerged from data. Third, the writer analyzed the data by using content/thematic analysis (Riessman, 2008
in Zacharias, 2011:103). It began by assigning categories to participants’ transcript, and
then based on the participants’ responses the writer classified similar responses into the same categories. Last, after all the data had been analyzed, the writer drew conclusion and provided the finding for this study.
Data analysis
After interviewing the participants, their responses were analyzed and discussed in order to answer the research question. From the data, the writer developed five
emerging themes for the study of ED students’ perspectives toward the role of first
language in their guided writing. The first theme was facilitating in generate idea, the second theme was fostering writing on familiar and unfamiliar topic, the third theme was improving a creative writing, how creative and artistic any types of writing could be. Creative writing is important, Hyland (2003) defines, “expressivism is an important approach as it encourages writers to explore their beliefs, engage with the ideas of
others, and connect with the readers” (p. 29). Elbow (1988) in Hyland (2003) added
that the goal of exploring students’ creative ability was to improve their creative
FINDINGS
1. Enhance generating idea
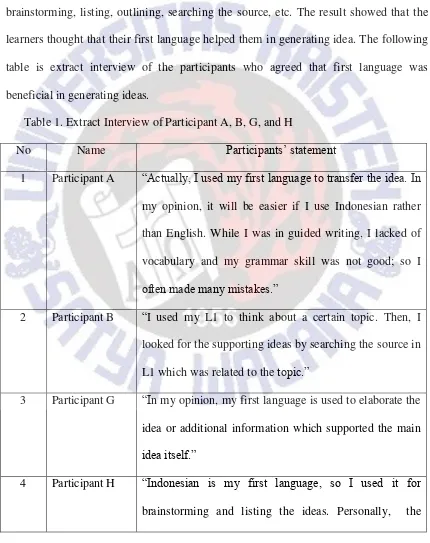
Generating idea is a crucial step in writing process in which the learners deliver and develop more ideas on the topic that they have chosen. The learners generate ideas by brainstorming, listing, outlining, searching the source, etc. The result showed that the learners thought that their first language helped them in generating idea. The following table is extract interview of the participants who agreed that first language was beneficial in generating ideas.
Table 1. Extract Interview of Participant A, B, G, and H
No Name Participants’ statement
1 Participant A “Actually, I used my first language to transfer the idea. In my opinion, it will be easier if I use Indonesian rather than English. While I was in guided writing, I lacked of vocabulary and my grammar skill was not good; so I
often made many mistakes.”
2 Participant B “I used my L1 to think about a certain topic. Then, I looked for the supporting ideas by searching the source in L1 which was related to the topic.”
3 Participant G “In my opinion, my first language is used to elaborate the idea or additional information which supported the main
idea itself.”
purpose of using Indonesian was as a tool to remember the ideas.”
From the data, it was found that most of the participants used Indonesian to generate ideas. The writer concluded they believed that L1 could facilitate generating ideas. Their ways in generating idea were various; some of them did brainstorming, listing, and outlining, while others generated ideas by searching and gathering suitable information. Although their ways in generating ideas were different, they did it based on their preferences, which one was more suitable with their own writing style.
In my analysis, the reason why the participant chose Indonesian was that Indonesian was easier than English, because Indonesian is their first language and they use it for daily communication. They really understood how Indonesianwas used. In addition, L1 gave background knowledge or previous experience to L2 writing. Learners had much experience in their L1, so they would come up with many ideas from their L1. As participant G said, if she used her L1, she could elaborate more ideas to support the main topic. Here, we could see that first language was used to keep the idea in mind. In other words, L1 served as a fundamental role when the learners were thinking about the ideas.
to English structure. Regarding to that issue, L1 was beneficial for beginner learners of English, especially for those who have not acquired English proficiency well.
The finding indicated that L1 gave much contribution to the pre writing stage, which facilitated the idea process of thinking and provided an easier way to transfer the knowledge. Because the learners grasped many ideas, they could develop the content as well as they develop the idea. This finding was similar to (Weijen et al., 2009) who found that L1 appears to be positively related to L2 text quality for goal setting, composing ideas and structuring.
