APPROVAL
THE MASTERY OF SUBJUNCTIVE:
A CASE STUDY AT THE THIRD YEAR STUDENTS OF
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL AT LEMBAGA PENDIDIKAN
PRIMAGAMA LUBANG BUAYA
A PAPER
Submitted to Letters and Humanities Faculty In Partial Fulfillment of the requirements for
the Degree o Strata. 1
By
ADI SUPRIADI
101026021565
Approved by Advisor
Abdul Hamid. M.Ed.
NIP: 150181922
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH LETTERS
FACULTY OF ADAB AND HUMANITIES
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH
LEGALIZATION
The paper entitled “The Mastery of Subjunctive: A Case Study at the Third Year Students of Senior High School at Lembaga Pendidikan PRIMAGAMA Lubang
Buaya has been defended before the Letters and Humanities Faculty’s Examination on August, 10 2009. The paper has already been accepted as a partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Strata. 1.
Jakarta, October 12, 2009
Examination Committee
Chair Person, Secretary,
Dr. Muhammad Farkhan, M.Pd. Drs. A. Saefuddin, M.Pd.
NIP: 150 229 480 NIP: 150 261 902
Members:
Danti Pujianti, MM, M.Hum. Elve Oktafiyani, M.Hum.
DECLARATION
I hereby declare that this submission is my own work and that, to the best of my knowledge and belief, it contains no material previously published or written by another person nor material which to a substantial extent has been accepted for the award of any other degree or diploma of the university or other institute of higher learning, except where due acknowledgement has been made in the text.
Jakarta, October 12, 2009
ABSTRACT
ADI SUPRIADI, the Mastery of Subjunctive: A Case Study at the Third Year Students of Senior High School at Bimbingan Belajar Primagama Lubang Buaya. A paper, Letters and Humanities Faculty, State Islamic University “Syarif Hidayatullah” Jakarta July 2009.
The objective of this study is to evaluate how far the students understand about subjunctive which the teachers teach. The data obtained through participant observation are analyzed qualitatively using relevant theories.
The research uses field study. The sample of the research is randomly taken from the population of the third year students of senior high school at Lembaga Pendidikan Primagama Lubang Buaya in the academic year of 2008/2009. The data collected through the test are analyzed qualitatively using descriptive comparative analysis technique.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
In the name of Allah, the most Beneficent and the most Merciful
First of all, praise belongs to Allah, the Cherisher and the Sustainer of the world, and then the writer would like to thank so much for all chances which He gives observe his world with full of guidance and aid to pass it through. And may his peace and blessing be upon the seal of the prophets, the messengers of Allah, especially Muhammad, his family, and all his companions. And the writer thanks his parents and family especially his beloved mother, Mrs. Sukaesih Yayan, the perfect-beloved woman who always loves the children with her drops of sweat for her children’s better life.
Thanks to the most meaningful persons whom the writer assures for his work which will not finish without their aid and supports. Therefore, the writer would like to thank:
1. Prof. Dr. H. Bambang Madiono and Mrs. Hj. Taty Bambang Madiono who give the writer love so much that the writer can survive.
2. Mr. Eddy Prananto Pati which always guides the writer’s life
3. DR. H. Abdul Chair, the Dean of the Faculty of Adab and Humanities, State Islamic University Syarif Hidayatulah Jakarta.
5. Dr. H. Muhammad Farkhan, M.Pd, the Chief of English Letters Department, Drs. A. Saefudin, M.Pd., the Secretary, Drs Arifin Toy MLS, the Academic Advisor of Department of English Letters.
6. All lecturers and staffs of the Faculty of Adab and Humanities.
7. Bimbingan Belajar Primagama Lubang Buaya and the staffs especially Irwan Nurianto, S. S1, the Branch Manager of Primagama Lubang Buaya.
8. The staffs of Universities of Indonesia and Atmajaya for all references of this study.
9. The writer’s close friends, Abdul Malik Addarani, Firdaus, Sofyan el-Tsauri, Norman Mulyana, and Whantoe Cah Petir who always support and care about the writer, and all of the writer’s friends who are not mentioned one by one in this papers.
10.Iin Indriani, the writer’s lovely girl who always gives the writer motivation. 11.The cute brother, Muhammad Harits Hidayatullah who always makes the
writer happy.
Jakarta, January 19, 2009
TABLE OF CONTENTS
APPROVEMENT ... ... i
LEGALIZATION ... ... ii
DECLARATION ... ... iii
ABSTRACT ... ... iv
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT... ... v
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... ... vii
CHAPTER IINTRODUCTION ... ... 1
A. Background of the Study ... ... 1
B. Focus of the Study ... ... 3
C. Research Question ... ... 3
D. Objective and Significance of the Research ... ... 3
E. Organization of the Paper ... ... 4
F. Research Methodology ... ... 5
CHAPTER II THE THEORETICAL FRAMEWORKS. ... ... 8
A. Definition of Subjunctive... ... 8
B. Kinds of Subjunctive ... ... 10
C. Mastery. ... ... 21
CHAPTER III PROFILE OF PRIMAGAMA ... ... 23
A. Profile of Primagama ... ... 23
B. Subjunctive Subject ... ... 26
C. Books Used ... ... 26
D. Teachers ... ... 27
F. Evaluation Subject ... ... 29
CHAPTER IV THE MAIN RESEARCH ... ... 30
A. Data Description ... ... 30
B. Data Analysis ... ... 32
1. Present Subjunctive ... ... 32
2. Past ... ... 36
C. DISCUSSION ... ... 37
CHAPTER V CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS ... ... 61
A. Conclusions ... ... 61
B. Suggestions... ... 62
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... ... 63
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Study
Graduation is a main purpose for every student especially who is in the last semester of the final academic year. To graduate, every student has to study hard. Of course, there are some subjects of examination which students must have. Here, the writer focuses on students who are in the third grade of senior high school as they are the main respondents of the writer’s research study. The students are supposed to understand all subjects which become the standardization of middle and final exam such as Math, English and Indonesian Language. However, here, the writer focuses on English as the research study.
participate to make their study better. Essays or questions which every institution places give are almost same as schools give. It is English standardization which always appears in school’s exam such as Concord or Agreement, Tenses, Conditional Sentences, Subjunctive, Modal and Modal Perfect, Reading Comprehension and Vocabulary, Dependent and Independent Clause, and Word Order. Unfortunately, schools have not taught or even do not teach the students about them in detail, but the course places give comprehension more detail and make the students understand.
