CANCER EPIDEMIOLOGY
&
CANCER RISK FACTOR
Wirsma Arif Harahap
Surgical Oncologist
What this lecture about ?
•
Learning more about cancer epidemiology
•
Investigating risk factors implicated cancer
development
Disease Free Survival / Interval
•
The time that a person with a disease lives
Survival Analysis
•
To describe the survival times of members of a
group
- Survival function
- Hazard function
- Kaplan-Meier curves
•
To compare the survival times of two or more
groups
Etiology
&
RISK FACTORS
•
HEREDITARY
HEREDITARY
•
MUTATION
Environmental Risk Factors
•
Tobacco
–
Most important cause of cancer
–
Leading preventable cause of death
Environmental Risk Factors
•
Ionizing radiation
–
Emission from x-rays, radioisotopes, and other
radioactive sources
–
Exposure causes cell death, gene mutation, and
chromosome aberrations
–
A u ulatio of utatio s → a er
Environmental Risk Factors
•
Ultraviolet radiation
–
Causes basal cell carcinomas, squamous cell
carcinomas, melanomas
–
Principle source is sunlight (UVA, UVB)
–
“pe ifi ge e utatio s → i fla
atio
Environmental Risk Factors
•
Electromagnetic fields
–
Carcinogenic ?
•
Are they, or are ’t they?
•
Living arround high voltage wire.
Environmental Risk Factors
•
Diet
–
Xenobiotics
•
Toxic, mutagenic, and carcinogenic
chemicals in food
•
Examples
–
Compounds produced in the cooking of fat
meat or protein
–
polycyclic aromatic
hydrocarbons
–
Industrial contaminants (diesel exhaust,
pesticides in food & water)
Environmental Risk Factors
•
Obesity*
–
Body mass index =
Weight kg
Height (cm)
2
Underweight
< 18.5
Normal
18.5
–
24.9
Overweight
25
–
29.9
Obese
30
–
34.9
I
35
–
39.9
II
Extreme Obesity
> 40
III
also waist circumference
Environmental Risk Factors
•
Obesity
–
Adipose tissue is active endocrine and
metabolic tissue
–
In response to endocrine and metabolic
signaling, adipose tissue releases free fatty
acids
•
Leads to i suli resista e → hro i
hyperinsulinemia
•
Correlates with
colon, breast, pancreatic
Environmental Risk Factors
•
Exogenous hormones
–
Hormone replacement therapy
•
Endogenous hormones
–
Adipose tissue metabolizes androgen precursors to
estrogens (breast, uterine cancer)
–
Adipose ells ↑ ir ulati g i suli levels a d IGF
-
1 →
↓ liver sy thesis “HBG leadi g to ↑ estradiol
–
High i suli levels → ↑ ovaria , possi ly adre al
synthesis of androgens.
Environmental Risk Factors
•
Alcohol
–
Risk factor for oral cavity, pharynx, hypopharynx,
larynx, esophagus and liver cancer (
breast
–
maybe 2007)
Environmental Risk Factors
•
Hepatitis B/C
hepatocellular cancer
•
Sexual reproductive behavior
–
Carcinogenic
human papilloma virus
•
HPV-16 (60%), HPV-18 (10%), HPV-31/35
(5% each)
–
cervical cancer
–
Persistence
–
prerequisite for cancer
Environmental Risk Factors
•
Physical activity
–
Reduces cancer risk
•
↓ i suli a d IGF
-1
•
↓ o esity
•
↓ i fla
atory ediators a d free radi als
Environmental Risk Factors
•
Occupational hazards
–
Substantial number of occupational
carcinogenic agents
•
Asbestos
•
Dyes, rubber, paint, explosives, rubber
Environmental Risk Factors
•
Air pollution
–
Inhales 20,000 L/day
–
potential for appreciable
doses of pollutants
–
Industrial
–
arsenicals, benzene, chloroform,
formaldehyde, sulfuric acid, mustard gas, vinyl
chloride and acrylonitrites
–
Radon
–
radioactive gas, uranium decay
–
rocks
Risk factors associated with the development
of breast cancer
family history and genetic factors
previous history of breast cancer in one breast
fibrocystic disease (atypical hyperplasia)
ionizing radiation
age at menarche and menopause
age at first delivery, number of children
nulliparity
Risk factors associated with the development
of breast cancer
diet
alcohol
physical activity
ORAL CANCER
Wirsma Arif Harahap
Konsultan Bedah Tumor
What is oral cancer?