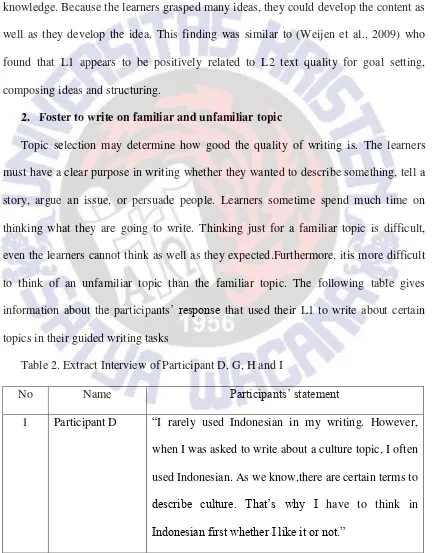
2. Foster to write on familiar and unfamiliar topic
Topic selection may determine how good the quality of writing is. The learners must have a clear purpose in writing whether they wanted to describe something, tell a story, argue an issue, or persuade people. Learners sometime spend much time on thinking what they are going to write. Thinking just for a familiar topic is difficult, even the learners cannot think as well as they expected.Furthermore, itis more difficult to think of an unfamiliar topic than the familiar topic. The following table gives information about the participants’ response that used their L1 to write about certain topics in their guided writing tasks
Table 2. Extract Interview of Participant D, G, H and I
No Name Participants’ statement
1 Participant D “I rarely used Indonesian in my writing. However, when I was asked to write about a culture topic, I often used Indonesian. As we know,there are certain terms to
describe culture. That’s why I have to think in
2 Participant G “I forgot, but at that time I was asked to write a text; the text was taken from one of my ideas in my free writing draft. At that time, I wrote about rice, I meant I wanted to describe how ‘Indonesian rice’ and ‘Indian rice’ looked like. Then, I found a difficulty to describe
it, I didn’t know, I was so confused.”
3 Participant H “Perhaps, I used Indonesian to write about a knowledge topic, which is a little bit complicated. For example UV ray actually contains vitamin D, but it can cause a skin cancer. So, Indonesian helped me a lot to
write on an uncommon topic.”
8 Participant I “I usually wrote about my personal experience or a story related to my daily life. I think I could write easily and quickly, if I used Indonesian in writing
something which happened close to my life.”
Participant G also found difficulty in describing “Indian rice”. Because the term that she wanted to describe was foreign culture. She used her L1 to clarify the description of Indian rice. L1 was acceptable to clarify in L2 writing, yet the learners had to know first the concept of the things that they wanted to describe in order to avoid error or misunderstanding. Similar to participant D and G, participant H was confused when she was asked to write about a scientific topic. Because she was in English education field, she did not much know about science. If that case happened, the learners might search supporting information in their L1. After that, they transferred the information to L2. Here, information transferring could be in a form of L1 meaning transformation or L1 word transformation.
The writer concluded that the learners found L1 as a perfect tool for the learner to get some information, because they have not found much information or insufficient knowledge about an unfamiliar topic in the target language. It meant that the learners
did not have much L2 knowledge as they had in their L1. Hence, learners’ L1
memories were advantageous to support or explain the meaning interpretation from L1 to L2 writing.
3. Assist vocabulary learning
Vocabulary determines the quality of writing. The more varied vocabulary, the better writing would be. Therefore, it is a must for learners to have much vocabulary in order to improve their writing quality. The following table provides the participants’ statements that thought that their L1 was very advantageous in learning L2 new words.
Table 3. Extract Interview of participant A, B, and K
No Name Participants’ statement
1 Participant A “I could not make a good and well-formed sentence in English directly, so I used Indonesian first then translated it to English. To write a higher quality of writing in Indonesian, perhaps, we could not do. So, how can we write complex sentences in English? For example, I want to describe ’that brown window frame is beautiful and it has spiraled and rounded pattern.’ If I wrote that sentence in Indonesian, It was easier. However, it would be hard, if I wrote it in English.” 2 Participant B “If I did not know the meaning in English, for me it is
better to translate it directly or look up in the dictionary to find the meaning. I usually translated
some phrase that I did not know.”
that word.”
We could clearly see from the data that L1 was a translation tool to search for L2 word. L1 translation generally arose when learners were stuck with L2 word. Then again, they used their L1 to look for L2 vocabulary. Furthermore, their tendency of L1 use would increase when they wanted to create a complex sentence. Referring to the
participant A’s experience, she got trouble in forming L2 word. As a result, she might
this case, learners put a certain word with others language components in a sentence. It was a way to test intelligibility of the sentence. In conclusion, it could be drawn a conclusion that L1 translation was not enough to support L2 vocabulary learning. Therefore, learners need to know about vocabulary use on how to put words in writing appropriately.
4. Improve creative writing
It is true that learners need to understand grammar and vocabulary in writing. However, L2 writing was not only these things. They should consider about creative ability in sharing or expressing their ideas or thought. The following table is interview results that show guided writing students’ creativity in L2 writing.
