1
AN ANALYSIS OF TEACHERS’ TALK MANAGEMENT USED
BY ENGLISH TEACHERS AT SMA YAPIP SUNGGUMINASA
(A Descriptive Research at the Twelve Grade)
A Thesis
Submitted to the Faculty of Teacher training and Education
Muhammadiyah University of Makassar in Partial Fulfillment of the Recruitment for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan
AULIYANI
10535651615
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION MUHAMMADIYAH UNIVERSITY OF MAKASSAR
FAKULTAS KEGURUAN DAN ILMU PENDIDIKAN
UNIVERSITAS MUHAMMADIYAH MAKASSAR
SURAT PERNYATAAN
Nama : Aulyani
NIM : 10535 6516 15
Program : English Education
TITLE : AN ANALYSIS OF TEACHERS’ TALK MANAGEMENT USED BY ENGLISH TEACHERS AT SMA YAPIP SUNGGUMINASA
(A Descriptive Research at the Twelve Grade)
Skripsi yang saya ajukan di depan tim penguji adalah hasil karya saya sendiri bukan hasil ciplakan dan tidak dibuatkan oleh siapapun.
Demikian pernyataan ini saya buat dengan sebenar-benarnya dan bersedia menerima sanksi apabila pernyataan saya tidak benar.
Makassar, 17Februari 2020
Yang membuat perjanjian
FAKULTAS KEGURUAN DAN ILMU PENDIDIKAN
UNIVERSITAS MUHAMMADIYAH MAKASSAR
SURAT PERJANJIAN
Nama : Aulyani
NIM : 10535 6516 15
Program : English Education
TITLE : AN ANALYSIS OF TEACHERS’ TALK MANAGEMENT USED BY ENGLISH TEACHERS AT SMA YAPIP SUNGGUMINASA
(A Descriptive Research at the Twelve Grade)
Dengan ini menyatakan perjanjian sebagai berikut:
1. Mulai dari penyusunan proposal sampai dengan selesai skripsi saya, saya akan menyusun sendiri skripsi saya.
2. Dalam menyusun skripsi, saya akan selalu konsultasi dengan pembimbing. 3. Saya tidak akan melakukan penjiplakan (plagiat) dalam menyusun skripsi saya. 4. Apabila saya melanggar perjanjian saya seperti yang tertera pada butir 1,2 dan 3
maka saya bersedia menerima sanksi sesuai dengan aturan yang berlaku. Demikian perjanjian ini saya buat dengan penuh kesadaran.
Makassar, 17 Februari 2020 Yang membuat perjanjian
MOTTO
There is no Limit of
struggling.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Alhamdulillahi Robbil Alamin. The researcher expresses her highest gratitude to the almighty Allah SWT, Who has given His guidance, blessing, and mercy to her in completing this thesis. Salam and Shalawat are addressed to the last prophet Muhammad SAW.
The researcher expresses her sincerely deepest gratitude to her parents Abidin and Sumarni who always pray, motivate and sacrifice everything for her success. Further, the researcher expresses her gratitude for all of her sister and brother for the support in her education.
The researcher realized that in carrying out the research and writing this thesis, many people have contributed their valuable suggestion, guidance, assistance, and advice for the completion of this thesis. Therefore, the researcher would like to acknowledge them:
1. Prof. Dr. H. Rahman Rahim, SE., MM, Rector of Muhammadiyah University of Makassar for his advices during her study at the university
2. Erwin Akib, M.Pd., Ph. D, Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty for all advices and motivation
3. Ummi Khaerati Syam, S.Pd., M.Pd, Head of English Education Department for all motivations
4. Nurdevi Bte Abdul, S.Pd.,M.Pd the first consultant for the valuable suggestion, motivation, support and guidance in writing this thesis 5. Wildhan Burhanuddin, S.Pd., M.Hum the second consultant for all of
the invaluable knowledge, professional expertise, and motivation along the researcher finished this thesis.
6. The researcher beloved classmates HEROES English Department 2015 for sweet memories and unforgettable moment during his study in the university
7. All of lecturer and staff of English Education Department who cannot be named one by one for all of the suggestions and advices
8. These awesome friends: Dian Furqani, Mar’atun shalihah, Meisarah Hendri Tri Wulandari, Nurjannah, Lutfi, Nurhasanah, Fitrah Rahmadani for the great cooperation, support, and sharing in studying and writing this thesis
9. For all who gave valuable suggestion, guidance, assistance, and advice in completing this thesis
Makassar, December 2020 Researcher
ABSTRACT
AULYANI. 2020. An Analysis of Teachers’ Talk Management Used by English Teachers at SMA YAPIP SUNGGUMINASA. A thesis of English Education
Department Faculty of Teacher Training and Education University of Muhammadiyah Makassar. Supervised by Nurdevi Bte Abdul and Wildhan Burhanuddin.
This study aimed at finding out the kinds and the function of teachers’ talk management used in English teaching process at SMA YAPIP Sungguminasa. This study used qualitative research design. The instrument which was used to collect the data were observation checklist, interview and video recording to support them. The data were collected from two English teachers who teach in different classes.
The result of the research showed that (1) there were two kinds of teachers’ talk management used by Teacher A and Teacher B in learning process namely beginning the lesson, running, and ending the lesson. Management talk used by Teacher A in class XII MIA classified into 13 parts namely; everyday greeting, taking the register, getting down to work, starting something new, making things clear, sequencing activities, checking progress, stopping, checking the time, stopping work, making announcement, saying goodbye, and clearing the class. Furthermore Teacher B in class XI IIS classified into 10 parts namely; everyday greeting, taking the register, getting down to work, starting something new, making things clear, checking progress, checking the time, setting homework, stopping work, and saying goodbye. (2) The function of teachers talk management that was said by two English teachers there were conveying information, delivering lesson in structured way, and managing or arranging communication. Therefore the analysis of teachers’ talk management in the classroom was beneficial for teachers to plan and conduct enhanced learning situation.
Keywords: Teachers’ talk, kinds of management talk, function of management
ABSTRAK
AULYANI. 2019. Analisis Manajemen Bicara Guru yang Digunakan oleh Guru Bahasa Inggris di SMA YAPIP SUNGGUMINASA. Tesis
Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris Fakultas Keguruan dan Ilmu Pendidikan Universitas Muhammadiyah Makassar. Dibimbing oleh Nurdevi Bte Abdul dan Wildhan Burhanuddin.
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui jenis dan fungsi manajemen bicara guru yang digunakan dalam proses pengajaran bahasa Inggris di SMA YAPIP Sungguminasa. Penelitian ini menggunakan desain penelitian kualitatif. Instrumen yang digunakan untuk mengumpulkan data adalah checklist observasi, wawancara dan rekaman video untuk mendukung mereka. Data dikumpulkan dari dua guru bahasa Inggris yang mengajar di kelas yang berbeda.
Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa (1) ada dua jenis manajemen bicara guru yang digunakan oleh Guru A dan Guru B dalam proses pembelajaran yaitu memulai pelajaran, menjalankan, dan mengakhiri pelajaran. Manajemen bicara yang digunakan oleh Guru A di kelas XII MIA diklasifikasikan menjadi 13 bagian yaitu; salam sehari-hari, mengambil register, mulai bekerja, memulai sesuatu yang baru, membuat segalanya menjadi jelas, mengurutkan kegiatan, memeriksa kemajuan, menghentikan waktu, menghentikan pekerjaan, membuat pengumuman, mengucapkan selamat tinggal, dan membereskan kelas. Selanjutnya Guru B di kelas XI IIS diklasifikasikan menjadi 10 bagian yaitu; salam sehari-hari, mengambil register, mulai bekerja, memulai sesuatu yang baru, memperjelas, memeriksa kemajuan, memeriksa waktu, mengatur pekerjaan rumah, menghentikan pekerjaan, dan mengucapkan selamat tinggal. (2) Fungsi manajemen bicara guru yang dikatakan oleh dua guru bahasa Inggris adalah menyampaikan informasi, menyampaikan pelajaran dengan cara terstruktur, dan mengelola atau mengatur komunikasi. Oleh karena itu analisis manajemen bicara guru di kelas bermanfaat bagi guru untuk merencanakan dan melakukan peningkatan situasi belajar.
