CLASSIFICATION OF INTERNET
LANGUAGE LEARNING RESOURCES
BASED ON BLOOM’S TAXONOMY AND
THE FOUR LANGUAGE SKILLS
THESIS
Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the
degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd) in Teaching English
By:
Ajeng Hidayatul Maghdalena
NIM D95213111
ENGLISH TEACHER EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TARBIYAH AND TEACHER TRAINING FACULTY
SUNAN AMPEL STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
ABSTRAK
Maghdalena, Ajeng Hidayatul. (2017). Klasifikasi Sumber-sumber Pembelajaran Bahasa di Internet Berdasarkai Bloom Taksonomi dan Empat Keterampilan Bahasa. Skripsi. Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya. Pembimbing: MokhamadSyaifudin, M.Ed, Ph.D&Dra. Irma Soraya, M.Pd
Kata Kunci: Sumber-sumber Pembelajaran Bahasa di Internet, Materi Pembelajaran Bahasa, Bloom Taksonomi
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter discusses the area of the study that will be covered in heading; background of study, research questions of the study, objectives of the study, significance, scope and limitation, and then the definition of the key terms.
A. Research Background
Nowadays, the development of technology and internet has been widely applied in education. The use of World Wide over the past decade has been dramatically increase because of the use of modern technology in teaching languages1. With the development
of technology and the Internet in education, it is possible now to study with distance learning using internet to link between students and teacher. Then, they may interact with others in different locations by using technology. It means that teacher should recognize the trend toward the use of internet in this modern era. They should realize that the innovation in teaching environment can
be done by using internet, because today’s students are facing the
virtual world2.
Furthermore, according to Chih-hung, a young teacher of writing and CALL says that by using internet, it can increase the use of electronic document and save papers, because the use of hard-copy documents has been burden for institution, teachers, and the environment3. Then, it helps the teacher to prepare handouts for
the larger class, and then the teacher does not need to make a lot of copies materials, because by using electronic documents they can share it easily without using any papers. Additionally, according to Ming-Jen’s statement, he says that providing links to some materials are better than supplying hardcopy4.
In term of recognizing the trend of the use of technology and internet in education, a curriculum of English Teacher
1 Yu-li Chen Ã, “A mixed-method study of EFL teachers ’ Internet use in language instruction”, Vol.24, Taiwan: 2008, 1016
2
Education Department in Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya also applies the development of technology and internet in educational side. The proof is the existence of CALL ( Computer-Assisted Language Learning) class in sixth semester. This class is preparing students in designing materials and media by using technology and internet that can be applied in teaching-learning process. According to fifth students’ CALL class in this department, they say that in a semester the class has many kinds of interactive and interesting tasks; such as video conferencing, collaborative writing, making timelines, making podcasts, etc. which must be
posted in individual learners’ educational blog. Then, they are
needed to do online discussion in several sessions of the semester through Schoology. Those explanations are in line with Chun and
Plass’ statement about CALL class. They say that multimedia
program with video, sound, graphics, and text which allow learners to be exposed to the target language can be got by providing this program. According Laura Schola as the district and technology coach, she states that Schoology is a new innovation of digital learning and teaching that resembles Facebook. It has several facilities such as resources, attendance, analytics, course, assignment, discussion which is created by Jeremy Friedman in May 2009 precisely New York America. By using Scoology, the educators can do things as simple as posting assignments, quizzes and links to additional resources or as sophisticated as conducting online courses, providing one-on-one remediation, or hosting discussions5. Besides, students do their discussion and their
assignment in everywhere and every time without facing their friends and lecturer directly as long as they have internet connection. All of the materials are required students to learn about the newest technology to improve language skills. Many internet language learning resources are introduced during this program in a semester and it provides between the teachers and students with creative and practical ideas, for the example is providing links to go to the various addresses and the students only need clicking those addresses.
3
However, based on the researcher’s experiences when joining
CALL class in a semester, the researcher got difficulties to find and use the internet language learning resources that appropriate with
the researcher’s teaching purposes. Therefore, the researcher did a
preliminary research on five students in sixth semester who are joining in CALL class. The researcher asked their opinion about the benefit of using internet in education, especially for their teaching practice or their real teaching. Based on their answers, it can be concluded that most of them mention the benefit of using technology and internet, but they also mention the difficulties to use it, such as they still getting confused to find out the appropriate materials with their teaching purposes, because since very often the results of the searching in internet language learning resources are so vast and not focused. Moreover, teacher should use internet language learning resources as an empowering tool to improve their language abilities, especially for their language skills such as reading, listening, writing, and speaking. Besides, according to
Lin’s explanation, she says that today it has been a necessary basic
quality and ability for people to search for information using internet resources6. It means that teacher needs the assistance to
keep up the expanding internet language resources, such as classifying the internet language resources based on certain categories. By classifying the internet language resources, it can be guided the language teacher to explore those resources and choose the right ones for their teaching purposes.
Related with classification of internet language learning resources based on certain categories, the researcher chooses the classification of internet language learning resources based on
bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills. In term of bloom’s
taxonomy, cognitive development is a part of bloom’s taxonomy.
According to Forehand’s statement, cognitive development is a
multi-tiered model of classifying thinking according to six cognitive levels of complexity, such as remembering, understanding, applying, analysing, evaluating, and creating7. Then, according to
Kathryn Zawisza’s explanation, bloom’s taxonomy is a powerful
6 Eleonora Villegas and Reimers. Teacher Professional Development: An International Review of Literature (Paris:International Institue For Educational Planning, 2003). 7Forehand, M. “Bloom's taxonomy: Original and revised. In M. Orey (Ed.), Emerging
4
tool to help develop learning objectives, because it explains the process of thinking8. Thus, it is necessary to find out the appropriate
materials that is taken from internet language learning resources
with the students’ cognitive level for improving their language
skills, therefore the teaching-learning process can be running well.