Table 4. Extract Interview of Participant C and H
No Name Participants’ statement
1 Participant C “When I wrote about my experience that I liked the most, I added a poem in my narrative writing task.
Thats’true I translated some word in the poem to
English.”
2 Participant H “Because my first language is Indonesian, I often used it. It will be easier when I shared my ideas, even, the idea is more expressive and the content of the writing itself would also improve. The habit of L1 writing helped me to share the idea expressively, but do not
The writer was surprised that beginner learners did produce a sort of aesthetic text in their narrative task when they were in Guided writing course. Perhaps only the learners who had much experience in L2 writing wrote creatively. Typically, creative thought emerged from the habit of writing and sharing the idea. That was true when the participants were asked about their habits in writing and some of them said they often wrote in L1. Therefore, they could come up with such an idea. From the data, the writer concluded that the habit ofL1 writing affected to L2 writing. The sharing of the idea both in L1 and in L2 was the same, but in L2 writing the learners had to deal with a suitable language structure. Because the learner had much experience in L1 writing, they knew how they played the language. Later on, they transformed the knowledge from the L1 to L2 writing.
Creative expression could be expressed through the poem, proverb, vocabulary variation, personal belief and so on. As participant C said she expressed the idea through the poem. Putting poem in writing gave a different nuance, so it aroused the
readers’ curiosity to read more. Here, different nuance meant different vocabulary,
different tone, and the way the writers told their story was different too. As the poem was an art that contained a cliché meaning such as metaphor, the reader might interpret
differently. This finding was similar to Cumming’s study, (2003) in Hyland (2003) that
based on their interest. Since many ideas that they got, they were forced to find their ways on how the idea would be expressed.
5. Lead to error
Despite the fact that L1 gave many roles for guided writing students, the participants also admitted that L1 caused an error when they performed in L2 writing. This following table is interview result from the participants who experience errors.
Table 5. Extract Interview of Participant C and J
No Name Participants’ statement
1 Participant C “Yes, I’ve experienced negative errors. At the
beginning of the first or second semester I didn’t know
the English term for ‘terimakasih sebelumnya ‘, so at
that time I translated it to ‘thanks before.’ It is totally
incorrect because of my first language translation,
whereas the correct one is ‘thanks in advance’.”
2 Participant J “I often make mistakes when I write ‘interested with’,
in fact it should be’ interested in.’ Another example
was ‘related with’ or ‘related to’. That sounds
Indonesian. I also have experienced making an error in tenses, too. You know Indonesian does not have present, past, perfect etc. To write aku sedang menonton TV ( I was watching TV), sometimes I was
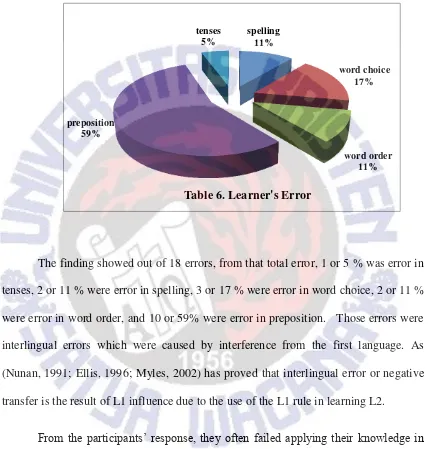
The following table shows the distribution of grammatical error that often be done by the participants.
The finding showed out of 18 errors, from that total error, 1 or 5 % was error in tenses, 2 or 11 % were error in spelling, 3 or 17 % were error in word choice, 2 or 11 % were error in word order, and 10 or 59% were error in preposition. Those errors were interlingual errors which were caused by interference from the first language. As (Nunan, 1991; Ellis, 1996; Myles, 2002) has proved that interlingual error or negative transfer is the result of L1 influence due to the use of the L1 rule in learning L2.
From the participants’ response, they often failed applying their knowledge in
preposition. The error preposition happened because L1 and L2 shared the same
meaning but express in different ways. For instance participant J’s experience, she
wanted to write “interested in”, but she wrote “interested with.” Interested with was the
result of direct L1 translation “tertarik dengan”. Because English has many
prepositions, which are used or set by other words based on the context, the learners
spelling 11%
word choice 17%
word order 11% preposition
59%
tenses 5%
often got confused of how to use the preposition properly. In contrast, Indonesian preposition are constant; it means that there is no different meaning if it is set with other words.
Second, the word error also had been experienced by the participants. Lack of grammar comprehension led to word order error. For example “ruang tunggu” was
translated to “room waiting”, whereas the correct pattern should be “waiting room.”