•
Usually squamous cell (epithethial)
•
Abnormal neoplasm of the mouth
Statistics
•
30,000 people a year diagnosed
•
8,000 deaths
•
Higher then:
•
Cervical cancer
•
Hodgkin’s disease
•
Brain cancer
•
Liver cancer
•
Testicular cancer
•
Kidney cancer
Statistics on Oral Cancer
•
Accounts for 2% of all cancers
•
40 years of age and older are at a higher risk
•
Over 35,000 people will be diagnosed
•
Over 7,600 will die from the disease
Who is at risk?
•
People over the age of 40
•
Men vs. Women
•
Ethnicity
•
Socioeconomic Status (SES)
•
Being a heavy smoker and drinker
•
Chronic irritation
•
People with HPV-16 and HPV-18 are at
HPV and oral cancer
•
1% of oral cancer is linked to HPV
•
HPV infects epithelial cells
•
On a cellular level the mouth is similar
to the vagina and cervix
Signs and symptoms
•
Sores or lesions that won’t heal
•
Lump or thickening in the cheek
•
White or red patches on the gums, tonsils, or
mouth
•
Chronic sore throat
•
Difficulty swallowing
Staging
Side Effects of Treatment
•
Swelling
•
Sore mouth
•
Difficulty chewing,
swallowing, or talking
•
Changes to appearance
•
Weight loss
•
Inability to wear
dentures for a period of
time
•
Fatigue
•
Lowered immune
system
•
Nausea
•
Vomiting
•
Mouth sores
Linkage to Oral Cancer
•
Persistent gum disease can lead to oral cancer
and other potential life threatening conditions
like:
–
Heart Disease
–
Stroke
–
Diabetes
–
Chronic Kidney Disease (CDK)
–
Preterm Birth
Health Disparities
•
Health Disparities are differences in health
conditions or outcomes among specific
population groups in the United States.
–
Some include:
•
Environmental factors
–
rural and urban poor
•
Economical factors
–
working poor
•
Cultural factor
–
language barrier
•
Accessibility to care
•
Quality of care
Prevention
•
Ways To Educate People
–
Advertising & Visuals
–
Developing Culturally Appropriate Messages
–
Educate in local schools, colleges, health clinics,
churches, and community centers
•
Why It Is Important
–
Early Detection
Tumor Immunology
Wirsma Arif Harahap
1) Immune responses that develop to cancer cells
2) Escape of cancer cells
3) Therapies: clinical and experimental
Cancer cells can be viewed as
altered self cells that have escaped
n o r m a l g r o w t h - r e g u l a t i n g
mechanisms.
Evidence for Tumor Immunity
Spontaneous regression:
melanoma, lymphoma
Regression of metastases after removal of
primary tumor:
pulmonary metastases from renal carcinoma
Infiltration of tumors by lymphocytes and
macrophages:
melanoma and breast cancer
Lymphocyte proliferation in draining lymph
nodes
Higher incidence of cancer after
Tumor Immunity
General Principles
Tumors not entirely self
Express non-self proteins
Immune-mediated recognition of
tumor cells may be positive
mechanism of eliminating
transformed cells
Tumor Antigens
Tumor Specific Antigens
Present only on Tumor cells
Recognized by cytotoxic T cells
Bound by class I MHC
Several antigens in humans found that are
not unique for tumor, however are
generally not expressed by normal tissue
Melanoma-associated antigen-1 (MAGE-1):
Embryonal protein normally expressed in testis
Tumor Antigens
Tumor Associated Antigens
Not unique to tumors, shared by
normal cells
Differentiation- specific antigens
CALLA (CD10) in early B cells
Antitumor Effector
Mechanisms
Cytotoxic T-cells
MHC restricted CD-8 cells (viruses)
NK cells
Destroying tumor cells without prior sensitization
Macrophages
Ifn-gamma
Humoral Mechanisms
Antitumor Effector
Mechanisms
Cytotoxic T-cell
NK cell
Macrophage
Humoral
Mechanisms
Tumor Immunology
Cancer immunosurveilance:
immune system can recognize and
destroy nascent transformed cells
Cancer immunoediting:
immune system kill and also induce
changes in the tumor resulting in tumor
escape and recurrence (epigenetic
IMMUNOSURVAILLANCE
Argument for:
Increased cancer in immunodeficient hosts
200x increase in immunodeficiencies (lymphoma)
X-linked lymphoproliferative disorder (XLP
EBV related
Escape Mechanism Theories
Selective outgrowth of antigen-negative variants
Loss or reduction of HLA (escape T-cells)
Immunosuppression (Tumors secrete factors
Tumor killing
Non-specific: NK cells,
γδ
T cells
(NKG2D), macrophages, NK T cells
Immune Recognition of
Tumor
Antibodies recognize intact antigens while T cells
recognize processed antigens associated with
Anti-tumor immunity involve the same mechanisms as in
anti-infection immunity, transplantation immunity or allergy.
