commit to user
i
A COMPARISON OF EXPERIENTIAL MEANING ANALYSIS IN THE
TRANSCRIPT OF BARACK OBAMA’S SPEECHES ABOUT IRAQ WAR AND IRAN ELECTION CRISIS
(A Study Based on Systemic Functional Linguistics)
THESIS
Submitted as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
For Sarjana Sastra Degree from English Departement
Faculty of Letters and Fine Arts
Sebelas Maret University
By:
MUHAMMAD SYAFI’I AL HAMID
C0306036
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF LETTERS AND FINE ARTS
SEBELAS MARET UNIVERSITY
SURAKARTA
commit to user
commit to user
commit to user
iv Name : Muhammad Syafi’i Al Hamid
NIM : C0306036
Hereby, I declare that this thesis entitled “A Comparison of Experiential
Meaning Analysis in the Transcript of Barack Obama’s Speeches about Iraq War and
Iran Election Crisis (A Study Based on the Systemic Functional Linguistics)” is
originally composed by myself. The people’s work or statements are written in
quotations.
If in the future, it is proven I cheat; I am ready to take responsibility even
withdrawing of my academic title.
Surakarta, 30 May 2011
The researcher
commit to user
v
“No mountain too high when there is a will, it’s just how to take a first step”
-Hamid-
“jangan pernah bergantung pada motivasi dari orang lain, karena memotivasi diri sendiri itu lebih ampuh and berguna”
-Hamid-
“ tujuan bukan yang utama, yang terpenting adalah prosessnya”
-Iwan Fals-
“It is not enough to know what to say, but it is necessary to know how to say it”
commit to user
vi
I DEDICATE THIS THESIS WHOLEHEARTLY
TO MY BELOVED MOM AND DAD
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
SENTRAYA BHUANA
commit to user
vii
Alhamdulilahirahirabil’alamin, all praises and thanks to Allah S.W.T, the
Almighty God, for the blessing and guidance so that this thesis could be
accomplished. There were many difficulties I faced in accomplishing this thesis.
Nevertheless, due to the supports and helps from the people surrounding me, finally I
could finish this thesis. Hence, I would like to express my deep gratitude from my
heart to:
1. Drs. Riyadi Santosa, M.Ed., Ph.D as the dean of Faculty of Letters and
Fine Arts, my thesis supervisor, and also my academic supervisor.
Thanks for the guidance, assistance, and advice during my study and in
accomplishing my thesis.
2. Prof. Dr. Djatmika, M.A., as the head of English Department. Thanks for
giving approval to this thesis to be examined.
3. All the lecturers of English Department who have taught me, thanks a lot
for the valuable knowledge given for me. Hopefully, it will be beneficial
for me and other people.
4. My family thanks a lot for the advices, supports and endless love for me.
Especially, my beloved mom and dad who always pray me all the night.
You are the best and I am very happy having both of you.
5. My beloved Sentraya Bhuana and friends, thanks for the unforgotten
experiences, adventures, and many things I got with you. You drove me
commit to user
viii
bima, lala, rizki, wisnu, jabat, mo’onk, dila, vendra, hanif, and also the
other friends that I could not mention one by one, I will be missing you, I
love you all.
7. All my friends in ‘Graha Ukm FSSR’. Thanks for everything, it’s a nice
moment to remember when we ever had many times to discuss, chat,
joke and laugh together. Sorry, I still could not be a good ‘Lurah Ukm’
for you.
8. Thanks also for every one who had helped and supported me to finish
this thesis.
I have tried maximally to accomplish this thesis. But, I realize that this thesis
is still far from perfect. Hence, all suggestions are welcomed for the sake of me and
also the subject of the studies.
The researcher
commit to user
ix
TITLE ... i
APPROVAL BY THE THESIS CONSULTANT ... ii
APPROVALS BY THE THESIS EXAMINERS ... iii
PRONOUNCEMENT ... iv
MOTTO ... v
DEDICATION ... vi
ACKNOWLEGMENT ... vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... ix
LIST OF FIGURES AND TABLES ... xii
ABSTRACT ... xiii
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Research Background ... 1
B. Problem Statement... 3
C. Research Objectives ... 5
D. Research Questions ... 6
E. Research Benefits ... 6
F. Scope of the Research ... 7
G. Thesis Organization ... 8
CHAPTER II LITERATURE REVIEW ... 9
A. Barack Obama ... 9
B. Iraq War ... 11
C. Iran Election Crisis ... 13
D. Speech and News Conference ... 15
commit to user
x
E. Systemic Functional Grammar ... 19
F. Text and Context ... 20
G. Metafunctions ... 23
H. Ideational Meaning ... 25
I. Transitivity ... 26
1. Process and Its Participants ... 27
1) Material Process ... 28
2) Mental Process ... 29
3) Relational Process ... 30
a) Attributive relational process ... 31
b) Identifying relational process ... 31
4) Behavioral Process ... 32
a) Verbal behavior process ... 32
b) Mental behavior process ... 32
5) Verbal Process ... 33
6) Existential Process ... 33
2. Circumtances ... 34
3. Extra Causer ... 39
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 42
A. Research Design ... 42
1. Research Paradigm ... 42
2. Research Method ... 43
a) Research Location ... 43
b) Sampling ... 44
commit to user
xi e) Data Analysis46
f) Procedure Data Analysis 51
CHAPTER IV FINDINGS ... 52
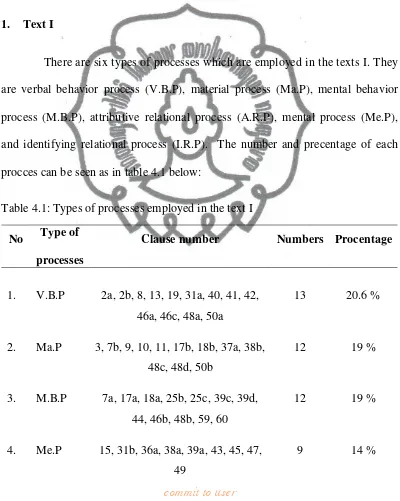
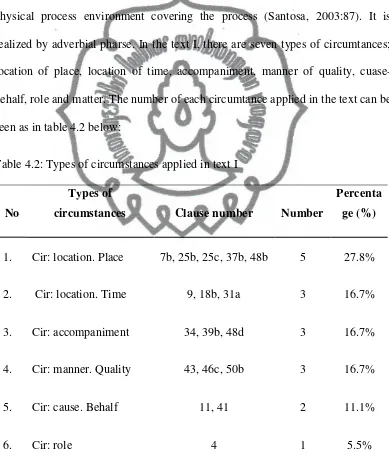
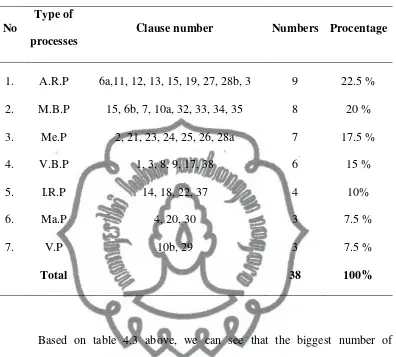
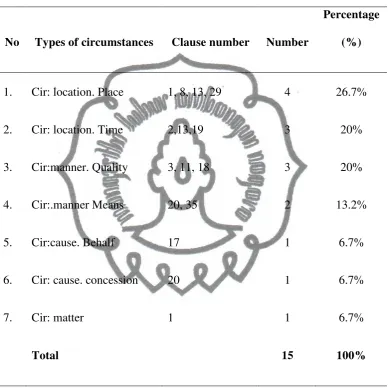
A. Types of Processes and Circumstances Employed in the Texts52 1. Text I ... 53
2. Text II ... 62
B. The Ways of the Processes and circumstances Employed in the Texts ... 73
1. The Relation of the Processes Applied in the Texts ... 74
2. The Comparison of the Use and Function of the Processes ... 86
C. The Reasons of the Processes Employed in the Texts ... 94
1. Text ... I94 2. Text II ... 97
CHAPTER V CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION ... 103
A. Conclusion ... 103
B. Recommendation ... ... ... 107
