AN ANALYSIS OF FIGURATIVE LANGUAGE
TRANSLATION IN
THE PURSUIT OF HAPPYNESS
MOVIE
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Vidyadhari Wikan Pribadi Student Number: 141214124
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA YOGYAKARTA 2018
i
AN ANALYSIS OF FIGURATIVE LANGUAGE
TRANSLATION IN
THE PURSUIT OF HAPPYNESS
MOVIE
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Vidyadhari Wikan Pribadi Student Number: 141214124
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA YOGYAKARTA 2018
A Sarjana Pendidikan Thesis on
AN ANALYSIS OF FIGURATIVE LANGUAGE
TRANSLATION IN
THE PURSUIT OF
HAPPYNESSMOVIE
By
Vidyadhari Wikan Pribadi Student~urnber: 141214124
Approved by Advisor
Truly Almendo Pasaribu S.S., M.A.
11
ASarjana PendidikanThesis on
AN ANALYSIS OF FIGURATIVE LANGUAGE
TRANSLATION IN
THE
PURSUIT OF HAPPYNESSMOVIE
By
VIDYADHARl WIKAN PRIBADI
Student~UIDber:141214124
Defended before the Board ofExaminers on 22 May 2018
and Declared Acceptable
Boardof Examiners
: Christiila Lhaksmita Anandari, Ed.M.
: Truly Almendo Pasaribu, S.S.,M.A
: Carla Sib Prabandari, S.Pd., MHUID.
: Christina Lhaksmita Anandari, Ed. M.
Chairperson : Yobana Veniranda, S.Pd., MHUID., M.A., Ph.D. (
H1 ':
Secretary Member Member Member Yogyakarta, 22 May 2018 111STATEMENT OF WORK'S ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that this thesis, which I have written, does not contain the work or parts of the work of other people, except those cited in the quotations and the references, as a scientific paper should
Yogyakarta, May 22, 2018 The Writer
A
Vidyadhari Wikan Pribadi 141214124
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN
PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswa Universitas Sanata Dharma:
,
Nama : Vidyadhari Wikan Pribadi NomorMahasiswa : 141214124
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
AN ANALYSIS OF FIGURATIVE LANGUAGE
TRANSLATION INTHE PURSUIT OF HAPPYNESSMOVIE
Beserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan demikian saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk media lain., mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistribusikan secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikan di internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin dari saya maupun memberikan royalti kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini yang saya buat dengan sebenarnya.
Dibuat di Yogyakarta Pada tanggal: 22 Mei 2018 Yang menyatakan,
A
Vidyadhari Wikan Pribadi
vi
ABSTRACT
Pribadi, Vidyadhari Wikan. 2018. An Analysis of Figurative Language Translation in The Pursuit of Happyness Movie. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Department of Language and Arts Education, Faculty of Teachers Training and Education, Sanata Dharma University.
Translation is a process of transferring meanings from a source language into a target language. One of translation products is subtitling in the movie. Figurative language, also found in the movie. Therefore, translators should pay attention on translating figurative language in the movie. The researcher chose The Pursuit of Happyness movie because there were many figurative languages which found in the movie.
The research had two research questions. The first research question is “What types of figurative language are found in The Pursuit of Happyness movie?” The second research question is “How acceptable are the translations of figurative language translated in the movie?” The researcher used Abrams’ theory to answer the first question and Larson’s theory to answer the second research question.
In order to answer the research questions, the researcher used document analysis method. The steps which researcher used were watching, identifying, classifying, analyzing, checking, and validating. The researcher analyzed the figurative language which stated in The Pursuit of Happyness movie and the Indonesian subtitle of the figurative language translations.
The researcher found 179 figurative languages in the movie. The figurative languages were divided into three kinds namely 148 metaphors (83%), 23 hyperboles (13%), and 8 similes (4%). The researcher also analyzed the acceptability degree of figurative language translation. The result are the translations of metaphor are 77.8% included into Ideal-Acceptable translation, 7.4% included into Acceptable translation, 7.4% included into Unaccaptable translation, and 7.4% included into Failed translation. The translations of hyperbole are 65.1% included into Ideal-Acceptable translation, 17.2% included into Acceptable translation, 4.2% included into Unaccaptable translation, and 13.5% included into Failed translation. The translations of simile are 87.5% included into Ideal-Acceptable translation and 12.5% included into Acceptable translation. As a result, metaphor, hyperbole, and simile are found in the movie and the translation of figurative language a good translation because 86% of translation is acceptable.
Keywords: figurative language, translation, subtitle, acceptable, The Pursuit of Happyness movie.
vii ABSTRAK
Pribadi, Vidyadhari Wikan. 2018. An Analysis of Figurative Language Translation in The Pursuit of Happyness Movie. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa dan Seni, Fakultas Keguruan dan Ilmu Pendidikan, Sanata Dharma University.
Penerjamahan adalah sebuah proses pemindahan makna dari satu bahasa asal ke bahasa sasaran. Salah satu produk dari penerjemahan adalah subtitle di film. Majas juga ditemukan di film. Maka dari itu, penerjemah harus memperhatikan mengenai penerjemahan majas di film. Peneliti memilih film The Pursuit of Happyness karena terdapat banyak majas yang ditemukan di film.
Peneliti memiliki dua rumusan masalah. Rumusan masalah yang pertama adalah “Jenis majas apa saja yang ditemukan di film The Pursuit of Happyness?” Rumusan masalah yang kedua adalah “Bagaimana tingkat penerimaan dari penerjemahan majas di film?” Peneliti menggunakan teori dari Abrams untuk menjawab rumusan masalah yang pertama dan teori dari Larson untuk menjawab rumusan masalah yang kedua.
Untuk menjawab rumusan masalah, peneliti menggunakan metode dokumen analisis. Langkah-langkah yang digunakan adalah menonton, mengidentifikasi, mengklasifikasi, menganalisis, mengecek, dan mengesahkan. Peneliti menganalisis majas yang terdapat di film The Pursuit of Happyness dan penerjamahan majas di subtitle ke dalam Bahasa Indonesia.
