Home
Volumes
Submit Paper
Manuscript Status Author Guidelines Editorial Board
Technical Board
Indexing and Abstracting Subscribe to JATIT Contact Us
FeedBack |Links |Contact Us| Site Map
Welcome to Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
Editorial Board
EDITOR IN CHIEF
Prof. Niaz Ahmad
FCE, MOE, Islamabad, PAKISTAN
EDITORIAL BOARD
Dr. CHRISTEL BAIER
Faculty of Computer Science, Institute for Theoretical Computer
Science, Technical University Dresden, GERMANY.
Dr. YUSUF PISAN
Department of Software Engineering, Faculty of Information
Technology, University of Technology, Sydney, AUSTRALIA.
Dr. YUXIN MAO
School Of Computer & Information Engineering Zhejiang Gongshang
University, CHINA
Dr. MUHAMMAD SHER
Faculty of Basic and Applied Sciences, Department of Computer
Science, International Islamic University, Islamabad. PAKISTAN.
Dr. ZARINA SHUKUR
Computer Science Dept., Fakulti Teknologi dan Sains Maklumat,
University Kebangsaan Malaysia, 43600 Bangi, MALAYSIA.
Dr. NOR AZAN MAT ZIN
Department of Information Science, Faculty of Information Science &
Technology, National University of Malaysia (UKM) 43600 UKM BANGI,
MALAYSIA.
Dr. KHAIRUDDIN BIN OMAR
Faculty of Information Science and Technology, Universiti Kebangsaan
Malysia, 43600 Bangi Selangor Darul-Ehsan, MALYSIA.
Dr. TENGKU MOHD. BIN TENGKU SEMBOK
Faculty of Information Science and Technology Universiti Kebangsaan,
Malaysia, 43600 Bangi Selangor Darul-Ehsan, MALYSIA.
Dr PRABHAT K. MAHANTI
Department of Computer Science and Applied Statistics (CSAS),
Hazen Hall Room 311, University of New Brunswick, Saint John, New
Brunswick, CANADA.
Dr. R. PONALAGUSAMY
Department of Mathematics, National Institute of Technology,
Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, INDIA.
Dr. NITIN UPADHYAY
Computer Science & Information Systems Group, Birla Institute of
Editorial Board -Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Techn...
http://www.jatit.org/Editorial_Board.php
Technology and Science (BITS), Pilani-Goa Campus, NH-17B Bypass
Road, ZuariNagar, Goa, INDIA.
Dr. A. SERMET ANAGN
Eskisehir Osmangazi University, Industrial Engineering Department,
Bademlik Campus, 26030 Eskisehir, TURKEY.
Dr. YACINE LAFIFI
Department of Computer Science, University of Guelma, BP 401,
Guelma 24000, ALGERIA.
Dr. CHRISTOS GRECOS
School of Computing, Engineering and Physical Sciences, University of
Central Lancashire, Preston PR1 2E, UNITED
KINGDOM.Dr. JAYANTHI RANJAN
Institute of Management Technology, Raj Nagar, Ghaziabad, Uttar
Pradesh, INDIA
Dr. ADEL M. ALIMI
National Engineering School of Sfax (ENIS), University of SFAX,
TUNISIA
Dr. SIKANDAR HAYAT KHIYAL
Department of Computer Science, Fatima Jinnah Women University,
Rawalpindi, PAKISTAN
Dr. ADEL MERABET
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, Dalhousie
University, Halifax, CANADA
DR. HEMRAJ SAINI
CE&IT Department, Higher Institute of Electronics, Bani Walid. LIBYA
Dr. MAUMITA BHATTACHARYA
SOBIT, Charles Sturt University, Albury - 2640, NSW, AUSTRALIA
Dr. SEIFEDINE KADRY
Lebanese International University, LEBONON
Dr. AIJUAN DONG
Department of Computer Science, Hood College Frederick, MD 21701.
USA
Dr. S.S.RIAZ AHAMED
Mohamed Sathak Engineering College, Kilakarai, & Sathak Institute of
Technology, Ramanathapuram , Tamilnadu, INDIA
Dr. ZURIATI AHMAD ZUKARNAIN
University Putra Malaysia, MALAYSIA
Dr. CHELLALI BENACHAIBA
University of Bechar, ALGERIA
Dr. MOHD NAZRI ISMAIL
University of Kuala Lumpur (UniKL) MALYSIA
Dr. VITUS SAI WA LAM
The University of Hong Kong, CHINA
Dr. WITCHA CHIMPHLEE
Dr. SIDDHIVINAYAK KULKARNI
University of Ballarat, Ballarat, AUSTRALIA
Dr. S. KARTHIKEYAN
Caledonian College of Engineering, OMAN
Dr. DRAGAN R. MILIVOJEVI
Ć
Mining and Metallurgy Institute Bor Zeleni bulevar 35, 19210 Bor,
SERBIA
Dr. ABDUL AZIZ
Professor of Computer Science, University of Central Punjab,
PAKISTAN
Dr.P.DANANJAYAN
Professor, Department of ECE, PEC, Puducherry, INDIA.
Dr. E. SREENIVASA REDDY
Principal - Vasireddy Venkatadri Institute of Technology, Guntur, A.P.,
INDIA
Dr. SANTOSH DHONDOPANT KHAMITKAR
Ramanand Teerth Marathwada University, Nanded. Maharashtra
431605, INDIA
Dr. M. IQBAL SARIPAN
(MIEEE, MInstP, Member IAENG, GradBEM)
Dept. of Computer and Communication Systems Engineering, Faculty
of Engineering, Universiti Putra MALAYSIA
Dr. E. SREENIVASA REDDY
Principal - Vasireddy Venkatadri Institute of Technology, Guntur, A.P.,
INDIA
SHAHBAZ GHAYYUR
Faculty of Basic and Applied Sciences, Department of Computer
Science and Software Engineering, International Islamic University,
Islamabad. PAKISTAN.
Dr. T.C.MANJUNATH,
Professor & Head of the Dept.,Electronicis & Communication Engg.
Dept,
New Horizon College of Engg.,Bangalore-560087, Karnataka, INDIA.
Dr. Nacer eddine ZAROUR
LIRE Laboratory, Computer Science Departement, University Mentouri
of Constantine (UMC)
Dr. RIKTESH SRIVASTAVA
Assistant Professor, Information Systems, Skyline University College
P O Box 1797, Sharjah, UAE
Dr. Mohd ZAINAL ABIDIN AB KADIR,
PhD, MIEEE
Centre of Excellence on Lightning Protection (CELP)
Dept. of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Faculty of Engineering,
UPM, Selangor, MALAYSIA
Dr. OUSMANE THIARE
Gaston Berger University, Department of Computer Science, UFR
S.A.T
BP 234 Saint-Louis, SENEGAL
Dr. SIDDHIVINAYAK KULKARNI
Graduate School of Information Technology and Mathematics
University of Ballart AUSTRALIA
Editorial Board -Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Techn...
http://www.jatit.org/Editorial_Board.php
Dr. BONNY BANERJEE
Senior Scientist Audigence, FL, USA, The Ohio State University,
Columbus, OH, USA
Dr. NICKOLAS S. SAPIDIS
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Western
Macedonia
Kozani GR-50100, GREECE.
