STUDENTS’ ABILITY IN CONSTRUCTING READING
QUESTION ITEMS IN CRITICAL READING CLASS
THESIS
Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the degree of
Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd) in Teaching English
By:
Risalatil Umami D35209030
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF EDUCATION AND TEACHER TRAINING
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY OF SUNAN AMPEL
SURABAYA
ABSTRACT
Umami, Risalatil. 2016. Students’ Ability in Constructing Reading Question items
in Critical Reading Class.A Thesis. English Education Department, Faculty of
Education and Teacher Training, State Islamic University of SunanAmpel Surabaya. Advisor: Rakhmawati, M.Pd
Key Terms: Students’ ability, constructing question, critical reading, bloom
taxonomy
This research was conducted to know students’ ability in constructing reading
question items based on cognitive level of bloom taxonomy’s perspective and their difficulties in constructing the questions. This research use descriptive qualitative method. The subject of the research are twenty five students of critical reading class academic year 2015-2016 faculty of education and teachers training UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya. The test and questionnaire were used as the instrument of this research. The test was used to obtain the data about the
students’ ability in constructing reading question items based on cognitive level of
bloom taxonomy’s perspective. Furthermore, the questionnaire was used to obtain the data about students’ difficulties in constructing question items. The finding shows that the students’ ability in constructing reading question items based on
cognitive level of bloom taxonomy’s perspective are fair. In low-thinking level of bloom taxonomy; remembering 11,38% question of the students in this level, 15,44% students question in understanding level, and 22,76% students’ question in applying level. Therefore, in high-level thinking of bloom taxonomy’s
perspective; 29,26% students’ question were in analyzing level, 18,69% students’
question were in evaluating level, and only 2,34% students’ question were in creating level. It means still there are students in low-thinking level. Whereas,
most of the students’ difficulties in constructing question are on grammar
terms.Based on the data finding in this research, some suggestions are given to the lecture, especially for the lecture who teaches in critical reading class to increase
the students’ ability in critical thinking. And for the students especially for university’s students to increase their ability to think critically, because they are a university’s students, they must have a critical thinking. It is also suggestion for the next researcher to conduct such this research from internal and external aspect
TABLE OF CONTENT
Page
TITLE SHEET………... i
ADVISOR APROVAL SHEET ………..………. ii
APPROVAL SHEET ……… iii
ABSTRACT ……….… viii
PERNYATAAN KEASLIAN ………. ix
TABLE OF CONTENT ……….……... x
LIST OF CHART …..………... xii
LIST OF TABLE ………. xiii
LIST OF APPENDICES ……….. xiv
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Study ……….………...…….. 1
B. Research Question ……….………...… 8
C. Objective of the Study ……….………. 8
D. Significance of the Study ……….……… 9
E. Scope and Limitation ……… 9
F. Definition of the Key Terms ……… 9
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Theoretical Foundation 1. Definition of Reading ………....………. 12
2. The Importance of Reading ……… 13
3. Reading Comprehension ………...………. 15
4. Reading Comprehension Question ………..………... 16
5. The Difficulties in constructing question....….…...………. 21
6. Bloom Taxonomy ………..……… 23
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHOD
A. Research Design ………37
B. Research Subject ………... 39
C. Source of Data ………...39
D. Research Procedure ………... 40
E. Data Collection Technique ……….….. 41
F. Research Instruments ……… 43
G. Data Analysis Technique ………... 44
CHAPTER IV: FINDING AND DISCUSSION A. Research Finding ……….. 46
B. Discussion ……….…… 55
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A. Conclusion ……… 64
B. Suggestion ……… 65 REFERENCES
LIST OF CHART
LIST OF TABLE
Table 2.1: Cue question of bloom taxonomy ……… 31
Table 4.1: Table 4.1: The result of students’ question on remembering level……... 49
Table 4.2: The result of students’ question on understanding level……….. 50
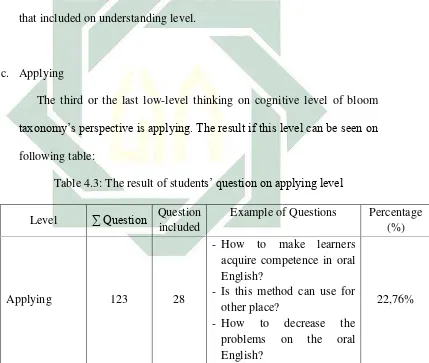
Table 4.3: The result of students’ question on applying level ……….…. 51
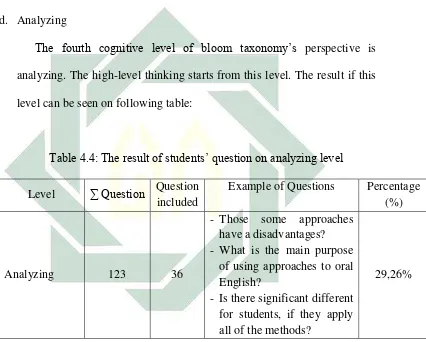
Table 4.4: The result of students’ question on analyzing level ……….. 51
Table 4.5: The result of students’ question on evaluating level ………... 52
Table 4.6: The result of students’ question on creating level ………... 53
LIST OF APPENDIX
Appendix 1: Text as Assessment (test) “Methods to Oral Practice” Appendix 2: Form of students’ constructing question items
Appendix 3: Questionnaire
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter provides the background of the study, the research question, the objective of the study, significance of the study to let the reader recognize about the value of the study, scope and limitation, and definition of the key terms.
A. Background of the Study
Reading is one of language skills that cannot be separated from other language skills because the students‟ ability in one aspect will support their ability
in mastering the others. It is an important educational goal, because without reading, other language skills would not be improved. The ability of students in reading is important because by having the ability of reading, they will be able to improve general language skills in English; reading can enlarge the students‟
English vocabulary and it can help students to improve their writing or speaking abilities. It can be concluded that reading is one of the keys to success for everyone who wants to be an educated person.
