A THESIS
Submitted to the faculty of Teacher Training and Education
Makassar Muhammadiyah University in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the degree of education in English department
MAYA SORAYA
105351127316
MUHAMMADIYAH MAKASSAR UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF TEACHER
TRAINING AND EDUCATION ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
SURAT PERNYATAAN Saya yang bertandatangan di bawah ini:
Nama : Maya Soraya
NIM : 10535 11273 16
Jurusan : Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris
Judul Skripsi : The Impact of Using WebQuest on EFL Students’ Reading Comprehension at FKIP Unismuh Makassar (A Pre-Experimental Study Of English Department Of University Muhammadiyah Makassar)
Dengan ini menyatakan bahwa skripsi yang saya buat di depan Tim penguji adalah hasil karya saya sendiri bukan hasil ciptaan orang lain ataupun dibuatkan oleh siapa pun.
Demikianlah pernyataan ini saya buat dengan sebenar-benarnya dan saya bersedia menerima sanksi apabila pernyataan ini tidak benar.
Makassar, 16 Maret 2021 Yang Membuat Pernyataan
SURAT PERJANJIAN Saya yang bertandatangan di bawah ini:
Nama : Maya Soraya
NIM : 10535 11273 16
Jurusan : Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris Fakultas : Keguruan dan Ilmu Pendidikan Dengan ini menyatakan perjanjian sebagai berikut:
1. Mulai dari penyusunan proposal sampai dengan selesainya skripsi saya, saya akan menyusun sendiri skripsi saya, tidak dibuatkan oleh siapa pun. 2. Dalam menyusun skripsi, saya akan selalu melakukan konsultasi dengan
pembimbing.
3. Saya tidak akan melakukan penjiplakan (plagiat) dalam menyusun skripsi ini.
4. Apabila saya melanggar perjanjian saya seperti yang tertera pada butir 1, 2 dan 3 maka saya bersedia menerima sanksi sesuai dengan aturan yang berlaku.
Demikian perjanjian ini saya buat dengan penuh kesadaran.
Makassar, 16 Maret 2021 Yang Membuat Perjanjian
MOTTO
All achievements are not pure effort, but there is always prayer behind an achievement
DEDICATION
A Thesis for My Beloved Family
Especially for My Parents,Both of My Best Sisters and My Brothers, Also My Family High Fliyers in My Class
ALSO, For My Own Self I Deserve this Billion Times
ABSTRACT
Maya Soraya. 2020. The Impact of Using WebQuest on EFL Students’ Reading Comprehension at FKIP Unismuh Makassar (A Pre-Experimental Study at the Third Semester of English Department of Muhammadiyah Makassar). Faculty of Teacher Training and Education. University Muhammadiyah of Makassar. (Supervised by Saiful and Muhalim)
The objective of this study is to find out the impact of using WebQuest in teaching reading comprehension which consist of the students‘ improvement of literal reading comprehension in term main idea and supporting details. This study used experimental. In collecting data, the researcher took the data from pre-test and post-pre-test. The population of the research was the third semester at FKIP Unismuh Makassar that consisted of 20 students.
The results of the research showed that the students‘ mean score of pre-test before treatment was 52.30%. While after treatment, the mean score of post-test was 94.90%. Therefore, the significant between pre-test and post-test was 81.45%.. The result of the data analysis indicated that there was a significant improvement in the students‘ reading ability after being taught using WebQuest. It was proved by the result of the statistical analysis of the degree significance P=0.05 with degree of freedom (df)=19 indicated that the t- test (3.6) and t-table is (2.093) and significant. (2-tailed) 0.000. This suggests that the data of posttest as the final result gave significant improvement. It‘s concluded that the use of WebQuest is able to give greater contribution in teaching and learning reading comprehension.
ABSTRAK
Maya Soraya. 2020. Dampak Penggunaan Webquest Terhadap Pemahaman Membaca Siswa EFL di FKIP Unismuh Makassar. (Studi Pre-Experimental Semester III Jurusan Bahasa Inggris Muhammadiyah Makassar). Fakultas
Keguruan and Ilmu Pendidikan. Universitas Muhammadiyah Makassar. (Dibimbing oleh Saiful dan Muhalim)
Tujuan penelitian ini adalah untuk mengetahui pengaruh penggunaan WebQuest dalam pembelajaran pemahaman membaca yang terdiri dari peningkatan pemahan membaca literal siswa pada ide pokok dan detail pendukung. Penelitian ini menggunakan pre-experimental. Dalam penggumpulan data, penelitian menggambil data dari pre-test dan post-test. Populasi penelitian adalah semester 3 di FKIP Unismuh Makassar yang berjumlah 20 siswa.
Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa nilai rata-rata pre-test siswa sebelum menggunakan pembelajan adalah 52.30%. Sedangkan setelah pembelajaran, nilai rata-rata post-test adalah 94.90%. oleh karna itu, signifikansi antara pre-test dan post-test adalah 81.45% hasil analisis data menunjukkan bahwa ada peningkatan yang signifikan dalam kemampuan membaca siswa setelah diajarkan menggunakan WebQuest. Hal ini dibuktikan dengan hasil analisi statistik tentang tingkat signifikan P=0.05 dengan tinkat kebebasan (df)=19 menunjukkan t-test (3,6) dan t-table adalah (2.093) dan signifikan. (2-tailed) 0,000. Hal ini memperlihatkan bahwa data post-test sebagai hasil akhirnya memberikan peningkatan yang signifikan. Hal ini menyimpulkan bahwa penggunaan WebQuest mampu memberikan konstribusi yang lebih besar dalam pengajaran dan pembelajaran pemahaman membaca .
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
In the name of Allah, the Beneficent, the Merciful.
Praise and gratitude be to Allah for giving Strength and guidance for the researcher in order that this thesis will be finished thoroughly. Peace and blessing be upon Prophet Muhammad SAW, his families, his relatives and every one of his followers.
This thesis was written to fulfill one among requirements to get the scholar degree at the English Department of Faculty Teacher Training and Education, Muhammadiyah University of Makassar. Special thanks to:
1. The researcher‘s Great Parents Hj. Fatmawati and Mahmuddin
2. Prof. Dr. H. Ambo Asse, M. Ag as the Rector of Muhammadiyah University of Makassar,
3. Erwin Akib, S. Pd., M. Pd., Ph. D. As the Dean of Faculty of Teacher Training and Education, Muhammdiyah University of Makassar.
4. Ummi Khaerati Syam, S.Pd., M.Pd. as Head of the English Department of Faculty of Teacher Training and Education, Muhammdiyah University of Makassar.
5. The highest appreciatin and deepest thankful are due Dr. Saiful, S.Pd., M.Pd, as the first consultant, Muhalim, S.Pd., M.Pd., Ph.D, as the second consultan that always give motivation, suggestion, support, and advise in writing.
6. All of the lectures in the English Department, for teaching precious knowledge and for giving wonderful study experience.
7. The researcher‘s beloved all of his relatives who support him.
8. The whole researcher‘s wonderful friends from the English Department, especially Immortal Class that the researcher can‘t write all of their name.