Peneliti menemukan 179 majas di film. Majas dibagi menjadi tiga jenis: 148 metafora (83%), 23 hiperbola (13%), dan 8 simile (4%). Peniliti juga menganalisis tingkat penerimaan dari penerjemahan majas. Hasilnya adalah penerjemahan dari metafora adalah 77.8% penerjemahan dapat diterima dengan baik, 7.4% penerjemahan dapat diterima, 7.4% penerjemahan tidak dapat diterima, dan 7.4% gagal diterjemahkan. Penerjemahan dari hiperbola adalah 65.1% penerjemahan dapat diterima dengan baik, 17.2% penerjemahan dapat diterima, 4.2% penerjemahan tidak dapat diterima, dan 13.5% gagal diterjemahkan. Penerjemahan dari simile adalah 87.5% % penerjemahan dapat diterima dengan baik dan 12.5% penerjemahan dapat diterima. Dapat disimpulkan bahwa metafora, hiperbola, dan simili ditemukan di film dan penerjemahan majas di film tersebut merupakan penerjemahan yang baik karena 86% terjemahan dapat diterima.
Kata kunci: figurative language, translation, subtitle, acceptable, The Pursuit of Happyness movie.
viii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, I would like to thank Allah SWT for blessing and giving me spirit to finish this research. He is the biggest helper for everything that I am doing. Without His blessing and His permission, I would not be able to write this thesis and this thesis would not be done.
I would like to express my gratitude to my thesis advisor, Truly Almendo Pasaribu, S.S., M.A., for her time, patience, and guidance to finish this thesis. I also thank to all lecturers in English Language Education Study Program for giving me knowledge during these four years’ study, especially to Laurentia Sumarni, S.Pd., M.Trans.St. who helped me to validate the data.
I dedicate my research to my family who inspires and supports me to be a bachelor. I thank to my parents, Ir. Henu Purtanto and Dra. Lusi Margiyani, who asked me to finish this thesis soon and continue my life in a real world. Even they support me from distance, I could feel their prayer and their spirit for me. I also thank to my beloved older brother, Rihatma Punta Dewa, and my beloved little sister, Mehrunisa Wikan Pribadi, who always release me from stress with their jokes.
Last but not least, I would like to give suns for my boyfriend, Yusuf Ofananta, who always gives me his time and always companies me anytime and anywhere to finish this thesis. I also thank to Octana Ayu, PBI E, ViWaNoSi, ANU, Thesis’ friends, and other friends for the help, motivation, and sharing.
ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL PAGES ... ii
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ... iv
PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI ... v
ABSTRACT ... vi
ABSTRAK ... vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... viii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... ix
LIST OF TABLES ... xi
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xii
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Research Background ... 1
B. Research Questions... 4
C. Research Significance... 4
D. Definition of Terms ... 5
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ... 9
A. Theoretical Description ... 9
1. Figurative Language ... 9
2. Translation ... 12
3. Subtitling ... 17
4. The Pursuit of Happyness Movie ... 18
B. Theoretical Framework... 19
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 20
A. Research Method ... 20
B. Research Subject ... 21
x
D. Data Analysis Technique ... 23
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION ... 25
A. Types of Figurative Language ... 25
1. Metaphors ... 27
2. Hyperboles ... 30
3. Similes ... 32
B. Acceptability Degree of Figurative Language Translation ... 34
1. Ideal-Acceptable Translation ... 37
2. Acceptable Translation ... 39
3. Unacceptable Translation ... 40
4. Failed Translation ... 42
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS, IMPLICATIONS, AND RECOMMENDATIONS ... 45 A. Conclusions ... 45 B. Implications ... 46 C. Recommendations ... 47 REFERENCES ... 49 APPENDICES ... 50
xi
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
3.1 Type of Figurative Language Based on Abrams’ Theory (1999) ... 22
3.2 Acceptability Degree Based on Larson’s Theory (1984) ... 22
4.1 Percentage of Figurative Language ... 26
xii
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix Page
A. Type of Figurative Language ... 52 B. Acceptability Degree ... 64
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter provides the introduction of the research. In this chapter, the researcher divides into four parts. The first part is about the background of the research which contains of the topics that the researcher would be discussed and reasons why the researcher chooses the topic. The second part is research questions which is used to guide the research. The next part is research contribution of study to education. The last part is definition of terms that explain about the theories which are used in the research.
A. Research Background
Translation is a process of transferring a meaning from source language to target language (Newmark, 1988). Translation could be very important for people who do not know about a language. Therefore, they have to translate the source language to their language in order to know the meaning. There are many things to be paid attention in translating. According to Arnold, Balkan, Meijer, Humphreys, and Sadler (2001), some problems in translation are ambiguity, structural and lexical differences between languages, and multiword units. The most important thing of translating is the meaning could be delivered correctly and acceptable from source language to target language (Larson, 1984).
There are a lot of examples of translation’s products. One of the translation’s products is subtitling. Subtitling is one of the method to transfer the language used in translating types of audiovisual communication (Liu, 2014).
Subtitling could be found in the videos, movies, or songs. Subtitling is made to translate the conversation from source language to target language or it could help disabilities to understand the videos, movies, or songs by reading the subtitle.
Some Indonesian teenagers often use English subtitle while they are watching a western movie. Some people use Indonesian subtitle to get better understanding about the movie. The subtitle could be found easily from any sources. The researcher found many websites which provide the subtitle of movies. The users could download freely and installed easily. However, not all websites provide good translation on subtitling. Translators or people who made the subtitle sometimes made errors or unacceptable translations. One of websites which provides subtitle of movies is www.Subscene.com. This website is the most popular website of subtitling a movie which provides complete and accurate subtitle from a lot of languages. In one language, there are several subtitles which the users could choose the best subtitle for them.
One language and other language have different characteristics because a language has many elements and aspects which make it different from other languages. One of the aspects of a language is figurative language. Abrams (1999) states on his book, “Figurative Language is a conspicuous departure from what users of a language apprehend as the standard meaning of words, or else the standard order of words, in order to achieve a special meaning or effect.”
The researcher chooses The Pursuit of Happyness movie to be analyzed because the movie is famous and meaningful. The Pursuit of Happyness is a movie from San Francisco in 1981. The movie tells about a struggling salesman,
Christopher Gardner, who takes custody of his son as he is poised to begin a life-changing professional endeavor. The wife leaves them because they are bankrupt. Chris and his son have to move from one place to other every night. Every day, he has to sell machine, drop his son to day-care, and trained in the office. They have very hard life. At the end of the movie, their life gets better because Chris gets the job.
The researcher was inspired by a paper from one of English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University students named Ryan Andhika Pratama who graduated in 2016. The title of the paper is “An Analysis of Idiomatic Expression Translation in School of Rock Movie”. He was analyzing subtitle translation from www.Subscene.com used Larson’s theory of translation. The theory of an ideal translation by Larson has three criteria, those are Accurate (A), Clear (C), and Natural (N). The result of his paper is 82.5% of idiomatic translation of the movie could be translated accepted.