Kata kunci: Pembicaraan guru, jenis pembicaraan manajemen, fungsi
LIST OF CONTENTS
COVER ... i
TITLE PAGE ... ii
APPROVAL SHEET ... iii
SURAT PENGESAHAN ... iv SURAT PERNYATAAN ... v SURAT PERJANJIAN ... vi MOTTO ... vii ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... viii ABSTRACT ... x
LIST OF CONTENTS ... xii
LIST OF TABLES ... xiv
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION A. Background ... 1
B. Problem Statements ... 3
C. Objective of the Research ... 3
D. Significance of the Research ... 3
E. Scope of the Research ... 4
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE A. Some Previous Related Findings ... 5
C. Conceptual framework ... 22
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHOD A. Research Design ... 23
B. Research Subject ... 23
C. Instrument of the Research ... 23
D. Procedure of Collecting Data ... 24
E. Technique Data Analysis ... 25
CHAPTER IV: FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION A. The Findings ... 28
1. Kinds of Teachers Talk Management ... 28
2. Function of Teachers Talk Management ... 40
B. The Discussions ... 43
1. Kinds of Teachers Talk Management ... 43
2. Functions of Teachers Talk Management ... 46
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A. Conclusions ... 48
B. Suggestion ... 49 BIBLIOGRAPHY
APPENDICES (Instrument: Observation Checklist, Protocol of Interview)
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1.1: Expressions of Entering the Classroom……….12
Table 1.2: Expressions of Everyday greetings………12
Table 1.3: Expressions of Meeting a New Class………13
Table 1.4: Expressions of Taking the Register………...13
Table 1.5: Expressions of Dealing with the Lateness……….14
Table 1.6: Expressions of Getting Down to Work………..15
Table 2.1: Expressions of Starting Something New………...15
Table 2.2: Expressions of Make Things Clear………16
Table 2.3: Expressions of Sequencing Activities………...16
Table 2.4: Expressions of Checking Progress………17
Table 2.5: Expressions of Stopping………17
Table 3.1: Expressions of Checking the Time………18
Table 3.2: Expressions of Setting Homework………....19
Table 3.3: Expressions of Stopping Work………..19
Table 3.4: Expressions of Making Announcements………...20
Table 3.5: Expressions of Saying Goodbye………21
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
This chapter consists of background, problem statement, and an objective of the research, the significance of the research, and scope of the research.
A. Background
The system of education in Indonesia compared to other developing countries in Asia particularly, need to be considered. The most common problem in the system of education is human resources, which needs to be exploited, to create reliable human resource, which can be done through education. For this reason teacher plays a big role in developing a country, especially in this coming of globalization era. Educational professions cannot be underestimated. They have to have tough acquirement. That is why English teachers should produce a good quality brand. The quality of a teacher and the qualified method of teaching is a major requirement. Arifin (2015) states that talk is one of the major ways that teachers convey information to learners, and it is also one of the primary means of controlling learner behavior.
Teachers need to be active and talkative in class in stage only to motivate learners. Being passive in teaching English will not help at all. Therefore, teacher talk must be able to express, pronounce and explain English language correctly and efficiently so the learners could get what is best from their teacher. Many educator and teacher particularly in English not giving attention to the importance
of teacher talk, as an input in the acquisition of foreign language teaching. It is suggested that interaction adjustment were made by teacher to make comprehension checks, repetition of student statements, and use of mother tongue. Among a number of professionals in the fields of second language acquisition, there appears to be an increasing conviction that teacher talk is necessary as facilitations in the English teaching process. In the recent years, many researchers are only focus on the teacher techniques on teaching through many kinds of methods, somehow teachers’ language is much more important to be focus on, but it is rarely found. Teacher’s language has become an important issue to investigate and discuss. Chaudron (1988) says that teacher talk is one of major issues in second language classroom research. This is quite true with which many of the classroom language research deal with teacher’s language (Ellis, 1990; in Allwright and Bailay, 1991).
Based on the explanation above, the researcher chooses SMA YAPIP Sungguminasa because the teachers here used teacher talk. The researcher can analyze teacher talk that used by English Teachers in SMA YAPIP Sungguminasa. Regarding to the identification of the previous facts, the researcher interested in conducting a research under the title “An Analysis of
Teachers’ Talk Management Used by English Teacher At SMA YAPIP SUNGGUMINASA (A Descriptive Research at the Twelve Grade)”.
B. Problem Statement
Based on the background above, the researcher formulated research questions as follow:
1. What kinds of teachers’ talk management used in teaching process at SMA YAPIP SUNGGUMINASA?
2. What are the functions of teacher talk management in teaching process?
C. Objective of the Research
The problems that investigated in this research was formulated as follow: 1. To find out the kinds of teachers’ talk management used in teaching
process at SMA YAPIP SUNGGUMINASA.
2. To find out what are the functions of teacher talk management in teaching process.
D. Significance of the Research
Theoretically, the result of this research was expected to provide adequate information about the teachers’ talk management used by English teachers. This research also expected to give a clear reference for English teachers about the use of teachers’ talk inside the classroom. It may serve as a reflection for English teachers to enhance their teaching experiences for the purpose of maintaining the quality of English language teaching inside the classroom. The results also give more information about the kinds of activities that used teacher talk in English teaching process.
Practically, the result of this research was expected to serve as references that are useful and beneficial for next researcher in conducting further research about this study.
E. Scope of the Research
The scope of the research was to analyze the kinds of teachers’ talk management that the English teachers used in teaching and learning process at SMA YAPIP SUNGGUMINASA. These kinds’ reveals beginning the lesson, running and ending the lesson in the used of management’ talk in the classroom.
5 CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter deals with some previous related findings consisting of theories and concepts related to this study, pertinent ideas mainly focuses on teacher talk and English teaching process, resume and conceptual framework.
A. Some Previous Related Findings
In order to make the teaching and learning process more effective, many researchers have been analyzed. The related research has been analyzed and observed by the researcher. Some of related researches are mention below:
1. Astuti (2013) in her article found that some categories of teacher talk beginning from the highest questions, using or accepting ideas of students, praising, criticizing and accepting feelings. Regarding the students talk, this study has shown two types of students talk covering responses and initiation. 2. Setiawati (2012) in her article found that the teacher investigated were quite
creative in using many kinds of Teacher Talk features, that is warm-up chat, direct instructions, indirect instructions, directions for activities transitions, giving feedback, checking understanding. The use of features will avoid the monotonous situations in the classroom. It will help students get deeper knowledge and insight of the subject learned.
3. Yanfen and Yuqin (2010) in their article investigated ways of teacher talk preferred respectively by teachers and students. It was found that in initating and interaction, invitation is the first preferred choice by both teachers and students, but the least employed one. Question is more preferred by teachers
and the least preferred by students, but it is the mostly used one. Direction is not preferred by teachers but more used, and students prefer them to question. In ways to follow up, when students produce no answer or incorrect answer, teachers usually prefer ways of prompting, and this is what teachers really did in class. However, students prefer to be informed by the teacher. When students provide the expected answer, they still prefer to be commented, rather than being just simply acknowledged. Encouragement is always welcome. It is suggested that teachers should pay attention to their language in the process of interaction with students, so as to provoke more interaction in class.
4. According to Nafrina (2007) in addition to this linguistic aspects of “Teacher Talk”, there are other aspects of Teacher Talk which are as important 4 as these linguistic aspects that language teachers can use in their talk not only neutrally to convey comprehensible information but also to express positive attitudes toward their students in the classroom.