Moreover, according to Bates and Slobodina’s statement, they
say that critical the integration of CALL, creative designing supported activities by using technology, and enhance students’ active learning are the issue for teacher in this modern era. Teacher need to dig deeply the knowledge how to take advantages of internet language learning resources that can be applied in teaching-learning process, because there is no reason why teacher should not take advantages of internet language learning resources which have many kinds of materials. It is appropriate with Tsun-hsiang’s statement that the internet provides good resources and authentic materials for language teacher teaching9. Then, according to
Pelgrum, he says that the comprehensive knowledge of the potentiality of technologies and the possibilities for language
instruction applications are teacher’s need in this 21st era. All of
these can enrich their instruction and teaching resources in teaching-learning process. Besides, according to Johnstone’s statement, he says that internet language learning resources are tools for teachers which supported the materials for creating, adapting, and using the resources as well as they need10. Teachers should
know well how to get the internet language learning resources that
appropriate with students’ cognitive development based on bloom’s
taxonomy and the four language skills to assure the quality of education and educational practices because the two of the most important in educational goals are to promote retention and transfer11. Retention means the students’ ability of remember what
they have learned, and transfer is the ability of students who do not
8Kathry Zawisza, “Using Bloom’s Taxonomy to Write Effective Learning Objectives”, (https://tips.uark.edu/using-blooms-taxonomy/ accessed on 11 June 2017)
9 Yu-li Chen Ã, “A mixed-method study of EFL teachers…1022
10Ilkka Tuomi, “Open Educational Resources: What they are and why do they matter Report prepared for the OECD”. October, 2006
5
only remember what they have learned but also they are able to use it to solve the problems12.
There are three researchers regarding to this issue have been widely conducted. In Australia, Jeong-Bae Son has similar focus on classification of internet resources for language teaching13. His
research discusses about the place and role of online language teaching tools in CALL and present a category list of the tools. He classifies of online tools becomes twelve categories based on the main features and the functions. Another similar research is done by Yang S H U Ching in Taiwan14. The study examines learners’
subjective responses to the use of the World Wide Web within the context of a research project on American states. Data was collected using observations and surveys including demographic information and student perceptions via subjective-quantitative and qualitative questionnaire items. The result of this study is classified based on challenges of using the web, advantages of using web, and the learner attitudes towards the web. Additionally, another research about this concern was conducted by J.J. Sylvia entitled Using Bloom's Taxonomy to Assess Social Media. She tries to classify the social media for teaching-learning process based on bloom’s taxonomy15.
Based on those reasons which already explained above, this study is conducted to make differences from the previous study. This study will focus on classification of internet language learning
resources that facilitate the students’ cognitive development based on bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills. Therefore, the
teacher will be easier and faster to select the right internet language learning resources that appropriate with their teaching purposes.
B. Research Question
In relation to the background of the study above, this study is intended to examine the following questions:
12 Lorin W. Anderson, et al. A Taxonomy For Learning Teaching And Assessing…64 13 Jeong-Bae Son. “Online Tools for Language Teaching”. Vol.15, No.1, University of
Southern Queensland, Australia. June, 2011.
14 Yang, S. H. U. C. Language Learning On the World Wide Web : An Investigation of EFL Learners’ Attitudes and Perceptions, 24(2), 155–181. 2001.
6
What are the classification of internet language learning
resources that can facilitate the students’ cognitive development based on bloom’s taxonomy and the four
language skills?
C. Objectives of the Study
This research will be aimed to find out:
The classification of internet language learning resources which
are able to facilitate the students’ cognitive development based on bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills.
D. Significance of the Research
This result of the study is expected to give contributions, such as:
1. Generally in English Teacher Education Program, this research can be one of references to find out easier and faster some internet language learning resources that provides many kinds of materials for EFL teaching which appropriate
with the students’ cognitive development based on bloom’s
taxonomy and the four language skills.
2. For students who take English Teacher education, this research can helpful for their teaching practice by having some internet language learning resources, because it can be found easier and faster on the table of classification of internet language learning resources that appropriate with
students’ cognitive development based on bloom’s taxonomy
and the four language skills. The next students of English Education also can take this study as the resource related to the effectiveness of internet resources for facilitating the
students’ cognitive development based on bloom’s taxonomy
and the four language skills.
3. While for lecturer, this research can raise their knowledge when they want to find out internet language learning resources that facilitate students’ cognitive development
based on bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills
7
Sunan Ampel Surabaya as the assistance and guidance to find out some internet language learning resources which have
many kinds of English materials for facilitating students’ cognitive development based on bloom’s taxonomy and the
four language skills.
4. In particularly, it can be the effective way to find out some internet language learning resources for EFL easier and faster. Thus, the main point is all of them can select the right internet language learning resources that appropriate with
their teaching purposes based on bloom’s taxonomy and the
four skills.
E. Scope and Limitation
The scope of this study is a Web-Site
(http://www.englishtests.webs.com/) that comes from Agarwal’s
study which is explained on an international journal entitled Internet-Based Language Learning and Teaching16. This study
shows many kinds of internet language resources materials for all
level of learner’s ability on seven categories, such as my favourites,
my test, video lessons, grammar, listening, reading, and some more. On those table, it consist of online dictionaries, games, quizzes, instant scoring of test with the explanation, etc. People can access
all of it by clicking on this link “http://www.englishtests.webs.com/
“17. It means that the focus of this study is only this website “http://www.englishtests.webs.com/“ that contain of four selected web resources based on the four language skills, such as http://learnenglishteens.britishcouncil.org/skills/reading-skills-practice is for reading skill, http://www.esl-lab.com/ is for listening skill, www.myenglishpages.com is for writing skill, and http://www.audioenglish.org/ is for speaking skill.
The limitation of this study is the classification of the internet language learning resources based on a study of Agarwal which
appropriate with the categories of students’ cognitive development
based on bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills.
16M. Kumar Agarwal, “Internet-Based Language Learning and Teaching”, Vol.1, No.8, February 2010
8
Remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and
creating are included in Bloom’s taxonomy and reading, listening,
writing, and speaking are include in four language skills.
Furthermore, to make it clearer, the researcher has a role “if an
internet language learning resources already classified into a level
of cognitive development based on Bloom’s Taxonomy and the four
skills, it does not mean that it will impossible to classified it again
in another table”.