Therefore, the writer intends to conduct the research on students at one of the course places namely “Primagama”. It is about “How students understand every essay or questions given, especially the writer focuses on understanding about Subjunctive. Subjunctive is one of English subjects which usually appears on essays of the middle and final exam of schools. Actually, not only subjunctive is difficult but also the others are. Subjunctive is a sentence expressing a wish which is opposite with a fact, it is usually signed by “wish, if only, would rather” or expressing a condition which is not true dealing with a fact. It is signed by “as if” and “as though”. For example, I wish she were here.
predicate is were or had been (in simple past or past perfect tense) form. This makes the students wrong in choosing the correct answers. Due to, in this research the writer hopes the students more understand about subjunctive.
B. Focus of the Study
In this study, the writer will analyze the test-results of subjunctive in the forms of present and past subjunctive which are collected from the selected respondents.
C. Research Question
To focus this research, the writer proposes the following questions:
1. Have the third year students of senior high school at Lembaga Pendidikan Primagama” Lubang Buaya in the Academic Year of 2008/2009 mastered the subjunctive?
D. Objective and Significance of the Research
The first objective is to fulfill the requirement for the degree of strata 1 (S1) of the Faculty of Adab and Humanities. Besides, the writer expects readers will get more knowledge about subjunctive and it gives a description about subjunctive based on theoretical frameworks. He also hopes the result of study can show the causes of Primagama students’ problem in understanding subjunctive.
The research might have beneficiaries for all students of English Department to have more knowledge about subjunctive.
E. Organization of the Paper
This paper consists of five chapters: the first is introduction which explains about background of the study, scope of the study, the question research, objective and significance of the research, organization of the paper, and research methodology.
F. Research Methodology
1. Method of the Research
This research is “the Mastery of Subjunctive at the Third Year Students of Senior High School at Lembaga Pendidikan Primagama” which finds in the test instrument about subjunctive. In this study, the writer uses descriptive method to describe an object based on the readably visible fact and the writer applies the field research. Field research involves the collection of primary data or information that is new. This is collected through surveys and questionnaires that are made out specifically for a purpose.
2. Population and Sample
The population that the writer selected is the students of Bimbingan Belajar Primagama Lubang Buaya in the third grade of senior high school in the Academic Year of 2008-2009 and the sample which the writer selected is thirty students only to do the test about subjunctive. The writer conducted the research of subjunctive because subjunctive is Primagama’s syllabus.1 (see page 97).
1
Primagama, Garis-garis Besar Program Pengajaran (GBPP) Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan
3. Unit of Analysis
The unit of analysis of this study is the test-results from the thirty-selected students. The writer took the number of the students because there were thirty students in which for the third grade of senior high school at Bimbingan Belajar Primagama Lubang Buaya in Academic Year of 2008-2009. This grade contains three classes and each class consists of 10 students. Besides, Primagama’s English teachers have important role for the writer’s research to get the data in the class because the writer attended the class directly to know how the teachers teach the students about subjunctive and what the teaching methodology the teachers use.
4. Data Analysis Technique
The writer uses descriptive comparative analysis technique in this research to compare the different structure between the students’ answers (test results) and the written theories. In calculating the test results, the writer uses the following formula:2
P=
N F
x 100%
P = Percentage
F = Frequency of wrong answers N = Total Number of Test
2
5. Data Collection
To find out the data, the write uses test. The writer gives the test which focuses on subjunctive in two forms (present and past subjunctive) to the respondents (the sample of students). It is essay test which consists of 25 items covering Present Subjunctive and Past Subjunctive. The instrument of the research was selected from “Fundamental of English Grammar by Faidlal Rahman Ali, SE. Par, Pustaka Widyatama, 2007” and “www.wikipedia.org/wiki/Subjunctive”, “Suskes SPMB Ringkasan Materi dan Prediksi Soal-soal SPMB by Drs. Paidi Dewabrata, Sudarso, and Ratna Kinawati, SPd, PRIMAGAMA, 1999, “Smart Solution Primagama Bahasa Inggris by PRIMAGAMA, 1999. This is expected that the writer can get representative data relating to the goals of this research. The test-instruments can be seen in (Appendix page. 91).
6. Time and Venue
CHAPTER II
THE THEORETICAL FRAMEWORKS
A. Definition of Subjunctive
There are some explanations from some linguists who explain about subjunctive differently for example in his book “English Grammar-A Function-Based Introduction, Philadelphia T. Givon says, “Subjunctive is a grammatical category that appears in many languages, but is normally ignored in English”.3
a. I’d appreciate it if he didn’t show up. b. We’d prefer it if she went somewhere else.
According to Michael Swan in his book “Practical English Usage” that the subjunctive is the name of a special group of verb-forms (e g I were, she be, he return) which are used in a few cases to talk about events which are not certain to happen - which we hope will happen, or imagine might happen, or want to happen.4
He gives some examples:
If I were rich, I would not work at all.
3
T. Givon,English Grammar A Function-Based Introduction,(Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company, 1993), vol. II, p. 274.
4
J. D Murthy in his book “Brush up Your English Grammar” says,
Subjunctive is a verb which is used to express a wish, hope, desire, intention or resolution in noun clause in the present and improbability in the past.5
www.wikipedia.org/wiki/Subjunctive says in grammar, the
subjunctive mood (sometimes referred to as the conjunctive mood) is a verb mood that exists in many languages. It is typically used in dependent clauses to expresses wishes, commands, emotion, possibility, judgment, necessity, or statements that are contrary to fact at present. The details of subjunctive use vary from language to language. The past subjunctive is used after the verb to wish: I wish he were here or I wished he were there. This use of the subjunctive is sometimes known as the "volitional" subjunctive.6
www.telus.net/linguisticsissues/subjunctive says, subjunctive is a special kind of present tense, using an infinitive that has no –s in the third person singular. It is often used when talking about something that somebody must do.7
I insist (that) your friend leave this house at once.
The subjunctive is a formal construction. It is more commonly used in American English than in British English, and more often in the written form
5
J. D Murthy, Brush up Your English Grammar, (New Delhi: Nice Printing Press, 2000) p. 104.
6
http://www.wikipedia.org/wiki/Subjunctive. Accessed on May, 20, 2008. p.1.
7
than in the spoken form. It was used much more frequently in old English, but many of these forms have now disappeared in modern English.
Faidlal Rahman Ali, SE. Par says in his book “Fundamental of English Grammar” (A practical Guide), Subjunctive is a form of wish which is used to express an event or condition hoped happen, but in fact it does not happen. The pattern of subjunctive is wish, as if, as though, if only, would rather.8
B. Kinds of Subjunctive
There are many explanations of subjunctive which the writer puts in this paper but only the explanation of A. Faidhal Rahman Ali, SE. Par the writer uses because according to explanations which the teachers’ Primagama teach is the same. Therefore, the writer uses this explanatio. He divides subjunctive into two kinds.
