Informasi Dokumen
- Penulis:
- Rachma Safira Nur Azizah
- Pengajar:
- Budi Setyono, Dr., M.A.
- Sugeng Ariyanto, Drs., M.A.
- Sekolah: Jember University
- Mata Pelajaran: English Language Education
- Topik: The Effect of Using PLAN Strategy on Senior High School Students’ Narrative Text Reading Comprehension Achievement
- Tipe: Thesis
- Tahun: 2016
- Kota: Jember
Ringkasan Dokumen
I. Introduction
This chapter sets the stage for the research by outlining the background, problem statement, objectives, and significance of the study. The background section highlights the importance of reading comprehension in English language learning, particularly within the Indonesian 2013 curriculum and the challenges faced by students, such as unfamiliar vocabulary in authentic materials. It introduces the PLAN (Predict, Locate, Add, Note) strategy as a potential solution to improve reading comprehension, citing its effectiveness in previous research and its suitability for narrative texts. The problem statement clearly articulates the research question investigating the significant effect of the PLAN strategy on students' narrative text reading comprehension achievement. The objectives section states the aim of determining the existence of this effect, while the significance section details the expected benefits for English teachers, students at SMAN 1 Jombang, and future researchers.
1.1 The Background of the Research
This section emphasizes the crucial role of reading comprehension in English language acquisition, aligning with the Indonesian 2013 curriculum's emphasis on reading comprehension in the National Examination. It identifies the challenges students face, specifically the difficulty with unfamiliar vocabulary in authentic materials. The section introduces the PLAN strategy as a potential solution, referencing its effectiveness in previous studies and its suitability for improving narrative text comprehension. This contextualization establishes the research's importance in addressing a practical issue in English language education within a specific Indonesian context.
1.2 The Problem of the Research
This concise section directly states the core research question: Does the PLAN strategy significantly impact senior high school students' narrative text reading comprehension achievement at SMAN 1 Jombang? This clearly defined question forms the focal point of the research, guiding the methodology and analysis.
1.3 The Objective of the Research
The objective reiterates the research question, focusing on determining the significant effect of the PLAN strategy on students' narrative text comprehension at SMAN 1 Jombang. This provides a clear and focused statement of the research's goal.
1.4 The Significance of the Research
This section elaborates on the practical implications of the research findings for different stakeholders. It highlights the potential benefits for English teachers in adapting the PLAN strategy for improved instruction, for students at SMAN 1 Jombang in enhancing their reading comprehension skills and motivation, and for future researchers in exploring variations of the PLAN strategy or expanding its application in different contexts. The section underlines the broader educational significance of the study.
II. Review of Related Literature
This chapter presents a comprehensive overview of existing theories and research relevant to the study. It delves into the concept of reading comprehension, exploring different levels of comprehension (literal and inferential) and their significance in understanding narrative texts. The chapter defines reading comprehension achievement and the aspects of reading skills assessed (finding general and specific information). It then provides a detailed explanation of narrative texts, including their generic structure and different types. A significant portion is dedicated to the PLAN strategy, explaining its four steps (Predict, Locate, Add, Note), its procedure in teaching reading, advantages, disadvantages, and its impact on reading comprehension based on previous studies. Finally, the chapter concludes by stating the research hypothesis.
2.1 Reading Comprehension
This section defines reading comprehension, drawing on various scholarly sources to present a nuanced understanding of the process. It highlights the active nature of comprehension, emphasizing the reader's interaction with the text and the integration of prior knowledge. The discussion emphasizes the importance of both decoding skills and meaning-making to achieve true comprehension. This lays the groundwork for understanding the complexity of the skill being evaluated in the research.
2.2 Reading Comprehension Level (a. Literal Comprehension Level; b. Inferential Comprehension Level)
This section differentiates between literal and inferential comprehension levels. Literal comprehension involves understanding explicitly stated information, while inferential comprehension requires drawing inferences and understanding implicit meaning. It explains how these levels relate to finding general and specific information in a text, respectively. This theoretical framework is crucial for interpreting the results of the reading comprehension tests used in the study, as they assess both literal and inferential understanding.