F. Definition of Key Terms
In order to have the same idea and to avoid misunderstanding of this study, the researcher clarifies the term used in this study as follow:
1. EFL Teaching
As cited from a journal entitled EFL Teaching and EFL Teachers in the Global Expansion of English, Berns and Paulston state that English is not a primary language that they are used in their daily life, where English is not the mother tongue of the majority of the population, and the situations of EFL teaching is the majority of teachers of English are not native speakers due to obvious reasons. In this study, the researcher has the same opinion about EFL teaching, because English is not the primary language that they are used in daily life and most of English teachers are not native speakers. 2. Internet Language Learning Resources.
According to Johnstone’s statement, he says that
internet language learning resources is anything that can be used to organize and support learning and teaching process that consist of tools for teachers and support materials to enable them to create and adapt it18. Thus, all of the internet language
learning resources for EFL teaching as the English material will
be classified in this study based on bloom’s taxonomy and the
four language skills.
18Rupert Herington, “Teaching EFL/ESL Students How To Use Search
9
3. Language Learning Materials.
Based on Materials Development in Language Teaching book, the definition of language learning material is anything which is used by teachers or learners to facilitate the learning of a language19. The materials can be cassettes, videos,
CD-ROMs, dictionaries, grammar books, newspaper, native speaker, internet resources, etc. In short, they can be anything
which is used to improve the learners’ knowledge or experience
of the language. Therefore, related with this study teacher can use the internet language learning resources as the teaching materials by selecting and choosing it based on their teaching purposes that will be classified based on classification of
bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills.
4. Bloom’s Taxonomy.
According to Forehand’s statement on his e-journal, he states that bloom's taxonomy is a multi-tiered model of classifying thinking according to six cognitive levels of complexity20. It means that there are six level of cognitive
development that is started from the simplest ability to the most complex ability, such as remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating. Thus, the
categories of bloom’s taxonomy in this study is about the
cognitive development that will be the main focus of classification of internet language learning resources.
19Brian Tomlinson, “Materials Development in Language Teaching”, (Cambridge University Press: 1998), 2
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
A. Review of Related Literature
1. Internet Use in Language Instruction
According Marzano’s statement, he said that for regarding the effective teaching and learning process, teacher must be focused on improving students learning and develop a viable tool for fostering expertise in teaching1. Therefore, in order to
have a successful teaching and learning process, teacher needs supplies and resources, such as literature textbooks, writing textbooks, handouts, worksheet, internet resources, etc. Then, related with this modern era, teacher should recognize the trend toward the use of internet that has been widely applied in language teaching Furthermore, as cited from a journal entitled A Mixed-method Study of EFL Teachers’ Internet use in language instruction, some researchers state that it has been dramatically increasing the development of technology in teaching language on the World Wide Web over the past decade. It has become possible and feasible for language teachers to make effective use of instructional materials, especially in teaching language. Besides, one benefit of using internet resources is the most recent and pertinent information for students can be easily retrieved by the teacher2. Besides, the development of hypertext and hypermedia within the context of the World Wide Web, both teachers and students can search and access authentic materials.
2. Types of Internet Resources and Tools for Teaching:3 According to a website of Yale University, it has information about kinds of internet resources and tools. It is divided into seven categories which describe as follow:
1 Peggy Schooling, Ed.D-Michael Toth-Robert Marzano, Ph.D, “The Critical Importance
of A Common Language of Instruction”, Marzano Center, 2013. 1 2 Yu-li Chen Ã, “A mixed-method study of EFL teachers…1016
11
a. Audio recording and editing : an online tool for recording, sharing audio messages and editing, such as Audacity, Vocaroo
b. Photo editing : an online tool for editing photos, such as Pixlr, SumoPaint
c. Multimedia projects: a set of online tools for creating multimedia-enhanced language learning materials, activities, and assessment (requires initial registration), such as CLEAR’s Rich Internet Applications which has many tools:
1)
Audio Dropbox: a drop box for students’ audio recordings that can be put on any webpage2)
Broadcasts: a podcasting program for languagelearning
3)
Conversations: a tool for recording questions for students to answer them asynchronously4)
Mashups: a great tool that allows for combiningvideo, audio, text, and interactive exercises
5)
QuizBreak: a flexible program for creating funlanguage games
6)
Revisions: a platform that supports process writing7)
Scribbles: a tool for handwriting practice online8)
SMILE: a tool for creating interactivelanguage-practice exercises
9)
Video Dropbox: a dropbox for students’ video recordings that can be put on any webpage10)
Viewpoint: an audio and video repository thatallows for recording audio and video files online, or uploading existing media.
11)
Worksheets: interactive worksheets that allow for audio/video recording, multiple-choice and matching questions, etc.12
e. Presentation: an online presentation and collaboration tool that allows for creating multimedia slideshows and commenting using voice, text, audio file, or video, such as VoiceThread, Prezi.
f. Video conferencing: software for text chatting, instant messaging, and video calling (requires installation), such as Skype.
g. Video production and editing: an easy-to-use online tool for creating videos, such as: Animoto.
3. Internet Language Learning Resources
On 1st February 2010, there is a study about
internet-based language learning and teaching which is conducted by Agarwal as the teacher of Riga Technical University. This university is not only focused on providing high quality education, but also conducts advanced research and innovation and technology. Therefore, it can be concluded that both of technology and education have relation for increasing and improving education, especially for EFL teaching process.
On his study, he tries to classify many kinds of internet language learning resources on his web-site. He classifies those web resources become seven categories, such as my favourites, my test, video lessons, grammar, listening, reading, and some more, which has different contents for each table.
This table can be found on
(http://www.englishtests.webs.com/). Only clicking the table, people directly go to the web resources that have many kinds of language materials for improving the four language skills. (See Appendix 2.1)
13
organization for cultural relations and educational opportunities. Then, their work in English purposes is to bring high-quality language materials to every learner and teacher who wants them. Besides, they can teach English and train teacher through radio, web and television broadcasts. Therefore, that is a reason why the researcher choose this web-site, because the table consist of many kinds of English materials. The table of language materials on the web-site are appear below:
Figure 2.1 Agarwal’s Web Resources (Learn and Test English with Dr.Kumar,
14
The figure 2.1 is the result of a study about the internet language learning resources that conducted by Agarwal in 2010. He classified 61 web resources based on seven categories with different web address. Additionally, according to Brian Tomlinson, he summaries some researchers’ opinion about the basic principles of materials development for teaching of languages:
a. Materials should require and facilitate learner self-investment4.
