editor:
Ratih Dewanti-Hariyadi
Lilis Nuraida
Desty Gitapratiwi
Nelis Immaningsih
Purwiyatno Hariyadi
A/ERFR/T
W
-
CENTER-Southeast Asian Food and Agricultural Science and Technology (SEAFAST) Center
CURRENT ISSUES AND
CHALLENGES' IN FOOD SAFETY
SCIENCE-BASED APPROACH FOR FOOD SAFETY MANAGEMENTProceeding of The International Seminar 'Current Issues and Challenges in Food Safety: Science-Based Approach for Food Safety Management'
Bogor, December 2-3, 2009
Organized by:
Southeast Asian Food & Agricultural Science & Technology (SEAFAST) Center Bogor Agricultural University
International Commision on Microbiological Specifications for Foods (ICMSF) Norman Borlaug Institute for International Agriculture
Texas A & M University
Editor:
Ratih Dewanti-Hariyadi Lilis Nuraida Desty Gitapratiwi Nelis Immaningsih Purwiyatno Hariyadi
Southeast Asian Food & Agricultural Science & Technology (SEAFAST) Center, Bogor Agricultural University
Current Issues and Challenges in Food Safety
CURRENT ISSUES AND CHALLENGES IN FOOD SAFETY
SCIENCE-BASED APPROACH FOR FOOD SAFETY MANAGEMENT
Proceeding of The International Seminar 'Current Issues and Challenges in Food Safety: Science-Based Approach for Food Safety Management'
Bogor, December 2-3, 2009
Editor
Ratih Dewanti-Hariyadi Lilis Nuraida Desty Gitapratiwi Nelis Immaningsih Purwiyatno Hariyadi
Publisher
Southeast Asian Food & Agricultural Science & Technology (SEA FAST) Center Bogor Agricultural University
Bogor-Indonesia
National Library Republic of Indonesia ISBN 978-602-96665-3-3
Acknowledgement
Thanks to Leo Wibisono Arifin, Vesica Dwi Ariesta, Amelinda Angela, Vita Ayu Puspita, Palestina Santana, Virna Berliani Putri, Zulaikhah and Nurwandi NC
for preparing manuscript of this proceeding
Copyright©2010
Southeast Asian Food & Agricultural Science & Technology (SEAFAST) Center, Bogor Agricultural University
ii
I
Proceeding of the International Seminar
CONTENT
Preface ... iii Welcome Speech of Rector of Bogor Agricultural University ... xi Organizers ... xv
Keynote Speech
Cold Chain: Managing Food Safety for Fresh Produce and Frozen Food Product ... 1
Derk Van Mackelenbergh
PLENARY PRESENTATION
Microbiological Food Safety
A Modern Approach to Food Safety Management ... 9
Martin Cole
Use of Epidemiological Data for The Improvement of Food Safety ... 21
Fu miko Kasuga
Implementation of Food Safety Management at Industry Level in Developing Countries: Is GmpjHaccp Confusing? ... 29
Ratih Dewanti-Hariyadi
Chemical Food Safety
Controlling Allergens: Industry Perspective ... 41
Soo Chuah
Food Safety Issues in Food Packaging - Aseptic Technology
Approach ... 51
Hari Yanto Tekno Yuwono
Science-based Approach to Food Safety
Predictive Microbiology ... 61
Tom Ross
Ri sk Analysis: Using Risk Assessment to Establish Risk Based
Metrics ... 75
Leon Gorris
Role of Microbiology Criteria and Limitations of Sampling ... 89
Tom Ross
Current Issues and Challenges in Food Safety
Safety of Food Biotechnology
Safety of Food Biotechnology Products ... 1 03
James Maryanski
Safety Assessment of Genetically Modified Food in Indonesia ... 111
Maggy Thenawidjaja Suhartono
TECHNICAL PRESENTATION
Managing the Safety and Quality of Fresh Produce
Risk Assessment Of Listeria Monocytogenes In Raw Vegetables ... 121 Son Radu
Good Agricultural Practice: A Vital Program for Ensuring
Microbial Safety of Fresh Produce ... 139
Maria Auxilia T. Siringan
Biosafety of Vibrio Parahaemolyticus in Raw Salad Vegetables at Retail and Farm Level ... 147
Tunung Robin
The Effect of Blanching Method, Storage and Temperature to the Charcteristics of Cowpea Tempeh Subtituted by 40% Soybean ... 167
Mery Tambaria Damanik Ambarita
Microbiological Risk Assessment of Fresh Water Aquaculture
Fish in Malaysia: from Farm to Table ... 187
Rizal Damanik
Implementation of Food Safety and Quality Management at Industry Level
Control of Salmonella in Nut Processing ... 199