From this reason, the researcher was inspired to do the similar research but in other scope. The researcher is interested in analyzing the subtitling translation from English to Indonesian of a movie. The differences between this research and Pratama’s paper are stated in the field of the study and the subject of the research. This research focused on the translation of figurative language because the researcher found a lot of figurative languages in the movie. A figurative language could be found easily in daily conversation and also in the dialogue of a movie. While Ryan’s paper analyzed School of Rock movie, this research analyzed The Pursuit of Happyness movie.
The purpose of the research is to find the types of the figurative language based on Abrams’ theory in the movie and whether the translation of figurative language subtitle from English to Indonesian version in The Pursuit of Happyness movie is correct or not according to acceptable translation based on Larson’s theory. The focus of the research is to analyze the translation of three figurative languages: simile, metaphor and hyperbole which contain in the subtitle of The Pursuit of Happyness movie. Addition, the metaphor is divided into two kinds. They are orientational metaphor and structural metaphor. The researcher chooses those three figurative languages because they could be found easily in the dialogue. In addition, those figurative languages are common used in daily activity and daily conversation. Therefore, the researcher hopes that this research would be understood easily by the readers.
B. Research Questions
The researcher formulates two research questions to guide the research based on the research background. The research questions are:
1. What types of figurative language are found in The Pursuit of Happyness movie?
2. How acceptable are the figurative language translated in the movie?
C. Research Significance
This part explains the research contributions to education. The researcher expects this research could be used and useful for Sanata Dharma University,
English Language Education Study Program students, English learners and future researchers.
1. Sanata Dharma University
The researcher expects that the research could enrich the undergraduate data research section, especially on figurative language and translating. Therefore, the research could be used to all Sanata Dharma University students.
2. English Language Education Study Program Students
The researcher expects that the research could give better understanding of translating figurative language, especially for English Language Education Study Program students. Moreover, the research could inspire and enlightened to make a thesis for them.
3. English Learners
The researcher expects that the research could be the reference to other English learners to help them to get information and get better understanding of translating figurative language.
4. Future Researchers
The researcher expects that the research could give information and inspiration to enrich other studies. The future researcher could try to find further analysis about figurative language and get deeper to analyze the translating of figurative language.
D. Definition of Terms
In this chapter, the researcher would give the definition of terms which are used in the research. There are eight definitions would be explained in this part.
Those are: figurative language, metaphor, hyperbole, simile, translation, subtitle, acceptable of translation, and The Pursuit of Happyness movie.
1. Figurative Language
The researcher uses a book from M. H. Abrams (1999). According to Abrams, figurative language is unusual words which are used to achieve special meaning or effect. From the book, the researcher found two classes of figurative language: figures of thought or tropes and figures of speech or rhetorical figures. There are several types of figurative language according to Abrams. However, the researcher only focus on three figurative languages to be discussed. They are metaphor, hyperbole, and simile.
2. Metaphor
According to Abrams (1999), metaphor is an expression to show one thing into another different thing without any comparison. According to Lakoff (1980), metaphor is unusual words or language about idea and action. He mentions three kinds of metaphor. However, the researcher focuses only two kinds of metaphor. They are orientational metaphor and structural metaphor. Orientational metaphor is a metaphor by using orientational metaphor. Structural metaphor is showing one terms activity into another activity.
3. Simile
According to Abrams (1999), simile is comparing two different things which have similarities by using characteristics. The common words which indicate simile are like or as. Different with metaphor, simile compares two distinctly different things explicitly.
4. Hyperbole
Hyperbole is an overstatement about fact, feeling, or something (Abrams, 1999). The purpose of hyperbole is to show how important or unimportant the thing. According to Arvius (2003), hyperboles do not have literal meaning because hyperboles use special effects which the literal meaning of hyperbole is unbearable.
5. Translation
The researcher uses a book from Mildred L Larson (1984). According to Larson, translation is transferring one language into another language. The purpose of translation is transferring the meaning from source language into target language. From the book, there are three criteria of acceptable translation. The criteria are Accurate (A), Clear (C), and Natural (N). According to Larson, a translation is classified into four classes, those are Ideal-Acceptable (I-Acc), Acceptable (Acc), Unacceptable (Unacc), and Failed (F).
6. Subtitle
Subtitling is one of method to transfer language used in translating types of audiovisual communication (Liu, 2004). The subtitling is used for some audiovisual products such as movie, video, television, cinema, computer games, and performances. Subtitling is made to translate audio conversation into written
conversation in order to help the audience to get better understanding of the conversation. Subtitle also helps disabilities to understand the conversation. 7. Acceptable of Translation
Acceptable means adequate or suitable. In the context of translation, acceptable means the translation is suitable to the target language. According to Newmark (1988), a translation should use appropriate language and acceptable usage to the target language. According to Larson (1984), acceptable translation is a translation which contains of at least two criteria from the criteria: Accurate (A), Clear (C), and Natural (N).
8. The Pursuit of Happyness Movie
The Pursuit of Happyness is a movie from San Francisco in 1981 directed by Gabriele Muccino. The movie is inspired by a true story of Chris Gardner (Will Smith), a salesman in San Francisco, who is struggling to build his life and his son’s life, Christopher (Jaden Smith). His wife, Linda (Thandie Newton), gives up of their life and chooses to leave them to New York. At the end of the story, Chris gets the job and their life is getting better.
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter provides related theories which are used for further discussion in this research. The researcher divides this chapter into two parts. The first part is theoretical description which provides the discussion of relevant theories. The second part is theoretical framework which provides the summary and synthesize to answer the research questions.
A. Theoretical Description
The researcher has five key words. However, the researcher only has four main focuses to be explained and discussed in this part because one of the keywords is included into another key words. The focuses are figurative language, translation, subtitle, and The Pursuit of Happyness movie. The acceptable is included into translation part. In this part, the researcher would elaborate the theory of each focus.
1. Figurative Language
The purpose of using figurative language is to deliver three elements of language, they are clarity, forth, and beauty (Tajali, 2003: 100). According to Abrams (1999), figurative language is unusual words in daily conversation which is used to achieve special meaning or effect.
The researcher focuses on three of figurative languages. They are simile, metaphor, and hyperbole. The researcher chooses those three figurative languages because they could be found easily in the dialogue.
a. Similes
Gibb and Wales (2009) mentions “simile is a figure of speech whereby two concepts are imaginatively and descriptively compared.” According to Hussain (2014) simile means “resemble and likenesses” which mean comparing two objects with similarities. Simile is a comparison between two different things by using “like” or “as” (Abrams, 1999). Pierini (2007) adds more characteristics of simile by using seem, look like, act like, sound like, similar to, the same as, and as when.