For gaining students learners’ attention, invest interest, effort in learning activities, materials can help them to achieve it by giving the topic control and engaging them in learner-centered activities.
b. Materials should provide the learners with opportunities to use the target language to achieve communicative purposes5.
Most of researcher agree that the learners should get the opportunities for communicate with other people rather than just to practice in the class. Therefore, the teacher should provide the authentic materials which consist of the real situation in daily life.
c. Materials should take into account that learners differ in learning styles6.
Different learners have different style in learning, such as visual, auditory, kinesthetic, studial, experimential, analytic, global, dependent, and independent. Teacher should understand and try to provide materials which can facilitate all of learner’s learning style. By using internet language learning resources, there are various interesting English
4 Brian Tomlison, Materials Development in Language Teaching… 11
5 Brian Tomlison, Materials Development in Language Teaching (Cambridge University Press, 1998), 14.
15
materials for the learners. The knowledge is not only from the book, but also from the internet which more interesting.
4. Bloom’s Taxonomy: Original and Revised
a. The History of Bloom’s Taxonomy7
In 1948, the Convention of American Psychological Association led Bloom to spearhead a group of educators who eventually undertook the ambitious task of classifying educational goals and objectives. Their intent was to develop a method of classification for thinking behaviors that were believed to be important in the processes of learning. At the time, educators were wrestling with a number of questions, many prompted by the influx of World War II veterans enrolling in college. The veterans wanted a good education, but what makes an education “good”? How could instructors ensure that learners graduated with more than just lower-level factual knowledge? Then, one of Bloom’s students, Lee S. Shulman, recalls when these questions were raised, educators were just beginning to consider assessment.
Bloom, as the director of the examiner’s office at the University of Chicago was developing assessments to measure the learning. When he tried to share ideas and test items with other evaluators, he found that instructors agreed that they wanted learners to “understand,” but they had very different ideas about what understanding meant. Bloom imagined a taxonomy that would organize educational goals into a hierarchy. It seems like the biologists who classify the living of creatures into categories that ascend from species to kingdom. The taxonomy
16
that bears his name is based on the work of hundreds of collaborators, including reviewers, contributors of case studies and examples, and a core of working group for about 30 people. Then, the result of their efforts are published in 1956. It is officially known as Taxonomy of Educational Objectives. Bloom often called this work The Handbook.
However, the educators, instructional designers, researchers, and evaluators who apply this classification generally call it as Bloom’s Taxonomy. This recognizes Bloom’s foundational contribution to the project: He convinced his collaborators to organize learning behaviors on a continuum from the simplest to the most complex. b. The Original Taxonomy Of Cognitive Domain
In 1956, Bloom said that the cognitive domain involves knowledge and the development of intellectual skill. Cognitive domain is included in recalling specific facts, procedural patterns, and concepts that serves in the development of intellectual abilities and skills8. There are six categories of cognitive
domain which is starting from the simplest ability to the most complex ability, or it can be called as degrees of difficulties. In an effort to decrease the confusion of the six level of bloom’s taxonomy, the table of cognitive domain are appear below:
8Forehand, M. “Bloom's taxonomy: Original and revise”
17
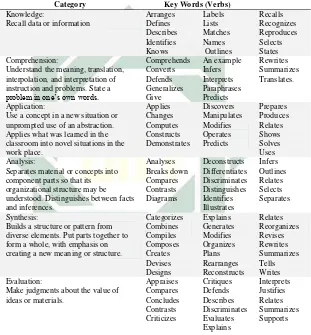
Table 2.1 The Original of Bloom’s Taxonomy
Category Key Words (Verbs) Knowledge:
Recall data or information
Arranges Defines Describes Identifies Knows Labels Lists Matches Names Outlines Recalls Recognizes Reproduces Selects States Comprehension:
Understand the meaning, translation, interpolation, and interpretation of instruction and problems. State a
problem in one’s own words.
Comprehends Converts Defends Generalizes Give An example Infers Interprets Paraphrases Predicts Rewrites Summarizes Translates. Application:
Use a concept in a new situation or unprompted use of an abstraction. Applies what was learned in the classroom into novel situations in the work place. Applies Changes Computes Constructs Demonstrates Discovers Manipulates Modifies Operates Predicts Prepares Produces Relates Shows Solves Uses Analysis:
Separates material or concepts into component parts so that its organizational structure may be understood. Distinguishes between facts and inferences. Analyses Breaks down Compares Contrasts Diagrams Deconstructs Differentiates Discriminates Distinguishes Identifies Illustrates Infers Outlines Relates Selects Separates Synthesis:
Builds a structure or pattern from diverse elements. Put parts together to form a whole, with emphasis on creating a new meaning or structure.
Categorizes Combines Compiles Composes Creates Devises Designs Explains Generates Modifies Organizes Plans Rearranges Reconstructs Relates Reorganizes Revises Rewrites Summarizes Tells Writes Evaluation:
Make judgments about the value of ideas or materials.
Appraises Compares Concludes Contrasts Criticizes Critiques Defends Describes Discriminates Evaluates Explains Interprets Justifies Relates Summarizes Supports
c. The Revised of Bloom’s Taxonomy
18
curriculum theorists and instructional researchers, and testing and assessment specialists published a revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy entitled A Taxonomy for Teaching, Learning, and Assessment9.
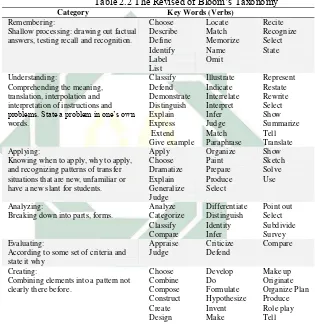
Table 2.2 The Revised of Bloom’s Taxonomy Category Key Words (Verbs)
Remembering:
Shallow processing: drawing out factual answers, testing recall and recognition.
Choose Describe Define Identify Label List Locate Match Memorize Name Omit Recite Recognize Select State Understanding:
Comprehending the meaning, translation, interpolation and interpretation of instructions and
problems. State a problem in one’s own
words. Classify Defend Demonstrate Distinguish Explain Express Extend Give example Illustrate Indicate Interrelate Interpret Infer Judge Match Paraphrase Represent Restate Rewrite Select Show Summarize Tell Translate Applying:
Knowing when to apply, why to apply, and recognizing patterns of transfer situations that are new, unfamiliar or have a new slant for students.
