Instructional Media in Teaching English to Young
Learners
(A Case Study in Elementary Schools in Kuningan)
A Research Paper
Wildan Nurul Aini
(0804507)
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
INDONESIA UNIVERSITY OF EDUCATION
Instructional Media in Teaching
English to Young Learners
(A Case Study in Elementary Schools in
Kuningan)
Oleh
Wildan Nurul Aini
Sebuah skripsi yang diajukan untuk memenuhi salah satu syarat memperoleh gelar Sarjana pada Fakultas Pendidikan Bahasa dan Seni
© Wildan Nurul Aini 2013 Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia
Januari 2013
Hak Cipta dilindungi undang-undang.
PAGE OF APPROVAL
INSTRUCTIONAL MEDIA IN TEACHING ENGLISH TO YOUNG LEARNERS
(A Case Study in Elementary Schools in Kuningan)
A Research Paper
By
Wildan Nurul Aini
0804507
Approved by:
Main Supervisor, Co-Supervisor,
Pupung Purnawarman, M.S. Ed., Ph. D. Iyen Nurlaelawati, M.Pd
NIP.196810231998031001 NIP. 197709062009122002
Head of English Education Department Faculty of Language and Arts Education
Indonesia University of Education
ABSTRACT
This research entitled “Instructional Media in Teaching English to Young Learners” was aimed to investigate (1) the use of instructional media by the teachers in teaching English to young learners; (2) the problems that they encounter in using instructional media; also (3) problem solving of the media utilization problems. This study was conducted in elementary schools in Kuningan. To collect the data, the researcher employed observation and interview techniques. The result of the study indicates that there are four types of instructional media which are generally used by the teachers, comprising: (1) boards; (2) realia; (3) pictures; and (4) books. Each of them is used in various ways. Meanwhile, the teachers faced problems in both process of selecting and using instructional media. The strategy used to solve the problems during selection process was utilizing available media. Meanwhile, to overcome the problem during the use of instructional media were by requesting technician help, borrowing instructional media supply from other class and preparing back-up instructional media.
ABSTRAK
Penelitian ini yang berjudul “Instructional Media in Teaching English to
Young Learners” bertujuan untuk mengetahui (1) penggunaan media pembelajaran oleh guru dalam mengajar bahasa Inggris untuk anak-anak; (2) masalah-masalah yang para guru hadapi dalam menggunakan media pembelajaran; juga (3) pemecahan masalah terhadap masalah-masalah yang dihadapi dalam penggunaan media pembelajaran. Penelitian ini dilaksanakan di beberapa sekolah dasar di daeran Kuningan. Untuk mengumpulkan data, peneliti menggunakan observasi dan wawancara. Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa ada empat jenis media pembelajaran yang pada umumnya digunakan oleh para guru, yaitu: (1) papan tulis; (2) realia; (3) gambar; dan (4) buku. Masing-masing media pembelajaran tersebut digunakan oleh para guru dengan cara yang berbeda. Sementara itu, para guru menghadapi berbagai masalah baik dalam pemilihan maupun penggunaan media pembelajaran. Strategi yang digunakan untuk mengatasi berbagai masalah dalam proses pemilihan media adalah dengan menggunakan media pembelajaran yang sudah tersedia di sekolah. Sedangkan, untuk mengatasi masalah dalam penggunaan media pembelajaran adalah dengan meminta bantuan dari teknisi, meminjam perediaan media pembelajaran dari kelas yang lain dan mempersiapkan cadangan media pembelajaran.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PAGE OF APPROVAL ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
STATEMENT OF AUTHORIZATION ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
PREFACE ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
ABSTRACT ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... vii
LIST OF TABLES ... ix
LIST OF FIGURES ... x
LIST OF APPENDECIS ... xi
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION ... Error! Bookmark not defined. 1.1 Background of Study Error! Bookmark not defined.
