AN ERROR ANALYSIS ON DERIVATIONAL
SUFFIXES IN THE STUDENTS’ WRITING
ASSIGNMENTS OF ENGLISH TEACHER
EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF STATE
ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY OF SUNAN AMPEL
SURABAYA
THESIS
Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the
degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd) in Teaching English
By
Wahyul Ulya
D05213033
ENGLISH TEACHER EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHER TRAINING
SUNAN AMPEL STATE UNIVERSITY
SURABAYA
PERNYATAAN KEASLIAN TULISAN
Yang bertanda tangan dibawah ini
Nama : Wahyul Ulya
NIM : D05213033
Semester : VIII
Fakultas/Prodi : Tarbiyah dan Keguruan/Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris
Dengan ini menyatakan sebenar-benarnya bahwa skripsi yang berjudul “An Error Analysis on Derivational Suffixes in The Students’ Writing Assignments of English Teacher Education Department of State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya” adalah benar-benar merupakan hasil karya sendiri. Segala materi yang diambil dari karya orang lain hanya digunakan sebagai acuan dengan mengikuti tata cara dan etika penulisan karya ilmiah yang ditetapkan oleh jurusan.
ADVISOR APPROVAL SHEET
This thesis by Wahyul Ulya entitled “An Error Analysis on Derivational
Suffixes in The Students’ Writing Assignment of English Teacher Education Department of State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya” has been approved by the thesis advisors for further approval by the boards of examiners.
Surabaya, July 17th, 2017 Advisor I,
EXAMINER APPROVAL SHEET
This thesis by Wahyul Ulya entitled “An Error Analysis on Derivational
ABSTRACT
Ulya, Wahyul. (2017). An Error Analysis on Derivational Suffixes in The Students’ Writing Assignments of English Teacher Education Department of State Islamic University of
Sunan Ampel Surabaya. A thesis. English Teacher
Education Department, Faculty of Education and Teacher Training, State Islamic University Sunan Ampel Surabaya. Advisor: Hilda Izzati Madjid, MA and Rakhmawati, M.Pd.
Key words: Error Analysis, Derivational Suffixes.
ABSTRAK
Ulya, Wahyul. (2017). An Error Analysis on Derivational Suffixes in The Students’ Writing Assignments of English Teacher Education Department of State Islamic University of
Sunan Ampel Surabaya. Skripsi. Pendidikan Bahasa
Inggris, Fakultas Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya. Pembimbing: Hilda Izzati Madjid, MA and Rakhmawati, M.Pd.
Kata Kunci: Error Analysis, Derivational Suffixes.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE SHEET ... i
ADVISOR APPROVAL SHEET ... ii
EXAMINER APPROVAL SHEET ... iii
MOTTO ... iv
DEDICATION SHEET ... v
ABSTRACT ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGMENT ... vii
PERNYATAAN KEASLIAN TULISAN ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... x
LIST OF TABLES ... xii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xiii
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Background of the Study ... 1
B. Research Questions ... 6
C. Objective of the Research ... 6
D. Significance of the Research ... 6
E. Scope and Limits of the Study ... 7
F. Definition of Key Terms ... 7
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ... 9
A. Error ... 9
B. Error Analysis ... 10
C. Affixation ... 15
D. Derivational Suffixes ... 17
E. Previous Studies... 20
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHOD ... 25
A. Research Design ... 25
B. Research Setting and Subject ... 26
C. Data and Source of Data ... 26
E. Data Collection Technique ... 28
F. Data Analysis Technique ... 29
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION ... 31
A. Research Findings ... 31
B. Discussion ... 38
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS ... 58
A. Conclusions ... 58
B. Suggestion ... 59 REFERENCES
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
In this chapter the researcher presents some important key points, namely research background which consists of the reason or why the researcher is interested in the topic, research questions that come up with some cases, objective of the research that show the aims of conducting this research, segnificance of the research , scope and limit of the research, and definition of key terms that define the variables used in this research provided to avoid misunderstanding of those terms.
A. Research Background
Learning language has become a crucial thing since it is used as an instrument to communicate with each other. Through language people can understand what others actually mean both spoken and written. Using language correctly is not as easy as we think since there is a set of rules that must be followed called structure or grammar. Every language has its own system which is different from another, one another also may have similar complexity, but there is no exact similarity that occurs between them. By this complexity, the language is potential to produce more utterance in enriching its vocabulary. Like in English, it has the ability to produce more new words.
New words are made on the basis of patterns of meaning correspondence between existing words. It is not only creating new word but also creating new meaning. Furthermore, new words are the existing words which are likely undergo certain word-formation processes.1 There are some types of word-formation processess that should be known, there are coinage, borrowing, compounding, blending, clipping, back-formation, conversion, acronyms and affixation.2
Morphology refers to the process on how the words of a language are formed to create meaningful messages.3
1
Ritama Ririn - M. Zaim - Rusdi noor Rosa, “Grammatical Semantic Constrain of Derivational Affixes of Minangkabaunese Used in Singgalangdaily Newspapper” English Language and Literature E-Journal / ISSN 2302-3546, p 222.
2George Yule, The Study of Language (Third Edition), (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006), p 52.
3
2
Morphology identifies and classifies the morphemes and describes the types of combinations that build words in the language.4 In morphology, there are inflectional and derivational morphemes. According to Katamba, an affix is a morpheme which only occurs when it is attached to some other morpheme or morphemes such as a root or stem or base.5 In addition it can be concluded that a morpheme which attached the root or steam is called affix.
It can not be denied that English has a complicated affixation. Thus, it makes learning English more challenging. Consequently, English foreign learners might find it difficult and likely produce errors in productive skills especially in the written form.6 Students might make error in the writing process since they are foreign English language learners. This condition was experienced by the forth semester students of State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya which is based on the preliminary observation, affixation errors were found in their English writings. In this case, the researcher took five students’ writing assignments to be analyzed about the affixation. Then, the researcher compared between preffix and suffix errors. In fact, the learner mostly used suffixes rather than preffixes. Therefore, the researcher tends to analyze about suffix erros.
From that preliminary observation, some sentences were indicated have errors. First, suffix error were found in sentence
“We have a plan to compute our library system in order to
make it organized and eassy to access”. In this sentence, suffix -ize should be added to word compute to indicate verb. For example, “We have a plan to computerize our library system in
order to make it organized and eassy to access”. Second, in
sentence “Dropping your book at the public library can be
considered public disturbanced”. In this sentence, the word
that is used should be in noun. The word disturb added with suffix –ance to make it noun without suffix –ed. For example,
4Robert Lado, Language Teaching: A Scientific Approach, (New York: McGraw-Hill, 1986), p 13.