Dr. NAZRI BIN MOHD NAWI
Software Engineering Department, Faculty of Science Computer
Information Technology, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn
MALAYSIA
Dr. JOHN BABALOLA OLADOSU
Ladoke Akintola University of Technology, Ogbomoso, NIGERIA
Dr. ABDELLAH IDRISSI
Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Science, Mohammed V
University - Agdal, Rabat, MOROCCO
Dr. AMIT CHAUDHRY
University Institute of Engineering and Technology, Panjab University,
Sector-25, Chandigarh, INDIA
Dr. ASHRAF IMAM
Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh-INDIA
Dr. MUHAMMAD UMER KHAN
Department of Mechatronics, Faculty of Engineering, Air University,
Islamabad. PAKISTAN
Dr. MOHAMMED ALI HUSSAIN
Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering, Sri Sai Madhavi Institute of
Science & Technology, Mallampudi,
Rajahmundry, A.P, INDIA
Dr. KHALID USMANI
Department of Computer Science, Arid Agriculture University,
Rawalpindi, PAKISTAN.
Dr. GUFRAN AHAMD ANSARI
Qassim University, College of Computer Science, Ministry of Higher
Education, Qassim University, KINGDOM OF SAUDI ARABIA
Dr. Defa Hu
School of Information, Hunan University of Commerce, Changsha
410205, Hunan, P. R. of CHINA
MANAGING EDITORS
Saleha Samar
(managing_editor at jatit.org )
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
Shahzad A. Khan
( publisher at jatit.org )
Lecturer IMCB, FDE Islamabad.
(
Managing Editor/Linguist & In-charge Publishing
)
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
jatit.org Publishing Policy Review Process Code of Ethics
board if you hold a PhD in computing and have at-least 10
publications in International Journals/Conferences. Please drop your
CV at managing_editor at jatit.org. Members lists and requests are
reviewed at the end of every year in regional advisory panel meeting.
Editorial Board -Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Techn...
http://www.jatit.org/Editorial_Board.php
Home Volumes Submit Paper Manuscript Status Author Guidelines Editorial Board Indexing and Abstracting Subscribe to JATIT Contact Us Frequency : MONTHLY
FeedBack |Contact Us |Links | Site Map
Welcome to Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
Submit Paper / Call for Papers
Journal receives
papers in
continuous flow
and we will
consider articles from a wide range of Information Technology disciplines
encompassing the
most basic
research to the most innovative technologies. Please submit your papers
electronically to our submission
system at
http://jatit.org /submit_paper.php in an MSWord, Pdf or compatible format so that they may be evaluated for publication in the upcoming issue. This journal uses a blinded review process; please
remember to
include all your personal
identifiable information in the manuscript before
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
June 2014 | Vol. 64 No.1
Title: A FUZZY APPROACH FOR REPRESENTATIVE NODE SELECTION IN CROSS LAYER TCP
Author: A. CHANDRASEKAR, Dr. S. ARUMUGAM
Abstract: A cross-layer based improved Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) protocol ensuring fair throughput and reliability was proposed in the previous investigations. In this protocol, data path was segmented, and representative nodes are maintained in every segment for any TCP connection. A Transmission Controller Module (TCM) is used by the representative node to determine bandwidth and delay in transmission and a Local Acknowledgement (LACK) message is sent to the source. Each LACK’s
reception source calculates congestion window’s desired size, based on the forward path bandwidth, and
Round Trip Time (RTT) values on forward path thereby avoiding congestion for larger extents, and increasing network data transmission rate. This study proposes to extend TCP. Representative nodes use fuzzy logic concept, dynamically. A node becomes a representative node when its two hop neighbours have poor link quality, high mobility and reduced bandwidth. The fuzzy rule generated in this study ensures increased throughput and reduced delay compared to conventional TCP.
Keywords: Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), Local Acknowledgement (LACK) message, Fuzzy Logic
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: SWBC - SECURITY IN WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS BY BROADCASTING LOCATION CLAIMS
Author: S.MEENATCHI , C.NAVANEETHAN ,N.SIVAKUMAR , P.THANAPAL , J.PRABHU
Abstract: Secure data transfer in Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) is a challenge, as there are always chances for intruders to form a clone node to interrupt data packets. The proposed system Security in Wireless Sensor Networks by Broadcasting Location Claims (SWBC) engages with Area Based Clustering Detection (ABCD).ABCD divides the WSN into sub areas by implementing division of angle equally and nodes in the sub area elects a Witness node by using maximum neighbour nodes approach. Witness nodes are selected near to the central node to the transmission within the range. Witness nodes gets the location claims of the source node and central node manages the witness nodes where both central node and witness node identifies the intruder by broadcasting the location claims to all the nodes. By simulation SWBC gives the best security compared to the existing techniques like RED, and LSM. Simulation results enhance lifespan of WSNs, decreases the data traffic, detection of intruder before replication of data packets.
Keywords: SWBC, WSN, ABCD, Broadcast
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: EFFICIENT REMOVAL OF IMPULSE NOISE FROM VIDEO USING ADAPTIVE THRESHOLD ALGORITHM
Author: P. LATHA, Dr. M. A. BHAGYAVENI, S. R. PREETHI
submitting it for review, we will edit the necessary information at our side. Submissions to JATIT should be full research / review papers (properly indicated below main title).
pixel is replaced only if it is identified to be a noisy pixel by the proposed adaptive threshold algorithm otherwise the original pixel is retained. Thus it results a better filtering technique when compared to median filters and its modified filters. It is proved that the proposed algorithm is more suitable for high noise environment. The parameters Mean Square Error (MSE) and Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR) are measured for determining the visibility and similarity of output video frames.
Keywords: Impulse Noise, Adaptive Threshold, Noise Detection, Color Video Processing
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: DESIGN, ANALYSIS AND OPTIMIZATION OF A NEW STRUCTURE OF MICROSTRIP PATCH ANTENNA FOR RFID APPLICATIONS
Author: ALI EL ALAMI , SAAD DOSSE BENNANI , MOULHIME EL BEKKALI , ALI BENBASSOU
Abstract: In this paper, we propose a new structure patch antenna excited by two identical microstrip lines having a common feeding adapted to 50 ohm and intended to applications of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID). The slots inserted at the patch antenna have a direct impact on improving the radiation characteristics in terms of reflection coefficient, voltage standing wave ratio, input impedance and directivity over a range of frequencies ranging from 2 GHz up to 2.9 GHz.
The analysis and optimization have been performed using the simulator HFSS (High Frequency Structure Simulator) based on the finite element method. Next, in order to validate our simulation, we use another electromagnetic simulator CST MWS (Computer Simulation Technology- MicroWaves Studio) which is based on the finite integration method. The simulation results of the two simulators agree well practically.
Keywords: Patch Antenna, Microstrip Line, RFID Application, Reflection Coefficient, VSWR, Input Impedance, Directivity, Simulators HFSS And CST.