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... 110
commit to user
xii
LIST OF FIGURES AND TABLES
List of figures
Figures 2.1: Language as the realization of social context ... 22
Figures 3.1: The flow of analysis of the study ... 47
List of tables Table 1.1: Examples of analyzing processes in texts ... 4
Table 3.2: Examples of the kinds of processes applied in the texts ... 49
Table 4.1: Types of processes employed in the text I ... 53
Table 4.2: Types of circumstances applied in the text I ... 60
Table 4.3: Types of processes applied in the text I ... 63
Table 4.4: Types of circumstances applied in the text II ... 71
Table 4.5: Types of processes and their function in the text I ... 74
Table 4.6: Types of processes and their function in the text I ... 80
Table 4.7: The comparison of the processes applied between text I and text II ... 87
Table 4.8: The comparison of the function of processes applied in the texts ... 88
Table 4.9: Three functions of verbal behavior processes applied in the text I ... 96
commit to user
xiii ABSTRACT
MUHAMMAD SYAFI’I AL HAMID. C0306036. 2011. A Comparison of
Experiential Meaning Analysis in the Transcript of Barack Obama’s Speeches about
Iraq War and Iran Election Crisis.
This research focuses on the experiential meaning analysis of Barack Obama’s speeches about Iraq War and Iran election crisis which are analyzed in a comparison analysis. The objectives of the research are to find out the types of processes employed in the texts, the ways of processes employed in the texts, and the reasons of the processes employed in the texts. The research belongs to the qualitative research and also descriptive method. This research applied purposive sampling to select the source of data and also applied total sampling technique to collect the data. It was done because the data were taken from all major clauses of the texts. The source of the data were taken from the transcript of Barack Obama’s speeches about Iraq War given on October 2002 in The Federal Plaza in Chicago and the Iran election crisis given in a news conference on June 23, 2009. The data was analyzed using transitivity system and compared by using componential analysis to find the differences and similarities between text I and text II. Finally, having analyzed and seen the relationship both the texts, the researcher found up the cultural values supported by the secondary data.
Having analyzed the texts using transitivity system, the researcher concluded that there are different types of processes and their ways applied in the texts. The findings show that the differences occur in the use of the processes and their functions. The dominant process applied in text I is verbal behavior process. Then it is followed by mental behavior process, material process, mental process, identifying relational process and attributive relational process. Meanwhile, the dominant process applied in text II is attributive relational process. Then it is followed by mental behavior process, mental process, verbal behavior process, identifying relational process, material process and verbal process.
The dominant use of verbal behavior process in text I functions to show more condition and situation related to the crisis in Iran. There is only small attitude that can be seen through the processes applied in text II. Finally, Barack Obama tends to emphasis in showing his attitude of disapproval in text I. Meanwhile, in text II he only focuses on describing about the condition of Iran Crisis.
commit to user
1 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Research Background
Systemic Functional Linguistics (abbreviated as SFL) was developed by
M.A.K Halliday in 1960s. SFL is a part of social semiotic approach to language. It
views language as a foundation of the building of human experiences and as a
system of meaning. There are three general meanings that are constructed in each
text; ideational meaning, interpersonal meaning, and textual meaning. Those
systems are known as metafunctions which work in lexicogrammar rank. In the
social context, it has general functions such as; to enact our social relationships, to
represent our experiences to each other, and to organize our enactments and
representation as meaningful text (Martin & Rose 2003: 6).
Ideational meaning is one of three systems realized in the metafuctions.
Ideational meaning functions to construct mental picture in the people’s mind
about the reality of what is going on. It is classified into two, experiential meaning
dealing with the experiences as inter-related part of a whole and logical meaning
used to connect the experiences. In clause rank, experiential meaning is
represented by the transitivity systems. Meanwhile, logical meaning can be
commit to user
Experiential meaning is used to understand the reality by construing the
events or happenings. In the context of situation, experiential meaning focuses on
the institutional activity which is done by the people. It means that it works in
‘field’ area of the context of situation. It figures three participants or elements
which construct the happenings or events. The first one is processes which
happen, the second one is participants who are involved in the happenings, and the
last one is circumstances which encase the happenings.
Since the experiential meaning is used to understand the social events or
happenings in the reality, we examine the processes which occur in text which are
produced by the people as a semiotic approach to language. The term of text here,
in the Systemic Functional Linguistics (SFL), it is not only written text in the
small sense, but also spoken text. The term text is used in linguistics to refers to
any passage, spoken or written, of whatever length, that does form a unified whole
(Halliday and Hasan, 1976).