1. Present Subjunctive9
It is used to express an event or condition at present or future. a. Present Subjunctive with wish
• I wish (that) she were not late
The fact: She is late
8
Faidlah Rahman Ali, SE, PAR, Fundamental of English Grammar a Practical Guide, (Jakarta: Pustaka Widyatama , 2007) p. 184.
• I wish (that) he came to school now
The fact: He doesn’t come to school now
b. Present Subjunctive with as if/as though
• She acts as if she were rich
The fact: She is not rich
• He behaves as though he knew the answer
The fact: He doesn’t know the answer
c. Present Subjunctive with if only
• If only they were not sick
The fact: They are sick
• If only you invited him
The fact: You don’t invite him
d. Present Subjunctive with would rather
• I would rather he saved his money
The fact: He doesn’t save his money
• I would rather you were serious
The fact: You are not serious
2. Past Subjunctive, it is used to express an event or condition at fast. a. Past Subjunctive with wish
• I wished (that) she had not been late
• I wished (that) he had come to school yesterday
The fact: He didn’t come to school yesterday
a. Past Subjunctive with as if/as though
• She acted as if she had been rich
The fact: She was not rich
• He behaved as though he had known the answer
The fact: He didn’t know the answer
b. Past Subjunctive with if only
• If only they hadn’t been sick
The fact: They were sick
• If only you had invited him
The fact: You didn’t invite him
c. Past Subjunctive with would rather
• I would rather he had saved his money
The fact: He didn’t save his money
• I would rather you had been serious
According to the books “Sukses SPMB Ringkasan Materi dan Prediksi Soal-soal SPMB and Smart Solution Primagama Bahasa Inggris that Subjunctive is a sentence that expresses wish or will which is opposite with fact and is signed by wish, if only would rather, as if and as though.10
It gives the pattern below:11
Present Subjunctive
Subjunctive
Verb II/were
Fact
Do not, does not/is not, am not, are
not
I wish she were here now She is not here now
She wishes she arrived here now She does not arrive here now Past Subjunctive
Subjunctive
Had + V3/had + been
Fact
Did not/was not, were not
I wish she had been here yesterday She was not here yesterday She wishes she had arrived here
yesterday She did not arrive here yesterday
10
Drs. Paidi Dewabrata, Sudarso and Ratna Kinawati, SPd.,Sukses SPMB Ringkasan Materi dan Prediksi Soal-soal SPMB, (Primagama, 1999), p. 7.
11
In addition, the books divide subjunctive into two kinds, they are:
1. Present Subjunctive12
It expresses a wish or condition which is opposite with present fact.
For example:
He wishes he were the President
(Fact: He is not the President)
He acts proudly as if he knew the answers
(Fact: He doesn’t know the answer)
2. Past Subjunctive
It expresses a wish or condition which is opposite with past fact.
For example:
I would rather you hadtold me the news. (Fact: You did not tell me the news)
She stared at me as though she had not known me. (Fact: She knew me)
12Ibid.
According to www.telus.net/linguisticsissues/subjunctive that subjunctive is divided into eight kinds.13
1. That-clause
It is often used with a that-clause, especially in American English, to formally express the idea that something is important or essential.
• I demand that he leave at once.
2. Verbs used with the Subjunctive
Other verbs that are commonly used with the subjunctive are: advise, ask, beg, decide, decree, desire, dictate, insist, intend, move, order, petition, propose, recommend, request, require, resolve, suggest, urge, and vote.
• Tom suggested that his friends stay over for the night. • Sam proposed that Tom telephone his accountant. • She recommended that he go and see a doctor.
• The manager requested that everyone put their requests in writing. • He insisted that she stay until the end of the week.
• The Queen commands that he attend the ceremony.
• He urged that a business manager be hired to help things run more
smoothly.
• I simply requested, politely, that she refrain from smoking in my
house.
• Sam recommended that you join the committee.
• The professor asked that Tim submit his research paper before the end
of the week.
13
3. The verb ‘be’
‘Be’ has special subjunctive forms: I be, you be, she be, they be,etc.
• It is vital that you be truthful about what happened. • He suggested that she be more vocal in the next meeting. • She urged that the matter be resolved in a family court.
• Hadrian decreed that a new temple be built in the honor of Jupiter.
4. Adjectives used with the Subjunctive
Some adjectives can be followed by a subjunctive verb, like anxious, determined, and eager.
• He was determined that they not separate.
• The political campaign is eager that their candidate step out of the
shadows.
• I am anxious that he discuss this with me soon.
Certain adjectives can also be used with the subjunctive and `It`, like
advisable, critical, desirable, essential, fitting, imperative, important, necessary, vital.
• It is imperative that you get home before dark. • It is important that everyone follow the rules.
• It is necessary that everyone be calm in times of danger. • It is essential that you arrive before 5pm.
• It is critical that the prime minister address those sensitive issues. • It was vital that everything be done on time.
5. Nouns used with the Subjunctive
There are also nouns that can be followed by a subjunctive verb, like advice, condition, demand, directive, intention, order, proposal, recommendation, request, suggestion, wish.
• My advice is that the company invest in new equipment.
• She is free to leave, on condition that she commit no further offence. • His deep wish is that his daughter go to university.
6. Less Formal Usage
There are several alternatives to the very formal standard subjunctive: Should
This construction is more common than the subjunctive in British English:
• Tom suggested that his friends should stay overnight. • She recommended that he should go and see his doctor.
The Indicative
This construction is also used sometimes in British English, but is rare in American English:
• She has demanded that the machinery undergoes vigorous tests
to ensure high quality.
For + Infinitive
• It is essential for everyone to be informed of the new
regulations. No Tense Change
In colloquial English, it is possible to not make a tense change:
• She demanded that he left.
• She felt that it was necessary that she wrote a thank you letter
to them.
7. Fixed Expressions using the Subjunctive
…, as it were (in a way, so to speak)
Be that is it may... (Whether that is true or not…)
Come what may… (Whatever happens…)
Far be it from me to
disagree/criticize (To appear less hostile when disagreeing) God bless you.
God save the Queen!
Heaven help us! (An exclamation of despair)
Heaven forbid! (An exclamation that you hope something
won’t happen)
If need be... (If it is necessary)
Long live the bride and groom!