Chaven Suchart
Integrated Food Safety Management-Kraft Approach ... 213
Soo Chuah
Shelf-Life Prediction of Seasoning Powder Made from Whole
Fermented Fish (Peda) by Using Arrhenius Method ... 221
Meta Mahendradatta
Chemoreaction Drying and its Effect on Black Pepper Quality ... 235
Nur Wulandari
Proceeding of the International Seminar
Application of NMR Based Metabolomics and Multivariate Data Analysis for Quality Control of Herbal Material ... 243
ancy Dew; Yuliana
anaging Food Safety and Quality in Food Services and Retail Industries
anaging Food Safety in Food Retail: A Lesson Learnt ... 259
Andi Nur'aida
Food Safety Management in Aerofood Angkasa Citra Sarana
(ACS) Catering Service ... 265
Hoerip Satyagraha
Formalin Contamination in Children's Street Foods at Schools in Surakarta, Central Java, Indonesia ... 273
Indrias Tri Purwanti
Isolation Of Enterobacter sakazakii (Cronobacter Spp) from Powdered Infant Formula and Other Dry Foods Obtained from
Bogor Area, Indonesia ... 281
Rlltih Dewanti-Hariyadi
POSTER PRESENTATION
Inhibition of Duku (Lansium domesticum) Spoilage using Ozone ... 287
Anny Yanuriati
utrition Properties and the Prospect of Six Amorphophallus
Species of Tubers in Java ... 299
Yuzammi
IGewang (Corypha utan lam.) as Local Food in Timor Island and
Its Nutritional Properties ... 307
Joko Ridho Witono
Two Stages Tea Chemical Withering during Peak Season ... 321
lJadan Rohdiana
The Physiology of Organs and Organism of Mus Musculus
Induced Repeatedly with Formalin-Contaminated Fish and
Chlorophyllin ... 329
Alfonds Andrew Maramis
Current Issues and Challenges in Food Safety
The Occurrence of Pseudomonas sp in Grouper Fish Fillets
(Plectropoma leopardus) at Bone Pante ... 345
Rieny Sulistijowati
HACCP Plan for Green Tea Product of PT GT and its
Implementation ... 359
Raniayu
Establishment and Implementation Sanitation Standard
Operating Procedures (SSOP) in Green Tea Processing ... 369
Ratna Handayani
Utilization of Leaves of Kunyit (Curcuma domestica Val.), Ruku-Ruku (Ocimum gratissimum. L) and Mangkokan (Nothopanax
cutellarium Merr.) in Steamed Fish (Rastrelliger Sp) Processing ... 383
Novelina
Effect Of Time-Temperature and Amylose Content of Rice on
the Color and Texture of Rice-Based Emergency Canned Food ... 391
Elvira Sya msir
Safety of School Children Foods in Indonesia ... 399
Nuri Andarwulan
The Role of Women in Community Management of Biosecurity
and Food Safety ... 415
Eka Martiningsih
APPLICATION OF NMR BASED METABOLOMICS
AND MULTIVARIATE DATA ANALYSIS FOR
QUALITY CONTROL OF HERBAL MATERIAL
Nancy Dewi Yuliana1.2, Hye Kyong Kim2, Frank van der Kooy2,
Henrie Korthourt3, Young Hae ChoP, and Rob Verpoorte2
1 Dept. Food Science and Technology, Bogor Agricultural University,
Bogor, Indonesia
2 Dept. Pharmacognosy, Sect. Metabolomics, Institute of Biology,
Leiden University, The Netherlands
3 Fytagoras BV Plant Science, Leiden, The Netherlands
ABSTRACT
Despite of lack of solid scientific proof for its efficacy and safety, up to now herbal medicines are widely used both in developed and developing countries. Standardization by focusing on active constituents or marker compounds is important but sometimes it is not sufficient to guarantee the quality of herbal preparations. NMR based metabolomics is a reliable tool to provide a wealth of information concerning plant metabolites since it is able to comprehensively detect a diverse groups of plant metabolite in a single run. In combination with multivariate data analysis, the obtained NMR data can be applied to determine any adulterants or substitutes in commercial herbal preparation which cannot be detected by other chromatographic methods. Here we reviewed three projects of our lab in Leiden, focusing on the application of NMR based metabolomics and multivariate data analysis, particularly principal component analysis for quality control of herbal medicines.