1.2 Formulation of Problems Error! Bookmark not defined.
1.3 The Scope of the Study Error! Bookmark not defined.
1.4 Aims of the Research Error! Bookmark not defined.
1.5 Significance of the Study Error! Bookmark not defined.
1.6 Research Methodology Error! Bookmark not defined.
1.6.1 Research Design Error! Bookmark not defined.
1.6.2 Research Site and Participant Error! Bookmark not defined.
1.6.3 Data Collection Error! Bookmark not defined.
1.6.4 Data Analysis Error! Bookmark not defined.
1.7 Clarification of Terms Error! Bookmark not defined.
1.8 Organization of Paper Error! Bookmark not defined. CHAPTER II LITERATURE REVIEW ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
2.1 English Language Teaching Error! Bookmark not defined.
2.2 Teaching English to Young Learners Error! Bookmark not defined.
2.3 Children’s Characteristics Error! Bookmark not defined.
2.3.1 Characteristics of Young Learners Error! Bookmark not defined.
2.3.2 Theories of Children Development Error! Bookmark not defined.
2.4 Instructional Media in Teaching English to Young Learners Error! Bookmark not defined.
2.4.2 Types of Instructional Media Error! Bookmark not defined.
2.4.3 The Roles of Media in Teaching Learning ActivitiesError! Bookmark not defined.
2.4.4 The Application of Instructional Media in Teaching English to Young Learners Error! Bookmark not defined.
2.4.5 Media Selection Error! Bookmark not defined. CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
3.1 Research Design Error! Bookmark not defined.
3.2 Research Site and Participant Error! Bookmark not defined.
3.3 Data Collection Error! Bookmark not defined.
3.4 Data Analysis Error! Bookmark not defined.
3.5 Procedure of the Study Error! Bookmark not defined. CHAPTER IV FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
4.1 The Use of Instructional Media by the Teachers in Teaching English to Young Learners Error! Bookmark not defined.
4.1.1 Types of Instructional Media Used by the Teachers Error! Bookmark not defined.
4.1.2 The Utilization of Instructional Media by the Teachers Error! Bookmark not defined.
4.1.3 Teachers’ Selection of Instructional Media Error! Bookmark not defined.
4.2 The Problems Encountered by the Teachers in Using Instructional Media to Teach English to Young Learners Error! Bookmark not defined.
4.2.1 The Problems in Selecting Instructional Media Error! Bookmark not defined.
4.2.2 The Problems in Using Instructional Media Error! Bookmark not defined.
4.3 The Strategies Used by the Teachers to Face the Problems in Using Instructional Media to Teach English to Young Learners Error! Bookmark not defined.
4.3.1 The Strategies to Solve the Problems in Selecting Instructional Media
Error! Bookmark not defined.
4.3.2 The Strategies to Solve the Problems in Using Instructional Media Error! Bookmark not defined.
CHAPTER V CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS ... Error! Bookmark not defined. 5.1 Conclusions Error! Bookmark not defined.
5.1.2 The Problems Encountered by the Teachers in Using Instructional Media to Teach English to Young Learners Error! Bookmark not defined.
5.1.3 The Strategies Used by the Teachers to Face the Problems in Using
Instructional Media to Teach English to Young Learners. Error! Bookmark not defined.
5.2 Suggestions Error! Bookmark not defined. REFERENCES ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
APPENDICES ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
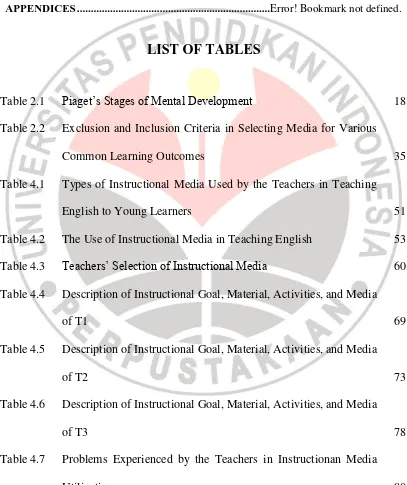
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2.1 Piaget’s Stages of Mental Development 18
Table 2.2 Exclusion and Inclusion Criteria in Selecting Media for Various
Common Learning Outcomes 35
Table 4.1 Types of Instructional Media Used by the Teachers in Teaching
English to Young Learners 51
Table 4.2 The Use of Instructional Media in Teaching English 53 Table 4.3 Teachers’ Selection of Instructional Media 60 Table 4.4 Description of Instructional Goal, Material, Activities, and Media
of T1 69
Table 4.5 Description of Instructional Goal, Material, Activities, and Media
of T2 73
Table 4.6 Description of Instructional Goal, Material, Activities, and Media
of T3 78
Table 4.7 Problems Experienced by the Teachers in Instructionan Media
Table 4.8 The Availability of Instructional Media 83 Table 4.9 Strategies of the Teachers to Face the Problems 90
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 2.1 Dale’s Cone of Experience 22
LIST OF APPENDECIS
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
1.1 Background of Study
In Indonesia, teaching English to young learners is a part of curriculum. It is based onMinisterial Decree No.22 Year 2006, dated May 23rd 2006, which states that English subject can be given to elementary students as a local content. This decree results in the existence of English in elementary schools which is taught starting from the fourth grade for two credit hours every week.