…, so be it. (We can’t do anything to change it)
Perish the thought! (A suggestion or possibility is unpleasant or
ridiculous)
8. Were-Subjunctive
In hypothetical sentences, were is usually used instead of was:
• If I were you, I’d learn how to drive. • I wish it were Friday.
It is important to note that was can also be used (although still considered incorrect by some grammarians), and is, in fact, more common in informal English.
• Sometimes I wish I was/were taller.
J. D Murthy in his book “Brush up Your English” divides subjunctive into two kinds—Presents Subjunctive and Past Subjunctive. Here they are:
Form of the Subjunctive Mood14
Present Subjunctive Past Subjunctive
The Verb Be Other Verbs The Verb Be Other verbs
I be I like We be We like You be You like He be He likes They be They like
I were I liked We were We liked You were You liked He were He liked They were They liked
14
1. The Present Subjunctive
(a). It is used in traditional phrases expressing a wish of hope.
• Long live the queen!
• May God save the country! • May heaven help you!
(b). In noun clauses expressing desire, intention and resolution.
• • •
• It is suggested that fly over bridge be built across the railway tract. •
• •
• We recommended that the manager be dismissed from service. •
• •
• We proposed that a committee be appointed to look into the matter.
2. The Past Subjunctive
(a). After the verb ‘wish’
• She wishes she were a beauty queen. • We wish we were in Delhi.
• I wish I stayed at home.
(b). It is used after if to express improbability or unreality in the present.
• If we went there, we could see her. • If I knew English, I could go to America.
• If we had money, we could live in a large house.
(c). After ‘as if and as though’
(d). After the phrase it is time +subject+past tense to indicate that it is already late.
• It is time we went there • It is time I wrote to her • It is time they stopped work
(e). After the phrase would rather+subject to indicate preference.
• I would rather you applied for the post
• I would rather you discontinued your parents. • She would rather he lived with his parents.
C. Mastery
Mastery is a noun borrowed from old French ‘maistrie’ from ‘maistre’15. According to Merriam, mastery is:
1. a. The authority of a master: Dominion b. The upper hand in a contest of competition 2. a. Possession or display of great skill or technique
b. Skill or knowledge that makes one master of a subject16 Meanwhile Noah Webster defines mastery as:
“1. Mastery; Dominion; power of government or commanding 2. Superiority or victory in competition or war; the upper hand
15
Robert K. Barnhart, The Barnhart Concise Dictionary of Etymology, USA: HW. Wilson Company, 1995, p. 562.
16
3. A struggle for advantage 4. A masterpiece
5. Mastery ability; expert knowledge; eminent skill or power”17
From some definitions above, the writer uses definition written by Merriam in 2.b and Noah Webster in point 5. The writer concludes that mastery means complete knowledge or great ability in a subject, in this research the subject is subjunctive.
17
CHAPTER III
PROFILE OF PRIMAGAMA
A. Profile of Primagama18
Education is a pillar of human resources development which is organized intensively and professionally. By using the concept of students’ potency development, Primagama is established to help students in understanding subjects that schools give. Therefore, students have optimal achievement and can go to higher education level.
As the former of Primagama, Purdi E. Chandra is sure that Primagama which was established on March 10, 1982 can do great efforts and help the government for educational affairs. The existence of Primagama is more legal because the implementation of constitution number 2, 1989 about National Educational System. One of the constitution contents is the responsibility of educational implementation; it is basically not only burned by the government but also families and society. Constitution of National Educational System (Sisdiknas) 2003 version 26 chapter 1 “Informal education is applied for every body who needs educational service having the function as the substitute, addition of formal education for supporting education forever.
18
To give the legal law for Primagama, it was established Primagama foundation with the notaries Daliso Rudianto, SH. Number 123, 1985. It is firmly given license by Department of social and education (Dekdikbud) SK Number 054/I 13/MS/KPTS/1999. Primagama, therefore, grows year to year significantly and becomes the credible educational institution. Besides, Primagama is the holder of copyright for Primagama as the educational institution based on constitution number 6, 1982 about the copyright of constitution number 7, 1987 of change for the constitution number 6, 1982 about the copyright on July, 3, 1995 and is on the registration at directorate for copyright, paten, and mark with the number of registration 014127.
Nowadays Primagama has 328 branches. The branches spread in 157 cities and 29 provinces (data per March 10, 2005). The exploration of these service regions is purposed to serve students’ necessity for the quality of educational service level can suitable with the regions where they live. From the certain data, Primagama grows fast because of:
1. Primagama brand image as the educational institution. 2. Organizers’ management professionalism.
Primagama’s vision and mission, they are:
1. Vision
To be the best, the biggest and the well-known institution of course place in Indonesia.
2. Mission
a. To be the best educational institution nationally at ranking (giving the best services and interest to organizations, owners, and consumers).
b. To be a place where every employee can improve prosperity together and together to improve prosperity (giving the service and interest professionally).
c. To be a company that can create good and credible partners (giving the best services and interest to organizations and partners).
d. To be a place for every one who wants to be professional, creative and improve the skills (giving the best services and interest to consumers and owners).
B. The Subjunctive Subject
Subjunctive is a part of English subjects which is taught by teachers of Primagama to the students of Primagama who are in the third grade of Senior High School. Subjunctive is part of Primagama curriculum which usually appears on middle or final exam. The teachers teach Subjunctive to the students at first semester but they review at the next semester in order that students understand more easily about subjunctive.
The English teachers of Primagama, therefore, often give some essays or questions dealing with the subjects which are taught as an evaluation, one of them is subjunctive. This has a purpose to give more understanding to the students. This evaluation usually uses a method by giving the test of questions maximally 50 questions and minimally 25 questions about English includes subjunctive.
C. Books Used
D. The Teachers
Primagama has some English teachers which graduated from reputable universities—Indonesian University, Gajah Mada University, State Jakarta University, State Islamic University Jakarta, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia Bandung and The State Institute of Islamic Studies Yogyakarta. The teachers who teach English for the third grade students are Mr. Slamet Nursalim, and Miss Dian Apediani SPd. Their function is helping the writer’s research more easily because the writer can attend and know how the teaching runs. Here are their profiles:
1. Name : Slamet Nursalim
Place/date of birth : Purworejo/October 24, 1965 Home Address : Jln. BCS Gang N. No.2 Rt.03/05
Kelurahan Pegangsaan Dua Kelapa Gading Jakarta Utara Graduation : IAIN Jogyakarta
2. Name : Dian Apediani
Place/date of birth : Garut/September 29, 1984
Home Address : Jln. Kramat No. 79 Lubang Buaya Jakarta Timur (13810)
Graduation : Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia Bandung Majoring in English Literature
Work Experience : 2006-now Translator
2007 Pusaka Senior High School 2007 Bunda Elementary School 2007-now Private English Teacher 2007-now Primagama
E. Methodology of Teaching
As the writer told above that the methodology which Primagama teachers use is giving explanation and test by samples of questions, review and problem solving to students about the subjects. Here every student is hoped to understand and learn it more comprehensively and choose correct answers when they have school’s exam.
