IMPROVING STUDENTS’ WRITING SKILLS BY
USING
SNOWBALL THROWING GAMES
(A Classroom Action Research at the Tenth Grade Students of Senior High School (SMAN 1) Tengaran in the Academic Year of 2017/2018)
GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board of Examiners as a Partial Fulfillment of the requirements for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris (S.Pd.)
In the English Education Departement of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
Written by:
KINGKING MEITA PUDYANINGTYAS
NIM. 113-13-087
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
SALATIGA
MOTTO
“The capacity to learn is a gift, the ability to learn is a skill, the willingness to learn is a choice”.
- Brian Herbert” -
“Learning is not just knowing what to do, but doing what we already know.”
- Nourma F. Fauziyah -
“Intelligence and character that is the goal of true education.”
DEDICATION
This graduating paper is sincerely dedicated to:
1. Allah SWT who always besides me, take care me, and always give healthy for me so I have finished this graduating paper
2. My beloved parents, my beloved father M. Marjoko and the best mother for my life Endang Sri Mulyani. Thank you for everything, such as your loving, your support, your guidance and your pray. May Allah bless you forever and always take care of you everywhere.
3. My beloved sister Dyah Eska Winanti and my little brother Agung Prih Adi who always support and motivate me to finish this graduating paper. 4. My beloved best friend Danar Setyawan who always give motivation and
support for me and always accompany me to finish this graduating paper.
5. Kurowo’s Squad Rateh Ambarwati, Eka Widi Riyanti, Wasilatut
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Alhamdulillahirobbii „alamin…. All praises and thanks are just for Allah Subhanahu wa Ta’ala, the Almighty God and the Lord of the universe, only for His mercy and guidance I can finish my graduating paper, because the researcher could complete this graduating paper as one of the requirements for the degree of Sarjana Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris in English Education Department of Education Faculty of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga in 2017. Peace and salutation always be given to our prophet Muhammad SAW who has guided us from the darkness to the lightness.
This success would not be achieved without support, guidances, advices, helps, and encouragements from individual and institution. Therefore, I would like to express deep appreciation to:
1. Dr. Rahmat Hariyadi, M.Pd. as the Rector of State Institute of Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
2. Suwardi, M.Pd. as the Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty 3. Dr. Sa’adi, M.Ag., the counselor of this graduating paper. Thanks for
suggestion, direction, and recommendation for this graduating paper for beginning until the end.
4. Noor Malihah, Ph.D. as the Head of English Education Departement of State Institute of Islamic Studies (IAIN) of Salatiga
5. All lecturers of English Education Departement. The writer deeply thanks you all for your advices, knowledge, motivation, advice, attention, insight, values, etc.
6. All the lecturers of State Institute of Islamic Studies (IAIN) of Salatiga. 7. All of the staffs who have helped the writer in processing graduating paper
administration.
9. My beloved sister Dyah Eska Winanti and my little brother Agung Prih Adi who always support and motivate me to finish this graduating paper. 10.My beloved best friend Danar Setyawan who always give motivation and
support for me and always accompany me to finish this graduating paper. 11.All of my friends from TBI C 2013
12.All of people who cannot be mentioned one by one, thanks for your motivation, support, help, learn, love and care, thanks you so much.
Finally, this graduating paper is excited to be able to provide useful knowledge and information to the readers.
Salatiga, 31stAugust 2017 The Researcher
TABLE OF CONTENT
GRADUATING PAPER
DECLARATION ... i
DECLARATION AND PUBLICATION ... ii
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR ... iii
BOARD OF EXAMINERS ...iv
MOTTO ...v
DEDICATION ...vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ...vii
TABLE OF CONTENT ...ix
LIST OF FIGURE AND TABLES ...xi
ABSTRACT ...xii
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Background of the Study ... 1
B. Problems of the Study ... 4
C. The Objective of the Study ... 4
D. The Significance of the Study ... 4
E. The Limitation of the Study ... 5
F. Definition of Key Terms ... 6
1. Improving ... 6
2. Writing Skill ... 6
3. Snowball Throwing ... 6
G. Graduating Paper Outline ... 6
CHAPTER II THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK ... 8
A. Previous Study ... 8
B. Writing Skill ...10
1. Definition of Writing Skill ...10
2. The Purpose of Writing ...11
3. The Difficulties of Writing...11
4. The Characteristic of Writing...12
5. The Process of Writing...14
6. Macro and Micro Writing Skill ...16
8. Assessing Writing ...19
C. Descriptive Text ...22
1. Definition of Descriptive Text ...22
2. The Purpose of Descriptive Text ...22
3. Language Features of Descriptive Text ...23
4. Generic Structure of Descriptive Text ...24
5. Teaching Writing Descriptive Text ...24
D. General Concept of Games ...26
1. Definition of Games ...26
2. The Purpose of Games ...26
E. Snowball Throwing Game 1. Definition of Snowball Throwing Game...27
2. The Advantages of Snowball Throwing Game ...28
3. The Steps of Snowball Throwing Game ...28
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD AND DATA PRESENTATION ...30
A. Research Setting ...30
1. General Concept of SMAN 1 Tengaran ...30
2. The Condition of Teacher and Staff ...31
3. The Facilities of SMAN 1 Tengaran ...35
4. The Organization Structure ...36
5. The Setting of Time ...37
6. The Schedule of the Research ...37
7. The Distribution of Groups ...39
8. The List of Students in Writing Class ...40
B. Research Method ...42
1. The Setting of the Research ...42
2. Method of the Research ...42
3. The Procedure of the Research ...44
4. Method of Analysis ...46
a. Technique of Collecting Data ...46
b. Technique of Data Analysis ...48
CHAPTER IV THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE STUDY ...51
A. Field Note ...51
1. Cycle I ...51
2. Cycle II ...61
B. Discussion ...72
1. Analysis of Students’ Participation ...72
2. Analysis of Students’ Improvement ...73
B. Suggestion ...76
BIBLIOGRAPHY ...78
APPENDICS ...81
Curriculum Vitae ...82
Syllaby ...83
Lesson Plan ...86
1. Lesson Plan of Cycle I ...86
2. Lesson Plan of Cycle II ...97
Observational Checklist... 108
Result of the Tests ... 114
Teaching Material ... 127
LIST OF FIGURE AND TABLES
FIGURE
Figure 3.1 Figure by Kemmis ...44
TABLES Table 2.1 Scoring Rubric for Aspect of Writing ...20
Table 2.2 Table of Scoring in Writing ...21
Table 3.1 The Lists of teacher in SMAN 1 Tengaran ...31
Table 3.2 The List of Staff in SMAN 1 Tengaran ...34
Table 3.3 The List of Facilities of SMAN 1 Tengaran ...35
Table 3.4 The Table of Time...37
Table 3.5 Table of Activities ...37
Table 3.6 Table of Major ...39
Table 3.7 Students’ List of X Bahasa...40
Table 4.1 Students’ Observational Checklist of Cycle I ...53
Table 4.2 Teachers’ Observational Checklist of Cycle I ...54
Table 4.3 Score of Students’ Pre-test and Post-test of Cycle I ...56
Table 4.4 Students’ Participation Checklist in Cycle I ...59
Table 4.5 Students’ Observational Checklist of Cycle II ...63
Table 4.7 Teachers’ Observational Checklist of Cycle II ...65
Table 4.8. Score of Students’ Pre-test and Post-test of Cycle II ...67
Table 4.9 Students’ Participation Checklist of Cycle II ...70
Table 4.10 Students’ Participation Sheet ...72
Table 4.11 Mean of Students’ Score Cycle I and Cycle II...73
ABSTRACT
Pudyaningtyas, Kingking Meita.2017. “Improving Students‟ Writing Skills by Using Snowball Throwing Games (A Classroom Action Research of the Tenth Grade Students of SMAN 1 Tengaran in the Academic Year 2017/2018). Graduating Paper of English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty at the State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga. Counselor: Dr. Sa’adi, M.Ag.