Referring to that example, there was English pattern, which could be reversible. Sometimes the learners were confused to differentiate what word should come first, for
example “ I don’t have enough money” not “ I don’t have money enough”, here the
adjective should come first and then followed by the noun.
Third, the word choice error was also often made by beginner level of English. Thus, they translated the vocabulary and sometime the translation worked. However, it also turned to error because English has many kinds of vocabulary whose meaning is contextualized. Participant C translated “terimakasih sebelumnya“ to “thanks before”. It seemed that participant C did lack of vocabulary comprehension, so she just translated directly. If we looked literally, the translation was correct, but the meaning was uncommon in English.
sentence should be “Joni is watching television.” Furthermore, whether Joni watches television in the morning, at noon or in the evening, the grammar would change also.
We could clearly see that all the errors above were caused by direct first language translation. The two main reasons why they translated directly was that first, they did not know the term in English, so that they transferred it to L2. Second, they probably knew the term in the target language but they did not know the usage of that term properly.
CONCLUSION
The purpose of this study was to investigate ED students’ perspectives toward
the role of first language in their guided writing. To examine students’ perspectives,
semi-structured interview technique was used. The study revealed that first language was considered as essential factor which gave many positive roles instead of negative one in foreign language writing. The finding also showed that first language was permitted for beginner learners especially in giving many ideas.
vocabulary variation. Fourth, L1 translation was really useful for searching L2 word especially in forming a complex L2 sentence or word. The participants learnt new vocabulary from L1 translation, whether they looked up in the dictionary or translated directly to L2 word. Last, first language was one factor which caused error. The discussion has shown that the most common error was preposition. The participants also made errors in word choice, tenses, word order, and spelling. Those errors were interlingual error or L1 interferences.
It can be concluded that the tendency of first language use depended on how much their L2 knowledge or how successful they learnt the target language. If the participants always relied on the first language, it meant that they have not succeeded enough in learning the target language. Conversely, if they have enough L2 knowledge, they would reduce their tendency of L1 use. This finding was similar to the previous study by Husein and Mohammad (2010) who found:
At the lower level proficiency of writing can be a very complex activity due to difficulties
students face in generating ideas in the second language, identifying the linguistic structures
and using the appropriate vocabulary. In most cases students refer to their L1 in order to carry
out the task. However, it is always believed that at lower levels of proficiency students tend to
use L1 during L2 writing more than intermediate or advanced levels of proficiency
students.(p.185)
Reflecting to the result of this study, which supports and opposes for the L1 role, it gives consideration for the English department teachers whether L1 should be addressed in their classroom or not, especially when designing the classroom activities, selecting suitable material and the teacher’s explanation. By doing so, the guided
writing students’ may use their first language to support their learning, for example the
more. However, the teacher must give limitation of L1 use in the classroom or in the writing process to avoid error, so the students will not rely too much on L1. In other words, this study suggested that the teachers should adjust with their students’ proficiency. For whom and when the first language should be maximized and minimized.
Nevertheless, this study cannot be generalized to all contexts. In this case, the limitation of the study is on the finding. The role of the other Indonesian, which is the context of this study, may result differently. Because someone’s first language may be different from others. Moreover, the participants are university students from second years who still are in the beginner level. Thus, the result will be different if L1 was used by university students who are in intermediate or advanced level because they have much experience in L2 learning. For that reason, it is suggested that further studies are needed to investigate more about how first language influences L2 writing done by intermediate or advanced level students. It is interesting to know how wonderful ED students' creativity in writing. Therefore, study on L1 composition which
can foster the students’ creative ability is also needed. Later, the students will not only
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
With the completion of my thesis, I am extending praise and thankfulness to
Jesus Christ for his love, blessed and guidance in accomplishing my study. I also give
special thanks to my beloved parents who always support in several ways. I would like
to acknowledge my deepest gratitude to my supervisor, Dra. Martha Nandari, M.A,
who always gives guidance, suggestions, time, patience and extra help in doing my
study. Also, I would like to express my appreciation to my examiner, Sesilia Rani
Setyo Sari, M.Hum, for her willingness to examine my study, without her help my
study would not have been finished. In this opportunity, I give thanks to my
participants, 2011er (eleveners) who spend time to be interviewed. Finally, I want to
express my love to my beloved best friend, Zilpa, Pembayun, Herinta, Arinta and etc,
REFERENCES
Cohen, A & Brooks-Carson, A. (2001). Research on direct versus translated writing :
Students’ perspectives and their results. The Modern Language Journal, 85, 169-188.