According to Nation, Reading is a source of learning and source of enjoyment.1It means that reading can enlarge the students‟ knowledge. As a source of learning, reading can recall the vocabulary and grammar that already
1
2
learned. It can help the students to learn new vocabulary and grammar and through success in language use. Reading can be source of enjoyment. If the students gain skill and fluency in reading, their enjoyment can increase.
In each stage and the process of learning, asking activity always used. Question is one of the stimuli to think it good for student in learning process. Based on Nurhadi in Bounty, question is the parent of contextual learning strategy, the beginning of knowledge, the heart of knowledge, and an important aspect of learning.2Question is one of the main activities in the learning of reading in English class. When students more active to create questions and understand the spirit of learning they will be motivated and increased. Based on the level of education, university students are expected to be able to think highly and critically.
One of the important capabilities mastered by students is the ability to think critically for higher-level thinking. It is one of the stages of thinking that cannot be separated from everyday life. Every student is directed to have a higher-order thinking because the ability to think critically make someone has critical thinking. Critical thinking is important to gain the information which was gotten, to have better chances and to life with the society. It is like Robinson`s opinion, if students are perform in a highly technical society, they must be prepared with life-long learning and critical thinking skills is necessary to obtain and process
2
3
information in an ever-changing world.3When someone thought about something which wants to be done, the person needs to decide whether the thing is appropriate or not. To do this well, the person had to have a good ability in critical thinking.
Critical thinking plays an important role in language education. Wallace stated that critical thinking skills should be embedded in the subject matter and woven into language education.4Since language is an important tool for acquiring knowledge, therefore it is important to acquire the critical thinking ability of the students and its possible link to their language proficiency.
The English learners can measure their ability to think critically through reading, especially in understanding the texts which are read. When they read a text, they can think about the concept, see the value from many points of view, able to make a logical conclusion, and link their ideas with the text they read. By doing these activities, the students are able to measure their ability to think critically through reading. As Nodoushan‟s statement that measuring students` ability to think critically using a test of reading could be justified on the following part. Firsts, many of the critical thinking tests through reading texts with questions related to interpretation, inference, analysis, and evaluation. Second,
3Figen Kanik. Doctoral Dissertation. An Assessment Of Teachers’ Conceptions Of Critical Thinking
And Practices For Critical Thinking Development At Seventh Grade Level. (Middle East Technical University. 2010), 1.
4
C. Wallace. Critical reading in language education. (Palgrave Macmillan. 2005) accessed on 15thJune
4
there were high correlations between tests of critical thinking skills and the reading text. It was showed by studies in both United States and the Middle East.5
Critical thinking gives much contribution to the successful of someone`s reading, especially in reading class. In thinking process, this is proposed toengage students when talking about text they read. This activity leads the studentsto be critical. By having this ability, the students will able to answer the questions of reading test, give evidences, facts, or proof to make a convince answer and elaborate information of the text with their own ideas.
In education department, especially in English Teacher Education Department of Faculty of Education and Teacher Training of State Islamic University Sunan Ampel Surabaya, have to high critical thinking is important for candidates of the teacher to be a creative, professional and active teacher. Without having this ability the students will not be able to show their view and their well-constructed argument. As Judge, Jones and McCreery say that if the students are able to confront others‟ ideas in this way it enables the students to construct their
own judgments, which in turn enhances their self-confidence in exploring any evidence or literature and its implications.6
Critical thinking is also important for shaping creative candidates of English teachers. The students need to think critically to come up with creative solution to
5Mohammad Ali Salmani Nodoushan. International Journal of Language Studies (IJLS) – volume
8(2). (Massachusetts: EBSCO Publishing, Inc. 2014), 124. 6
5
a problem. It must also be the circumstance that the new ideas being produced are useful and relevant to the task at hand. Critical thinking plays a central role in evaluating new ideas, selecting the best and adapting them if necessary.
Regardless the major, in fact, critical thinking plays an important role inshaping the students` creativity. In this case, the candidates of English Teacher inState Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya must have ability to thinkcritically. It cannot be imagined that a candidate of teacher are unable think critically. It means that the candidate is unable to construct the argument well, to create creative teaching instruments, and to teach the students well. Critical thinking improves language, writing and presentation skills. Thinking clearly and systematically can enhance the way expressing ideas. In learning how to analyze the logical structure of writings, critical thinking also enhances comprehension abilities. Without knowing the ability to think critically, the candidates of teacher will never know whether they are able to construct the argument well or not.
Beside think critically university students‟ must have high-level thinking.
6
based on that some type of learning requires a process of cognition more than the others, but has a more general benefits. In Bloom's Taxonomy revision involves the analysis (C4), evaluating (C5) and creates (C6) are considered high-level thinking.
Taxonomy is useful as a tool to ensure accuracy in communication with regard to organizing and interrelation, in this case the taxonomy of educational objective. Some models include taxonomy of educational objective in the cognitive aspects of taxonomy refers to bloom. Bloom divides the learning achievement of students in the cognitive domain into six levels, which is given to remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating.7
Related with this research, there was similar research which had straight relationship with this research; first, the research which has been done by Istiharoh entitled “Students‟ Ability to Think Critically in Critical Reading Class
at English Teacher Education Department UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya”. Here, Istiharoh measure the students‟ ability in critical thinking from internal and
external aspect.8Second previous research was taken by Fahmi Qudratullah entitled “Penerapan Pembelajaran Berbasis Masalah Mengacu Pada Taksonomi Bloom untuk Melatih Kemampuan Berpikir Tingkat Tinggi Siswa”. That research describes the teacher‟s step in implementing problem-based learning refers to
7
Bloom, Benyamin S. 1979.Taksonomy of Educational Objectives (The Classification of Educational Goals) Handbook I Cognitive Domain.London: Longman Group Ltd.
8
7
bloom taxonomy to train high-level capabilities of students.9 Then, related with this research, although the object is similar, university students. The researcher here is focusing on students‟ ability to constructing reading question item in English Education Department and students‟ ability in that question made based
on cognitive level of bloom taxonomy perspective.