Apply Choose Dramatize Explain Generalize Judge Organize Paint Prepare Produce Select Show Sketch Solve Use Analyzing:
Breaking down into parts, forms.
Analyze Categorize Classify Compare Differentiate Distinguish Identity Infer Point out Select Subdivide Survey Evaluating:
According to some set of criteria and state it why
Appraise
Judge Criticize Defend Compare Creating:
Combining elements into a pattern not clearly there before.
Choose Combine Compose Construct Create Design Develop Do Formulate Hypothesize Invent Make Make up Originate Organize Plan Produce Role play Tell
9Forehand, M. “Bloom's taxonomy: Original and revise”
19
The graphic below illustrates the differences between Bloom’s original taxonomy and the 2011 revised taxonomy10:
Figure 2.2 Changes in Bloom’s taxonomy of Educational Objectives, (The International Assembly for Collegiate Business Education, Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives and Writing Intended Learning Outcomes
Statements ( Lenexa, Kansas-USA, 2014-2016), 4, accessed on 19 October, 2016
The most obvious differences between the 1956 and 2001 versions is in revising the taxonomy between evaluation and synthesis. The highest level is not the evaluation, but a new category of creating becomes the highest level. This category was originally recognized as synthesis. Another significant change is the category names. Changing the name of six categories is in noun form becomes the verb form.
Then, according to Zawisza’s explanation, she said that bloom’s taxonomy is the powerful tool to help develop learning objectives, because it explains the process of thinking. Therefore, in this study the researcher used the categories of bloom’s taxonomy to identify the internet language learning resources.
20
5. The Four Language Skills11
a. Reading
According to Hornby, he said that when people look at the written or printed words or symbol and they are understand the meaning of those, it means that they are reading. Besides, according to Harmer’s explanation, there are two types of reading; Extensive and intensive reading. When the teacher have their own reading program for the students which includes materials, guidance, tasks, and libraries, it means that the teacher applies extensive reading. On the other hand, intensive reading means detailing focus on reading text and complementing with some activities, such as study about grammar or vocabularies. It will be better if the students have opportunities to choose what they want to read, therefore they will read some text with pleasure and the teacher can motivate the students to read intensively and extensively by engaging them with different topics and tasks.
Then, according to the theory of micro and micro reading skill that stated by Brown and Abeywickrama in 201012, commonly for micro skills
those websites are recognize a core of words and interpret word order patterns and their significance, recognize cohesive devices in written discourse and their role in signaling the relationship between and among clauses, and for macro skills those websites are recognize the communicative functions of written texts, according to forms and purpose, then infer context that is not explicit by activating schemas (using background knowledge), from described ideas, infer links and connections between events, deduce causes and effects, and detect such us relations as
11 Muñoz Bastíasin, “Tegration Of The Four Skills Of The English Language And Its
Influence On The Performance Of Second Grade High School Students”, (Chili, 2011),
17, 23, 27, 32
21
main idea, supporting idea, new information, given information, generalization and exemplification, then develop and use a battery of reading strategies, such as scanning and skimming, detecting discourse markers, guessing the meaning of words from context, and activating schemata for the interpretation of texts. b. Listening
According to Harmer, he mentions two different kinds of listening. First, Extensive Listening “refers to listening which the students often do for pleasure or some other reason. The audio material they consume in this way often on CDs in their cars, on MP3 players, DVDs, videos or on the internet should consist of texts that they can enjoy listening to because they more or less understand them without the intervention of a teacher or course materials to help them.
Then, according to the theory of micro and micro listening skill that stated by Brown and Abeywickrama in 201013, commonly for micro skills
those websites are recognize English stress patterns, words in stressed and unstressed positions, intonation contours, and their role in signing information, and for macro skills those websites are recognize the communicative functions of utterances, according to situations, participants, and goals, then infer situations, participants, goals using real-world knowledge, and from events and ideas described, predict outcomes, infer links and connections between events, deduce causes and effects, and detect such us information generalization and exemplification, then develop and use a battery of listening strategies, such us detecting key words, guessing the meaning of words from context, appealing for help, and signaling comprehension thereof.
13 H. Douglas Brown – Priyanvada Abeywickrama, Language Assessment: Principles and
22
c. Writing
According to Richards & Renandya, they mention that writing is the most difficult skill for L2 learners, since they need to generate ideas, organize them and translate these ideas into readable text which can be very difficult for students. Then, Harmer mentions some important aspects that are considered in writing such as Handwriting, even though communication takes place electronically nowadays. However, there are example in which students write by hand, for example in language exams.
Related with writing skill, the researcher connected with the theory of micro and macro writing skill that stated by Brown and Abeywickrama in 201014. Particularly, there are some websites are
produce an acceptable core of words and use appropriate word order patterns, use cohesive devices in written discourse. Those are the objectives of micro skills in writing skills. Then, for the micro skills are use the rhetorical forms and conventions of written discourse, appropriately accomplish the communicative functions of written texts according to form and purpose, convey links and connections between events and communicate such relations as main idea, supporting idea, new information, given information, generalization, and exemplification, recognize a core of words and interpret word order patterns and their significance, recognize cohesive devices in written discourse and their role in signaling the relationship between and among clauses, and for macro skills those websites are recognize the communicative functions of written texts, according to forms and purpose, then infer context that is not explicit by activating schemas (using background knowledge), detecting discourse markers, guessing the
23
meaning of words from context, and activating schemata for the interpretation of texts.
d. Speaking
Hornby defines speaking is an activity where people are having a conversation or talking with somebody. Besides, according to Hadfield, he says that speaking is an interaction among people which is the listener can give response to the speaker and deliver the massage. However, it is still difficult for learner of EFL having interaction each other, because they need to understand what they speak.
Related with speaking skill, the researcher connected with the theory of micro and macro speaking skill also that stated by Brown and Abeywickrama in 201015. Commonly, there are some
websites are produce the English patterns, words in stressed and unstressed positions, rhythmic structure, and intonation contours, produce fluent speech at different rates of delivery, produce speech in natural constituents: in appropriate phrases, pause groups, and sentence constituents. Those are the objectives in micro speaking skills. Then, the macro skills are appropriately accomplish communicative functions according to situations, participants, and goals, convey links and connections between event and communicate such relations, conversation rules, floor and –yielding, interrupting, and other sociolinguistic features in face-to-face conversations, convey facial features, kinesics, body language, and other nonverbal cues along with verbal language.