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: HONEYBEE PROTECTION SYSTEM FOR DETECTING AND PREVENTING NETWORK ATTACKS
Author: AMAN JANTAN, ABDULGHANI ALI AHMED
Abstract: An effective system inspired from honeybees protection mechanism in nature is proposed to detect and prevent network attacks. The proposed approach consists of multi-agents deployed in distributed locations in the network to discriminate normal from malicious activates. These agents recognize a network attack using a mechanism contains Undesirable-Absent (UA) or Desirable-Present (DP) methods. The mechanism of recognizing the attacks is achieved through monitoring, detection and decision stages of protection. The UA method is used in the monitoring stage for matching the normal behaviour based on absence of attacks’ signatures. The DP method is used in the detection stage for
matching the malicious behaviours based on existence of attacks’ signatures. The detected attack is
reported for prevention in the decision stage. Neural network which trained by Back Propagation algorithm (BP) is used to learn the patterns of network attacks. The performance of the proposed honeybee system is evaluated using KDD’99 dataset. The obtained results show that the protection
mechanism is deployable and capable to detect various types of attacks while maintaining a low rate of false alarms.
Keywords: Network Attacks; Honeybee Protection System; Neural Networks; Back Propagation Algorithm.
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: A UNIFIED MODEL FOR ROAD NETWORKS USING AGENT TECHNOLOGY
Author: T.KARTHIKEYAN, S.SUJATHA
Abstract: The research work in this paper proposed and evaluated a dynamic unified model for Road Networks using various developed agents. An LTCDM (Linear Traffic Control Dynamic Model) is a multivariate dynamic model which uses a graph in which the vehicles are represented as nodes considering time series of flows at the various data collection site and uses finite capacity queuing theory. This dynamic and integrated model constructs real time decision making based on the host architecture and road network loads. The proposed model make use of Congestion Aware Multi Agent Path- planning (CAMAP) Algorithm to achieve social optimum by minimizing aggregate functioning time of all the
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology - June 20...
http://www.jatit.org/volumes/Vol64No1/sixtyfourth_1_2014.php
agents to handle congestion effectively in this model. The aim of the research focuses on the development of LTCDM for road networks by integrating various mobile agents for handling traffic in road networks dealing with travel time uncertainty, congestion detection, severity, prioritization of emergency vehicles and finding best alternative path to avoid congestion. The proposed model also enhances the better quality of service for road networks by improving safety applications, finding best route and drivers comfort. The experimental study described in this paper has been carried out by NS2, SUMO and MOVE .By simulation results, it has been proved that the proposed integrated dynamic and unified model LTCDM attain high throughput and scalability compared with the existing models on road networks.
Keywords: LTCDM, MATLB, PCM, FMSA, IMAC, QOS
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: EFFICIENT ENERGY BASED CONGESTION CONTROL SCHEME FOR MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS
Author: S.SHEEJA, DR.RAMACHANDRA V PUJERI
Abstract: In recent years, MANET is the popular and growing network used in various applications. Here the mobile nodes are randomly moving without any access point. Due to mobility of nodes, energy consumption of the network goes higher. More energy consumption occurs due to retransmission of packets and occurrence of packet loss unlimitedly. So the main goal of the network is to ensure more energy efficiency. To provide minimum energy consumption and avoiding more congestion, energy consumption model and multipath routing scheme is needed in networks. In this research paper, we developed an Efficient Energy based Congestion Control Scheme (EECCS) for congestion avoidance and to improve energy efficiency of the mobile nodes. Here the cross layer design is deployed to improve the network performance. The multipath routing is focussed to avoid congestion and to increase network lifetime. We also demonstrated the energy consumption mathematical model to illustrate the node’s
minimum energy consumption level in the network. Probability of the retransmission of packets is reduced with the help of calculating the energy level of data and acknowledgment packets. By using extensive simulation, the proposed scheme achieves minimum energy consumption, low packet loss ratio, high packet delivery ratio, low end to end delay and overhead than our previous schemes like ECAS, CLSMRSCA.
Keywords: MANET, Probability Of Retransmission Of Packets, Cross Layer Design, Multipath Routing, Energy Consumption Model , Packet Delivery Ratio, Packet Loss Ratio, End To End Delay, Overhead And Network Lifetime
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: LATENCY AND ENERGY AWARE BACKBONE ROUTING PROTOCOL FOR MANET
Author: P.FRANCIS ANTONY SELVI, M.S.K.MANIKANDAN
Abstract: Earlier woks on latency reduction in mobile ad hoc network (MANET) routing, lead to huge energy consumption due to the heavy load on each mobile node. There is a trade-off between energy reduction and latency reduction. Moreover, existing latency reduction techniques rarely consider retransmission latency, queuing latency and MAC layer latency apart from routing latency. In this paper, we propose to design a latency and energy aware backbone routing protocol for MANET. In the proposed protocol, backbone nodes collect the information of Residual Energy, Delay, MAC contention and Load from the nodes using neighbor monitoring mechanism. The collected information is stored in the Local Topology table from which the best routing paths are selected using the backbones.
Keywords: Latency Reduction, MANET, Energy Consumption, MAC, Routing Protocol
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: VLSI IMPLEMENTATION OF KEY DEPENDENT SUBSTITUTION BOX USING ERROR CONTROL ALGORITHM FOR SUBSTITUTION-PERMUTATION SUPPORTED CRYPTOGRAPHY
Author: B. SENTHILKUMAR, V. RAJAMANI
properties of the (8, 4) Extended Hamming Code and its error control logic to produce 256 unique elements in one S-box over finite Galois Field (GF) (28). Row – Column Index based selection of four
8bit vectors and their modulo-2 addition is employed for both byte substitution and its inverse. Proposed substitution method provides optimal substitution output probability with 40320 S-boxes for a single message byte over GF (28). Proposed method removes the direct relationship between linear and algebraic expressions of S-box vectors and byte substitution technique of S-box for strengthening our structure against linear and differential attacks. High nonlinearity penetration of original input message bits is achieved by applying shift based key schedules for round transformations and bit permutation based S-box vectors in proposed byte substitution. Proposed design is simulated and synthesized using VHDL coding for Spartan3E FPGA (XC3S500E-PQG208) and the simulation results are shown. Various substitution output results are shown by proposed S-boxes simulation for its optimal application. This paper concludes that novel Key dependent Substitution Box using Error Control Algorithm is an alternative solution to the existing threats on cryptography algorithms.
Keywords: Key dependent S-box, Extended Hamming Code, Substitution-Permutation cryptosystem, Row-Column Indexed byte substitution, Crypto-coding.
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: A NOVEL HYBRID AUTHENTICATION METHOD BASED ON ORIENTATION MAPS AND SERVER AIDED SIGNATURE FOR M COMMERCE SECURED TRANSACTIONS
Author: R.ARUN PRAKASH, K.M.MEHATA, C.CHELLAPPAN
Abstract: Mobile commerce (m-commerce) refers to the ability to perform wireless commerce transactions using mobile applications in mobile devices. It is an innovative concept and is emerging in a context of an established norms, regulations and standards. This paper presents a study of adoption determinants for mobile commerce, focusing on end-users of a mobile commerce pre-paid service. The main objective of the study is twofold; to determine an algorithm that improves security and decreases the time delay for processing of an adoption model by applying it to the results of the study. In order to investigate the field of mobile commerce service adoption, information related to its’ end-users was gathered. The framework
was applied to the results of the study in order to validate its concepts. We proposed a model based biometric identification with SAS algorithm to obtain digital signature over the conventional method of merely algorithms to acquire signature. Biometric Identification Systems are widely used for unique identification of humans mainly for verification and identification. Biometrics is used as a form of identity access management and access control. Fingerprints are considered to be the best and fastest method for biometric identification. Hence we have adopted the finger print recognition for improving security. They are secure to use, unique for every person and do not change in one's lifetime. The findings of the case study indicate strong support for triangulating the three perspectives namely secured access, lesser processing delay and better signature generation method. The results of the same have been analysed and presented in this paper.