2.3 Reading Comprehension Achievement
This section defines reading comprehension achievement in the context of the research, emphasizing its assessment through tests focusing on both literal and inferential comprehension. It explains how the chosen assessment aligns with established methods for evaluating reading comprehension skills. This clarification ensures the validity and reliability of the method used to measure the dependent variable.
2.4 The Aspects of Reading Skills (a. Finding the General Information; b. Finding the Specific Information)
This section clarifies the specific reading skills assessed in the study: identifying general and specific information. It defines each skill and explains how they are measured within the context of narrative text comprehension. This section ensures clarity regarding the targeted aspects of reading comprehension, enhancing the study's methodological rigor.
2.5 Type of Text (a. Nonfiction Text; b. Fiction Text)
This section distinguishes between fiction and nonfiction texts, providing a broad overview of the characteristics of each type and their relevant subtypes. It then clarifies the focus of the study on narrative texts as a type of fiction. This section establishes the genre-specific context of the research, highlighting its relevance within the field of literary studies and English language teaching.
2.6 Narrative Text
This section provides a detailed explanation of narrative texts, including their generic structure (orientation, complication, resolution) and various subtypes. It highlights the significance of narrative texts in educational settings and their suitability for developing various language skills. This focused discussion ensures a clear understanding of the text type used in the study.
2.7 The Concept of Predict Locate Add Note (PLAN) Strategy (a. Predict; b. Locate; c. Add; d. Note)
This section gives a comprehensive overview of the PLAN strategy, detailing each of its four steps. It explains how each step contributes to the overall goal of enhancing reading comprehension and relates the strategy's components to established reading comprehension theories. This detailed description is essential for understanding the intervention used in the research.
2.8 The Procedure of Teaching Reading Using PLAN Strategy
This section outlines the pedagogical approach employed in using the PLAN strategy in the classroom. It likely discusses the instructional steps and activities implemented to teach students how to effectively utilize the PLAN strategy for reading comprehension. This section bridges the theoretical description of the strategy with its practical application in the research.
2.9 The Advantages and the Disadvantages of Using PLAN Strategy in Reading Comprehension
This section presents a balanced perspective on the PLAN strategy by discussing its potential benefits and limitations. It likely explores the strengths of the strategy in improving comprehension and its potential drawbacks, such as time constraints or challenges in implementation. This critical evaluation enhances the research's objectivity and credibility.
2.10 The Previous Research Outcomes on Predict Locate Add Note Strategy
This section reviews prior research on the PLAN strategy, summarizing key findings and identifying areas of agreement and disagreement among studies. It provides a context for the current research by highlighting the existing body of knowledge on the efficacy of the PLAN strategy and the research gaps that the current study aims to address.
2.11 The Research Hypothesis
This section formally states the research hypothesis, providing a testable prediction about the relationship between the independent variable (use of the PLAN strategy) and the dependent variable (students' reading comprehension achievement). This clearly articulated hypothesis is central to the research design and data analysis.