Keywords: Writing Skill, Snowball Throwing,
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
In this chapter the researcher presents of background of the study, problems of the study, objective of the study, significance of the study, the limitation of study, definition of key term, research method and graduating paper outline.
A. Background of the Study
Language is a tool of communication. It is used by all people in the world as means of communication. Anyone cannot interact with others without language, thus it is very important to learn language. According to (Sapir, 1921: 8) that a language is a purely human and non-instinctive method of communicating ideas, emotions, and desires by means of a system of voluntarily produced symbols. In English learning, there are four language skills; they are listening, speaking, reading and writing. On the other hand, Alexander LG (1975:8) says that the most important of all basic language skills are speaking and writing since to some extent they presuppose the other two. Generally, language can be spoken and written, so it is also necessary to learn writing.
organizing, rethinking, and recognizing. In writing skill, the students have to master vocabulary and know how to use grammar in making texts or sentences. It is an important skill because it will be applied in many aspects of life. Through writing, people are supposed to be able to express their ideas in writing form. There are many ways to express writing andone of them is through a text. So, the students must have extensive knowledge and they need a lot of practices to apply their writing ability to write something.
Teaching writing is not a simple job because there are several cases which can be taught like, create grammatical written productions such as sentence, paragraphs, essay, or long texts in a coherent and cohesive construction. It was supported by Serra (2013:1)that teaching writing in the classroom is the biggest challenges for teachers, because the students do not want to do writing and they never encourage themselves to do it and they also do not enjoy it. So, teachers should find media, method, or technique that is suitable with students’ development and create students’
interest in teaching and learning process in the classroom especially writing learning process. The writer wants to apply games in teaching English especially teaching writing.
Using games is one of the good ways to solve the students’
games are not only function as time filling activities but they also can bring some educational values that enable the students to learn the languages. So, games can make the students feel deeply involved in the lesson and also feel happy and enjoy. One of games to teaching writing is snowball throwing games.
According to Bayor (2010) as quoted by Ira (2013:3), Snowball throwing games is one of the active learning models which in practice involve a lot of students. The teacher’s role here is only as giving guidance
on the topic of early learning and subsequent demolition of the course of learning.
Based on the observation, the students may be confused what to write although they know the topic which has been given by their teachers. They are confused to write their ideas about the topic. They tend to difficult to memorizing vocabulary and error grammar because they do not interest with English learning especially writing subject. So, based on the students’ problem that they are faced, the writer wants to apply games in
teaching English especially teaching writing.
Research the First Grades Students of Senior High School (SMAN 1)
TENGARAN in the Academic Year 2017 / 2018)”. The researcher wants to change students’ participation and improve students’ achievement on
writing skill.
B. The Problem of the Study
Based on the background of the study above, there are many problems that can be identified are as follows:
1. How does the implementation of Snowball Throwing Game improvestudents’ participation of writing skill forthe first grades
students of senior high school at SMAN 1 Tengaran in the academic year of 2017/2018?
2. Is the Snowball Throwing Game effective to improve students’ writing skill on the first grades students of senior high school at SMAN 1 Tengaran in the academic year of 2017/2018?
C. The Objective of the Study
The objective of the study is to find out us the following:
1. To describe the implementation of Snowball Throwing Game to improve students’ participation in writing skill for the first grades
students of senior high school at SMAN 1 Tengaran in the academic year of 2016/2017.
2. To see whether Snowball Throwing Game improve writing skill or not.
The researcher hopes that the result of this study gives information about the level of students’ writing ability. The researcher also hopes that
the research of using snowball throwing game in teaching and learning writing will be useful for teachers, the students, and the researchers.
1. For the Teachers
The positive result of this research can support the English teacher to apply this method in teaching learning writing, and the teachers can change their old method in English teaching so make the teachers more creativity. As a result, teaching and learning process more interesting, enjoy, fun and it cannot make bored and confused anymore in choosing the appropriate method to students.
2. For the Students
The positive result of this research can support the students to improve the students’ writing skill. Teaching writing by using
Snowball Throwing Game can make the students relax and enjoy in teaching learning process. So, learning writing process easily without any difficulties and problems.
3. For the Researcher
The positive result of this research can support the researcher to enrich the method of writing skill. The researcher knows deeply about teaching writing by using Snowball Throwing Game.
This study concerns to “Improving Students‟ Writing Skill by Using
Snowball Throwing Game”. In order to focus on this research, so the result is valid and must be boarded from the problem. The topic must be limited in order to investigates the problems more accurately, precisely, and correctly. Therefore, this research especially would be focused on how can the implementation and influence in the student’s ability in writing skill in teaching and learning process using Snowball Throwing Game.
F. Definition of Key Term
The writer wants to clarify and explain the terms of the title to avoid ambiguity in perception of some terms used in this study. The definition is as following:
1. Improving
Improving is a process of becoming or making to the better (oxford university press, 2003:216). In other dictionary, we can find the word improve which means to make better in quality or to make more productive to become better (Webster, 1994:487)
2. Writing Skill
Writing skill is specified into the skill in organizing ideas (Rohman, 2009:5). Writing is representing the information to the reader in written form.
Snowball throwing games is one of the active learning method for the direct attention of learners to the material presented (Suprijono (2009:128).
G. Graduating Paper Outline
This research is organized into five chapter as follows:
Chapter I presents the introduction. It explains the comprehensive background of the study which discusses the reason of why the researcher wants to improve students’ writing skill by using Snowball Throwing
Game. This chapter also reveals statements of problem, objectives of the study, limitation of the study, the significance of the study, the definition of key terms, and organization of graduating paper.