This research was conducted at Sunan Ampel State Islamic University Surabaya. There are some underlying points that the researcher does the research in this university. According to the data from preliminary study that the average of the students‟ score of critical reading test is 13,17 in which the highest level is 32. It means that the students‟ ability is low because it is under 50% of the highest
level of score. Whereas in education department, especially in English Teacher Education Department of Faculty of Education and Teacher Training of state Islamic University Sunan Ampel Surabaya, have to high critical thinking is important for candidate of the teacher to be a creative, professional, and active teacher. Because they are will to construct the argument well, to create creative teaching instruments, and to teach students well.
In this case the researcher was evaluated how is preparation of the 6th semester student in the Faculty of Education and Teachers Training UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya in constructing reading question items which they prepared as an educator that will bring success or failure of their students in their lessons. The
9
8
researcher used cognitive level of bloom taxonomy perspective to evaluate their reading question.
B. Research Question
Based on the statement above, the research question of the study are:
1. How students‟ ability in constructing reading question items based on cognitive level of bloom taxonomy‟s perspective?
2. What are the students‟ difficulties in constructing reading question items?
C. Objective of the Study
This research is conducted to find out the students` ability in constructing reading question items in critical reading class at English Teacher Education Department of Faculty of Education and Teacher Training of State Islamic University Sunan Ampel Surabaya 2016.Based on statement of research problem, the study is aimed:
1. To know whether the students‟ constructing reading question is in high-level thinking or not.
9
D. Significance of the Study
Researcher expects this research will give some benefits, at least such below: 1. Lecturers
a. The result of this research can be used by the lecturers to find the best way to teach critical thinking in critical reading class.
b. The lecturer can increase the students‟ ability in critical thinking 2. The students can measure their ability in critical thinking whether their
ability is high, fair or low.
E. Scope and Limitation
Based on focus of this study, there are two scopes of this research. Those are cognitive level of bloom taxonomy perspective and critical reading class.This research is limited to the sixth semester class D of critical reading students in faculty of education and teachers training UIN Sunan Ampel Jl. A. Yani Surabaya.
F. Definition of the Key Terms
10
1. Ability
Thurstone said which was quoted by Tapsfield in his book defined ability is best understood.10 Tucker stated that the word ability refers to the capabilities of human nature. It can either be moral or immoral abilities. The ability to perform immorally derives from the physical abilities, but the decision to do so clearly issues from minds.11
In this research the term `ability` means that maximal performance of students when they think critically in reading class.
2. Critical Reading Class
Critical reading is an analytic activity. The reader rereads a text to identify patterns of elements -- information, values, assumptions, and language usage-- throughout the discussion. These elements are tied together in an interpretation, an assertion of an underlying meaning of the text as a whole.12
Critical reading class in this research is the last level of reading class in English teacher education department. Students have to take this lecture in sixth semester.
10
Ian Dennis - Patrick Tapsfield (Ed.) Human Abilities, Their Nature and Measurement.(United States of America: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. 1996), 200.
11
John Allen Tucker. ItōJinsai'sGomōJigi and the Philosophical Definition of Early Modern Japan.(Brill, 1998), 153.
12
11
3. Bloom Taxonomy
Benjamin Bloom developed a classification of levels of intellectual behavior in learning. This taxonomy contained three overlapping domains: the cognitive, psychomotor, and affective.13
This research is focus on bloom taxonomy. It is categorization or classification purposes for education in the cognitive domain. That emphasizes the intellectual aspect consists of six levels. That is remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating.
13
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
In a research, it is important to describe the theories related to the problems of this study, which are used as foundation and reference in order to give relevant knowledge in the field.
A. Theoretical Foundation
1. Definition of Reading
There are some definitions about reading. Menyan and Leeuw as quoted by Zainudin that reading is a digestive process and it has two principles, they are learning by understanding, which means selecting, discriminating and organizing.1The second principle is flexibility. It must take time to read slowly when the meaning of word is difficult. Reading is one of four skills in English that the students should acquire. Nunan stated that ―reading is a process of readers combining information from text
and their own background to build meaning.2 This means that the readers should combine their knowledge and what the information they read. It is very important skill that the students need for the success of their studies.
1
Zainuddin, The Use of Group Work in Teaching Reading for the First Year Students of MAN Pamekasan, (English Departement, IAIN sunanAmpel, 2009),9
2
13
Reading is an interaction between the reader and the writer, Albert said that the text provides information that author wants the reader to understand in certain ways.3 It means that the writer hopes that the reader can understand the information provided in the text.
2. The Importance of Reading
Reading is one of the most important skills in learning language besides listening, speaking, and writing. According to Damian, reading is an activity that involves greater level concentration and gives conversational skill to reader.4It acquired a lot of knowledge. Besides, reading can improve students‟ attention span and comprehension. In general, there are two reasons why reading is important in daily life: a. Reading will help to achieve some clear aim or information.5It means
that reading is one of the ways to get information.
b. Reading is needed for career, to study purposes, or simply for pleasure.6 Teacher or students reads a book to improve their knowledge and people read comic, magazine, or novel for pleasure.
3
Harris Albert J. 1962. Effective Teaching of Reading, (New York: David McKay Company),35
4
Damiansofsian.http://ezinearticles.com/?the-importance-of-reading&id.(accessed on September 15th 2014)
5
As cited in thesis of Ainy (Surabaya: IAIN SunanAmpel) ,14
6
14
For language teaching, reading is useful to know language acquisition.7It also can help to improve students‟ English ability. Brown said that reading competence is important because it underlines success in all areas of study in high school, but it is essential to personal enrichment and development of intelligent citizenship8. It means that increasing the ability of reading indicates a student's success in other subject areas. If their reading is good, others must be good too.
In addition to that Nuttal states that reading can be used to improve their language components.9 It means that by reading, the students may improve their language skill, such as their grammar and vocabulary.
So, reading is important for daily life. By reading we can get pleasure;information and more knowledge. Beside, in language teaching reading is useful for language learning or to develop intelligent of citizenship.