5Francis Katamba, Morphology, (New Tork: St. Martin’s Press, 1993), p 44
6Sri Rejeki,Frequent errors in students’work: an error analysis of the writing of grade XI
3
“Dropping your book at the public library can be considered
public disturbance”. Third, in sentence “I just realized that
Alice dependent friend”. In this sentence, the word depend
should be added with suffix –able to indicate adjective. For example, “I just realized that Alice dependable friend”. Fourth, in sentence “Economical problems such as inflation andunemployment are difficult to cope with”. In this sentence, because of the presence derivational suffix –al, the construction of economical is incorrect. For example, “Economic problems such as inflation andunemployment are difficult to cope with”. Fifth, in sentence “The day was filled with happily as they all celebrated their team winning the match”. In this sentence, the word that is used should be in noun. The word happy added with suffix –ness to make it noun not suffix –ly. For example, “The day was filled with happiness as they all celebrated their team winning the match”.
Affixation also becomes problem for foreign students in Bandung international school. Based on the research, English affixation is a subject which is difficult to be understood by the foreign students. This matter occurs because of English grammar is different from their mother tongue’s grammar.7 Beside that, based on the researcher’s experience during learning English, one of common language errors in writing is on how to form a word into other words. This kind of topic is discussed in morphology especially in the part of derivation.
Derivation makes a language rich of meaningful words. According to Haman, Zevenbergen, Andrus and Chmielewska, derivations are words derived from one stem or base word by attaching to them affixes, both prefixes and suffixes. These affixations are used to make new words in the language and are often used to make words of a different grammatical category from the root, for example the addition of suffix –ify to noun‘beauty’ will form a new verb ‘beautify’ which means ‘to make beautiful’.8
7 Rika Widawati, Kesalahan Afiksasi dalam Pembelajaran Bahasa Indonesia bagi Penutur
Asing, (Unpublished Thesis. Bandung: Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia,2012) 8
4
Some example of derivational affixes error that are made by the students in the process of English learning based on the researcher’s experience during learning English are ommission error on using affixes (changes the word from adjective to adverb) “Beautiful”→ “Beautifuly”(Incorrect) →
“Beautifully”(Correct), addition errors on using affixes
(changes the word from noun to adjective) “Beauty” → “Beautifully”(Incorrect) → “Beautiful”(Correct), misformation errors on using affixes (changes the word from verb to adjective) “Act” → “Action”(Incorrect) → “Active”(Correct), and so on.
The grammatical rules of derivational affixes are sometimes easy enough for some students to understand. Although the grammatical rules are easy enough for them, some students also still have problems because they are not careful, they do the task carelessly. For example, they do not add –ness to change adjective into noun. Beside that, there are some difficult grammatical rules that make the students do not understand and they are confused when they learn about it. For example, they are confused to choose what appropriate suffix to change adjective word into adverb word. From those explanations, it can be inferred that many students have problems when they learn derivational affixes especially in suffixes.
The problem of course will cause the reoccurring of errors or mistakes. However, making errors in the process of learning is natural because we can not understand the lesson before we try to understand and make errors. Errors in the process of foreign language learning are caused by the interference of mother tongue.9 Moreover, every language has different patterns and rules that should be paid attention to by the target language learners. So that’s why, errors in foreign language learning especially English are the cases which are difficult enough to avoid. Dulay pointed out that people can not learn language without making systematically errors. Thus, making
Children and Adults in Polish and English. (Polish: Polish Psychological Bulletin, Vol. 40, 2009)
9
5
error is a part of learning. Moreover, errors could be served as an indicator of progress and success in mastering language.10
In this study, the researcher chooses english teacher education department of State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya. The researcher is interested in conducting research at that department because the students are taught derivational suffixes subject at Morphosyntax class. So that, when they have learned derivational suffixes, logically they will apply and concern on the use of derivational suffixes especially in their writing. In addition, when she did a survey for english teacher education department of State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya students, it showed that most of students were still confused to differentiate the kinds of derivation and they could not perform them correctly. The researcher thought that it is necessary to analyze students’ error in derivational suffixes especially in writing because it has significant role in language using. The analysis of students’ errors is something advantageous in order to know students’ needs then finding the solution for it. The research hopes that the findings in the analysis of students’ affixation errors can be useful for education progress.
Therefore, from that point of view above the researcher is interested to conduct a research entitled “An Error Analysis on Derivational Suffixes in The Students’ Writing Assignments of English Teacher Education Department of State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya”.
6
A. Research Question
This research was conducted to analyze the students’ error in using derivational suffixes in writing. Thus, the researcher addresses a question in this study:
1. What are derivational suffix errors in the students’ writing assignments of English Teacher Education Department of State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya? 2. What are the most frequent derivational suffix errors in the
students’ writing assignments of English Teacher Education Department of State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya?
B. Objective of The Research
Based on the statement of the problem above, this study aims to find the matter below:
1. To know the derivational suffix errors in the students’ writing assignment of English Teacher Education Department of State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya.
2. To know the most frequent derivational suffix errors in the students’ writing assignment of English Teacher Education Department of State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya.
C. Significance of The Research
This research offered benefits for some parties such as, lecturers, students, the researcher, and other readers. The researcher explained each part briefly.
1. The Lecturer
The research can be used for measuring the students’ ability in learning derivational suffixes. The lecturer has to be aware of the students’ error. The lecturer should give a better and clearer explanation especially about the students’ difficulties in learning derivational suffixes. Then, the lecturer should design and improve more appropriate method in the next teaching so that the students could reach the learning goal easier.
2. The students
7
suffixes that is difficult for students so they can write their English writing assignment correctly.
3. The reader
The research can be used to help the readers’ understanding of derivational suffixes.
4. The researcher
The research can be used to expand knowledge and experience of the researcher about derivational suffixes. D. Scope and Limit of The Research
The scope of this study is on students’ errors in changing words using derivational affixes. Since we know that affixes are divided into three parts, namely prefix, suffix, and infix, but this study only focuses on the suffix. The researcher chooses derivational suffix errors because she thinks that it is the most common word formation which oftenly used by students, not only for speaking but also for writing assignment.
This study is limited into fourth semester students of Argumentative writing class of English Teacher Education Department of State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya academic year 2016-2017.