•
Complement
•
Lysozyme
•
Cytokines
•
Phagocytosis
•
NK cells
IMMUNOTHERAPY
Replace suppressed components of
immune system or stimulate
endogenous responses
Adoptive Cellular Therapy
Incubation of lymphocytes with IL-2 to
generate lymphokine activated killer (LAK) cells
with potent antitumor activity
Enriched tumor specific cytotoxic T cells
Cytokine Therapy
Activate specific and nonspecific
(inflammatory) host defenses.
Interferon-a, TNF-a, Il-2, IFN-g
IFN-a activates NK cells, increase MHC expression on
tumor cells
Antibody-Based Therapy
Antibodies as targeting agents for delivery
of cell toxins magic bullet
Direct use of antibodies to activate host
immune system
2) Cytokine therapy
-IFN, IL-1, IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, GM-CSF, TNF
Interferons
IFN alfa and beta - antiviral state, IFN gamma – activation
IFN-alfa >> hematologic malignances, melanoma, renal cancer, breast
cancer (low degree of malignity)
-increase of tumor cell MHCI and mph MHCII >> CTL activity
-IFN gamma >> increase the activity of Tc, NK, mph,
Tumor necrosis factors
- TNF alfa and beta > -decrease the proliferation of tumor cells and killing
-decrease the angiogenesis
- adverse reactions
_______________
Systemic administration of high level of a given cytokine has been shown
to lead to serious and even life threatening consequences.
TIL and LAK cells
-
in vitro Tc activation (X-irradiated tumor cells and IL-2)
-
activation with IL-2 without tumor cells >> LAK cells
(activated NK, NC cells)
-
systemic IL-2 >> vascular leak syndrom, shock
Tumor cell Vaccines
- autologous tumor cells +BCG
Invasion
And
Metastasis
Wirsma Arif Harahap
Surgical Oncologist
Biology of tumor growth
The natural history of malignant tumors
can be divided into four phase:
A. Transformation
B. Growth of transformation cells
C. Local invasion
Spread of Cancer
Local Invasion (direct extension)
Metastasis (spread at a distance)
Lymphatic (via lymph vessels and nodes)
Hematogenous (via blood vessels)
Body Cavity Seeding (pleural and
Routes of tumor spread
•
Hematogenous (
bloodstream
)
- sarcomas
•
Lymphatic (
lymph nodes
)
- Carcinomas
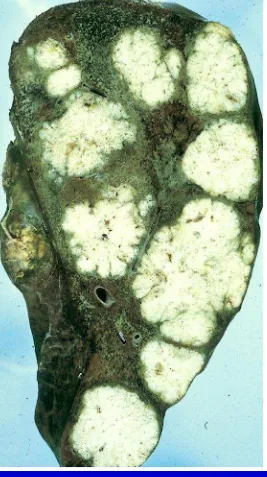
Colon CA: Metastasis to Liver
Biology of tumor growth
1. Local invasion
1. Local Invasion
a.
Progressive infiltration, invasion, and
destruction of the surrounding tissue
b.
Ill-defined and non-encapsuled
c.
The particular growth pattern of
malignant tumors
Mechanisms of invasion and metastasis
Invasion of the extracellular metastasis
a.