Chapter II presents the theoretical framework of this research will be the main discussion which consists the previous studies connecting with improving students’ writing skill by using snowball throwing, the general
concept about writing skill which includes are the theory of writing, macro and micro skill in writing, and general concept about snowball throwing which consists the theory of cooperative learning, the definition of snowball throwing, the instruct in how to play of snowball throwing, the advantages and disadvantages of snowball throwing game.
Chapter IV is about findings and discussions. It presents the result of the analysis of collected data which consists the result of the test.
Chapter V is about the conclusions of the study and several suggestions related to the results of the study.
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
This chapter presents review of related literature used in this study. The reviews of related literature have a goal of providing studies and information concerned with the research problems. It consists of previous of the study, theory of writing, theory of descriptive text, the general concept of game, theory of Snowball throwing game.
A. Previous of the Study
In this research, the writer takes a review the previous research which related reference as comparison. The literature review is as follow:
In the research paper the writer takes one literature review or previous study that related with the writers’ title in the research. The first research is entitled “Implementation of Snowball Throwing Games in
Improving Students Activity (A Classroom Action Research of Class XI-3 Accounting SMK N 7 Yogyakarta in the Academic year of 2012/2013)”.
Those research was written by Triyanti Rukmana Ambarwati is the student of Yogyakarta State University. The research findings show that the level of students learning activity can increase with the implementation of snowball throwing games technique in accounting learning process.
The second research is entitled “Use of The Snowball Throwing for
experimental quantitative research format which is referred to as true experimental design. One is the experimental group (EG) and the other is the control group (CG). It can be concluded that the students who were taught by using the STT have a better performance than those who were not. As a follow up for this research, it is suggested that English teachers should use various techniques in teaching. In teaching speaking, the STT can be an alternative technique to be applied by the teachers.
The third research is entitled “The Effect of Snowball Throwing on
Students‟ Speaking Achievement (An Experimental of SMK Sandy Putra 2
Medan in the academic year 2015/2016)”. This study was conducted by
using experimental research design. the instrument used to collect the data was oral test. The result of this study shows that achievement in teaching speaking by using Snowball Throwing was higher than using Lecturing Model. It implies that Snowball Throwing is appropriate to be applied for teaching speaking.
Therefore, the writer intends to apply snowball throwing to increase students’ interest especially in writing skill. There is no previous research
that try this game especially in writing skill. So, the writer is interested in this game to be implemented in writing skill.
B. Writing Skill
1. The Definition of Writing Skill
Writing is one of four macro skills to be mastered as we learn a language and is one of the productive skills. Being a productive skill means that during the practice, we act to produce the language. Hedge (2000:308) states that writing itself is indeed an active skill as in the act of creating a text, we need to do some steps like setting goals, generating ideas, organizing information, selecting appropriate language usage and use, making a draft, reading and reviewing it, then revising and editing. The stages of writing process which is to help students in learning writing, so if they already followed the writing process they will be able to acquire this skill easily and be able to make a good writing.
On other hand, Brown (2001:336) says that writing is the process of putting ideas down on paper to transform thoughts into words, to sharpen the main ideas, to give them structure and coherent organization. Another linguist, Hyland (2004: 9) explains that writing is a way to share personal meanings. The people can construct their own views on topic. They will share their views on a topic to each other then. A person’s views
Therefore, when the people or the students constructs their views (ideas), they have to make it understandable and acceptable. So, writing is very significant for students in term that should take notes from their teacher, make a report, and finish assignments from the teacher. It can be also an indicator to show that they have gained the information. It is significant for students to master writing skill the researcher. If they do not master it, it will be difficult for them to share their teacher or their friends anything in written form.
2. The Purposes of Writing
Every activity has a purpose, so do writing. Writing also has a purpose. According to White (1986:18) writing means learning, because of that writing has several other purposes for students in writing or it also called several other functions of writing for students. They are:
a. Writing can improve the students’ academic performance. b. Writing allows a writer to create and maintain a marketable
image of him or herself in the eyes of potential and current employers.
c. Writing enhances personal and community relationships.
3. The Difficulties of Writing
skills like writing readiness and grammatical rules. On other hand, Raimes (1983:3) states that students need to learn writing not only because it is needed in order that they can communicate with their writing skill and in the activity of writing, students must be learning to apply their grammar, syntax, their knowledge of writing, and they must be having a lot of vocabulary so it makes the students lose their interest to learn English especially writing skill.
Writing is considered to be the most difficult skill than the other skill. It was stated by Richard and Renandya (2002:303) that difficulties of writing not only in generating ideas and organizing ideas but also in translating these ideas into readable text. It can be said that writing is not only a simply skill to transfer spoken information into a text, but also it needs a particular aspect to send a message into a text clearly. It was supported by White and Arndt (1998:3) that writing is far from being a simple matter of transcribing language into written symbols. It is a thinking process in its own right and it can be said that writing is seen as process which needs special requirements, such as intellectual effort that cannot be gained in short time.
From the statements above, it can be concluded that writing is a complex skill that can be mastered by practice.
4. The Characteristic of Good Writing
elements in good writing are content, organization, vocabulary, syntax, and mechanic. Good writing must express as follow:
a. Content
Writing must convey the logical development of ideas. Essay addresses the assigned topic; the idea is concrete and toughly developed; no extraneous material; essay reflects (Brown, 2004:244)
b. Organization
The writing must consist of introduction, body, and conclusion. Appropriate title, effective introductory paragraph, topic is stated, leads to body, transitional expressions used; arrangement of material shows plan; conclusion logical and complete (Brown, 2004:245).
c. Grammar
Writing should use correct of relative clause; native-like fluency in English Grammar; prepositions, modals, articles, verb forms, and tense sequencing; no fragments, or run-on sentences.
d. Mechanic
all needed capitals, paragraph, and intended (Brown, 2004:245).
e. Style
Writing should engage its reader through original insight and precise (Brown, 2004:245).
5. The Process of Writing
Before getting into the final product, the student needs to know few steps of writing processes. Hoshima and Hogue (2007:15) said that writing is never a one stop process, it is an ongoing creative act. When people start to write, of course they have already been thinking about what to write and how to write it and to make a good writing, people cannot directly write what comes to their mind but they need to follow several steps and sometimes they need go back and forth the writing process.
According to Richard and Renandya (2006:316), the process of writing as a classroom activity incorporates the four basic writing stages. It is planning, drafting (writing), revising (redrafting) and editing and three other stages externally imposed on students by teacher, namely responding (sharing), evaluating, and post-writing.