As stated above a text can be analyzed by transitivity system, the
researcher is interested in using transitivity system to analyze the experiences
represented in the texts which are taken from Barack Obama’s speeches. The
reason why the researcher took Barrack Obama’s speeches is due to those
speeches are phenomenal. Many people assume that his speeches have huge
impact and get much attention in social life of the world. Hence, the researcher
would like to find out the experiential aspect which is applied in the Barack
commit to user
the speeches, how the processes are employed and why the processes are
employed.
B. Problem Statement
Distributing a message or meaning through text can be applied on story,
essay, song, or even on a speech. Speech is used by the speaker to deliver the
message in front of many people. Speech can be used as a media for showing the
attitude or thought of the speaker toward something. It can also be used for
persuading the hearers to do something as the speaker wants.
The message of the speech can be seen by analyzing the processes and
other elements in the transitivity systems of ideational meaning. We can know
what the speaker thinks about an issue, how the speaker affects the hearer to have
same opinion or to do something, and finally we can understand what the speaker
intends to.
Related to what the researcher has stated above, Barack Obama is the
44th and current president of United States who has affected many people by his
speeches. Most of his speeches get much attention from the hearers. Hence, the
researcher is interested in observing the processes occur in two of his phenomenal
speeches. The first one is the speech about Iraq War. This speech conducted on
October 2002 in the Federal Plaza, Chicago. In this speech Barack Obama showed
his thought about war, especially in the Iraq War. In this case, the researcher
wants to know the processes employed in the speeches, how Barack Obama
employed those processes and why Barack Obama employed those processes in
commit to user
following examples are some of the processes employed by Barack Obama in
showing his attitude toward war.
“I don't oppose all wars. What I am opposed to is a dumb war. What I
am opposed to is a rash war”.
We can analyze those texts by using transitivity to know the processes
occur as the tables below:
Tables1.1: Examples of analyzing process in texts
I don’t oppose all wars
Behaver Verbal. Behavioral. Process Phenomenon
What I am opposed to is a dumb war
Token Iden. Rel. Pro Value
What I am opposed to is a rash war
Token Iden. Rel. Pro Value
From the tables above, we can see that Barack Obama uses verbal
behavior process in order to show his attitude about war. After showing his
attitude through verbal behavior process, Barack Obama uses identifying
relational process to give the next explanation about the previous statement. In
this case, we can see that identifying relational process occur two times after
verbal behavior process. In the transitivity system, identifying relational process is
off-commit to user
course he has a particular purpose by employing identifying relational process in
two times. In this case, we need to analysis the text as a whole in order to know
why he used those processes. Each process which is used has a purpose and could
not be separated from the other processes in creating a meaning as a whole.
Besides, we need also the additional information related to the theme as a
secondary data in order to support the finding cultural values.
For a comparison, the researcher took another speech given by Barack
Obama at Egypt’s prestigious Cairo University in downtown Cairo, Egypt, on
June 2009. The speech was delivered by Barack Obama in a news conference
concerning about the situation since the Iran election crisis began. In this case, the
researcher wants to know whether there is any different process employed by
Barack Obama in both speeches, especially in responding about the issue
happened in two conflicting countries through this research entitled “A Comparison of Experiential Meaning Analysis in the Transcript of Barrack
Obama’s Speeches about Iraq War and Iran Election Crisis”.
C. Research Objectives
Based on the problem statement above, the objectives of the research are
to describe the experiential meaning of each text and to compare the experiential
meaning of the Barack Obama’s speeches about Iraq War and Iran Election crisis.
commit to user
1. To find out the comparison of processes and circumstances
employed by Barack Obama both in his speech about Iraq War and
Iran election crisis.
2. To find out the ways of the processes and circumstances employed
in Barack Obama’s speeches about Iraq War and Iran election crisis.
3. To find out the reasons why Barack Obama uses those processes
both in his speech about Iraq War and Iran election crisis.
D. Research Questions
The research contains some questions dealing with the experiential
meaning. The questions proposed in this research are:
1. What processes and circumstances are employed by Barack Obama
both in his speech about Iraq War and Iran Election Crisis?
2. How are the ways of the processes and circumstances employed in
both his speech about Iraq War and Iran Election Crisis?
3. Why does Barack Obama use the processes by Barack Obama both
in his speech about Iraq War and Iran Election Crisis?
E. Research Benefits
There are some benefits of this research that can be proposed by the
commit to user
1. This research is aimed to know what the experiential meaning occurs
behind the speech of Barack Obama both in the speech about Iraq
War and Iran Election Crisis.
2. This research is important to give better understanding of
experiential meaning as a part of ideational meaning as one of the
other functions in the metafunctions.
3. This research is presented as reference for other researchers and
steak-holder for the sake of linguistic studies especially in Systemic
Functional Linguistic Studies.
F. Scope of the Research
This research focuses to examine the experiential meaning in the two
speeches given by Barack Obama. The first speech is about Iraq war given on
October 2002, in The Federal Plaza, Chicago and the second one is about the
situation since the Iran election crisis given in a news conference on June 23,
2009.
Since the Ideational meaning consists of experiential meaning and
logical meaning, in order to limit the research and detail research, the researcher
focuses on the experiential meaning represented by transitivity system. This
research also focuses on the major clauses in the transcript of the speeches due to
commit to user
G. Thesis Organization
This research is systematically written according to thesis organization
which consists of five chapters:
CHAPTER I involves INTRODUCTION. It consists of the Research
Background, Problem Statement, Research Objectives, Research
Questions, Research Benefits, Scope of the Research and Thesis
Organization.
CHAPTER II involves LITERATURE REVIEW. This chapter covers Barack
Obama, Iraq War, Iran Election Crisis, Speech and News
Conference, Text and Context, Systemic Functional Grammar,
Metafunctions, Ideational Meaning, and Transitivity.
CHAPTER III involves RESEARCH DESIGN. This chapter covers Research
Paradigm, Research Location, Sampling, Data and Source of
Data, Data Validity, Data Analysis, and Procedure of Data
Analysis.
CHAPTER IV involves FINDINGS. It covers The Types of Processes Employed
in the Texts, The Way of the Processes Employed in the Texts,
and The Reasons Why the Processes Employed in the Texts.
commit to user
9
CHAPTER II
LITERATURE REVIEW
This chapter consists of several subchapters. This chapter discusses
Barack Obama, Iraq War, Iran election crisis, speech and news conference, text
and context, systemic functional grammar, metafunctions, ideational meaning, and
transitivity.
A. Barack Obama
Barack Obama is the 44th and current president of United States. He was
born in Honolulu August 4, 1961. At present, he is the first African American to
hold the office. He became president of United States after he won the general
election in November 2008. He previously served as United States Senator from
Illinois from January 2005 until he resigned after his election to the presidency.
