ABSTRACT
Wandut, K. Wilhemina. 2015. Designing a set material for English Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: English Education Study Program. Sanata Dharma University.
English Conversation is one of the extracurricular activities in SMP Negeri 15 Yogakarta that give students extra time to learn English in the school. The goal is
increasing students’ ability in English especially speaking.
This research aims to create an instructional design for the students in English
Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. The writer uses three instruments to
gain the data. They are: a) observation, b) questionnaire, and c) interview.
This research used Research and Development as the methodology. In order to make the instructional design, the writer elaborates six stages by combining Dick & Carey and Kemp model. The six stages are: a) Identifying instructional goals, b) Identifying Learners’ characteristic, c) Writing performance objectives, d) Developing Materials and strategies, e) Developing and Conducting formative and evaluative evaluation, and f) Evaluating instrument. After making the instructional design, the writer asks two lecturers from Sanata Dharma University and the teacher of English Conversation to be evaluators for the instructional design.
The writer presented the instructional design to six chapters, namely: This is Me, Let me Tell you Something, My Dream My Future, Healthy Life, I Love
Indonesia and Helping Others. Each chapter has five stages. They were: Let’s Take a Look, Let’s Find Out, Let’s Analyze, Let’s Practice and Let’s Produce. Based on result of questionnaire distributed to the evaluators, the instructional design is acceptable but it should be revised.
ABSTRAK
Wandut, K. Wilhemina. 2015. Designing a set material for English Conversation at
SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: English Education Study Program. Sanata
Dharma University.
English Conversation di SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta adalah salah satu program ekstrakurikuler yang memberikan kesempatan lebih bagi siswa – siswi untuk belajar bahasa inggris. Tujuannya adalah untuk meningkatkan kemampuan berbicara siswa.
Tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah menyusun seperangkat materi pembelajaran yang dapat diimplementasikan di English Conversation di SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. Penulis menggunakan tiga instrument dalam pengambilan data yaitu: a) Observasi, b) Kuesioner, dan c) wawancara.
Penelitian ini menggunakan metode Research and Development. Untuk membuat materi pembelajaran tersebut, penulis menyusun enam poin yang merupakan kombinasi model pembelajaran dari Dick & Carey dan Kemp. Keenam poin tersebut adalah: a) Identifying instructional goal, b) Identifying Learners characteristic, c) Writing Performance Objectives, d) Developing Materials and strategies , e) Developing and Conducting formative and evaluative evaluation, and f) Evaluating instrument. Setelah membuat materi pembelajaran, penulis meminta dua dosen dari universitas Sanata Dharma dan guru English Conversation untuk mengaluasi materi pembelajaran tersebut.
Penulis menyajikan materi pembelajaran dalam enam bab yaitu: This is Me, Let me Tell you Something, My Dream My Future, Healthy Life, I Love Indonesia and Helping Others. Setiap bab dibagi menjadi lima langkah yaitu: Let’s Take a Look,
Let’s Find Out, Let’s Analyze, Let’s Practice and Let’s Produce. Berdasarkan hasil kuesioner yang telah didistribusikan, para evaluator menyatakan bahwa materi pelajaran ini dinyatakan dapat dipakai tapi masih perlu direvisi.
Kata kunci: instructional design, English conversation, Dick & Carey and Kemp
DESIGNING A SET OF MATERIALS FOR ENGLISH
CONVERSATION AT SMP NEGERI 15 YOGYAKARTA
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Wilhelmina Kurnia Wandut Student Number: 111214169
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
i
DESIGNING A SET OF MATERIALS FOR ENGLISH
CONVERSATION AT SMP NEGERI 15 YOGYAKARTA
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Wilhelmina Kurnia Wandut Student Number: 111214169
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
iv
DEDICATION PAGE
Have courage and be kind
-
Cinderella
-I dedicate this thesis to:
My beloved Daddy for being everything to me. I mean
everything. I’m so grateful being your first daughter.
And also my lovely Mom for always being a good example to
me and making me as I’m now.
vii ABSTRACT
Wandut, K. Wilhemina. 2015. Designing a set material for English Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: English Education Study Program. Sanata Dharma University.
English Conversation is one of the extracurricular activities in SMP Negeri 15 Yogakarta that give students extra time to learn English in the school.
The goal is increasing students’ ability in English especially speaking.
This research aims to create an instructional design for the students in
English Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. The writer uses three
instruments to gain the data. They are: a) observation, b) questionnaire, and c) interview.
This research used Research and Development as the methodology. In order to make the instructional design, the writer elaborates six stages by combining Dick & Carey and Kemp model. The six stages are: a) Identifying instructional goals, b) Identifying Learners’ characteristic, c) Writing performance objectives, d) Developing Materials and strategies, e) Developing and Conducting formative and evaluative evaluation, and f) Evaluating instrument. After making the instructional design, the writer asks two lecturers from Sanata Dharma University and the teacher of English Conversation to be evaluators for the instructional design.
The writer presented the instructional design to six chapters, namely: This is Me, Let me Tell you Something, My Dream My Future, Healthy Life, I Love
Indonesia and Helping Others. Each chapter has five stages. They were: Let’s Take a Look, Let’s Find Out, Let’s Analyze, Let’s Practice and Let’s Produce.
Based on result of questionnaire distributed to the evaluators, the instructional design is acceptable but it should be revised.
viii ABSTRAK
Wandut, K. Wilhemina. 2015. Designing a set material for English Conversation
at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: English Education Study Program.
Sanata Dharma University.
English Conversation di SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta adalah salah satu program ekstrakurikuler yang memberikan kesempatan lebih bagi siswa – siswi untuk belajar bahasa inggris. Tujuannya adalah untuk meningkatkan kemampuan berbicara siswa.
Tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah menyusun seperangkat materi pembelajaran yang dapat diimplementasikan di English Conversation di SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. Penulis menggunakan tiga instrument dalam pengambilan data yaitu: a) Observasi, b) Kuesioner, dan c) wawancara.
Penelitian ini menggunakan metode Research and Development. Untuk membuat materi pembelajaran tersebut, penulis menyusun enam poin yang merupakan kombinasi model pembelajaran dari Dick & Carey dan Kemp. Keenam poin tersebut adalah: a) Identifying instructional goal, b) Identifying Learners characteristic, c) Writing Performance Objectives, d) Developing Materials and strategies , e) Developing and Conducting formative and evaluative evaluation, and f) Evaluating instrument. Setelah membuat materi pembelajaran, penulis meminta dua dosen dari universitas Sanata Dharma dan guru English Conversation untuk mengaluasi materi pembelajaran tersebut.