5. Rod Ellis (1985) has formulated his own view about teacher talk: “Teacher talk is the special language that teachers use when addressing L2 learners in the classroom. There is systematic simplification of the formal properties of the teacher’s language… studies of teacher talk can be divided into those that investigate the type of language that teachers use in language classrooms and those that investigate in the type of language they use in subject lessons.” He also commented “the language that teachers address to L2 learner is treated as
a register, with its own specific formal and linguistics properties” (Ellis, 1985).
All of the previous researches have similarity in this study that was the use of teacher talk as the main focus of the research. However, all of the previous research and this study have some differences. The previous research analyzed the kind of teacher talk features, categories of teacher talk, and investigated ways of teacher talk. Besides, the researcher investigated the kinds of teachers’ talk management in English Teaching Process and also was investigated the function of teachers talk management.
B. Some Pertinent Ideas
1. Definition of Teacher Talk
Nunan (1992) states teacher talk is of crucial importance, not only the organization of the classroom but also for the processes of acquisition. Even though the student in this setting do not have the similar exposure of the languages they follows second language setting, some achievement are similar, teacher talk really a major role the acquisition of a foreign language. In learning English the motives behind the teacher talk is to make the interaction in class comprehensible.
Xiaou-yan (2006) express two opinions about teacher talk. The first is that we can see that one variation of language can be said to be special if the teacher talk is used in the English class, so that the teacher can have its own distinctive characteristics that are different from the others, because of the limitation of physical arrangement. The second we can see that teacher talk is a communicative
activity that aims to communicated with students and can develop students' abilities in foreign languages.
Dong-lin (2008) defines teacher talk as a special variety or register of language especially marked by a special set of vocabulary associated with a profession or occupation. It is the oral form of teacher talk instead of written form that is under the investigation. Teacher talk is used in class when teachers are teaching students linguistic knowledge, cultivating their intellectual ability and managing classroom activities. The other statement about teacher talk comes from Osborne’s (1999) teacher talk is defines as speech used by teachers that is characteristically modified in four area: phonology, lexis (consisting of morphology and vocabulary), syntax, and discourse.
Krashen in Zaidah (2014) defines that teacher is foreigner talk in the classroom, the language of classroom management and explanation, when it is in the second language. He explains that the inter language talk has a simple code and one of them is that they get their second language from what their teacher says. In this case the teacher probably will not talk often. However, teachers can find other ways that they can understand it by bringing native speakers into their presence. This method is believed to be very useful in helping them to understand. In addition to experiencing the changes in linguistics, they can also increase their knowledge of the world. So, as more teachers explain using their second language, this will help the students in increasing their knowledge of English.
Nunan (1991) states that teacher talk in second language teaching is a direct input that the students can competence. This can be achieved if the teacher talk has the following characteristic:
1. Clear
Teacher talk is says to be clear if the students do not find any difficulties to understand it. It should be simple language and should not contain ambiguity. 2. Effective Efficient
Teacher talk is says to be effective and efficient if the student can use it actively, fluently and correctly after listening to it.
3. Appropriate
Teacher talk is says to be appropriate if it is used according to the desired situation and condition (Rasyid, 2013).
Teacher talk is defined as any words or sentences said by the teacher during the interaction in teaching-learning process, including when the teacher gives explanation, feedback, ask question and so on (Mujahidah, 2012). It indicates that any kind of talk spoken by the teacher is called teacher talk. The teacher talk plays an important role in teaching process since it can increase students’ language store as they listen to the real authentic material (Rivers, 1987). Another importance of teacher talk in the language classroom is that the role of the teacher as the provider of comprehensible input.
It is commonly established that teacher talk plays a significant role to language teaching. It refers to the special language that the teacher uses when interacting with the students in the classroom. Regarding to the detonation
above, it is somehow obvious that teacher talk dominates the classroom interaction. It is perhaps that talk in classroom is structured differently from other kinds of talk because of the very nature of instruction. Pica as quotes by Goh and Silver (2004) has lay out several reasons for this. One is ex- potations about teacher and learner roles. We expect teachers to ask questions and students to answer. If students ask too many questions, teachers might feel that their authority is being challenged. Also, teachers often make every attempt to ensure comprehension-ability for the students, thus avoiding the need for negotiation for meaning. The teacher talk has seven categories, namely (1) deals with feelings, (2) praises or encourages, (3) uses ideas of students, (4) asks question, (5) gives information and corrects without rejection, (6) gives direction, and (7) criticizes students’ response and behavior (Moskowitz, 1971 as cited in Brown, 2001).
2. Kinds of Teacher Talk
Doff in Muhayyang (2010) divides two types of teacher talk, instructional and management. Instructional talk is employed to present the lesson or language content. Instructional talk divided into 5 parts such as giving explanation, giving direction, giving correction, asking question, and answering question. Management talk is used to manage classroom activities. Management talk divided into 20 parts such us entering the classroom, everyday greeting, meeting a new class, talking the register, dealing with lateness, getting down to work, starting something new, making things clear, sequencing activities, checking progress, giving/taking turn, control and discipline, stopping, ending the teaching
sequence, checking the time, setting homework, stopping work, making announcement, saying good bye, and clearing the classroom. But, this research will only focus on management teacher talk in English teaching learning process. 3. Management Talk
The teaching and learning process will be effective and meaningful for the student if the teacher knows the management talk used in classroom activities. Doff 1988 states that management talk is used to manage classroom activities. The language of management in which it is used to manage teaching and learning activities in a well regulated manner.
According to Rasyid (2013) management talk deals with the enforcement of classroom activities, such as entering the class, greeting students, arranging the students’ seats, calling the rolls or checking the students’ presence, and dealing with lateness. Management talk consists of transactional expressions that are used to manage the interaction in the class from the very beginning to the very end of the class session. Education management talk will touch students’ thought and feelings, and will stimulate students to behave as expected.
Hughes and Moate (2007) classify the teacher talk that can be used by the teacher in everyday classroom routines. It will help the teachers to develop some of the core linguistics skill that the teacher will need to work effectively in the classroom and will carry over into more confident classroom management and enhanced pedagogical skills.
a. Beginning the lesson
Doff in Zaidah (2014) the beginning the lesson is a natural motivating opportunity for teacher to help students to get used to listening to English. It is a good idea to remind students that the phrases they are hearing and using at the beginning of the lesson are also useful outside the classroom. Some types of beginning the lesson that can be applied by the teacher in his/her classroom are as follows:
1. Entering the classroom
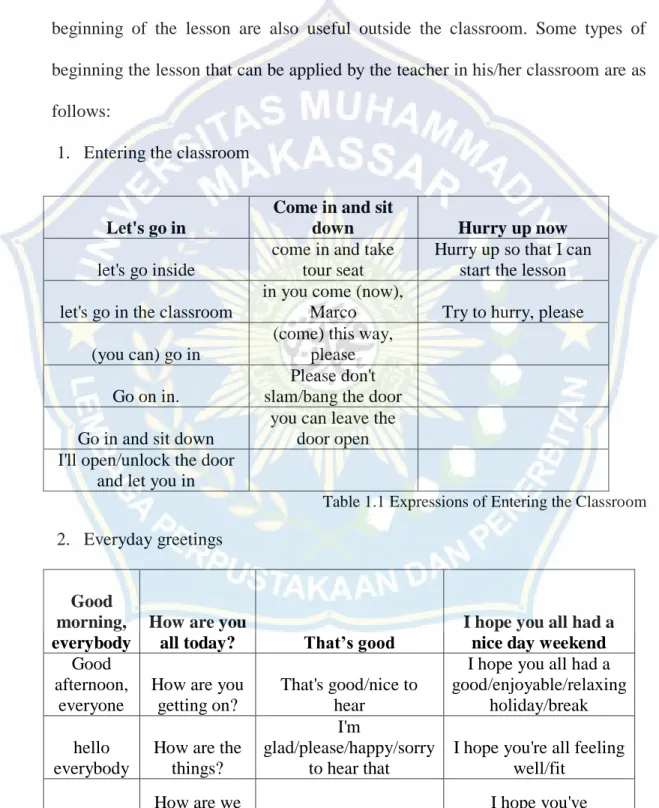
Table 1.1 Expressions of Entering the Classroom
2. Everyday greetings
Let's go in
Come in and sit
down Hurry up now
let's go inside
come in and take tour seat
Hurry up so that I can start the lesson let's go in the classroom
in you come (now),
Marco Try to hurry, please (you can) go in
(come) this way,
please Go on in.