His first day governed United States as an elected president took place on January
20, 2010.
Obama started his study in the elementary school in Jakarta, Indonesia, in
1967. In 1971, Obama returned to Honolulu to live with maternal grandparent and
continued his study from fifth grade until his graduation from high school in 1979.
Following his school, Obama moved to Los Angeles in 1979 to attend Occidental
College. Later, he transferred to Columbia University in New York City, where he
majored in political science with a specialty in International Relation and
commit to user
was the president of the Harvard Law Review and president of journal in the
second year. After graduating with Juris Doctor (J.D) magna cum'laude from
Harvard in 1991, he returned to Chicago. He then accepted a two-year position as
a Visiting Law and Government Fellow at the University of Chicago Law School
to work on his first book. He then served as a professor at that university for
twelve years- as lecturer from 1992 to 1996, and a Senior Lecturer from 1996 to
2004 in teaching constitutional law.
His political career began when he was elected to the Illinois senate in
1996 as Senator from Illinois's District. In the 1998, he was reelected to the
Illinois senate defeating Republican Yesse Yehudah in the general election, and
was reelected again in 2002. In January 2003, Obama became chairman of the
Illinois Senate's Health and Human Services Committee when Democrats
regained a majority. He was formally announced as a candidate from Democratic
Party and as the opponent of George W. Bush from Republican Party in January
2003. Afterward, Obama resigned from the Illinois Senate in November 2004
following the general election. He became U.S senator in 2005 to 2008. On
February 10, 2007, Obama announced his candidacy for president of the United
States. Obama emphasized the issues of rapidly ending the Iraq War, increasing
energy independence, and providing universal health care. In 2009, Obama won
the general election and was elected to be the president of United States.
Many people assume that one of the aspects which supports Barack
Obama in reaching his successful is his ability as communicator. His amazing
commit to user
According to Shel Leanne in her book Say it like Obama, she describes Obama’s
speeches: clear, inspiring, and motivating (Leanne, 2009: xvi).
In his speech of political campaign, Obama much emphasized on Iraq
War as one of the issues spread in the United States. He was the rival of the
George W. Bush administration's 2003 invasion of Iraq. He spoke out against the
Iraq War when the day President Bush and congress agreed on join resolution
authorizing of Iraq War. There were many speeches presented by Barack Obama
concerning about Iraq War. He addressed another anti-war rally in March 2003
and told the crowd that "it's not too late" to stop the war. On February 27, 2009 he
declared that the Invasion of Iraq would end by 18 months.
(http://en,wikipedia.org/wiki/BarackObama).
B. Iraq War
Iraq war is also known as the occupation of Iraq, the second Gulf War,
and Operation Iraqi freedom. It is a military campaign that began on March 20,
2003. The invasion of Iraq was led by troop from the United States under the
administration of President Goerge W. Bush and the United Kingdom under the
Prime Minister Tony Blair. The invasion was caused by the issue that Iraq has the
"weapon mass of destruction" (MDW). The governments of the United States and
United Kingdom asserted that the possibility of Iraq employing the weapon
threatened their security and their coalition or regional allies.
In 2002, the United Nations Security Council passed Resolution 1441
commit to user
verify that it was not in possession of weapons of mass destruction and cruise
missiles. The United Nations Monitoring Verification and Inspection Commission
(UNMOVIC) was given access by Iraq under provisions of the U.N resolution but
found no evidence of weapons of mass destruction.
The invasion of Iraq led to an occupation and the eventual capture of
President Hussein. Violence against coalition forces and among various sectarian
groups soon led to the Iraqi insurgency, strife between many Sunni and Shia Iraqi
groups, and the emergence of a new faction of al-Qaeda in Iraq. In 2008, the
UNHCR reported an estimate of 4.7 million refugees (16% of the population) with
2 million abroad (a number close to CIA projections) and 2.7 million internally
displaced people. In 2007, Iraq's anti-corruption board reported that 35% of Iraqi
children, or about five million children, were orphans. The Red Cross stated in
March 2008 that Iraq's humanitarian situation remained among the most critical in
the world, with millions of Iraqis forced to rely on insufficient and poor-quality
water sources.
In June 2008, U.S. Department of Defense officials claimed security and
economic indicators began to show signs of improvement in what they hailed as
significant and fragile gains. Iraq was fifth on the 2008 Failed States Index, and
sixth on the 2009 list. As public opinion favoring troop withdrawals increased and
as Iraqi forces began to take responsibility for security, member nations of the
Coalition withdrew their forces. In late 2008, the U.S. and Iraqi governments
approved a Status of Forces Agreement effective through January 1, 2012. The
commit to user
aimed at ensuring cooperation in constitutional rights, threat deterrence,
education, energy development, and other areas.
In late February 2009, newly elected U.S. President Barack Obama
announced an 18-month withdrawal window for combat forces, with
approximately 50,000 troops remaining in the country "to advise and train Iraqi
security forces and to provide intelligence and surveillance". General Ray
Odierno, the top U.S. military commander in Iraq, said he believes all U.S. troops
will be out of the country by the end of 2011, while U.K. forces ended combat
operations on April 30, 2009. Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki has said he
supports the accelerated pullout of U.S. forces. In a speech at the Oval Office on
31 August 2010 Obama declared "the American combat mission in Iraq has
ended. Operation Iraqi Freedom is over, and the Iraqi people now have lead
responsibility for the security of their country." Beginning September 1, 2010, the
American operational name for its involvement in Iraq changed from "Operation
Iraqi Freedom" to "Operation New Dawn". (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IraqWar)
C. Iran Election Crisis
A crisis is defined by Pauchant and Mitroff (1992:12) as a disruption that
physically affects a system as a whole and threatens its basic assumptions, its
subjective sense of self, and its existential core. Meanwhile, Haywood makes
simple definition of crisis as "an emergency condition", (Haywood, 2008). From
the definition above we can see that crisis is an unexpected condition and it is a
commit to user
such as, economical aspect, political aspect, social aspect, and so on.
A crisis hit Iran after the Iranian presidential election started on 12 June
2009. The crisis was caused by the protests following the Iranian presidential
election against the disputed victory of Iranian President Mahmoed Ahmadinejad.
The opposition candidate Mir-Housein Mousavi was dissatisfied by the result of
the election. He sent a letter to the Guardian Council to cancel the election and
claimed that he was the real winner. He also met the Supreme Leader to discuss
the elections.