In teaching English to elementary school students, teachers deal with
young learners whose characteristics are different from adult learners‟. One of
children characteristics regarding their cognitive development is stated by Piaget (1972) as cited in Pinter (2011, p.9) who believes that in each stages children have
quality of thinking which “is relatively consistent across different tasks”. For
elementary schools students, their cognitive developments lay on concrete operational stage. In this stage, children begin to think logically and use their experience to solve problem. Nevertheless, they are only able to solve problem
which “are applied to concrete examples and objects in real life” (Pinter, 2011, p.
12). It is different from the adults which can solve abstract or hypothetical problem and also think several possible factors affecting something.
when children pay attention to the teacher or focus on the learning. Musthafa (2010) argues that unlike adults who have long attention span, children only have attention span less than 15 minutes.
Knowing those characteristics of children is an essential requirement for the teacher in creating effective instruction (Musthafa, 2010). Effective instruction
is “an instruction that enables students to acquire specified skills, knowledge, and
attitudes.” (Reiser & Dick, 1996, p.3). In relation to this, Curtain and Dahlberg (2000) as cited in Musthafa (2010) argue that the instruction should be built “on
topics and contexts that are relevant to the young learners.” Besides, students‟
experience should also be considered in choosing teaching method, media and assessment (Barratt-Pugh and Rohl, 2000, cited in Musthafa, 2010) in order to conduct effective instruction.
On the other hand, Glover and Bruning (1987) believe that effective instruction can be achieved when students receive information which is made meaningful, such as information that is related to students‟ daily life. In this case, Brown (2001) defines meaningful learning as a learning which integrates existing knowledge of the student with the new one. He believes that by meaningful learning, English lesson can be comprehended and applied by young learners for longer period than un-meaningful learning.
teaching learning activities and support students in reaching instructional objectives. Utilizing the appropriate instructional media is required because of
several benefits. One of the benefits is to enhance students‟ motivation. By using
instructional media e.g. showing pictures and having the students heard music, the students give more attention to the teachers, moreover, their curiosity is increasing towards the subject (Reiser& Dick, 1996). Other benefits are stated by Ruis, et al (2009) comprise (1) solving lack of experiences problem for the students, (2) reaching everything out of the class, (3) creating direct interaction between the students and environment, also (4) integrating experience from the concrete to the abstract information.
Unfortunately, the practice of TEYL, especially in creating effective instruction by English teachers in Indonesia, is disharmony with how it is supposed to be. For instance is regarding the use of instructional media. As mentioned in previous paragraph, using instructional media have several benefits including creating meaningful learning which needed by young learners in learning. Therefore, it is assumed that English teachers need appropriate instructional media in the instruction. However, according to Mutohhar (2009), in real practices, English teachers only use traditional instructional media to transfer material to the students. They seldom utilize the appropriate instructional media
which benefit for students‟ comprehension. Furthermore, Mutohhar (2009) reveals
that the reason of lack instructional media utilization by the teacher is difficulty in getting good instructional media. Moreover, those high quality instructional media
On the other hand, research studies about the use of instructional media by the elementary school teachers have been conducted. One of them is carried out by Abdo and Semela (2010). The former is a researcher from Hawassa University, Ethiopia, while the latter is from University of Tübingen, Germany. They conducted the study in Gedeo Zone in Sourthen Ethiopia. The study shows that the teachers in elementary schools are infrequent using instructional media in teaching learning process. Some factors influencing the use of instructional media by the teachers comprise availability of instructional media, manageability of classroom tasks and administrative supports.
Another research regarding the use of instructional media was conducted by The British Educational Communications and Technology Agency (Becta) in
2003 (as cited by Březinová, 2009). The research is regarding the use of
Interactive Whiteboard (IWB) in teaching English and some benefits of using it. The result of the research shows that there are some benefits using IWB as instructional media: (1) encourage the use of teaching materials which is more varied and creative; (2) increase students‟ motivation in teaching learning process; and (3) help the students to participate in class.
In Indonesian context, research regarding the use of interactive media in teaching speaking to young learners was conducted by Hakim (2011). This research reveals that by using the media, the students are more motivated to try showing their ability in speaking and giving contribution in front of the class.