Pre-writing is an activity that encourage the students to write in the classroom. It stimulates thought for getting started. This is also strengthened by Roberts (1985:1) pre-writing includes the thinking, researching, and reading that you do before you begin the first draft, and its purpose is to allow you to find a focus on your topic. It was strengthened by Blanchard and Root (1993: 41) Pre-writing is a way of warming up brain before writing, just as warm up body before exercise. It means that correctness is not necessary. The important thing is about producing ideas as many as possible.
b. Drafting
According to Smalley, Ruetten, Kozyrev (2001: 8) Drafting is the actual writing of paragraph, essay, or a text. In this stage, the writers are focused on frequency of writing and not pay attention with the grammatical accuracy.
c. Responding
Response can be oral or written. It can be done by the teachers or peers. It has a central role-play in the successful implementation of process writing. Response will help students to evaluate their writing.
d. Revising
Richards and Renandya (2002:317) stated that revising is not merely checking for language errors (editing), it is done to improve global content and the organization of ideas so that the writer’s intent is made clearer to the reader.
e. Editing
At this stage, according to Richard and Renandya (2002:18), editing is the stage where the students are engaged in tidying up their text as they prepare the final draft for evaluation by checking a paper for mistakes in grammar, punctuation, usage and spelling.
f. Evaluating
This stage is done by the teacher. According to Richard and Renandya (2006:318), the teacher evaluates the students writing by scoring the students’ writing and showing students’ mistake. In evaluating the students’ writing, the teacher is
scoring using analytical or holistic. g. Post-Writing
This stage includes publishing, sharing, reading aloud, or displaying the texts on the notice board. Students, must be made to feel that they are writing for a very real purpose.
6. Macro and Micro writing skill
micro aspect and macro aspect. In micro aspect, the students practice specific written forms at the level of word or sentence (handwriting or typing, spelling, punctuation). On other hand, in macro aspect, the students emphasize on content and organization. In this case, they express themselves using their own words, state a purpose for writing, and specify an audience. More detail description is given by Brown (2004:220). He states that micro-skills are related to imitative and intensive types of writing task whereas are related to responsive and extensive writing. The descriptions are as follows:
a. Microskills
1. Produce graphemes and orthographic patterns of English. 2. Produce writing at an efficient rate of speed to suit the purpose. 3. Produce an acceptable core of words and use appropriate word
order patterns.
4. Use grammatical system (e.g., tense, agreement, pluralization, patterns, and rules).
5. Express a particular meaning in different grammatical forms. 6. Use cohesive devices in written discourse.
b. Macroskills
1. Use the rhetorical forms and conventions of written discourse. 2. Accomplish appropriately the communicative functions of
3. Convey links and connections between events and communicate such relations as main idea, supporting idea, new information, given information, generalization, and exemplification.
4. Distinguish between literal and implied meanings when writing.
5. Correctly convey culturally specific references in the context of the written text.
6. Develop and use a battery of writing strategies, such as accurately assessing the audiences’ interpretation, using
prewriting devices, writing with fluency
From the macro and micro skills mentioned above, it can be concluded that the main point of micro skills is about grammar mastery and the macro skills are about larger elements like the process of generating ideas, and the use of writing organization. It is mentioned that mastery of grammar is also emphasized at the micro skill requirements of writing. Grammar as linguistic aspect of writing mentioned above includes are tense, agreement, and pluralization are still considered as a difficult aspect to master in this research.
a. Mastering the mechanics of letter formation.
b. Mastering and obeying conventions of spelling punctuation. c. Using grammatical system to convey one’s intended meaning. d. Organizing content at the level of the paragraph and the complete
text to reflect given/new information and topic, comment structures.
e. Polishing and revising one’s initial efforts.
f. Selecting an appropriate style for one’s audience.
7. Genre of Writing
According to Brown (2004:219), the same classification scheme is reformulated here to include the most common genres that a second language writer might produce, within and beyond the requirements of a curriculum. Genres of writing are:
a. Academic writing
Papers and general subject reports, essays, compositions, academically focused journals, short-answer test response, technical reports, Theses, and dissertations.
b. Job-related writing
Messages (e.g. phone messages), letters/email, Memos (e.g. interoffice), reports (e.g. job evaluations, project reports, schedules, labels, signs, advertisement, announcements and manuals.
Letters, emails, greeting card, invitations, short message, notes, calendar entries, shopping lists, reminders, financial documents, diaries, personal journals, and fiction (e.g. short stories, poetry).
8. Assessing Writing
The process assessment is designed to prove how the students write, the decision they make as they write, and the strategies they use. Therefore, the aim of process assessment is to give information about the students’ performance such as how far the students’ progress in
writing is and whether any change is needed in the way of teaching strategy or not.
Brown (2001:335) says product assessment focuses on assessing the students’ final composition, while Hyland (2003:226) states that
writing product can be assessed through employing some methods scoring. There are three types of rating scales generally used in scoring writing. They are holistic, analytic, and trait-based scoring.
organization, cohesion, adequacy of vocabulary for purpose, accuracy of grammar, and mechanical accuracy for spelling and punctuation.
Based on the theories above the scoring rubric, adapted from Cohen (1994: 328-329): Table 2.1 Scoring Rubric for Aspects of Writing
Component of Writing
Scale Indicator Qualification
5 Main ideas stated clearly and accurately, change of opinion very clear
Excellent
4 Main ideas stated fairly clearly and
accurately, change of opinion relatively clear
Good
Content 3 Main idea stated somewhat unclear or inaccurate, change of opinion statement somewhat weak
Average
2 Main ideas stated not clear or accurate, change of opinion statement weak
Poor
1 Main ideas stated not all clear or accurate, change of opinion statement very weak
Very poor
5 Well organized and perfectly coherent Excellent
4 Fairly well organized and generally coherent
Good
Organization 3 Loosely organized but main ideas clear, logical, but incomplete sequencing
Average
2 Ideas disconnected, lacks logical sequencing Poor
1 No organization, incoherent Very poor
5 Very effective choice of words and use of idioms and word forms
Excellent
4 Effective choice of words and use of idioms and word forms
Good
Vocabulary 3 Adequate choice of words but some mistake of vocabulary, idioms, and word forms
Average
2 Limited range, confused use of words, idioms, and word forms
Poor
1 Very limited range, very poor knowledge of words, idioms, and word forms.
Very poor
5 No errors, full control of complex structure Excellent 4 Almost no errors, good control of structure Good
Grammar 3 Some errors, fair control of structure Average
2 Many errors, poor control of structure Poor 1 Dominated by errors, no control of
structure
5 Mastery of spelling and punctuation Excellent 4 Few errors in spelling and punctuation Good Mechanics 3 Fair number of spelling and punctuation
errors
Average
2 Frequent errors in spelling and punctuation Poor 1 No control over spelling and punctuation Very poor
In addition, according to Brown (2004:246) the good writing must involve some elements in good writing such as content, organization, vocabulary, syntax, and mechanic. The evaluation which using analytic method elaborate writing product into five components. They are organization, logical development ideas, grammar, punctuation / spelling / mechanic, and style and quality of expression. They are used to decide the criteria of scoring in writing.