Official results, released by the Interior ministry, stated that Mahmoud
Ahmadinejad had got 62.6%. Meanwhile his closest challenger, Mir Hossein
Mousavi, received only 33.8%. The two other candidates won a much smaller
percentage of the vote. Mohsen Rezai gained 1.7% and Mehdi Karroubi just 0.9%.
The ministry put turnout at 85%.
All opposition candidates rejected the official results and claimed that the
votes were manipulated and the election rigged. According to an analysis by
Professor Walter R. Mebane, Jr. from the Department of Statistics of the
University of Michigan, considering data from the first stage of the 2005
presidential election produces results that "give moderately strong support for a
diagnosis that the 2009 election was affected by significant fraud". The UK-based
think-tank Chatham House also suspected fraud in the voting process for a
number of reasons.
There were many protests came from the groups who oppose the elected
commit to user
Green Revolution, Green Wave or Sea of Green, reflecting presidential candidate
Mousavi's campaign color, and also Persian Awakening. The events have also
been nicknamed the "Twitter Revolution" because of the protesters' reliance on
Twitter and other social-networking Internet sites to communicate with each
other. Islamic politician Ata'ollah Mohajerani blasted the election as "the end of
the Islamic Republic". In response to the protests, other groups rallied in Tehran
to support Ahmadinejad.
The crisis reached into the bad condition. Police suppressed both peaceful
demonstrating and rioting using batons, pepper spray, sticks and, in some cases,
firearms. The Iranian government has confirmed the deaths of 36 people during
the protests while unconfirmed reports by supporters of Mousavi allege that there
have been 72 deaths (twice as many) in the three months following the disputed
election. Iranian authorities have closed universities in Tehran, blocked web sites,
blocked cell phone transmissions and text messaging and banned rallies.
(http://en, wikipedia.org/wiki/IranElectionProcess)
D. Speech and News Conference
Communication could not be separated with human life. As social human
being, people communicate with others to express their thoughts and feelings.
People communicate in their own purposes to fulfill their needs. There are many
ways used by the people to communicate with others. When people communicate
to others, they will produce a text as a device to show their ideas or feelings. Text
commit to user
the purpose of communication by real people in actual circumstances (Thomas
Bloor and Meriel Bloor. 2004: 5).
Speech and news conference are two examples of the texts used to
communicate or express one's ideas in social life. They are effective and quick
ways used by the people in order to give information to public. Using speech and
news conference people can also motivate somebody or group of people to do
something.
1. Speech
In general term, speech belongs to the public speaking. It is an act of
process of making speeches in public (Webter's Third New International
Dictioanry). Meanwhile, the Cambridge International Dictionary of English
defines speech as a formal talk given usually to large number of people on a
special occasion. According to Onong Uchjana Effendy in his book of Public
Relation- Suatu Studi Komunikologis-, speech in the small sense is not only an
informative description contains of information or explanation, but also it must be
persuasive.
"Pidato dalam pengertian sempit adalah seni berbicara didepan utnum atau public. Pidato tidak hanya merupakan paparan informatif yang berisi keterangan atau penjelasan, tetapi persuasif, yakni mengandung ajakan atau bujukan sehingga para hadirin tergerak hatinya untuk melaksanaknnya"(Onong Uchjana, 1998:162).
From some definitions above we can see that speech is an activity of talk
commit to user
mass people in order to give information, explain something, and even persuade
someone to do something. In this case, the listeners are supposed to think
continually, feel, and do as the speaker want.
Speech belongs to the formal communication. It is commonly held by a
person who has a high position in the social class. Besides, speech is given or
presented to a special audience in the particular time and place. There are many
examples of speeches in a society such as, inauguration speech, campaign speech,
religion speech, and presidential speech.
Good speech will give good impression for the listeners. Mastering a
good speech will drive a person to reach the good career. Barack Obama has got
the advantages because of his skill in giving speech. His great skill in giving
speech has influenced many people to have political movement and accept his
ideas. Shel Leanne in her book, Say it like Obama, states that Obama could ensure
every one through his speech.
Besides, a person who is able to master in giving speech, he can control
the mass and influence them with his dogma. It shows how great the power of
speech can influence the huge number of people in the world. It is similar with the
Keraf’s statement:
commit to user
2. News conference
A news conference or a press conference is a media event in which
newsmakers invite journalists to hear them speak and, most often, ask questions.
In this event, newsmakers possibly get information in the same time and place
from the speaker. A joint press conference instead is held between two or more
talking sides. It is like with what Emeraldy chatra and Narsullah stated in their
book, 2008, Public Relations: Strategi kehumasan dalam mengahadapi krisis.
"Konferensi pers adalah event yang memungkinkan wartawan secara bersama-sama menerima informasi dari sebuah organisasi" (Emeraldy chatra and Nasrullah. 2008:163)
In a news conference, one or more speakers may make a statement, which
may be followed by questions from reporters. Sometimes only questioning occurs;
sometimes there is a statement with no questions permitted. A media event at
which no statements are made, and no questions are allowed, is called a photo
opportunity. A government may wish to open their proceedings for the media to
witness events, such as the passing of a piece of legislation from the government
in parliament to the senate, via media availability. Television stations and
networks especially value news conferences: because today's TV news programs
air for hours at a time, or even continuously, assignment editors have a steady
appetite for ever-larger quantities of footage.
News conferences are often held by politicians (such as the President of
the United States); by sports teams; by celebrities or film studios; by commercial
commit to user
almost anyone who finds benefit in the free publicity afforded by media coverage.
Some people, including many police chiefs, hold news conferences reluctantly in
order to avoid dealing with reporters individually.
A news conference is often announced by sending an advisory or news
release to assignment editors, preferably well in advance. Sometimes they are held
spontaneously when several reporters gather around a newsmaker.
News conferences can be held just about anywhere, in settings as formal
as the White House room set aside for the purpose or as informal as the street in
front of a crime scene. Hotel conference rooms and courthouses are often used for
news conferences. (http://en,wikipedia.org/wiki/NewsConference)
E. Systemic Functional Grammar
Systemic Functional Grammar (SFG) is a model of grammar developed
by Michael Halliday in the 1960s. It is a study of linguistics which focuses on the
discourse analysis. This study emphasizes meaning as the fundamental aspect in
analyzing language. As stated by Halliday that a language is interpreted as a
system of meanings, accompanied by forms through which the meanings can be
realized (1994: xiv). This opinion is also supported by Martin who believes
functional linguistics has a conceptualization of language as a resource of
meaning (1992:3).