Indonesia – based on the research, the researcher intends to conduct a study regarding the implementation of media in teaching English to young learners. The research is conducted in three elementary schools in Kuningan, West Java. This study will find out media which is used by the teachers in teaching English to young learners. Besides, it will also depict a portrayal of problems that the teachers encounter and how they solve the problem in using the media. And last, it
investigates students‟ response towards the media used.
1.2 Formulation of Problems
Based on the background mentioned, research questions in this study are formulated as follow:
1) How do the teachers use instructional media in teaching English to YoungLearners?
2) What problems do the teachers encounter in using instructional media to teach English to Young Learners?
3) What strategies do the teachers employ to overcome the problem in using instructional media in teaching English to Young Learners?
1.3 The Scope of the Study
This study highlights the description of instructional media used by
underlines the problems of the teachers in using the media and how they solve them.
1.4 Aims of the Research
In line with the research questions stated, the study is aimed:
1) To explore the use of media by the teachers in teaching English to young learners
2) To discover problems that the teachers encounter in using media to teach English to young learners
3) To depict strategies used by the teachers to overcome the problem in using media in teaching English to young learners.
1.5 Significance of the Study
This study is expected to be significant for several parties. Firstly, it is expected to give portrayal for the teacher regarding the use of instructional media and its problems in its implementation. Also it can give a description concerning what strategies can be used to solve the problems in using instructional media. Later on, this description can be useful for the teacher in their own class to make a better English teaching activity.
school can get more attention from them, for example by providing more instructional media for teaching learning activities.
Last but not least, the result of the study is meaningful for young learners. By getting information from the result of the study, it will lead to the improvement in terms of media in TEYL. So, when the use of instructional media has improved, the teaching learning activities will be more effective, and young learners are more motivated to learn English.
1.6 Research Methodology
1.6.1 Research Design
To discover how the teachers use instructional media, problems faced by them, and how they solved the problems, this research uses case study method. In this study, the researcher investigates phenomenon in real situation of elementary schools regarding the use of media. Yin (2002, p. 1) argues that case study
method is “preferred strategy when „how‟ or „why‟ questions are being posed,
when investigator has little control over events and when the focus is on a contemporary phenomenon within some real-life context.”
data collection techniques. The data are then analyzed to answer the research questions stated.
1.6.2 Research Site and Participant
The study is conducted in three elementary schools in Kuningan, West Java. The elementary schools selected in this study have different levels based on qualification from National Institution of Accreditation. Meanwhile, participants of the study are three English teachers of each elementary school.
1.6.3 Data Collection
To obtain the data, the study uses two kinds of instrument: classroom observation and interview.The first instrument is classroom observation. It is employed to attain information about teaching learning activities specifically about the teachers and the students‟ behavior. According to Fraenkel&Wallen (2006), observation is conducted to get more detailed and accurate information of what students and teacher doing in the class than interview does. So, by using this instrument, all of the aspects and details in the lesson can be captured. It also gives complete information for the researcher regarding how the teachers use the media. The observation used is non-participant observation. This particular kind of observation is conducted where the researcher acts as a complete observer, who
doesn‟t participate in classroom activities (Fraenkel&Wallen , 2006).
to solve them. It is also a tool for researcher to check the information gained from observation, whether or not it is appropriate. The type of interview that is used is in-depth interview, which is “a qualitative research technique that involves conducting intensive individual interviews with a small number of respondents to explore their perspectives on a particular idea, program or situation” (Boyce & Neale, 2006, p.3).
1.6.4 Data Analysis
Both of classroom observation and interview produce different kinds of data. Field note is the result of classroom observation, while interview script is the result of in-depth interview.
Those data are analyzed in several steps. Creswell (2008) divides the steps into: (1) collecting data, (2) preparing data for analysis, (3) reading through the data, (4) coding the data, and(5) coding the text for themes and description to be used in the research paper.
In collecting the data, the researcher gathers the data from classroom observation and in-depth interview. After that, it is prepared to be analyzed by organizing them into certain classification, comprising group of interview data and group of field note. Later on, these data are transcribed. The interview recording will be transcribed into interview script.
is interrelated with another theme which will be used to answer the research question.
After the data have been collected, they are analyzed by researcher. All of the data from observation and interview are organized in certain way to answer the research questions.
