I certify that this is a project report entitled "FRAMEWORK OF COMPETITIVE STRATEGIES FOR EXISTING SHOPPING CENTERS IN MALAYSIA". 72 5.2.2 Objective 2 - To compare the evaluation of competitive strategies for existing shopping malls in Malaysia between different age groups and genders.
General Introduction
Background of the Study
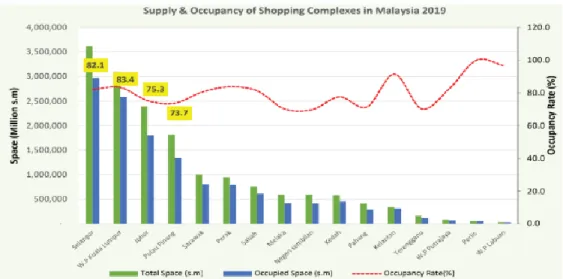
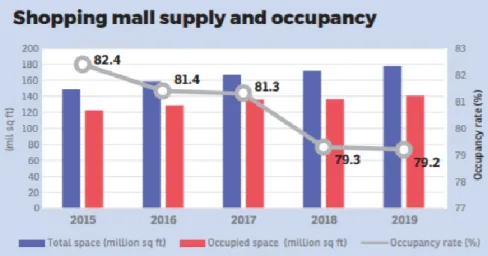
Some of the new malls may struggle to build market share, which becomes more fragmented due to the glut of malls. In addition, Chinese tourists, who spend the most, spend around $260 billion worldwide in shopping malls in Malaysia (MCRA, 2019).
Problem Statement
Therefore, this study aims to propose competitive strategies that can be adopted by existing malls. Consequently, it reduces the poor performance and abandonment of existing malls in Malaysia and promotes the economic and social development of Malaysia.
Research Aim
Recently, these retail markets have faced significant challenges, which are the impact of the intra-regional competition, economic slowdown, the rapid development of e-commerce and the experiential market influencing customer behavior. By adopting appropriate competitive strategies, it is able to attract and retain tenants and at the same time, it can drive more customers to the malls.
Research Objectives
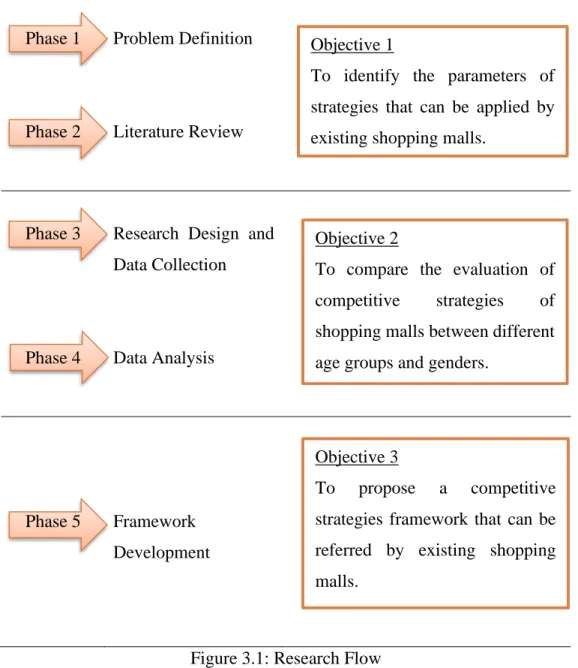
Research Methodology
The target of this study was buyers in the Klang Valley and the central limit theorem was adopted to achieve sufficient sampling for this research.
Research Scope
Chapter Outline
Problem
Literature
Research Design
Data
Framework
Chapter Summary
In addition, the research methodology is discussed, and the chapter outline outlines the main structure of each chapter in the study.
Introduction
Background of Shopping Malls in Malaysia
SStwo Mall, located in Petaling Jaya, was closed in March 2015 due to its unwelcome performance. The mall opened in 2010 and closed less than four and a half years later.