7
ibid
8
Brown, et al. Teaching Secondary Language: Alternative Approach. (Ohio: Newburry House Publishers Inc, 1970.)161
9
involving interaction between readers and what they carry to the text such as knowledge and strategies used in reading and also variables related to the text such as interest and understanding11. Reading comprehension can be defined as how good a student understands text how good the student uses cognitive and metacognitive processes and offer information about the text.12 Klinger also stated that reading comprehension can be defined as the process of constructing meaning by coordinating a number of complex processes that include word reading, word and world knowledge and fluency. It indicates that reading comprehension is not only aboutunderstanding the text but it is about the complex processes that involve interactions between reader and the text he reads dealing with understanding the literal meaning of text, critical thinking about message of text, and appreciation of what the author delivered through the text.13
10
Susan L. Cooledge, Doctoral Dissertation “L2 Reading and Hypertex: A Study of Lexical Glosses and Comprehension among Intermediate Learners of French” (New York: The University of Arizona 2004), 13.
11
Klinger etall.Teaching Reading Comprehension to students with learning difficulties.(New York: The Gullford Press. 2007, 8.
12 Klinger et all. Teaching Reading Comprehension ……… 15 13
16
4. Reading Comprehension Question
1) Comprehension Question
Comprehension question are expected not only to facilitate but also to challenge at least three levels of comprehension: literal, inferential, and evaluative or critical.14
a. Literal comprehension is level of understanding the text wherein a reader has access and can recognize and recall details in the text. It requires recognition and recall of ideas, information and happening explicitly stated in the reading selection.
The example of them are finding date of flight; who is…; what/
where did she/ he…; what happened where or during …; find out
the differences between … and …?
b. Inferential or interpretative comprehension is the level of understanding wherein readers can read meanings which are not directly stated on the texts. This level requires the orchestration and the manipulation of information from the text as well as within the readers.
The question are, for example, how did she converse with …; what was the weather like; do you think …; what will happen
next….;
14
17
c. Evaluative or critical comprehension refers to the understanding of a text which requires readers to use an adequately developed knowledge base and new information including prior knowledge, intuition, and imagination to make hypotheses; to draw conclusion, to make reasonable predictions, connections between conclusion and critical judgments about what texts.
The examples of the questions are what strange ideas did …have?
; Why was … true? ; How do you feel about this character?; what do you think ….‟s attitude?
When questions move beyond a literal understanding, students'
answers have to be motivated by information in the text. Then in inferential
questions the students’ answer can have clearly correct and incorrect
responses or the answers are correct as long as they depend primarily on
students' reactions to what they read. Evaluative or critical answers not only
depend primarily on students' reactions to what they have read, but also they
need to reflect a global understanding of the text.
2) Forms of Questions
Forms of question are the techniques to test the students learning result.15There will be some techniques to test students learning result. The difference of each technique is caused by the purpose of the test. In case of assessing reading, there will be some of
15
18
certain techniques which are able to ease the teacher to test their students. The technique below is proposed from Arthur Hughes‟ book
entitled testing for language teachers and J Charles Aldersons‟ book
entitled assessing reading. a. Multiple Choice
Multiple choices arecommon techniques to test students‟ comprehensions toward the text. Students will answer multiple choice questions by eliminating the distracter by their logical analysis that they have gotten by reading the text.16 For example:
Memorizing is easier when the material to be learned is..
a. In a foreign language
b. Already partly known
c. Unfamiliar but easy
d. Of no special interest
Here, the students will choose an answer based on the choices above.
b. Matching Technique
Here, two sets of question and answer have to be matched against each other.17 Such as matching the vocabulary to their
16
Charles Alderson. Assessing Reading.Cambridge: Cambridge University Press: 2000.
17
19
meaning or matching the heading of the paragraph to their corresponding paragraph, For example:
1. Narrative a. To tell the past experience 2. Procedure b. To tell how to make some thing 3. Recount c.To amuse the readers
They will be intended to match the word on the left to the meaning or explanation in the right.
c. Ordering Task
In ordering task students are given scrambled set of words, sentence, paragraph or text and have to put them into their correct order.18 For example:
A. It was called the last waltz 1. D
B. The street was in total darkness 2. C. Because it was one he and Richard had learnt at school3.
D. Peter looked outside 4.
E. He recognize the tune 5.
F. And it seemed deserted 6.
G. He thought he heard someone whistling 7.
18
20
d. Dichotomous Items
This technique is called true and false technique whereas the students are presented with a statement which is related with the text and decide whether the statement is true or false.19 This test is intended to test the ability of infer meaning. For example:
1. John is the youngest in his family T / F 2. John sister always comes home late T / F
Here the students will decide whether the statement above is true or false based on the text that they have read.
e. Short Answer Test
In this technique students are asked a question which requires a brief response. The short answer technique will work well to test the ability to identify the referents, predict the meaning of unknown words from context, and write items related to the structure of text.20 For example:
What does the word “it” (line 26) refers to? ___________
Which town listed in table 4 has the largest population?____
19
Ibid. 20
21
f. Gap Filling
This technique is particularly useful in testing reading. It can be used to get the students response. Students read the text and in the same time they read the summary of the text whereas some of the keyword has been removed. Their task is to restore and or fill the missing keywords; consequently they have to understand the main ideas of the original text to find the right keywords.21 For example:22
To support his claim that the mafia is taking over Russia, the author points out that the sale of __________ __________ in Moscow has increased by _________ per cent over the last two years.
5. The Difficulties in Constructing Questions
Sam Warib says that most of important point that students are reluctant in constructing questions is because the lacking of grammar, vocabulary, and spelling23. Mastering these components is very important in constructing questions. The following concepts are presented below:
21
Charles Alderson. Assessing Reading.Cambridge: Cambridge University Press: 2000.
22
Arthur Hughes, Testing for Language Teacher. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007.