It is related to the name of this study that SFG carries two concepts:
systemic and functional. The term "systemic" derives from the basic of the
commit to user
interrelated sets of options for making meaning. It can also be said that SFG is a
theory of choice of meaning. Meanwhile the term "functional" indicates that the
approach is concerned with the contextualized, practical uses to which language is
put. It means that this study concerns in the way language is used rather than is
formed. Language, either said or written, has evolved to satisfy human needs.
That is why SFG is opposite to formal grammar, which focuses on compositional
semantics, syntax and word classes such as nouns and verbs. In other words, SFG
is study of language based on the function in context rather than the formal one
(Halliday, 1993: xiii).
Systemic functional grammar presents a view of language in terms of
lexicogrammar approach; a term that embraces the idea that vocabulary (lexis) is
inextricably linked to grammatical choice. It involves the idea that language
consists of a set of system, which offer the speaker (or writer) an unlimited choice
of ways of creating meanings (Thomas Bloor and Meriel Bloor.2004:3). It means
that it is concerned primarily with the choices the grammar makes available to
speakers and writers. These choices relate speakers and writers intentions to the
concrete forms of a language. Traditionally the "choices" are viewed in terms of
either the content or the structure of the language used.
F. Text and Context
It has been stated that SFG or SFL focuses on the discourse analysis. It
examines the meanings which occur in text produced by the people. Text is used
commit to user
language, text carries out the social function of social process in the society. Thus,
text always represents norms and values where the text is produced. As Halliday
stated, text is semantic unit, not the grammatical one like clause or sentence
(1994: xvii). Text is a result of choice of meaning since it consists of meaning
represented in the communicable form. The term of text here is not only written
text in the small sense, but also spoken text. The term text is used in linguistics to
refers to any passage, spoken or written, of whatever length, that does form a
unified whole (Halliday and Hasan 1976).
A text can be observed from two points of view. Firstly, text can be
observed as a process. In this case, text is a process of social interaction and
activity among the participants in expressing the social function. Secondly, text
can be observed as a product. Thus, text can be recorded, saved, and released for
other social processes (Santosa, 2003:18).
Text which is produced by the people could not be separated from the
context. Whenever and wherever the text is produced by the people, it always
deals with its context as a unified device in expressing social function and
meaning. Language as a text always occurs in two contexts. Those are context of
culture and context of situation. Context of culture can be norms and values in the
society where the text is produced. Meanwhile, context of situation is a term
covering all the things going on in the world outside the text. It can be analyzed
through three conceptual frameworks: field, tenor and mode (Martin and
Rose.2003:243). The relationship of language as text in its context can be seen as
commit to user
Figure 2.1: language as the realization of social context
Social context:
1. Context of situation:
Field, Tenor, Mode
2. Context of culture
(Adapted from Santosa, 2010)
Field refers to what is happening, to the nature of the social action that is
taking place: what is that the participants are engaged in, in which language
figures as some essential component (Halliday & Hasan 1985: 12). It can be said
that field tends to describe when, where, why and how it happens. Field represents
ideational function in the metafunctions system.
Tenor refers to who is taking part, to the nature of the participant, the
status and their roles: what kind of role relationship obtain, including permanent
and temporary relationships of one or another, both types of speech roles they take
on in the dialogue and the whole cluster of social significant relationships in
which they involved (Halliday & Hasan 1985 : 12). Martin also defines tenor as
the negotiation of relationships among its participants (1992: 523). In the system
of metafunction, interpersonal meaning is represented by tenor.
Mode refers to what part language is playing, what it is that the Social context
commit to user
participants are expecting language to do for them in the situation: the symbolic
organization of the text, the status that it has, and its function in the context
(Halliday & Hasan 1985:12). Mode also involves two components; channel and
medium. Chanel concerns how the language is used in a text whether in spoken or
written text. Medium means the medium used to express the language whether
one-way or two-way communication (ibid. 52). Mode represents interpersonal
function in the metafunction system.
Based on the explanation above, we can see that text and context has a
close relation. It can not be separated because text always brings its context in
doing certain jobs to express social function. We will know how language
constructs meaning by connecting text and its context; context of situation and
context of culture.
G. Metafunctions
According to Halliday, functional bases of grammatical phenomena are
divided into three broad areas, they are called metafunctions: ideational,
interpersonal and the textual. These three functions underlie all the use of
language either to understand the environment or to act to the others (1985: xii).
Written and spoken texts can be examined with respect to each of these
metafunctions in register analysis.
Ideational function is meaning derived from language as to construe
reality. It constructs mental picture in the people's mind about the reality what is
going on. Ideational function is divided into experiential meaning and logical
commit to user
world. It is the use of language to reflect the experience of its participants as the
agent who is doing the activities. Logical meaning works above the experiential
meaning. It organizes our reasoning on the basis of our experience. It is used to
understand the relation between participants and its process (Santosa, 2003 : 20).
Ideational function can be analyzed through its lexicogrammar. Some
grammatical units representing ideational meaning are transitivity, group system,
and lexis, including congruency.
Interpersonal function is meaning derived from language to behave
socially (Santosa, 2003: 20). It describes social interaction among its participants.
The participants that conduct in interaction event consist of speaker and listener
who interacts each other in the form of giving something or demanding
something. Halliday called this as the most fundamental type of speech role. He
explained these types of interaction as giving means inviting to receive, while
demanding means inviting to give. The commodities exchanged in interaction
event are: 1. good and services, 2. information (Halliday, 1985: 68).
Textual function means we act semiotically to construe reality and behave
socially (Santosa, 2003: 20). It deals with the message delivered by the text by
organizing ideational function and interpersonal function in coherent. Halliday
explained that textual function can be analyzed through theme-rheme system.
Theme is the element which becomes the point of departure of the message. It
represents about what the clause is concerned. Meanwhile, rheme is the rest of the
message which the theme is developed. A clause consists of theme-rherne which
commit to user
Those three systems of function in the metafunctions are closely
connected to its context of situation. They reveal three conceptual frameworks of
context of situation. Filed is represented through ideational meaning, tenor is
represented through interpersonal meaning, and mode is represented through
textual meaning (Halliday and Hasan, 1985: 34)
H. Ideational Meaning
It has been stated that ideational meaning is meaning derived from the
language as to construe the reality (Santosa, 2003: 20). It is the use of language
which represents the experience of the participants. Halliday also states that
ideational meaning is a mental picture of reality, to make sense of people's
experience of what goes around them and inside them (Halliday and Hasan, 1985:
106).