Penulis menyajikan materi pembelajaran dalam enam bab yaitu: This is Me, Let me Tell you Something, My Dream My Future, Healthy Life, I Love Indonesia and Helping Others. Setiap bab dibagi menjadi lima langkah yaitu:
Let’s Take a Look, Let’s Find Out, Let’s Analyze, Let’s Practice and Let’s
Produce. Berdasarkan hasil kuesioner yang telah didistribusikan, para evaluator menyatakan bahwa materi pelajaran ini dinyatakan dapat dipakai tapi masih perlu direvisi.
Kata kunci: instructional design, English conversation, Dick & Carey and Kemp
ix
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I would like to give my greatest gratefulness to Jesus Christ for putting every single thing in my life. He gives me everything more than I deserve. Also, I would like to thank Hail Mary for always helping me.
I would to offer my gratitude to Christina Lhaksmita Anandari, S.Pd., Ed.M., for the patience in guiding me finish this thesis. I want to thank her for
every lesson, advice, opinion and evaluation. I would also like to thank Yuseva Ariyani Iswandari S.Pd., M.Ed., as my academic advisor, for her support and
motivation during my study.
I also want to say thank to my evaluators Dra. Novita Dewi, M.A. (Hons), Ph.D., Patricia Angelina Lasut S.Pd., M.Hum and Dita Novenesa
S.Pd., for giving opinions, advices and evaluations to my instructional design.
I would like to thank SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta for giving me the chance to make a research there. I also want to give thanks to the all lecturer in Sanata Dharma University especially in English Education Study Program. Thanks for
making me as I am now.
My deepest gratitude also goes to my dad, Titus Wandut and my mom, Kristina Peda Boku for always loving, trusting, and supporting me. I owe them
x
Moreover, I would like to thank to all of my friends in college time: ELESP 2011 class C, my best friends in Amigos, my lovely sisters in Kost
Arimbi. Also my best friends who never get bored to spend time with me: Ija, Mba Widhy, Mba Dwi, Cece, Ria Tintun, Ta, and Jummy. I love you all guys.
Thanks for always accepting me as who I am. Last but not least, I would like to thank all of the people whom I cannot mention one by one for their support to finish this thesis.
Wilhelmina Kurnia Wandut
xi
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE ……… i
APPROVAL PAGE ……….…… ii
DEDICATION PAGE……….…. iii
PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI..……… iv
STATEMENT OF WORK ORIGINALITY ……… v
ABSTRACT ……….. vii
ABSTRAK ………..……… viii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ……….. x
TABLE OF CONTENTS ……….. xii
LIST OF TABLES ……… xiv
LIST OF FIGURES .……….. xv
LIST OF APPENDICES……… xvi
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION A. Research Background ..……… 1
B. Research Problem ..……….. 4
C. Problem Limitation ..……… 5
D. Research Objectives ..……….. 5
E. Research Benefits ..……….. 5
F. Definition of Terms ..……… 6
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Theoretical Description ………... 8
1. Instructional Design………. 8
2. Teaching English……….. 17
3. The Theory of Speaking……… 18
4. Communicative Language Teaching………. 21
5. Review of Related Studies……… 22
B. Theoretical Framework ……… 26
CHAPTER III: METHODOLOGY A. Research Method ……….. 28
B. Research Setting ……… 32
C. Research Participants………. 32
xii
E. Data Analysis Technique……… 35
F. Research Procedures……….. 47
CHAPTER IV: RESULT AND DISCUSSION A. Identifying the Instructional Goal……….. 39
B. Identifying Learners’ Characteristic………...… 40
C. Writing Performance Objectives……… 52
D. Developing Materials and Strategy ………... 54
E. Developing and Conducting Formative and Summative Evaluations………. 58
F. Evaluating Designs…..……… 59
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION A. Conclusion ..……… 63
B. Recommendation………. 63
REFERENCES ……… 66
xiii
LIST OF TABLES
Table
3.1 Multiple Choice……… 30
3.2 Likert Scale ………. 31
3.3 Open-ended Question………... 31
4.1 Observation Sheet……… 41
4.2 Observation’s criteria………..……… 41
4.3 Result of Observation……….. 42
4.4 Students’ Background………. 43
4.5 Students’ Opinion about the Materials of English Conversation ….…… 44
4.6 The Challenges Face by the Students in English Conversation ...…….. 46
4.7 The English Conversation’s Material Desired by the Students………... 47
4.8 Teacher’s Background………... 49
4.9 Students’ Problems………..……… 49
4.10 Media……… 50
4.11 Method……….……… 50
4.12 Topics……… 51
4.13 Assessment……… 52
4.14 Topic Included to Instructional Design………. 53
4.15 Topic and Objectives……….. 53
4.16 Rubric for Assessment……….... 58
4.17 Materials Evaluation Part 1 – The Objectives……… 59
4.18 Materials Evaluation Part 1 – Materials………. 60
xiv
4.20 Materials Evaluation Part 2 ……… 61
xv
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure
2.1 Dick and Carey’s Model of Instructional Design……… 10
2.2 Kemp’s Model of Instructional Design………. 14
2.3 Writer’s Model of Instructional Design………. 24
4.1 Let’s Take a Look ……….. 55
4.2 Let’s Analyze –Vocabulary……….... 56
xvi
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix 1 Instruments of Need Analysis………. 68
Appendix 2 Recapitulation of learners’ Questionnaire of Need Analysis……….. 75
Appendix 3 Interview Transcript ……….. 79
Appendix 4 Materials Evaluation Questionnaire………... 87
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter presents the introduction of the research. It consists of six sections, namely the research background, the research problem, the problem limitation, the research objective, the research benefits and the definition of terms.
A. Research Background
English is an international language which is widely used and becomes one of important languages around the world. Indonesia is one of the countries that has known English for many years. It is also included as lesson in education system. Moreover, Junior High Schools and Senior High Schools in Indonesia choose English as one of the requirement subjects to pass the national examination. This phenomenon shows that Indonesians are expected to be able to communicate in English.
This research deals with this program in the terms of providing an appropriate design for English Club as the extracurricular in a school. The writer chose the students of English club at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta as the subject of the research. However, the club in this school is well-known as English
Conversation (EC). It is because through this club the school wants to increase
students’ ability in speaking.