23
22
a. Vocabulary
Most of the students have problems in writing a question, because they lack of vocabulary. Vocabulary is one element of language skills applied in learning and teaching English. To be able to learn it, the students must understand and master many English word. To apply English skill, vovabulary must be learned by them because it is the target language depends one some one‟s knowledge of
vocabulary in this case, vocabulary is one of other components of skill of a language both spoken and written form. The essence of mastering vocabulary is learning how to determine meaning24. The students also get difficulty in choosing the word that suit to its subject. Sam A Soesanto stated that good writing a question is made of words that suit the subject and the expected audience. Add say, to speak or to write is to choose word. You must choose them consciously; think about the word you use, their shades of meaning and their effect on your readers.25
b. Grammar
In constructing questions, grammar is very important. It means that by mastery grammar, the students can produce the correct
24
Mun.Fika et al. Complete English Grammar.Surabaya: Apollo. 1991
25
23
sentences. As stated the relationship between the mastery of sentence structure and ability in write a question has rhetorical consequences. Sam Warib stated that understanding grammar is an excellent basis for good listening, speaking, reading, and writing26. Particularly, for those whole native language patterns are very much different from English. Good write questions usually have a grasp of grammatical element. Based on the statement above it is very important for the students to master the grammar of English in order to able to construct correct sentence as a basic to the successful in asking questions, without have knowledge about grammar they will not be able to use it, so that, the reader can not catch the points of the message.
6. Bloom Taxonomy
The word Taxonomy comes from the Greek meaning “tassein” it is
mean classify and “nomos” which means rules.27 The meaning of
taxonomy is the classification or grouping which is based on certain characteristics. Meanwhile, according to major Indonesian dictionary taxonomies are rules and principles that include object.28In this case the
PelajaranMatematikamenggunakanTaksonomi Bloom, (Skripsi yang tidakdipublikasikan Surabaya : IAIN SunanAmpel, 2011), h.8
28
24
taxonomy of educational objectives is useful as a tool to ensure accuracy in communication with regard to organizing and interrelation.29
Referred to Bloom's taxonomy is categorization or classification of educational goals the cognitive domain. Namely cognitive behaviors that emphasize the intellectual aspects such as knowledge, understanding, and a person's level thinking skills. In addition there are also cognitive, affective and psychomotor domains. Affective domain includes domains related to attitudes and feelings. While the psychomotor domain associated with the realm of manipulative and physical abilities. However, in this research, the researcher is confined to the cognitive domain.
Bloom‟s cognitive domain comprises six processes which require
learners to demonstrate knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation as learning progress from „lower order‟ to
„higher order‟ thinking.
Bloom's Taxonomy has improved in line with the changing times and technology. LorinW.Anderson and David R. Krathwohlhaverevising the Bloom taxonomy in 1990. The results in improvements published in 2001 under the name of Bloom's taxonomy revision.
Taxonomy changes of nouns (in Bloom's taxonomy) became a verb (in taxonomy revision). This change was made to fit the educational goals.
29
25
Educational purposes indicating that the student will be able to do something (verb) with something (noun). The following image Bloom's taxonomy changes before and after revision:30
In the classification , the revised Bloom's taxonomy of cognitive domains are divided into six categories, namely remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating and creating.
a) Remembering
Remembering is an attempt to regain the knowledge of memory or memory has been exceeded, both newly obtained and that has long earned. Remembering is thedimensions of which play an important role in the learning process meaningful and problem solving. This
30
Anderson, L.W., danKrathwohl, D.R. 2001. A Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching, and Assesing: A
26
capability is used to solve a variety of problems that are much more complex.
Remembering includes recognizing and recalling. Recognize related to knowing the past knowledge pertaining to concrete things, such as date of birth, home address,and age, while recall is a cognitive process that requires knowledge of the past quickly and accurately.
The remembering question is often used during or after reading a passage to encourage learners in the class to recall the content of the passage.31
b) Understanding
Understanding is regard to building an understanding of a variety of sources such as messages, reading and communication. Understandingthat regard to classify activities (classification) and comparing.Classifies will appear when a student tried to identify the knowledge that is a member of a particular knowledge category.
Classifies originated from a specific sample or information subsequently discovered concepts and general principles. Comparing refers to the identification of the similarities and differences of two or
31
27
more objects, events,ideas,problems, or situations. Comparing the cognitive processes related to finding one by the characteristics of the objects being compared.
Critical reading question which requires students to translate the passage are not relevant in the classes since both teacher and learnersuse the target language. However, learners are required to interpret and extrapolate meaning during and after reading.32
c) Applying
Applying refers to cognitive processes utilize or employ a procedure to carry out the experiment or solve problems. Apply related to the dimensions of procedural knowledge. Implement activities include running procedure and implementation.
Implement arise if students choose and use procedures for matters. Students still feel unfamiliar with this, the students need to recognize and understand the problems first and then establish the appropriate procedures to resolve problems. Implements closely related to other dimensions of cognitive processes are understood and creating.33
32
Ibid
33
28
A critical reading teacher will ask application question about the topic before, during and after reading a passage. Questioning before a reading encourages students to anticipate what is possible; questioning during the reading directs learners to focus on the function of the topic; and questioning after the reading directs learners to apply the concepts in a new context.34
d) Analyzing
Analyzing is solving a problem by separating each part of the problem and seeks relevance of each section and find out how these linkages can cause problems. The analyzing is the type of ability that a lot demanded of learning activities in schools. Various subjects require students to have the ability to analyze properly. Demands for students to have the ability to analyze often tend to be more important than the other dimensions of cognitive processes such as evaluating and creating. Most of the learning activities lead students to be able to distinguish between fact and opinion, lead to the conclusion of supporting information.
34
29
In critical reading, analysis questions can be used during and after reading activities to encourage learners to understand the content and the structure of the given passage.35
e) Evaluating
Evaluation includes checking and criticized. Check led to the testing activities of the things that are not consistent or failure of an operation or product. If it is associated with the thought process of the plan and implement the check will lead to the determination of the extent to which a plan is going well. Criticizing is lead to the assessment of a product or operation based on external criteria and standards. Criticizing related to critical thinking. Students are assessed by looking at the negative and positive sides of a thing, and then assessed using this standard.
Evaluation is concerned with the ability to judge the value of material, the solution to a problem or the facts about particular cultures.
Critical reading may use evaluation as a means of focusing on learners‟ personal judgments derived from their existing schemata.36
35
Anderson, L. W. (1999). Rethi ki g Bloo ’s Ta o o : I pli atio s for testi g a d assess e t.