F. Evaluation Subject
To know whether the students understand or not, the writer attended the class and saw the teachers review and give them some questions of the subjects taught, and then after the students finish the questions, the teachers discuss them together in the class. Here, the teachers know the students “understand or not”. This evaluation is so effective that the students more understand quickly.
CHAPTER IV
THE RESEARCH FINDING
A. Data Descriptions
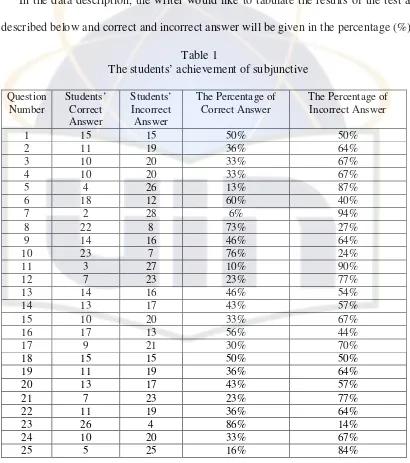
In the data description, the writer would like to tabulate the results of the test as described below and correct and incorrect answer will be given in the percentage (%).
Table 1
The students’ achievement of subjunctive
Question
The Percentage of Correct Answer
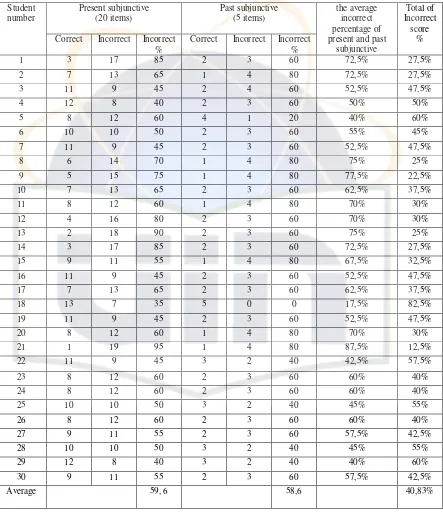
Table 2
The Students’ Incorrect Score Achievement
Present subjunctive
Correct Incorrect Incorrect
%
Correct Incorrect Incorrect
%
the average incorrect percentage of present and past
B. Data Analysis
Here below are the items of Present and Past Subjunctive which are analyzed.19
a. Present Subjunctive (20 items)
1. “You look tired. Why don’t you take a rest?” “I wish______; I still have to finish this report”. A. I would be able
B. I can
C. I will be able D. I could
E. I had been able
2. He orders the people as if he were the owner of the restaurant. From the above statement, we may conclude that______. A. he was worked hard to own the restaurant
B. he has been the owner of the restaurant C. he is proud of his restaurant
D. he is just an ordinary employee E. he is a successful businessman 3. “Is Evi still sick?”
“Yes, I wish she ____ here now to help me type the report”. A. is
B. will be C. were D. had been E. would be
4. My brother isn’t old enough to drive, but he wishes he ____ now.” A. had been
B. will be C. is D. were E. are
19
Drs. H. Paidi Dewa Brata, M.Pd. and Sudarso, S.Pd, Panduan Belajar Kelas 12 SMA IPA/IPS
5. She is always busy with her work. I wish I ______her more often. A. visit
B. would visit C. am visiting D. have visited E. could visit
6. Hamid has won a medal for swimming. I wish I _____as good as he is.
7. Mother said to our guest, “I wish you ___leave me now.” A. didn’t have to
B. haven’t got to C. won’t have to D. aren’t having to E. weren’t having to
8. “I am sorry I don’t know the answer but I really wish I____. A. know
B. knew C. have known D. will know E. had known
9. He wishes it ____a holiday today. A. be
B. is C. was D. were E. had been
10.His daughter wished he ____ her bike. A. buy
11.He wishes he ___ her but he can’t. A. can help
B. could help C. doesn’t help D. hasn’t help
E. could have helped
12.He acts as if he ____ English properly. A. know
B. knew C. knows D. had known E. were knowing
13.He treats us as if we were all foolish. This sentence means _____
A. he doesn’t think we are foolish B. we don’t treat him to be foolish C. we aren’t sure that he is foolish D. we are really foolish
E. we aren’t all foolish
14.The gentleman acts so proudly as if he were a millionaire. In fact the gentleman _____a millionaire.
A. were not B. was not C. is not D. was E. is
15.“Let’s go swimming!”
“I wish I ___we have a test tomorrow I still have to study”. A. am able
16.She went to the blackboard as if she knew how to solve the problem. The underlined word means ____
A. She actually can’t solve the problem
B. She ought to know how to solve the problem C. She definitely knew how to solve the problem D. She should know how to solve the problem E. She succeeded how to solve the problem
17.I am planning to go to a party tonight, but it is raining very hard now. I wish ___ raining now.
A. it stops B. it has stopped C. it will stop D. it had stopped E. it would stop
18.Lita : Hi, why do you look so sad? Something wrong? Adi : Yeah, I wish I had time to have a date with Amel. A. Lita promises to meet Amel
B. Both Lita and Adi will visit Amel C. Adi loses his chance to meet Amel D. Adi and Lita have no time for a date E. Neither Lita nor Adi has a date with Amel 19.Adi : I wish I had a certificate of deposit.
Amel : Why?
Adi : The interest rate is high now.
From the dialogue we can conclude that Adi _____ A. has a certificate of deposit
B. doesn’t have money kept in a bank C. enjoys the high interest paid by the bank D. is going to deposit his money in the bank E. has no interest to open an account in a bank
20.I am sure he is not the man in charge of the sales department. But now, he ____
A. acts as if he is the sales manager B. is acting as if he would be the sales
C. would have acted as if he had been the sales manager D. would act as if he was the sales manager
b. Past Subjunctive (5 items)
21.“Did you get compensation for your car?” “No, I didn’t. If only______.”
A. I would insure it B. I had insured it C. I will insure it D. I wouldn’t insure it E. I should insure it
22.“If only his son had studied harder.” It means ____.
A. his son didn’t study harder B. his son had studied harder C. his son has studied harder D. his son will not study harder E. his son never studies harder
23.He would rather they ____ their work before they got out. A. finish
B. finished C. can finished D. had finished E. were finishing
24.The girl behaved as though she ____ mad. A. were going
B. was going C. had gone D. has gone E. will go
25.I wish you ____ to stay at home because I am sure you would have enjoyed the concert very much.