Cook, V. (1991). Second Language Learning and Language Teaching. Edward Arnold/ Hodder Headline Group : Melbourne.
Darus, S., &Ching, K. (2009). Common errors in written English essays from one Chinese student : A case study. European Journal of Social Science, 10(2), 242-253.
Ellis, R. (1996). The Study of Language Acquisition. Oxford : Oxford University Press.
Friedlander , A. (1990). Composing in English : Effects of a first language writing in English as a second language. In B. Kroll (ed.), Second Language Writing : Research Insights for Classroom. NY : Cambridge University Press.
Gass, S. M., & Selinker, L. (2008).Second Language Acquisition : an Introductory Course. NY: Routledge.
Husada, H.S. (2007). The second language acquisition of English concord. TEFLIN Journal, 18(1), 94-108.
Hyland, K. (2003). Second Language Writing. NY : Cambridge University Press.
Jun, Zhang.(2008). A comprehensive review of studies on second language writing. HKPU Papers in Applied Linguistic Studies12.
Krashen, S. D. (1988). Second Language Acquisition and Second Language Learning. Englewood Cliff : Prentice Hall.
Krashen, S.D. (1981). Second Language acquisition and second language learning. The Role of First Language in Second Language Acquisition. Retrieved from http ://www.sdkrashen.com/SL_Acquisition_and_Learning/index.
Lee, Siok, H. (2003). ESL learners’ vocabulary use in writing and effect of explicit vocabulary acquisition. ELSEVIER journal, 3,537-561.
Liu, Kuanping. (2004). Effects of different thought pattern on Chinese students’ EFL
writings. Foreign Language Research, 5, 18-25.
Myles, J. (2002). Second Language writing and research : The writing process and error analysis in students text. TESL-EJ6(2).
Nation, Paul. (2003). The role of first language in foreign language learning. Asian EFL Journal, 5(2).
Nugrahaeni, D. A. (2012).The analysis of grammatical error on guided writing students. SatyaWacana Christian University, Salatiga.
Nunan, D. (2000). Language Teaching Methodology. Pearson Education Limited :Edingburg.
Urdaneta, Julio. (2011). Spanish- English writing structure interferences in second language learners. Gist Education and Learning Research Journal, 5, 158-179.
Weijen, V., Bergh, H., Rijaardam, G., & Sanders, T. (2009). L1 use during L2 writing : an empirical of study a complex phenomenon. Journal of Second Language Writing, 18, 235-250.
William, Jessica. (2007). Teaching Writing in Second Language and Foreign Language Classrooms. Beijing : World Publishing Corporation.
Xia, Liu. (2008). Literature review on the use and effect of L1 in L2 writing.US-China Foreign Language, 6(5), 50-53.
Yu, Aiju. (2012). Analysis of the problems of the Chinese college students classroom. International Studies, 5(5), 199-203.
APPENDIX A Interview Questions
1. What is your understanding of first language in writing process?
2. Could you describe in a step-by step manner, what do you do when you are going to write in Guided writing?
3. Do you believe that practice L1 writing more can improve your English writing?
4. What pattern do you use while composing ideas in English writing? L1 pattern or L2 pattern?
5. How often do you use your first language in your writing process?
6. In what way do you usually use your first language in your writing process? 7. Have you experienced translating Bahasa Indonesia to English before writing in
English? Why?
8. Have you experienced a negative error or a positive error while you use your first language pattern thinking while writing in English?
APPENDIX B
Interview question
1. Menurut pendapatmu, penggunaan bahasa pertama dalam proses penulisan bahasa Inggris itu seperti apa?
2. Dapatkah anda mendeskripsikan langkah-langkah yang biasanya anda lakukan sebelum menulis dalam bahasa Inggris?
3. Apakah anda setuju bahwa menulis di bahasa pertama lebih sering dapat meningkatkan penulisan di bahasa Inggris?
4. Grammar bahasa apa yang anda gunakan ketika menyusun ide-ide dalam penulisan bahasa Inggris?
5. Seberapa sering anda menggunakan bahasa pertama dalam penulisan bahasa Inggris?
6. Dalam hal apa anda menggunakan bahasa pertama ketika menulis dalam bahasa Inggris?
7. Apakah anda pernah menerjemahkan langsung dari Bahasa Indonesia ke Bahasa Inggris?
8. Apakah anda mengalami “ negative error” and “positive error” karena menggunakan bahasa pertama anda?
9. Apa yang anda rasakan jika menggunakan bahasa pertama anda ketika menulis dalam bahasaInggris?