1.7 Clarification of Terms
In this study, there are some terms which need to be clarified in order to evade some kind of misinterpretation. The terms are:
1. Young Learners
According to McKay (2006), in terms of school level, young learners refer to students in primary or elementary schools. In terms of age, they refer to children whose ages are about five to 12 years old.
2. Instructional Media
Instructional media is defined by Scanlan as all of materials that can be used by the teachers to conduct teaching learning activities and support student in reaching instructional objectives. While Reiser and Dick (1996) argue that
instructional media is “the physical means by which instruction is delivered to
students”. Several examples of instructional media are flashcard, OHP,
1.8 Organization of Paper
This paper consists of five chapters comprising introduction, theoretical foundation, research methodology, findings and discussion, and conclusion and suggestion.
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 Research Design
To discover how the media used by the teachers, problems faced by them in using media, and how they solved the problems, this research used case study design. Consideration in choosing case study as research design was because the study intended to capture certain phenomenon and real situation existed in elementary schools. Moreover, researcher in this study examined the phenomenon without any control and involvement over it. Yin (2002, p. 1) argues that case
study method is ―preferred strategy when ‗how‘ or ‗why‘ questions are being
posed, when investigator has little control over events and when the focus is on a contemporary phenomenon within some real-life context.‖
To be more specific, this research was a descriptive case study. Descriptive case study is a type of case study which is used to develop data that describe clearly the complexity of an experience (Stake, 1995). In addition, the qualitative method was employed to describe data which are obtained by two techniques in collecting data which comprised observation and interview. And after collecting data, data were analyzed to answer the research questions stated.
3.2 Research Site and Participant
labeled as School A, School B, and School C. The selection of the setting was based on several reasons. The first one is level of accreditation. The schools had different level of accreditation from National Accreditation Agency. School A has not got accreditation level yet, School B got ―B‖ level of accreditation.
Meanwhile, School C got accreditation level ―A‖, which is the highest level of
accreditation. This information was taken from Education Office (DinasPendidikan) Kuningan.
Second reason in choosing these schools is the location. The schools were located in three different areas in Kuningan. School A was located in suburban area, School B was in rural area, while School C was in downtown area. Although the schools were scattered in three different areas in Kuningan, fortunately they were still accessible from researcher location, so it did not hamper the researcher to conduct the research.
Each of schools had different facilities. In school A, instructional media provided in the classroom was only two whiteboards. There was no picture
hanging on the wall which can be used for the learning. Meanwhile, students‘
seating arrangement was made classically. The wooden desks were lined up and the students sit on the wooden chairs behind each desk. The classroom contained 16 desks and they were shared by one or two students. It is due to the number of students which was only 17 students.
Meanwhile, the classroom was equipped by one whiteboard and one blackboard. However, similar to School A, there was no picture which can be used for English teaching learning. As the other elementary schools, the seating arrangement was in classical way, in which the desk and chairs was lined up into several rows. In School B, the students were in a huge number. The class contained 44 students, so each desk was shared by two or three students.
The last was School C. Although this school had the highest accreditation level, it had no big difference compared with the other two schools in this study. The instructional media available in the class was whiteboard and cupboard containing books and supply of markers. In the classroom, there was also hanged a poster – about parts of body – which can be used in instruction. In terms of seating arrangement, again, the classical arrangement was used in this classroom. Meanwhile, number of the students in school C was less than School B but more than School A and generally two students shared each desk.
The participants of the study were one English teacher from School A, School B, and School C. Requirement for the teachers which were involved to be participant is using media in teaching English. It is due to purposes of the study which is to find the utilization of instructional media by the teacher. Besides using media in teaching learning activities, there is no other requirement for the teachers in this study.
1. Teacher 1 (T1)
Teacher 1 was female. She studied in English Department in one university in Cirebon and got her undergraduate degree in 2005. She began to teach English in elementary school was in 2004, before she graduated. Before teaching in her current elementary school, she taught in three different schools. Therefore, she had 7 years teaching experience to young learners. Meanwhile, her status was still honorary teacher.
2. Teacher 2 (T2)
Teacher 2 was male. Like T1, T2 also was graduated from English Department but in different university. He studied in one university in Kuningan. His teaching experience started from his 6th semester in 2008 in current elementary school –School B. Thus, he had been teaching for 4 years. As teacher 1, his status was still honorary teacher.