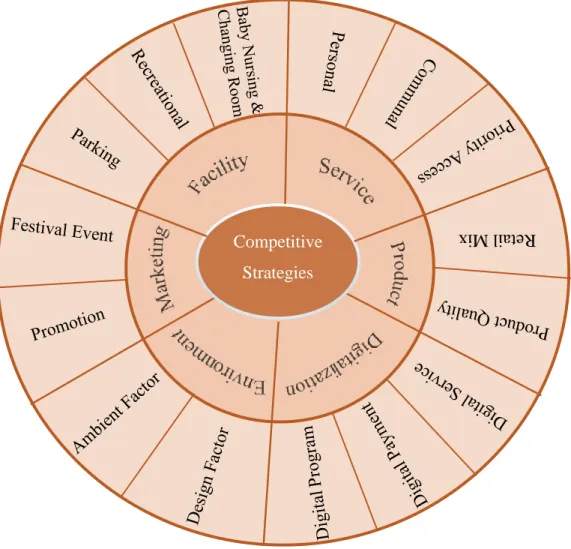
Competitive Strategies of the Existing Shopping Malls
- Facility
- Parking Facility
- Recreational Facility
- Baby Nursing and Changing Rooms Facility
- Service
- Personal Service
- Communal Service
- Priority Shopping Access Service
- Product Assortment
- Retail Mix
- Quality of Product
- Digitalization
- Digital Service
- Digital Payment
- Digital Program
- Environment
- Design factor
- Ambient Factor
- Marketing
- Promotional Activity
- Festival Event
In summary, the retail mix is one of the competitive strategies of. existing mall in Malaysia. In summary, the digital service is one of the competitive strategies for the existing shopping centre.
Conceptual Framework of the Competitive Strategy
Research shows that the event atmosphere provides positive cues or stimuli that regulate the mood of buyers (Ghee and Ahmad, 2010). First, the mall can focus on facility dimension including parking, leisure, baby nursing and changing room facilities to increase the satisfaction level of customers. Furthermore, tenant mix and product quality must be focused to increase the choices and lifestyle quality of customers.
Nowadays, shopping center can also emphasize on digitalization, including digital service, digital payment and digital program to catch up with the advanced technological age. Finally, marketing approach of shopping center is significant as promotional and festival events cause a positive impact on the psychological aspect and purchasing behavior of customers.
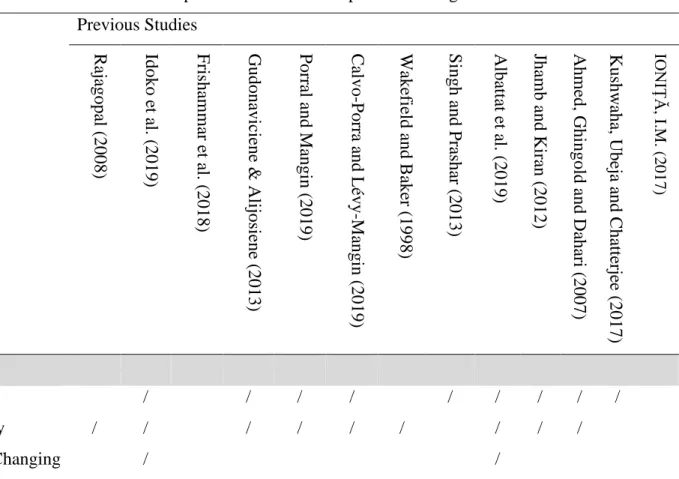
The characteristics of shoppers with the competitive strategies A cohort theory by Ryder (1965) reveals that the characteristics of shoppers will
- Ages of shoppers and the competitive strategies
- Genders and the competitive strategies
In summary, there is a difference between different age groups regarding shopping mall competitive strategies based on these previous studies. Ryder's (1965) gender cohort theory emphasized the importance of shopping attributes in influencing the shopping attitudes of different sexes of shoppers. On the other hand, the participation of married men in shopping may depend on the status of the woman's job. 2004) discerned that different genders will have different levels of satisfaction during hedonic shopping.
They revealed that men use salesperson assistance to a greater extent than women, and women prioritize convenience and product selection in shopping malls to a greater extent. In summary, there is a difference between different gender cohorts on the competitive strategies of shopping malls based on these studies.
Chapter Summary
Women tend to purchase specific categories such as groceries and clothing, while men are responsible for purchasing specialized products such as automobiles and home maintenance (Buttle, 1992). However, Fischer and Arnold (1994) indicated that different genders have different perceptions and behaviors regarding shopping. Men and women may differ in certain consumption patterns, product preferences, and responses to marketing strategies and product selection (Zeithaml, 1988).