E. Definition of Key Terms
Related to this research, there are some key terms that nee to be specified in order to avoid misunderstanding of the contents of the study. There are as follows:
1. Error Analysis
According to H. Douglas Brown, error analysis is the study of the learner’s error, which can be observed, analyzed, and classified to reveal something of the system operating within the learner.11 In this syudy, error analysis describes and explains the errors of derivational suffixes made by learners in their written production in their target language. The errors need to be analyzed carefully since errors are parts of learning. A study of students’ errors in derivational suffixes are obtained through the students’ writing assignment at argumentative writing class of english teacher education department of State Islamic
11
8
University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya by using some procedures of analysis proposed by Ellis’s theory of error analysis which is also supported by Brown’s theories. 2. Derivational Suffix
According to Peter T. Bauer derivational suffix is a group of letters at the end of a word which changes the word’s meaning and often part of speech.12 This material has been taught to the fourth semester students of english teacher education department of State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya. But, most of the students were still confused to differentiate the kinds of derivational suffixes and they could not perform them correctly especially in their writing product. It is known from the result of analyzing the students’ writing assignment at english teacher education department of Islamic State University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya.
12
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
In a research, it is important to describe the theories related to the problems of the study, which are used as foundation and reference in order to give relevant knowledge in the field. In this chapter, the researcher discussed some important theories related to this research. The researcher revealed some important aspects such as error, error analysis, word formation, affixation and derivational suffix. In addition, some previous studies related to this linguistic field also will be revealed.
A. Error
Error is familiar for foreign language learner because it is part of learning process.1 However, some people cannot define it in the proper meaning. Therefore, the researcher explained further definition of error according to some theories.
1. Definition of Error
Dulay defined error as the flawed side of learner speech or writing. They are those parts of conversation or composition that deviate from some selected norm of mature language performance.2 It means that the area of learner’s errors can be found in the speech such as in their conversation and writing. Further, the teachers have responsibility to overcome their students’ language errors. The teacher have come to realize that making error is an inevitable part of learning, because to achieve English acquisition, the students must get through some errors first, and the they can learn from their own errors.
Brown said that in order to analyze learners’ errors in a proper perspective, it is crucial to make a distinction between mistake and errors, which are technically two very different phenomena. A learner makes a mistake when writing or speaking because of lack of attention, fatigue, carelessness, or some other aspects of performance.3 Mistakes can be self-corrected when attention is called.
1 Rod Ellis, Second Language acquisition, (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1997), p. 13 2 Heidi C. Dulay, Language Two (New York: Oxford University, 1982) p. 138
10
Whereas, an error is the use of linguistic item in a way that a fluent or native speaker of the language regards it as showing faulty or incomplete learning. In other words, it occurs because the learner does not know what is correct, and thus it cannot be self-corrected.
From the statements above, it can be concluded that errors is caused by lack of knowledge about her target language or by incorrect hypotheses about it; and mistakes caused by temporary lapses of memory or confusion. Another way to differentiate between error and mistake is if the learners can correct themselves, it is probably mistake, but if they can not, it is an error.
B. Error Analysis
Error analysis is one of the important topics in this research. Error analysis is very famous for many researchers because it is one of study field in language learning. The researcher explaines the part of error analysis such as the definition of error analysis and procedure of error analysis. 1. Definition of Error Analysis
Error analysis is the study of the learner’s error, which can be observed, analyzed, and classified to reveal something of the system operating within the learner.4 Brown claims that it can keep too closely focused on specific languages rather than viewing universal aspects of language.
One of the presuppositions of error analysis is that the making of errors indicates learning difficulty. It is assumed that when the learners make errors, they have difficulties in learning. This statement is supported by Brown,
“Learning foreign language (in this case, English) often meets a lot of difficulties. When the learners learn the target, they might face more problems than they learn their own mother tongue, although they understand and can apply their own language easily. It does not mean that they will be able to comprehend the target language easily. Sometimes the difficulties
4
11
appear because of the differences the target language and the native language”.5
In addition, it would be quite unreasonable to expect the learners of a target language not to exhibit such slip of the tongue, since they are subject to similar external and internal condition when performing in their first or second language. Mostly, the learners can not avoid making errors in learning the target language. The errors happen because of interference from the first or the second language of the learners.
Researchers and teachers of second language soon came to realize that the errors made by the learners in the process of constructing a new system of language needs to be analyzed carefully because it can be used for the keys to the understanding of the process of second language acquisition. Corder noted,
“A learner’s errors are significant in (that) they provide the researcher evidence of how language is learned or acquired what strategies and procedures the learners is employing in the discovery of the
language”6
In addition, Johansson stated that an analysis of the learner’s errors gives us evidence of their competence in the foreign language. We also gain valuable information concerning learners’ difficulties at different stages. Such information is important for the planning of courses and the construction of teaching materials.7
From the descriptions above, it is concluded that analyzing errors in the process of learning is an important aspect because by knowing the errors, we can know the learners’ difficulties in the process of learning. Therefore, it can also help the progress and the success of learning. 2. Procedures of Error Analysis
Error analysis is the process of analyzing the learners’ error in acquiring a language. Thus, there are some steps
5 Ibid, p. 41 6 Ibid, p. 217
12
that should be followed by the researcher. Ellis has designed that there are are stages in doing the error analysis namely identifying error, describing error and explaining error. Those points will be explained briefly.8 a) Identification of Errors
The first step in analyzing learners’ errors is to identify the errors. To identify the error, we have to take note or write out the sentences which contain the error, and then mark or underline the error word or phrase. Identification of error is needed to compare the error word or phrase produced by the learners with correct one in the target language. For example, a learner produces Her mental is strong. It is clear that the sentence contains error, the correct sentence should be Her mentality is strong. By comparing the two sentences, we can see that the learners used a word mental instead of mentality. The error is due to omission error in using derivational suffixes –ity. b) Description of Errors
The second step in analyzing learners’ errors is to describe the errors. In this step, the researcher describes the error by classifying first the error of derivational suffix in form of table, which consist the error words or phrases produced by the learners. All of errors that have been identified can be described into two ways. The first technique is to classify the errors based on grammatical categories. All the suffix errors are gathered and described based on the types of derivational suffix. The second way is describing error based on the surface structure taxonomy.
Surface strategy taxonomy highlights the ways surface structure are altered. Dulay noted:
“Learners may omit necessary items or add unnecessary ones; they may misform items or misorder them.”9
8Rod Ellis, Second Language Acquisition, (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1997), p. 57 9
13
Classifying errors using surface strategy taxonomy can give a clear description about cognitive processes that underline the learners’s reconstruction of the new language or language being learned. It also make us aware that learners’ errors are the result of their active way in using the temporary principles to produce the target language. Here is the detailed description of each category used in surface strategy taxonomy. There are omission, addition, misformation and misordering.
Omission is a type of error which is characterizes by the absence of an item that must appear in a well-formed utterance.10 it is divided into two major sub divisions: omission of content morphemes [(e.g Her ... will be unforgettable). In this sentence the learner omits ‘kindness’. This sentence should be reconctructed as : Her kindness will be unforgettable]; omission of grammatical morphemes [(e.g Moana is a very beauty girl). This example shows the omission of grammatical morpheme –ful which is characterized as derivational morpheme of the word “beauty”].