B. Previous Studies
In this part, the researcher reviews the previous study that conducted by Jeong-Bae Son which has similar focus on classification of internet tools for language teaching that is entitled “Online Tools for Language Teaching” which
24
conducted in Australia16. His research discusses about the place
and role of online language teaching tools in CALL and present a category list of the tools. Then, according to the main function and the features, he classified the internet resources into twelve categories, such as learning content management, communication, live and virtual words, social networking and bookmarking, blogs and wikis, presentations, resources sharing, website creation, web exercise creation, web search engine, dictionaries and concordances, and utilities. However, this study is different with that study, because it is more specific in classifying of Agarwal’s study about the internet language learning resources which is able to facilitate the students’ cognitive development based on bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills. The classification is only focus on web resources that classified by Agarwal in his study for EFL teaching that has related with bloom’s taxonomy and language skill (writing, speaking, listening, and reading) where the teacher can easily to find out the appropriate internet language learning resources in online educational websites for EFL teaching in every stages of students’ cognitive development.
Another research has been conducted by Yu-Li Chen in Taiwan with her research entitled A mixed-method study of EFL teachers’ Internet use in language instruction17. The researcher was intended to answers about the factors that influence the teachers in integrating the Internet into their instruction. Then, the result shows that teacher training is the most prominent determinant factors of Internet use, but before getting the result of the study, the researcher tries to classify many kinds of internet tools and resources. She wants to know about kinds of internet tools and resources that are very often used by the teachers in that place. However, this study only classify of a website as the internet language learning resources that comes from Agarwal’s study, and it will be included into the table of Bloom’s Taxonomy and the four language skills.
16 Jeong-Bae Son. “Online Tools for Language Teaching”. Vol.15, No.1, University of Southern Queensland, Australia. June, 2011
17 Yu-li Chen Ã, “A mixed-method study of EFL teachers ’ Internet use in language
25
Another research about this concern was conducted by J.J. Sylvia entitled Using Bloom's Taxonomy to Assess Social Media18. This study is conducted for assessing social media using bloom’s taxonomy, because in this modern era, when students are often use social media in socializing, it does not guarantee that they know how to use social media for education field. Then, the researcher classifying the social media for teaching-learning process based on bloom’s taxonomy. Although J.J Sylivia’s study uses bloom’s taxonomy also, but it is still different with study, because J.J Sylivia classifies the social media. It is not internet language learning resources for EFL teaching.
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHOD
This part of study deals with research methodology which is designed as technique to collect and analyze the data.
A. Research Design
Dealing with this research, qualitative descriptive method applies in this research to find out the research question. Then, according to Newman and Benz statement, they said that qualitative approach as naturalistic approach which observe and interpret reality with the purpose of developing a theory that will explain what was experienced1.
In this case, the researcher used qualitative method for reclassifying a study about classification of internet language learning resources that has conducted by Agarwal. In Agarwal’s study, it was showed many kinds of internet language resources materials for all level of learner’s ability on some tables with different categories, such as my favourites, my test, video lessons, grammar, listening, reading, and some more which explained on an international journal entitled Internet-Based Language Learning And Teaching on February 20102. The classification between
Agarwal and this study is different in the categories. The categories of this study is classifications of internet language learning resources that facilitate students’ cognitive development based on bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills.
B. Research Presence
The presence of the researcher in this study is as non-participant observer, which means that the researcher do not reach
1 Isadore Newman and Carolyn R. Benz, Qualitative-quantitative Research Methodology: Exploring the Interactive Continuum (the United States of America: Southern Illinois University Press, 1998), 3.
27
the full involvement in participants’ activity3. The researcher visited
the websites for observing the content and then analyzed it based on the instrument. The researcher gave checklist on the instrument based on the content of the websites. If the websites appropriate with the instrument, the websites will be classified, but when the websites does not appropriate with the instrument, it can be reduced. Thus, the researcher got the primary for this study.
C. Research Location
This study taken place on this websites
http://www.englishtest,webs.com/ as the main resources which provided many kinds of internet language learning resources which came from Agarwal’s study as the writer of an educational journal entitled Internet-Based Language Learning and Teaching which is published on 1st February 2010. The researcher visited this
websites http://www.englishtest,webs.com/ and analyzed it based on the instrument of cognitive development based on bloom’s taxonomy revised in 2001 and the four language skills.
D. Data and Source of Data 1. Data
The data that will be used in this study is Agarwal’s study entitled Internet-Based Language Learning and Teaching which provides many kinds of internet language learning resources where the result of this study is showed on a table that can be found on this website http://www.englishtests.webs.com/. Therefore, the focus of this study is only internet language learning resources on his website which has seven categories, such as my favourites, my test, video lessons, grammar, listening, reading, and some more. (See Figure 2.1)
2. Source of Data
Dealing with the data, the sources of data came from the observation of the internet language learning
28
resources based on Agarwal’s study that is showed on the table on this website http://www.englishtests.webs.com/.
The researcher and the observation checklist were as the instruments for classifying the internet language learning resources that can facilitate the students’ cognitive development based on bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills, such as http://www.esl-lab.com/ is for listening skill,
http://learnenglishteens.britishcouncil.org/skills/reading-skills-practice is for reading skill, www.myenglishpages.com is for writing skill, and http://www.audioenglish.org/ is for speaking skill. It means, the classification is based on the cognitive development based on bloom's taxonomy theory which is revised by Lorin Anderson, and team on 2001 and the four language skills.
E. Research Instrument
In this case, the instrument is totally needed in collecting data of the research. Therefore, the researcher designed the instruments for finding the answer of research question in a technique included observation checklist the web resources that can facilitate the students’ cognitive development based on bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills.