Table 2.2 Scoring in Writing
No Components Score
1 Content 30
2 Organization 20
3 Vocabulary 20
4 Syntax 25
5 Mechanic 5
JUMLAH 100
C. Descriptive Text
Descriptive text is a text which describes person, place, mood, situation, and etc.Similar to Tompkins (1994:111) said that descriptive writing is painting pictures with words, meaning that in writing a descriptive paragraph, a writer should try to visualize something or someone using vivid words in order to show a clear picture of what he or she is describing. In addition, Smalley, et al., (2001:66) support that descriptive writing uses sensory details to paint a picture of a place, a person, or an object. The details in descriptive writing should not only be logically arranged but also vivid.
The general characteristics of descriptive writing includes are elaborate use of sensory language (what is heard, seen, smelt, felt, and tasted and figurative language such as simile, hyperbole, metaphor, symbolism, and personification (showing rather than telling the reader what something or someone is like through the use of active verbs and precise modifiers.
2. The Purpose of Descriptive Text
Based on the definition above the purpose of descriptive text is to present the reader with a picture of person, subject or setting. Similar to Fred D. White (1986:61-62) said that there are several aims of descriptive text:
a. To see means to help the reader to see the objects, persons, and sensations your present, as you might guess.
c. To persuade means the writer describes something to make readers interested.
d. To re-create make a reader making something.
e. To demonstrate means the writer wants to demonstrate something to a reader.
3. Language Features of Descriptive Text
Language features of the descriptive text have been observed by Knapp and Watkins (2005) as quoted by Ghina (2015:25) includes:
a. Specific participant (teacher, house, cat, etc)
b. Simple Present Tense (I have a cat, he wears glasses, sings, etc)
c. Use “linking verbs” (is, are, has, have)
d. Various adjective functioning to describe, number classify (two strong legs, sharp, beautiful, etc)
e. Relational verbs are used when classifying and describing appearance/qualities and parts or function of phenomena (Knapp and Watkin, 2005:99)
4. The Generic Structure of Descriptive Text
The first part is used to introduce phenomenon of thing which will be described or provides information about the subject matter.
b. Description
The second part is usually used to describe the parts of qualities, characteristics of the subject.
In addition, Emilia (2011:27) explains that in this part, the writer also can write some aspects, such as Description of Aspects which consists lists and elaborates the parts or qualities of the subject matter and Description of Activities could be behaviors, functions, or uses of the object described.
5. Teaching Writing Descriptive Text
The teacher must always remember the main purpose of teaching writing. Generally, teaching writing descriptive texts starts from describing everyday/concrete knowledge and gradually moving to technical or abstract understanding). The followings and provided by Knapp and Watkins (2005) as quoted by Ghina (2015:26) to teach students how to write descriptive text:
a. First, teacher must consider the level of language development of the students.
b. Teacher should plan language activities that will bring out students’ everyday/concrete knowledge of specific object or
c. As an experimental activity, teacher can take students out of the classroom to observe object or situation they will describe. d. Teacher can conduct a brainstorming session with the class to
gather information on the specific aspects of the object or situation.
e. Using the information, teacher can ask students to write a short description of the object or situation.
f. Teacher discusses each classification by asking students to compare and contrast them. Then the teacher can move on to discuss each description, again by comparing and contrasting them.
g. Teacher can select several descriptions and ask students to edit and revise those descriptions so it can best represent students’
knowledge on the object or situation.
h. Provide students with other object or situation and ask them to write description of that object or situation.
D. The General Concept of Games
1. The Definition of Games
do the tasks unwillingly. Games can be very useful to make the class more active still learn. He also states that a game is an activity which consists of rules, a goal, and an element of fun. By using games, teachers can use any stage of lesson to the target of teaching learning process of English because games serve a memory aid and a repetition drill, a chance to use a language freely, and a means to teach language (Hadfield, 2003:4).
2. The Purpose of Games
There are many reasons why the teacher in teaching learning activities should apply games. Games are fun because game give the students enjoyment and pleasure. Another reason are stated by Prensky (2007:11). They are as follows:
a. Games have goals because games give the students motivation to learn more.
b. Games are interactive. Games can make the students do something.
c. Games have outcomes and feedback. Those give the students learning.
d. Games have conflict, competition, challenge.
e. Games have a problem solving. They spark the students’ creativity.
g. Games have a story because those give the students emotion. Those give the students challenge to win the games.In conclusion, there are many reasons why the teacher should apply games in the class. The students are happy and relax when they play it. The students can learn the materials more. It does not only learn the materials but the students also can play in the class in the same time.
E. Snowball Throwing Game
1. The Definition of Snowball Throwing Game
According to Bayor (2010) as quoted by Ira (2013:3), snowball throwing game is one of the active learning model which in practice involves a lot of students. It is one of the cooperative learning model that focuses on group work using discussion in which every group asks questions to another so that the group will work cooperatively to solve the problem. Besides that, Suprijono (2009:128) states that snowball throwing games is one of the active learning method for the direct attention of learners to the material presented. So, this game will be more interactive if the students enjoy with learning process.
There are many advantages of using snowball throwing games in the classroom, they are as follows:
a. The students are motivated and challenged.
b. This game provides language practice in the various skills of speaking, writing, listening, and reading.
c. Snowball throwing game encourage students to interact and communicate with other students.
d. Snowball throwing trains agility of the students. e. Snowball throwing trains concentration of students.
f. Snowball throwing is a means to eliminate boredom in learning.
3. The Steps of Snowball Throwing Game
According to Suprijono (2009:129), There are steps of implements Snowball Throwing Game, they are as follows:
a. Teacher deliver the material that will be learnt.
b. Teacher make groups and call the chairman of each group to give an explanation about the material being taught to their students / members.
d. Each student is given a sheet of paper, to write down one question concerning any matter which has been described by the group leader.
e. The paper containing these statements or questions was made into a ball and tossed one student to another student about 15 minutes.
f. Then, each student has one ball or one question and give the opportunity for the students to answer questions that are written in ball-shaped paper in turn.
g. Evaluation h. Closing
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHOD AND DATA PRESENTATION
In this chapter the researcher has to collect data from the objects of research that called informants. This research is conducted at SMA N 1 Tengaran.
A. Research Setting
1. General Description of SMAN 1 Tengaran
SMA N 1 Tengaran is one of senior high school in Kembangsari Village and around there. This school was built at June, 2nd 198. The school is located at Jendral Soemitro Street, Karangduren Village, Tengaran District, Semarang Regency. This schoolis very strategic because it is near with Kembangsari Market, so that it is very easy to find this school (www.sma1tengaran.sch.id).
There are many progresses on the building in every year. For instance, there are some wide field and a lot of trees so it makes the students were comfort and interested to study there.The headmaster of this school in the academic 2017/2018 is Mr. Subroto, M.Pd. The students in SMAN 1 Tengaran in academic year of 2017/2018 are 1379 students.