Keywords: M Commerce, Biometric Authentication, RSA Signature, SAS Signature, Feature Extraction
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: CUSTOM FUSION BASED ON BARYCENTER
Author: ABDELBAKI ISSAM, BEN LAHMAR EL HABIB, LABRIJI ELHOUSSIN
Abstract: Searching for information on the Internet is not only an activity newly rediscovered, but also a strategic tool to achieve a wide variety of information. Indeed, it’s extremely important to know how to find the
information quickly and efficiently. Unfortunately, the Web is so huge and so little structured, that gathering precise, fair and useful information becomes an expensive task. In order to define an information retrieval tool (meta search engine) that brings together multiple sources of information search, interest must be credited to the merger phase of search engines results. On the other hand, information search systems tend primarily to model the user with a profile and then to integrate it into the information access chain, to better meet its specific needs.
This paper presents a custom fusion method based on physical Barycenter method and values retrieved from the user profile. We evaluated our approach on multiple domains and we present some experimental results.
Keywords: Information search system, meta-search engine, Fusion, Barycenter, User profile.
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology - June 20...
http://www.jatit.org/volumes/Vol64No1/sixtyfourth_1_2014.php
Title: SECURITY BASED WEIGHTED CLUSTER ROUTING IN MANET
Author: Mrs.J.NANDHINI, Dr.D.SHARMILA, K.DHIVITHRA, K.S.BALASUGANYA, D.GOWRI
Abstract: In close to future computing atmosphere, usually expected the recent progresses and advances in computing and communication technologies. Mobile Adhoc Network (MANET) is one of the promising fields for analysis and development of wireless network. Routing in wireless MANET has to be economical and saving of resources. One in every of the approaches to understand these items is completed by dividing the network into clusters and every cluster have a Cluster Head (CH) that’s
answerable for the nodes associated among the cluster. Due to the dynamic atmosphere and random topology, the CH election technique has to be done per applicable criteria. This paper aims at weight based cluster routing with the improvement of QoS along with security. Here CH is chosen with relevance to weighted parameters like bandwidth, energy efficiency and link quality thereby giving higher QoS and elliptic curve digital signature algorithm which provides security from attacks by victimization Network Simulator-2. On scrutiny with CBRP protocol, this weight based cluster routing protocol achieves the QoS in economical and efficient manner.
Keywords: MANET, CBRP protocol, Security, Clustering, QoS.
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF CLASSIFICATION MODELS FOR DETECTION IN IP NETWORKS INTRUSIONS
Author: ABDELAZIZ ARAAR, RAMI BOUSLAMA
Abstract: Intrusion detection is an essential mechanism to protect computer systems from many attacks. We presented a contribution to the network intrusion detection process using six most representative classification techniques: decision trees, BayesNet, NaïveBayes, Rules, SVM, and Perceptron multi-layer network. In this paper, we presented a feature selection using random forest technique, towards two dimensional dataset reductions that are efficient for the initial and on-going training. The well known KDD'99 Intrusion Detection Dataset is tremendously huge and has been reported by many researchers to have unjustified redundancy, this makes adaptive learning process very time consuming and possibly infeasible. 20 attributes are selected based on errors and time metrics. Performance and accuracy of the six techniques are presented and compared in this paper. Finally, improvement of supervised learning techniques is discussed for detecting new attacks. The different results and experiments performed using the principal component analysis and the enhanced supervised learning technique are thoroughly presented and discussed. We showed that J48 is the best classifier model for IDS with reduced number of features. Finally, avenues for future research are presented.
Keywords: IDS, KDD99, Feature Selection, Classification, Decision Trees, Rules, Bayesnet, Naïvebayes, SVM, And Perceptron Multi-Layer Network
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: AN EFFECTIVE CROSS RATE PACKET AGGREGATION SCHEME FOR VIRTUALIZED NETWORK CLOUD COMPUTING
Author: A. KAMALESWARI, P. THANGARAJ
Abstract: Virtualization enables the cloud computing. The bottleneck of transferring packets from driver domain to Virtual Machines (VMs) in I/O channel was eliminated by Basic Aggregation and Destination based Aggregation scheme, but it is limited to aggregating packets for a particular destination and missing out more effective packet combinations. This can cause significant loss in capacity as packets on high quality links get demoted to low transmission rates. In this paper, using a new packet aggregation scheme, the network performance is improved. The proposed scheme aggregate the packet based on data rate dynamically on the I/O channel characteristic and it achieves better communication in cloud network, it balance the data rate between wired and wireless. The proposed model named as Cross Data Rate based Aggregation (CDRA) divides packet in MAC queue into groups based on the data rate, packets are to be transmitted at driver domain to VM. The algorithm aggregates packets in the same group and broadcasts the aggregated frame at the data rate of that group. CDRA aggregates packets for all links that have varying data rate and able to transmit packets out of order. The experimental evaluation shows that selectively demoting packets can further improve performance.
Keywords: Aggregation, Cloud computing, Cross-Data Rate, Driver domain, Virtualization.
Full Text
Title: ZONE BASED RELATIVE DENSITY FEATURE EXTRACTION ALGORITHM FOR UNCONSTRAINED HANDWRITTEN NUMERAL RECOGNITION
Author: K.N. SARAVANAN1, Dr. R. ANITHA
Abstract: The recognition of handwritten characters and numerals has been a challenging problem among the researchers for few decades. This paper proposes a relative density feature extraction algorithm for recognizing unconstrained single connected handwritten numerals independent of the languages. The proposed method consists of four phases, namely, image enhancement (dilation), representation (zone based), feature extraction (relative density) and recognition (minimum distance classifier). The handwritten numerals must be enhanced with dilation, in order to connect the broken digits. After enhancement, the dilated binary images can be represented as a mid-point aspect ratio class interval values. There can be M * N zones and subsequently there would be 2M*N relational density exist using mid-point aspect ratio class interval values. In order to minimize the number of features, a subset of W relative densities has been extracted from the binary image since the relative density is too large to be handled efficiently. The minimum distance classifier technique has been used to recognize the given numerals. The proposed algorithm would be an alternative to recognize the handwritten numerals for recognizing unconstrained single connected handwritten numerals. The method sounds promising with a recognition rate of 92.8567%.
Keywords: Handwritten numeral recognition, Feature extraction, Zoning, Minimum distance classifier, K-NN classifier.