Makassar, November 2020
The Researcher
TABLE OF CONTENT
COVER ... i
APPROVAL... ii
LEMBAR PENGESAHAN ... iii
SURAT PERNYATAAN ... iv
SURAT PERJANJIAN ... v
MOTTO AND DEDICATION ... vi
ABSTRACT ... vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENT ... xi
LIST OF TABLE... xiii
LIST OF FIGURE... xiv
LIST OF APPENDICES... xv
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Background ... 1
B. Research Question ... 4
C. The objective of the Research ... 5
D. Significance of the Research ... 5
E. Scope the Research ... 5
CHAPTER II REVIEW OF LITERATURE ... 6
A. Previous Related Research Findings ... 6
1. Definition of Reading ... 7
2. Definition of reading comprehension ... 8
3. Kinds of reading comprehension ... 9
4. Level of reading comprehension ... 10
5. Factor affecting reading comprehension ... 11
6. Measuring reading comprehension ... 12
C. The Concept of WebQuest... 13
1. Definition of WebQuest ... 13
2. The function of WebQuest... 17
3. WebQuest in reading comprehension ... 17
4. The implementation of WebQuest in reading comprehension 18
5. Teaching WebQuest ... 23
D. FrameWork ... 24
E. Hypothesis ... 25
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD ... 26
A. Research Design ... 26
B. Research Variable ... 27
C. Population and Sample of Research ... 27
D. Instrument ... 27
E. Data Collecting procedure ... 28
F. Data Analysis ... 30
CHAPTER IV FAINDING AND DISCUSSION ... 34
B. Discussion ... 40
CHAPTER V CONCLUSSION AND SUGGESTION ... 43
A. Conclussion ... 43
B. Suggestion ... 43
LIST OF TABLE
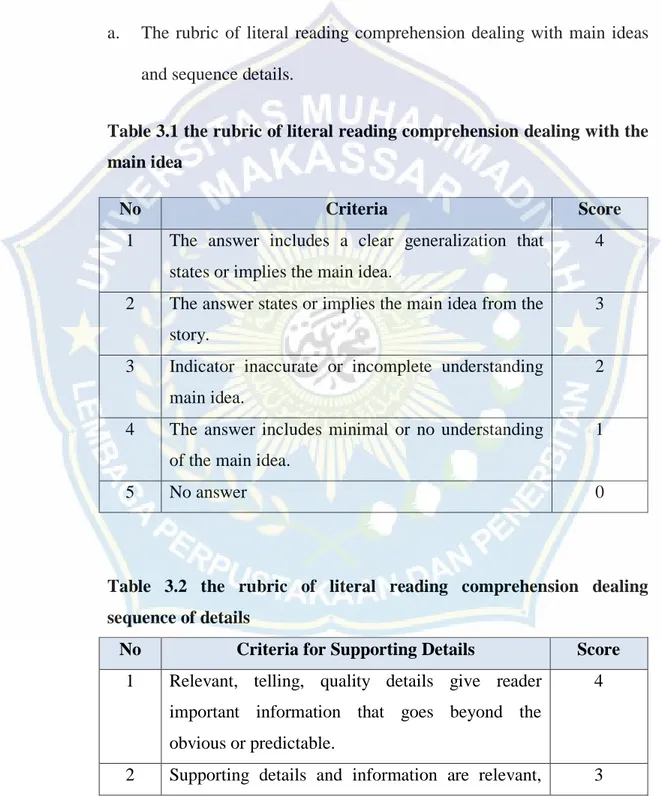
Table 3.1 The Rubric of Literal Reading Comprehension dealing with the Mai Idea.
Table 3.2 The Rubric of Literal Reading Comprehension dealing Sequence of Details.
Table 3.3 The Scoring Rank of the Students.
Table 4.1 The Mean Score of students‘ literal reading comprehension in Experimental Class.
Table 4.2 The Mean Score of The Significance Improvement of The Students Literal Reading Comprehension in Experimental Class.
Table 4.3 The Rate Percentage and Frequency of the Students‘ Literal Reading Comprehension in Experimental Class.
LIST OF FIGURE Figure 2,2 The Conceptual Framework
LIST OF APPENDICES APPENDIX A The Result of Analysis
A. Appendix A.1 Data of Pre-Test and Post-Test of experimental Class B. Appendix A.2 The Rate Percentage of Students‘ Scores
C. Appendix A.3 Calculating Of The Mean Score of Pre-Test and Post-Test D. Appendix A.4 Scoring Analysis of Pre-Test and Post-Test
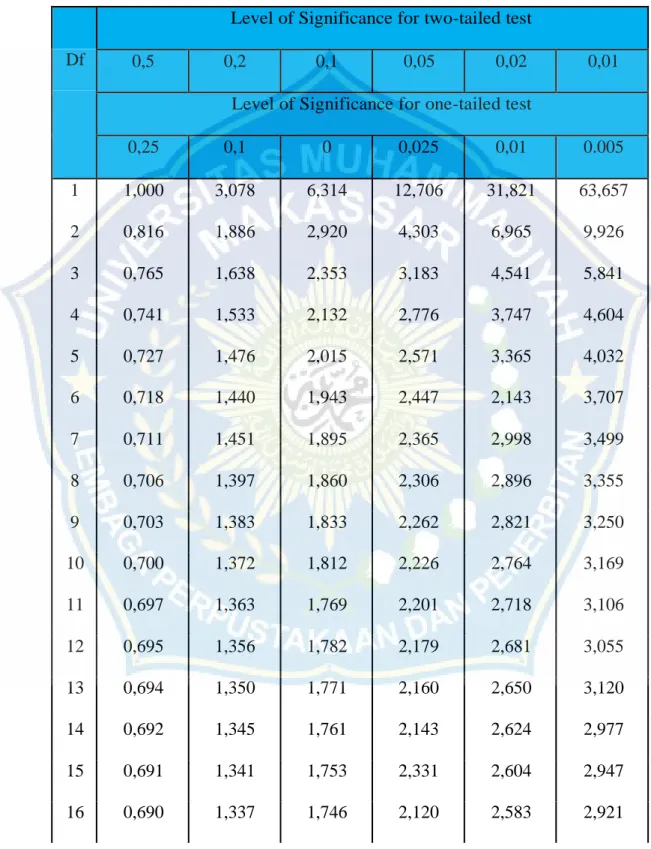
E. Appendix A.5 Table Distribution of T-Table
APPENDIX B The Instrument of Pre-Test and Post-Test APPENDIX C Lesson Plan of Experimental Class
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. Background
English is an international language, used in many countries as a means of communication, and has a great role to play in many areas of life, such as politics, business, trade and diplomatic relation. Furthermore, English cannot be isolated from the advancement of technology, science, economics and education. As a result, the government of Indonesia has agreed that English is a foreign language in Indonesia.
Harmer (2003) notes that all four basic language skills are listening, speaking, reading and writing. These four skills should include the teacher in the teaching and learning process in the class room. Speech and writing refers to effective abilities when reading and listening to responsive skills.
Reading is one of the most critical language skills that students need to master. Through this activity, students will create their own language and experience. They got the details and the insights they need to hear. They were even able to know what they didn‘t know before.
There are many kinds of reading text in reading, such as narrative, recount, report, descriptive, explanation, analytical exposition, hortatory exposition, procedure, news item and so on.
Almost students can‘t understand reading well, can‘t draw the conclusion they read and can‘t decide the main idea of reading. According to Dwiarti (2005),
there are four problems faced by students in seeking a main idea of the text: 1) lack of interest in reading, 2) lack of background information, 3) lack of vocabulary, 4) lack of knowledge of the parts of the paragraph
Based on my observation in English Department students at Muhammadiyah University of Makassar, especially in terms of reading comprehension, it is tough to understand what they are reading, and it is difficult to find the main ideas they read because most students are not interested in reading books. After all, books can make students bored and bored with thickness book.