Addition is a type of errors which are characterized by the presence of an item which must not appear in a well-formed utterance.11 It usually occurs in the later stages of second language acquisition or learning. In this stage, learners usually have already acquired target language rules. Learners are often too faithful to use certain rules which result in errors. At least there are three types of addition errors have been observed in speech of both first language and second language learners: ‘Double Markings’ are described as the failure to delete certain items which are required in some linguistic construction but not in other. [(e.g Moana doesn’t goes to school). This sentence has double marking of both auxiliary ‘does’ and an inflectional affixes ‘–es’
10 Ibid, p. 154
11
14
in goes]; ‘Reguralization’ is when there are both regular and irregular forms in language, learners sometimes get confused to apply the correct rule in a certain construction. Sometimes they apply the rule used to produce the regular ones to those that irregular. [(e.g She drinked a tea last night). In this case, the learner regularizes the rule of irreguler word. She considers the past participle word ‘drink’ is ‘drinked’ instead of ‘drunk’]. ‘Simple Addition’ is neither a double marking nor regularization. [(e.g The cat doesn’t live in the water). The addition of auxiliary marker ‘does’ is not appropriate used in that sentence, because there is the plural subject. The reconstructed sentence is ‘The dogs don’t live in the water’].
Misformation is a type of error which are characterized by the use of the wrong form of the morpheme or structure.12 There are ususally three types of misformation which have been frequently reported in the literature: ‘Regularization’ (e.g She likes talking herself); ‘Archi-forms’ (e.g I met her last night. Her brought many books); ‘Alternating forms’ (e.g I seen his yesterday).
Misordering is type of errors which are characterized by the incorrect placement of a morpheme or group of a morpheme in an utterance. In other word, misordering error happens when the learner misplaces an item or group of item in a sentence. [(e.g They not do work here). The sentence should be: ‘The do not work here’.]
In describing the learners’ errors, the researcher applies the first way, which is describing errors based on grammatical categories.
c) Explanation of Errors
The last step in analyzing the learners’ errors is explaining the errors. In this step, after analyzing error words in the table, the researcher explain the result of the error words or phrases more complex and
12
15
classifies the dominant errors which occur in students’ writing. Therefore, the reader can comprehend the error words clearly by themselves.
C. Affixation
The process of affixation in morphology can be divided into prefixes, infixes and suffixes. Quirk et al states that affixation is adding a prefix or a suffix to the base with or without a change of word class.13 An affix is a bound morpheme which may be attached at the beginning or end of a base word. In this case, as affix is a morpheme, with only occurs when attached to some other morpheme, or morphemes such as root of stem or base. It is a morpheme that cannot stand alone or bound morphemes. The process of affixation in morphology can be divided into:
1. Prefixes
Prefix is a syllable or syllables which appear in front of the root and change the meaning of the root.14 It means that prefix is affix that precedes the root and can change the meaning of the root. Prefix can be used only for derivational morphemes.
All prefixes in English are derivational so that they create new meaning or new words.15 Most prefixes do not change part of speech but change the meaning. The prefix which changes the part of speech, for example:
prefix a- changes noun and verb into adjective: ablaze, asleep, astir, astride, abed, abroad
prefix be- changes noun into verb: befriend, bedeck, becalm, besmirch
prefix en- changes adjective and noun into verb:enlarge, ensure, encircle, encase, entrap. There are many kinds of prefixes likes re-, un-, in-, dis-, mis-, ex-, en-, im-, il-, sub-, tele-, hyper-, neo-, inter-, kilo-, mega-, mini-, fore-, co-, bi-, auto-, counter-, anti-,
13Randolph Quirk, Sidney Greenbaum, A University Grammar of English, (Longman: University of London, 1973), p. 430
14Sharon Wynne, Texes English as a Second Language (ESL), (Boston: XAMonline, Inc., 2010), p. 4
16
poly-, under-, super-and etc. Those kinds of prefixes of English can be classified semantically into some groups, such as: negative prefixes (un-, in- , im-, il-, ir-, non-, a- , de-, dis-, mis-, anti-, dys-), prefixes of repetition (re-), locative prefixes (super-, sub-, inter-, intra-, trans-), prefixes of time and order (fore-, pre-, post-, neo-, ex-), prefixes of quantity (uni-, bi-, tri-, multi-, semi-, omni-, micro-, macro-, hyper-, over-).16
2. Infixes
Infixes are bound morphemes that are inserted within the words. There are no infixes in the English language, but in the languages such as Tagalog and Bontoc (in the Philippines), Infixes are represented by the morphemes preceded and followed by a hyphen; e.g., -um-.
3. Suffixes
Suffix is a letter or letters added to the end of the root that can change the word class and also the meaning of the root.17 It means that suffix is affix that follows the root and can change the word class and the meaning of the root. Suffix can be used for derivational morphemes and inflectional morphemes.
Such as: -ance in the word appearance. -able in the word understandable. –ing in the word singing.
Mostly, the derivational morphemes are affixes. An affix is a morpheme which only occurs when attached to some other morpheme or morpheme such as a root or stem or base.18 On the other said affixes are morphemes that cannot stand alone or bound morphemes. English derivational adds morphemes principally by prefixing or suffixing.
Katamba explains that derivational morphemes form new words, first by changing the meaning of the base to which they are attached. In English, it is usually called derivational prefix, for example ‘kind’ vs ‘unkind’ (both
16http://www.unizd.hr/Portals/36/kolegiji/morphology/Morphology 5 [Compatibility Mode].pdf
17 Ibid. 18
17
are adjectives but with opposite meanings). Second by changing the word-class that a base belong to. In English it is usually called derivational suffix, for example the addition of -ly to the adjective ‘kind’ produce the adverb ‘kindly’. As rule, it is possible to derive an adverbs by adding the suffix –ly to an adjectival base.19
D. Derivational Suffixes
A suffix is a group of letters at the end of a word which changes the word’s meaning and often part of speech. However, there are some suffixes that do not change part of speech but the meaning, such as suffix –ship, hood, ity, let, -ist, -ian do not change part of speech (noun).20
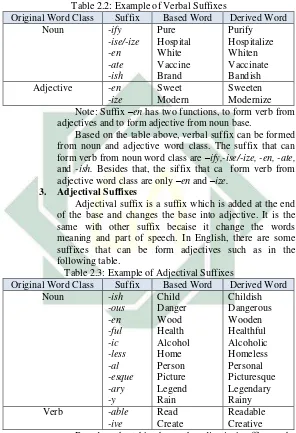
There are many kinds of suffix such as al, ance, ation, ence, er, ist, ion, dom, ment, ish, ous, an, esque, ate, ful, ic, like, able, less, ly, ise, ize, ate, en, ify, ness, -ism, -ive, -ory, -y, -ship, and –ity. According to form class of derivatives that they produce, suffixes are classified into: suffixes forming noun (nominal suffixes), suffixes forming verbs (verbal suffixes), suffixes forming adjectives (adjectival suffixes) and suffixes forming adverbs (adverbial suffixes).21 1. Nominal Suffixes
Nominal suffix is a suffix which is added at the end of the base and changes the base into noun. In other word, the suffix is placed in the end of the base and from this combination produces a new lexeme. In English, there are some suffixes that can be used in forming nouns from verb and adjective base form. They are mentioned on the table bellow.