The hedonic value of shopping for women is typically related to the tendency to seek variety, the physical environment of stores, and overall shopping satisfaction, while there is no mediation for men. Moreover, Kavussanu and Roberts (2001) found that men have lower task orientation compared to women and thus concluded that the value of utilitarian purchase for men may be less. 2007) examined that differences in shopping attitudes between male and female shoppers.
Introduction
Research Method
- Quantitative Research Approach
- Qualitative Research Approach
The findings can be tested and verified to make them more reliable, but setting up a research model is difficult. The result of a quantitative approach is simple, but can also be misleading or subjective due to the bias of researchers (Devault, 2019). For qualitative research methods, richer data can be collected, but it is more difficult to analyze.
In addition, it refined the quantitative data, but the findings cannot normally be evaluated for the study community and population. Qualitative research offers multiple ways to collect data on sensitive topics, but it is time consuming.
Justification of Selection
Research Design
Previous events or incidents relevant to the topic are reviewed to emphasize the research question of the study. Before the study problem is identified, a solution is investigated to ensure the viability of the studies (Kothari, 2004). Developing a research design involves deciding on the necessary data, the related theories and variables, the participants and the sources, the procedures of data collection and analysis methods (McCombes, 2019).
Then a conclusion must be stated and this must be related back to the research question. The success in achieving the research objectives, contribution, limitation and recommendation of this research are discussed.
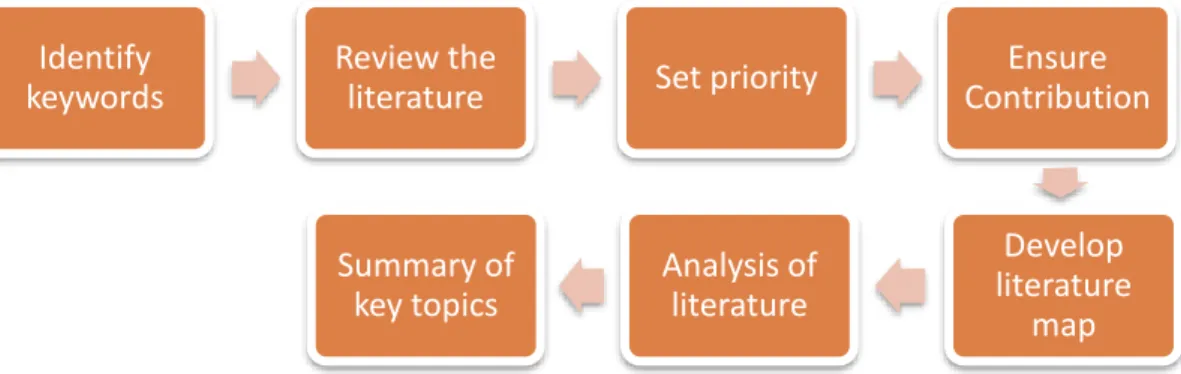
Literature Review
The outcome of the findings should be referred back to the literature review to support or justify the findings in the discussion session. The situation of shopping centers in Malaysia is explored and discussed in a literature review. Next, the fourth step is to ensure that the contributions of the articles are able to increase the understanding of the literature review.
A conceptual literature map is created in the literature review to visualize how the research contributes to the literature. The literature review concludes with a summary of key themes and discusses how specific research contributes more to the literature and fills a gap in past studies.
Quantitative Data Collection
- Questionnaire Design
- Sampling Determination
- Questionnaire Distribution
Convenience and snowball sampling method were selected to distribute the questionnaire surveys in this research. Convenience sampling is a type of non-probability sampling method where the sample is collected from a group of people who are conveniently reachable by the researcher (Edgar and Manz, 2017). In this research, family and friends of the researcher are targeted to distribute the questionnaire surveys.
Therefore, as the sample size increases, the sample mean and standard deviation would be closer in value to the population mean and standard deviation. After designing the questionnaire and determining the sample size, the questionnaires were distributed to the target respondents through online approaches.