An example of simile is That car goes like a bullet. It means that the speed of the car is very fast. Another example is in Samuel Taylor Coleridge’s poem entitled The Rime of the Ancient Mariner. It states “And ice, mast-high, came floating by, As green as emerald.” It does not mean the color of ice is green, but the ice is very beautiful which could represent as emerald.
b. Metaphors
Lakoff (1980) explains that metaphor is an unusual language rather than usual language which is used in daily conversation. Metaphor is not only about arrangement of words but it is about a person’s conceptual system. Lakoff adds three kinds of metaphor: orientational metaphor, structural metaphor and ontological metaphor.
1) Orientational metaphor is a metaphor by using spatial orientation such as up, down, in, out, front, back, on, off, and below. The spatial orientations come from the truth that bodies we have and the function as they do in our physical environment. For example: get up, wake up, and stand up. From those examples, up is showing about conscious. Therefore, the physical basis of those examples are people or animals stand up when they awaken.
2) Structural metaphor is showing one kind of activity in terms of another activity. Structural metaphor has wider source of elaboration than orientational metaphor. Structural metaphor lets people to do more than orientation concepts only. For example, argument is war. From the example, argument conceived in term of war because both of them contain of unfair and irrational things.
3) Ontological metaphor is projection of entity or substance status which does not have that status inherently. Most of ontological metaphor are not noticed being metaphorical because one of the reason is ontological metaphor shows very limited range of purposes. The example of ontological metaphor is I am a little rusty today.
Understanding a metaphor needs imagination and creativity which make no right or wrong metaphor translation but strong or weak metaphor translation (Davidson, 1995). Abrams (1999) adds that in metaphor, there is no comparison between two things. He adds an example of metaphor from a Stephen Spender’s poem which describes the eye as a sense of a landscape:
Eye, gazelle, delicate wanderer, Drinker of horizon’s fluid line.
According to Newmark (1988), there are two purposes of metaphor, cognitive and artistic. The cognitive is to show a condition, an idea, somebody, a thing, or the feature. While the artistic is to influence the feeling, to amuse, to amaze, or to appreciate.
c. Hyperboles
A hyperbole makes an effect or exaggerate of fact or something to show how very important or very unimportant that thing (Abrams, 1999). The other purpose of using a hyperbole is to entertain and to get more attention (McCharty and Carter, 2004). For example, I cannot live without my phone in my hand. It is impossible when the speaker would die if the speaker does not hold the phone in the hand. The speaker wants to tell that the speaker needs the phone and would not leave the phone.
According to Arvius (2003), hyperboles use special effects which do not have literal meaning because a literal interpretation of hyperboles is impossible and absurd. By using hyperbole to promote a product, the sentence sounds more enticing, impressive, and persuasive (Novgarina, 2010)
2. Translation
Translation is used to transfer from source language texts into target language texts whether the texts are written or spoken (Ordudari, 2007). Ordudari adds the purpose of translation is to remake different types of texts into another language and make the texts easier to be understood. Therefore, the readers’ understanding would increase.
There are six methods of translation according to Newmark (1988) which are presented in diagram V of Newmark.
Literal translation is translating source language in a good structure by choosing the closest constructions from target language. Faithful translation is reproducing exact background of the meaning of source language in a good structure into target language. Semantic translation focuses on the culture and aesthetic value which sometimes to translate religious texts, legal texts, and literature texts. Free translation is freely to translate something that preserves the meaning of original. Idiomatic translation is translating the original meaning from source language to target language. Communicative translation is reproducing the acceptable original contextual meaning from source language.
According to Yang (2010), there are two translation strategies for a translator to translate a language namely domestication and foreignization. Domestication is translating which still linked to the readers’ orientation. Although, foreignization is translating from source language to target language which the translations still keep distance to the source language. Shi (2014) adds about domestication and foreignization that the domestication translation could not be existed without using some foreignization while foreignization translation could not be existed without using some domestications also.
SL emphasis TL emphasis
Literal translation Free translation
Faithful translation Idiomatic translation Semantic translation Communicative translation
Arnold, Balkan, Meijer, Humphreys, and Sadler (2001) mentions three problems that a translator usually faces while translating. First is ambiguity. Ambiguity is general fact in language. Not all words only have one meaning. A word could be having different meaning based on the context of the sentence. If a word has more than one meaning, it is called as lexical ambiguous. If a sentence or phrase has more than a structure or meaning, it is called as structurally ambiguous. Second is lexical and structural mismatches. Every language has different lexical and structure. Therefore, to translate the source language to target language the translators should classify the words and the concepts to express the target meaning. The last is multiword units such as idioms and collocations. Multiword unit is a special case because it could be translated use normal rules. Idioms and collocations, for example, have more than one word in each of them. While translating idioms and collocations the translators should have good knowledge and good understanding of the meaning.
Larson (1984) classifies the translation into four classes; Ideal-Acceptable (I-Acc), Acceptable (Acc), Unacceptable (Unacc), and Failed (F). The translation could be classified based on the criteria that Larson mentions on his book. Larson divides the criteria into three; Accurate (A), Clear (C), and Natural (N).
Accurate means the translation could be translated correctly. The meaning and the messages from the source language could be transferred into the target language accurately. Some translators sometimes make mistakes while analyzing the meaning of the source language. Therefore, the accuracy of translation could not be obtained correctly. Accuracy is very important because in the translation,
the most important thing is the meaning and the messages could be transferred from the source language into target language (Newmark, 1988).
Clear means the translation could be understood for the target language audience. All the features of translation are stated into correct form and have clear meanings. The words and the contexts also chosen the correct one. Therefore, the meaning and the messages are understandable for the target language audience. It would be hard to get the meanings and the messages if the translators wrong in choosing the words also the contexts and making the translation without making the translation understandable.
Natural means the words and illustrations which the translators used are appropriate in the target language. The translators should be aware about the words which are suitable to translate from source language to target language. The words and the illustrations should be common used in the target language. It would help the target language audience understand the meanings and the messages easily.
As mentioned previously, Larson classifies the translation into four classes. The classes depend on how many criteria are consisting into the translation. The translation included into Ideal-Acceptable (I-Acc) class if the translation consists all of three criteria; Accurate (A), Clear (C), and Natural (N). If the translation consists two of the criteria, it would be included into Acceptable (Acc) class. While the translation only consists of one criterion, it would be included into Unacceptable (Unacc) class. Whereas, the translation does not consist of any criteria at all, it would be included into Failed (F) class.