C. Discussion
The writer analyzes only the questions (table 1) whose the percentage students’ incorrect answers are 60% and above to find out the problems found by students in mastery of subjunctive. Then, the data analyzed are fifteen questions namely question 2 (64%), 3 (67%), 4 (67%), 5, (87%), 7 (94%), 9 (64%), 11 (90%), 12 (77%), 15 (67%), 17 (70%), 19 (64%), 21 (77%), 22 (64%), 24 (67%) and 25 (84%).
The collected data that will be analyzed are as follows: 1. Question 2 (Present Subjunctive)
• The purposes:
- to measure the students’ ability of present subjunctive - to find out the problems faced by the students
• Indicators:
- the students know the pattern of present subjunctive
- the students know the difference between present and past subjunctive
- the students know the fact sentence of present subjunctive
• The item:
“He orders the people as if he were the owner of the restaurant”
From the above statement, we may conclude that______. A. he was worked hard to own the restaurant
D. he is just an ordinary employee E. he is a successful businessman
From table 1 above the writer finds 19 students cannot answer the question correctly. Here the analysis:
The right answer is option D (he is just an ordinary employee). From the data has been gathered, this is what exactly happens; 3 students no 6, 18, 27 (10%) choose option A (he was worked hard to own the restaurant), 14 students no 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 9, 12, 13, 16, 20, 21, 24, 25, 28 (46%) choose option (he has been the owner of the restaurant), one student no 15 (3%) chooses option C (he is proud of his the restaurant), 11 students no 4, 7, 10, 11, 17, 19, 22, 23, 26, 29, 30 (36%) choose option D (he is just an ordinary employee),
2. Question 3 (Present Subjunctive)
• The purposes:
- to measure the students’ ability of present subjunctive - to find out the problems faced by the students
• Indicators:
- the students know the pattern of present subjunctive
- the students know the difference between present and past subjunctive
- the students know the fact sentence of present subjunctive
• The item:
“Is Evi still sick?”
“Yes, I wish she ____ here now to help me type the report”. A. is
B. will be C. were D. had been E. would be
From table 1 above the writer finds 20 students cannot answer the question correctly. Here the analysis:
15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 22 (33%) choose option C (were). They choose it correctly because the statement of wish in present tense, based on the pattern of present subjunctive whatever the subject, its predicate is were because in the fact Evi is not here now to help you type the report, one student no 27 (3%) chooses had been. Here, both answers between were and had been are subjunctive but had been is used for past subjunctive. The last, 5 students no 24, 25, 26, 28 (16%) choose would be.
3. Question 4 (Past Subjunctive)
• The purposes:
- to measure the students’ ability of past subjunctive - to find out the problems faced by the students
• Indicators:
- the students know the pattern of past subjunctive
- the students know the difference between present and past subjunctive
- the students know the fact sentence of past subjunctive
• The item:
“Did you get compensation for your car?” “No, I didn’t. If only______.”
From table 1 above the writer finds 20 students can not answer the question correctly. Here the analysis:
The right answer is option B (I had insured it). From the data has been gathered, this is what exactly happens; 10 students no 2, 3, 4 (33%) choose option A (I would insure it), 10 students no 1, 5, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17, 18, 28, 29 choose B (I had insured it). They choose it correctly because the statement above is past tense which is signed by did. It means that the subjunctive is past perfect (had+been/had+verb III) and in the fact you didn’t insure it, 1 student no 11 (3%) chooses option C (I will insure it), 9 students no 6, 9 19, 20, 23, 24, 25, 27, 30 (30%) choose option D (I wouldn’t insure it).The last, no one choose option E (I should insure it).
4. Question 5 (Present Subjunctive)
• The purposes:
- to measure the students’ ability of present subjunctive - to find out the problems faced by the students
• Indicators:
- the students know the pattern of present subjunctive
- the students know the difference between present and past subjunctive
• The item:
My brother isn’t old enough to drive, but he wishes he ____ now.” A. had been
B. will be C. is D. were E. are
From table 1 above the writer finds 26 students cannot answer the question correctly. Here the analysis:
The right answer is option D (were). From the data has been gathered, this is what exactly happens; 9 students no 1, 12, 16, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 24 (30%) choose option A (had been), 7 students 5, 10, 11, 23, 25, 29, 30 (23%) choose option B (will be), 10 students no 2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9, 13, 14, 15, 28 (33%) choose is. This is the common error because they might think that the subject
he has concord with is. It same as the item number 3 above, 4 students no 4, 17, 26, 27 (13%) choose option D (were), it is present subjunctive with were,
5. Question 7 (Present Subjunctive)
• The purposes:
- to measure the students’ ability of present subjunctive - to find out the problems faced by the students
• Indicators:
- the students know the pattern of present subjunctive
- the students know the difference between present and past subjunctive
- the students know the fact sentence of present subjunctive
• The item:
Hamid has won a medal for swimming. I wish I _____as good as he is.
A. were B. should be C. will be D. am E. can be
From table 1 above the writer finds 28 students can not answer the question correctly. Here the analysis:
should appear at conditional sentence type I or simple future tense, one student no 20 chooses option D (am). He chooses it because she might think that the predicate or concord of I is am. It is true in simple present but in subjunctive whatever the subject, the predicate is were or had been. And the last, there are 17 students no 1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 14, 23, 29, 30 (56%) choose can be. This choice has same meaning as will be. Hoping something happens, it indicates to conditional sentence not subjunctive.
6. Question 9 (Present Subjunctive)
• The purposes:
- to measure the students’ ability of present subjunctive - to find out the problems faced by the students
• Indicators:
- the students know the pattern of present subjunctive
- the students know the difference between present and past subjunctive
- the students know the fact sentence of present subjunctive
• The item:
“I am sorry I don’t know the answer but I really wish I____. A. know
From table 1 above the writer finds 16 students cannot answer the question correctly. Here the analysis:
The right answer is option B (knew). From the data has been gathered, this is what exactly happens. There are 6 students no 1, 8, 13, 14, 17, 25 (20%) choose option A (know), 14 students no 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 15, 18, 19, 20, 22 (46%) choose B (knew). It is the true answer because the statement above is present subjunctive with wish and it means in the fact I don’t know the answer and I hope to know the answer, 1 student no 26 (3%) chooses option C (have known), 3 students no 6, 21, 23 (10%) choose option D (will know). This answer should appear in conditional sentence or simple future. The last, there are 6 students no 2, 16, 24, 27, 28, 29 (20%) choose option E (had known). The answer of were and had known are possible answer but the item above is present subjunctive, the verb after wish is verb II (past tense) but the “had known” is past subjunctive.