3. Teacher 3 (T3)
3.3 Data Collection
Since it was qualitative study, the researcher used two kinds of instrument, which were classroom observation and interview, to obtain the data. The first instrument was classroom observation. It was employed to attain information
about teaching learning activities especially about the teachers‘ and students‘
behavior. It was in line with Fraenkel&Wallen (2006) who state that observation is conducted to get more detailed and accurate information of what students and teacher doing in the class than interview does. So, by using this instrument, all of the aspects and details in the lesson can be captured and give a complete information for the researcher.
The observation was non-participant observation. Non-participant
observation is where the researcher acts as complete observer who doesn‘t
participate in classroom activities (Fraenkel&Wallen, 2006). The researcher observed and made field notes regarding how the teachers use media in teaching learning activity, what problems that they faced and what strategies the teachers gave to solve the problems in using media.
statement. Description column also provided in order to allow the researcher write down any useful information from the observation (see Appendix A).
The observation itself was taken three times in each school. The first observation was conducted in fourth grade class, the second one was in the fifth grade class, and the last was in the sixth grade class. There were two main considerations in choosing three different classes to be observed. The first is because the time was very limited. If the researcher chose the same class for three observations, it would take time longer. In addition, each teacher admitted that there would be several events that might probably hamper the research process. Therefore, to make the time efficient, it would be better for the researcher to choose three different classes in each school.
The next reason is based on the teachers‘ statement that the use of
instructional media by the teacher would not be affected by students‘ grade. In
short, it was assumed that the teacher would use, more or less, the same instructional media to those different classes. Thus, by using three different classes, the observations might have the same results as by using only one class for this study.
Another instrument used was interview. Type of interview used was
in-depth interview, which is ―a type of interview which researchers use to elicit
information in order to achieve a holistic understanding of the interviewee‘s point
of view or situation; it can also be used to explore interesting areas for further
The interview was used to the teachers in formal and informal way. The first interview was used by the researcher to get information from the teacher about the problems in using media and the way to solve them. Meanwhile, the second interview, which was informal, was a tool for researchers to find out planning of the teacher considering material, activities and media that would be used in teaching learning activity. Moreover, it was also to check the information attained from observation, whether or not it was appropriate.
The formal and informal interviews were done in different time. Formal interview was held in a certain occasion after three observations had conducted, while the informal interview was done before and after each observation. Both of interviews used Bahasa Indonesia in order to make the participant relaxed and avoid misunderstanding between the researcher and participant during the interview process. Moreover, the interview processes were recorded by the researcher then the recordings were transcribed.
The questions of the interview were based on the interview schedule which was made by the researcher. However, since it was in-depth interview, the questions could be added and developed as needed. Content of formal interview questions comprised:
1. What preparation does the teacher do before the class?
2. Does the teacher have a special time allocation to prepare instructional media? 3. What kind of media which mostly used by the teacher?
5. Are all the instructional media provided by the school?
6. Does the teacher mostly use the instructional media which are provided by the school or self-made?
7. What are the problems faced by the teacher in utilizing instructional media? 8. How does the teacher solve the problems?
And, the content of informal interview before the observation comprised: 1. What is the material of the lesson?
2. What are the activities for the teaching learning process?
3. What are instructional media used for the teaching learning process?
Meanwhile, for the informal interview after the observation, the researcher confirmed information which was taken during the observation.
3.4 Data Analysis
Both of classroom observation and interview produce different kind of data. Field note was the result of classroom observation, while interview script was the result of in-depth interview.
In collecting data, the researcher gathered the data from classroom observation and in-depth interview. After that, it was prepared to be analyzed by organizing them into certain classification, for example group of interview data and group of field note. Later on, these data were transcribed. The interview recordings were transcribed into interview script.
Thereafter, the researcher read through the data to get general sense of the data (Creswell, 2008). Then, the data were coded until the researcher found the theme of the data. Finally, after getting the theme, it was interrelated with another theme which, at the end, was used to answer the research question.
After the data have been collected, it was analyzed by researcher. All of the data from observation and interviews were organized in certain way to answer the research questions.
3.5 Procedure of the Study
In conducting the study, the researcher did three main stages of study: (1) preliminary observation, (2) pilot study, and (3) primary study.
Preliminary observation was conducted by the researcher to one English teacher in each of three elementary schools, which became site of this study. The observation was carried out by giving the teachers questionnaire. It was purposed to find out whether or not the teachers use media in teaching English to the students.
or not the interview questions were understandable, whether the questions should be added or reduced, etc.