Loosening up of tumor cells from each other:
E-adhering expression is reduced
b.
Attachment to matrix components: cancer
cells have many more receptors of lamina
and fibronectin.
c.
Degradation of extra cellular matrix:
The three steps of invasion
Liotta, LA. Tumor invasion and metastasis-role of the extracellular matrix.
Cancer Res 46: (1986)
Matrix degradation by
proteinases
Metalloproteinases (MMPs)
Serine proteinases (plasmin, uPA)
Cysteine proteinase (Cathepsin B,L)
Aspartyl proteinases (Cathepsin D)
Threonine proteinases
Biology of tumor growth
1. Local invasion
Metastasis
Definition:
development of secondary implants
Why do metastases establish
where they do?
•
“Seed and soil” hypothesis
- Paget
Importance of microenvironment
Stephen Paget, Lancet 1:571, 1889
“When a plant goes to seed,
its seeds are carried in all directions;
but they can grow only if they fall on congenial soil.”
•
Mechanical/Anatomical hypothesis - Ewing
The Clinical Problem
30% of patients present with overt
metastases
30-40% appear clinically free of
metastases, but occult lesions appear
later
30% do not metastasize and can be
–
Melanoma can metastasize when very
small
–
Colon and breast adenocarcinomas have a
greater tendency to metastasize as get
larger
–
Basal cell carcinomas of the skin rarely
metastasize
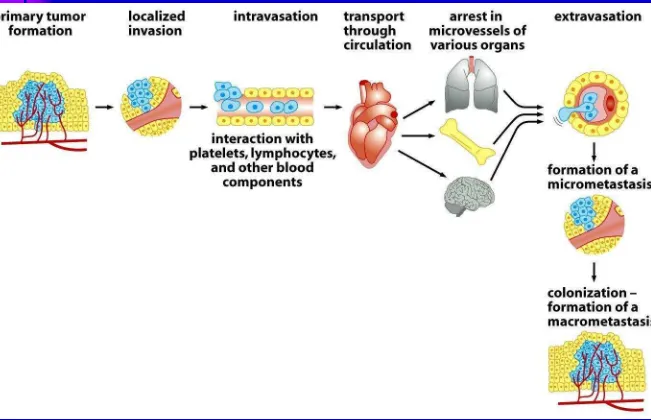
Steps to Metastatic Disease
Rate Limiting Steps?
Route of Metastasis
1. Lymphatic Metastasis
2. Hematogenous Metastasis
Route of Metastasis
1. Lymphatic Metastasis
2. Hematogenous Metastasis
ķ
Lymphatic metastasis
a.
This is the most common pathway for
initial dissemination of carcinoma.
b.
Tumor cells gain access to an afferent
lymphatic channel and carried to the regional
lymph nodes.
In lymph nodes, initially tumor cell are
c.
Through the efferent lymphatic channels
tumor may still be carried to distanced lymph
rode, and
enter the bloodstream by the way of
the thoracic duct finally.
Route of Metastasis
1. Lymphatic Metastasis
2. Hematogenous Metastasis
Route of Metastasis
1. Lymphatic Metastasis
2. Hematogenous Metastasis
ĸ
Hematogenous metastasis
a.
This pathway is
typical of sarcoma
but is also used by carcinoma
b.
Process:
tumor cells
→
small blood
c.
follow the direction of blood flow. Tumors
entering the superior or inferior vena cava
will be carried to the lungs tumors entering
the portal system will metastasize to the liver.
d.
Some cancers have preferential sites for
metastases, lung cancer metastasize to the
brain,
Prostate cancer frequently metastasize to the
bones.