III. Research Methodology
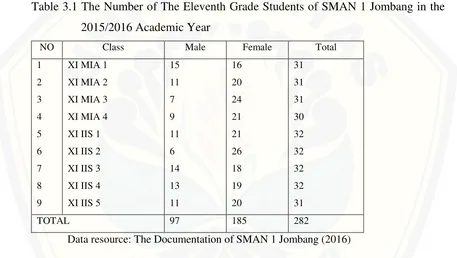
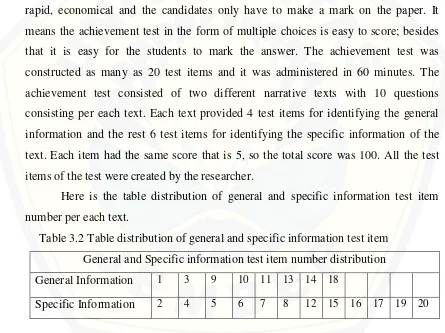
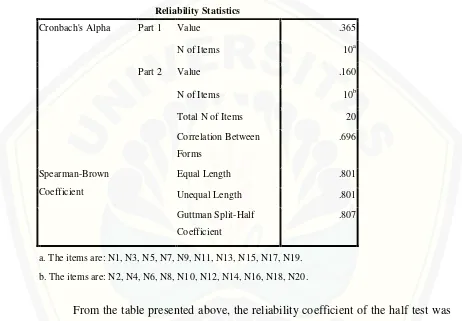
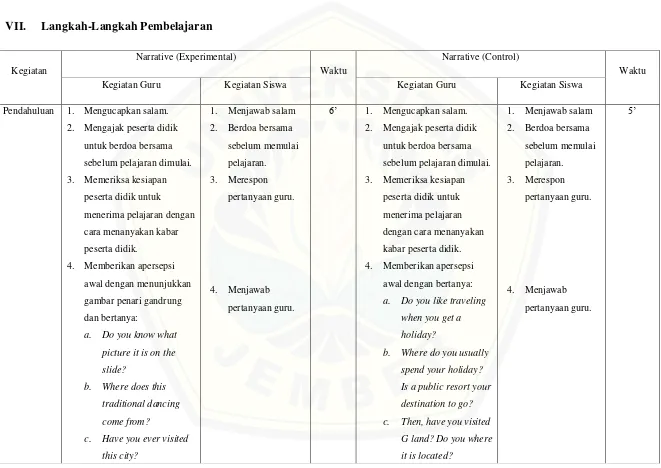
This chapter describes the research design, operational definitions, participant selection, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques. The research design is identified as quasi-experimental, outlining the rationale for this choice. The operational definitions clearly explain the key terms, such as "PLAN strategy" and "reading comprehension achievement." The methods for determining the research area and participants are detailed, along with a justification for the selected sampling technique. The data collection methods include a reading comprehension test (with details on its validity and reliability analysis) and potentially other methods such as interviews or observations. The chapter concludes by specifying the statistical techniques used for data analysis.
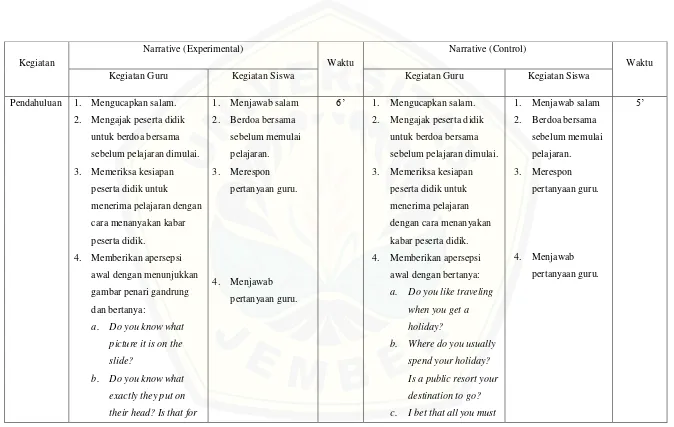
IV. Result and Discussion
This chapter presents the findings of the study and interprets them in relation to the research questions and hypotheses. It includes the results of the homogeneity analysis, illustrating the process of forming the experimental and control groups. The teaching and learning activities in both groups are described, highlighting the differences in instruction. The chapter then presents the posttest results, including descriptive statistics and inferential statistics (e.g., t-test results) used to test the research hypothesis. The chapter concludes with a discussion section that interprets the results, comparing them to existing literature and considering possible limitations of the study.
V. Conclusion and Suggestion
This chapter summarizes the key findings of the research, restating whether the research hypothesis was supported or rejected. It draws conclusions based on the analysis and offers practical suggestions for English teachers, students, and future researchers. The suggestions for teachers focus on the pedagogical applications of the PLAN strategy, while suggestions for students emphasize the importance of active reading strategies. Suggestions for future researchers point towards potential extensions of the study, including modifications or adaptations of the PLAN strategy, focusing on different text types or age groups, or addressing the identified limitations.
VI.References
This section lists all the sources cited throughout the thesis, following a consistent citation style.
VII.Appendices
This section contains supplementary materials, such as research instruments (questionnaires, tests), data tables, interview transcripts, and permission letters.