1. Observation Checklist
29
evaluating and creating. Besides, reading, listening, writing and speaking are included on the four language skills. Therefore, researcher uses this table for classify the internet language learning resources that is adapted and modified from theory of cognitive development based on bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills. (See Appendix 3.1)
F. Data Analysis Technique
In this study, the researcher analyzed the data descriptively because of qualitative method was used. The researcher transcribed the result of classification the internet language learning resources that can facilitate the students’ cognitive development based on bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills which observed by Agarwal’s study as the main data in this research. Finally, the researcher interpreted the data as the need to answer the research question that will be discussed into the finding of the research. In essence, the data obtained from observation checklist is analyzed through these following detailed techniques:
1. Data Reduction
In reducing data, the researcher needed to get the primary data that only needed by the researcher. Choosing and focusing on the main topic of the research means reducing data.4 Therefore, the researcher codes data as
follow to reduce the data in this study:
a. Making the checklist observation as the instrument by adapting two theories that has related with cognitive development based on bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills. (See Appendix 3.1)
b. Observing all of the web resources on Agarwal’s table. Then, giving checklist the web resources based on categories of cognitive development based on bloom’s taxonomy with their keywords and the four language skills.
30
2. Data Display
After reducing the data, the researcher tries to set the technique for displaying the data. Because of this study uses qualitative method, the data display can be formed in short essay, graphic, matrix, network, flowchart, table, etc.5 By
displaying the data, the researcher is expected to understand the data which have been classified based on bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills in good structure. Thus, the researcher displays the data as follows:
a. The result of classification the internet language learning resources based on bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills on the table.
1) In this study, the researcher shows the classification of the internet language learning resources that can facilitate the students’ cognitive development based on bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills which already got the reduction to get the primary data that appropriate with the instrument.
b. Description of the internet language learning resources based on every level of bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills.
1) The researcher tries to count the percentages of the internet language learning researcher in every levels of bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills through this following formula:
Count of Web Resources
Total of Agarwal’s Table � =
Furthermore, the researcher interprets those data in discussion part based on the theory used in this study. 3. Conclusion (Drawing of Verifying)
In this study, the researcher drawn the conclusion based on the data that had been interpreted by reflecting on the research question, because the last technique of analyzing the data is drawing conclusion and it can answer
31
the research question. However, sometime it still happen when the research question cannot be answered, because qualitative research is not static when the researcher observed.6
G. Checking Validity of Findings
For getting the validity of the findings, the researcher conducted the observation by visiting the websites more than three times when classifying it into the table of bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills. Thus, the data were more accurate.
H. Research Stages
The stages in this study are structurally conducted as follow: 1. Preliminary research
In order to clarify the problems linked to this research, the researcher started this study by conducting preliminary research since from 15th February-1st March 2017. By
doing this preliminary research, the researcher got information about not only students but also the teachers got difficulties to find out and understand the real function of many kinds of internet language learning resources when they want to apply it in their real teaching or practice teaching English for increasing the students’ cognitive development and improve their language skills. They needed the guidance for the English teacher to explore those resources and chose the right ones that appropriate with their teaching purposes. Therefore, in this study the researcher classified the internet language resources which can be guided the language teacher to explore those resources and choose the right ones for their teaching purposes.
2. Designing Investigation
In this step, the researcher designed investigation for identifying the content of the websites which are have many kinds of English materials. It can be videos, reading
32
passages, audio files, tests, and so on. Because of the various content of the websites, the researcher identified it by using the table of bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills which was adopted and modified from Anderson, L.W. & Krathwol, D.R. entitled A Taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing and Muñoz Bastíasin entitled Tegration Of The Four Skills Of The English Language And Its Influence On The Performance Of Second Grade High School Students which was validated by the expert. (See Appendix 3.1)
3. Implementing Investigation
In term of investigating the websites, the researcher began to observe the websites on the Agarwal’s table as the main topic in this study. One by one, the researcher opened it and then gave the checklist based on cognitive development of bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills’ table as the instrument. Besides, the researcher took a note about the interesting information based on the finding on the websites as additional information.
4. Analyzing data
After obtaining data from the instrument used in this research, the researcher analyzed the data in attempt to get the answer of the research question directly.
5. Concluding data
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
In this chapter, the researcher presents the research finding and discussion. It reports the finding and the result of the data collection. Detailed description of the result obtained from this study is presented.
A. Research Findings
The researcher has conducted the research from 3rd
April - 31st Mei 2017 through the techniques of collecting data
as stated in the research method. Then, in term of answering the research question about classification of the internet language learning resources that can facilitate students’ cognitive development based on bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills, the researcher took a data from a study that conducted by Agarwal about classification of internet language learning resources on February 2010.
The result of his study can be accessed through this web resources “http://www.englishtests.webs.com/1. Then, the table of
his study can be seen below:
[image:44.420.73.384.89.505.2]
34
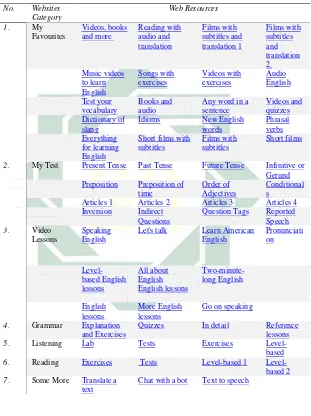
Table 4.1 Agarwal’s Table
No. Websites
Category
Web Resources
1. My
Favourites Videos, books and more Reading with audio and translation Films with subtitles and translation 1 Films with subtitles and translation 2 Music videos to learn English Songs with exercises Videos with exercises Audio English Test your vocabulary Books and audio
Any word in a sentence
Videos and quizzes Dictionary of
slang
Idioms New English words Phrasal verbs Everything for learning English
Short films with subtitles
Films with subtitles
Short films
2. My Test Present Tense Past Tense Future Tense Infinitive or Gerund Preposition Preposition of
time
Order of Adjectives
Conditional s
Articles 1 Articles 2 Articles 3 Articles 4 Inversion Indirect
Questions
Question Tags Reported Speech
3. Video Lessons
Speaking English
Let's talk Learn American English Pronunciati on Level-based English lessons All about English English lessons Two-minute-long English English
lessons More English lessons Go on speaking
4. Grammar Explanation and Exercises
Quizzes In detail Reference lessons
5. Listening Lab Tests Exercises
Level-based
6. Reading Exercises Tests Level-based 1
Level-based 2
7. Some More Translate a text
35
In table 4.1, Agarwal classified those internet language learning resources based on seventh categories, such as my favourites, my test, video lessons, grammar, listening, reading, and some more. Agarwal created 16 web resources about English grammar quizzes and collected 45 web resources about English lessons that are created others. It means that there are 61 web resources in table 4.1.