Basically, there are three basic concepts realized in ideational meaning.
First, it talks about the processes in the reality. It describes about the actions,
happenings, feelings, situations and so on. Second, ideational meaning describes
the participant involved in those processes. The participants can be human being
or things. The last, ideational meaning also talk about circumstances which
accompany the happenings including time, place, manner, and so on (Halliday,
1994: 106). We can conclude from the statements above that ideational meaning
tells about what the process happen in the social events, the participants who are
involved in the happenings and the circumstances which exist when the events
commit to user
As stated before, ideational meaning is divided into experiential meaning
and logical meaning. Experiential meaning represents the experience of the
participant in the social events. Meanwhile, logical meaning concerns with the
relation among its participant and its process. It is the logical connection between
one experience to others in the reality. At clause rank, experiential meaning is
represented by transitivity. Then the experiences revealed by experiential meaning
are connected each other by logical meaning. It shows the relationship among the
processes and the participants. Logical meaning itself can be analyzed through
clause system and group system.
I. Transitivity
It has been stated before that experiential meaning can be represented by
transitivity system. Halliday stated that the transitivity system construes the world
experience into a manageable set of process types (Halliday, 1994: 106). It means
that transitivity system construes the experiences of the participants and what is
going on in that time through the types of the processes happen in the social
events. In expressing the experiences and the happening, in principle, there are
three components used in the transitivity system. Those three components are:
a. The process itself
b. The participants in the process
c. The circumstances accompanying with the process
The existence of the process has a close relationship to the participant.
commit to user
Meanwhile, the circumstance is a conditional aspect which follows the two
components above. It can be needed or not depending on the situation of the social
events. In the transitivity system, the process of happening is the central point.
The process itself is realized by verbal group. Meanwhile, the others components;
the participant is realized by nominal group and the circumstance is realized by
adverbial group. The concepts of process, participant and circumstance are
semantic categories which explain in the most general way how phenomena of the
real world are represented as linguistic structures.
1. Process and its participants
According to Halliday, there is a basic difference to explain experiences
represented by the process. He explained that there are two main experiences.
They are outer experience and inner experience. The outer experience is what we
experience as going on out there, in the world around us. It is about the actions
and events: things happen; participants do things, or make them happen.
Meanwhile, the inner experience is what we experience as going on inside
ourselves, in the world of consciousness and imagination. It is a kind of replay of
the outer experience, recording it, reacting to it, and partly a separate awareness of
our states of being. It can be said that the outer experience is the process of the
external world; meanwhile the inner experience is the process of consciousness.
The grammatical categories are those of material process and mental process
(Halliday, 1994: 107).
commit to user
material process and mental process, must be added another component in order to
make it coherent. In this case, relational process is the third component to relate
one fragment of experience to another. Finally, there are three main processes in
the transitivity system. Those are mental process, material process and relational
process. But there are other types of processes might be found in transitivity
system. The other types of process are behavioral process, verbal process, and
existential process. Behavioral process occurs on the borderline between material
and mental process. On the borderline of mental and relational process is verbal
process. The last one is existential process on the borderline between the relational
and material process (Halliday, 1994: 106).
1) Material process
Material process is a process of physical action and happening. It realizes
what is going on and what the participants do. As stated by Martin that material
covers both concrete and abstract processes realize in the happenings and doings.
He also states that concrete material process has also come to serve as a model for
construing experience of change in abstract phenomenon (1997:103). Material
process involves some participants. Those participants are:
a. Actor : it is participant who or which does something.
b. Goal : it is a participant that suffers or undergoes the process. It is also
affected by the event.
c. Range : it is the expansion of process or scope of process.
d. Beneficiary : it is a participant benefiting from the process. It is split into client
commit to user
services, while recipient is participant who or which receives the
goal.
The examples of material process are such as below:
a) Material process in active
Garry repairs the car
Actor Process: material Goal
b) Material process in passive
The car is repaired by Garry Goal Process: material Actor
c) Material process with recipient
My father gives me a motorcycle
Actor Process: material Recipient Goal
d) Material process with client
She bought her a new t-shirt
Actor Process: material Client Goal
e) Material process with range
John
Mary
Plays
cleans
the drum (extension of process) the
room (scope of process)
Actor Process: Range
2) Mental Process
Mental process is a process of sensing. It is like with the Halliday's
commit to user
three basic frameworks of the mental process above can be put into general terms:
(1) perception, (2) affection, (3) cognition (Op.Cit, 118). Perception relates to the
process of sense such as, seeing, hearing, tasting and smelling. Affection is a
process that relates to the feeling like loving, fearing and liking. Meanwhile
cognition deals with the cognitive activities such as thinking, assuming, and
understanding.
In the mental process, senser and phenomenon are the participants. In this
case, Halliday states that there is always one participant (senser) who is human
that is one who senses. Meanwhile, phenomenon is a participant which is felt,
thought and seen. The phenomena itself is divided into three types. They are
micro phenomenon which consists of a thing, macro phenomenon which consists
of a thing and embedded process, and meta-phenomenon which deals with an
idea.
Jane loves
saw
wondered
her husband (micro)
her child eating the cake (macro)
why he did not come to the party (meta) Senser Process: mental Phenomenon
3) Relational process
According to Halliday, relational process is a process of being. The term
being itself is not 'being' in the sense of existing. It refers to something is being
said to 'be' something else. It can be said that a relation is being set up between
two separate entities. It can be done by giving attribute or assessment. Thus,
commit to user
identifying relational process.
a) Attributive relational process (ARP)
Halliday stated that in the attributive mode, an entity has some
quality ascribed or attributed to it. From this statement we can conclude
that attributive relational process (ARP) is a process which relates
participants by giving attribute to something else. The participants in the
attributive relational process are carrier and attribute. Carrier is a
participant given attribute or a thing which bears the attribute.
Meanwhile, attribute can be participant realized in noun phrase or
identifying feature realized in adjective adverbial. ARP occurs in active
form. Thus, attributive relational process (ARP) is not reversible.