The writer lists three reasons why this research is worthy to be researched. Those reasons become the background of this research. First, the writer wants to offer a new design which is appropriate for the students on English Conversation based on the research that has been done. Second, even though the goal of this
English Conversation is training students’ speaking ability, the interest of students
in speaking is still minim. Third, since the English Conversation is an extracurricular, it has to offer an interesting and fun learning of English for the students. Therefore, this research also offers another way to learn a design with new strategies and good materials development which are based on students’ condition to avoid the boredom. Those reasons become the starting points for the writer to develop this research.
Although, the programs of extracurricular are not written in curriculum but it should be included in annual calendar. In Indonesia, the policy of extracurricular has been stated in the decree of Education and Cultural Department No. 0461/U/1964 states, “Extracurricular has important roles including developing student knowledge, connecting the course, accommodate student’s talent and
interest also coaching the whole characteristic as human being” (Depdikbud, 1998).
English Club is one of the extracurricular activities which is established for some reasons depending on the school or the goals of the Club itself. English Club can be a tool to accommodate students who have interest and passion in English but they do not have enough time to learn in classroom. English Club can also help students to increase their English skill. Another reason of English Club is to facilitate students who have specific skill in English. Furthermore, English Club offers a relaxed environment for students to practice English.
As one of the schools which has the English Club but the in different name, SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta also wants to gain those goals even though this school chooses to focus on the speaking ability. Based on the observation, the students’ competence in reading and writing are better than speaking. Therefore,
the school provides English Conversation that aims to train the speaking ability of the students. The numbers of students who join this program are around 40 students who come from grade seven and eight. Since they decide to join the
can produce English good enough. Furthermore, around 65% of the students ever joined English courses and leaning English since they were in elementary schools. The school provides two kinds of teacher for the English Conversation. They are native teacher and Indonesian teachers. However, both of them teach the students in almost the same way which focuses on the speaking ability. The schedule is on 02.00 pm until 03.30 pm after they finish the school. As what has been stated that in curriculum 2013, the duration of English is two hours in a week. This becomes the reason why students mostly decide to participate in
English Conversation. They still need to learn English more outside the
classroom. Moreover, there are other reasons why the students join the English
Conversation for examples: they have passion in English and want to increase
their English ability, and chase their dreams related in English.
B. Research Problem
Based on the background that has been stated in previous, the writer formulates the problem of the research as follows.
1. How does the design material for English Club at SMP Negeri 15 look like?
C. Problem Limitation
The scope of this research focuses on the designing the set of materials for
English Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. The writer finds out the
instructional materials. Furthermore, the writer identifies the characteristic, level, and background of the students. It is helpful to decide the best method and technique of teaching for the students in SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta.
D. Research Objectives
In order to answer the formulated problem, the writer makes a set of designing materials based on the students’ needs in SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. The writer designs some units of materials fundamentally that can be implemented in English Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta.
E. Research Benefits
The research is contributed to the development of knowledge particularly in English development. Besides, the research is conducted in order to give benefits for English teachers of English Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta, the students of English Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta, and the future researchers.
1. English Teachers
2. Students of English Conversation
The students can use the instructional materials as their media to learn English as well. Besides the topics related to their daily life, the can also develop their English through the exercises provided.
3. Future Researchers
This research can be used as the references for the future researchers who are going to conduct a research about designing a set material and who are going to have further research about the English Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta.
F. Definition of Terms
This part elaborates the definitions that are frequently used in this research. These are the basic understanding of the terms. It is divided into three parts, namely extracurricular, English Conversation of SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta, and instructional design.
1. Extracurricular
2. English Conversation of SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta
English Conversation (EC) at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta is a tool for
student to learn English in a fun environment. In English Conversation, students have opportunities to practice many different skills based on real situation. Moreover, English club encourages students to help each other achieve the club’s objectives. The member of students who join English Conversation are around 40 students and come from grade VII and VIII.
3. Instructional Design
According to Morrison, Ross, Kalman and Kemp (2011), “Instructional design is a systematic design process based on what we know about learning theories, information technology, systematic analysis, educational research and management method” (p.6). Based on this definition, it can be concluded that an
8
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter is divided into three sections, namely theoretical description, review of related study, and theoretical framework. Theoretical description involves related literature which is important and useful in designing instructional materials. In the review of related study, the writer provides the relevant studies with this research. Theoretical framework elaborates the relation between the theories and the research.
A. Theoretical Description
This section is divided into four parts, namely instructional design, teaching English, theory of speaking and Communicative Language Teaching. These theories used as guidelines to make a new instructional material for English
Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. The details of the theories are
explained as follows.
1. Instructional Design
The two instructional designs are chosen because of two reasons. First, Dick & Carey’s (2009) model is a well-known model that is applied in the methodology used in this research. Further explanation can be found in Chapter III. Second, according to Kemps (1977), his instructional design which is well-known as Kemp’s model is a flexible process. There is interdependence among the eight elements. The writer can start with whichever element is ready to start with and the move back and forth to the other steps. These are also the reasons why writer combines the instructional design. Another reason is the writer considers that the steps in the instructional designs help the writer to create a new instructional design that can be applied in English Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. Furthermore about those models are presented detailed in this part. a. Dick and Carey’s Model
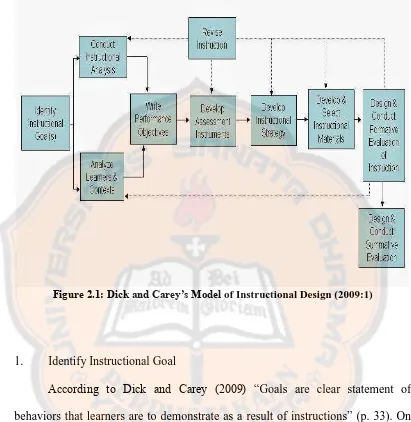
Figure 2.1: Dick and Carey’s Model of Instructional Design (2009:1)
1. Identify Instructional Goal
According to Dick and Carey (2009) “Goals are clear statement of
1. Conduct Instructional Analysis
On this stage teachers need to identify the exact performance used to connect the present performance and the desired performance. It means that what is done by learners during the instructional materials should be the same with the desired performance. Teacher also should convince that the relevant between steps taken in performing goal with objectives should be achieved by learners. Therefore, the materials and performances learned by learners support and lead them to the goals of learning.