7. Question 11 (Present Subjunctive)
• The purposes:
- to measure the students’ ability of present subjunctive - to find out the problems faced by the students
• Indicators:
- the students know the difference between present and past subjunctive
- the students know the fact sentence of present subjunctive
• The item:
He wishes it ____a holiday today. A. be
B. is C. was D. were E. had been
From table 1 above the writer finds 27 students cannot answer the question correctly. Here the analysis:
The right answer is option D (were). From the data has been gathered, this is what exactly happens. There are 2 students no 13, 21 (6%) choose option A (be). It is possible answer also if the writer sees the explanation of J. D Murthy in his book Brush up Your English and the subjunctive from www.telus.net.linguisticsissues/subjunctive, but as the writer explains that the explanation which he takes is from Faidlal Rahman Ali, SE. Par in his book “Fundamental of English Grammar(A practical Guide)”, 4 students no 2, 8, 16, 20 (13%) choose option B (is). They choose it because they might think that the concord of the subject it is is, 11 students no 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 15, 22, 25 (36%) choose option C (was). It is absolutely incorrect because was is not concord to the time signal of present tense today but it should be concord to
option D (were). This is the true answer because the statement above is present subjunctive with wish; in the fact he knows that it isn’t a holiday today. And the last, there are 10 students no 1, 12, 14, 17, 18, 19, 24, 26, 27, 30 (33%) choose option E (had been). Both “had been” and “were” are subjunctive but the item above is present subjunctive, and “had been” is past subjunctive.
8. Question 12 (Past Subjunctive)
• The purposes:
- to measure the students’ ability of past subjunctive - to find out the problems faced by the students
• Indicators:
- the students know the pattern of past subjunctive
- the students know the difference between present and past subjunctive
- the students know the fact sentence of past subjunctive
• The item:
His daughter wished he ____ her bike yesterday. A. buy
From table 1 above the writer finds 23 students cannot answer the question correctly. Here the analysis:
The right answer is option D (had bought). From the data has been gathered, this is what exactly happens. No student chooses option A (buy), 7 students no 19, 20, 22, 24, 26, 27, 30 (23%) choose option B (buys). They choose it because they might think that the concord of he is verb I (s-es) in present tense, 8 students no 11, 15, 16, 21, 23, 25, 28, 29 (26%) choose option C (bought), 7 students no 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 10, 18 (23%) choose option D (had bought). It is the true answer because the statement above is past tense with wished in which time signal is yesterday, therefore, the subjunctive is past perfect. It means in fact that his daughter didn’t get the bike because he didn’t buy for her. And the last, there are 8 students (26%) choose option E (will have bought).
9. Question 15 (Past Subjunctive)
• The purposes:
- to measure the students’ ability of past subjunctive - to find out the problems faced by the students
• Indicators:
- the students know the pattern of past subjunctive
- the students know the fact sentence of past subjunctive
• The item:
The girl behaved as though she ____ mad last night. A. were going
B. was going C. had gone D. has gone E. will go
From table 1 above the writer finds 20 students cannot answer the question correctly. Here the analysis:
10.Question 17 (Present Subjunctive)
• The purposes:
- to measure the students’ ability of present subjunctive - to find out the problems faced by the students
• Indicators:
- the students know the pattern of present subjunctive
- the students know the difference between present and past subjunctive
- the students know the fact sentence of present subjunctive
• The item:
He treats us as if we were all foolish. This sentence means _____
A. he doesn’t think we are foolish B. we don’t treat him to be foolish C. we aren’t sure that he is foolish D. we are really foolish
E. we aren’t all foolish
From table 1 above the writer finds 21 students cannot answer the question correctly. Here the analysis:
11, 12, 13, 14, 19, 24, 26, 27, 30 (53%) choose option D (we are really foolish) and 9 students no 16, 17, 18, 20, 22, 23, 25, 28, 29 (30%) choose option E (we aren’t all foolish).
11.Question 19 (Present Subjunctive)
• The purposes:
- to measure the students’ ability of present subjunctive - to find out the problems faced by the students
• Indicators:
- the students know the pattern of present subjunctive
- the students know the difference between present and past subjunctive
- the students know the fact sentence of present subjunctive
• The item:
“Let’s go swimming!”
“I wish I ___ but we have a test tomorrow I still have to study”. A. am able
B. could be C. could D. will be able E. be able
From table 1 above the writer finds 19 students cannot answer the question correctly. Here the analysis:
students no 1, 3, 5, 10, 12, 13, 14, 17, 18, 19, 24, 26, 27, 30 (46%) choose option B (could be), 11 students no 4, 6, 7, 9, 11, 15, 16, 20, 22, 23, 25, 28, 29 (36%) choose option C (could). This is the true answer because the item above is present subjunctive with wish, the subjunctive is verb 2 (past tense), 2 student no 2 and 8 (6%) choose option D (will be able), and 1 student no 21 (3%) chooses be able.
12.Question 21 (Present Subjunctive)
• The purposes:
- to measure the students’ ability of present subjunctive - to find out the problems faced by the students
• Indicators:
- the students know the pattern of present subjunctive
- the students know the difference between present and past subjunctive
- the students know the fact sentence of present subjunctive
• The item:
She went to the blackboard as if she knew how to solve the problem. The underlined word means ____
A. She actually can’t solve the problem
From table 1 above the writer finds 23 students cannot answer the question correctly. Here the analysis:
13.Question 22 (Present Subjunctive)
• The purposes:
- to measure the students’ ability of present subjunctive - to find out the problems faced by the students
• Indicators:
- the students know the pattern of present subjunctive
- the students know the difference between present and past subjunctive
- the students know the fact sentence of present subjunctive
• The item:
I am planning to go to a party tonight, but it is raining very hard now. I wish ___ raining now.
A. it stops B. it has stopped C. it will stop D. it had stopped E. it stopped
From table 1 above the writer finds 19 students can not answer the question correctly. Here the analysis:
12 students no 1, 7, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17, 19, 23, 26, 30 (40%) choose option C (it will stop), it should appear in conditional type 1, 1 student (3%) chooses option D (it had stopped), it is possible answer also but it is should be in past subjunctive, for example, “I was planning to go party last night, but it was raining hard yesterday. I wish it had stopped raining yesterday”. 11 students no 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 18, 24, 27 choose option E (it stopped), it is the true answer because the item above is present subjunctive with wish, the subjunctive is verb II (past tense).
