INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN TECHNOLOGY (IJRT) ISSN No. 2394-9007
Vol. V, No. II, April 2018 www.ijrtonline.org
Impact Factor: 4.012
Published under
Asian Research & Training Publication
ISO 9001:2015 Certified
68
Energy Improved Ad-hoc On Demand Distance
Vector Routing Protocol for MANET
Abstract— Proposing energy efficient routing protocols for Mobile Ad hoc Network (MANET) is challenging task. Performances of many of these routing protocols have been evaluated focusing on metrics such as delay, routing overhead, and packet delivery. We will discuss about the Energy consumption in a MANET routing protocols. A performance comparison of original AODV and Proposed EI-AODV protocols with respect to average energy consumption and routing energy consumption are explained thoroughly. We are distributing packet on ten different routes so, energy of overall network will improve. The execution measurements utilized for assessment are Packet delivery ratio, throughput and Average Delay. The simulation will be done using NS2.
Keywords: NS-2, AODV, CBR, CH, MANET.
I.INTRODUCTION
MANET is a collection of self organized mobile nodes with dynamic topologies and no fixed infrastructure. Nodes communicate with each other through wireless channel. Nodes form a group of wireless nodes which agree to forward packets for each other. When network topology changes nodes still remains connected. In the absence of central control of the network. Operation, the control and management of the network is distributed among the mobile nodes. The nodes are required to collaborate amongst themselves. The flexibility of mobile nodes allows nodes in the network to join and leave the network at any instance. Limited bandwidth, memory and processing capabilities are major disadvantage and due to open medium these are more prone to malicious attacks. Interest in this area is growing since last few years because of its practical applications and requirement of communication in mobile devices.
In fig. 1, Node 1, Node 2 and Node 3 are the mobile nodes and they are connected to each other through wireless links.
Manuscript received on April, 2018.
Lakhan Sisodiya, M.Tech Scholar, Department of Computer Science &
Engineering, Oriental Institute of Science & Technology, Bhopal, M.P., India.
Prof. Khushboo Saxena, Asst. Professor, Department of Computer Science
& Engineering, Oriental Institute of Science & Technology, Bhopal, M.P., India.
Fig. 1: Node 1, Node 2 & Note 3 are the mobile nodes
A. Current Challenges/Open Research Issues:
In a mobile ad hoc network, all the nodes cooperate with each other to forward the packets in the network, and hence each node is actually a router. Thus one of the most important issues is routing. This thesis concentrates mainly on routing issues in ad-hoc networks. In this section, some of the other issues in ad hoc networks are:-
Routing
Quality of Service (QoS) Internetworking
Power Consumption Security and Reliability
B.AODV (Ad hoc On-demand Distance Vector Routing):
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN TECHNOLOGY (IJRT) ISSN No. 2394-9007
or equal to it. RREP is unicast to source in this case. Else node is an intermediate node having no information about route then broadcast the RREQ to its neighbors. If nodes have already processed the RREQ packet before then they reject it. When RREP is received by the source then nodes set up forward pointer to the destination.As soon as RREP is received by source, it can initiate data packet transfer to destination. If afterwards source receives RREP having a greater sequence number or contains the same sequence number but with a smaller path length, then source update its routing information for that destination and starts using this new route. When the link breaks between source and destination then nodes send route error packet (RERR) to source informing that destination is no more reachable. On receiving RERR by source, it again initiates route discovery procedure.
C. Energy Aware Routing in Mobile DHOC:
Wireless mobile devices are useful if they can be used anywhere. But we have limited battery power of using it, Therefore, in wireless communication; one of the most challenging problems is power management. Several energy aware routing protocols have been developed. Most of these routing protocols aim to minimize the energy consumed per packet needed to deliver this packet to its destination. Some of the more sophisticated routing algorithms associate a cost with routing through a node with low power reserve. Other routing protocols aim to maximize the network lifetime. All previous protocols are using single path to distribute data traffic through the network. The routing protocols, described previously are based on the single path routing between a source and a destination. However, in a reasonably well-connected network, there may exist several paths between a source-destination pair. The concept of multipath routing is to give the source node a choice at any given time of multiple paths to a particular destination by taking advantage of the connectivity redundancy of the underlying network. The multiple paths may be used alternately, namely, traffic taking one path at a time, or they may be used multiple paths simultaneously .Multi-path routing consists of three components: route discovery, route maintenance, and traffic distribution among multiple paths
II.PROPOSED WORK
Energy Consumption for AODV:
Proposing energy efficient routing protocols for Mobile Ad hoc Network (MANET) is challenging task. Performances of many of these routing protocols have been evaluated focusing on metrics such as delay, routing overhead, and packet delivery. Although, no studies have been done to investigate energy aspect of these routing protocols. Thus, we will discuss about the Energy consumption in a MANET routing protocols. A performance comparison of original AODV and Proposed EI-AODV protocols with respect to average energy consumption and routing energy consumption are explained thoroughly. We are distributing packet on ten different routes
so, energy of overall network will improve. The execution measurements utilized for assessment are Packet delivery ratio, throughput, and Average Delay. The simulation will be done using NS2.
We have proposed the model for EI-AODV it is an important part of routing protocols. There are two data model Route-Info and Packet-Distribution Distribution, in the Packet-Distribution there are two fields. Route-Name and Packet-Reader
The Algorithm is given below:
1. Source When Data Packet received following these steps a. Retrieve Destination from packet
b. Is Route Available?
