Informasi Dokumen
- Penulis:
- Elly Wardani
- Lusi Putri Dwita
- Imam Hardiman
- Ani Pahriyani
- Dwitiyanti
- Tuti Wiyati
- Pengajar:
- Prof. Dr. Hamka
- Sekolah: Universitas Muhammadiyah Jakarta
- Mata Pelajaran: Mikrobiologi
- Topik: Modul Praktikum Mikrobiologi-Virologi
- Tipe: Modul Praktikum
- Tahun: 2020
- Kota: Jakarta
Ringkasan Dokumen
I. Praktikum 1: Pengenalan & Sterilisasi Peralatan Umum Laboratorium Mikrobiologi
This section introduces fundamental microbiology laboratory equipment and sterilization techniques. It emphasizes the importance of aseptic techniques in maintaining the integrity of experiments and preventing contamination. The academic value lies in establishing a solid foundation for practical microbiology work, crucial for subsequent experiments and research. Pedagogically, this section utilizes a hands-on approach, enabling students to familiarize themselves with essential tools and procedures, building essential laboratory skills and fostering a sense of responsibility towards maintaining a sterile work environment.
1.1 Kompetensi Dasar
This subsection outlines the core competencies students are expected to achieve after completing this practical session. This includes a thorough understanding of common laboratory equipment and their functions, a grasp of basic sterilization concepts, and the development of practical skills in executing sterilization techniques with accuracy and precision. These competencies are essential for successful performance in further microbiology studies, emphasizing the importance of both theoretical knowledge and practical application.
1.2 Indikator Capaian
This section details the specific, measurable outcomes that demonstrate the students' mastery of the competencies. Students are expected to correctly identify and explain the functions of various basic microbiology laboratory equipment. Further, they must demonstrate the understanding of sterilization concepts and effectively execute sterilization procedures on common equipment and test media. These clearly defined indicators provide a benchmark against which student learning can be effectively assessed.
1.3 Tujuan Praktikum
This section explicitly states the learning objectives for this practical session. Students must demonstrate familiarity with common laboratory equipment and their functions, articulate the differences between various sterilization techniques, and successfully execute the sterilization of both equipment and test media. These aims directly relate to the broader learning outcomes of the course and ensure students focus on achieving specific skills-based goals.
1.4 Uraian Teori
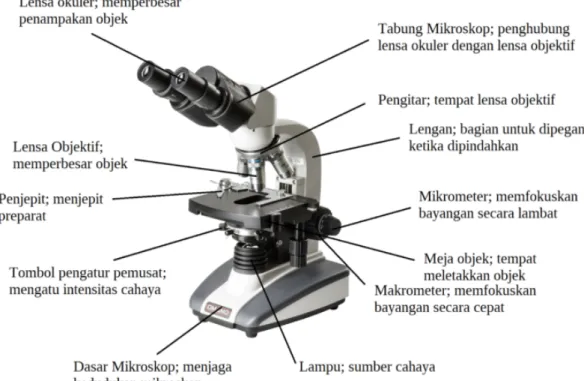
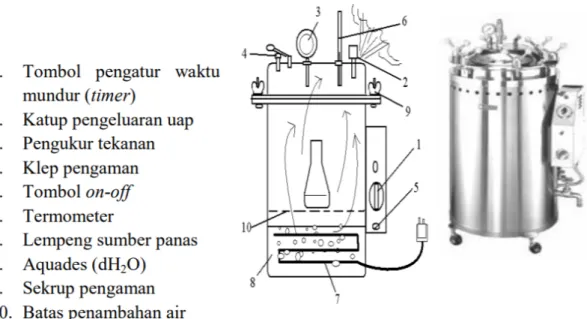
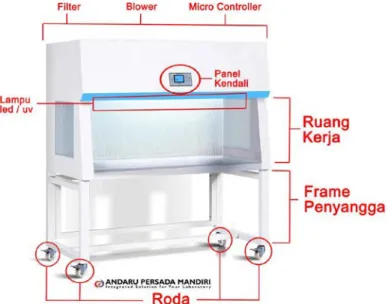
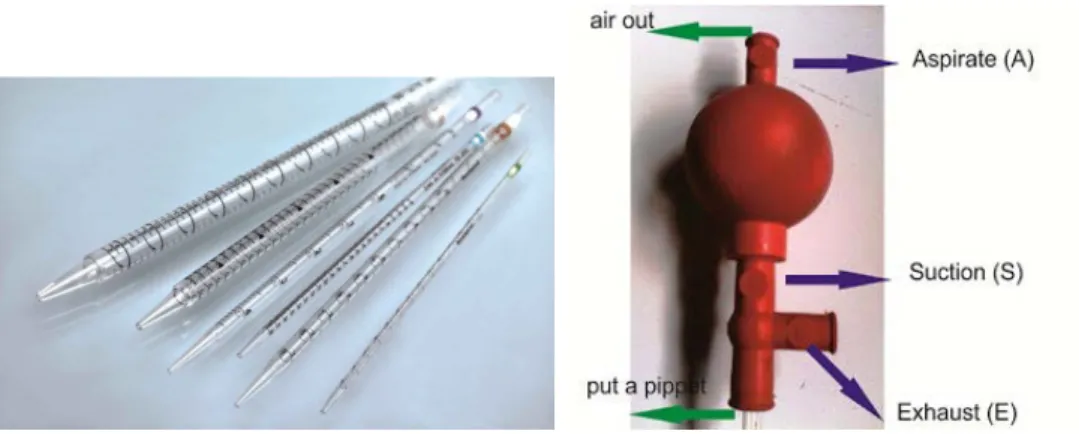
This subsection provides a theoretical framework for the practical work, covering the principles of operation for various pieces of equipment, such as the light microscope (Figure 1), autoclave (Figure 2), incubator (Figure 3), and hot plate stirrer (Figure 4), among others. It also delves into the concept of sterilization, including various methods (mechanical, physical, and chemical), highlighting the importance of each technique in maintaining sterility and preventing contamination within the laboratory setting. The inclusion of diagrams (Figures 1-17) enhances understanding and retention of the presented material.
1.5 Pelaksanaan Praktikum