However in order to correct reading deficiency, educators need to find ways to adapt to newer models for students. It is not only for educators, but also for students who need to share their responsibilities and work together to decide how learning objectives can be achieved. The collaboration is expected to create a situation that will lead to a stronger academic climate in the new paradigm. According to Leland and Krathwohl (2002), there are two teaching models, namely the industrial model and the inquiry model, which define the teaching-learning process through the characteristics of the participation of the participants. The industrial model indicate that students expect to be able to submit to the teaching approach and educators have a dominant role to play in deciding the course of the process. The inquiry model represents the role of students who are more interested in enriching their knowledge and experience. The learning model that needs to be improved is how IT plays the same strategic role in the process. Barnie Dodge, lecturer at the University of San Diego, USA, has developed
Webquest selection method. Webquest is a media that can be used by educators to use media that provide supporting or complementary material that is supported online.
WebQuest is an inquiry-oriented activity where there is any or all information that interacts with students from Internet resources is optionally complemented by video conferencing (Bernie Dodge: 1995). WebQuest is all information that involves students from online outlets, complemented by video conferencing. WebQuest designs the learning material provided in the WebQuest. This lesson plan allows students to do their homework to find on-site information or connections. The purpose of the WebQuest is to train students to learn how to operate the Internet through the use of resources and the development of the internet. WebQuest is really useful to students because students can get rid of boredom in their studies because they are directly connected to the Internet or face their real language and the real world. The WebQuest structure can consist of short periods of one to three classes and long periods of up to one month.
To improve reading comprehension, one of the most valuable tools for students that technology and the Internet because since it is quite advanced in this era, most students are already using technology and the Internet. There are actually quite a few students who are more interested in seeking knowledge on the Internet than any other media. And information related to learning materials. The limited selection of educational media in schools makes students more interested in using the Internet as a learning resource.
Mobile phones are one of the most highly advanced technology to search for anything we needed. Most students are more wasting their time to read using a mobile phone than to read books that are no pictures that can make the students are not interested in reading because contents of the book are only no writing and content of the book is very thick that could make the students are not interested in reading it, whereas if the students read in WebQuest students will be more interested in reading the stories they read because reading in WebQuest students can develop their reading comprehension because in WebQuest many materials can make students better developed in reading and have very many pictures that make students interested in the story contents or information. And if we use cell phones to open a link, WebQuest very easy for someone to carry it around.
In this study, the problem is that students are less motivated in reading. Most students can read, but it is difficult to understand the content of reading they read. Because students are not interested in reading a very thick book or a book does not make them excited, so they rarely read books and information that impact on their reading comprehension. If the lecturers give them the task in their reading comprehension lesson, the students just copy and paste the information available on the Internet. When they present their work, they do not understand what they showed because just copy and paste.
B. Research Question
Referring to the previous background, the researcher used formula a research question as follow:
―Does the use of WebQuest influence the EFL students‘ literal reading comprehension?‖
C. The objective of The Research
About the problem statement above, the objective of this research is to find out whether WebQuest affect the EFL students' reading comprehension at FKIP Unismuh Makassar.
D. Significance of The Research
The significance of the research expects to be useful and helpful information for the English teachers, especially in using WebQuest in the quality of teaching and learning process in terms of reading comprehension. For students, the result of this research it expects to be useful information in developing students' reading comprehension skills. Also, it‘s hope that any obstacles faced by the researcher would be a consideration in finding any better ways to make improvements for the better learning condition. This research may also be useful information as the basis of the study for any researchers who want to conduct in the same topic or something that relates to this research.
E. Scope The Research
The research will find out and solve the problem of the student's lack of understanding of reading comprehension. This research will be conducted at a university. The research will focuses on literal reading comprehension in terms of main idea and supporting details.
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF LITERATURE
A. Previous Related Research Findings
Several studies already have been conducted by some researchers. Many studies have performed by the research related to using strategies, methods, techniques, or media in improving students' ability to learn English. Some of them are, According Widyarini. F (2015), in her journal entitled ―Using WebQuest to Improve Students Reading Comprehension," Her study concluded the teaching of reading in students by using WebQuest simultaneously improves students' reading comprehension. The next experts by Anggry (2018), in her journal entitled ―Implementing WebQuest Study Research to Improve Students Reading Comprehension‖ indicated that WebQuest based learning activities to make students more engaged in the learning process. The other study did by Rachmawati. U. (2018), in her journal entitled ―Using WebQuest to Improve Students' Reading Comprehension," Her application WebQuest concluded quite successfully to improve students' reading comprehension. The next experts by Weda. S. (2017), in her journal entitled ―WebQuest Effect on Students' Reading Comprehension," Her study concluded the use of WebQuest improves student achievement in reading comprehension and students interested in learning reading comprehension.
Based on the preview study above, the research focus on the application of the quasi-experimental teaching method to the pre-test and post-test control group. In
this study, the learning achievement of reading comprehension increased the students using WebQuest. This research was conducted at school and involved students. Unlike previous research, this study focuses on understanding reading learning using WebQuest. Previous studies also only involved students in junior high school in being a sample in their education, but in this study used students at the University Muhammadiyah of Makassar. The quantitative approach is used to investigate the effectiveness of this method. The research focuses on the application of the pre-experimental teaching method to the pre-test and post-test. B. Concept of reading comprehension
1. Definition of Reading
Many specialists defined reading. Reading is an essential skill that must be held by students because reading cannot separate from the teaching and learning process.
According to saiful (2018), reading is an action study and interpretation performed by the reader to urge the author to provide a massage in written media. Nuttal in asrianti (2005) states that reading is to remembered in order to be understood, but read and analyze the printed page. Smith and Robinson in Asrianti (2015) mention that they the reader‘s active effort to understand the author‘s message. The reader is curious in and is attempting to reconstruct what the writer wants of the experts. Haris and Sipay in Asrianty (2015) say reading is important. Interpretation of verbal symbols, written or printed.
2. Definition of reading comprehension
Widyarini F (2015). Reading comprehension is one of the main skills required to broaden the reader's viewpoint and gave them the ability to see the world and opportunities. The next experts Eaman (2017) Reading comprehension is a critical ability in the adult world written without which individuals struggle with the directions or feedback or follow new knowledge using written language. The other experts is Kirby (2007) who states that reading comprehension is a phase in which we understand the text that we interpret.
Weda (2010) conceptualizes reading comprehension is one of the most successful ways of to learn English and has a similar relationship to an active writing style. The next experts by Farhadi (2005). Reading comprehension is a dynamic mental mechanism in which the reader interacts with the text in order to infer meaning. Gary (2011) further argues that reading comprehension is a way to make sense out of text.
Reading comprehension is the theory of students to understand what they are reading and what the meaning of the text they are reading or the ability to manage text. Reading comprehension is really important to someone, since we need to find the meaning of words in text reading means finding a word or phrase that precedes or follows a word so that the intent, the meaning and the meaning of a word can be understood.
3. Kinds of reading comprehension
In reading comprehension, we must have skimming, scanning, previewing, close reading, guessing from context, paraphrasing abilities. Skimming is a speed-reading tool that can save time and help readers search a lot of information. This is distinct from other ways of high-speed reading, such as preview and scanning. Skimming can give readers a sense of passage or a general novel, not comprehensive details. The purpose of skim reading is not to read the text in its entirety, but to find out what short details the reader is looking for, and if determines what needs to be read more carefully. So, in skimming through the text, the reader needs to practice so that people can learn keywords and phrases that can cover all the knowledge they are reading. The reader must scan the part, skip the bits, and get a general idea of what it is do skimming.
Scanning is a very high-speed reading that the reader does when they‘re looking for correct details. As the reader scans, the reader has questions in his mind as he scans. We don't read every word in the scan, but only the keywords will answer our questions.