Table 2.1: Example of Nominal Suffixes
Original Word Class Suffix Base Word Derived Word
Verb -ation
-ion -ure -al
Explain Predict Close Refuse
Explanation Prediction Closure Refusal
19Ibid. p.47
20Peter Thomas Bauer, English Word Formation. (City of Cambridge : Cambridge University Press, 1983), p. 220
18 -er/-or -ment -ee -y -age -ance -ant Sing Develop Employ Injure Marry Perform Account Singer Development Employee Injury Marriage Performance Accountant Adjective -cy
-ness -y -dom -th -ity Excellent Happy Jealous Free Warm Specific Excellency Happiness Jealousy Freedom Warmth Specificity
Noun - ship
- hood -ity -let -ist -ian Friend Mother Human Book Economy History Friendship Motherhood Humanity Booklet Economist Historian
Note: Suffix –al has two function, to form noun from verb base and to form adjectives from noun base. Suffix–y also has two functions, to form noun from verbs or adjectives base and to forms adjectives from noun bases.
Based on the table above, nominal suffix can be formed from verb and adjective word class. The suffix that can form noun from verb word class are –ation, -ion, -ure, -al, -er/-or, -ment, -ee, -y, -age, -ance and -ant. Besides that, the suffix that can form noun from adjective word class are –cy, -ness, -y, -dom, -th, and -ity. However, there are also some nominal suffix that do not change the word class, such as suffix –ship, -hood, -ity, -let, -ist, -ian. 2. Verbal Suffixes
19
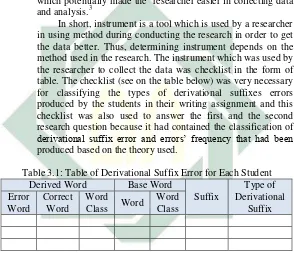
Table 2.2: Example of Verbal Suffixes
Original Word Class Suffix Based Word Derived Word
Noun -ify -ise/-ize -en -ate -ish Pure Hospital White Vaccine Brand Purify Hospitalize Whiten Vaccinate Bandish Adjective -en
-ize
Sweet Modern
Sweeten Modernize Note: Suffix –en has two functions, to form verb from adjectives and to form adjective from noun base.
Based on the table above, verbal suffix can be formed from noun and adjective word class. The suffix that can form verb from noun word class are –ify,-ise/-ize, -en, -ate, and -ish. Besides that, the siffix that ca form verb from adjective word class are only –en and –ize.
3. Adjectival Suffixes
Adjectival suffix is a suffix which is added at the end of the base and changes the base into adjective. It is the same with other suffix becaise it change the words meaning and part of speech. In English, there are some suffixes that can be form adjectives such as in the following table.
Table 2.3: Example of Adjectival Suffixes
Original Word Class Suffix Based Word Derived Word
Noun -ish -ous -en -ful -ic -less -al -esque -ary -y Child Danger Wood Health Alcohol Home Person Picture Legend Rain Childish Dangerous Wooden Healthful Alcoholic Homeless Personal Picturesque Legendary Rainy
Verb -able
-ive
Read Create
20
form adjective from noun word class are –ish, ous, en, -ful, -ic, -less, -al, -esque , -ary and -y. Besides that, the suffix that can form adjective from verb word class are only –able and –ive.
4. Adverbial Suffixes
Adverbial suffixes is a suffix which is added at the end of the base and changes the base into adveb. The main derivational suffixes in forming adverb are –ly, -wise, – ward(s) and -ways. The example of those suffixes can be seen in the following table below.
Table 2.4: Example of Advertbial Suffixes
Original Word Class Suffix Based Word Derived Word
Adjective -ly/-y Slow Slowly
Noun -wise
-ward -ways
Length Back Side
Lengthwise Backward Sideways Based on the table above, the adverbial suffix can be formed from adjective and noun word class. The suffix that can form adverb from adjective word class is only –ly. Besides that, the suffix that can form adverb from noun word class are –wise, -ward and –ways.
In adverbial suffix, there are some rules adding –ly to words forming adverb, such as adding –ly to words ending in consonant (stupid → stupidly); If the root word ends in a ‘y’, change the ‘y’ to an ‘i’ and then add ‘ly’ (angry → angrily); If the root word ends in ‘-le’, the ‘e’ is changed to ‘-y’ (gentle → gently). If the root word ends in ic’, add ‘-ally’ (magic → magically).