The profile of SMA Negeri 1 Tengaran
a. School name : SMA Negeri 1 Tengaran
Regency
c. Village : Karangduren
d. District : Tengaran
e. Regency : Semarang
f. Province : Central Java g. Pos Code : 50775
h. Phone number : (0298) 321656
i. Area : Village
j. Accreditation : A
k. Teaching learning process : Morning l. Building area : 20.833 m2
(Source: administration staff of SMAN 1 Tengaran (August, 11th 21017)
2. The Condition of Teacher and Staff
The important role in teaching and learning process is a teacher. Meanwhile, staff or officer who always help the teacher to create teaching and learning process. Both teacher and staff will make teaching and learning better.
Teachers are those who transfer knowledge to students about some materials and skills during teaching and learning process. They facilitate the students to get students’ achievement and talent.
No Name Status 1 Subroto, S.Pd. M.Pd. Headmaster
2 Supriyono, S.Pd. Teacher of Physics
3 Drs. Widiharso, M. Si. Teacher of Accounting Economics 4 Rosdiana, S.Pd. Teacher of Mathematic
5 Drs. Nur Rohmat, M.Pd Teacher of Guidance and Counseling
6 Bambang Wiyanto, S.Pd. Teacher of Civic Education 7 Ariyani, S.Pd Teacher of Biology
8 Dra. Agustin Dwi A Teacher of Chemistry
9 Dra. Tin Hadriani Teacher of English Language Literature
10 Dra. Retno Triyatmi Teacher of Mathematic 11 Drs. Budhi Nugroho Teacher of Geography 12 L Agus Sri Mulyono Teacher of Chemistry 13 Marjoko, S.Pd Teacher of Mathematic 14 Djoko Erwiyono, S.Pd Teacher of Physics 15 Stefana P. Pahalanti Teacher of History
16 Mahanani Utami, S.Pd. Teacher of Indonesia Language 17 Yuli Setyorini, S.Pd. Teacher of English Language 18 Bejo Marsono, S.Pd. Teacher of English Language 19 Wiyono, S.Pd. Sports’ Teacher
21 Sulistyarini, S.Pd. Teacher of Mathematic
22 Endang Setyaningsih, S.Pd Teacher of Indonesia Language 23 Bambang Prihadi Art and Cultural Teacher 24 ST Danang Pamungkas Teacher of English Language 25 Dra. Cirillia Elvi .P. Socio-anthropology teacher 26 Waslam, S.Pd Teacher of Physics
27 Ulfa Kurniawati, S.Pd Teacher of Geography 28 Tri Puji Rahayu, S.Pd. Teacher of Mathematic
29 Aula Sari Husnawati, S.Psi Teacher of Guidance and Counseling 30 Lely Wachyuningsih, S.Pd Teacher of Guidance and Counseling 31 Anggraeni Pamungkasih,
S.Pd
Teacher of Javanese Language
32 Yunike Sriyami, S.Th Teacher of Cristian Religion 33 Ari Probowati Socio-anthropology teacher 34 Martini, S.Pd Teacher of Economics 35 Maya Farida, S.Pd Teacher of Enterpreneurship 36 Jimin, S.Pd Teacher of Islmic Religion
37 Novia Astuti, S.Pd Teacher of Biology 38 Happy Tiur Hamida .S., S.Pd Teacher of Sociology 39 Nur Kholiq, S.Pd. Sport Teacher
42 Diarti, S.Sn Art and Cultural Teacher
43 Panut, S.Pd Teacher of Indonesian Language 44 Hardiana Widyastuti, S.S Teacher of Japanese Language 45 Fajar Hidayati, S.Pd Teacher of Chemistry
46 Drs. Sugiyanto Teacher of Economics 47 Suwarno, S.Pd Teacher of Geography
48 Novia Astuti, S.Pd Teacher of Biology and Mathematic 49 Lukman Jatmiko, S.Pd. Teacher of Indonesian Language 50 Arum Wardani, S.Pd. Socio-anthropology Teacher 51 Ida Moelyatiningsih, S.Pd Teacher of Civic Education
52 Drs. Nur Rohmat, S.Pd Teacher of Guidance and Counseling 53 Yuli Haryanti, S.Pd. Teacher of Guidance and Counseling
54 Adhe Putra Fauzan, S.Pd. Sport Teacher
55 Sugiyani, S.Pd. Teacher of Civic Education 56 Suroto, S.Pd. Teacher of Physics
57 Suci Umiyati, S.Pd. Teacher of Mathematic 58 Zamzuri, S.Pd.I Teacher of Islamic Religion 59 Theresiana Ayu Andharweni,
S.Pd.
Enterpreneurship Teacher
Table 3.2. The list of staff / officer of SMAN 1 Tengaran
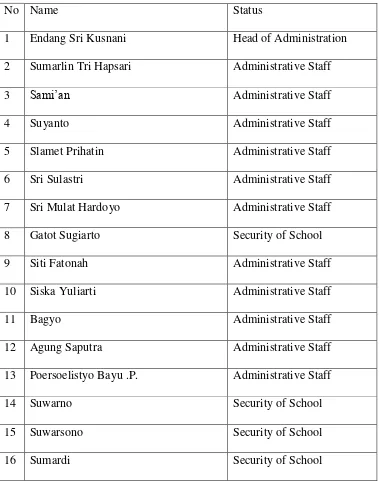
No Name Status
1 Endang Sri Kusnani Head of Administration 2 Sumarlin Tri Hapsari Administrative Staff
3 Sami’an Administrative Staff
4 Suyanto Administrative Staff
5 Slamet Prihatin Administrative Staff
6 Sri Sulastri Administrative Staff
7 Sri Mulat Hardoyo Administrative Staff
8 Gatot Sugiarto Security of School
9 Siti Fatonah Administrative Staff
10 Siska Yuliarti Administrative Staff
11 Bagyo Administrative Staff
12 Agung Saputra Administrative Staff
13 Poersoelistyo Bayu .P. Administrative Staff
14 Suwarno Security of School
15 Suwarsono Security of School
16 Sumardi Security of School
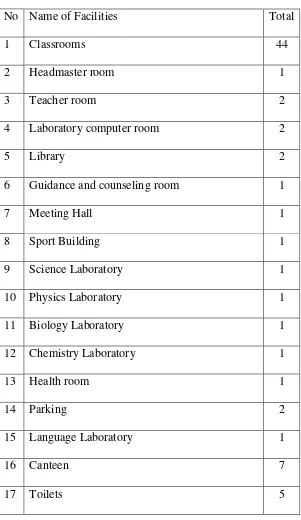
3. The Facilities of SMA N 1 Tengaran
are needed by teachers, school, and the students to support teaching learning process. It could be seen in the table below:
Table 3.3
the list of facilities of SMAN 1 Tengaran
No Name of Facilities Total
1 Classrooms 44
2 Headmaster room 1
3 Teacher room 2
4 Laboratory computer room 2
5 Library 2
6 Guidance and counseling room 1
7 Meeting Hall 1
8 Sport Building 1
9 Science Laboratory 1
10 Physics Laboratory 1
11 Biology Laboratory 1
12 Chemistry Laboratory 1
13 Health room 1
14 Parking 2
15 Language Laboratory 1
16 Canteen 7
18 Music room 1
19 Administration room 1
20 Mosque 1
21 Field 3
4. The Organization Structure
The organization structure of SMAN 1 Tengaran as follows: Headmaster : Subroto, S.Pd.M.Pd Students Affair : Wiyono, S.Pd
Supriyono, S.Pd.