Scanning easily reads to find particular information Brown (2000: 308) notes that the will scan soon be looking for specific bits or pieces of information in the document. By scanning, the reader means either searching through the text to find relevant details to get an initial understanding of whether the text is appropriate for a particular purpose. When scanning, readers can see students' eyes wandering through the text before they check,
whether it is a location, type of food, some kind of verb, or specific details. In order to allow students to search efficiently, students also need to have clear beliefs where students can find the knowledge they need from document.
Previewing is something that we‘ve done in our details lives. For example, when we get a letter, we normally first look at the sender's address or cramp to find out who sent it and where it came from a reader. Then we‘re going to make some assumptions on what‘s going to happen. We may take a lot of information about the text that we‘re going to read by previewing for a few seconds.
Close reading requires careful attention to all the words and sentences in a selection to understand its full meaning (later and Osborn).
Context Guessing is the best strategy to do when we come to a term that we don‘t know when we‗re reading. Using previous knowledge of the subject and concepts in the text as references to the meanings of unfamiliar words, instead of stopping to look at them.
Paraphrase is an approximation of the meaning of a word or phrase that uses another word or phrase, often to make it easier to understand, according to Richard and Schmindt (2002: 384). You quote stops at the end of the section to check comprehension by the information and ideas in the text. 4. Level of reading comprehension
Burn-in Saiful (2019), divides the comprehension into four levels of skills. Each of these skills could explain as follow:
a. Literal Reading
Literal reading or reading the lines requires a lower level of capacity to think. It refers to the ideas and details that appear state on printed pages.
b. Interpretative Reading
Interpretative consider being a higher level of capacity to think. The concern is to reading lines or making an inference.
c. Critical Reading
Critical reading has a higher level than the previous two. It includes analyzing, comparing the ideas found in the printed content with the findings of established criteria on their appropriateness and timeliness. d. Creative Reading
Creative reading allows the readers to reply on the basis of the text and to use their understanding, creativity and understanding.
5. Factor affecting reading comprehension
Anderson in Anita (2006: 18) describes the factors affecting reading comprehension. In this opinion, it means to reside in the text information itself. Meaning reached when the reader integrates the personal background knowledge, purpose for reading strategies, and text to get definition.
The description above implies that to get perfect comprehension in the reading process, and there are some factors, either internal or external, that should be monitor. there are five categories of the factor affecting reading comprehension, namely:
a. Background experience
It refers to the previous experience that the readers have already known before and relates to the reading materials that they read. b. language ability
if someone faces a reading whose language they have never heard, it will be difficult to understand the reading text. The cause is nothing else because of the limitations of the vocabulary they have.
c. Thinking ability
It means that the reader ability to analyze the reading materials. d. Affection
It means that the readers have to know about some psychological factors that can affect the readers' comprehension. The element is interest, motivation, attitudes, etc.
e. Reading purpose
It refers to the reader's purpose why they read the reading materials. It is usually done by making some question or predicting as a stepping stone to get comprehension. (Anderson in Arif (2006: 16). 6. Measuring reading comprehension
Measuring reading comprehension can measure through:
a. The literal level of understanding is where students need to know what works in the plot, what the main characters are, and where the story took place.
b. Levels of understanding that students need to consider what the author says, what is central to them, and how these details fit into what you already know.
c. The third level is indicative of something that delivers, students will infer from what is said and proof of what is accompanied by generalizations.
C. The Concept of WebQuest 1. Definition of WebQuest
The WebQuest was launched by Bernie Dodge and Tom March in 1995 and was developed on the basis of constructivist philosophy, promoting collaborating learning and instruction of scaffolding. According to Dodge (1997), WebQuest is an inquiry-oriented learning format in which all the content that students gain comes from the web. In language learning, WebQuest not only enables students to improve their language skills by exploring their structured web resources (Laborda, 2019) but also helps students become better learners by increasing their autonomy and demonstrating students satisfaction (Lou), 2010). WebQuest can also be an alternative learning tool that can help students learning English.
According to Dodge (1998), WebQuest very well designs, which consists of six components, namely: Introduction, tasks, processes, resources, evaluation, and conclusions. The Introduction is used to launch the subject by presenting interesting background information and blueprints for the entire hunt. The task and method section provides a general overview of the tasks
and the step-by-step processes to be followed in order to accomplish the task. A collation of information resources required to complete the task has been illustrated in the resources section. Knowledge sources can include web records, databases that can be searched on the Internet and books, and other documents that are physically accessible in student environments. The assessment aspect is typically in the form of a heading that will be used to evaluate student work, and the conclusions will lead to an attempt to close, inform students of what they have learned and allow them to extend their knowledge to other fields. There are two types of WebQuest, namely: Short-term WebQuest, and Long-Short-term WebQuest. Short-Short-term WebQuest focuses on the development and incorporation of student information that can be accomplished within one to three hours, while Long-Term WebQuest emphasizes the ability to develop and develop knowledge. As such, it can take between one week and one month in the classroom (Dodge, 1997).
WebQuest includes in inquiry learning. The proces of inquiry involves four processes. The first is to define the questions that need to be answered in order to find potential answers. The teachers answer and organize the answers according to the material after they locate the material on the basis of the questions. Teachers will then determine relevant and quality tools to help students address the questions identified. The result of this is helpful for students to be able to find the right and accurate facts. The third step is to manipulate the tools available to them to ensure that the right information is found and answers to the particular questions explored. The final step is to
formulate the answers identified by the students and to identify how these answers contribute to the original query. Teachers devise correct answers to provide input on the work of students, according to Coffman (2009: 7)
WebQuest is not familiar to teachers and students. This is an inquiry-oriented activity where most, if not all of the resources studied and examined by students are accessible on the Internet. Teachers direct the services that students are searching for. Variety and sense of satisfaction must exist for the source. This gives students the assumption that the materials are new and will allow them to enter the world. According to (Coffman 2009: 33), the aim of this learning media is to allow students to find content in a meaningful and interesting way.
WebQuest is a modern way to attract the students in reading English passages, which can be categorized as very practical in usage. Vocational school students need more original texts that refer to their majors. The benefit of using this program is the realism and the novelty of the objects, texts. Students should look search for more real knowledge about their needs and desires. This starts with the use of real-world evidence and knowledge contained on the Internet (Coffman, 2009: 33-34).
WebQuest allows students to ask questions, make a hypothesis, test a hypothesis, and show new understanding to others, according to Coffman (2009: 34-35). By using this media, students can ask a lot of questions about to the subject so that they can get information that is relevant for the subject
to be discussed. Students than make conclusion based on the knowledge they receive. In order to obtain the correct information that the instructor require, students must test the hypothesis. This can be done by cross-checking with their partners and teachers. Finally, students are asked to show their new interpretation of the content they‘ve been looking for to others. Students may place information in their long-term memory by following these four steps.
A successful WebQuest cannot stand alone without any solution. In successful WebQuest, teachers are asked to concentrate on a variety areas that are relevant for students' needs. Explain the fields that must be present in this good medium. It is easier to provide learning expectations and goals, authentic practices and evaluations, collaboration teaching method, opportunities to build and explore knowledge through discovery and experimentation, resources to recognize real-world data and the latest relevant information, and technology tools and resources to lift the issue of big ideas, according to Coffman (2009: 35). If WebQuest has these requirements, they categorize them as good criteria for teaching and learning. WebQuest is preparing the learning material presented in the WebQuest, which is sourced from the Internet and can also be presented on the Internet. This lesson plan allows students to do their job of searching for knowledge on the web or on connection.
