1
Chapter 5
2
Learning Objectives
• When you finish this chapter, you will:
– Understand why managers must keep abreast of software developments.
– Recognize the different generations of
programming languages and how they differ. – Understand the difference between application
3
Learning Objectives
– Know the strengths and weaknesses of tailored software vs. off-the-shelf software.
– Be able to cite the latest major developments in application and system software.
4
Software: Instructions
to the Computer
• A computer program is a series of instructions
to a computer to execute any and all processes.
• Computers only “understand” instructions
5
Programming Languages
• Programming languages
– Abbreviated forms of instructions that translate into machine language
– New programming languages make
6
Programming Languages
• Machine Languages (ML)
– Only languages computers can directly
interpret to carry out instructions
– ML coding: time-consuming and error-prone
– ML programmers: concerned with hardware
details
7
Programming Languages
• Assembly Languages
– Represent a string of ‘0s’ and ‘1s’ for machine language instruction
– More English-like; codes shorter than machine languages
– Assembler translates into machine language – Advantages of machine or assembly languages
• Programmer in control of hardware
8
Programming Languages
• Procedural Languages
– Third-generation (procedural) languages are more English-like than assembly languages.
– Programmers focus on the procedure of the application problem at hand.
9
Programming Languages
• Fourth Generation Languages (4GL)
– 4GLs are more English-like than procedural languages.
– Programmer only has to select an action
without having to specify the action’s formula or procedure.
– Easy to learn and use; shorter application development time.
10
Programming Languages
• Visual Programming
– Languages that let programmers create field windows, scroll-down menus,
click buttons, etc., by choosing from a palette
– Appropriate code written automatically – Accelerates work
11
Programming Languages
• Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
– Emphasis on the objects involved in the task, not on the procedure
– An object encapsulates a data set with the code that is used to operate on it
– Standardized programming modules can be reused
12
[image:12.720.22.720.62.473.2]Programming Languages
Figure 5.3 Advantages of object-oriented
13
[image:13.720.33.709.51.510.2]Programming Languages
14
[image:14.720.25.720.45.513.2]Programming Languages
15
Programming Languages
– Application Software vs. System Software
• Application: a program developed to
address a specific business need; software for development of such programs.
• System: programs designed to carry out general routine operations, such as
16
Application Software
• Application-specific programs
– Programs designed to perform
specific jobs