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: NOVEL FRAMEWORK FOR THE PORTFOLIO DETERMINATION USING PSO ADOPTED CLUSTERING TECHNIQUE
Author: B.UMADEVI, D.SUNDAR, DR.P.ALLI
Abstract: Methods based on the Econometrics, Statistics, Machine learning, heuristics and data mining methods are used to predict the market behavior and investment decisions. In this paper we have presented a novel approach for the portfolio creation using the PSO adopted K-Means. Then the NARX and the Markowitz model have been employed to carry over the efficient determination of the portfolio. The data from the Nifty from March 2010 to October 2010 has been used. The Stocks from various sectors are used to build the portfolio. The proposed work is promising and the results obtained are outperforming. Future work could be concentrated on the various multi objective optimizations as the Markowitz model paves the way to the future research.
Keywords: PSO K Means, Nonlinear Autoregressive Exogenous (NARX) Network, Markowitz Model.
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: DYNAMIC VOLTAGE RESTORER USING THREE PHASE AC-AC CONVERTER
Author: V.JAYALAKSHMI, DR.N.O.GUNASEKHAR
Abstract: In this paper, Dynamic Voltage Restorer using Z source AC - AC converter has been proposed to mitigate the voltage sag/ swell. Dynamic Voltage Restorer (DVR) is an effective custom power devices used to protect the sensitive loads against voltage sag and swell. The three phase Z source AC-AC converter has been employed to perform the direct AC/AC conversion. The Z source network can produce any desired output AC voltage, which is a greater or less voltage than the line voltage. Hence it enhances the voltage restoration capability of DVR. The gating pulses for the bidirectional switch are generated using sinusoidal PWM technique and its associated circuitry. This proposed topology is simulated under voltage sag /swell using Matlab / Simulink and the simulation results are presented to show that the system effectively compensates the voltage sag/ swell.
Keywords: Dynamic Voltage Restorer, Voltage Sag, Voltage Swell, Z- Source AC-AC Converter.
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: OPTIMAL LOCATION OF FACTS DEVICES FOR POWER QUALITY ISSUES USING PSO AND BAT ALGORITHM
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology - June 20...
http://www.jatit.org/volumes/Vol64No1/sixtyfourth_1_2014.php
Author: S.BALASUBRAMANIYAN, T.S.SIVAKUMARAN
Abstract: This paper proposes an optimal location of FACTS devices in power system using Evolutionary algorithms. Using the proposed method, the location of FACTS controllers, their type and rated values are optimized simultaneously. From the FACTS family, series device Thyristor Controlled Series Compensator (TCSC), Shunt device Static Compensator (STATCOM) and series and shunt device Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) are considered. The proposed algorithms are very effective methods for the optimal choice and placement of FACTS devices to improve the power quality of power systems. The proposed algorithm has been applied to IEEE -30 bus system.
Keywords: Bat Algorithm, FACTS devices, Optimal location, PSO algorithm, Power Quality
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: MRAS BASED SENSORLESS INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE USING VARIABLE STRUCTURE CONTROL
Author: R.KANNAN, Dr. J. KANAKARAJ
Abstract: Induction motor drives are widely used in industries for its simple and easy control. Variable structure controller (VSC) for an induction motor drive is an effective method of control in case of non linearities and uncertainties to enhance robustness. Dynamic performance of Induction motor drives is an essential characteristic for many industrial applications. Quality of the product is an industry and the profit of the industry are mainly depends on the performance of the induction motor drive. Transient state performance of the VSC based an induction motor drive to be improved. Since conventional VSC based induction motor drive has PI controller based speed controller. To enhance the performance of the system this paper proposes Model reference Adaptive System based speed controller in VSC. The design is simple and easy to be implemented. The entire system is simulated using Matlab / Simulink to analyze the performance of a drive. Performance of a drive using Model reference Adaptive System VSC is analysed and compared with conventional Proportional and Integral VSC. To analyze the dynamic performance of the system machine is subjected to constant and variable load in this paper.
Keywords: Induction Motor, variable structure controller, Model reference Adaptive System, PI controller.
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: AN INVESTIGATION OF SUMMARY BASED CLASSIFIERS
Author: ESTHER HANNAH. M , PRAKASH KUMAR, SASWATI MUKHERJEE
Abstract: The work presents a comparative investigation of the performance of some of the well-known machine learning classifiers in the task of summarization. The objective of this paper is to evaluate the capability of classification algorithms in predicting summary sentences and compare its prediction performance against ten well-known machine learning models in the context of the DUC 2002 dataset. Classical classification algorithms based on Trees, Rules, Functions, Bayes and Lazy learners are used in the study. We have used 350 text documents from DUC2002 (Document Understanding Conference 2002) for prediction. This paper evaluates the capability of classification algorithms in predicting candidate sentences for summary generation. The results indicate that the prediction performance of machine learning classifiers in the task of text summarization is better than the baseline performance.
Keywords: Summarization, Classification, Evaluation, Machine Learning, Feature Extraction
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: A NOVEL COALITION GAME THEORY BASED RESOURCE ALLOCATION AND SELFISH ATTACK AVOIDANCE IN COGNITIVE RADIO AD-HOC NETWORKS
Author: A.VELAYUDHAM, G.V.S GOHILA, B.HARIHARAN, M.M RAMYA SELVI
resources. This self-centered cognitive radio can critically degrade the performance of the network. So a skillful resource allocation strategy should be adopted to avoid these selfish attacks in the network. The conventional resource allocation approaches in the cognitive network are fully dependent. In this scheme, the coalitional game theory incorporates multiple PU and SU in a pool, in which the PU allow other SU’s to make use of its resources in contract or agreement on a timely basis. This scheme adopts
efficient resource allocation in a multichannel cooperative system. This proposed system follows the core concept and also supports Shapley value in order to have a non-empty core in the network. The Shapley value equally distributes the payoff throughout the users in the network. It insists that the performance of the proposed scheme has been improved to a near optimum value of 93.7% rather than the performance of the existing COOPON system which figured to only about 74%. By this resource allocation approach, the selfish attacks can be prevented and thereby the efficiency of resource utilization in the network can be considerably increased.
Keywords: Cognitive Radio, CRAHN, Selfish Attacks, Pool, Coalitional Game Theory, Shapley Value
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: DYNAMIC STRUCTURED PRIVILEGES WITH MULTI-OWNER DATA SHARING FOR DYNAMIC GROUPS IN THE CLOUD
Author: A.VELAYUDHAM, M.M RAMYA SELVI, B.HARIHARAN, G.V.S GOHILA
Abstract: Cloud Computing is a general term used to describe a new class of network based computing that takes place over the Internet. The most basic and important service offered by cloud is data storage. However the major obstacle in the multi owner data sharing for the wide deployment of cloud computing is identity privacy while preserving data. In the existing approaches, a secure multiowner data sharing scheme, named Mona is used, for dynamic groups in the cloud that uses the group signature and dynamic broadcast encryption techniques. But this method to invoke and revoke of client is not dynamic on user privileges. Also the system supports only static groups. In the proposed scheme, we present an efficient structure for facts and figures sharing scheme to achieve dynamic privileges. Using this structure, any data owner can change the service class of each user dynamically and change the structure of privileges flexibly when it is needed. The proposed is also designed to support group migration between the users so that the users can revocate and change the group at any time. Thus by using the dynamic structure privileges, the system performs linearly with the increase in the number of users. But in the existing approaches, when the number of users increases the time execution is also increased which makes the system time consuming.