2. Function of WebQuest
The WebQuest has been developed by Dodge. Bed, and it‘s March. T. in 1995 an attempt was made to implement a learning and teaching environment for computer-based students and teachers and to integrate the World Wide Web into classroom teaching. WebQuest helps students and teachers to access materials and information from the Internet. The use of time by students focuses on the use of expertise and encourages the quality of thought and understanding of students.
3. WebQuest in reading comprehension
To develop reading comprehension, one of the most useful resources for students that technology and the Internet because now very sophisticated and this era, most students are already using technology and the Internet. Now there are quite a lot of students who are more interested in finding information on the Internet than any other media. and information related to learning materials. limited availability of instructional media in schools make students more interested in using the Internet as a learning resource.
Mobile is one technology that is very sophisticated to look for something that we need. Most students more were wasting his time reading using a mobile phone than to read the book because in the books does not make students interested in reading because in the books there is no picture make students interested in reading and make students tired of reading books, whereas if students read on the web or link students will be more interested in reading them because in reading on the web or link very many pictures that
make students interested in it and if we use mobile phones to open web or link it very easy for someone to carry them everywhere compared to the book.
4. The implementation of WebQuest in reading comprehension
Several stages involve in using WebQuests in reading comprehension class as follows:
a. Search in google about WebQuest
c. When the home of zunal WebQuest open. Please look for "WebQuest Search" on the left side
d. In WebQuest, search provides 3 items: Keywords, Grade, and Subject. Filling in the keywords: Reading comprehension, grade: college/adult, and subject: English/Art. And the search.
e. Moreover, several themes showed. Choose one of the appropriate themes.
f. This one of the themes, "Reading Comprehension." Pay attention in the left side. There are 9 items as follows: Welcome, Introduction, task, process, evaluation, conclusion, teacher page, author, and review.
g. First, Introduction refers to brainstorming before doing the tasks.
i. Third, process. In these stages, all of the material in written or in video that completed with the tasks is provided.
j. Fourth, evaluation. In this stage, the teacher fills out the rubric of the task.
k. The last conclusion, teacher page, author, and review as the additional information from the previous stages.
5. Teaching in WebQuest
Coffman (2009: 34) states that WebQuest is a fine examples of constructivist learning. The instructor proses a "big idea" query and offers appropriate tools and educational methods for students to explore and discover the knowledge problem.
Dodge (1997) in Ruddle (2005: 267-8) notes that the use of WebQuest can offer critical attributes, such as introduction, task, information, process guidance, and conclusion. Introduction involves setting the stage and presetting some context information. The role chosen by the instructor should be feasible and interesting. A set of information sources, most of which are web-based is needed to complete the task. The production of the process is that the students will go through the process to achieve the task. The other hand, advice is committed to the organization of the knowledge required. The final conclusion that it brings the search to close, teaches students of the materials they study and helps them to learn.
An inquiry-oriented activity encompasses major ideas issues as well as learning standards and objectives and should provide authentic tasks to engage students in exploring and developing their own understanding about a subject (Coffman, 2009: 36).
The instructor will reveal the subject or problem relevant to the next materials by using the WebQuest. This will boost students‘ desire to learn because they know what they‘re going to talk about. Here, stating the next
materials is done in more exciting ways. As a result of using Internet to learn through this the instructor is required to create an enjoyable and acceptable condition for students to learn both in groups and on an individual basis. The students work in a collaborative group which will discuss a series of questions maintaining a big subject. The learning materials based on the standard of competences and basic competencies. Coffman (2009: 56) says that in WebQuest students work in interactive groups on an acceptable subject that is consistent with learning expectation and allows them to discuss the content in more detail.
D. Frame Work
The conceptual framework underlying this research illustrate in the following diagram
Figure 2,2 The Conceptual Framework
In this research, the researcher will analyze the implementation the effect of using WebQuest to improve students' reading comprehension. Before the treatment using WebQuest researcher have gave pre-test, after the test researcher implementing WebQuest in the class, after pre-test and treatment
Input Teaching Reading Process Using WebQuest in teaching reading comprehension process Output Whether using WebQuest can improve students reading comprehension
researcher gave the final test or post-test to know the data that WebQuest can improve students‘ reading comprehension.
D. Hypothesis
The hypothesis of this research are:
Hi: WebQuest does improve students reading comprehension.
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD A. Research Design
In this research, the researcher used pre-experimental design with one-group pre-test–post-test design. In this research design, there was no control group. The researcher gave pre-test to student, then, researcher gave the students' treatment about reading comprehension using WebQuest. After treatment, the researcher gave the student post-test.
One-Group Pretest-Posttest Design
Pretest Independent Posttest
Y1 X Y2
Notes:
Y1: Pre-test
X: Independent variable; Reading Comprehension using WebQuest.
Y2: Post-test
B. Research Variable 1. Independent Variable
The Independent variable of the research is the use of WebQuest in reading comprehension.
2. Dependent Variable
Dependent variable was the students‘ reading comprehension. C. Population and Sample of Research
In this part, the researcher is described about sample and population of the research:
1. Population
The population of the research is all the third semester of EFL at Unismuh Makassar. It consisted approximately 132 students that divided 6 classes, and each class consisted 20 students.
2. Sample
In this research, the researcher used a qouta sampling technique, select based on the characteristic of a population and the objective of study. The number of samples taken is 20 students for class C.
D. Instrument
Research instruments were tools for collecting data. In this study, researchers used one type of instrument, the reading test to make students easy to memorize key words from the text. The type of text used to assess students is narrative text to find main ideas and supporting details. The research instrument consisted of
1essay question items. Tests were given to students twice, namely pre-test and post-test. Tests were given to students‘ numbers was six numbers.
E. Data Collecting procedure
In collecting data, the researcher took the data from pre-test and post-test. Pre-test administered to the subject before applying WebQuest. Meanwhile, post-test administered after applying WebQuest.
Pre-test and post-test contain the same test items. They were just different in time allocation. These pre-test and post-test taken by evaluation. Therefore, these tests must valid and reliable. Then, the present researcher uses these items as the pre-test and post-test which includes three steps. Those are pre-test, treatment, and post-test.
1. Pre-test
At the first meeting, the researcher gave a pre-test through google meet to read some text that seen similar to the students in measuring their reading comprehension. The researcher asked the students to read the texts. Students gave 90 minutes to answer the question from the pre-test.
2. Treatment
The procedures of treatment are:
a. The learning process takes place through google meet. Researcher use WebQuest as a learning media and the researcher explains how to use Webquest, then the researcher explains the material about reading comprehension in literal reading comprehension and explain about
main idea and supporting details in the narrative text. The researcher teaches narrative text each meeting through google meet.
b. The researcher demonstrated through WebQuest how to find main idea in the text and sentences.
c. The researcher demonstrated through WebQuest how to find supporting details in the text and sentences.
d. The students listened to the researcher through google meet, and they are given chance to reading the text in the WebQuest.
e. At the next step, the researcher provides texts in the WebQuest. f. Instruct students on how to use the WebQuest and instruct them to
answer the question that related to the supporting details and main idea the students explain their each text.
g. Students are treated using WebQuest to improve students‘ reading comprehension was repeated in two meetings with different text. h. In the last meeting, the researcher reviewed the students
understanding that the students had learned in previous meeting. 3. Post-test
Post-test administrated after implementing treatment. The post-test items are the same with pre-test items. Pre-test and post-test also have some application when they are conducted in google meet. Researcher gives evaluation to student trough google meet. The students answer the test in 90 minutes. The purpose of this post-test was to know the students‘ reading comprehension after implementing WebQuest.