E. Previous Studies
Here, the researcher reviews some previous studies which are related to this study as follows:
1. The first previous study was done by Nihlah Afthoniyah (UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya, 2012), entitled “An Error Analysis of English Morphological Inflection Made by The
First Year Students of SMK Yasmu Manyar Gresik”. In her
21
research. To colect the data, she usedstudents’ test and documentation. The result shows that students made error in English morphological inflaction. The types of errors in the use of five English morphological inflections (plural inflection, possessive inflection, progressive inflection, past tense inflection, and third person singular inflection) shows that possessive inflection erroris on the first rank (78 or 34,06%). The factors causing errors in the use of five English morphological inflections show that false concept hypothesized is on the first rank (50 or 48,54%).22 2. The second previous study was done by Siti Almaidah
(UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya, 2015), entitled
“Misformation Error in Using Negative Prefixes by
Students of English Teacher Education Department at Uinsa Surabaya”.In her research, she focused on students’ mistake in changing the words into negative qualities by using prefix and the most frequent misformation errors made by the students. She limit the negative prefixes only six categories of prefixes such as in -, un-, non-, a, dis-, and mis-. It was conducted by descriptive quantitative research. To colect the data, she only used students’ test. The result shows that the varieties of students’ mastery of negative prefix still fail, because the total number of error was 248 in misformation of negative prefixes and the most frequent misformation error is in prefix un- 124 error (50,21%).23
3. The third previous study was done by Bahjatul Uyun (UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya, 2014), entitled, “An Analysis of Collocation Errors in Students’ Writing 3 of English Teacher Education Department at Uin Sunan Ampel Surabaya”. In her research, she focused on the types of collocations error which are commonly used by the students. It was conducted by descriptive qualitative
22Nihlah Afthoniyah), An Error Analysis of English Morphological Inflection Made by The
First Year Students of SMK Yasmu Manyar Gresik”.(Undergraduate Thesis, UIN Sunan
Ampel Surabaya, 2012)
23Siti Almaidah, Misformation Error in Using Negative Prefixes by Students of English
22
research. To colect the data, she only used documentation students’ writing product. The result shows that there are many collocation errors found on students’ writing product. The most collocation used by students in their writing is (1) Verb-Preposition, with 44 error collocations. (2) Verb-Noun, with 43 error collocation (3) Adjective-Noun, with 22 error collocations (4) Noun-Preposition, with 17 error collocation. (5) Adjective-Preposition, there are 32 error collocations (6) Adverb-Adjective, there are 9 error collocation.24
4. The fourth previous study was wroten by Alifa Nurul Barokah (IKIP PGRI Semarang, 2011), entitled “Analysis Derivational Words Found in Articles of Cool and Smart Magazine Published on May, 2011 as a Contribution in Teaching Morphology”. His study was conducted to find out the derivational words found in the articles of Cool and Smart Magazine published on May, 2011, to find out the word class of derivational words, and to find out the meaning of derivational words. The result of the study shows that there are 36 derivational words from of noun, such as civilization, signature, freedom, making and user; 6 derivational words from of verb, such as, dissolve, decorate; 30 derivational words from of adjective, for example, African, dangerous, personalandamazing; 15 words from of adverb such as, generally, usually, appropriately, and easily.25
5. The fifth previous study was done by Sri Romadhon Eko Yuliyanti (Sate Islamic Studies Institute STAIN Salatiga, 2012), entitled “The Analysis of Derivational Process of English Nouns as Found in some of the Jakarta Post
Articles (Published on January, 2nd 2012)”. In her
research she is eager to analyze derivational process of English nouns as found in some of the Jakarta post articles
24Bahjatul Uyun), An Analysis of Collocation Errors in Students’ Writing 3 of English
Teacher Education Department at Uin Sunan Ampel Surabaya.(UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya, 2014)
25Alifanurul Barokah, “Analysis Derivational Words Found in Articles of Cool and Smart
Magazine Published on May, 2011 as a Contribution in Teaching Morphology”,
23
(published on January, 2nd 2012). This research discussed about the process of English noun words that added by derivational affixes in the some of the Jakarta post articles. This research used library research. Focusing on the problem statements, there are five cases. They are what are the derived nouns found in some of the Jakarta post articles, does the process of affixation change the category of the base words, do the new derived words change in the meaning, do the affixations occur in the specific root and what are the categories of the derived noun. The result of her study is she found 90 English nouns add trough derivational process. There are megawatt, disincentives*, discontent, non-European, immigrant, undertaking, and etc. A lot of number word of verbs, adjective, and nouns which derives a new English noun. And the last the derivational processes of English nouns have changes the meaning all of the new words from the original words.26 6. The sixth previous study has been done by Ning Mulia
(State University of Surabaya, 2010), entitled “An Analysis of the Errors on the Derivational Affixes Found in the Students’ Writing”. In her research, she focused on the types of derivational affix errors and the causes that are factors which have influenced to the occurrence of derivational affix errors. She described and counted the errors based on the causes of derivational affix errors. To collect the data, she only used students’ test.27
7. The seventh previous study is a research concerning Morphology by Ririn Kusumawati (Universitas Islam Negri Malang. 2010), entitled “Morphological Error Found in the English Essays of the Fifth Semester Students
of English Letters and Language”. This study investigates
morphological error in the essays of the fifth semester students of English Letters and Language Department of UIN Malang in 2008. The objectives of this study are to
26Sri Romadhon Eko Yuliyanti, “The Analysis of Derivational Process of English Nouns as
Found in Some of the Jakarta Post Articles,(Published on January,2nd 2012)”,
(Ungraduated Thesis, Sate Islamic Studies Institute STAIN Salatiga, 2012)
27Ning Mulia,“An analysis of the Errors on the Derivational Affixes Found in the Students’
24
find out the kinds of morphological error in The result of this study shows that there are several morphological errors in are; Omission, addition, misformation and misordering except contain morpheme and article which belong to the branch of omission. The total number of morphological errors is 61 times. Based on the findings, she found that the most dominant kind of morphological error is omission with 25 times used or 40.98 %.28
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD
In this chapter, the researcher focuses on revealing what are the methods of conducting the research in systematic way. Firstly, the researcher decided the research design which fit with this study. Then, the researcher decided the research setting and th subject for this research. The researcher also explained the source of the data, research instrument, data collection technique and data analysis technique.
A. Research Design
As stated in the purpose of the study, this research was conducted to get the information about the derivational suffix errors in the students’ writing assignment of english teacher education department of state islamic university of Sunan Ampel Surabaya. This study used descriptive qualitative which was designed to obtain information to determine the nature of a situation and to describe what exists in a current study objectively. Ibrahim stated that descriptive research is a research which controls and interprets about condition and phenomena such as relation, point of view, attitudes, process, and the influences of condition.1 Ary supported that descriptive qualitative is designed to obtain information concerning to the current status of phenomena.2 It includes collecting data to answer the problems dealing with the current status of people being faced at this moment. We usually call them subject of the study.
This research used that method because it was appropriate to the objectives of the research which focused on the derivational suffixes which are commonly occurred in students writing product and also this research focused on students’ derivational suffixes errors in their writing assignment. Because they had learned derivational suffixes subject at morphosyntax class. So that, when they had learned derivational suffixes, logically they will apply and concern on the use of derivational suffixes in their writing. The results of
1Nana Sudjana, Penelitian dan Penilaian Pendidikan (Bandung: Sinar Baru Algensindo, 2009), 65
26
the research emphasized more toward the data interpretation found in the field. The results are not written in the form of figures and tables with statistical measures, but it is illustrated in the form of describing words to the results and it is presented in narrative.
B. Research Setting and Subject
In this study, the researcher took the students from the fourth semester of English Teacher Education Department at state Islamic university of Sunan Ampel Surabaya academic year 2016-2017 to employe as the subject of this research. Actually, the total students of argumentative writing were 120 students who are divided into five classes; A, B, C, D, E. But, the researcher only took C class (content of 30 students but the researcher only take 13 students) and E class (content of 13 students) with the same lecturer. The English lecturer on this class applied assignment of making argumentative writing every week during the semester, but the researcher only took three assignments of students’ writing.