• General-purpose programs
17
Application Software
• Custom-Designed Applications
– Advantages:
• Meeting the organization’s needs exactly • In-house developers are sensitive to the
organizational culture
– Disadvantages:
• High cost
• Production schedule subject to long delays
18
[image:18.720.0.720.50.499.2]Application Software
19
Application Software
• Packaged Software
– Advantages:
• Low cost • High quality • Vendor support
• Immediate availability
20
[image:20.720.21.720.50.512.2]Application Software
21
Applications Software
• Packaged Software
– Word processors
– Electronic spreadsheets
22
Packaged Software
• Multimedia
– Can handle many different types of data such as text, voice, and image
– Powerful means of communicating
23
Packaged Software
• Virtual Reality (VR)
– Mimics sensory reality
– Some sophisticated VR software includes use of goggles, gloves, earphones, and a moving base
24
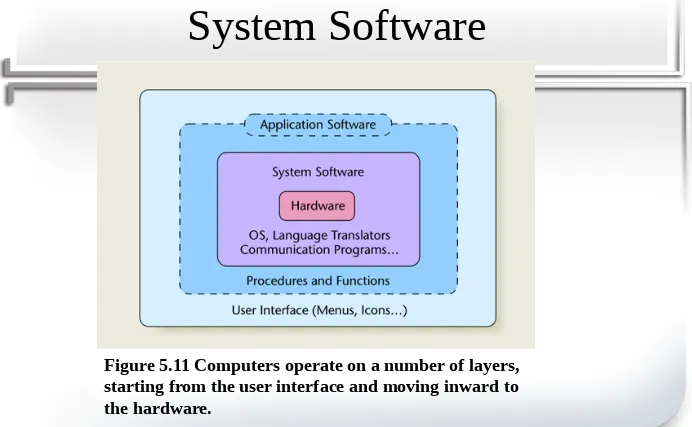
System Software
• Manages computer resources and
performs routine tasks not specific to
any application
– Copying and pasting sections and files – Printing documents
– Allocating memory
25
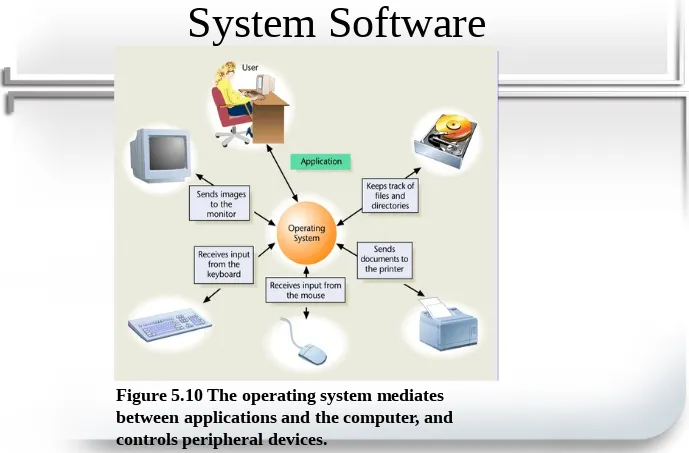
System Software
• Operating Systems (O/S)
– Most important system software
• Developed for a certain microprocessor or microprocessors
• Addresses technical details such as registers and RAM addresses
26
[image:26.720.23.712.50.503.2]System Software
27
[image:27.720.23.715.59.486.2]System Software
28
System Software
– Operating System Functions
• Systems Management • User Interface
• Memory Allocation
• Multitasking, Multiprogramming, and Multiprocessing
• Times and Statistics
29
System Software
• Compilers and Interpreters
– Compiler
• Scans source code and translates into object code
• Generates error message and does not compile when an error is found
• Allows users to save programs in object code
– Interpreter
• Checks one statement at a time
30
System Software
• Data Communication Programs
– Controls and supports data
communication activities in a network
• Setting up rules that govern transmission and reception of data
• Connecting and disconnecting communication links
• Assigning priorities among terminals in a network
31
System Software
• Proprietary vs. Open Source
– Proprietary O/S: limited to using applications compatible with it
– Open O/S: compatible with virtually all applications.
• Completely open O/S does not exist
– Some O/Ss (e.g., Unix) are said to be
32
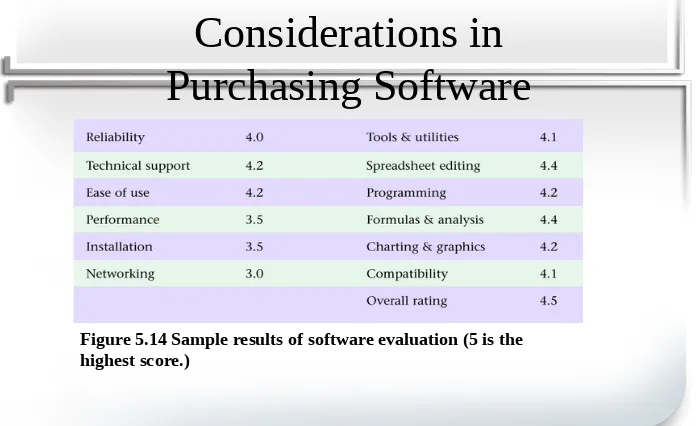
[image:32.720.23.720.61.487.2]Considerations in
Purchasing Software
33
• Many business applications stored only the last two digits of year dates.
• If no corrective action taken, businesses might have experienced chaos on January 1, 2000.
– ISs interpreting 00 as 1900 instead of 2000 • Experts predict the Y2K bug will haunt many
organizations several years after 2000.