36
30
f) Creating
Creating include generalizing and producing. Generalize the issue and discovery activities represent alternative hypotheses are required. This relates to generalize divergent thinking which the core of creative thinking is. Producing leads to planning to solve the problems given. Producing related to the other dimensions of knowledge that is factual knowledge, conceptual knowledge, procedural knowledge, and met cognition knowledge.37
Creatingis difference with other cognitive dimensions of thinking because on another dimension as to understand, implement, and analyze student work with information that is already known previously, while on creating student work and produce something new.
Creating activities in the critical reading class can include: (a) solving problems which are described in the text; or (b) communicating with the author in the target language.
The following table of cue question based on bloom‟s taxonomy of critical thinking:38
Table 2.1: Table of cue question of Bloom Taxonomy
37
Anderson, L.W., danKrathwohl, D.R. 2001. A Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching, and Assesing: A
Revisio of Bloo ’s Ta o o of Edu atioa lO je tives.New York: Addison Wesley Longman, Inc. Hal. 66
38
31
Lower-Order Thinking Skills Higher-Order Thinking Skills
1. Remembering
What is the definition of ….?
1. Analyzing
What are the parts or features of …? How is ____ related to …?
Why do you think ….? What is the theme ….? What motive is there …?
What conclusions can you draw …? How would you classify …?
How can you identify the different parts …?
What evidence can you find …?
What is the relationship between ….??? How can you make a distinction between
…?
What examples can you find to …? How would you solve ____using what
What approach would you use to …? How would you apply what you
How can you elaborate on the reason …? What alternative can you propose …? How can you invent …?
What way would you design …?
33
B. Previous Study
In this research, it is essential to find review of previous studies to avoid the repetition. Some similar studies had been conducted by some researcher about reading question and bloom taxonomy perspective. The previous study was done by Novianti entitled “AnalisisKemampuanBerpikir
Tingkat TinggiSiswadengan Gaya
BelajarTipeInvestigatifdalamPemecahanMasalahMatematikaKelas VII di
SMP N 10 Kota Jambi”The purpose of this study was to analyze the
high-level thinking skills of students who have the type of investigative learning styles based on Bloom Taxonomy Perspective in solving mathematical problems and to analyze mistakes and barriers experienced by students in solving investigative concept of sets and Venn diagrams in problem solving.39 The result of her research is showed that the first students of type investigative is in very low category at 30%, because the students did not met two indicators of the ability to think critically, that is creating and evaluating. While the second students of type investigative both middle category is 70%, because in these students just one indicator that did not met of the ability to think critically, that is evaluating. It can be concluded that the average percentage of the subjects categorized as having a high level thinking skills learning style investigative type in a category is that with an average of 50 %.
39
34
The second was done by Qudratullah with the title,
“PenerapanPembelajaranBerbasisMasalahMengacuPadaTaksonomi Bloom
untukMelatihKemampuanBerpikir Tingkat TinggiSiswa.”This research is
descriptive research. This research are aims to know the process of implementing problem-basedlearning refers to Bloom‟s Taxonomy to train high thinking skills of students and to determine the ability of high-level thinking students. The conclusion of this research is application process of problem-based learning that refers to Bloom‟s Taxonomy to train the ability to think high level consist of three components. First, implementation class in this research has well. Second, the students‟ activities in participating subject generally have experienced. Third, students‟ response in problem-based learning refers to Bloom‟s Taxonomy to train high-level thinking skills of
students getting less positive response.40
The third is “PengembanganSoalUntukMengukurKemampuanBerpikir Tingkat TinggiPokokBahasanBarisandanDeretBilangan di KelasIXAkselerasi
SMPXaverius Maria Palembang” which has been conducted by Lewy,
Zulkardi, and Aisyah in Mathematics Education Journal First, they tried to develop problems to measure higher order thinking skills with produce valid and practical prototype problemsto measure higher order thinking skills in number sequences and series for acceleration class Grade IX. Second, they
40M. FahmiQudratullah, Skripsi: “
35
tried to see the effects of the problems to measure higher order thinking skills on students‟ achievement in Number Sequence and series was tried out to
students.41 The results of analysis are: First, problems prototype which is developed has been valid and practical. Second, based on developing process can be obtained that problems which is developed contains potential effect to higher order thinking skills of Accelerations Class Grade IX of SMPXaverius Maria Palembang shown by written test result score 35.59. It means that students‟ thinking skill is good category. The final conclusion of this research
is the problem which is developed can be used to measure high order thinking skills in Number Sequence and Series.
The latest research was done by Fadhilah in 2015 with the research entitled “Student Teachers’ Ability in Designing Assessment Instrument at
English Teacher Education Department UIN SunanAmpel.” Here, the
researcher focused on analyzing student‟s teachers‟ assessment instrument based on the requirement of standardization assessment and identifying the causing factor that make student teacher unable to fulfill the assessment requirement. The conclusion of the research is some of student teachers could not meet the indicators, still their assessment is categorized as good
41
Lewy, Zulkardi, NyimasAisyah. JurnalPendidikanMatematika:
“PengembanganSoalUntukMengukurKemampuanBerpikir Tingkat
TinggiPokokBahasanBarisandanDeretBilangan di KelasIXAkselerasi SMPXaverius Maria
36
assessment. It means that they are able to design the assessment based on standardization.42
Considering those previous studies, this research was different. The difference of those previous studies are that this research focus on students‟ ability to constructing reading question item in English Education Department and students ability in that question made based on cognitive level of bloom taxonomy perspective. While the previous studies focus on development problem or question to measure high-level thinking students‟ skill and the object of the research are teacher and question it.
42
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHOD
In this chapter, the researcher describe the research design which would be used in this study, research subject, source of data, research procedure, data collection technique, research instrument, and data analysis technique. To make them clear, the researcher elaborated them one by one in the following part of this thesis.