Please don't
slam/bang the door Go in and sit down
you can leave the
door open I'll open/unlock the door
and let you in
Good morning, everybody
How are you
all today? That’s good
I hope you all had a nice day weekend
Good afternoon,
everyone
How are you getting on?
That's good/nice to hear
I hope you all had a good/enjoyable/relaxing
holiday/break hello
everybody
How are the things?
I'm
glad/please/happy/sorry to hear that
I hope you're all feeling well/fit
Table 1.2 Expression of Everyday Greeting 3. Meeting a new class
Table 1.3 Expressions of Meeting a New Class 4. Taking the register
Let’s see if everyone’s
here Who’s absent?
Where’s Mari this morning?
Who wasn’t here last time?
What was the matter?
I’ll just check who’s here Who’s missing/away/n ot here today? What’s wrong/ the matter with Mari? Was anybody/absent/missi ng last time? What was the problem ? I have to take/check attendance
Are you all here?
Has anybody seen Mari
Who was absent last time?
Have you been
ill? all doing this
morning?
had/you're having a nice/good day so far
How's everyone feeling today? How's it going? Let me introduce my self My name is Mrs. Hanson
Our lesson are on Monday morning and Wednesday
afternoon It’s nice to meet you all
Allow me introduce myself
I'm your new English teacher
I'll be teaching you on Tuesday and Friday
I’m very pleased to meet/see you all (again) Perhaps you're wondering who I am I'll be teaching you English this year
I’ve got three lessons a week with you
I’m looking forward to working with you Let me tell you
something
about myself
We’ll meet three times a week
I’ll be fun getting to know you all
Our lesson start 07.30 every Monday and
Thursday
From your timetable/schedule, you can see we start at
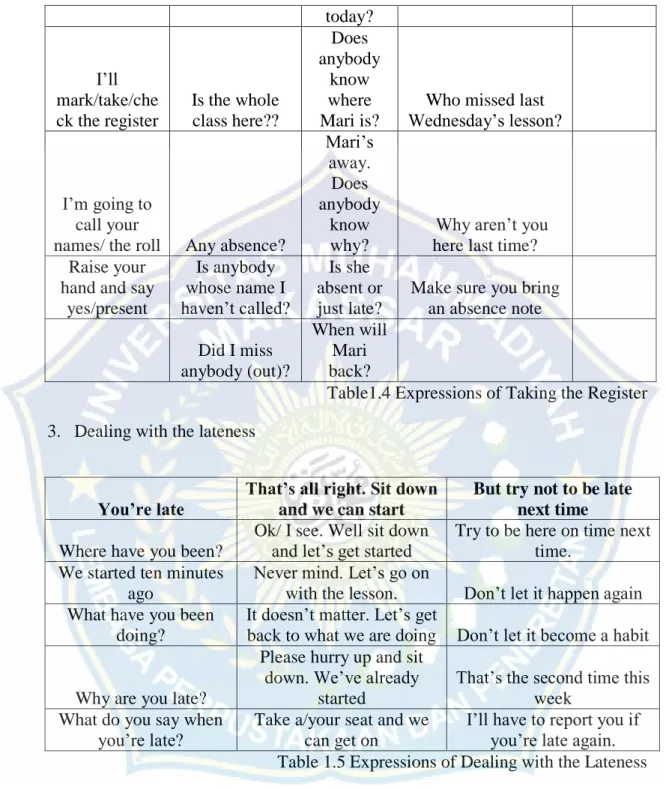
today? I’ll mark/take/che ck the register Is the whole class here?? Does anybody know where Mari is?
Who missed last Wednesday’s lesson?
I’m going to call your
names/ the roll Any absence?
Mari’s away. Does anybody know why?
Why aren’t you here last time? Raise your
hand and say yes/present Is anybody whose name I haven’t called? Is she absent or just late?
Make sure you bring an absence note Did I miss anybody (out)? When will Mari back?
Table1.4 Expressions of Taking the Register 3. Dealing with the lateness
You’re late
That’s all right. Sit down and we can start
But try not to be late next time
Where have you been?
Ok/ I see. Well sit down and let’s get started
Try to be here on time next time.
We started ten minutes ago
Never mind. Let’s go on
with the lesson. Don’t let it happen again What have you been
doing?
It doesn’t matter. Let’s get
back to what we are doing Don’t let it become a habit Why are you late?
Please hurry up and sit down. We’ve already
started
That’s the second time this week
What do you say when you’re late?
Take a/your seat and we can get on
I’ll have to report you if you’re late again. Table 1.5 Expressions of Dealing with the Lateness 6. Getting down to work.
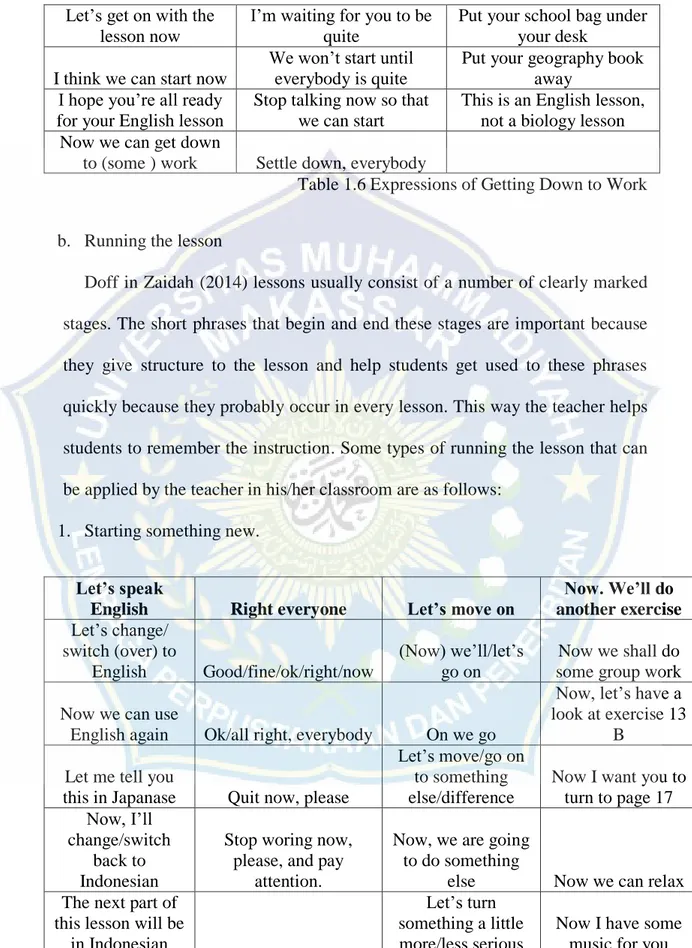
All right. It’s time to start our English
lesson
Ok. Everybody. I’m waiting to start
Put your things away and close your desk,
please
Let’s start the lesson
Is everybody ready to
Let’s get on with the lesson now
I’m waiting for you to be quite
Put your school bag under your desk
I think we can start now
We won’t start until everybody is quite
Put your geography book away
I hope you’re all ready for your English lesson
Stop talking now so that we can start
This is an English lesson, not a biology lesson Now we can get down
to (some ) work Settle down, everybody
Table 1.6 Expressions of Getting Down to Work b. Running the lesson
Doff in Zaidah (2014) lessons usually consist of a number of clearly marked stages. The short phrases that begin and end these stages are important because they give structure to the lesson and help students get used to these phrases quickly because they probably occur in every lesson. This way the teacher helps students to remember the instruction. Some types of running the lesson that can be applied by the teacher in his/her classroom are as follows:
1. Starting something new.
Let’s speak
English Right everyone Let’s move on
Now. We’ll do another exercise Let’s change/ switch (over) to English Good/fine/ok/right/now (Now) we’ll/let’s go on Now we shall do some group work Now we can use
English again Ok/all right, everybody On we go
Now, let’s have a look at exercise 13
B Let me tell you
this in Japanase Quit now, please
Let’s move/go on to something else/difference
Now I want you to turn to page 17 Now, I’ll
change/switch back to Indonesian
Stop woring now, please, and pay
attention.