2. Identify Entry Behaviors and Learner Characteristics
On this stage, teacher are required identifying the background and general characteristics of the learners includes skills, experience, motivation levels, and basic demographics. The information should have enough details to identify the correct starting point of the instruction so that students do not waste time reviewing material they have already known and do not omit content they need to know. This step helps teacher in designing the materials, techniques and strategies used. It also helps teachers to start the learning process at level that appropriate for students.
3. Write Performance Objectives
learning situation or when they are in real situation using the skills and knowledge from the instruction in daily life.
4. Develop Criterion-Referenced Test Items
On this stage, teachers develop tests or evaluation to assess the performance of the learners. The test item is a benchmark which is to measure whether learners have already reached the objectives and are ready to move to new skill. Furthermore, it can also evaluate the instructional design whether it already supports the student to get the learning outcomes.
5. Develop Instructional Strategy
The term instructional strategy is used generally to cover the various aspects of choosing a delivery system, sequencing and grouping cluster and content, describing learning components these will be included in the instruction, and selecting media for delivering instruction.
6. Develop and Select Instructional Materials
On this stage, the teachers need to design the instructional which can be implemented by learners in real context. Therefore, teachers select the instructional materials to focus on the goals that should be accomplished by the learners. The materials are the most chosen topic by the students.
7. Develop and Conduct Formative Evaluation
need improvement before releasing the instruction for the actual use. It can be from the media, strategies or techniques that used before.
8. Develop and Conduct Summative Evaluation
On this last stage, the teachers are required to develop and conduct summative test to verify the effectiveness of the instructional materials to the learner’s target. If the teachers find inappropriate materials during the instruction,
it will be rejected and will be evaluated. It can also be evaluated by learners. Based on the summative test teacher can decide students who need to learn more and those who are ready with the next level.
Dick and Carey’s (2009) model explores the steps taken to create a good
instructional design detailed. It can be seen that all of the steps are connected to make the goals of the instructional design can be delivered successfully to the students. Therefore, in order to get good instructional designs, according Dick and Carey (2009), a teacher must perform all of the steps.
b. Kemp’s Model
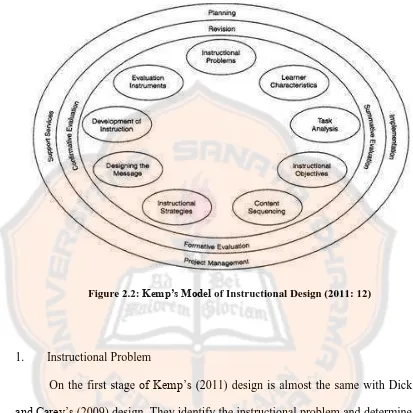
Figure 2.2: Kemp’s Model of Instructional Design (2011: 12)
1. Instructional Problem
On the first stage of Kemp’s (2011) design is almost the same with Dick and Carey’s (2009) design. They identify the instructional problem and determine
the goals of the program that will be designed. The goal of instruction can help the teacher to find the solution of students’ problem during the instructions.
2. Learners’ Characteristic
On this stage, the teachers are required to explore the characteristics and needs of the learners. It helps the teachers to design an appropriate instructional design for the learners. Moreover, identifying the learners’ characteristic can help
3. Task Analysis
This is one of the most important stages of design process. On this stage, the teachers need to include the knowledge and procedure in instructional design which support learners master the learning objectives. Kemp (2011) also states that “One of the keys steps of the design process is defining the content needed to address the instructional need or problem” (p. 97).
4. Instructional Objectives
The teachers are required to identify the instructional and learning objectives. Teachers have to specify what exactly learners must learn and master as the outcomes of learning. According to Kemp, et al. (2011), “There are three objectives domains of instructional design: cognitive domain, psychomotor domain and cognitive domain.”
5. Content Sequencing
On this stage, teachers should arrange the content of learning effectively. This stage presents an important role which will be used in helping learners understand and learn the information. It goals to determine the most appropriate sequence while presenting the information.
6. Instructional Strategies
learners to connect the information from instructional design with the existing knowledge.
7. Designing the Message
On this stage, teachers should convince the messages or goals of the instructional are delivered successfully to the learners. Therefore, teachers should find a good way which can introduce the content to learners, show the best way to implement the instructional design, and convey the most important information of the learning.
8. Developing Instructional Materials
On this stage, teachers need to select and explore more resources and materials to support activities of learners. Kemp et al. (2011), “The development of the instruction materials is the implemented of the instructional design” (p. 243). This is very important since the condition of learners might cause teacher to develop the instructional materials that have been prepared.
9. Evaluation Instruments
On the last stage, teachers develop evaluation instruments that will be used to asses and evaluate learner’s mastery of the learning objectives. It can also be
used to assess the instructional design whether it has answered the learning outcomes which expected from learners successfully.
the goal is to have the flexibility to solve problems as they arise, it can also make the end result or product more efficient and free of error. Therefore, when the teachers or instructors find any error in the instructional design, they may directly evaluate and revise it.
2. Teaching English
a. Approach or Method of Teaching English
The term approach of English is the same with method used to teach English. The development of teaching approach of English results many approaches. In this research, the writer chooses three kinds of approaches which are stated by Marzano and Kendall since those approaches can represent the idea of the writer. First, approach focuses on knowledge. Second, approach focuses on issue. Third, approach focuses on the student exploration. The approaches can be seen detailed in this part:
1. Focus on Knowledge
This approach concerns to emphasize the introduction of knowledge to the learners. Therefore, the goal of this approach is learners get new knowledge. For example, learners are introduced a knowledge about procedure text and the function (objective 1). After that, learners learn about the generic structure of the procedure text (objective 2).
2. Focus on Issues
seeing the generic structure of the procedure text, students are asked to determine the generic structure on another procedure text based on their understanding (objective 3).
3. Focus on Students Exploration
Marzano and Kendall (2007) state, “The third approach has student inquiry and self-analysis as its focus. Here the emphasis is on self-exploration as well as on knowledge of a subject area” (pp. 149-150). In this approach, teachers let the learners explore the material with their ideas. For example, teacher can ask the learners to make their own text procedure by using the generic structure (objective 4).
b. The Design of Teaching English
There are four elements of English teaching process in classroom according to Richards and Rogers (2001). They are the linguistic content, the role of teacher, the role of learners and the role of materials. The term linguistic content which is well-known as syllabus involves general and specific goal that will be done on teachers in classroom. “The purposes of a syllabus are almost as varied as the possible contents but can be grouped into several categories. A syllabus can be a contract, a permanent record and learning tool”.