A. Research Design
According to Creswell, Research is a process of steps used to collect and analyze information to increase our understanding of a topic or issue.1 In this research, the researcher choose qualitative design by using descriptive approach since the purpose of this study is to understand and describe the phenomenon that happens to the subject being observed in natural contexts. This descriptive study is used to gain certain information about a certain phenomenon that happens when this study is conducted.2 Moreover, this study is designed to obtain information and description concerning to the
students’ ability in constructing reading question items from cognitive level of
bloom taxonomy perspective.
1
Jhon W. Creswell, Educational Research Fourth Edition, (Person: 2011)p.3
2
38
While according to Tayie, qualitative research viewed from the reality dimension, there is no single reality. Each observer creates reality as part of research process; it is subjective and exists only in reference to the observer. Furthermore, the qualitative researcher examines the entire process believing that reality is holistic and cannot be subdivided. The qualitative researcher believes that human beings are fundamentally different and cannot be pigeonhole that makes the qualitative scholars attempt to produce a unique explanation about a given situation or individual. The setting of qualitative research is conducted in field, or in natural surroundings which has purpose trying to capture the normal flow of events without trying to control the extraneous variables.3
Moreover, in this research, the researcher deals with the research of
students’ ability inconstructing reading question based on cognitive level of
Bloom Taxonomy perspective. It means that it would need depth description related to the cognitive level of Bloom Taxonomy itself. As a result, this research conducted through descriptive approach to get a depth understanding.
Descriptive approach would recognize whether the students’ ability is in high
or low level based on cognitive level of Bloom Taxonomy perspective. Thus, the type of qualitative with descriptive approach was used in this research with aimed to investigate the students’ ability in constructing reading question items based on cognitive level of Bloom Taxonomy perspective, the level of
3
39
question that have been made by Critical Reading students’, and the students difficulties in constructing question.
B. Research Subject
This study takesthe students ofCritical Reading Class in Faculty of Education and Teachers Training UIN SunanAmpel Academy Year 2015/2016. It is because they are as a student at the Faculty of Education and Teachers Training has been prepared as a qualified educator. They have also been equipped with the materials that have made them think in a higher level. Of course they also have been able to create questions that can bring success
for their prospective student’s future. Therefore, the researcher do
researchinsixth semester of critical reading classof English teacher education department UINSA and the researcher was taking in class D consist of 6 male and 19 female students from critical reading class because this research consist to constructing reading question items. The researcher does the research on Monday, 6th June 2016.
C. Source of Data
40
Suhardi’sthesis.4 The types of data are qualitative data which are obtained
from assessment and questionnaire. Data obtained through observation will be strengthened by reading question items that made by students in critical reading class. The sources of data in this study are the sixth semester students’ of English Teacher Education Department UIN SunanAmpel.
The result of the observation, reading question items that made by students in critical reading class and the questionnaire are processed as a data. The data explains and answer the research question about the students’ ability in constructing reading question items based on cognitivelevel of Bloom
taxonomy’s perspective and the students’ difficulties in constructing the
question items, with the result that the research can describe the level of the question made by students in critical reading class based on cognitive level of bloom taxonomy’s perspective.
D. Research Procedure
This research accomplished through the stage of preliminary research, implementation, and concluding the data. Each of the stage is elaborated below.
1. Preliminary research
The researcher consults to the lecture to decide the test.
4
41
2. Implementation
After doing pre research, the researcher made planning, the planning are design the research, design the instrument, and do the research. The implementing the research by analyzing students assessment and
calculate the questionnaire to know students’ ability and their difficulties
in constructing questions. 3. Concluding
After analyzing all of the data, conclusion is drawn from the result of research.
E. Data Collection Technique
Toconduct the research, in collecting data the researcher usetwo techniques.
1. Assessment (test)
A test is method of measuring a person’s ability, knowledge, or
performance in a given domain.5In this research, the test is used to
answer the research question number one; the students’ ability in
constructing reading question items whether their ability is low, fair or
high level based on cognitive level of Bloom Taxonomy’s
perspective.The test adapted from Asian Social Science Journal
5
42
entitled “Methods to Oral English Practice”. For the detail can be seen on appendix 1.
2. Questionnaire
Questionnaire is a technique of collecting data by delivering or distributing a questionnaire to the respondent with the hopes that they will respond the questionnaire.6According to Sugiyono there are two types of questionnaire, those are close form questionnaire and open form questionnaire. Open form questionnaire is a question that hopes the respondent to write his or her answer about something descriptively. On the other hand, close form questionnaire will help the respondent to answer quickly, because the researcher gives an alternative answer to them.7
In this research the researcher used close form questionnaire, the students were given some question with two alternative answers (yes/no), which had to be chosen by the students. The researcher given ten questions items which have to be answered. The questionnaire was related to difficulties in constructing question items.For the detail can be seen on appendix 3.
6
Dr. Juliansyah.Noor, S.E,M.M. MetodologiPenelitianSkripsi, Tesis, Disertasi, danKaryaIlmiya, 87.
7
43
The questionnaire was distributed after the students did the test. This questionnaire is expected to answer the research question
number two; the students’ difficulties in constructing reading question
items.
F. Research Instruments
In this part, the researcher will use the instrument to complete all data which are needed in this research. In this research, the instruments which are used by the researcher are assessment (test) and questionnaire.
1. Assessment (test) sheet
This instrument used to answer the first research question. It contained instruction to measure the students’ ability in constructing reading question items whether their ability is low, fair, or high level
based on cognitive level of Bloom Taxonomy’s perspective. The
researcher used Journal text as a test. From this journal the researcher ask students to make five questions.
2. Questionnaire
44
gather other information related to the students’ ability in constructing
reading question based on cognitive level of Bloom Taxonomy perspective. The researcher provided the questionnaire that consists of some questions related to it. This questionnaire was also use as self-assessment for the students’ weather they know theirdifficulties in constructing question.
G. Data Analysis Technique
In this study, the researcher analyzed the data by using descriptive qualitative. All the data obtained by the researcher are presented in the form of description. The researcher analyzes the data which is earned from the assessmentandquestionnaire. The answer of the assessment and questionnaire are identified by the researcher in order to answer research question about the level of reading comprehension that have been created by critical reading students and their difficulties in constructing the question items. After identifying the data which are obtained from assessment and questionnaire,
the researcher describes the students’ ability in constructing reading
comprehension question items from cognitive level of bloom taxonomy perspective.