F. Data Analysis
1. Criteria of Score Analysis
To score the students' answer, the researcher used the following formula as follow as:
a. The rubric of literal reading comprehension dealing with main ideas and sequence details.
Table 3.1 the rubric of literal reading comprehension dealing with the main idea
No Criteria Score
1 The answer includes a clear generalization that states or implies the main idea.
4
2 The answer states or implies the main idea from the story.
3
3 Indicator inaccurate or incomplete understanding main idea.
2
4 The answer includes minimal or no understanding of the main idea.
1
5 No answer 0
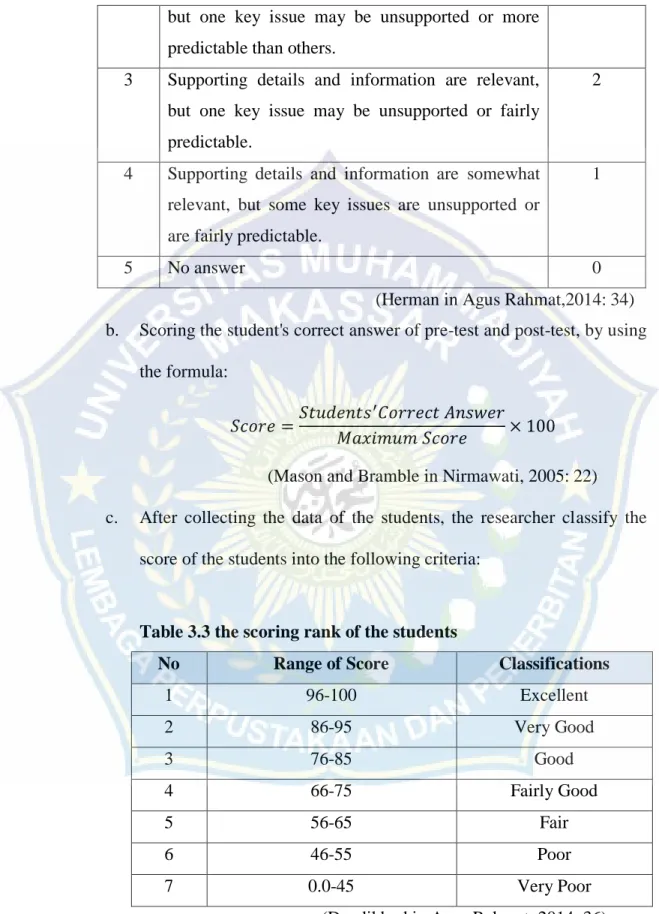
Table 3.2 the rubric of literal reading comprehension dealing sequence of details
No Criteria for Supporting Details Score 1 Relevant, telling, quality details give reader
important information that goes beyond the obvious or predictable.
4
but one key issue may be unsupported or more predictable than others.
3 Supporting details and information are relevant, but one key issue may be unsupported or fairly predictable.
2
4 Supporting details and information are somewhat relevant, but some key issues are unsupported or are fairly predictable.
1
5 No answer 0
(Herman in Agus Rahmat,2014: 34) b. Scoring the student's correct answer of pre-test and post-test, by using
the formula:
(Mason and Bramble in Nirmawati, 2005: 22) c. After collecting the data of the students, the researcher classify the
score of the students into the following criteria:
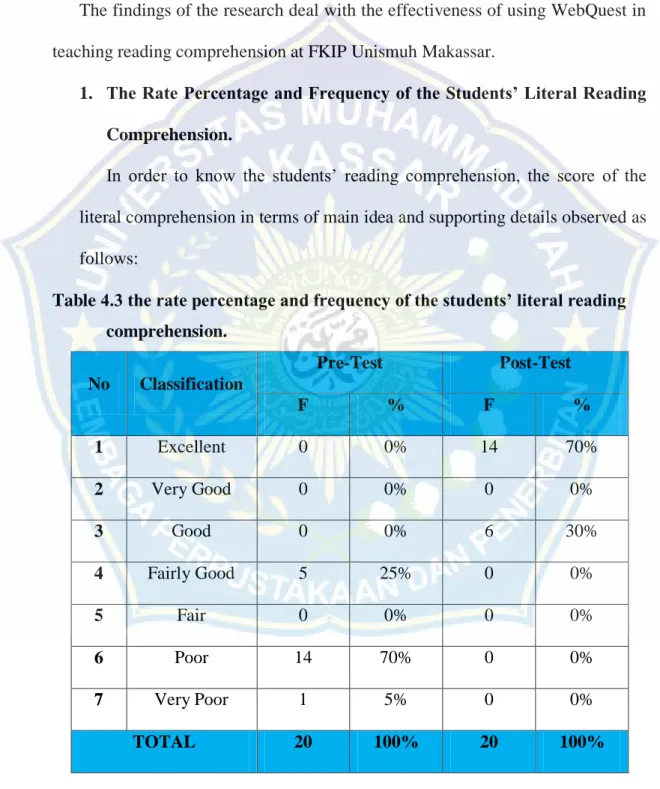
Table 3.3 the scoring rank of the students
No Range of Score Classifications
1 96-100 Excellent 2 86-95 Very Good 3 76-85 Good 4 66-75 Fairly Good 5 56-65 Fair 6 46-55 Poor 7 0.0-45 Very Poor
2. Calculating the Mean Score and the Value of the Test
a. Calculating the mean score of the students' answer in both pre-test and post-pre-test by applying the formula below:
Notes: X: Mean Score
∑X: Sum of all score
N: Number of students/sample
b. To know the improvement of the students' reading comprehension, the researcher will use the percentage technique below:
Notes: P: Percentage of the students X1: Mean score of pre-test X2: Mean score of the post-test
(Gay, 1981: 298)
c. This technique employs to find out the significant difference between the pre-test of experimental class and control class, and also to find out the significant difference between post-test of experimental class and control class, the researcher calculating the value of the test by applying formula below:
̅ √ ( ) ) Where : ̅ : Mean Score
: The Sum All of Score
N : The Total Number of Student T : Test of Significance
(Gay, 2012)
After the t-test is finding, the result of the t-test is compare with the t-table. If the t-test is higher than t-table, it means that this research is useful and inversely, if the t-test is lower than t-table, it means that this research is not effective.
CHAPTER IV
FINDING AND DISCUSSIONS
A. Finding
The findings of the research deal with the effectiveness of using WebQuest in teaching reading comprehension at FKIP Unismuh Makassar.