Data Analysis
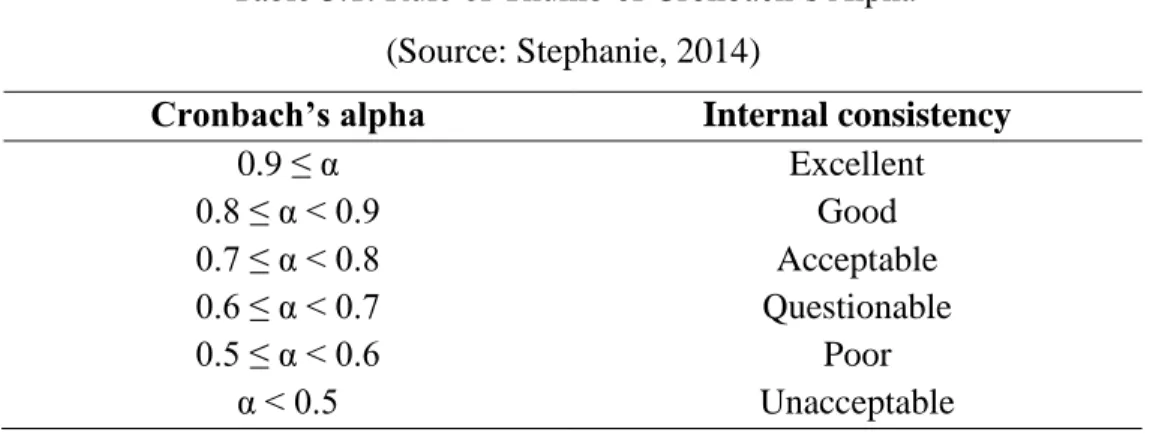
- Cronbach’s Alpha Reliability Test
- Arithmetic Means
- Kruskal-Wallis Test
In this research, this test is used to analyze and evaluate the data according to the respective average ranking of different age groups against the competing strategies. Two hypotheses were formulated in order to detect the significant differences on the competitive strategies between the age groups for this study. Null hypothesis, (H0) indicates that there is no significant difference on the competitive strategies between the age groups, while,.
Alternative hypothesis (H1) indicates that there is a significant difference in the competition strategies between the age groups. The calculated H-value is used to determine the hypothesis by comparing with the critical chi-square value.
- Mann-Whitney U Test
- Summary of Chapter
- Introduction
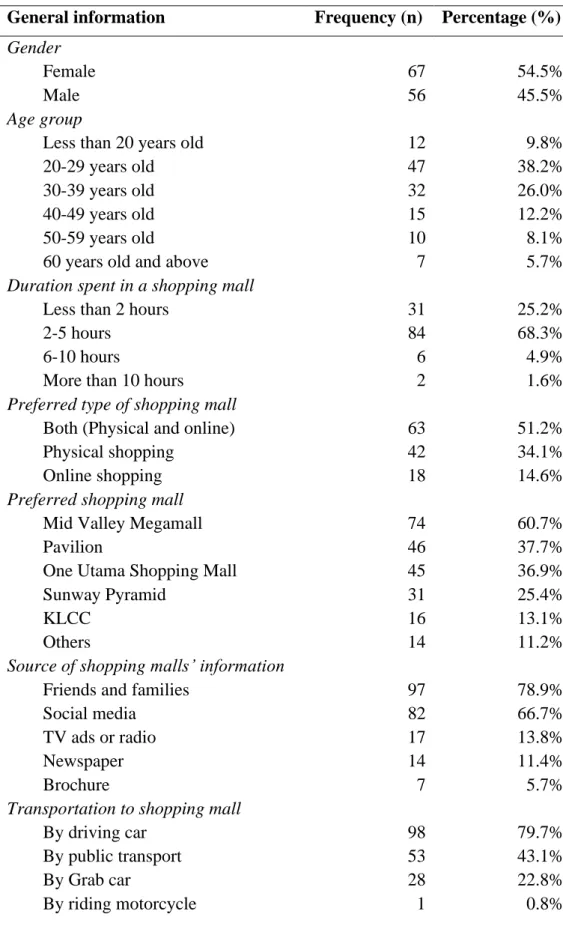
- Demographic of Respondents
- Cronbach’s Alpha Reliability Coefficient
- Arithmetic Means of Competitive Strategies Parameters
- Mean Ranking of Main Competitive Strategies
- Mean Ranking of Competitive Strategies Sub-Parameters
- Kruskal-Wallis Test
- Mann-Whitney U Test
E1e Increase the connection with nature through greenery in the shopping center (eg plants, flowers or branches). On the other hand, the lowest average ranking is the digitization of the shopping center (mean value = 3.58). E2d Ensure good hygiene in the shopping center 4.76 1 C2a Offer good quality products without rot or.