Source Language Target Language There is a kind of fish called Gede. It is
black and white except for the belly which is all white. It has a flat, broad nose, and whiskers on its mouth.
Ikan yang disebut Gede adalah ikan yang berwarna hitam dan putih. Tetapi, perut bawahnya hanya berwarna putih. Gede memiliki hidung yang pesek dan besar serta janggut di mulutnya.
Table above is an example of Ideal-Acceptable translation class because the translation consists of all criteria. All information from source language are transferred accurately into target language. No information is omitted or added from the source language. If the target language audience read the translation, the target language audience would understand because the translation is clear and easy to understand. When they read the translation, it feels smooth and flow because the translator also uses appropriate words to translate the source language.
Source Language Target Language
There is a kind of fish called Gede. It is black and white except for the belly which is all white. It has a flat, broad nose, and whiskers on its mouth.
Ada ikan yang disebut Gede. Dia berwarna garis-garis hitam dan putih. Tetapi, perut bawahnya hanya berwarna putih. Dia memiliki hidung yang pesek dan lebar. Dia memiliki janggut di mulutnya.
Table above is an example of Failed translation class. The translation is not accurate because the translator adds information about the color. In the translation, the translator adds garis-garis which means stripes in source language. However, the source language does not mention about the stripes at all.
The translation also not clear because it has ambiguity meaning. The words ada ikan yang disebut Gede have ambiguity meaning because it is not clear whether Gede is a single name of fish or it is a type of fish. The translation is not natural because the translation uses repetition style which makes the translation does not feel smooth and flow.
3. Subtitling
Subtitling is written, immediate, and additive translation (Gottlieb, 1992). Subtitles do not consist of translating the text only, but subtitles help the audience in the picture and audio also. Subtitle combined with the picture on the screen which helps the audience understand about the scene. According to Jorge (2012), subtitling is transferring the translation of the spoken dialogue by different speakers of source language into written dialogue of target language. Usually, the subtitles are placed in the bottom of the screen.
Subtitling has limitation of space and time which make subtitling has direct effect in the final result. According to Gottlieb (1992), the limitation of space is depending of line and character of the subtitles. Subtitles should be no more than two lines where are placed in the center at the bottom of the screen without disturbing the picture of the screen. Each line should not more than 35 characters. The characters are included letters, spaces, and symbols. The limitation of time is between a second until maximum six seconds on the screen.
4. The Pursuit of Happyness Movie
The Pursuit of Happyness is a movie from San Francisco in 1981 which tells about Christopher Gardner and his son’s life. The wife leaves them because of economic problems. Here the short synopsis of The Pursuit of Happyness movie.
The Pursuit of Happyness is a story which takes place in San Franscisco in 1981. This movie tells about a father, Crish, who tries to find a job and money for his son, Chrispother. Crish states six journeys of his life in this movie. The first one is riding bus. Riding bus is a part of his life because every day he has to carry Chrispother to daycare. After that he has to come one hospital to another hospital to sell his bone scanner machine, which is the one and only source of income of his life. The second is being stupid. Why being stupid? It is because in this part, Crish believes a hippie girl to take care his machine and he gives that girl some money for it. However, the hippie girl takes the machine and runs away from Crish. The third part is running. Crish states this part because he is running to catch the bus to get his machine back. The fourth part is future fight. In this part, Crish struggles for his life. He has to try to sell his machine, take care of his son, train on his new office, and find a place to sleep at night. The fifth is paying taxes. In this part, after Crish gets some money, bank takes almost all of his money. He has to pay all his taxes until he is bankrupts. And the last is happiness. This part happens when he is accepted in the office.
B. Theoretical Framework
This part is a summarize from the theories which related to the research that the researcher used to answer the research questions. The researcher formulates two research questions. The first research question is the types of figurative language and the second research question is the acceptability degree of figurative language translation.
In order to answer the first research question, the researcher uses Abrams’ (1999) theory about kinds of figurative language. The researcher does not use all figurative languages form the Abrams’ theory because not all figurative language could be found in the dialogue. Therefore, the researcher focuses on three figurative languages, they are simile, metaphor, and hyperbole. Addition, the researcher uses two kinds of metaphor from Lakoff (1980). They are orientational metaphor and structural metaphor. The researcher focuses on three figurative languages only because from the dialogue and the subtitle of the movie, those types of figurative language could be found easily.
In order to answer the second research question, the researcher uses translation theory from Larson (1984). There are three criteria of an acceptable translation to know whether the translations are acceptable or not. The criteria are Accurate (A), Clear (C), and Natural (N). Larson divides the acceptable degree into four classes, they are Ideal-Acceptable (I-Acc), Acceptable (Acc), Unacceptable (Unacc), and Failed (F).
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter is related to the method which is used in the research. The chapter is divided into five parts: research method, research subject, data gathering technique, and data analysis technique.
A.Research Method
In order to elaborate the types of figurative language based on Abrams’ theory (1999) and the acceptability degree of translation figurative language based on Larson’s theory (1984), the researcher used qualitative research method which is document analysis. Document analysis is a form of qualitative research where the documents are interpreted by the researcher (Voice, 2010). Bowen (2009) states that document analysis includes skimming, reading, and interpreting.
Based on Creswell (2007), there are three steps of analyzing a document: preparing and organizing, coding, and the last is representing the data. Preparing and organizing is a step how to get and collect the data. Coding is a step to make a list of the data. The purpose is to choose which data to be analyzed. The last is representing the data is a step to represent the data into form which makes easy to understand.
According to Bowen (2009), document analysis has some advantages and limitations. The advantages are: “Efficient Method, Availability, Cost-effectiveness, Lack of Obtrusiveness, Stability, Exactness, and Coverage.” Not
only advantages, document analysis has limitations also. The limitations of document analysis according to Bowen are: “Insufficient Detail, Low Retrievability, and Biased Selectivity.”
B.Research Subject
Subject of the research is a movie which is directed by Gabriele Muccino entitled The Pursuit of Happyness. The researcher uses a script from www.scripts.com to help the researcher analyzes the figurative language translation in the movie. The movie is inspired by a true story of Chris Gardner (Will Smith), a salesman in San Francisco, who is struggling to build his life and his son’s life, Christopher (Jaden Smith). His wife, Linda (Thandie Newton), gives up their life and chooses to leave them to New York. Chris has to sell bone scanner from one hospital to another hospital to fulfill their needs. Besides that, he has to attend unpaid stockbroker-training program. Every night, Chris and Christopher have to find new place to sleep because they do not have enough money to rent a house or apartment. At the end of the story, Chris gets the job and their life is getting better.