This section provides a detailed step-by-step guide for students to conduct the practical session. It includes a list of required materials and equipment, followed by a structured procedure. This structured approach allows students to engage actively with the material, allowing for guided learning that supports the development of essential practical skills in a microbiology setting. The detailed instructions ensure that the students can conduct the experiment successfully and obtain meaningful results.
1.6 Evaluasi
This section outlines the assessment criteria for the practical session. It includes a table for recording experimental results, and guidelines for writing the lab report. This structured evaluation approach ensures that student performance aligns with stated learning outcomes and provides specific feedback for improvement.
1.7 Soal Latihan
This section presents thought-provoking questions to reinforce learning and test understanding of the concepts and procedures covered. The questions encourage critical thinking about the importance of sterility, the application of sterilization methods in everyday life, and the differences between various pieces of equipment used in the practical session. This is a key element of formative assessment, facilitating the consolidation of knowledge and skills.
1.8 Daftar Pustaka
This section provides a list of references used to support the theoretical content of the practical session. The cited sources offer students additional avenues to explore the subject matter further and develop their understanding of the scientific basis underpinning the practical work. This is crucial for building academic integrity and encouraging further independent learning.
II. Praktikum 2: Medium Pertumbuhan Mikroorganisme
This section focuses on the preparation and types of microbial growth media. The academic value stems from understanding the nutritional requirements of microorganisms and how different media can be formulated to support the growth of specific organisms. Pedagogically, it involves practical application, teaching students how to prepare both simple and complex media, solidifying theoretical knowledge with hands-on experience. The diverse types of media explored contribute to a complete understanding of microbiological techniques.
2.1 Kompetensi Dasar
This section defines the essential skills and knowledge that students should acquire. Students should be able to identify and understand various types of growth media commonly used in microbiology, comprehending their respective functions. The ability to prepare both natural and synthetic media is also emphasized, highlighting the practical aspects of microbiological techniques. This ensures a foundational understanding for future work in the field.
2.2 Indikator Capaian
This section details measurable outcomes demonstrating competency. Students should be able to name and describe the functions of common microbiology media. They must effectively prepare both natural and synthetic media, and they should be able to pour media and create different agar types (plates, slants, and deep tubes). This provides specific targets for assessment, ensuring students achieve practical skills and theoretical knowledge.
2.3 Tujuan Praktikum
This section lists the objectives for the practical session. Students must demonstrate their understanding of different media types and their functions. They should be able to differentiate between media types and successfully pour media to create agar plates, slants, and deep tubes. This provides clear, concise objectives for students to focus on, aligning with the broader course objectives.