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
This research was aimed at seeking utilization of instructional media by the teachers to teach English to young learners in elementary schools in Kuningan, West Java. This study investigated how the teachers used the instructional media, what problems they encounter in using those instructional media and what strategies they employ to solve the problems.
5.1 Conclusions
5.1.1 The Use of Instructional Media by the Teachers in Teaching English
to Young Learners
Based on the study, it can be concluded that there are types of instructional media that were generally used by English teacher in elementary schools in Kuningan area. Those instructional media were boards, books, pictures, realia, VCD player and LCD projector. However, the use of VCD player and LCD projector as instructional media in the instruction was still is low frequency of usage.
other hand, picture also had diverse usage by the teachers for drilling, presenting and checking meaning (understanding) and discussing. Furthermore, the realia were utilized to engage the students in the instruction, also elicit the information from the students before going to the core lesson.
The instructional media selected by the teachers were examined in relation to the three crucial factors in choosing media—practicality, students’ appropriateness, and instructional appropriateness—posed by Reiser and Dick (1996). This study found out that most of instructional media selected by teachers were both practical and appropriate to the instructions. But, unfortunately they were less appropriate to the students’ characteristics. In fact, the students’
appropriateness of the instructional media is obviously crucial to create effective and meaningful learning, especially for young learners who needed very special attention to the way they learn.
5.1.1 The Problems Encountered by the Teachers in Using Instructional
Media to Teach English to Young Learners
Problems were also experienced by the teachers in the process of utilizing media. The teachers often encountered technical problems, for instance running out of supply and the dysfunction of high-tech instructional media used. The last was personal problem. It dealt with the difficulty experienced by the teacher in explaining content in the instructional media.
5.1.2 The Strategies Used by the Teachers to Face the Problems in Using
Instructional Media to Teach English to Young Learners.
Due the existence of various problems in both selecting and using instructional media, the teachers had several ways to overcome them. The first, to overcome problems in process of instructional media selection – regarding limited time and cost, unavailability of media in the school—all of the teachers had the same action, which is using the readily-available instructional media in the school. With all of the inadequacy in their school, they tried to optimize the instructional media provided to help the students reach the instructional goal. However, types of instructional media by the teacher differs each other. This was affected by teachers’ education background and experience.
5.2 Suggestions
After knowing that the utilization of instructional media in elementary schools still needs improvement, it is expected that for the teacher optimize the available instructional media for teaching the students. However, in selecting instructional media, the teacher should pay attention not only to its availability and practicality, but also to learning condition, activity, materials, and especially to students’ characteristics. It, somehow, determines whether or not the students’
learning is successful.
Next is suggestion for the responsible party, in this case, Education office. As the teachers stated, the instructional media supply in each school was very limited and also the cost for the supply. Therefore, it is expected that Education Office as responsible party can provide more instructional media to all of elementary schools in Kuningan with the equal distribution. It is because whether the elementary school students in downtown area or rural area needs the equal attention to support their learning. Besides, the Education Office also should give attention to the teachers’ competency in using the instructional media, high-tech media in particular. By giving special training or workshop for the utilization for the teacher, it will be a good choice to improve teachers’ competency, so the
technical problems in media utilization will be avoided.
REFERENCES
Abdo, M. &Semela, T. (2010). Teachers of Poor Communities: The Tale of Instructional Media Use in Primary Schools of Gedeo Zone, Southern
Ethiopia. DalamAustralian Journal Teacher Education.Vol.35 (7), 78-92. Ara, Shaheen. (2009). Use of Songs, Rhymes and Games in Teaching
English to Young Learners in Bangladesh.DalamThe Dhaka University Journal of Linguistics. Vol. 2 (3), 161-172.
Boyce & Neale. (2006). CONDUCTING IN-DEPTH INTERVIEWS: A Guide for Designing and Conducting In-Depth Interviews for Evaluation Input.
Massachusetts. Pathfinder International.
Brown, H. D. (2001). Teaching by Principles: An Interactive Approach to Language Pedagogy. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall
Březinová, B.J. (2009). Interactive Whiteboard in Teaching English to Young
Learners.Thesis.Brna:DepartmentOfEnglishLanguageandLiterature, Masaryk University.