C.Data Gathering Technique
In gathering the data, the researcher used two tables to easier while collecting the data and answering the research questions of the thesis. Table 3.1 is a table of type of figurative language based on Abrams’ theory and Table 3.2 is a table of acceptable translation based on Larson’s theory.
Table 3.1 Type of Figurative Language Based on Abrams’ Theory (1999)
Table 3.1 shows how the researcher classified the type of figurative language based on Abrams’ theory. The table helped the researcher to answer the research question number one, “What types of figurative language are found in The Pursuit of Happyness movie?”
Table 3.2 Acceptability Degree Based on Larson’s Theory (1984)
Table 3.2 shows how the researcher identified the translation of figurative language based on Larson’s theory. The table helped the researcher to answer the
Figurative Language Sentence Type
English Subtitle Indonesian Subtitle Criteria Acceptability Degree Accurate Clear Natural
research question number two, “How acceptable the figurative language translated in the movie?”
D.Data Analysis Technique
In order to get the data and analyze the data, the researcher did several steps. The steps were watching, identifying, classifying, analyzing, checking and the last was validating.
1. Watching
The researcher watched The Pursuit of Happyness movie. In order to get better understanding, the researcher used subtitle while watching the movie. Once used English subtitle and once used Indonesian subtitle.
2. Identifying
Besides watched The Pursuit of Happyness movie by using subtitle, the researcher also used an unofficial transcript from the movie to get the data easily. The researcher identified the transcript from www.scripts.com. The researcher underlined the figurative languages from the transcript.
3. Classifying
From the transcript, the researcher found the figurative language and identified what type of the figurative language. The researcher classified the figurative language used Abrams’ theory and put the data into Table 3.1 about type of figurative language based on Abrams’ theory (1988).
4. Analyzing
The researcher found the Indonesian subtitle of figurative language from www.Subscene.com and analyzed the figurative language whether the translations
were acceptable or not by using theory of Larson. The researcher gathered the data by putting the data into Table 3.2 about acceptability translation based on Larson’s theory (1984).
5. Checking
The researcher checked the data and made sure that the data were correct. Not only once, but the researcher re-checked again the data to minimalize the errors.
6. Validating
In order to make the data more valid, the researcher asked lecturers who are expert about linguistic and translation to check and to validate the data. The researcher would correct and asked them to check again.
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter presents the research result and discussion of the analysis of the research based on two research questions in Chapter I. Therefore, this chapter is divided into two parts based on the research questions. The first part is to answer research question number one and the second part is to answer research question number two. The purpose of the first research question is to analyze the types of figurative language which are found in the The Pursuit of Happyness movie. The second research question is to find out whether the translations of the figurative language are acceptable or not. In order to answer the two research questions, the researcher collected the data from the transcript which is from www.scripts.com of the movie and an Indonesian subtitle from www.Subscene.com.
A. Types of Figurative Language
In order to classify the data to answer research question number one, the researcher used theory from Abrams (1999). The researcher did not use all kinds of figurative language. The researcher only focused on three types of figurative language, they were metaphor, hyperbole, and simile. In addition, the researcher divided the metaphor into two kinds. The kinds of metaphor were taken from Lakoff’s theory (1980) because Lakoff classifies the theory clearly and the theory is easy to find in the data. The kinds of metaphor are orientational metaphor and
structural metaphor. After collecting and analyzing the data, the researcher found the result of percentage the uses of metaphor, hyperbole,and simile.
Table 4.1 Percentage of Figurative Language
No Figurative Language Frequency Percentage
1. Metaphor 148 83%
2. Hyperbole 23 13%
3. Simile 8 4%
Total 179 100%
The researcher found 179 figurative languages in The Pursuit of Happyness movie. The figurative languages are divided into three kinds. Metaphor is the dominant figurative language found in the movie. There are 148 metaphors (83%) which found in the movie. The metaphors are divided into two kinds, they are orientational metaphor and structural metaphor. There are 132 orientational metaphors (74%) and 16 structural metaphors (9%). After metaphor, there are 23 hyperboles (13%) found in the movie. The least figurative language which found in the movie is simile with 8 similes (4%).
Both metaphor and simile are comparing between two things. However, the researcher found the number of metaphor is much higher than simile. Metaphor more often used than simile because by using a metaphor, the speaker does not need to use any characteristics such as simile which a simile could be used if there is word like or as. Therefore, metaphor is simpler than simile and people could understand metaphor implicitly without any characteristics such as simile has (Keraf, 1984).
1. Metaphors
Metaphor is the highest number of figurative language which found in the movie. A metaphor is comparing one thing to another thing directly (Abrams, 1999). Lakoff (1980) explains that a metaphor is an unusual language which used in daily conversation. However, lot of people use metaphor in daily activity without they realize that they are using metaphor. From the data, the researcher found 148 metaphors which are divided into two kinds of metaphor: orientational metaphor and structural metaphor. There are 132 orientational metaphors and 16 structural metaphors.
a. Orientational Metaphors
Abrams (1999) on his book does not mention orientational metaphor. However, in The Pursuit of Happyness movie there are a lot of orientational metaphors stated in the movie. Therefore, the researcher added orientational metaphor as one of figurative languages which is discussed in this research. Orientational metaphor is a metaphor by using spatial orientation such as up, down, off, in, out, back, front, around, away, on, and below (Lakoff, 1980). From the data, the researcher found 132 orientational metaphors.
Excerpt from 00:01:35 00:01:36 Chris: Time to get up, man.
(A1)
Excerpt [1] Excerpt from 00:56:00 00:56:01 Chris: Keep up.
Excerpt [2]
The excerpt [1] and [2] show the example of orientational metaphor because those sentences contain of up which indicated that the sentences are included into orientational metaphor. Up is one of spatial words. Up itself means towards or get higher position. From the excerpt [1] and [2], get and keep still maintain their literal meaning. Get means receiving or obtaining something and keep means to continue to be in the specified condition or position. Those words could be included into metaphor when the words meet word up.
However, get up does not mean receiving higher position. The meaning of get up is to stand. Based on the context in the conversation, get up means awake. In the movie, Christopher is sleeping and Chris asks his son to awake and prepare himself to school. Therefore, the meaning of get up is awake. Meanwhile, keep up does not mean to continue going higher position. The meaning of keep up is to continue without stopping. In the context of the conversation, keep up means going faster. Every day, Chris and Christopher should come and stand in line in a building to get a room to sleep for free. Chris asks his son to run faster while he tries to get in line on time.