Keywords: Cloud Computing, Multi Owner Data Sharing, Group Signature, Broadcast Encryption, Dynamic Privileges
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: SURVEILLANCE OF VEHICLE OBJECTS WITH AERIAL IMAGES USING LOCALIZATION AND POSTURE BASED LOCAL GRADIENT MODEL
Author: R.C.KARPAGALAKSHMI, DR.D.TENSING
Abstract: Traffic scenes in road network needs to be monitored in different dimensional perspective to address the issues generated at various time instances. One of the major challenges observed in traffic scenes in road network is to address the vehicle tracking at different dimensional perspective for various time instances. One such application that has received greater significance is the mechanism to develop a full proof vehicle traffic control scheme. Videos fitted on different proposition of the signal junction able to view at respective image positioning and the overall traffic may rise to abnormality. Many studies have been examined for vehicle traffic control scheme. The recently used scheme is model based on simple object recognition and localization of road vehicles based on the position and orientation of vehicle image data. But the drawback of the approach is that if the shape of the vehicle and its pose varies in multiple junction coordination, the model based recognition is an inefficient one. To overcome the issues, in this work we are going to implement surveillance image object recognition and localization using improved local gradient model. The vehicle-object shape recognition and pose recovery in the traffic junction is carried out for varied traffic densities. An experimental evaluation is carried out to estimate the performance of the proposed Surveillance of Vehicle Object Recognition and Localization (SVORL) using improved gradient model in terms of vehicle density, traffic junction points, and computation time and compared with an existing model based on simple object recognition and localization.
Keywords: Vehicle Object Recognition, Object Localization, Improved Gradient Model, Ray Traced Templates, Road Extraction
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology - June 20...
http://www.jatit.org/volumes/Vol64No1/sixtyfourth_1_2014.php
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: EFFICIENT ENERGY BASED CONGESTION CONTROL SCHEME FOR MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS
Author: S.SHEEJA, DR.RAMACHANDRA V PUJERI
Abstract: In recent years, MANET is the popular and growing network used in various applications. Here the mobile nodes are randomly moving without any access point. Due to mobility of nodes, energy consumption of the network goes higher. More energy consumption occurs due to retransmission of packets and occurrence of packet loss unlimitedly. So the main goal of the network is to ensure more energy efficiency. To provide minimum energy consumption and avoiding more congestion, energy consumption model and multipath routing scheme is needed in networks. In this research paper, we developed an Efficient Energy based Congestion Control Scheme (EECCS) for congestion avoidance and to improve energy efficiency of the mobile nodes. Here the cross layer design is deployed to improve the network performance. The multipath routing is focussed to avoid congestion and to increase network lifetime. We also demonstrated the energy consumption mathematical model to illustrate the node’s
minimum energy consumption level in the network. Probability of the retransmission of packets is reduced with the help of calculating the energy level of data and acknowledgment packets. By using extensive simulation, the proposed scheme achieves minimum energy consumption, low packet loss ratio, high packet delivery ratio, low end to end delay and overhead than our previous schemes like ECAS, CLSMRSCA.
Keywords: MANET, Probability of retransmission of packets, Cross Layer design, Multipath Routing, energy consumption model , packet delivery ratio, packet loss ratio, end to end delay, overhead and network lifetime
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: A SURVEY OF RESEARCH AND PRACTICES IN MULTIPROCESSOR SYSTEM ON CHIP DESIGN SPACE EXPLORATION
Author: V.PRASANNA SRINIVASAN, A.P.SHANTHI
Abstract: This survey presents a perspective on the existing research and practices initiated for the Design Space Exploration (DSE) in Multiprocessor System on Chip (MPSoC) technology. Reduction in size as well as adding more functionality within a single chip by incorporating multiple processors remains the key in the development of the modern MPSoC. This rapid development has been made possible because of the techniques used for scaling down the size of the chip in the field of integrated circuits. MPSoC has been considered as the best candidate for applications such as networking, telecommunication, multimedia, etc. which require high computational demand, high performance, flexibility, high energy efficiency, and low cost design. The designers have the onerous task of building MPSoCs for such applications because they have huge design options in terms of Processing Elements (PEs), micro-architectural features, interconnects, etc. to be considered with specific constraints. Exhaustive search is prohibitive because of the sheer design space size as well as the time to market considerations. Coverage of design space during the exploration process, and evaluating a single design point for finding the optimal design are the two issues that should be considered in any DSE process. This paper provides a comprehensive survey on the existing DSE techniques at the system and micro-architectural levels, the evaluation methodologies and the tools/frameworks with their comparison with respect to the design parameters considered.
Keywords: Multiprocessor Systems On Chip (Mpsoc), Design Space Exploration (DSE), Embedded System Design, Design Space Pruning, Multi-Objective Optimization
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: DESPECKLING AND SEGMENTATION OF ULTRASOUND IMAGES OF CAROTID ARTERY FOR PLAQUE DIAGNOSIS IN HEALTH CARE
Author: D.SASIKALA, M.MADHESWARAN
Abstract: A new method for segmentation of the carotid artery for classifying it as diseased or normal towards plaque diagnosis is proposed in this paper. Kernel Fuzzy C- Means clustering is used for segmenting the longitudinal section of the carotid artery using which the wall layers of the artery are identified for classifying it as diseased or normal. As a pre-processing step a–nonlinear mean filter is used for speckle
noise may remove useful information in the images like small lesions or artefacts, plaque or calcification in the arteries. Hence a filter that detects the speckle in each and every pixel and suppresses the speckled pixel is proposed in this paper. The algorithm was applied on ultrasound images of the carotid artery for extracting the boundary of the arterial wall and detecting the wall layers for clinical purposes. The results show excellent performance of the method.
Keywords: Carotid Artery, Clustering, Speckle, Plaque, Segmentation.
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: APPLICATION OF BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE TO SUPPORT MARKETING STRATEGIES: A CASE STUDY APPROACH
Author: YOHANNES KURNIAWAN, ALI GUNAWAN, STEPHEN GREGORIUS KURNIA
Abstract: This paper discusses the business intelligence and its role to improve the company’s competitive
advantage through the utilization of various data, information and knowledge held by the company as a raw material in the decision making process. The tight of market competition and its changes has forced the marketers to apply an appropriate strategy in order to survive and to follow the market changes and even to come out as a market leader. The implementation of this business intelligence should be based on the understanding of basic concept of marketing, the focus on customer’s need, the sense of market
changing, and also the support of all components in the company.
Keywords: Business Intelligence, Marketing Strategies, Application.