45
test and questionnaire, the researcher use formula from Arikunto as stated below:8
P = percentage of students’
F = number of frequency of the respondent answer
N = numbers of respondents
In conclusion, the researcher begins to describe the findings in a chart percentage and present the data obtained descriptively. The description made by the researcher based on the data collection. Then the researcher analyzed the data in specific but brief and clear description.
8
SuharsimiArikunto, ProsedurPenelitian (SuatuPendekatanPraktik) , (Jakarta: RinekeCipta, 2006) P.152
P = X 100%
F
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDING AND DISCUSSION
This chapter presents the findings of this research. It deals with the presentation of the data, data analysis, and discussion about data obtained from test and questionnaire. The data analysis and discussion are presented descriptively.
A. Research Finding
There are two kinds of data used in this research, and the research finding present the result of the research based on those data.
The first data obtained from the result of the test given to the students is about to know students’ ability in constructing reading question items based on
cognitive level of bloom taxonomy’s perspective. The second data obtained from
the result of the questionnairedistributed to the students is about the students’ difficulties in constructing the questions.
47
1. Students’ ability in constructing reading question items based on
cognitive level of Bloom Taxonomy’s perspective.
In this research, test is used by the researcher to know the students’ ability in constructing reading question item has the high-level thinking in cognitive level of Bloom Taxonomy’s perspective or not. The test was given on Monday 6th of June 2016. In the test the students were ask to make five question based on the text. The text is from Asian Social Science Journal Vol.6, No. 6; June 2010 entitled Method to Oral English Practice by Liangguang Huang. From five questions that have been made by the students measured based on cognitive level of bloom taxonomy’s perspective; they are remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating. The students work on the test under the supervision of the researcher herself and the lecturer.
The following chart summarizes the data about the students’
constructing reading question items based on cognitive level of bloom
48
Chart 4.1 the students’ question based on cognitive level of Bloom
Taxonomy
The remembering (C1), understanding (C2), and applying (C3) are
low-level thinking categorize of cognitive low-level of bloom taxonomy’s perspective.
The high-level thinking is analyzing (C4), evaluating (C5), and creating (C6). Detail analysis of the data about students’ ability in constructing reading question items in critical reading class is explained below.
a. Remembering
The first cognitive level of bloom taxonomy’s perspective is
remembering. The result for this level can be seen in the following table: 0%
5% 10% 15% 20% 25% 30% 35%
49
Table 4.1: The result of students’ question on remembering level
Level ∑ Question Question included
Example of Questions Percentage (%)
Remembering 123 14
- What kind of materials that needed to achieve oral
The table shows that from one hundred and twenty three questions that have been made by the students, there are fourteen (11,38%) questions that included on remembering level.
b. Understanding
The second level on cognitive level of bloom taxonomy’s perspective
is understanding. The result of this level can be seen in the following table:
Table 4.2: The result of students’ question on understanding level
The table shows that from one hundred and twenty three questions that have been made by the students, there are nineteen (15,44%) questions that included on understanding level.
c. Applying
The third or the last low-level thinking on cognitive level of bloom
taxonomy’s perspective is applying. The result if this level can be seen on
following table:
Table 4.3: The result of students’ question on applying level
51
The table shows that from one hundred and twenty three questions that have been made by the students, there are twenty eight (22,76%) questions that included on applying level.
d. Analyzing
The fourth cognitive level of bloom taxonomy’s perspective is
analyzing. The high-level thinking starts from this level. The result if this level can be seen on following table:
Table 4.4: The result of students’ question on analyzing level
Level ∑ Question Question included
Example of Questions Percentage (%)
Analyzing 123 36
- Those some approaches have a disadvantages? - What is the main purpose
of using approaches to oral English?
- Is there significant different for students, if they apply all of the methods?
29,26%
52
e. Evaluating
The fifth level is evaluating. The result of this level can be seen on following table:
Table 4.5: The result of students’ question on evaluating level
Level ∑ Question Question
The table shows that from one hundred and twenty three questions that have been made by the students, there are twenty three (18,69%) questions that included on evaluating level.
f. Creating
The last or the highest-level thinking on cognitive level of bloom
taxonomy’s perspective is creating. The result of this level can be seen on
53
Table 4.6: The result of students’ question on creating level
Level ∑ Question Question
The table shows that from one hundred and twenty three questions that have been made by the students, only there are three (2,43%) questions that included in this level.
From the data above can be seen that still there is students who have low-level thinking it means their question still on remembering low-level. Therefore, in Bloom Taxonomy’s revision involves the analysis, evaluating, and creating are considered high-level thinking.
2. Students’ difficulties in constructing reading question items
To find out the students’ difficulties in constructing reading question
54
of the students after the test given. The researcher gave the students 10 items which have to be answered. The questionnaire was related to difficulties in constructing question items. The further result of the research through questionnaire was presented below:
Table 4.7: Questionnaire result
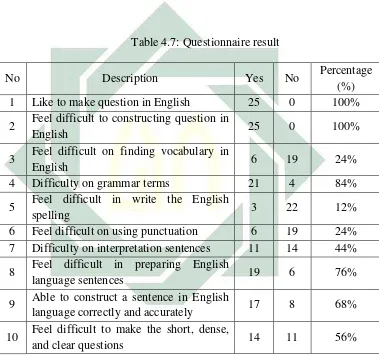
No Description Yes No Percentage
(%) 1 Like to make question in English 25 0 100% 2 Feel difficult to constructing question in
English 25 0 100% 7 Difficulty on interpretation sentences 11 14 44% 8 Feel difficult in preparing English
language sentences 19 6 76%
9 Able to construct a sentence in English
language correctly and accurately 17 8 68% 10 Feel difficult to make the short, dense,
and clear questions 14 11 56%
From the first until the tenth questions it could be explained that the
students’ difficulties in constructing question. All students (100%) said that