Excerpt from 01:19:02 01:19:04 Crazy man: Bring back my time machine.
(A125) Excerpt [3]
Excerpt [3] shows another orientational metaphor. Back means behind and bring means carry something. Bring back does not mean carry something in the
behind. According to the context, crazy man takes Chris’ bone scanner machine and Chris tries to take his machine. However, the crazy man does not want to return the machine and he says to Chris to return the machine. Therefore, the meaning of bring back in this context is return.
In the movie, the researcher did not only find orientational metaphor by using up and back. Beside up and back, the researcher found another spatial orientation which indicate orientational metaphor. The other spatial orientation to indicate the orientational metaphor which found in the The Pursuit of Happyness movie are out, on, in, around, off, down, behind, away, and ahead.
b. Structural Metaphors
Beside orientational metaphor, structural metaphor could be found in the movie. Different from orientational metaphor, a structural metaphor does not have special word to indicate whether the sentence is containing structural metaphor or not. According to Lakoff (1980), structural metaphor is showing one kind of activity in terms of another activity. In the data, the researcher found 16 structural metaphors.
Excerpt from 01:26:39 01:26:40 Chirs: We are cavemen.
(A137) Excerpt [4]
A structural metaphor could be found in the excerpt [4]. From the excerpt, Chris says that we are cavemen. The literal meaning of cavemen is person who lives in a cave. However, based on the context, Chris and his son are not cavemen.
He says that they are cavemen because he wants to ask his son to find a place to sleep while his son feels very tired and angry with him. As cavemen, they have to find a cave. Finally, they find a bathroom as their cave and they sleep in there for all night.
Excerpt from 00:46:43 00:44:44 Jay: You are a piece of work.
(A77) Excerpt [5]
Excerpt [5] shows a structural metaphor also. In the literal meaning, you are a piece of work means you are part of work because piece means any parts of something. However, based on the context, the meaning of piece of work is not part of work. From the context, Jay commends Chris after Chris is interviewed by the managers. Jay amazed about what Chris has done during the interview. Instead of using you have done good job, Jay chooses to say you are a piece of work because he wants to influence his feeling by giving appreciated using metaphor. Therefore, Jay says to Chris you are a piece of work by the meaning he has done very well job.
2. Hyperboles
The second figurative language which found in the movie is hyperbole. According to Abrams (1999), hyperbole makes an effect or exaggerate of fact or something to show how very important or very unimportant the thing. Hyperboles are used to make a special effect and get more attention. Based on the findings,
Excerpt from 00:13:55 00:13:57
Tom Brophy: As you can see, we got a hell of lot of applications here. (A22)
the researcher found 23 hyperboles stated in the movie. Excerpt [5]
In the excerpt [5], Tim says as you can see, we got a hell of lot of applications. The use of a hell of lot of does not mean that the applications are in the hell or the applications itself are the hell. Actually, a hell of lot of could be changed by many which the word is simpler than a hell of lot of. Based on the context, the speaker prefers to use a hell of lot of instead of many because the speaker wants to show how he is tired and stressed of getting applications which come during the day. If the speaker only uses many, the meaning of getting tired and stressed would not get the exaggerate feeling and the meaning could not be transferred correctly to the audience.
In the movie, the researcher found several hyperboles by using word hell in the sentence. The other sentence which uses hell is stated in the get the hell out of here. The hell in here is not to say about hell. The speakers use hell to show the anger and to show how the speakers emphasize their meaning.
Excerpt from 00:10:14 00:10:18
Chris: They all looked so damn happy to me.
(A15) Excerpt [6]
The other example of hyperbole found in the The Pursuit of Happyness movie is stated in the excerpt [6]. The sentence is they all looked so damn happy to me. So is used to indicate the large extent or degree of something. While damn is used to condemn something. The sentence is included into hyperbole because the sentence contains so and damn. Both of them are used to show how very
meaningful the sentence. The sentence is not effective because it contains of two words with the similar meaning. Therefore, the sentence is a hyperbole sentence. By using so and damn, the speaker wants to show a special effect and exaggerate the feeling. According to the context, Chris walks in the street in front of an office. All people come and go through Chris with smile on their faces. On that moment, Chris realizes that all people look happy. Therefore, Chris says they all looked so damn happy to me to show how the people look very happy on that day.
3. Similes
The third figurative language which found in the movie is simile. According to Abrams (1999), simile is comparing between two different objects. The most common characteristics of simile by using like and as. Simile is the least of figurative language in this research because to use a simile, a speaker should use like or as to compare something. The researcher found 8 similes in the data. There is an example of simile which stated in the The Pursuit of Happyness movie.
Excerpt from 00:45:51 00:45:56
Jay: Chris, I do not know how you did it dressed as a garbage man but you pulled it off.
(A75) Excerpt [7]
In the excerpt [7], Jay compares Chris and a garbage man by using as in you dressed as a garbage man in his sentence. Jay says so because Chris’ appearance looks like a garbage man. In the movie, Chris come to the office to
have interview but he does not wear appropriate clothes. A day before, Chris is painting his apartment while officers come and arrest him. Chris does not have time to change his painted clothes to a better clothes. Chris also has to stay at the police station until the next morning. From the prison, Chris run very fast to come on time to the office. Therefore, Chris still wears T-shirt, jeans, and painted face. Everybody on the interview room is shock because Chris does not wear formal clothes. Chris tries to explain that the night before he come to the office, he is arrested because he does not pay the parking ticket. In spite of this, Chris does the interview very well. Therefore, Jay says I do not know how you did it dressed as a garbage man but you pulled it off and compares between Chris and garbage man because the Chris wear clothes such a garbage man.
Excerpt from 00:21:35 00:21:38
Chris: So if I lost one, it was like losing a month’s groceries.
(A38) Excerpt [8]
The other simile could be found in the conversation is like in the so if I lost one, it was like losing a month’s groceries sentence. Like in that sentence compares between lost one and losing a month’s groceries. In the context, to fulfill Chris’ family needs, they only sell bone scanner machine. By selling one bone scanner, his family could buy food, pay the rent, pay the parking ticket, and pay another needs. Therefore, if they lost one machine, it means that they would not have money to fulfill their needs for a month.
B. Acceptability Degree of Figurative Language Translation
In order to answer the second research question, the researcher used Larson’s (1984) theory about three criteria to classify the acceptability translation. The criteria are Accurate (A), Clear (C), and Natural (N). Accurate means the translation could be translated correctly and suitable to the context. Therefore, the meaning could be transferred properly. Clear means the translation translated in a simple way and could be understood easily by the target language audience. By fulfilling the Clear criteria, the translation expects not make the target language audience confused. Natural means the translation uses appropriate words to the target language. By using appropriate words from the target language audience, the translation could be understood easier.