Figure 14.4 The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007) p. 591
Vascular Routes of Cancer Spread
Normal Flow
Red = arterial
Blue = venous; Purple = portal
Yellow = lymphatic
Breast vs Colon CA
Hematogenous Spread
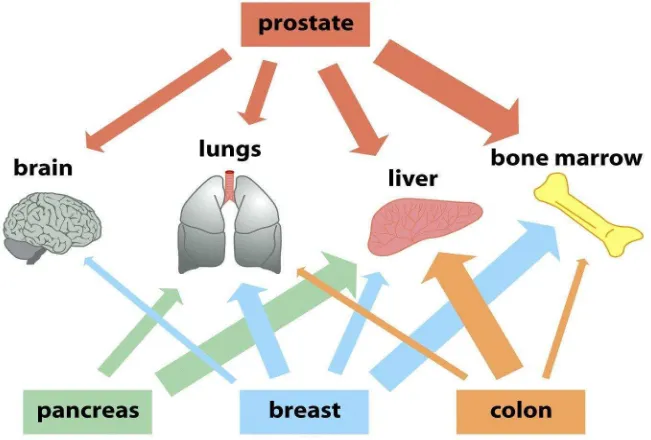
Organ site preference for metastasis
Breast adenocarcinoma
Bone, brain, adrenal
Prostate adenocarcinoma
Bone
Lung: SCLC
Bone, brain, liver
Melanoma - cutaneous
Brain, liver, colon
Thyroid adenocarcinoma
Bone
Kidney clear cell carcinoma
Bone, liver, thyroid
Testis carcinoma
Liver
Bladder carcinoma
Brain
Neuroblastoma Liver, adrenal
Colon cancer Liver
Figure 14.42 The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007)
p. 635
Factors Contributing to Metastatic Spread
1. Metastasis-Associated Up-regulated Genes
2. Host Responses (not necessarily
immunological)
Inflammatory responses Clot Formation
Cytokine and Growth Factor Production
3. Tumor Responses
Tumor-induced immune suppression
4. Possible Facilitation of Metastasis by
Treatment
Diagnostic and surgical manipulation
X-ray Damage
Immune suppression
by Drug Treatment
Factors Hindering Metastatic Spread
1. Metastasis-Suppressor Genes:
e.g. TIMP: Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases or
RhoGD1-2: Down-regulates Rho
–
Stimulator of Actin
Polymerization
2. Responses
Activated Macrophages
Natural Killer Cells
Cytotoxic Lymphocytes
3. Hydrodynamic Effects in Host circulation
Figure 14.50a The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007)
p. 645
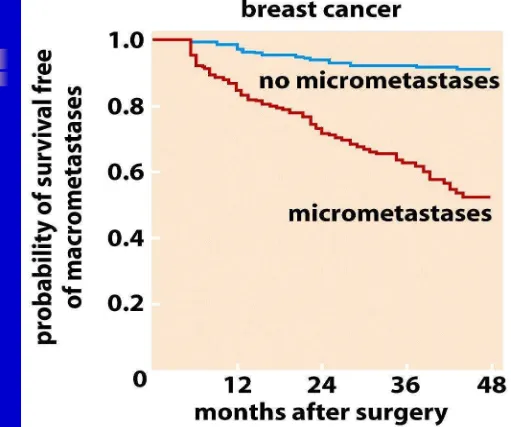
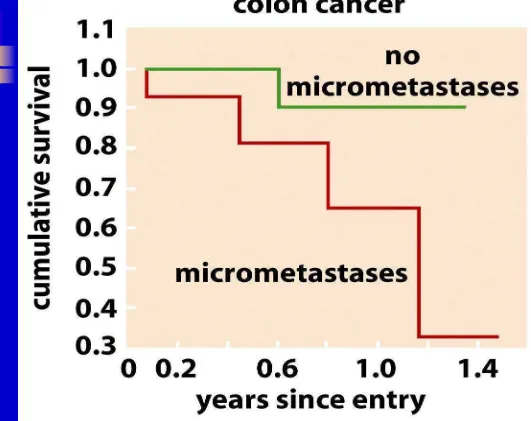
Presence of Micrometastases and Clinical Prognosis: Colon Cancer
Figure 14.50b The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007)
Colon Cancer: Five Year Survival
The slide below shows a relationship between the
size of the primary tumor and the risk of
Secondary Metastatic Growth
Growth at site of secondary arrest
Protection by fibrin clot?
Secondary Invasion
Out of vasculature into target tissue
Active
Passive
Growth of Metastatic Nodules
Angiogenesis
Invasion into metastatic organ site
Route of Metastasis
1. Lymphatic Metastasis
2. Hematogenous Metastasis
Route of Metastasis
1. Lymphatic Metastasis
2. Hematogenous Metastasis
Ĺ
Implantation metastasis
a.