Now, we are going to do something
else Now we can relax The next part of
this lesson will be in Indonesian
Let’s turn something a little more/less serious
Now I have some music for you
Now, English-only time
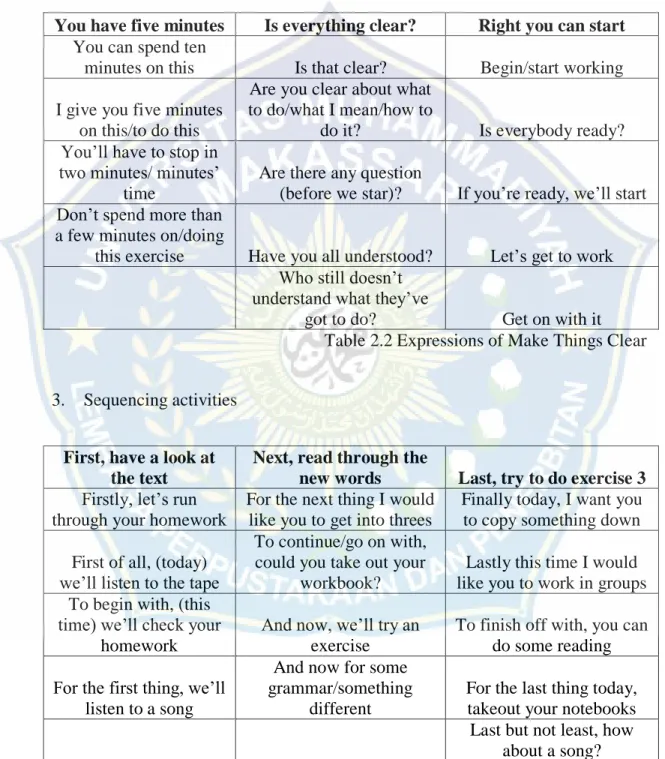
Table 2.1 Expressions Starting Something New 2. Make things clear
You have five minutes Is everything clear? Right you can start
You can spend ten
minutes on this Is that clear? Begin/start working I give you five minutes
on this/to do this
Are you clear about what to do/what I mean/how to
do it? Is everybody ready? You’ll have to stop in
two minutes/ minutes’ time
Are there any question
(before we star)? If you’re ready, we’ll start Don’t spend more than
a few minutes on/doing
this exercise Have you all understood? Let’s get to work Who still doesn’t
understand what they’ve
got to do? Get on with it Table 2.2 Expressions of Make Things Clear 3. Sequencing activities
First, have a look at the text
Next, read through the
new words Last, try to do exercise 3
Firstly, let’s run through your homework
For the next thing I would like you to get into threes
Finally today, I want you to copy something down First of all, (today)
we’ll listen to the tape
To continue/go on with, could you take out your
workbook?
Lastly this time I would like you to work in groups To begin with, (this
time) we’ll check your homework
And now, we’ll try an exercise
To finish off with, you can do some reading For the first thing, we’ll
listen to a song
And now for some grammar/something
different
For the last thing today, takeout your notebooks Last but not least, how
about a song? Table 2.3 Expressions of Sequencing Activities
4. Checking progress
Any problem? Where are you up to? What’s the matter?
Are you ok? All right? How far have you got? What’s the problem? Is there anyone who
needs help? Which question are you?
Is there something wrong? Who can’t manage on
his/her/their own? Is everything ok? Who is finding this
difficult? Is there something/anything the matter? Is there anybody having trouble/difficult the exercise?
Table 2.4 Expressions of Checking Progress 5. Stopping. OK, everybody. Two more minutes Have you finished? Right. That’s enough
All right, stop now
We’ll have a break before
going on
You will have to finish in a minute Are you done/through? That’s enough for now Stop what you’ve doing You can have/take a two-minute break I’ll have to stop
you in two minutes
Who’s/ who has finished?
That will do, thank you
Everybody stop what they are
doing Relax for a moment before we go on to something else (Just) a couple more minutes of minutes more
Who has done them all? You’ve done enough of that Stop writing/working We can take our coffee break now One minutes left/remaining/to go (Has) everybody who still hasn’t finished? You’ve probably had enough of that
All right. You can stop now Have you done/completed everything? We’re spent long enough on this Your time is up now. You were fast It’s time Finish up
for/you had a change
Table 2.5 Expressions of Stopping c. Ending the lesson.
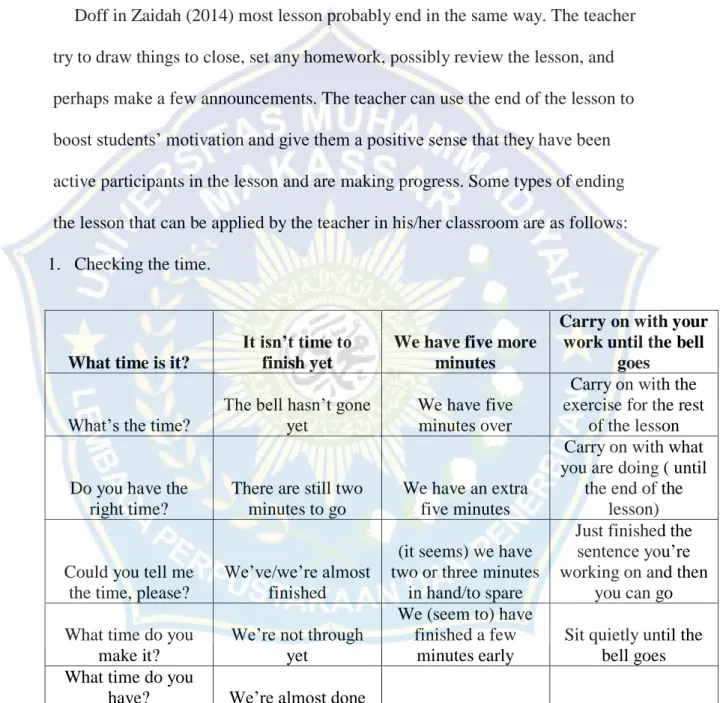
Doff in Zaidah (2014) most lesson probably end in the same way. The teacher try to draw things to close, set any homework, possibly review the lesson, and perhaps make a few announcements. The teacher can use the end of the lesson to boost students’ motivation and give them a positive sense that they have been active participants in the lesson and are making progress. Some types of ending the lesson that can be applied by the teacher in his/her classroom are as follows: 1. Checking the time.
What time is it?
It isn’t time to finish yet
We have five more minutes
Carry on with your work until the bell
goes
What’s the time?
The bell hasn’t gone yet
We have five minutes over
Carry on with the exercise for the rest
of the lesson Do you have the
right time?
There are still two minutes to go
We have an extra five minutes
Carry on with what you are doing ( until
the end of the lesson) Could you tell me
the time, please?
We’ve/we’re almost finished
(it seems) we have two or three minutes
in hand/to spare
Just finished the sentence you’re working on and then
you can go What time do you
make it?