He
Marry
is
becomes
smart
a teacher
Carrier Process: ARP Attribute
b) Identifying relational process (IRP)
Identifying relational process (IRP) is a process that relates one
participant and other participants by giving assessment (Ibid. 84). In
identifying mode, something has an identity assigned to it. It means that
one entity is being used to identify another (Halliday, 1994: 122). The
participants of IRP are token and value. Token is the subject in active
clause, while value is the subject in the passive clause. Since IRP is
reversible, token and value can be exchanged. There are some verbs
commit to user
Marry is my sister
Token Process: IRP Value
My sister is marry
Value Process: IRP Token
4) Behavioral process
According to Halliday, behavioral process is a process of physiological
and psychological behavior. This process lies between material process and
mental process. It is partly like material process and partly like mental process.
This process is split into two processes; verbal behavior process and mental
behavior process.
a) Verbal behavioral process
Verbal behavioral process is a process using verbal activity in doing
the action. The participants of verbal behavioral process are behaver,
receiver and verbiage. Behaver is the participant who does the process,
receiver is the participant to whom the saying from behaver is directed
and verbiage refers to what is said by behaver. Verbal behavioral process
may include verbs such as: talk, speak, call, discuss, abuse, flatter and so
on.
Marry talked to her about their new shoes
Behaver Process: VBP Reciever Verbiage
b) Mental behavioral process
commit to user
in doing action. There are two participants in this process. They are
behaver and phenomenon. Behaver is a participant who does mental
behavioral activities such as thinks and feels something, while
phenomenon refers to something suffers the process. This process may
include some verbs such a look at, survey, smile, cry, memorize, mediate
and so on.
He is watching television
Behaver Process: MBP phenomenon
5) Verbal process
Verbal process is a purely process of saying and it does not involve any
action (Santosa, 2003:81). It lies between mental process and material process.
The participants of verbal behavioral process are sayer, receiver and verbiage.
Sayer is a participants who or which says something, receiver is a participant who
receives what is said, while verbiage refers to what is said by the sayer. In this
case, Halliday also states that verbal process is different from mental process. It is
unlike mental processes, verbal processes do not require a conscious participant.
The sayer is not only human, but also things which can put out a signal (Halliday,
1994: 140). Some verbs realizing this process are ask, tell, say, etc.
I tell her a story
Sayer Process; Verbal Process Reciever Verbiage
6) Existential process
commit to user
something exists or happens (Halliday, 1994: 142). It lies between relational
process and material process. There is only one participant involved in this
process. It is existent as the participant and that is the object or event which is
being said to exist.
Existential process can be seen by the clause started with "there is/are..."
or the verb "exist". The word "there", in this case, has no representational function
or meaning like "there" for "direction or places" as the meaning. But, the word
"there" is needed as a subject in English clause, because English clause
grammatically must need a subject.
There is a new car in the parking area
Proc: existent Existent Circumtance
2. Circumstance
Circumstance is one of three elements exist in the transitivity system. It is
physical and non physical process environment covering the process (Santosa,
2003:87). Halliday also states that circumstance is associated 'with' or 'attendant'
on the processes. It refers to examples such as the location of an event in time or
space, its manner, or its cause: and these notions of when, where, how and why
the thing happens (Halliday, 1994:3 50).
Circumstance is realized by adverbial phrase. There are eight types of
circumstances: extent, location, manner, cause, accompaniment, role, matter and
angle.
1) Circumstance of extent
commit to user
terms of some unit of measurement. The interrogative forms for extent are How
far? How long? How many? How many times? It occurs either with or without
preposition (Halliday, 1994:152).
I have been walking for an hours
Circum: extent
2) Circumstance of location
This circumstance expresses the location of a process which can be
defined in terms of time and place. Circumstance of location-time can be realized
by hours, days, weeks, months etc. While circumstance of-location place is split
into three: place, space, and direction including passage, source, and destination.
Location circumstantial is used to answer the question of where? and when?
I have breakfast this morning
Circ: loc: time
I'm swimming in the swimming pool
Circ: loc: place
3) Circumstance of manner
According to Halliday, circumstance of manner is split into three
subcategories: means, quality, and comparison,
a) Manner: means
This circumstance refers to the means whereby a process takes
place. It is typically expressed by a prepositional phrase with the
commit to user
(Halliday, 1994:154).
I go to school on foot
Circ: manner: means
b) Manner: quality
It refers to the circumstance which is expressed by an adverb group,
with–ly, and adverb as head. It also characterizes the process in respect of
any variable that makes sense. The interrogative form for this
circumstance is how? (Halliday, 1994:154).
She walked silently
Circ: manner: quality
c) Manner: comparison
It is a circumstance that shows comparison its participants and
among its process. It is typically expressed by a prepositional phrase like
or unlike or an adverbial group of similarity or difference. It can be
checked using the interrogative for of what like?
He screamed loudly like thunder
Circ: manner: comparison
4) Circumstance of cause
This circumstance comprises into five sub-categories: reason, purpose,
condition, concession and behalf.
a) Cause: reason
commit to user
place. In other words, it is about what causes the process. This
circumstance is typically expressed by a prepositional phrase with
through or a complex preposition such as because of, thanks to, also the
negative form want of (Halliday, 1994: 155).
He did not go to school because of the rain
Circ: cause: reason
b) Cause: purpose
It represents the purpose for which an action takes places. It can be
said that it is about the intention behind the process. It is typically
expressed by a prepositional phrase with for or with a complex
preposition such as in the hope of, for the purpose of. The interrogative is
who for? (Halliday, 1994: 155)
I go home for having launch
Circ: cause: Purpose
c) Cause: condition
It is a circumstance realized in the text in order to give condition to
its process. It is expressed by in case of, in the event of. The interrogative
form is what if.
In case of raining I should wear my coat
Circ: cause: condition
d) Cause: concession
commit to user
It is expressed by some prepositional phrase such as in spite of, and
despite of.
The son is popular in spite of its simplicity
Circ: cause: concession
e) Cause: behalf
According to Halliday, this circumstance represents the entity,
typically a person, on whose behalf or for whose sake the action is
undertaken. It can be said that it is about who the process is for. It is
typically expressed by a prepositional phrase with for or with complex
preposition such as on behalf, for the sake of etc.
I advice you for the sake of your child
Circ: cause: behalf
5) Circumstance of accompaniment
According to Halliday, circumstance of accompaniment is the
circumstance which accompanies its participants in a process. It represents the
meaning 'and 'or 'not' as circumstantial. It is typically expressed by prepositional
phrase with prepositions such as with, without, besides, instead of etc.
The dog likes instead of meat
Circ: accompaniment
6) Circumstance of role
Role circumstantial shows the role done by the participant in a process.