Tumor cells seed the surface of body
cavities
b.
Most often involved is the peritoneal
cavity
c.
But also may affect
pleural,
Krukenberg Tumor
Krukenberg tumor
refers to a
malignancy
in the ovary that
metastasized
from a primary site,
classically the gastrointestinal tract
Diagnosis of Metastasis
Anamnesis
Physical Diagnosis
Lab
Imaging ( X ray, Ultrasound, CT scan
Symptom
Lung Metastasis
Nagging cough, dyspnea (bulky
metastasis). Pleural effusion
Liver Metastasis
Dyspepsia syndrome
Pain at epigastric
Bone metastasis
Bone pain, Pathologic fracture
Brain metastasis
Severe headache
Vertigo
Clinical Finding
Lymphadenopathy
Ascites fluid
Pleural Effusion
Hepatic nodule
Imaging
Chest X Ray
USG
Bone scan
CT Scan
MRI
Coin Lession
Colon Carcinoma Metastatic
[image:172.720.12.279.9.486.2]to Liver
Breast Carcinoma Metastatic to
Brain
Fig. 2.2b and c
Weinberg
Imaging on Metastatic Colon Carcinoma with
Radioactive-Iodine
SeeMets
Primary Glioblastoma Compared to Breast
Carcinoma Metastasis to the Brain
Figure 14.1 The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007). P. 588
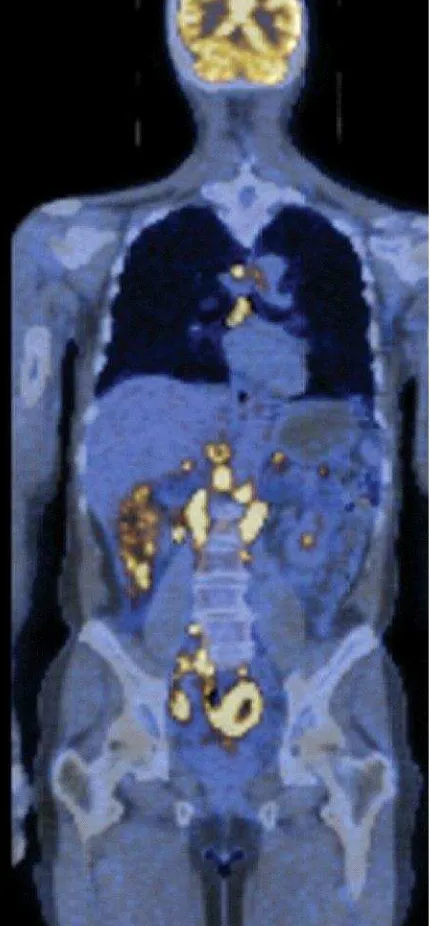
Metastatic non-Hodgkins Lymphoma
CT Scan and PET Scan (positron emission
tomography) of incorporated
radioactively-labelled deoxyfluoroglucose.
Prognosis
Lung / Liver metastasis : 8-12 months
Brain metastasis : 6 months
Treatment
Paliative treatment
Relieve of symptom : pain,
dyspneu,severe headache,dyspepsia etc
Risk and benefit of treatment
Usually : chemotherapy / hormonal
/radiotherapy
Prevention of Metastasis
Early Diagnosis
Prompt and Accurate Treatment
ADVERSE EVENT
(kejadian tidak diharapkan)
(KTD)
PRIMUM, NON NOCERE
FIRST, DO NO HARM
HIPPOCRATES’S TENET
What I want to talk about
Freedom from accidental injury due to
medical care, or medical errors
–
What I want to talk
about
A story
How common is adverse event?
Why does it happen?
How should we think ?
Mistakes are a fact of life.
It
’
s the response
to the error that counts
Florida Annual Accidental Deaths,
2003
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500
4000
4500
5000
Medical
Auto
Workplace
Air
5th leading cause
How hazardous is health care?