2.4 Uraian Teori
This section presents the theoretical background on microbial growth media, including their composition (basic ingredients, nutritional components, and additives) and classification (natural, semi-synthetic, and synthetic, based on their composition and use). The section also explains the importance of different media types, such as general purpose, selective, differential, and enrichment media. The image of different media types (Figure 20) serves as a visual aid.
2.5 Pelaksanaan Praktikum
This section outlines the practical procedures, including a detailed list of materials, equipment, and step-by-step instructions for preparing both natural (broth, nutrient agar, PDA, TEA) and synthetic media. This hands-on instruction allows students to apply their theoretical knowledge and develop essential laboratory skills in media preparation. The explicit instructions provided reduce ambiguity and ensure successful completion of the practical tasks.
2.6 Evaluasi
This section details the assessment of the practical. Students evaluate the physical properties of the prepared media, comparing natural and synthetic varieties, and discussing any observed differences. A detailed report, including observations and explanations, is required. This robust assessment method assesses both practical skills and understanding of theoretical principles.
2.7 Soal Latihan
These questions test students' understanding of media types, factors affecting media preparation, potential sources of contamination, and the functions of specific components. The questions encourage critical thinking and reinforce the key concepts of the practical session. This acts as formative assessment, strengthening student understanding before moving to subsequent topics.
2.8 Daftar Pustaka
This section lists references used for the theoretical content. These sources provide additional resources for students who wish to expand their knowledge and understanding. This promotes further research and reinforces the importance of academic integrity.
III. Praktikum 3: Isolasi Mikroorganisme
This section focuses on the isolation of microorganisms from various sources. The academic value lies in mastering aseptic techniques and understanding the principles of microbial isolation and purification. Pedagogically, this involves several practical techniques (streak, pour, and spread plate methods), directly applying previous knowledge of media and sterilization to obtain pure cultures. This practical section is crucial for further microbiological investigations.
3.1 Kompetensi Dasar
This section describes the essential skills to be developed: accuracy, precision, and meticulousness in performing microbial isolation tests. Students should develop proficiency in isolating microbes from different substrates (soil, food, pharmaceuticals, traditional medicine, water, and air) and demonstrate expertise in using various isolation techniques. This provides clear, measurable goals for the practical session.
3.2 Indikator Capaian
This section lists observable outcomes indicating competency. Students must proficiently isolate microorganisms from various sources, demonstrating precision and carefulness. They should also demonstrate skills in streak, pour, and spread plate methods. This allows for precise evaluation of student performance, targeting both practical skills and understanding of the underlying principles.
3.3 Tujuan Praktikum
This section states the objective: students must be able to perform microbial isolation tests on different sample types. This clear, concise objective directs the learning process, ensuring students focus on the core skills required for this particular practical session.
3.4 Uraian Teori
This section provides the theoretical basis for microbial isolation. It discusses the ubiquity of microorganisms, the importance of aseptic techniques to avoid contamination, and the definition of a pure culture. It further details sample preparation techniques (swab, rinse, and maceration; Figures 21-24), serial dilution (Figure 25), and different plating methods (streak, pour, and spread plate; Figures 26-28), including variations within the streak method (Figures 29-32). The descriptions are complemented by clear visuals.
3.5 Pelaksanaan Praktikum
This section provides step-by-step instructions for isolating microorganisms from air, the environment, and soil samples. It includes detailed procedures for each isolation method, fostering the development of practical microbiological skills and aseptic techniques. The inclusion of images (Figure 34) further enhances clarity and understanding of the process.
3.6 Evaluasi
This section outlines the evaluation process. Students record their observations on microbial growth from different sources and assess colony morphology using a standardized system. The evaluation focuses on the accuracy and precision of the isolation techniques and the ability to identify and describe colony morphology. This provides a systematic approach to assessing student learning.
Referensi Dokumen
- Khasiat dan Nilai Gizi Yoghurt ( Astawan, M. )
- Probiotics ( Chaitow, L. dan N. Trenev )
- All About Yoghurt ( Helferich, W dan D. Westhoff )
- Pembuatan Yoghurt Kedelai (Soygurt) dengan Menggunakan Kultur Campuran Bifidobacterium bifidum dan Streptococcus thermophilus ( Silvia )
- Pembuatan Soygurt Sinbiotik dengan Menggunakan Kultur Campuran Bifidobacterium bifidum, Streptococcus thermophilus, dan Lactobacillus casei galur Shirota ( Supriadi, Y. )