In order to classify the acceptability degree of translation, there are four classes of acceptability translation. The classes of acceptability degree translation are Ideal-Acceptable (I-Acc), Acceptable (Acc), Unacceptable (Unacc), and Failed (F). The classify is based on how many criteria which contain in the translation. If the translation contains of three criteria, it would be into Ideal-Acceptable class. If the translation contains of two criteria, it would be into Acceptable class. If the translation only contains of one criterion, it would be into Unacceptable class. Therefore, if there is no criterion which contain in the translation, it is Failed translation.
The researcher focused on analyzing the translation of figurative language only. The researcher analyzed whether or not the translations of figurative language are suitable to the context, easy to be understood by the target language
audience, and used appropriate words. Therefore, the result of translation is not coming from the whole sentence but coming from figurative language translation. However, the researcher still considers the context also. After collecting and analyzing the data, the researcher found the percentage of acceptability degree of figurative language translation.
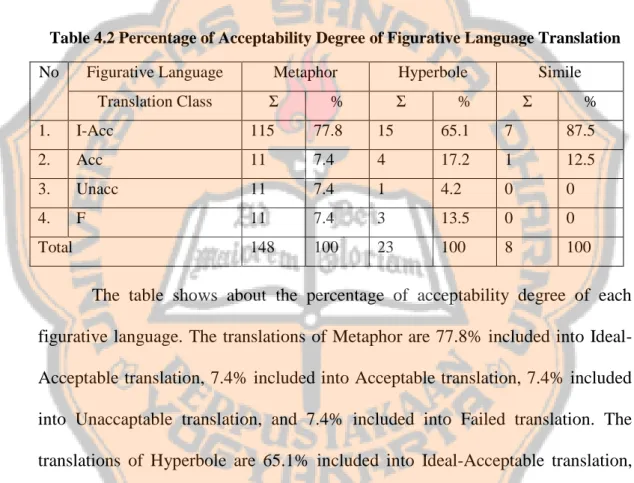
Table 4.2 Percentage of Acceptability Degree of Figurative Language Translation No Figurative Language Metaphor Hyperbole Simile
Translation Class Ʃ % Ʃ % Ʃ % 1. I-Acc 115 77.8 15 65.1 7 87.5 2. Acc 11 7.4 4 17.2 1 12.5 3. Unacc 11 7.4 1 4.2 0 0 4. F 11 7.4 3 13.5 0 0 Total 148 100 23 100 8 100
The table shows about the percentage of acceptability degree of each figurative language. The translations of Metaphor are 77.8% included into Ideal-Acceptable translation, 7.4% included into Ideal-Acceptable translation, 7.4% included into Unaccaptable translation, and 7.4% included into Failed translation. The translations of Hyperbole are 65.1% included into Ideal-Acceptable translation, 17.2% included into Acceptable translation, 4.2% included into Unaccaptable translation, and 13.5% included into Failed translation. The translations of Simile are 87.5% included into Ideal-Acceptable translation and 12.5% included into Acceptable translation.
From the table, the most acceptable type of figurative language translation is simile. There are only 8 similes in the data and all similes are included into acceptable translation. It is because similes have characteristics which are easy to identify and translate. The characteristics which found in the data are like and such as. Those words could be translated accurately, clearly, and naturally. Even though there are 148 metaphors in the research, not all metaphors could be translated acceptably. Metaphor has high frequency which is included into unacceptable translation. Therefore, the most acceptable translation is simile.
In other hand, hyperbole is the least acceptable translation of figurative language in the research. From 23 hyperboles found in the data, there are 4 hyperboles which included into unacceptable translation. All of the hyperboles which could not be translated acceptably are included into swear words. The translator did not translate the swear words or even the translations are not acceptable. The swear words which stated in The Pursuit of Happyness movie are to show the anger of the speaker. If the translator did not translate the swear words, the meaning and the feeling might be different. Therefore, the least acceptable translation of figurative language in the research is hyperbole. These are the examples and explanations of each classes of acceptable translation. The researcher also added suggestion of translation in Unacceptable translation and Failed translation.
1. Ideal-Acceptable Translation
A translation called an Ideal-Acceptable (I-Acc) translation if the translation contains three criteria from Larson. The researcher found 130 Ideal-Acceptable translations in the data. Ideal-Ideal-Acceptable translation is the higher frequency of the data. Based on these findings, the translation belongs to good translation because most of the translations are Ideal-Acceptable translations. All of the translations contain three criteria: Accurate, Clear, and Natural.
Figurative Language Subtitle
Excerpt from 00:01:35 00:01:36 Time to get up, man.
(B1)
Waktunya bangun.
Excerpt [9]
Excerpt [9] was taken from the first scene where Christopher is still sleeping and Chris tries to wake his son up. Chris come to Christopher’s room and find his son is still sleeping. After that, Chris says time to get up, man. However, Christopher still does not want to wake up and continue to sleep for a while because he is too lazy to wake up directly.
Excerpt [9] is an Ideal-Acceptable translation. Time to get up, man translated into waktunya bangun. Get up is an example of orientational metaphor. Get up means to stand. In Bahasa Indonesia, stand means berdiri. However, the translator translated get up into bangun not berdiri. In spite of this, the translation is accurate. According to the context, the suitable word to translate get up is bangun rather than berdiri. The translation is also clear because the chosen word is simple. Everybody could understand that get up could be translated into
bangun. Moreover, the context showed clearly that get up means bangun. As a result, the translation could be understood easily to the target audience. Moreover, the translation is natural because the translation uses common words which target
language audience usually use.
Excerpt [10]
Excerpt [10] came from scene when Chris rides a bus and in the bus there is a crazy man who says to Chris that his bone scanner machine is a time machine. The man says for several time until all people in the bus look at Chris and the man. While Chris goes down from the bus, the man still follows Chris and still says that the machine is time machine.
Excerpt [10] shows an Ideal-Acceptable translation. Like is a characteristic of simile and like is as conjunction means similar to something or somebody. In the excerpt [10], like is translated into seperti. The translation is accurate because the chosen word is suitable to the context. According to the context, the bone scanner machine is similar with time machine. Therefore, like is translated to be seperti is accurate. Moreover, the translation is clear because it is easy to understand by the target language audience. The chosen word is also appropriate
Figurative Language Subtitle
Excerpt from 00:05:21 00:05:22 Seems like a time machine.
(B5)