1
10
100
1,000
10,000
100,000
1
10
100
1,000
10,000
100,000
1,000,000
10,000,000
Number of encounters for each
fatality
T
ot
al liv
es
lo
st
p
er
y
ear
REGULATED
DANGEROUS
(>1/1000)
ULTRA-SAFE
(<1/100K)
Health Care
Mountain
Climbing
Bungee
Jumping
Driving
Chemical
Manufacturing
Chartered
Flights
Scheduled
Airlines
European
Railroads
Nuclear
Power
DATA KASUS DUGAAN MALPRAKTIK YANG SUDAH DILAPORKAN
1. 12 -02-04 Alm. Lucy Maywati RS Bersalin YPK Jkt Meninggal saat melahirkan caecar Polda Metro Jaya
Tgl Korban
Terlapor
Kasus
Lapor
2. 23-04-04 Wulan Yulianti RSCM Jkt Meninggal krn operasi pd usus Polda Metro Jaya 3. 28 -04-04 Alm Lucy Maywati RS Bersalin YPK Jkt Penggelapan M/R Polda Metro Jaya 4. 07-06-04 Jeremiah RS Budi Lestari Bks Operasi caecar mengakibatkan Polda Metro Jaya
RS Hermina, Bekasi luka & cacat
5. 11 -06-04 Mindo Sihombing RS Persahabatan Jkt Gagal operasi hernia Polda Metro Jaya 6. 15-06-04 Anissa Safitri RSCM Jkt Hidrocepalus Polda Metro Jaya 7. 24 -06-04 Alm. Jajang RSUD Sukabumi Jabar Wabah malaria di Sukabumi Polda Jawa Barat 8. 30-06-04 Alm. Lucy Maywati RS Bersalin YPK Jkt Meninggal saat melahirkan Polda Metro Jaya 9. 07 -07-04 Robinson L. Tobing RS Kodam Bkt Barisan Vegetativ State akibat operasi/ Polda Sumatra
Medan cacat permanen Utara 10. 12-07-04 Anissa Safitri Yayasan Amal Beduli Perbuatan tdk menyenangkan Polda Metro Jaya
Seribu, Jkt krn memulangkan pasien
11. 08 -07-04 Ngatmi RS Persahabatan Jkt Operasi kanker payudara Polda Metro Jaya 12. 14-07-04 Rohati RS Darmais Jkt Meninggal dunia akibat gagal Polda Metro Jaya
operasi kanker payudara
13. 18 -07-04 Dr Jane P PT Newmont Minahasa Pencemaran limbah B3 Mabes Polri Raya, Sulawesi Utara
17. 18 -07-04 Masna Stiman RS CM & RS MMC Jkt Keracunan mercury & arsen Mabes Polri
18. 26-07-04 Revy Anastasia RS Cikini Jkt Keracunan Obat Polda Metro Jaya
19. 09 -07-04 Revy Anastasia Apotik RS Cikini Jkt Keracunan Obat Polda Metro Jaya
20. 12-08-04 Rasyid Rahman Menkes Ahmad Sujudi Pencemaran nama baik dgn Mabes Polri
Mentamben P Yusgiantoro menyatakan tdk ada pencemaran Men LH Nabiel Makarim
21. 18 -08-04 Fellina Azzahra RS Karya Medika Jkt Meninggal krn salah operasi usus Polda Metro Jaya
22. 31-08-04 Again Isna Nauli RS Islam Bogor Kelalaian medis yg berakibat SATGA OPS Polda
cacat permanen Jawa Barat
23. 03 -09-04 Anggi & Anggeli RSCM Jkt Membiarkan pasien yg hrs dirawat Polda Metro Jaya
24. 03-09-04 Andreas RS Pasar Rebo Jkt Kelahiran yg mengakibatkan cacat Polda Metro Jaya
25. 03 -09-04 Maena Nurrocmah RS Setia Mitra Jkt Operasi usus Polda Metro Jaya
26. 15-09-04 Fellina Azzahra RS K Medika Cibitung Meninggal krn operasi usus Polda Metro Jaya
RSCM Jkt
27. 16-09-04 Leonardus W Pete RS Silom Gleaneglas Penyaderaan krn tdk mampu byr Polda Metro Jaya
28. 27-09-04 Wino Polres Sorong Papua Penganiayaan mengakibatkan Mabers Polri
Wiran mata dan dada rusak parah
29. 28-09-04 Lexyano Hamsalim RS Medistra Jkt Infeksi akibat operasi klip jantung Polda Metro Jaya
30. 28-09-04 Parrel Davin H.A RS Eva Sari Lalai mengakibtakan org lain Polda Metro Jaya