We’re not through yet
We (seem to) have finished a few
minutes early
Sit quietly until the bell goes What time do you
have? We’re almost done
2. Setting homework.
For your homework, please
do exercise 27A
I want you to finish off exercise 26 c at
home
There will be a test on this next week
Don’t forget about your homework This chapter/lesson/page/ dialogue is your homework Finish of this at home
There will be a test on chapter 5 to 8
next time
Remember you homework This is for your
homework for tonight/today/next
Monday
Finish off the exercise at home
You can expect a test on this in the
near future
Do you remember what you have to do
for your homework As/For (your)
homework I want you to
Do the rest of the exercise as your
homework for tonight
I’ll test you on the new words sometime next week
Are you all clear about your homework? Your homework for
tonight is to prepare chapter 17
Read the rest of the story at home Before (the) next
lesson I would like you to…
Go through this section again on your own at home I’ll go through/over it with you next time
Table 3.2 Expressions of Setting Homework
3. Stopping work.
It’s time to stop
So, today we’ve practiced asking
the time
We’ll finish this
next time That’s all for today
We’ll have to stop finish/ now
This time you have learned how to write
a letter
We’ll do/read/look at the rest of the chapter on Thursday
That will do for today. You can go
now I make it almost
time. We’ll have to finish /stop
here/there
In this lesson we’ve begun a new until
We’ll finish off this exercise in the
lesson
That’s about it for today There’s the bell, so
we must Stop working now
Let me just remint you/recap/go over
what we done
We’ll go/carry on with this chapter
We don’t have any more time
Let’s just review today’s lesson
We’ll come continue working on this chapter next week
Right, you may /can go
It’s about time we/you stopped
We’ll come back this another time
You can put your things away and go There’ll be more on
this next time Next time we’re going to have a look
at your projects
Table 3.3 Expressions of Stopping Work 4. Making announcements.
Wait a moment, please
I have something to tell you
Next time we’ll meet in room 23
Don’t forget the English club meeting this afternoon Just a moment/minutes/second, please I have something to say to you Tomorrow we’ll meet in room 14 Please remember don’t forget to bring your project
folders next time Hang on a
moment/second
I have some announcements to
make before you go
There’s come a change of room for next week
If you have time, watch Pride and Prejudice on RCTI
at nine Just hold on a moment Please listen
We’ll be meeting in room 19 instead Stay where you are for a
moment
Please pay attention
I’ll see you in room 7 after the
break/recess One more thing before
you go
The fourth period has been cancelled
next Tuesday Don’t go rushing off
There won’t be a English lesson on
Friday Back to your place
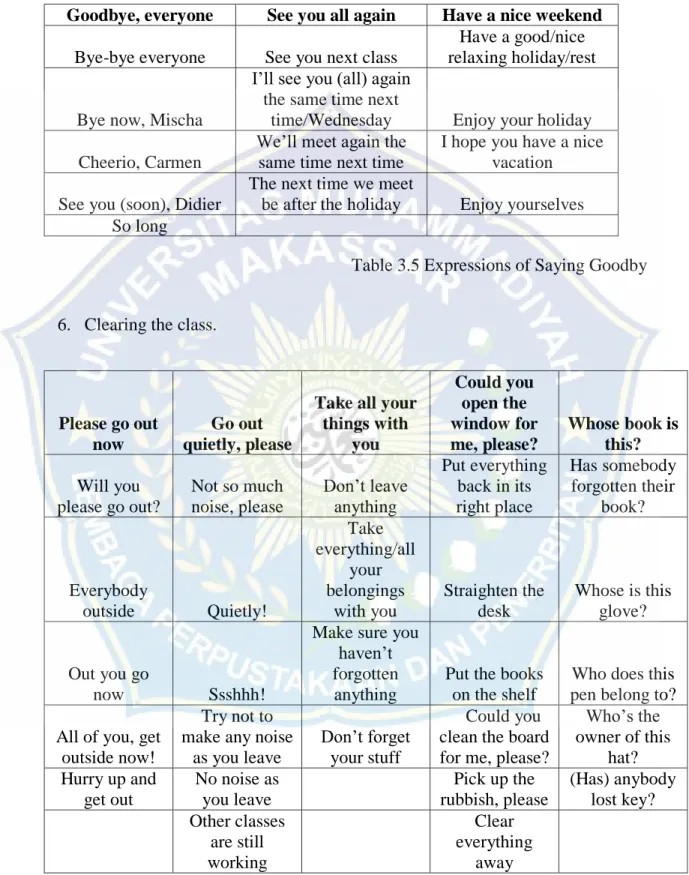
5. Saying goodbye
Goodbye, everyone See you all again Have a nice weekend
Bye-bye everyone See you next class
Have a good/nice relaxing holiday/rest Bye now, Mischa
I’ll see you (all) again the same time next
time/Wednesday Enjoy your holiday Cheerio, Carmen
We’ll meet again the same time next time
I hope you have a nice vacation
See you (soon), Didier
The next time we meet
be after the holiday Enjoy yourselves So long
Table 3.5 Expressions of Saying Goodby 6. Clearing the class.
Please go out now
Go out quietly, please
Take all your things with you Could you open the window for me, please? Whose book is this? Will you please go out? Not so much noise, please Don’t leave anything Put everything back in its right place Has somebody forgotten their book? Everybody outside Quietly! Take everything/all your belongings with you Straighten the desk Whose is this glove? Out you go now Ssshhh!
Make sure you haven’t forgotten
anything
Put the books on the shelf
Who does this pen belong to? All of you, get
outside now!
Try not to make any noise
as you leave
Don’t forget your stuff
Could you clean the board for me, please?
Who’s the owner of this hat? Hurry up and get out No noise as you leave Pick up the rubbish, please (Has) anybody lost key? Other classes are still working Clear everything away
C. Conceptual Framework
Figure1. Conceptual Framework
The conceptual framework above shows the situation of English teaching process. English language teaching for English as Foreign Language students in its process teacher talk usually combined between English and native language to make English teaching process more comprehensible. Based on the conceptual framework above, the researcher analyzed the kinds of management talk that teacher use in teaching and learning process, and the function of management talk that the teacher got from the used of management talk in the classroom.
Teacher Talk
Function of management talk
Management Talk
Kinds of Management Talk
4. Beginning the class 5. Running the class 6. Ending/ closing 1. Conveying Information 2. Delivering lesson in structured way 3. Managing and arranging Communication.
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD
This chapter consists of method of the research design, research subject, instrument of the research, procedure of collecting data and technique of data analysis.
A. Research Design
This research used a descriptive qualitative method, to give description about the use of teacher talk in teaching process. The researcher observed the kinds of the teacher talk management used by the teacher in the classroom.
B. Research subject
The research subject was two English teachers in SMA YAPIP SUNGGUMINASA who teach in different classes. The first subject was KK S.pd, 43 years old, undergraduate degree from Universitas Negeri Makassar, English Education Department as Teacher A. Next subject was SH S.pd, 46 years old, undergraduate degree from Universitas Islam Negeri Alauddin Makassar, English Education Department as Teacher B.
C. Instrument of the Research
The instruments of the research were observation checklist, interview and recorder to support the data from observation and interview. It is intend to know the kinds of activities in teaching and learning English at senior high school. The
observation checklist adopted from discussion of structure of classroom discourse (Mehan, 1979; Sinclair & Brazil, 1982) cited in Yanfen and Yuqin (2010).
1. Observation checklist aim to gain the data factually based on the observation checklist by looking at classroom situation. The observation conducted by observing teacher’ during classroom process. The researcher had joined the one whole process of English class before doing the interview. The researcher gives code to the observation checklist if saw that teacher used management talk in the classroom
2. Video recording supported the data from checklist. Recording furthered instrument in this research, it aims to record all the classroom activities and management teachers talk used in the classroom, furthermore recording can help the researcher to avoid mistakes in taking the data.
3. Interview aims to get accurate information from the teacher by delivering certain questions about management teacher talk. As an additional, the researcher used semi-structured interview guide on interviewing subject.