This research was conducted in Argumentative writing class of English Teacher Education Department of state Islamic university of Sunan Ampel Surabaya in the academic year of 2016-2017. This university was chosen by the researcher because the researcher had some considerations. Firstly, the reason is because the university has English Education Department that has morphosyntax class which teach the students about derivational suffixes. Secondly, the researcher chooses that class because this study is about analysing derivational suffixes error in students’ writing assignment and only the students in this writing class have learned about derivational suffixes. Thirdly, it is the difficulties of students in using derivational suffixes on their writing assignment and the experience of the resarcher who has become students in that class.
C. Data and Source of Data
27
context of derivational suffixes. The data were taken from the students’ weekly assignment of argumentative writing class of English Teacher Education Department of state Islamic university of Sunan Ampel Surabaya.
D. Research Instrument
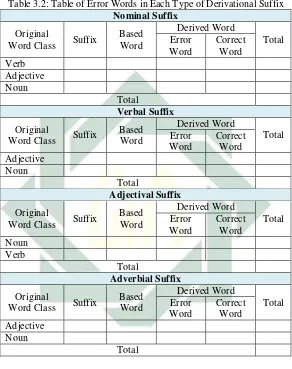
Each technique which is used to collect the data needs an instrument. Instrument is the measurement tool in the test which potentially made the researcher easier in collecting data and analysis.3
[image:36.420.70.364.157.410.2]In short, instrument is a tool which is used by a researcher in using method during conducting the research in order to get the data better. Thus, determining instrument depends on the method used in the research. The instrument which was used by the researcher to collect the data was checklist in the form of table. The checklist (see on the table below) was very necessary for classifying the types of derivational suffixes errors produced by the students in their writing assignment and this checklist was also used to answer the first and the second research question because it had contained the classification of derivational suffix error and errors’ frequency that had been produced based on the theory used.
Table 3.1: Table of Derivational Suffix Error for Each Student Derived Word Base Word
Suffix
Type of Derivational
Suffix Error
Word
Correct Word
Word
Class Word
Word Class
Note: This table is used to classify the error for each students’ writing assignment. Further, the error will be classified and counted based on each type of derivational error in the following table.
[image:37.420.71.363.73.442.2]
28
Table 3.2: Table of Error Words in Each Type of Derivational Suffix Nominal Suffix
Original
Word Class Suffix
Based Word Derived Word Total Error Word Correct Word Verb Adjective Noun Total Verbal Suffix Original
Word Class Suffix
Based Word Derived Word Total Error Word Correct Word Adjective Noun Total Adjectival Suffix Original
Word Class Suffix
Based Word Derived Word Total Error Word Correct Word Noun Verb Total Adverbial Suffix Original
Word Class Suffix
Based Word Derived Word Total Error Word Correct Word Adjective Noun Total
E. Data Collection Technique
Collecting data can be done in various setting, sources and ways including interview, questionnaire, observation, and documentation.4 In this research, the researcher used documentation technique.
4
29
The researcher asked the permission of the lecturer to ask and copy the students’ writing assignment. The researcher only asked three assignment of each student in that class. After that, the researcher read those argumentative writing assignment deeply and looked for the errors. Then, the researcher classified the error of derivational suffix based on the theory used.
The next step was the researcher counted the frequency and percentage each category based on the formula used. After knowing the percentages of derivational suffixes errors which students made, the researcher selected the highest percentages of derivational suffixes errors analysis.
F. Data Analysis Technique
The data of this study was the form of derivational suffix errors made by the students in their writing assignment given by the lecturer. After collecting data, the researcher analyzed the data by applying the procedures below:
1. Identification of Errors
In this step, the researcher read the students’ writing assignment to identify derivational suffix errors. She tried to find out the derivational suffix errors by underlying the errors. She tried to analyze the data as objective as possible.
2. Classification of Errors
After identifying the errors, the researcher described the errors by classifying the errors based on grammatical categories in form of table (all the suffix errors are gathered and classified based on the types of derivational suffix)
3. Calculation of Errors
Based on the errors classification above, the researcher counted the error in order to know the errors frequency made by the students of English Teacher Education Department of state islamic university of Sunan Ampel Surabaya. In this case, the researcher used formula proposed by Sudijono.5
30
f
P = --- X 100 N
P = Percentage
[image:39.420.69.364.121.386.2]f = Frequency of errors in each type N = Total number of errors
Table 3.3: Table for Error Frequency
Original Wors Class
Types of Derivational Suffix
Total (N) Nominal
Suffix
Verbal Suffix
Adjectival Suffix
Advrbial Suffix
f P% f P% f P% f P%
Noun Verb Adjective Adverb Total
4. Explanation of Errors
In this step, the researcher made a description of analyzing result on derivational suffix errors and the types of derivational suffix errors in the form of a brief description.
5. Drawing conclusion
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDING AND DISCUSSION
This chapter presents the collected data from students’ argumentative writing assignments of English Teacher Education Department of State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya and the analysis of it. The derivational suffix error and the error frequency obtained are showed as research findings. Finally, the analyzed data is explained based on the types of derivational suffix error in discussion part.
A. Research Findings
The data was obtained by collecting the weekly students’ writing assignment. There were 26 students who collect the writing assignment. They got different topic in making an argumentative essay every week. In this case, the researcher only used three writing assignment of each student to be analyzed.
In analyzing the writing assignment, the researcher identified the data in each word. After collecting and analyzing the data, the researcher found that there were still many error words in form of derivational suffix in the students’ writing assignment.