Secretary : Marjoko, S.Pd
ITreasure : Aulasari .H. S.Pd Head of Curriculum : Sulistyarini, S.Pd. Head of Administration : Endang Sri Kusnani 5. The Setting of Time
The research conducted from July 17th until August 11st schedule activities are as follows:
Table 3.4. table of time
No Activities Time Allocation
1 Preparing the research proposal May
2 Observation July
pre-test and post-test cycle II
5 Writing the report August
6. The Schedule of the Research
The schedule of the research was conducted in July until August. The table below will show my schedule of the research:
Table 3.5. Table of activities
No Date and Time Activities Place and Time 1 July 18th 2017 Observation : Giving the
(09.15 – 11.00)
7. The Distribution of Groups
The distribution of the groups in SMAN 1 Tengaran as follows:
Table 3.6. table of major
Class Group/Major Students’
The researcher conducted this action research in SMAN 1 Tengaran and especially concern in the first grade. This class group consists of 30 students. They are 10 of male and 20 of female. The data can be seen in the table below:
Table 3.7. The list of X Bahasa Students No Students’ Initial Male/Female
1 APP Female
2 AAS Male
3 AW Male
4 ACH Female
5 ANP Female
6 ESR Female
7 EMP Female
8 FAS Male
9 FS Female
10 FS Female
11 KA Male
12 LF Female
13 LAZN Female
14 LA Female
15 MJP Male
17 MAN Male
18 RDYK Female
19 RRH Female
20 RAV Female
21 SNM Male
22 SWS Male
23 ST Female
24 SP Female
25 SI Female
26 TO Female
27 VD Female
28 VQ Female
29 WS Male
30 YM Female
B. Research Method
1. The setting of the research
2. Method of the research
The researcher used Classroom Action Research (CAR) to conduct this research. Classroom action research designed to solve practical problems in the process of teaching learning, especially in teaching writing. CAR begins with a question about classroom experience, issues, or challenges. Action Research is about systematic study of attempts to improve educational practical actions andby means of their own reflection upon the effects of those action (Hopkins, 1993:45).
In research design classroom action research (CAR) there are 3 words. Research is activity to observe an object with certain methodology to get data or information which useful into develop quality about something which thin interesting by the researcher.Action is activity which intentional to conduct with certain provide. Class is a group of students receive lesson and teach by teacher in same time and place. So, classroom action research is an observation toward activity which intentional to rise and happen in a classroom.
According to Arikunto et al (2006:6-9) there are some principles of action research as follows:
a. The real activity in routine situation
SWOT is summary of Strength, Weakness, Opportunity, and Threat. Strength and weakness are used to identify researcher and it is subject. The opportunity and threat are identified out of the teacher or researcher and students (Arikunto, 2006:7).
d. Empiric and systematic endeavor. e. Using SMART
The meaning of SMART: S = Spesific
M= Manageable
A= Acceptable or achieveable R= Realistic
T= Time-bound
From the definition above, the writer concludes that classroom action research is done by the teacher in teaching and learning process to understand the situation and to improve students’ writing skill in
learning process (Arikunto, 2006:7).
The research design of CAR in this study is a collaborative classroom action research. It means the researcher collaborates with the English teacher of SMAN 1 Tengaran. In carried out the study, the researcher’s role is as an English teacher who teach writing by using
activities during the writing learning process. The purpose of this research is to gain understanding of teaching and learning within one’s
classroom and to use that knowledge to increase students learning. The writer also as researcher and teacher who carried out the use of snowball throwing game as a media in the class. The writer wants to make sure that the lesson plans of the use of snowball throwing game can run well in order that the teaching and learning process run effectively.
3. The Procedure of Research
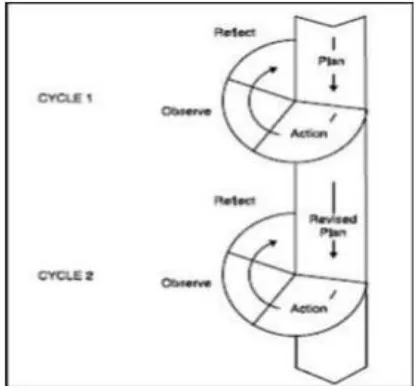
The writer uses the classroom action research procedure based on Kemmis and Mc Taggart, 2004:45) as quote by Samsu Sumadoyo, (2013:41). The procedures are divided into two cycles which consists of four activities. The procedures stated by Kemmis and Mc Taggart were briefly described in the following scheme.
a. Planning
The activities in the planning are:
1) Preparing materials, making lesson plan and designing the steps in doing action.
2) Preparing list of students’ name and scoring. 3) Preparing teaching aids.
4) Preparing sheets for classroom observation (to know the situation of teaching learning process when the method or technique or mode is applied).
5) Preparing a test. (to know whether student’s ability in writing improves or not)
b. Action
1) Giving pre-test.
2) Teaching writing using snowball throwing games 3) Team study.
4) Giving occasion to the students to ask any difficulties or problems.
5) Ask the students about some conclusions of writing activities. 6) Giving post- test.
c. Observation
students’ feeling, thinking and something they do in teaching-
learning process. d. Reflection
Reflection is a research finding analysis. This is to record what happens in observation. Reflection seeks to make sense of processes, problems and real issues in strategic action. Reflection belongs an evaluative aspect; it asks the writer to weight the experience, to judge whether or not the method can be problem solving to improve students’ writing skill.
4. Method of Analysis
In analyzing the data, the researcher used these following steps, they are:
a. Technique of Collecting Data
In this research, the writer used three data collection method namely test, observation, and documentation. The writer uses them to analyze the data and to describe the students’
improvement in writing skill through snowball throwing games. 1) Test
Test is sequence questions used to measure or evaluate how far is student’s ability, knowledge,
intelligence or attitude either individual or collective. The writer used two tests namely pre-test and post-test.
Pre-test is used to find out how far is the students’ writing ability before they are taught by using Snowball Throwing Game.