Cameron, L. 2005. Teaching languages to young learners. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
Cook & Cook.(2005). Child Development: Principles and Perspectives. Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Curtain, H. and Dahlberg, C.A. (2010).Languages and Children: Making the Match, New Languages for Young Learners, Grades K-8, 4/E. Boston: Allyn&Baconr
Damayanti, I.L. (2010). A Child-Friendly Way to Teaching Young Learners:The Implementation of M-U-F Framework.[Online]. Tersedia: http://didisukyadi.staf.upi.edu/files/2011/04/Ika-Lestari-Damayanti.pdf. [6 Juni 2011]
Fraenkel, J.R. & Wallen, N.E. (2006). How to design and evaluate research in education (6nded.). New York: McGraw Hill.
Glover, J.A. &Bruning, R.H. (1987).Educational psychology: principles and applications (2nded.). Boston: Little Brown Higher Education.
Goktas , et.al (2008). A Review of ICT Related Coursesin Pre-service Teacher Education Programs. DalamAsia Pasific Education Review. Vol.9 (2), 168-179
Hakim, L. (2011).The Implementation of The Interactive Learning Media in Teaching Speaking to Young Learners. [Online].Tersedia: http://repository.upi.edu/operator/upload/s_ing_043956_chapter5.pdf. [14Juni 2012]
Holmes. (2001). An Introduction to Sociolinguistics (2nd ed.).Harlow: Pearson Education Limited.
Mckay, P. (2006). Assessing Young Language Learners(3rd edition). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Mostafa, Magda. (2008). An architecture for Autism: Concepts of Design Intervention for The Autistic User. DalamInternational Journal of Architectural Research. Vol. 2, (1), 189-211.
Musthafa, Bachrudin. (2010). Teaching English to Young Learners in Indonesia:Essential Requirements.DalamEducationist Journal. Vol. 4, (2), 120-125.
Mutohhar. 2009. Teaching English for Young Learners (TEYL) Misunderstandings about TEYL in Elementary School. Available: http://jurnal.umk.ac.id/mawas/2009/Desember/TEACHING%20ENGLISH %20FOR%20YOUNG%20LEARNERS%20(TEYL).pdf[July 29th, 2012]
Nunan, D. (1999). Second language teaching and learning. Boston: Heinle and Heinle.
Onasanya.(2004). Selection and Utilization of Instructional Media for Effective Practice Teaching.DalamInstitute Journal of Studies in
Education.[Online], Vol.2, No.1. Available:
20MEDIA.pdf&ei=WhdwT8H4CofWrQfbw9GgDg&usg=AFQjCNHnoA YH1K-39VbiuoqhcjJC9jzafA&cad=rja. [March 26th, 2012]
Palomba, C.A. & Banta, T.W. (1999) Assessment Essentials: Planning, Implementing, and Improving Assessment in Higher Education. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Pinter, A. (2006). Teaching Young Language Learners.Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Pinter, A. (2010). Children Learning Second Languages.Hampshire: Palgrave MacMillan.
Reiser, R.A. & Dick, W. (1996).Instructional Planning: A Guide for Teachers (2nded.). Boston: Allyn& Bacon
Ruis, et al. (2009).Instructional Media. Jakarta: Ministry of National Education.
Scanlan, C. L. (n.d).Instructional Media: Selection and Use.[Online]. Available: http://www.umdnj.edu/idsweb/idst5330/instructional_media.htm. [June, 26th, 2012]
Seville-Troike, M. (2006).Introducing Second Language Acquisition.New York: Cambridge University Press.
Shin, J.K (2007).Teaching English to Young Learners.[Online].Available: www.nstru.ac.th/portal/data.../2009/.../1232942687_087864500.pdf [June 1st, 2012]
Smaldino, et.al. (2006). Instructional Technology and Media for Learning (8thed.). Ohio: Allyn& Bacon.
Smith, A.S. (1998). Focusing on Active, Meaningful Learning.DalamIdea Paper [Online].Available:
http://www.google.co.id/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=definition%20of%20meaningf ul%20learning&source=web&cd=7&ved=0CHQQFjAG&url=http%3A%2 F%2Fwww.theideacenter.org%2Fsites%2Fdefault%2Ffiles%2FIdea_Paper _34.pdf&ei=iNDnT8q6JY3prQeJ9PiJCQ&usg=AFQjCNGWDUh915pDm EmMR86qN7hTRu5RZg&cad=rja [June 25th, 2012]
Tileston, D.W. (2004). What Every Teacher Should Know About Media and Technology. California: Corwin Press.
Zainal,Z. (2007). Case Study as A Research Method. Dalam Jurnal
Kemanusiaan[Online], Vol 9. Available:
www.gslis.utexas.edu/~ssoy/.../l391d1b.htm [March 26th, 2012]