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: BONE FRACTURE DETECTION USING OPENCV
Author: SAMUEL FEBRIANTO KURNIAWAN, I KETUT GEDE DARMA PUTRA, A.A KOMPIANG OKA SUDANA
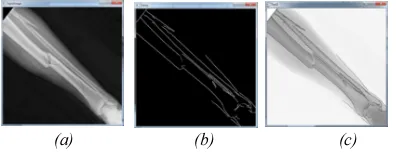
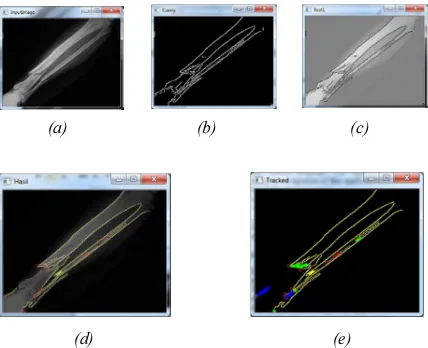
Abstract: Image processing is important in modern data storage and data transmission especially in progressive transmission of images, video coding (teleconferencing), digital libraries, image database, and remote sensing. The purpose of this project is to find out the accuration of an X-Ray Bone Fracture Detection using Canny Edge Detection Method. Fractured bone is a bone condition that suffered a breakdown of bone integrity. A disconnected connection between two cartilages also categorized as bone fracture. Normally, bones have elasticity and a great number of strength. Bone fracture only happen when the bones took a force beyond their elasticity or strength. This system is built using OpenCV library combined with Canny Edge Detection method to detect the bone fracture. Canny Edge Detection method is an optimal edge detection algorithm on determining the end of a line with changeable threshold and less error rate. The simulation results have shown how canny edge detection can help determine location of fractures in x-ray images.
Keywords: Fracture, Edge, Edge Detection, Canny, Threshold, x-ray images.
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: EVALUATION SUBQUERY METHODS IN MICROSOFT SQL SERVER 2008
Author: TANTY OKTAVIA
Abstract: Frequently user compiles a query to satisfy business process needs, whether directly using DBMS or connecting into application system. There are many methods that can be used to generate desired results to support transaction, but all the query processing should be run effectively and efficiently. A significant aspect of query processing is how to choose an efficient execution strategy to minimize resource usage. Based on competitive environment in industry, many companies compete with each other to be a number one. For this reason, company doing a lot of experiments, in order to accomplish a visions and mission objectives. One of those is increasing performance of the system to support daily activities. Nowadays, most of business process in company already integrated with information technology. All of data is consolidated by database, so user easily doing their job. According to this fact, user does not matter about how many transactions to be process per day, but how much time they need to process that transaction is the priority concern. Because of that, query optimization techniques become more important to be applied in many applications. In this research focused on measurement effectiveness of the method sub query which can be applied to reach optimal execution and present a comparative study
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology - June 20...
http://www.jatit.org/volumes/Vol64No1/sixtyfourth_1_2014.php
of various cost to declare Sub query. This study based on Microsoft SQL Server 2008 platforms.
Keywords: Query Processing, Microsoft SQL Server 2008, Sub query, Cost Control
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: EDCA LIMITATION WITH HIGH TRAFFIC REAL TIME APPLICATIONS
Author: AHMED ABU-KHADRAH, ZAHRILADHA ZAKARIA, MOHDAZLISHAH OTHMAN
Abstract: The simplicity of expanding and maintenance wireless network helped to use it widely in the public locations such as parks, airports and bus stations. Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) and Enhanced Distributed Channel Access (EDCA) protocols are used with WLANs. DCF protocol sends its data without any priority between different data types, and does not give any advantage of real time application such as voice over internet protocol (VOIP) or video conference. However EDCA protocol divides data to different class’s voice, video, best effort and background. Each class has its own priority
and parameters. The default values of EDCA protocol give voice traffic the highest priority. Quality of Service (QOS) parameters such as end to end delay, packet loss and jitter values determine if the protocol support QOS or otherwise. This paper evaluates the performance of DCF protocol and EDCA protocol by using OPNET simulation and shows the differences between them, depending on QOS parameter values. The result of simulation shows the limitation of EDCA protocol when increasing the number of VOIP users. Therefore the EDCA protocol tolerates specific number of real time applications with acceptable values of QOS parameters.
Keywords: DCF, EDCA, QOS
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: AN ECONOMIC APPROACH TO SPEED REGULATION OF INDUCTION MOTOR USING SUPER LIFT LUO CONVERTER
Author: P.ELANGOVAN, Dr.C .KUMAR, B .GOMATHY
Abstract: This paper proposes an economic approach for the speed control of Induction motor using positive output super lift Luo converter circuit. In the conventional method, the input of the inverter is derived from buck, boost or buck-boost converter which has the limitations over the DC link voltage level, complexity of control circuit and cost involved in system design. The proposed method uses positive output super lift Luo converter at the front end which boosts up the DC link voltage level in a wide range. The speed control of the induction motor is attained by controlling the firing angle of positive output super lift Luo converter instead of Inverter which leads to prevention of motor terminals from Common mode voltage stress. Super-lift Luo-converters are popular for high output voltage application over years. They have very high voltage transfer gains in geometric progression on stage-by-stage. The proposed system uses PI controller which is highly preferable for industrial applications. The simulation is conceded out by MATLAB/SIMULINK software.
Keywords: Induction motor, PI controller, Positive Output Elementary Super-Lift Luo Converter, Speed Regulation, Voltage Source Inverter
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: IMPLEMENTATION OF NONDOMINATED SORTING GENETIC ALGORITHM – II (NSGA-II)
FOR MULTIOBJECTIVE OPTIMIZATION PROBLEMS ON DISTRIBUTION OF INDONESIAN NAVY WARSHIP
Author: HOZAIRI, KETUT BUDA A, MASROERI, M.ISA IRAWAN
Abstract: The high number of crimes and infraction that occurred in the Indonesian seas show the weakness of Indonesia's marine security. This is caused by the limited number of warships of the Republic of Indonesia (KRI), the lack of budget provided by the State, the wide area of the marines in Indonesia that should be secured, and the less precise decision from the Navy in determining the safety operational management of Indonesian seas. Therefore, problems in securing Indonesian seas not only in the form of a single objective problem but has become a model of multi-objective problem. So there’s a way needed
This study will determine the best combination of a 100 solution recommended by NSGA II in the focus of the type of the ship, speed, radar range, endurance, the area vulnerability level, geography, human resources, so it can be obtained one ideal solution in the focus of the placements composition of 27 warships to the 7 sectors in the ARMATIM area by maximizing the coverage area and minimizing the operational costs.
The results of the optimization of NSGA-II with 100 iterations, it is resulted that 23 warships selected and 4 warships docking with a combination of warships in each sector (S1 = 2, S2 = 7 S3 = 6, S4 = 2, 3 = S5, S6 = 2, S7 = 1), the broader outcomes of the coverage area is 1, 722, 880 Mil2, so it can increase the security of territorial ARMATIM seas around 2% from the total secured area of 1,688,765 Mil2, and operational cost Rp. 4.521.548.485,- the optimization model is thus able to save about 10% of the State budget of the specified the budget of Rp. 5.000.000.000,-.
Keywords: Multiobjective Optimization Problems, NSGA II, Warship Distribution
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: DEVELOPMENT OF A CONVERGENCE SCHEME FOR ONE-TO-MANY COOPERATIVE WIRELESS SYSTEMS USING A NON-COOPERATIVE GAME
Author: OLUSEYE ADENIYI ADELEKE, MOHD FADZLI MOHD SALLEH
Abstract: In this paper, we propose a new scheme for ascertaining convergence in cooperative wireless communications, using a new type of game called the Bidding game. Previous related works have all considered networks with many source nodes interacting with either single or multiple relay nodes, but because of the need to consider how partners are selected as well as how power is allocated, we propose this new game-based convergence scheme, in which the conventional theories of economic bidding are applied and optimization tools are employed. In this work, we model the cooperative communication network as a single-user, multi-relay node system in which the source node acts as the auctioneer while the relay nodes or partners act as the bidders in the game. The resource being auctioned here is power. The relay node which offers the highest bid in terms of price is first selected by the source node and then allocated power by the source node and then the convergence scheme ascertains how fast convergence to equilibrium is reached in the game. We also show that there exists bidding and pricing mechanisms or strategies that lead to the maximization of network throughput or utility in cooperative communication networks. Simulations are run to validate our proposed scheme.