2. Post-test
Post-test is given after students are taught by using Snowball Throwing Game. The aim of post-test is to find out how far is the students’ writing skill after they learn by
using Snowball Throwing Game. 2) Documentation
Documentation is a number of data that presents the verbal data such as correspondence, journal, memory, report and others. This method is used to get school information which is used as the object of the research. The documentary data are achieved from letters, journal and others.
The documentation used is in the form of notes, book, transcript and the history book of SMA N 1 Tengaran.This method is used to know the information of the school, the condition of teachers, staff, students and the others.
3) Observation.
method is easily used to find concrete data. The writer is able to observe directly, the condition of buildings, the geographical location, student’s activities in teaching
-learning processes and others. b. Technique of Data Analysis
After collecting the data, the next step of the study is analysis. The data is analyzed in two ways;
1) Descriptive technique
Descriptive technique is used to know students’
participation and their activities in the classroom. In this case, the writer uses field note which record all of activities in the classroom.
2) Statistical technique
This technique is used to know the result of the students’
pre-test and post-test in the three cycles. The statistical calculations are staged as follows:
a) Mean Calculating
The calculation of mean is to know the average of the students’ score.
M =∑X
N
Explanation:
N = The total number of students b) Standard Deviation
The formula used for calculating standard deviation.
SD= ∑D
SD = Deviation Standard for one sample D = Difference between pre-test and
post-test
N = Number of observations in sample c) Percentage
Explanation:
P = Percentage
F = the sum of students’ passing KKM
CHAPTER IV
THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE STUDY
This chapter focuses on analyzing the collected data. The researcher as observer and the researcher presents the details of the findings. The findings consist of the result of the cycle I and cycle II. Each cycle consists of planning, action, observation, and reflection. The two cycles are treatment of the improving of students’ writing skill especially in descriptive text by using snowball throwing.
A. Field Note
The researcher arranged two cycles. Each cycle consists of some activities such as planning, action, observation, and reflection. Here the writer explains the cycle as follows:
1. Cycle I
In this part, the researcher carried out series of action namely planning the action which included one meeting.
a. Planning
The researcher prepares some preparations before entered the class, such as:
1) Materials and lesson plan 2) List of students’ name
4) Teaching aids (e.g. blank paper, camera) 5) Test Instrument (pre-test and post-test) b. Action
The implementation of action was conducted on Thursday at 09.15 until 11.00, 3rd August 2017. The researcher started the class with Mr. Bejo Marsana, S.Pd. who helped the researcher to introduce herself in front of the class. Then, he greeted and asked about their condition. Before the teacher began the learning, he asks the leader of the class to lead their friends to pray together. After that, he checked students’ attendance list.
Then, the teacher gave pre-test to the students for about 15 minutes before the teacher explaining the materials. When the students were doing the test, she walked around the class to check the students’ test. After the students have finished the pre-test, she collected the students’ test.
blank paper to each group and give instruction to play the game. They were very excited, enthusiastic and enjoyed it because the condition of the class is not boring and they can share their opinions. After that, they had finished to share their result of discussion, the teacher give feedback to them about the material. The material about descriptive text. Then, the researcher gave post-test to them and gave time to do it. The researcher asked them to submit it on the table. The time was over, the researcher continued the next meeting on Friday.
c. Observation
During the observation, the teacher asked the researcher to help the teacher in analyzed students and teachers activities in teaching learning process by fill up on the following table:
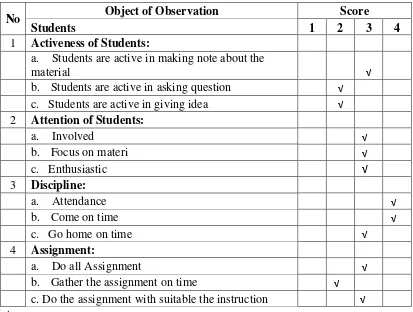
1. Students’ observation sheet
School : SMA N 1 Tengaran Class : X Bahasa
Date : August, 3rd 2017 Teacher : Bejo Marsana, S.Pd.
Observer : Kingking Meita Pudyaningtyas Instruction : Give check mark (√ ) in scorecoloum
Table 4.1. Students’ observation sheet
No Object of Observation Score
Observer : Kingking Meita Pudyaningtyas
Instruction : Give check mark (√) in score coloum that has available.
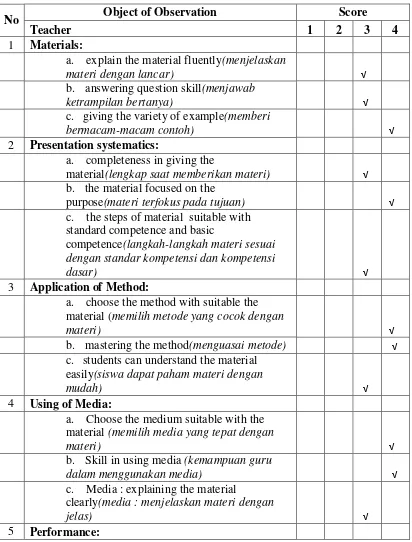
Table 4.2. the teachers’ observation sheet
No Object of Observation Score
Teacher 1 2 3 4 dengan standar kompetensi dan kompetensi
dasar) √
3 Application of Method:
a. choose the method with suitable the material (memilih metode yang cocok dengan
materi) √
b. mastering the method(menguasai metode) √
c. students can understand the material easily(siswa dapat paham materi dengan
mudah) √
4 Using of Media:
a. Choose the medium suitable with the material (memilih media yang tepat dengan
materi) √
b. Skill in using media (kemampuan guru
dalam menggunakan media) √
c. Media : explaining the material
clearly(media : menjelaskan materi dengan
jelas) √
a. The clarity of attitude (kelenturan guru terhadap sikap
siswa) √
c. Motivating the students(pemberian
motivasi kepada siswa) section, the researcher saw the students were very ashamed and doubt when they learnt English. Most of the students were silent when the teacher asked them to explain about descriptive text. Most of them were afraid to make mistakes because they had low mastery in grammar and vocabulary so they not interest with English learning.
In fact, most of them didn’t know to write a paragraph in
Table 4.3
The score of students’ pre-test and post-test in cycle I
27 VD 68 79 11 121
28 VQ 66 78 12 144
29 WS 60 73 13 169
30 YM 65 72 7 49
JUMLAH 1919 2246 327 3957
1) The calculate of mean of pre-test and post -test a. Mean of Pre-test I
M
=
∑𝑋 𝑁M
=
1919 30M = 63.96 b. Mean of Post-test I
M = ∑𝑌 𝑁
=2246 30
= 74.86
Mean of pre-test = 63.96
Mean of post-test = 74.86
Mean of pre-test ≥ than mean post-test
2) Calculating of Standard Deviation calculating students’ pre-test and post-test score.
The calculation can be shown below:
P = 𝑚2−𝑚1
The calculation which shows the class percentage of students who pass the KKM (the minimum of passing criteria) is:
P = 𝐹
𝑁X 100%
= 16