However, Agarwal’s categories were not based on blooms’ taxonomy and the four language skills which had clearer categories than Agarwal’s categories. In bloom’s taxonomy, there are six categories of cognitive domain which is starting from the simplest ability to the most complex ability, or it can be called as degrees of difficulties, such as remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating2 .
Furthermore, for analyzing the content of internet language learning resources that came from Agarwal’s study, the researcher used an instrument that was adapted and modified from two theories about bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills. (See Appendix 3.1) On the instrument, there are six level of cognitive development based on bloom taxonomy and the four language skills. Every level of cognitive development based on bloom’s taxonomy have different keywords, such as the keywords of remembering are choose, describe, define, identify, label, list, locate, match, memorize, name, omit, recite, recognize, select, and state. Those keywords were used for analyzing the content of the Agarwal’s web resources when the researcher visited it. Then, the researcher gave checklist on the instrument that represent the content of the web resources based on those keywords. While analyzing the keywords of bloom’s taxonomy, the researcher analyzed also the skill that provided on the web resources. For detailed web resources analysis, see appendix
2Forehand, M. “Bloom's taxonomy: Original and revise”
36
4.2. Having analyzed those web resources based on the instrument, few findings are identified as presented below:
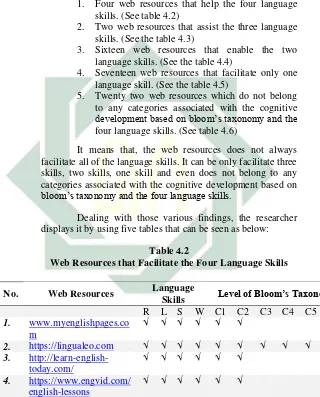
1. Four web resources that help the four language skills. (See table 4.2)
2. Two web resources that assist the three language skills. (See the table 4.3)
3. Sixteen web resources that enable the two language skills. (See the table 4.4)
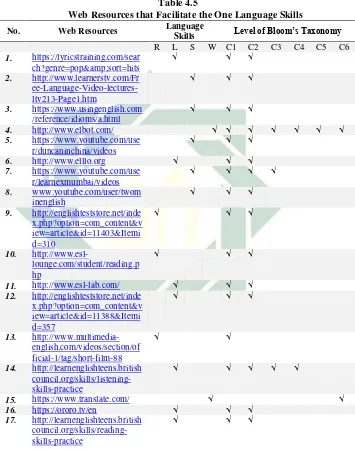
4. Seventeen web resources that facilitate only one language skill. (See the table 4.5)
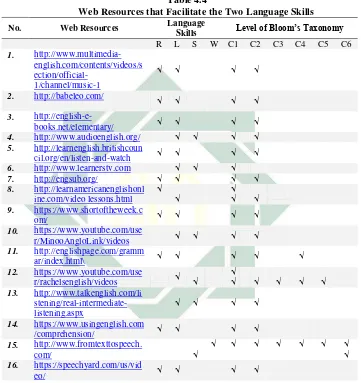
5. Twenty two web resources which do not belong to any categories associated with the cognitive development based on bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills. (See table 4.6)
It means that, the web resources does not always facilitate all of the language skills. It can be only facilitate three skills, two skills, one skill and even does not belong to any categories associated with the cognitive development based on bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills.
[image:46.420.66.386.106.503.2]Dealing with those various findings, the researcher displays it by using five tables that can be seen as below:
Table 4.2
Web Resources that Facilitate the Four Language Skills
No. Web Resources Language
Skills Level of Bloom’s Taxonomy
R L S W C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 1. www.myenglishpages.co
m √ √ √ √ √ √
2. https://lingualeo.com √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √
3.
http://learn-english-today.com/ √ √ √ √ √ √
4. https://www.engvid.com/
37
The table 4.2 shows that there are four web resources that provide some levels of bloom’s taxonomy and the four language skills at once. Those web resources can be references for English teacher when they want to take English materials. They can choose what skills that they want to teach, such us reading, listening, writing and speaking.
Table 4.3
Web Resources that Facilitate the Three Language Skills
No. Web Resources Language
Skills Level of Bloom’s Taxonomy
R L S W C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 1. https://www.youtube.
com/user/AlexESLvid /videos
√ √ √ √ √
2. https://www.youtube. com/user/ENGLISHC LASS101/videos
√ √ √ √ √
From table 4.3 above, the researcher got two web resources that facilitate two levels of bloom’s taxonomy and the three language skills. Listening, writing and speaking are facilittates by
https://www.youtube.com/user/AlexESLvid/videos, and for reading, and
[image:47.420.60.398.147.408.2]38
Table 4.4
Web Resources that Facilitate the Two Language Skills
No. Web Resources Language
Skills Level of Bloom’s Taxonomy
R L S W C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6
1.
http://www.multimedia-english.com/contents/videos/s
ection/official-1/channel/music-1
√ √ √ √
2. http://babeleo.com/
√ √ √ √
3.
http://english-e-books.net/elementary/ √ √ √ √
4. http://www.audioenglish.org/ √ √ √ √
5. http://learnenglish.britishcoun
cil.org/en/listen-and-watch √ √ √ √
6. http://www.learnerstv.com √ √ √
7. http://engsub.org/ √ √ √ √
8. http://learnamericanenglishonl
ine.com/video lessons.html √ √ √√ √
9. https://www.shortoftheweek.c
om/ √ √ √ √
10. https://www.youtube.com/use
r/MinooAngloLink/videos √ √ √ √
11. http://englishpage.com/gramm
ar/index.html\ √ √ √ √ √
12. https://www.youtube.com/use
r/rachelsenglish/videos √ √ √√ √ √ √ √
13. http://www.talkenglish.com/li
stening/real-intermediate-listening.aspx √ √ √ √
14. https://www.usingenglish.com
/comprehension/ √ √ √ √
15. http://www.fromtexttospeech.
com/ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √√
16. https://speechyard.com/us/vid
eo/ √ √ √ √
[image:48.420.48.409.77.460.2]