Keywords: Bidding game, Convergence, Cooperative communication, Power allocation, Relay node
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 10 June 2014 -- Vol. 64. No. 1 -- 2014
Full Text
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology - June 20...
http://www.jatit.org/volumes/Vol64No1/sixtyfourth_1_2014.php
© 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
249
BONE FRACTURE DETECTION USING OPENCV
1
SAMUEL FEBRIANTO KURNIAWAN,
2I KETUT GEDE DARMA PUTRA
,
3A.A KOMPIANG OKA SUDANA
1,2,3
Department of Information Technology, Udayana University, Indonesia
E-mail:
1samuelfebriantokurniawan@gmail.com
,
2
ikgdarmaputra@gmail.com
,
3
agungokas@hotmail.com
ABSTRACT
Image processing is important in modern data storage and data transmission especially in progressive
transmission of images, video coding (teleconferencing), digital libraries, image database, and remote
sensing. The purpose of this project is to find out the accuration of an X-Ray Bone Fracture Detection using
Canny Edge Detection Method. Fractured bone is a bone condition that suffered a breakdown of bone
integrity. A disconnected connection between two cartilages also categorized as bone fracture. Normally,
bones have elasticity and a great number of strength. Bone fracture only happen when the bones took a
force beyond their elasticity or strength. This system is built using OpenCV library combined with Canny
Edge Detection method to detect the bone fracture. Canny Edge Detection method is an optimal edge
detection algorithm on determining the end of a line with changeable threshold and less error rate. The
simulation results have shown how canny edge detection can help determine location of fractures in x-ray
images.
Keywords:
Fracture, Edge, Edge Detection, Canny, Threshold, x-ray images.
1.
INTRODUCTION
Digital image processing is an expanding area
with applications regarding to our daily lives,
especially in progressive transmission of images,
video coding (teleconferencing), digital libraries,
image database, remote sensing, and other
particular applied usage. Many image processing
and analysis techniques have been developed to aid
the interpretation of remote sensing images and to
extract as much information as possible from the
image. The huge collection of digital images are
collected due to the improvement in the digital
storage media, image capturing devices like
scanners, web cameras, digital cameras and rapid
development in internet. This leads to rapid and
efficient retrieval of these images for visual
information in different fields of life like medical,
medicine, art, architecture, education, crime
preventions, etc [1,2].
The medical imaging field has grown
substantially in the recent year and has generated
additional interest in methods and tools for
management, analysis, and communication of
medical
image.
Many
diagnostic
imaging
modalities, such as x-ray, magnetic resonance
imaging (MRI), digital radiography, and ultrasound
are currently available and are routinely used to
support clinical decision making. By using medical
imaging, physicians are able to glean qualitative
and quantitative information about anatomy and
physiology of the patients. With this advantages,
medical imaging has become central to medical
diagnosis. Thus, with the advances in computer
processing capabilities, it has become possible to
approach the problem of automating diagnosis in
medical imaging. This paper will focus on canny
edge detection that help radiologist in automated
diagnosis image. Radiologist often experiencing
difficulty on reading x-ray image. This can be
caused by the lack of lighting, fractures the hardly
seen by naked eyes, or noises the happened on
image capturing process. By building the system,
we hope the system can help people especially
radiologist on detecting bones anomaly that
happened on x-ray images [3].
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
10th June 2014. Vol. 64 No.1
© 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
250
2.
IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUE
Image processing techniques are employed to
develop this algorithm. It is discussed in detail in
this section.
2.1 Canny Edge
Edges are considered to be most important
image attributes that provide valuable information
for human image perception. Edge detection is a
very complex process affected by deterioration due
to different level of noise [4]. An edge is the
boundary between an object and the background.
Edge detection is identifying points in a digital
image at which the image brightness changes
sharply or more formally has discontinuities. The
purpose of detecting sharp changes in image
brightness is to capture important events and
changes in properties of the world [4].
Edge detection is used for identification of
blurred frame broad classification among smooth
and rough surface classification of cement and
asphalt. The Canny edge detection is performed on
the frames with the sensitive threshold values
(upper threshold 10000 and lower threshold 4900)
and again it is performed with the insensitive
threshold values (upper threshold 50000 and lower
threshold 9800) [4]. If a pixel has a gradient greater
than the upper threshold, then it is an edge pixel. If
a pixel has a gradient lower than the lower
threshold, it is not an edge pixel. If the pixel’s
gradient is between the upper and the lower
thresholds, then it is considered as an edge, only if
it is connected to a pixel that is above the high
threshold value as given in [5,11].
Canny is one of modern edge detection method
that founded by Marrdan Hildreth, who is doing
research in modeling human visual perception.
There are several criteria on edge detecting that can
be fulfilled by Canny Edge Detection:
1. Canny has better detection (for detection
criteria). Canny method capable to marks all
existing edges matching with user determined
parameter’s thresshold. Also giving high
flexibility on determining thickness level of
edge detection according to the required
conditions.
2. Canny has better localizing way (localize
criteria). Canny capable on producing minimum
gap between detected edge and the real image
edge.
3. Obvious response (response criteria). Only one
response for every edge. This make less
confusion on edge detection for the next image.
Chosing parameters on Canny Edge Detection
will giving effect on every result and edge
detection. The parameters are :
a.
Gaussian Deviation Standard Value.
b.
Thresshold Value.
The following is the steps to do Canny Edge
Detection.
1. Remove all noise on the image by implementing
Gaussian Filter. The result is an image with less
blur. It is intended to obtain the real edges of the
image. If we did not apply the Gaussian Filter
before, sometimes the noise itself will be
detected as an edge.
2. Detect the edge with one of these detection
operators, like Roberts, Perwit, or Sobel by do
horizontal searching (
Gx
) and vertical searching
(
Gy
). The following is the sample of edge
detection operator (Sobel operators).
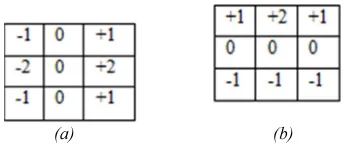
(a) (b)
Figure 1 Sobel Operator (a) Gx, (b) Gy
The result from both operators combined to
obtain the summary of vertical edge and horizontal
edge with this formula[6]:
(3)
3. Determining direction of the edge by using the
following formula:
ଶ
ଶ
(4)
ீ௬
ீ௫
(5)
Canny Edge Detection using two thresholds
(maximum threshold and minimum threshold). If
pixel gradient higher than maximum threshold,
pixel will be marked as an edge. If the pixel
gradient lower than minimum threshold, the pixel
will be denied as background image. If the pixel
gradie