INTRODUCTION
Herbal medicine has been used since ancient times to treat a wide range of diseases and to improve the health status of human beings. Despite the advanced development of modern medicine, herbal preparations are still widely used both in developed and developing countries. The reasons are various; the belief that herbals are made from natural sources therefore safer than chemical drugs
l
Science-Based Approach/or Food Safety Management
(which is not always true); diminishing trust to modern medicine due to its side effects; or lack of access to modern medicine (due to poverty or geographical factors) (Calixto, 2000; Elvin Lewis and Steve, 2005). Two important issues concerning the use of herbal medicine are proof of efficacy and safety. The last issue is the focus of this paper, highlighting on the possibility of adulteration or substitution with other plant which may not contain the reported active principles or even worse, contain toxic substances. As an example; in 1992 many young women in Belgium suffered from progressive permanent kidney damage after consuming a Chinese slimming herbal which consisted of Stephania tetrandra and
Magnolia officinalis. It is supposed that Stephania tetrandra was substituted with A ristolochia fangchi which contains aristolochic acid, a nephrotoxin and carcinogen (van Herweghem, 1998).
To address such issues, chemical standardization on the basis of active compounds or other marker compounds in case the active
compounds are unknown, is necessary. Chemical standardization involves the use of chromatographic or spectroscopic methods to identify active/marker compounds (Ong, 2004). Many analytical methods such as TLC, HPLC, LC/MS, and GC/MS can be used for that purpose. However, sometimes only targeting the marker compound is not sufficient to detect adulterants/substitutes, especially when chemical marker compounds are spiked into adulterants/substitutes while the adulterants/substitute may contain toxicant instead. In such a case, information concerning a wide range of metabolites present in the herbal preparation becomes necessary. This could be a hurdle since plants have a large number and wide variety of compounds, and herbal medicine may consist of two or more different plant materials. A wide spectrum of analytical techniques which are rapid, reproducible, and stable over time without an elaborative sample preparation is required (Choi et al., 2005). The aforementioned analytical methods have limitations to provide information about all metabolites due to the wide structural variation, as well as physical properties and chemical characteristics of compounds present in plant material (Jahangir et af., 2008).