3. The Theory of Speaking
about the important of teaching speaking and also to produce a well-designed material that can be implemented based on students’ needs.
a. The Nature of Speaking
Nunan (2003) states, “Many people feel that speaking in a new language is harder than reading, writing, or listening” (p.48). It happens for two reasons. First, unlike reading or writing, speaking happens in real time, usually the person whom we are talking is waiting for us to speak. Second, when we speak we cannot edit and revise what we wish to say, as if we are writing.
b. The Techniques in Teaching Speaking
There are some techniques in teaching speaking according to Nunan (2003) that can motivate students increase and develop their speaking skill. The techniques can be seen as follows:
1. Information Gap
Information gap is a useful activity in which one person has information that the other lacks (p. 56). They must use the target language to share the information. Besides, helping the students developing their speaking skill, this activity is also fun and interesting.
2. Jigsaw Activities
schedule of the plane. Both of the students should arrange the plan to go to the place. They should speak spontaneously in English.
3. Role – plays
As Nunan states, “Role-plays are excellent activities for speaking in
relatively safe the environment of the classroom” (p. 57). In this activity, students are given a certain role to play. For example, a student acts as a doctor and another student acts as a sick person. The doctor gives the person suggestion so that he can be healed from diseases.
4. Simulations
Simulations are more creative than role-plays. In this activity, teacher provides a realistic situation for language practice. For example, teacher sets market situation. Students as customers should buy the products and practice the transactional speaking with the seller.
5. Contact Assignments
4. Communicative Language Teaching
This part presents the method of teaching used in the design materials. The design materials used Communicative Language Teaching (CLT). This part is divided into three parts, namely principle of CLT, Approach of CLT and classroom activity of CLT.
a. The Principle of CLT
Communicative Language Teaching is found in the changes in the British language teaching tradition dating from the 1960s. There are some principles of CLT that could help the writer design the material for English Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta.
According to Finocchiaro and Brumfit (1983), “Some principles of CLT are language learning is learning to communicate and effective communication is sought. These principles were adapted to the design material.” Furthermore, they said that drilling may occur but peripherally, comprehensible pronunciation is sought and any device that helps learners is accepted- varying according to their age and interest (p. 156).
b. The Approach of CLT
are not merely its grammatical and structural features but categories of functional and communicative meaning as exemplified in discourse (p. 161).
c. Classroom Activity of CLT
The range of exercise type and activities compatible with a communication approach is unlimited. Providing that such exercise enable learners to attain the communicative objectives in the curriculum, engage learners in communication, and required the use of such communication processes as information, sharing, negotiation of meaning and interaction (p. 165). Some activities that can be implemented in the classroom based on CLT principle are need analysis, group process manager, text – based materials and task – based materials.
5. Review of Related Study a. Related Studies
This part explores the type of research which has been done by other researchers. There is a dissertation which designed to research, develop and validate a resource guide school leaders can use to facilitate social media use by school staff. The title is Research, Development and Validation of a School
Leader’s Resource Guide for the Facilitation of Social Media use by School Staff
and is compiled by Deanna L Gooch in Kansas State University on 1983. Moreover, it was developed using the research and development (R & D) methodology by Gall, Borg and Gall (2003) and Dick and Carey (2009).
Macromedia Flash Tutorial at Instructional Design and Technology Emporia
State University in December 6, 2002. On this thesis, Tucker emphasizes two reasons The Dick and Carey System Approach as the instructional design model. First, it is widely known a model that can be applied to a variety of context areas by novice to expert instructional designers. Second, this model is based on systematic process.
Puspasari (2007) in her study makes an instructional speaking materials using contextual teaching and learning for the eighth grade students for SMPN 2 Ponjong, Gunungkidul. In this research, she also combines two models of instructional designs becomes a new instructional design. The focus of the instructional design is increasing the speaking ability of the students. Ginting (2010) also conducts a research about designing a set of speaking materials using task based learning for English extracurricular in BOPKRI senior high school. In his research, Ginting (2010) explores about the speaking theories and method which are suitable to be implemented in the English extracurricular.
b. Writer’s Model
The writer combines Dick and Carey’s (2009) model and Morrison, Ross,
Kalman and Kemp’s (2011) model; which is well known as Kemp’s model to
make new design materials. The purpose is to design appropriate design materials which can be used in English Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. The reasons the writer chooses those models because of their strength which represents the writer’s ideas about ideal instructional design. In writer’s opinion, an ideal
consider the characters and learners’ need. Besides, the instructional design can
also give the chance for teacher to evaluate the learners’ achievements. The
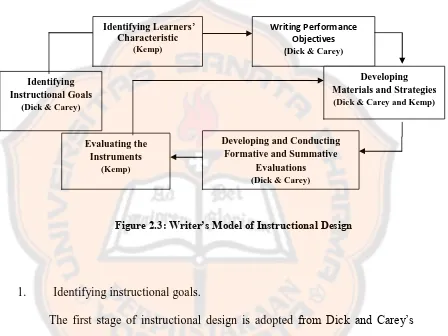
[image:43.595.96.544.198.534.2]writer’s model is divided into six stages that can be seen in Figure 2.3.
Figure 2.3: Writer’s Model of Instructional Design
1. Identifying instructional goals.
The first stage of instructional design is adopted from Dick and Carey’s (2009) models. On this stage, the teachers need to identify the objectives of the instructional materials. Before starting the instructional the teachers should have list of objectives that should be achieved by students as their learning outcomes. That is the reason why this stage becomes the first step of the design.
2. Identifying Learners characteristic
The second stage is taken from Kemp’s (2011) model. Figuring out the
learners’ characteristic helps the teacher to lead to the objectives. Analyzing students’ characteristic also provides teacher information about the methods and
Identifying Instructional Goals
(Dick & Carey)
Writing Performance Objectives
(Dick & Carey)
Developing and Conducting Formative and Summative
Evaluations (Dick & Carey)
Developing Materials and Strategies
(Dick & Carey and Kemp)
Evaluating the Instruments
(Kemp)
Identifying Learners’ Characteristic
strategies that will be used to develop the instructional design. After stating the instructional goal, the teachers need to find the students’ character because it can help the teacher to design the materials based on students’ characteristic.