If YES Get Path P Available from Packet Distribution c. Else Initiate Route Discovery
d. Check number of path in data structure Packet-Distribution
2. If path is less than ten Initiate Route Discovery
3. Update data structure Packet-Distribution from new path 4. If path new path is less than existing path replace with
new path
5. Send packet one by one on existing path in data structure Packet-Distribution
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN TECHNOLOGY (IJRT) ISSN No. 2394-9007
Vol. V, No. II, April 2018 www.ijrtonline.org
Impact Factor: 4.012
Published under
Asian Research & Training Publication
ISO 9001:2015 Certified
70 III.RESULT ANALYSIS
To analysis of original AODV and EI-AODV Network Simulator (NS2) was used. The simulate are run for existing AODV and under same environment it will again be run for ZYM-AODV or Modified AODV to see the comparison of performance on differences against Average Delay, Packet Delivery Ratio (PDR) and Throughput. The Modified AODV (EI-AODV) is simulated using with following scenarios settings:
TABLE I: SIMULATION SCENARIOS
Ns-2 Version ns-2.35 Number of nodes
Number of nodes Ns-2 Version 60 Number of sources 30
Area 1000 x 1000 Link layer type LL
Model Random Waypoint Network Interface Type
Mac Type Mac/802_11 Phy/WirelessPhy Propagation TwoRayGround
Speed 10,20,30,40, and 50 m/s Antenna Model Antenna/OmniAntenna
Buffer Size 100000 bits Transmission Range 250 meters Mac Type Mac/802_11 Packet Size 512 bytes Routing Protocol AODV Simulation Time 200s
A. Average Delay Vs Speed:
Fig. 3: Average Delay Vs Speed
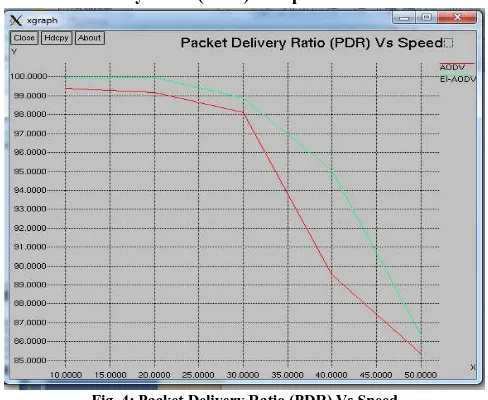
B. Packet Delivery Ratio (PDR) Vs Speed:
Fig. 4: Packet Delivery Ratio (PDR) Vs Speed
C.Throughput Vs Speed:
Fig. 5: Throughput Vs Speed
IV.CONCLUSION
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN TECHNOLOGY (IJRT) ISSN No. 2394-9007
Vol. V, No. II, April 2018 www.ijrtonline.org
Impact Factor: 4.012
Published under
Asian Research & Training Publication
ISO 9001:2015 Certified
71 V.FUTURE SCOPE
As compared to the existing AODV, our proposed scheme future work we will develop intermediate node and destination decision working for reduced source load , route maintain mechanism for improve source node energy.
REFERENCES
[1] Ket, N., & Hippargi, S. (2016, March). Modified AODV Energy
Aware Routing for optimized performance in mobile ad-hoc networks. In Wireless Communications, Signal Processing and Networking (WiSPNET), International Conference on (pp. 1030-1034). IEEE.
[2] Malek, AL-Gabri, L. I. Chunlin, Yang Zhiyong, AH Naji Hasan,
and Zhang Xiaoqing. "Improved the energy of ad hoc on-demand distance vector routing protocol." IERI Procedia 2 (2012): 355-361.
[3] S. Basagni, M. Conti, S. Giordano and I. Stojmenovic, “Mobile
Ad Hoc Networking: Cutting Edge Directions”, 2nd Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc, March 2013.
[4] Y. Lin, Y. Chen and S. Lee, “Routing Protocols in Vehicular AdHoc Networks: A Survey and Future Perspectives”, Journal of Information Science and Engineering, pp. 913-932, May 2010.
[5] M. Conti, “Principles and Applications of Ad Hoc and Sensor Networks”, in Handbook of Computer Networks: LANs, MANs, WANs, the Internet and Global, Cellular, and Wireless Networks, vol.2, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, USA, November 2007.
[6] J. Hoebeke, I. Moerman, B. Dhoedt and P. Demeester, “An
Overview Mobile Ad-hoc Network: Application and
Challenges”, in Proceedings of 43rd European Telecommunication Congress, Ghent, Belgium, 2004.
[7] K. G. Santhiya and N. Arumugam, “Energy Aware Reliable
Routing Protocol (EARRP) for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Using Bee Foraging Behaviour and Ant Colony Optimization” , International Journal of Computer Science Issues, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 171, March 2012.
[8] S. Misra and G. Rajesh, “Bird Flight-Inspired Routing Protocol for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks”, ACM Transactions on Autonomous and Adaptive Systems, vol. 6, October 2011.
[9] F. Bai and A. Helmy, “A Survey of Mobility Models in Wireless Adhoc Network”, University of Southern California (USA), 2004.
[10]T. Camp, J. Boleng and V. Davies, “A Survey of Mobility Models for Ad Hoc Network Research”, Dept. of Math. and Computer Sciences Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO , September, 2002.
[11] V.D. Patil and A.R. Deshmukh, “Performance Improvement of Routing Protocol Using Two Different Mobility Models In Vehicular Adhoc Vehicular Network”, International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing, vol.3 no.4, pp. 440-445, April 2014.
[12]M. S. Pilavare and A. Desai," A Novel Strategy Towards
Improving Efficiency of Load Balancing Using Genetic Algorithm in Cloud Computing ", proceeding of EEE Sponsored 2nd International Conference on Innovations in Information Embedded and Communication Systems ICIIECS‟15, pp.1-4, 2015.
[13]L. Benini, A. Bogliolo, and G. D. Micheli, “A survey of design
techniques for system-level dynamic power management,” IEEE
Transactions on Very Large Scale integration (VLSI) Systems,