According to Table 4.6, the highest average ranking of competitive strategy parameters is E2d= "Maintain good hygiene in the shopping center", which is categorized under "Environment" with an average value of 4.76. The elderly will therefore prefer to visit the shopping center which offers a reasonable price of parking spaces.
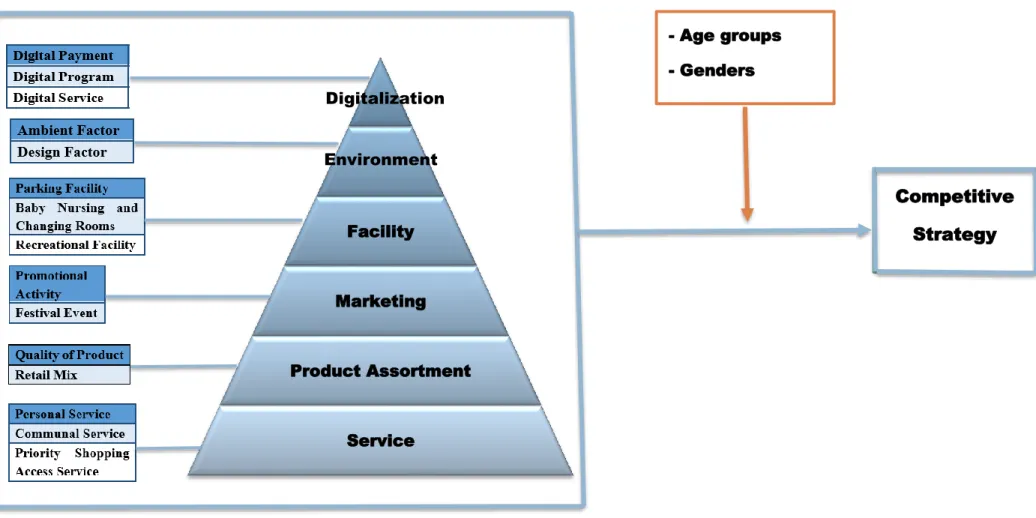
Refined Competitive Strategies Framework
The amended framework integrates the arithmetic means from the competitive strategies sub-criteria in the provisional framework. The ascending pyramid inferred that "Digitalization" has the lowest average rank, followed by "Environment", "Facility", "Marketing". The sub-criteria for competitive strategies are tabulated and arranged from highest to lowest mean in the refined framework.
Some significant differences of perceptions between age groups and genders about the competitive strategies are. By considering the different perspectives between age groups and genders, an appropriate and suitable competitive strategy framework can be developed to assist the shopping centres.
Chapter Summary
Introduction
Accomplishment of Research Objectives
- Objective 1- To identify the competitive strategies for existing shopping malls in Malaysia
- Objective 2- To compare the evaluation of competitive strategies for existing shopping malls in Malaysia between different age
- Objective 3- To propose a competitive strategies framework for existing shopping malls in Malaysia
The parameters of competing strategies were ranked using arithmetic means and tabulated in table 4.4 and table 4.5. Additionally, Kruskal-Wallis test revealed that 12 competitive strategies parameters found significant differences between age groups. After the data collection and analysis, a refined competitive strategies framework was therefore developed as illustrated in Figure 4.1.
The refined framework depicted the importance level of main competitive strategies obtained from the mean analysis in an ascending pyramid and the sub-criteria of competitive strategies are tabulated accordingly from highest to lowest ranking. The considerations of different perspectives of competitive strategies between age groups and genders are also added to develop a comprehensive competitive strategy framework for existing shopping centers in Malaysia.
Research Contribution
Other researchers can also refer to the proposed strategy framework as one of their resources when conducting relevant study.
Research Limitation
Research Recommendation
At the end of the research, case studies can be conducted to validate the framework proposed in the research to calculate the applicability in the retail industry. In addition, interviews are suggested to investigate more complete data and new strategies can be generated. Additionally, a balanced collection of questionnaires is suggested for future research to obtain balanced perspectives from different groups, levels, or characteristics of respondents.
To achieve a balanced collection of questionnaires, the researcher must check the response rate for each group of respondents. A balanced number of respondents in each category will increase the reliability and accuracy of the results.
Chapter Summary