1. Derivational Suffix Errors in Students’ Writing Assignment
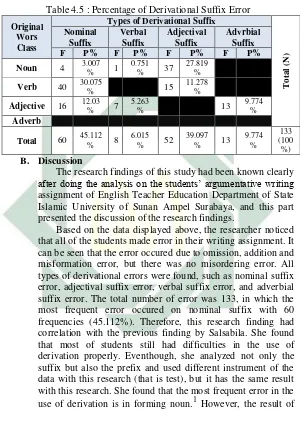
All the students made derivational suffix error in their writing assignment. After collecting and analyzing the data, the researcher found that there were 133 error words in form of derivatioal suffix and classified them into four types, they were nominal suffix error, verbal suffix error, adjectival suffix error and adverbial suffix error. Those are presented in the following tables:
a. Nominal Suffix Errors
[image:41.420.71.363.74.516.2]
32
Table 4.1 : Nominal Suffix Errors in Students’ Writing Assignment Original
Word Class
Suffix Base Word Derived Word T o ta l
Error Word Correct Word Verb -ment Amuse Enchant Move Govern Entertain Treat Enjoy Amusing Enchanting Moving Governer Entertainer Treaten Enjoyness Amusement Enchantment Movement Government Entertainment Treatment Enjoyment 7 -er / -or Lecture Consume Consume Manufacture Observe Direct Visit Facilitate Lectures Consument Consument Manufactor Observator Directur Visiters Facilitater Lecturer Consumer Consumer Manufacturer Observer Director Visitor Facilitator 8 -ation /-ition /-ion Expect Participate Protect React Explain Conclude Generate Expand Attract Experiment Compete Transport Add Pollute Compete Expecting Participating Protecting Reacting Explaining Conclution Generasion Expandsion Attractor Experimenter Competion Transportion Additional Pollutant Competitive Expectation Participation Protection Reaction Explaination Conclusion Generation Expansion Attraction Experimentation Competition Transportation Addition Pollution Competation 15
-dom Bore Bore
Bored Boring
Boredom Boredom 2
-th Grow Growing Growth 1
-y Scare Controvert
Scarey Controverce
Scary
Controversy 2
-ee Employ Employes Employee 1
33 Guide Maintain Guidence Maintaining Guidance Maintenance Adjective -ity / -y National Social Curious Responsible Mental Active Difficult Nationalty Socialty Curiousty Responsiblety Mentals Activeness Difficulth Nationality Sociality Curiosity Responsibility Mentality Activity Difficulty 7
-ion Abstract Appropriate
Abstractness Appropriatness
Abstraction Appropriation 2
-ance/ -ence Important Violent Independent Consequent Importence Violency Independency Consequention Importance Violence Independence Concequence 4
-ness Brave Happy
Bravement Happyness
Braveness Happiness 2 -ency Efficient Efficiention Efficiency 1
Noun
-ure Architect Architectural Architecture 1
-ist Psychology Pharmacy
Psychologist Pharmator
Psychology Pharmacist 2 -er Philosoph Philosophist Philosopher 1
Total 60
From verb as the original word class, there are: seven error words in using suffix “-ment”, eight error words found in using suffix “-er/-or”, fifteen error words found in using suffix “-ation/-ition/-ion”, two error words found in using suffix “-dom”, one error word found in using suffix “-th”, two error words found in using suffix “-y”, one error word found in using suffix “-ee”, four error words found in using suffix “-ence/-ance”.
From adjective as the original word class, there are: seven error words found in using suffix “-ity/-y”, two error words found in using suffix “-ion”, four error words found in using suffix “-ence/-ance”, two error words found in using suffix “-ness”, one error words found in using suffix “-ency”.
34
in using suffix “-ist”, one error word in using suffix “
-er”.
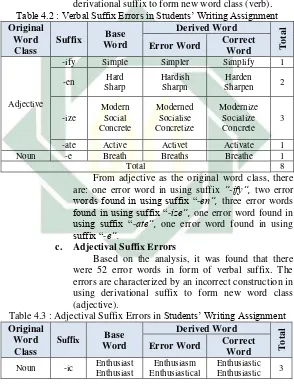
b. Verbal Suffix Errors
[image:43.420.70.364.142.529.2]Based on the analysis, it was found that there were 8 error words in form of verbal suffix. The errors are characterized by an incorrect construction in using derivational suffix to form new word class (verb). Table 4.2 : Verbal Suffix Errors in Students’ Writing Assignment Original
Word Class
Suffix Base Word Derived Word T o ta l
Error Word Correct Word
Adjective
-ify Simple Simpler Simplify 1
-en Hard Sharp
Hardish Sharpn
Harden Sharpen 2
-ize Modern Social Concrete Moderned Socialise Concretize Modernize Socialize Concrete 3
-ate Active Activet Activate 1
Noun -e Breath Breaths Breathe 1
Total 8
From adjective as the original word class, there are: one error word in using suffix “-ify”, two error words found in using suffix “-en”, three error words found in using suffix “-ize”, one error word found in using suffix “-ate”, one error word found in using suffix “-e”.
c. Adjectival Suffix Errors
Based on the analysis, it was found that there were 52 error words in form of verbal suffix. The errors are characterized by an incorrect construction in using derivational suffix to form new word class (adjective).
Table 4.3 : Adjectival Suffix Errors in Students’ Writing Assignment Original
Word Class
Suffix Base
Word Derived Word T o ta l
Error Word Correct Word
Noun -ic Enthusiast Enthusiast
Enthusiasm Enthusiastical
35
Atmosphere Atmospherical Atmospheric
-able Comfort Instagram
Comforteble Instagramable
Comfortable
--- 2
-al Controversy Electric Mystic Music Tropic Industry Agriculture Economic Procedure Historic Education Finance Picture Individu Motivation Controversil Electricity Mystis Musicle Tropica Industrical Agriculturial Economicial Prosedurial Historial Educatial Financal Pictural Individualized Motivating Controversial Electrical Mystical Musical Tropical Industrial Agricultural Economical Procedural Historical Educational Financial Pictorial Individual Motivational 15
-y Noise Wind
Noisey Windly
Noisy
Windy 2
-ly Friend Friendy Friendly 1
-ed Interest Interest
Interesting Interesting
Interested Interested 2
-ful Success Success Meaning Harm Successfull Successfull Meaningfull Harmfully Successful Successful Meaningful Harmful 4 -ous Danger Danger Danger Fame Mystery Fame Dangers Dangerouse Dangerouse Famouse Misteriuse Famuse Dangerous Dangerous Dangerous Famous Mysterious Famous 6
-ish Fool Fool Foolish 1
-ary Costume Customize Customary 1
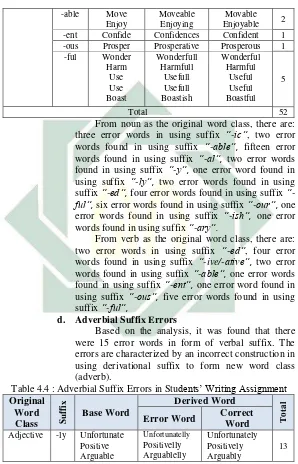
Verb
-ed Addict Introvert
Addiction Introverting
Addicted Introverted 2
36
-able Move Enjoy
Moveable Enjoying
Movable Enjoyable 2 -ent Confide Confidences Confident 1 -ous Prosper Prosperative Prosperous 1
-ful Wonder Harm Use Use Boast Wonderfull Harmfull Usefull Usefull Boastish Wonderful Harmful Useful Useful Boastful 5
Total 52
From noun as the original word class, there are: three error words in using suffix “-ic”, two error words found in using suffix “-able”, fifteen error words found in using suffix “-al”, two error words found in using suffix “-y”, one error word found in using suffix “-ly”, two error words found in using suffix “-ed”, four error words found