14.Question 24 (Present Subjunctive)
• The purposes:
- to measure the students’ ability of present subjunctive - to find out the problems faced by the students
• Indicators:
- the students know the pattern of present subjunctive
- the students know the difference between present and past subjunctive
- the students know the fact sentence of present subjunctive
• The item:
Adi : I wish I had a certificate of deposit. Amel : Why?
From the dialogue we can conclude that Adi _____ A. has a certificate of deposit
B. doesn’t have money kept in a bank C. enjoys the high interest paid by the bank D. is going to deposit his money in the bank E. has no interest to open an account in a bank
From table 1 above the writer finds 20 students cannot answer the question correctly. Here the analysis:
15.Question 25 (Present Subjunctive)
• The purposes:
- to measure the students’ ability of present subjunctive - to find out the problems faced by the students
• Indicators:
- the students know the pattern of present subjunctive
- the students know the difference between present and past subjunctive
- the students know the fact sentence of present subjunctive
• The item
I am sure he is not the man in charge of the sales department. But now, he ____
A. acts as if he is the sales manager B. is acting as if he would be the sales
C. would have acted as if he had been the sales manager D. would act as if he was the sales manager
E. acts as if he were the sales manager
From table 1 above the writer finds 25 students cannot answer the question correctly. Here the analysis:
B (is acting as if he would be the sales), no student chooses option C (would have acted as if he had been the sales manager), 5 students no 1, 11, 15, 20, 23 (16%) choose D (would act as if he was the sales manager)and 5 students no 16, 18, 19, 28, 29 (16%) choose option E (acts as if he were the sales manager). Only five students (16%) choose the correct answer, the answer is
acts as if he were the sales manager. The item above is present subjunctive with as if, which is questioned is the fact of the item.
Those problems above arise because the students have poor knowledge of the pattern of present and past subjunctive. They still use Concord or Agreement, like is or was collocates with she, he and it, but in Subjunctive whatever pronoun (I, you, they, we, she, he, it) collocate with were or had
been and another cause is teaching methodology such as problem solving, review and explanation.
The measurement used as follows:20
Incorrect Score Category
0 – 25 Very Poor
26 – 50 Poor
51 – 75 Enough
75 – 100 Good
From the data description, table 2, the writer can interpret the average score and categorize into measurement above. The average score of the students can be accounted by using average formulation:21
A =
N S
A = Average Score
S = Total Score
N = Number of student
After processing the data the writer accounts the average of score as follows:
The average of score of students’ achievement test is . According to the measurement above, the writer categorizes that the students’ mastery of subjunctive is poor. Based on the measurement, the score around 26 – 50 is categorized as poor. It
20
Drs. Riduwan, M.B.A, Metode dan Tkhnik Menyusun Tesis, (Bandung: Alfabeta, 2004), p.130.
21
Aryo Dewantara, S.Si, Kumpulan Rumus Lengkap Kelas X, XI dan XII SMA-Rumus Kantong Matematika SMA, (Jakarta: Pustaka Widyatama, 2008,) p. 79.
CHAPTER IV
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
A. Conclusions
The result of the research can be concluded that most of students at the third year students of Senior High School at Lembaga Pendidikan Primagama Lubang Buaya have poor ability in mastering subjunctive and there are a number of problems found by the students in mastering subjunctive, such as the use of “to be” in present and past subjunctive, the use of incorrect pattern of subjunctive between past tense form for present subjunctive and past perfect tense for past subjunctive. Besides, there some causes of the problems which make the students poor in Subjunctive, such as the influence of common grammar like tenses, the teaching methodology used by the teacher, and the lack of explanation about subjunctive more detail.
B. Suggestions
library to support the students’ ability of English Grammar especially subjunctive, to provide any different books containing subjunctive from any different publishers, to provide time for problem solving for the students who don’t understand any English subjects especially subjunctive. Besides, the English teachers are suggested to improve the effectiveness of teaching methodology by problem solving, and review, to improve learning process in teaching subjunctive by explaining the difference between patterns of subjunctive and other English subjects clearly. And for the learners to distinguish the pattern of present and past subjunctive, to know the fact sentence of the present and past subjunctive either in negative or positive sentence.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Anonymous, Garis-garis Besar Program Pengajaran (GBPP) Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan PendidikanKTSP 2006, Yogyakarta: Primagama, 2008-2009.
Barnhart, Robert K. The Barnhart Concise Dictionary of Etymology. USA: HW. Wilson Company, 1995.
Dewabrata, Paidi. Smart Solution Primagama Bahasa Inggris, Yogyakarta: Primagama, 1999.
Dewabrata, Paidi and Sudarso. Panduan Belajar 12 SMA IPA/IPS, Yogyakarta: Primagama, 2008.
Dewabrata, Paidi, Sudarso and Kinawati Ratna. Sukses SPMB Ringkasan Materi dan Prediksi Soal-soal SPMB. Jogya: Primagama, 1999.
Dewantara, Aryo. Kumpulan Rumus Lengkap Kelas X, XI dan XII SMA-Rumus Kantong Matematika SMA, Jakarta: Pustaka Widyatama, 2008.
Farkhan, Muhammad. Penulisan Karya Ilmiah. Jakarta: Cella, 2006.
Givon, T. English Grammar A Function-Based Introduction. Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company, 1993.
Murthy, J. D. Brush up Your English Grammar. New Delhi: Nice Printing Publishing, 2000.
Riduwan. Metode dan Teknik Menyusun Tesis, Bandung: Alfabeta, 2004.
Swan, Michael. Practical English Usage. London: Oxford University Press, 1980.
Webster, Merriam. Merriam Webster’s Collegiate Dictionary. USA: An Encyclopedia Company, 2003.
Webster, Noah. Webster’s New Twentieth Century Dictionary of the English Language. USA: William Collins and World Publishing Co., Inc, 1979.
http://www. eprints.ums.ac.id. 2009.
http://www.primagama.com. 2008.
http://www.telus.net/linguisticsissues/subjunctive. 2008.
THE TABULATION OF TEST INSTRUMENT
From the questions, the writer tabulates the data as follows:
1. “You look tired. Why don’t you take a rest?”
“I wish______; I still have to finish this report”.
2. He orders the people as if he were the owner of the restaurant. From the above statement, we may conclude that______.
3. “Is Evi still sick?”
“Yes, I wish she ____ here now to help me type the report”.
4. “Did you get compensation for your car?” “No, I didn’t. If only______.”
Student
A. I would insure
it I should insure
6. She is always busy with her work. I wish I ______her more often.