D. Procedure of Collecting Data
Data collection is the procedure used by the researcher to collect data. In conducting the first data which was obsevation checklist, the researcher had joined the English class where the teaching and learning process take place if the researcher saw the teacher used management talk in their classroom, the researcher give code to the observation checklist. The second data was interview, the researcher interviewed subjects/ teachers and did the following procedure:
1. Firstly, the researcher explained about the aim of the interview. 2. Next, the researcher interviewed the teachers.
3. The researcher asked questions to the teachers.
4. While the teachers answering the questions, the researcher recorded all of the teacher’s answers.
5. After interviewing, the researcher said thanks to the teachers for their time to answer the question.
6. Last, the researcher analyzed all the answers and summarized them by consideration with the observation’s result during the class that the researcher joined before.
E. Technique of Data Analysis
The collected data obtained from the result of observation and interview were analyzed to draw conclusions. According Moleong (2010), data analysis is the process of managing the data, organazing it into a goot pattern, category and basic unit. Thus, we could find the theme and formulate hypothesis as suggested by the data. The purpose of data analysis is summarizing and simplifying tha data in order to interpret and draw a conclution.
Furthermore, because of this research used qualitative research design, then it was be analyzed by using inductive analysis method. According to Miles and Huberman in Sugiyono’s (2014), the activities in qualitative data analysis is performed interactively and occurring continuously until complete, so that the data is already saturated. In addition, the activities in qualitative data analysis are data reduction, data display, and conclusion drawing/verivication.
1. Data Reduction
The data obtained in the field was quite a lot. It was necessary to note carefully and detail. Data reduction means: summarizing, choosing things that are fundamental, focusing on things that are important, looking for themes and patterns and discarding unnecessary. Reduce data will give a clear picture and facilitate researcher to conduct further data collection, and look for it when needed. Data reduction could be aided with electronic device such as a computer, to give the code on certain aspects. With the reduction, the researchers summarize, taking important data, make categorization, based uppercase, lowercase letters and numbers.
2. Data Model (Data Display)
Once the data was reduced, then the next step was display data. Display data in qualitative research will be done in the form of a brief description, chart relations between categories, flowchart and so on. Miles and Huberman in sugiyono (2014) state the most frequent form of display for qualitative data has been narrative text. That is most often uses to present data in qualitative research with narrative text. In addition in the form of a narrative, the data display can also be a graph, matrix, network (networks). In this research data display was narrative.
3. Conclusion drawing and verification
The third step was the conclusion and verification. Conclusions were presented still provisional, and would be changed if not found strong evidence that supports the next stage of data collection. However, if the
conclusion was supported by evidence of valid and consistent when the researcher returned to the field in collecting data, the conclusions that presented were the credible conclusions (trustworthy).
CHAPTER IV
FINDING AND DISCUSSION
This chapter deals with the findings of the research and discussion of the findings. The findings reveal what kinds of management talk used by the teacher in the classroom activities by using observation checklist, and the function of teacher talk management in teaching process by using interview to the teacher, beside that this research used recording to support the data. Discussion reveals some arguments and further interpretation of findings.
A. Findings
The findings consist of the data obtained through classroom observation checklist, interview, and the transcript of the video recording. The findings explained the kinds of management’ talk used in English teaching process at SMA YAPIP Sungguminasa and the function of teacher talk management used in teaching process.
1. Kinds of Teacher Talk Management that used in SMA YAPIP Sungguminasa
a. Everyday Greeting
In beginning the lesson, the teacher entered in the classroom and saying “everyday greeting” before the teacher started the lesson.
Extract 1 (Teacher A):
S : sit down please!
T : good morning, how are you? Ss : morning sir, im fine and you?
In Extract 1, Teacher A started the class by saying “good morning,
how are you?”. The expression was classified as everyday greeting. It is
the parts of the management talk in beginning the lesson.
Extract 2 (Teacher B):
S : sit down please!
T : thank you very much. Good morning everybody? How are you? SS : I’m fine.
T : will still remember our last material. About what? Our last material. We are discussing about what? We still remember about?
S : yes.
In Extract 2, Teacher B started the class by saying “Good morning
everybody?”, and “how are you?”. The expressions were classified as
everyday greeting. It is the parts of the management talk in beginning the lesson. Teacher B repeated the greeting because the teacher wanted the students pay attention.
b. Taking the Register
The teacher was taking the register to know if the whole of class is present or not.
Extract 3 (Teacher A):
T : Sementara kalian bekerja dengarkan namanya ya (while your
work, listen to your name)
T : Ade putra.
Ss : tidak adai. Absent. (He’s not coming. Absent) T : Amrianto
Extract 3 shows how Teacher A taking the register. The expression
“sementara kalian bekerja dengarkan namnaya ya” mean that the teacher
want to know who were present or not before studied.
Extract 4 (Teacher B):
T : Okay students who students absent today? How many student? S : Ardiansyah.
T : What about Ardiansyah? He is present? Ardiansyah?
Extract 4 shows how Teacher B taking the register. The expressions “Okay students, who students absent today?”, and “what
about Ardiansyah? He is present?” mean that the teacher want to know
who were present or not. Taking the register is one of the parts of management talk in beginning the lesson.
c. Getting Down to Work
The teacher was getting to work to demand the students started the lesson materials or study together.
Extract 5 (Teacher A):
T : well, buka bukunya halaman 50. Do you still remember the last material? (well, open your book page 50)
Ss : yes sir
Extract 5 shows how Teacher A is getting down to work. The expression “well, buka bukunya halaman 50” mean that the teacher demanded the students to read and discussed the material. Getting down to work is one of parts of the management talk in beginning the lesson.
Extract 6 (Teacher B):
S : yes.
T : About the kinds of … how knows? What is our last material? About?
S : Piranha fish.
T : About Piranha fish, okay sit down please. Eee, today we will
discuss about kinds of taste. And taste is very nice.
Extract 6 shows how Teacher B is getting down to work. The expression “today we will discuss about kinds of taste” mean that the teacher delivered the material will discussed. Getting down to work is one of parts of the management talk in beginning the lesson.
d. Starting Something New
The teacher was starting the class with telling the students to get ready and start the new lesson.
Extract 7 (Teacher A):
T : Masih ingat apa itu past tense? (do you still remember what is the meaning of past tense?)
SS : masih.
SS : bahas masa lampau sir (discuss about the day of long ago sir T : ya betul. Ok hari ini kita pindah ke present perfect tense. (That’s
right. Ok today we are move to present perfect tense.)
The Extract 7 was about starting something new. In this activity, Teacher A wanted to start new material by saying “ok, hari ini kita pindah
ke present perfect tense”. Starting something new is one of the parts of the
management talk in running the lesson.
Extract 8 (Teacher B):
T : About the kinds of … how knows? What is our last material? About?
S : Piranha fish.
T : students today we will discuss about kinds of taste. Jadi how we say in Indonesia? Taste. What is taste?
S : Perasa.
The Extract 8 was about starting something new. In this activity, Teacher B wanted to start the material by saying “students today we will
discuss about kinds of taste”. Starting something new is one of the parts of
the management talk in running the lesson.
e. Making things Clear
Making things clear was used by the teacher to check students’ understanding or make sure anything was clear.
Extract 9 (Teacher A):
T : paham sampai disini? Ada yang mau bertanya? (You got the point?
Does anyone have any questions?)
SS : tidak ada sir (No sir)
Extract 9 was about making things clear. The expression “paham
sampai disini? Ada yang mau bertanya?” means Teacher A wanted to
check students’ understanding or make sure anything was clear.
Extract 10 (Teacher B):
T : Jelasmi? tidak ada mau bertanya?(Is it clear? No questions?) S : ada bu. (me mam)
T : oh number what? S : Ini bu. (this is mam)
Extract 10 was about making things clear. The expression
“jelasmi? Tidak ada mau bertanya?” means Teacher B wanted to check
students’ understanding or make sure anything was clear.
f. Sequencing activities
Sequencing activities was used by the teacher to direct students to how they do their work.