Sinurat Rawamangun Jkt meninggal
31. 05-10-04 Rizka Hudha RS Harapan Bunda Jkt Lalai mengakibatkan kematian Polda Metro Jaya
32. 05-10-04 Masita Ariani Klinik Bedah Plastik Kegagalan bedah plastik pd hidung Dit Reskrim Polda
(Annisa) Bandung Jawa Barat
33. 07-10-04 Tyava Putra Juliarty Klinik Dharma Bakti 2 Keracunan obat mengakibatkan Polda Metro Jaya
34. 20-10-04 Chealfiro M.P RSCM Jkt Operasi Hemia Polda Metro Jaya 35. 20-10-04 Sahat Parulian RS Cikini Jkt Pencemaran nama baik Polda Metro Jaya 36. 06-11-04 Fatimah RSCM Jkt Kelalaian mengakibatkan kematian Polda Metro Jaya 37. 10-11-04 Panca Satriya Dr. Siti Fadillah S Dugaan tindak pidana membuat Mabes Polri
Hasan Kesuma (Menkes RI) perasaan tdk menyenangkan
38. 14-01-05 Siti Zulaeha RSUD Pasar Rebo Jkt Kesalahan dlm operasi Polda Metro Jaya 39. 16-02-05 Selli Wane Carolina RS Fatmawati Jkt Kesalahan dlm operasi pd tulang Polda Metro Jaya
belakang berakibat cacat
40. 24-02-05 Martha Manulang RS St Carolus Jkt Salah obat Polda Metro Jaya 41. 11-03-05 Chris RS Sumber Waras Jkt Kesalahan dlm operasi Polda Metro Jaya
RS Mitra Kemayoran Jkt
42. 11-03-05 Tumi RS Harun Jkt Kesalahan dlm operasi Polda Metro Jaya 43. 11-03-05 Erwin Said dr. GW Sp.B Pelaku tanpa seizin korban SIAGA OPS
mengambil ginjal korban Bandar Lampung 44. 12-05-05 Royke Bagalutu, SH Rosyid Rusdi Melarang membawa anak ke SATGAS OPS Jabar
Sandino Brata RS Hasan Sadikin Bandung (Asisten I Sukabumi)
45. 26-05-05 Royke Bagalatu, SH PT BIO FARMA Indo Pemberian vaksin polio yg tdk SATGAS OPS Jabar diakui WHO
46. 12-06-05 Nabila Ka Dinkes Jabar Anaknya kejang2, panas berak2 Polda Metro Jaya Dinkes Depok setelah imunisasi polio, kmd
Menkes RI meninggal PT Bio Farma Indonesia
47. 18 -06-05 Wagirin RS Pelabuhan Kelalaian Medis Polda Metro Jaya
Sumber : Dari berbagai sumber
Acceptable?
Health care is a highly complex, error
prone industry.
Medicine is not a hard science …
combination of art and practice
Aviation and Nuclear arms = High
Reliability Organizations
–
strong
safety record
Swiss Cheese Model of Accident Causation
Modified from Reason, 1991 © 1991, James Reason
Triggers
DEFENSES
Accident
Regulatory
Narrowness
Incomplete
Procedures
Mixed
Messages
Production
Pressures
Responsibility
Shifting
Inadequate
Training
Attention
Distractions
Deferred
Maintenance
Clumsy
Technology
LATENT
FAILURES
Goal Conflicts
and Double Binds
KESALAHAN MEDIS (Medical Error)
Kesalahan yang terjadi dalam proses
asuhan medis yang mengakibatkan atau
berpotensi mengakibatkan cedera pada
pasien.
Medical errors
are associated with
inexperienced clinicians, new procedures,
extremes of age, complex care and urgent
care. Poor communication, improper
documentation, illegible handwriting,
inadequate nurse-to-patient ratios, and
similarly named medications are also
known to contribute to the problem.
Example for M Error
Misdiagnosis
Giving the wrong drug or (wrong
patient, wrong chemical, wrong
dose, wrong time, wrong route)
Giving two or more drugs that
interact unfavorably or cause
poisonous metabolic byproducts
Wrong site surgery such as