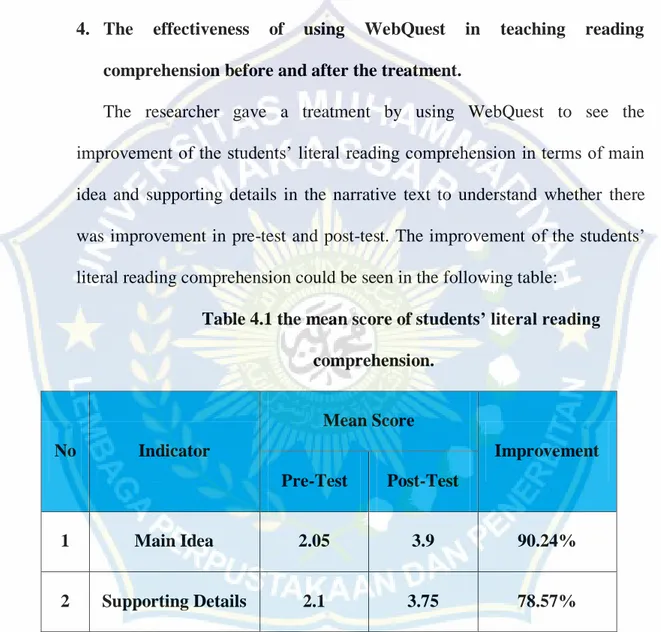
1. The Rate Percentage and Frequency of the Students’ Literal Reading Comprehension.
In order to know the students‘ reading comprehension, the score of the literal comprehension in terms of main idea and supporting details observed as follows:
Table 4.3 the rate percentage and frequency of the students’ literal reading comprehension. No Classification Pre-Test Post-Test F % F % 1 Excellent 0 0% 14 70% 2 Very Good 0 0% 0 0% 3 Good 0 0% 6 30% 4 Fairly Good 5 25% 0 0% 5 Fair 0 0% 0 0% 6 Poor 14 70% 0 0% 7 Very Poor 1 5% 0 0% TOTAL 20 100% 20 100%
Based on the table 4.3 showed that before treatment was given, there were 5 students (25%) got ‗Fairly Good‘, 14 students (70%) got ‗Poor‘ and 1 students (5%) got ‗Very Poor‘. And after the treatment was given, there were 14 students (70%) got ‗Excellent‘ and 5 students (30%) got ‗Good‘. Based on the result, the researcher concluded that the rate percentage and frequency in the post-test was higher than the rate percentage in the pre-test.
2. The significance Improvement of Students’ Literal Reading Comprehension
A pre-test was administrated before the treatment, and post-test which aimed to know where there was a significant improvement of the students‘ literal reading comprehension between the students who were taught by using WebQuest and those who were taught by conventional Approach. The Improvement of the students‘ literal reading comprehension could be seen in the following table.
Table 4.2 the mean score of the significance improvement of the students’ literal reading comprehension.
Mean Score
Improvement Pre-test Post-test
52.30 94.90 81.45
The 4.2 indicated that the significantly difference of the mean score of the students‘ literal reading comprehension between pre-test and post-test. The data analysis shows the students mean score improved from pre-test to
post-test. Before applying the treatment in pre-test, the students‘ mean score for literal reading comprehension was 52.30. After applying treatment or in post-test on the conventional approach, the students‘ mean score improved to be 94.90 for literal reading comprehension. It could be seen in the following graphic:
The mean score of the pre-test and post-test
The use of WebQuest became one of the applications in the teaching and learning process.
That there was the difference improvement of the students‘ achievement in experimental class at literal reading comprehension. The students‘ improvement for literal reading comprehension was 81.42. it meant that the using of WebQuest was able to improve the students‘ reading comprehension in terms of main idea and supporting details.
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 PRE-TEST POST-TEST
3. Based on this result, it concluded that the using of WebQuest could improve the students‘ reading comprehension in terms of main idea and supporting details at the third semester of English Department of Muhammadiyah Makassar.
4. The effectiveness of using WebQuest in teaching reading comprehension before and after the treatment.
The researcher gave a treatment by using WebQuest to see the improvement of the students‘ literal reading comprehension in terms of main idea and supporting details in the narrative text to understand whether there was improvement in pre-test and post-test. The improvement of the students‘ literal reading comprehension could be seen in the following table:
Table 4.1 the mean score of students’ literal reading comprehension. No Indicator Mean Score Improvement Pre-Test Post-Test 1 Main Idea 2.05 3.9 90.24% 2 Supporting Details 2.1 3.75 78.57%
Based on the table above, it showed that there was difference of the students score of pre-test and post-test in literal reading comprehension. The
data analysis shows that the students mean scores were improved from pre-test and post-test. Before applying the treatment in pre-test, the students‘ mean score in reading narrative text in term on main idea was 2.05, and the students‘ mean score in reading narrative text in term of supporting details was 2.1. Most of students‘ did not know how to organize the text. It was caused that they did not understand how to manage every part of the text. After that, the researcher gave treatment by using WebQuest and the score of the students‘ had improved. It showed in post-test where the students‘ mean score in reading narrative text in term of main idea was 3.9, and the students‘ mean score in reading narrative text in term of supporting details was 3.75.
The percentage of the students’ improvement
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 Supporting Details Main Idea
Graphic 4.1 the percentage of the students’ improvement in post-test
The graphic shows that the improvement of the students‘ achievement in literal reading in term of main idea was 90.24% and 78.57% in term of supporting details. It means that applying WebQuest was good to improve the students‘ reading comprehension in terms of main idea and supporting details. 5. Hypothesis Testing (T-Test of Significant)
The hypothesis was tested by using t-test in order to verify whether students‘ ability using WebQuest was different significantly from students‘ improved conventional approach. The hypothesis testing between pre-test and post-test can be known using t-test. The result of significant analysis of the level of significance 0.05 with degree of freedom (df) = N-1: where N: number of students was 20. It could be seen as follows:
Based on the level of significance 0.05 and the degree of freedom (df)=19 above, the value of the t-table = 2.093. The result of t-test can be seen in the following table:
Table 2.4 The significance of Students’ Reading Comprehension Value T-Test T-Table Comparison Classification Post-Test 3.6 2.093 t-test>t-table Significance Different
Table 4.4 shows that t-test value was greater than t-table value and in the t-table for α= 0.05 and degree of freedom (df) = t ratio was 2.093. Based on the calculation, the value of the t-test was greater than the ration on t-table 3.6>2.093. According to this result, it could be concluded that the null
hypothesis (H0) was rejected and the alternative hypothesis (H1) was accepted.
There was a significant difference between students in pre-test and post-test. B. Discussion
This research investigated the use of WebQuest in improving students' reading comprehension, focused on the students' literal reading comprehension at the third semester of University of Muhammadiyah Makassar. The research found that the students' reading comprehension using WebQuest showed the improvement of the students' reading comprehension it is evident from the mean score and percentage of the students‘ pre-test and post-test result.
Accrording to Widyarini F, 2015. In this section, the researcher discussed and compared the results of this research with some previous researches that also used WebQuest. Supported on the research, it‘s proven that teaching reading in students by using WebQuest simultaneously improves students‘ reading comprehension. However, it‘s worth to noting that using webQuest is effective and efficient when the activities and materials involve the students. Therefore, it‘s suggested that teachers should be more creative to use various material resources and make a motivating sort of WebQuest in teaching students‘ more interested and actively involved in teaching learning process. Additionaly, WebQuest also can improve the classroom climate including students‘ participation and motivation in class, which can be seen from the students‘ attitude in joining all activities during the research.
Using WebQuest allows students to actively work enthusiastically to work on assignments through WebQuest, they work with small groups and every one
students are actively involved. This can be seen from the results of the post-test students who answered the post test well after using the WebQuest, students also experienced a high increase after using WebQuest. (Widyarini. F, 2015)
According to Anggry A 2018, he journal stated the research findings show that the implementation of WebQuest technique could improve students‘ reading comprehension and sophistication climate of reading class. The research results indicated that these web-based learning activities could make students more engaged within the learning process.
The use of the WebQuest is believed to be effective to enhance students‘ reading comprehension. Students‘ reading problems are often reduced by applying the WebQuest facilitate students to be ready to comprehend authentic texts by relating it to their knowledge. The introduction section invites students to predict the content of the texts they‘re going to read. The task and process sections give opportunities for college students to grapes the texts provided. The evaluation and conclusion section sections offer a summary to students which helm them to evaluation their understanding. Students‘ gain score from pre-test to post-test which the questions are adequate to reading section of TOEIC increases. It‘s also proved that the utilization of internet and computer laboratory results in the students‘ motivation in reading thanks to chance for them to access authentic texts. (Rachmawati 2018)
The research showed that there was an improvement to the students‘ achievement in pre-test and pot-test of the 2 groups. The experimental class was more significantly improved than the students‘ result of the post-test of the control
by the mean score 80.23>76.40.Tthe difference of both scores was statistically significant supported the t-test value with significant level 0.05 in which the probability value is lower than the significant level 0.00. (Weda 2017)
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
This chapter deals with the conclusion and implication of the research findings, some suggestion regarding to the finding for the improvement of teaching reading comprehension by using WebQuest.