3. Writing Performance Objectives
This stage becomes the third step because after analyzing the students’
characteristic, the teachers need to list the performance of objectives to support the learners to achieve the goals. On the first stage, the teachers are required to list the objectives of the instructional but Dick and Carey (2009) suggest teachers to list the skill and knowledge that will be performed by students during the instructional.
4. Developing Material and Strategy
This stage is the combine of the Dick and Carey (2009) and Kemp’s (2011)
model. On this stage, teachers need to develop the materials and strategies contextual based on the learners’ need. Sometimes, teachers need to change the
materials and strategies from the first plan depend on the condition of the learners.
5. Developing and Conducting Formative and Summative Evaluation
Writer combines two stages from Dick and Carey’s (2011) model become
one stage. Formative evaluation is done in process of learning while summative evaluation is done at the end of instruction to judge learners’ performance and
6. Evaluating Instruments
The last stage is taken from Kemp’s model (2011). On this stage, teachers
need to evaluate learner’s performance to find out whether they already get the
learning objectives and are ready to move to another unit.
The writer chooses stages from Dick and Carey (2009) and Kemp’s (2011)
model to become a new instructional design. Those stages are chosen because the idea and activity are suitable with writer’s planning.
B. Theoretical Framework
In order to answer the problem of this research, the writer needs to understand and master the concept of instructional design both of Dick and Carey’s (2009) model and Morrison, Ross, Kalman and Kemp’s (2011) model.
Since the writer uses those concepts as guidelines to design an instructional which is appropriate to English Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta, the writer should understand the details of every step of the instructional design. Moreover, the writer needs to understand the theory of teaching English especially for speaking since the English Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta focuses on speaking ability.
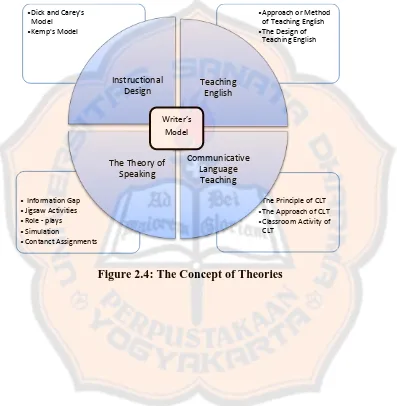
The writer collaborates the theories in order to create a new instructional design. The concept of all the theories can be seen in the in the figure 2.4.
Figure 2.4: The Concept of Theories
•The Principle of CLT •The Approach of CLT •Classroom Activity of
CLT • Information Gap
•Jigsaw Activities •Role - plays •Simulation
•Contanct Assignments
•Approach or Method of Teaching English •The Design of
Teaching English •Dick and Carey's
Model •Kemp's Model
Instructional
Design Teaching English
Communicative Language
Teaching The Theory of
Speaking
28
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This section elaborates the methods the technique and analyzing data, and reveals the boundaries of the research. This section divided in six parts namely: research method, research setting, research participant, instruments and gathering techniques, data analysis techniques, and research procedures.
A. Research Method
This research was Research and Development which is well-known as R&D. Borg (1987) defines “Research and development is a model developing in which the findings of research are used to design new products and procedures, which then are systematically field – tested, evaluated, and refined until they meet specified criteria of effectiveness, quality or similar standard” (p. 589). The writer chose this type of research because the steps of the research could help the writer answered the problem formulation. Moreover, R&D holds great promise for improving education because it involves a close connection between systematic program evaluation and program development.
The example of the educational research and development which is widely used is the system approach model from Dick & Carey (2009). Therefore, the writer also used this model as one of the references in making the design for
According to Roger, “collecting data is an integral part of science; the goal is to understand the pattern of relations among the variables” (p. 18). In order to answer the formulated problem of this research, the writer explored three methods to gather data from the participants. They are observation, questionnaire and interview.
1. Observation
The first method was observation. It was held since April, 14th 2015 until May, 19th 2015. This method purposed to give the blue print of the situation of
English Conversation in SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. According to Howard S.
Becker and Blanche Geer in the book Participant Observation and Interview (P.
323), “participant observation can thus provide us with a yardstick against which
to measure the completeness of data gathered in other ways, a model which can serve to let us know what orders of information escape us when we use other
method.” It is clear that observation can help the test-taker to gather more data. 2. Questionnaire
Conversation. This method also will be used by evaluators to give their opinion
and evaluation to the instructional design. a. Multiple Choices.
According to Brown, “the main reasons of the practically is easy to administer and be scored quickly” (p.194). Those are the reasons why the writer chose this item as one of the instruments in methodology. Multiple choices’ format is also the most popular method of testing a reading knowledge of vocabulary and grammar. The example of multiple can be seen as follows
3.1 Multiple Choice
1. Sejak kapan kalian belajar bahasa inggris a. TK
b. SD c. SMP
b. Likert Scale
According to Betram, “A psychometric response scale primarily used in
questionnaire to obtain participant’s preference or degree of agreement with a
statement or set of statements. Likert Scale is a non-comparative scaling technique and is unidimensional (only measure a single trait).” In this activity the respondent are asked to choose their level of agreement to the statements given by ordinal scale. There are four options which can be chosen by the participants. They are Strongly Disagree (SD), Agree (A), Disagree (D) and Strongly Disagree (SD). The example of Likert scale picture can be seen in Table 3.2
Table: 3.2 Likert Scale
No Statements SA A D SD
1. Do you think that the materials from English Club help you in learning English in classroom
√ √
c. Open-ended question
Open-ended question is one of the alternative questions which close to close-ended question. According to Ballou ( 2011) “The open-ended question does not provide answer categories. The person (respondent) who is asked an open-ended question formulates the answer and gives the responses in his or her own words. Although this structure gives the respondent more freedom in crafting an answer, it also increases the cognitive efforts.” The examples of open ended can bee seen in Table 3.3
3.3 Open-ended Question
1. How is the student’s ability in speaking English?
2. What is the most difficult problem faced by students in speaking?
3. Interview
The third method was interview. After having the questionnaire section, the writer chose participants to be interviewed. This was the last instruments that used to gain the data from participants. According to McNamara, (1999)
“Interviews are particular useful for getting the story behind a participant’s
repetition. Therefore, the writer used the purposive sampling to choose the participant to be interviewed. The participants are chosen based on their answer in the questionnaires.
According to Palys and Frazer, “purposive sampling is virtually synonymous with qualitative research. However, since there are many qualitative researchers might have, the list of purposive strategies is virtually endless and given list will reflect only at the rage of situation.”