Extract 11 (Teacher A):
T : jadi tugas kalian sekarang adalah memasangkan di blank space bagian yang kosong itu dengan salah satu dari 3 pilihan tersebut and
blank with one of these three options and make it group. Is it possible?)
SS : iye pak.
Extract 11 was about sequencing activities. The expression “jadi
tugas kalian sekarang memasangkan di blank space” and “make it group, bisa tidak?” means Teacher A given direction a correct sequencing to the
students work.
g. Checking Progress
Checking progress was used by the teacher to know the progress that the students found.
Extract 12 (Teacher A):
T : apa yang susah? (did you find any trouble?) Ss : apa artinya ini sir? (what does this mean sir?) (sambil menunjukkan buku)
Extract 12 shows that Teacher A wanted to know the progress that the Students’ found. The expression “apa yang susah?” means that the
teacher
checking the students’ progress.
Extract 13 (Teacher B):
SS : Iye bu. (yes mam) T : You find difficult words? S : No.
Extract 13 shows that Teacher B wanted to know the progress that the students found. The expression “you find difficult word?” and “ada
kata-kata yang sulit?” means that the teacher checks the students’
progress.
h. Stopping
Stopping was used by the teacher to remind students that the time for work on assignments is complete.
Extract 14 (Teacher A):
T : Have you finished? SS : iya sir. (yes sir)
T : sudah ditulis semua jawabnnya? (You’ve written all the answers?) SS : iya pak. (yes sir)
T : oke. Kita bahas sama-sama. (Ok. We’il discuss it together)
In extract 14 show how the teacher A stopping of students work by saying “have you finished?”. The expression was classified as a stopping. It is the parts of the management talk in running the lesson.
Extract 15 (Teacher B):
T : oke, sudahmi habis waktu, kumpulmi. (Ok. Time is up. Collect) SS : tunggu bu, namaku pi. (wait mam, I forgot to write my name)
In extract 15 was about stopping. The expression “oke sudahmi habis waktu, kumpulmi”. Means that Teacher B used the part of management talk in running the lesson.
i. Checking the Time
Checking the time was used by the teacher to remind the students about the time.
Extract 16 (Teacher A):
T : ya kalau begitu karena waktunya tersisa 8 menit, im going to ask once again, do you think that this item is difficult? Yg ini sulit? (Well, because you have eight minutes left, I am going to ask once again) S : No sir.
T : okay.
Extract 16 was about checking the time of Teacher A. The expression “ya kalau begitu karena waktunya sisa 8 menit” mean the teacher reminded the students that class time is almost over.
j. Setting Homework
Setting/taking homework was used when the teacher took homework to the students.
Extract 17 (Teacher B):
S : waktunya habis. (Time is over)
T : Ok students please you make a simple text about sense of report, jadi
make your task as homework, jadi coba membuat dirumah nanti bacaan tentang report yang menggambarkan, describe about something. Jadi cari text lain yah, yang isinya itu berisikan tentang
text that describe something. Find another text, which contains all kinds of reports. Ok leader please!)
S : Stand up please! Greeting to our teacher.
Extract 17 was about setting homework used by Teacher B. the expression “Ok students please you make a simple text about sense of
report, jadi make your task as homework, jadi coba membuat membuat dirumah nanti bacaan tentang report yang menggambarkan, describe about something” means the teacher took the homework to the students.
k. Stopping Work
Stopping work was used by the teacher to stop the lesson because the time was over.
Extract 18 (Teacher A):
T : oke, terimakasih banyak, leader siapkan! (Ok. Thank you very much, leader please!)
S : Attention please! Stand up please. And say greeting to our Teacher. SS : Assalamualikum warahmatullahi wabarakatuh.
T : Waalaikumsalam warahmatullahi wabarakatuh.
Extract 18 was about stopping work used by Teacher A. The teacher saying “oke terimakasih banyak, leader siapkan!” to stop the learning processed because the time was over.
Extract 19 (Teacher B):
T : Yes good! SS : Alhamdulillah.
T : Ok dear students the times over. S : waktunya habis. (time is up)
Extract 19 was about stopping work used by Teacher B. the expression “ok dear students the times over” means the teacher wanted to stop the learning process because the time was over.
l. Making Announcement
Making announcement was used by the teacher to get attention from the students when there were things to be conveyed.
Extract 20 (Teacher A):
T : kalau tidak ada halangan in our next meeting, we are going study
about Caption ya, itu adalah kalimat yang ada di bawah foto. Pelajari memangmi. (If it isn’t something urgent, in our next meeting, we are
going to study about caption ya. That is the sentence of the line under the photo. Learn it.)
SS : Iye pak. (Yes sir)
Extract 20 was about making announcement used by Teacher A. The expression “kalau tidak ada halangan in our next meeting” means the teacher wanted to announce something to the students because there was something to be conveyed.
m. Saying Goodbye
Saying goodbye was used by the teacher when time was over and wanted to end the lesson.
Extract 21 (Teacher A):
S : attention please! Stand up please. And say greeting to our Teacher. SS : Assalamualikum warahmatullahi wabarakatuh.
T : Waalaikumsalam warahmatullahi wabarakatuh. S : Sit down please!
Extract 21 was about saying goodbye used by Teacher A. The teacher closed the lesson by saying “Waalaikumsalam warahmatullahi
wabarakatuh” to the students.
Extract 22 (Teacher B):
S : Stand up please! Greeting to our teacher. SS : Assalamualaikum wr.wb
T : Waalaikumsalam warahmatullahi wabarakatuh.
Extract 22 was about saying goodbye used by Teacher B. The teacher closed the lesson by saying “Waalaikumsalam warahmatullahi
wabarakatuh” to the students.
n. Clearing the class
Clearing the class was used by the teacher to make sure if the class was clear or to remind the students if there are items left behind.
Extract 23 (Teacher A):
T : tolong jangan lupa buku cetaknya dikumpul semua! (Don’t forget to collect the book.)
Extract 23 was about clearing the class used by Teacher A. the teacher make sure to students by saying “tolong buku cetaknya jngan lupa dikumpul semua”. It is the part of management talk in ending the lesson. Based on the description above, the researcher concluded that the parts of management talk that the Teacher A used in the teaching and learning process were 1) everyday greeting, 2) taking the register, 3) getting down to work, 4) starting something new, 5) making things clear, 6) Sequencing activities 7) checking progress, 8) stopping, 9) checking the time, 10) stopping work, 11) making announcement, 12) saying goodbye, and 13) clearing the class.
Furthermore, the parts of management talk that the Teacher B used in teaching and learning process were 1) everyday greeting, 2) taking the register, 3) getting down to work, 4)starting something new, 5) making things clear, 6) checking progress, 8) stopping, 7) setting homework, 9) stopping work, 10) saying goodbye.
2. Function of Teacher Talk Management
In order to get real data from teacher to know the functions of teacher talk manegement in teaching process through interviews. The results of each interview are detailed below;
1. Conveying information
The teacher interviewed had an opinion on convey a particular information is a function of teacher talk management.
Extract 1 (Teacher A):
I : what do you think about the function of teachers talk management?
T : I think the function of teacher talk management is to convey a
particular information base on the teacher knowledge to his students. Furthermore, the teachers talk management is very useful
to manage our class according to the students’ ability, knowledge background, and classroom atmosphere during presenting material. Extract 1 was about opinion teacher A that the function of teacher talk management in teaching process is to convey a particular information based on teacher knowledge to his students.
Extract 2 (Teacher B)
I : What do you think about the function of teachers talk management?
T : In my opinion, the function of this management talk is almost the same as the management class that I usually do, which is the same as helping me deliver lessons to students in a structured way.
Management talk can help me easily convey information or convey learning well.
Extract 2 was about opinion teacher B that the function of teacher talk management in teaching process is to management talk can help her easily in conveying information or conveying learning well.