A. Conclusion
Based on the research findings and discussion in the previous, the application of using WebQuest in teaching reading comprehension improved the students‘ reading comprehension more significantly at the third semester students of Muhammadiyah University of Makassar in academic year 2020/2021.
The students‘ reading comprehension showed that the students‘ mean score improved as shown from the pretest to posttest. The students‘ mean score of pretest was 53,30 and it classified as poor. After, applying treatment the students‘ literal comprehension improved. It is proved by students‘ mean score in posttest was 94,05 and it classified as fairly good. So, the improvement of students‘ achievement in reading comprehension was 79,82%.
B. Suggestion
Based on the conclusion above, the researcher would like to give suggestions as follows:
1. Students should be presented with creative material for learning reading comprehension such as using WebQuest.
2. It is suggested that the teaching of reading comprehension be continually implemented to the students.
3. Further researches need to be conducted and explored more about the effectiveness of using WebQuest.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Abbas, Narjes, 2016. How can students improve their reading comprehension skill. Vol. 6. No. 2. 2016. Macrothink institute.
Ary, D., et al. 2010. Introduction to Research in Education ( Eight Edition ). The United State of America : Nelson Education
Anggry A, 2018. Implementing WebQuest Technique to improve students reading comprehension. ICTESS.
Coffman, Teresa. 2009. Engaging Students through Inquiry-Oriented Learning and Technology. United Kingdom: Rowman & Littlefield Education. Dwiarti, E. 2005. An Analysis of Students‘ Problems in Findings the Main Idea of
the Text at Second Years of SMU Kosgoro Sekampung, East Lampung. A Script, FKIP, University of Lampung.
Dodge 3, B. (1998). Web Quest: A strategy for scaffolding higher level learning. Retrieved September 3, 2013, from http://webquest.sdsu.edu./necc98.htm. Dodge.B. 1997. Some Thoughts About WebQuests. Retrieved from
http://WebQuest.sdsu.edu/about_WebQuest Html.
Dodge, B. (1995). WebQuests: A technique for internet-based learning. Distance Educator, 1(2), 10-13.
Dodge, B. (1995). Some Thoughts about WebQuests. San Diego: University of San Diego.https://www.scirp.org/(S(351jmbntvnsjt1aadkposzje))/reference /ReferencesPapers.aspx?ReferenceID=652651.
Eaman, 2017 Using WebQuest to promote reading comprehension for students whit learning disabilities, Roosevelt University. International journal of special education. Researchgate.
Farhadi, H. (2005). Techniques for Effective Reading. Iran: Iran University of Science and Technology.
Gay, L. R., Geoofrey E. Mills, Peter W. Airasian. 2012. Educational Research: Competencies for Analysis and Application Tenth Edition. USA: Pearson. Gay, LR, 1981. Education Research, Competencies for Analysis and Application.
USA: Charles E Merill Publishing co.
Gay, L. R., Geoofrey E. Mills, Peter W. Airasian. 2012. Educational Research: Competencies for Analysis and Application Tenth Edition. USA: Pearson.
Gary, 2011. Reading comprehension. ResearchGate.
Harmer, Jeremy. 2003. The Practice of English Language Teaching. London: Longman.
Haris & Sipay. 2015. Improving the Students‘ Reading Comperehension Through Reciprocal Teaching Strategy at the Class VII of Madrasah Tsanawiyah DDI Seppong Kab.Majene Sulbar. Thesis. Muhammadiyah University of Makassar.
Haterulez, 2012. Kind of Reading Comprehension Skills. Cemink‘s Voices.
http://beddebah-haterulez.blogspot.com/2012/09/kind-of-reading-comprehension-skill.html.
Kirby in Earman. 2007. Using Webquest to Promote Reading Comprehension for Students With Learning Disabilities. International journal of special education. Researchgate.
Kustaryo. 1998. Faktor faktor yang mempengaruhi kemampuan membaca. Jalarta: BumiAksara.
Nuttal. 2015. Improving the Students‘ Reading Comperehension Through Reciprocal Teaching Strategy at the Class VII of Madrasah Tsanawiyah DDI Seppong Kab.Majene Sulbar. Thesis. Muhammadiyah University of Makassar.
Rachmawati U. 2018. Using WebQuest to Improve Students‘ Reading Comprehension of the Second Grade at SMKN 1 Depok, Sleman In the Academic year 2011/2012. Eprints.uny.ac.id.
Richard and Scmindt in Heterluez (2012). Kind of Reading Comprehension Skolls. Cemink‘s Voices.
Saiful. 2019. In his thesis, The Effects of The PORPE Method on Students' Reading Comprehension and Metacognitive Awareness.
Smith & Robinson. 2015. Improving the Students‘ Reading Comperehension Through Reciprocal Teaching Strategy at the Class VII of Madrasah Tsanawiyah DDI Seppong Kab.Majene Sulbar. Thesis. Muhammadiyah University of Makassar.
Syaiful R, Wahib M, Ega B, 2014. Use of WebQuest based learning media in the productive learning process in high school. Vol. 1, No. 1, June 2014. Journal of mechanical engineering education. Ejournal.upi.edu.
Widyarini F, 2018 Using WebQuest to improve students' reading comprehension, IJSER. Vol. 6, Issue 10, October 2018. Academia.edu.
Weda S, 2018. The effect of WebQuest on the students reading comprehension. Yusra Y.
Zeynep K, 2009. WebQuest in EFL reading/writing classroom. Elsevier. Vol. 2, Issue 2. 14 January 2010. Scholar google.
APPENDIX A The Result of Analysis
F. Appendix A.1 Data of Pre-Test and Post-Test of experimental Class G. Appendix A.2 The Rate Percentage of Students‘ Scores
H. Appendix A.3 Calculating Of The Mean Score of Pre-Test and Post-Test I. Appendix A.4 Scoring Analysis of Pre-Test and Post-Test
J. Appendix A.5 Table Distribution of T-Table
APPENDIX B The Instrument of Pre-Test and Post-Test APPENDIX C Lesson Plan of Experimental Class
APPENDIX A.1
Data of Pre-Test and Post-Test of Experimental Class 1. The Row Score of Students’ Pre-Test in Experimental Class
No Sample Pre-Test Experimental Total Final Score Classification Reading Comprehension Literal Comprehension Main idea Supporting Details 1 S-1 3 2 5 66 Fairly Good 2 S-2 2 2 4 50 Poor 3 S-3 2 2 4 50 Poor 4 S-4 2 2 4 50 Poor 5 S-5 1 2 3 33 Poor 6 S-6 2 2 4 50 Poor 7 S-7 3 2 5 66 Fairly Good 8 S-8 2 2 4 50 Poor 9 S-9 2 2 4 50 Poor 10 S-10 2 2 4 50 Poor 11 S-11 2 2 4 50 Poor 12 S-12 2 2 4 50 Poor 13 S-13 2 2 4 50 Poor 14 S-14 2 2 4 50 Poor 15 S-15 2 3 5 66 Fairly Good 16 S-16 2 3 5 66 Fairly Good