B. Research Setting
This section presents the setting of time and place in which the research was conducted. This research was conducted in SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. It was located in Jalan Tegal Lempuyangan. no. 61. It was conducted since April, 14th 2015 May until 30th 2015. It included the observation, the distribution of the questionnaire and the interview with the teacher and the students.
C. Research Participants
This section elaborates the participants who are involved in this research. There were two kinds of participants in this research. They were the research and information collecting participant that consisted of the students and the teacher of
1. Research and Information Collecting
The participants in the research were students of the English Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. They were from grade VII and VIII. The range of their age was 13 – 15 years old. The writer used them to become participants to find out about their level, needs, situation and achievement in English.
2. Evaluators
The teacher of the English Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta and two lecturers from Sanata Dharma University were involved as participants on this part. They became the evaluators of the instructional materials. The teacher of English Conversation has had many experiences in teaching this
English Conversation and the lecturers from Sanata Dharma also already had
many experiences in teaching English for many years. Those participants gave opinions, evaluations and revisions for the instructional design.
D. Instruments and Data Gathering Technique
This section explores the instruments and data gathering technique used in this research. It is divided in three parts namely: observation, questionnaire and interview.
1. Observation
At the beginning of the lesson the teacher told the students the goals that they are going to achieve at the end of the lesson. She trained the students’ vocabulary by asking them to repeat the words. Another activity used was role play. The students learned giving direction by practicing in the classroom.
2 Questionnaire
There were two kinds of participants who used this instrument. They were research and information collecting participant and evaluators.
a. Research and information collecting participant
In this part, the writer used population in deciding the participants. The questionnaires for these participants were divided into two items. The first was multiple choices and the second was Likert scale. The questionnaire was distributed to the students on April 21th 2015. The reason in using multiple choices and Likert scale for students was helping the students to answer the questions easily since they just needed to choose one of the answers provided. It was also easy to administer by the writer.
b. Evaluators
2. Interview
After having the result of observation and questionnaire, the writer chose some participants based on their answer in the questionnaire sheets to be
interviewed. It aimed to have more explanation about the participants’ answer. There were also two kinds of participants who used this instrument. They are the students of English Conversation and The teacher of English Conversation.
a. The Students of English Conversation
On this section, the researcher used purposive sampling by choosing some participants to be interviewed. It was needed to validate the observation and instrument that has been made. Purposive sampling was chosen because the researcher needs to find some students to clarify the data. The participants were chosen based on their answers on the questionnaires part. Another reason was because they were students who have good competence, active or passive in the classroom.
b. The English Teacher of English Conversation
Furthermore, this instrument also was used to interview the teacher of
English Conversation. The goal was to find out the more information about the
background of the students and the condition of the English Conversation itself.
E. Data Analysis Technique
1. Data Analysis Technique of Research and Collecting
In order to make instructional materials, the researcher contributed the questioners to the students as the research and collecting participants. In this part, the data that are needed by the writer were the background of students about English, the opinion of the students about the English Conversation, the challenge the students faced in learning English, and the materials desired by the students. After gathering the result of the questioners, the data was analyzed using a formula which can be seen on the next page:
∑x = the number of students who have the same answers
∑n = the total number of the students
2. Data Analysis Technique of Preliminary Field Testing
After making the instructional material for English Conversation at SMP Negeri l5 Yogyakarta, the writer asked for validation include opinion, evaluation and revision. The answers of the participants on this section were analyzed by using a formula which can be seen as below:
x 100%
∑x = the participant’s answers
∑n = the total number of the participants
However, the writer also received the opinions, evaluations and revisions in sentences thus can help in making the better instructional materials.
F.Research Procedures
This section summarizes the steps taken in conducting the study. The writer elaborates nine stages to in conducting this research. Those steps can be seen as follows:
1. Collecting Data
The first step of conducting this research was collecting data. It included observation, questionnaire and interview. In this steps, the writer gained data as many as possible about the students, teacher and materials for the English
Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta.
2. Analysis data
After having all of the data, the second step was analysis data. On this step, the writer tried to analyze all of data to get instructional materials which suitable to be implemented in English Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta.
materials. The objectives and indicators were benchmarks for writer to design the materials.
4. Develop the materials
After having the objectives and indicators, the writer developed the materials based on the most chosen topic by the students. The materials given to the students should lead them to the objectives of the instructional. The materials developed can be seen in the appendix.
5. Developing strategy
After developing the materials, the writer needed to develop the strategy. It includes the method and techniques used to delivered the materials for students. The strategy can be identified by knowing the characteristic of the students. 6. Developing and conducting formative and summative evaluation
On this section, the writer is requested to develop and conduct formative and summative evaluation. It helped to check the level of understanding of the students. It also reflected whether the strategy and method using in instructional materials were appropriate for the students. Moreover, the activities could assess the students whether they are ready or not to move to next level.
7. Evaluating Design
39
CHAPTER IV
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
In this section, the writer elaborates the research findings and the analysis of the research. The writer presents the process of collecting data and rationale on answering the problem formulation which stated in Chapter I. The problem is “What does the design material of English Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 look
like?
In order to answer the problem, the writer organized the six stages that have been explained in Chapter II. The seven stages are: Identifying Instructional Goals, Identifying Learners Characteristic, Writing Performance Objectives, Developing Materials and Strategy, Developing and Conducting Formative and Summative Evaluations, and Evaluating Instruments. Those stages of the instructional design are elaborated on the following sections.
A. Identifying the Instructional Design
The goal of this instructional design is the goal of the English
Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta. This was the benchmark for the
students in SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta based on the observation of students’ level, background, needs and desire.
B. Identifying Learners’ Characteristic
On this second stage, the writer focused on finding out the level, background, problems and expectation of students about the instructional design. The respondents on this stage were the students of SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta who join the English Conversation and the teacher of the English Conversation. The writer conducted three ways to gain the information from the respondents. First was observation. It used to find out the level of the students. Second was questionnaire. It used to find out the background, opinion, challenges and desire of the students about the English Conversation. The third was interview which is used to comprehensive the result of the interview. The explanation of the three instruments can be seen as follows.
1. Observation
Table 4.1 Observation Sheet
Name :
Class:
Items Very Good Good Inadequate Very Inadequate Pronunciation
Vocabulary Grammar Fluency
In order to help calculating the data, the writer also provided the criteria of each item which can be seen in Table 4.2.
Table 4.2 Observation’s criteria
Items Very Good Good Inadequate Very
Inadequate Pronunciation Very good
intonation and very good stress, Good intonation and good stress Inadequate intonation and inadequate stress Very inadequate intonation and very inadequate stress Vocabulary Very good
word choices Good word choices inadequate word choices Very inadequate word choices Grammar No mistake
in a sentence, using good tenses,
Very few mistakes in a sentence and using good tenses
Many mistakes in a sentence and using inadequate tenses
So many mistakes in a sentence and using very inadequate tenses Fluency Very fluent,
After observing the students in some meetings by joining the English
[image:61.595.99.513.194.581.2]Conversation, the writer had the result presented in Table 4.3.
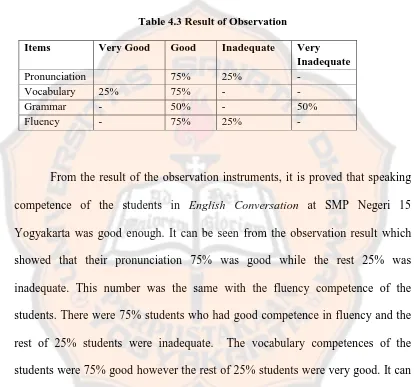
Table 4.3 Result of Observation
Items Very Good Good Inadequate Very Inadequate
Pronunciation 75% 25% -
Vocabulary 25% 75% - -
Grammar - 50% - 50%
Fluency - 75% 25% -
From the result of the observation instruments, it is proved that speaking competence of the students in English Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta was good enough. It can be seen from the observation result which showed that their pronunciation 75% was good while the rest 25% was inadequate. This number was the same with the fluency competence of the students. There were 75% students who had good competence in fluency and the rest of 25% students were inadequate. The vocabulary competences of the students were 75% good however the rest of 25% students were very good. It can be seen when they performed in front of the class.
On the other hand, the grammar competence of the students in English
Conversation at SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta was not really good. It can be seen
2. Questionnaires
The second instrument used to gain the data was questionnaires. The respondents of this instrument were the students in SMP Negeri 15 Yogyakarta who join the English Conversation. The questionnaire was distributed to the students on April 21th 2015. It categorized in four parts. The first part was the background of the students which consisted of four questions. The second part was the opinion of the students about the materials of English Conversation which consisted of five questions. The third part explored about the challenges faced by students in English Conversation and it consisted of two questions. The last part of the question was the desire materials expected by the students. The result of the questionnaire is presented in the following section.
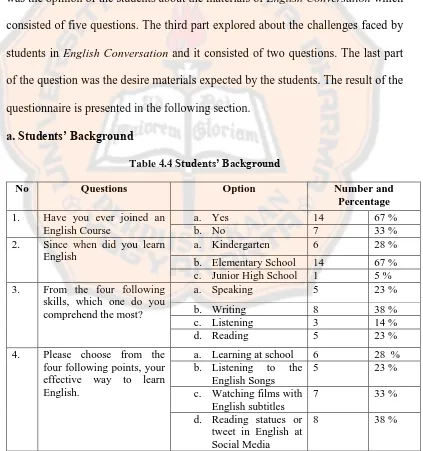
a. Students’ Background
Table 4.4 Students’ Background
No Questions Option Number and
Percentage 1. Have you ever joined an
English Course
a. Yes 14 67 %
b. No 7 33 %
2. Since when did you learn English
a. Kindergarten 6 28 %
b. Elementary School 14 67 % c. Junior High School 1 5 % 3. From the four following
skills, which one do you comprehend the most?
a. Speaking 5 23 %
b. Writing 8 38 %
c. Listening 3 14 %
d. Reading 5 23 %
4. Please choose from the four following points, your effective way to learn English.
a. Learning at school 6 28 % b. Listening to the
English Songs
5 23 %
c. Watching films with English subtitles
7 33 %
d. Reading statues or tweet in English at Social Media
[image:62.595.107.530.288.739.2]The finding of students’ background presented that 67% of the students
ever joined English course while the rest of the 28% never joined any English course before. The numbers of the students who have learned English since kindergarten were 28% and the students who have learned English in the junior high school was only 5% which means only one person. Most students have learned English since they were in elementary school. It can be seen that students who chose this option were 67%.
The skill which be the most comprehend by the students was writing skill since it got 38%. The numbers of students who chose speaking and reading skill were the same which was 23%. The rest of the students chose listening skill and it got 14%. This section showed that most of the students learned English from social media by reading the statuses and tweets. It got the highest percentage that was 38%. Besides, 33% students stated that they learned English by watching film using English subtitle and this option became the second most chosen. 28% students said that they learn English at school and the rest of them which was 23% stated that they learned English from listening to the English songs.
[image:63.595.113.517.612.744.2]b.
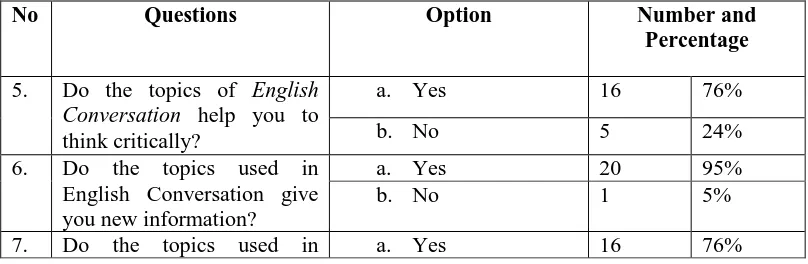
Students’ Opinion about the Materials of English ConversationTable 4.5 Students’ Opinion about the Materials of English Conversation
No Questions Option Number and
Percentage
5. Do the topics of English Conversation help you to think critically?
a. Yes 16 76%
b. No 5 24%
6. Do the topics used in English Conversation give you new information?
a. Yes 20 95%
b. No 1 5%
English Conversation related to daily life?
b. No 5 24%
8. Are the topics of English Conversation interested for you?
a. Yes 18 86%
b. No 3 14%
9. Do you like if there is reflection section at the end of the lesson?
a. Yes 17 81%
b. No 4 19%
The answers of the students in this section showed that most of the students thought the topics of English Conversationhelped them to think critically and had 76% for the answers. However, the rest 24% of students assumed that the topics for the English Conversation did not help them to think critically. Almost all the students agreed that those topics used in English Conversation could give the new information and it got 95%. While only 5% of students who did not think that the topics gave new information. The idea that the topics of English
Conversation wer