I'
Proceeding of International Seminar Current Issues and ChaLLenges in FOOd Safetyit;:'"
セ セ@ ""
セ@ QUALITY CONTROL OF HERBAL MATERIAL WITH NMR-BASED
.<:' METABOLOMICS AND MULTIVARIATE DATA ANALYSIS
The term metabolome represents the collection of all metabolites in a biological organism as the end product of their gene expression (van der Kooy et a/., 2009). One of the first application of nuclear magnetic spectroscopy (NMR) for ,fingerprinting of plant extracts was conducted in our lab, that was for characterizing plant cell cultures and quantitative analysis of sugars in the cell culture extracts (Schripsema and Verpoorte, 1991). Although the sensitivity is lower than other methods such as mass spectrometry (MS), NMR has some unique advantages since it is a quick non-destructive method which simultaneously detects diverse groups of plant metabolites in a single run (Choi et al., 2004). It is able to detect all molecules containing NMR-active nuclei and no selective ionization (like in MS) or the presence of chromophores (such as in ultraviolet spectroscopy) are required (van der Kooy et al., 2009). The huge data set reSUlting from NMR measurement need multivariate data analysis (MVA) methods for interpretation. The most commonly used MVA method is unsupervised principal component analysis (PCA). In PCA, the data are transformed into a new coordinate system so that the biggest variance by any projections of the data lie on the first coordinate (PC1), the second coordinate (PC2), and so on. The dimensionality of the data is reduced while the characteristics of the data set that contribute most to it are preserved (Eriksson et al.,
2006; van der Kooy et al., 2009). By using PCA it is possible to classify the data when only little information about the data is available (Eriksson et
a/.,
2006).In our lab, several studies related to quality control of botanicals by using NMR based metabolomics coupled with multivariate data analysis, in particular PCA, have been conducted. Herewith we give three examples of those studies.
1. Metabolic Fingerprinting of Ephedra Species Using lH-NMR Spectroscopy and PCA (Kim et a/., 2005)
Ephedra or Ma Huang, with ephedrine type alkaloids (e.g.
ephedrine, pseudoephedrine, methylephedrine and norephedrine) as the primary active ingredients, is used as a weight loss agent and to boost performance of athletes (Haller
Science-Based Approach/or FoodSa/ety m。ョ。ァ・ュセョエ@
and Benowitz, 2000; Calfee and Fadale, 2006). Ephedra sinica
considered as the main source of the active ingredients the ephedrine alkaloids, although other Ephedra species may also contain these alkaloids though in different concentrations. In this paper, the use of IH NMR coupled with PCA for the metabolite fingerprinting of Ephedra species was reported. The discrimination between 3 different species of Ephedra (E. sinica,
E. intermedia, E. distachya var. distachya) and nine commercial
Ephedra samples was shown.
セGャiG@ A
2111.11 J J
••
•
... Intu • • • • - ••
セ@ . . . 0 : '1
I • ,
セ@ ョNQiA|MM ⦅MZMNMGセセMMKMMMM⦅⦅⦅Lイ⦅⦅⦅Kii⦅G⦅イMMMMM M - -+-_ _ -j
>'
....+
セAiゥ@ • • •-
.'...
-.
-JIlUIi •• • • ••• • • • - *1.. • • • • s . •
. 0 0 • セ@ •
• 1 11: . l 0 S , S . +
·2nuu : ••• •••• ••• : 7 ,L. •••• ,
• • • • • • • 7 • • • • ᄋセ@
-4(IUII
ᄋセiui@
0.10
•
·14111 . 1)11) · I;an -I UII -HilI "A" -*11 .,((1 -o:n ·5(1) 4 .. -JIll -2m -UII II III) セii@ )11 4(1) セNi@ (ill )11 Inl 'XII ifill' lUI 1311 IJlII PCI (&4%)
B
7.34 ppm
'{O
Num
Proceeding of International Seminar Current issues UTIU セBBGGGエ[NGGisGGGG@ N セN@ "UUU セ アj・ャケ@
•• 4,,/-.
: s :• s :
...
IU
·
D
...
·
11 .. 1
·
i IU
·
...
"(I.m ,
. 6 6
...
... J iセ@
..
.
. .
: I :
: "[3 ' . :
J . ...
··.··3
8.08 ppm
.
,
1 t
:1 I, I セ@
7.56 ーセュ@
7.70 pprr
\
7.46 ppmセLNk@
"
'\;Iv セONMセG@Num
Science-Based Approach for Food Safety Management
,.
.
-$111.
.
.
mJ.
.
·
,
セ@ ウョャセャャ@
SIll·
·
,
11·
0
,
.
,.
, ,
:-1··"
: s :
•• s :
..
.,.
'4
.
,"
...
o'•• I •
.... 1 :
.
,0 ' セ@
.
.
: t.) •••
J •• , _ •••
. セセMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMセMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMセ@
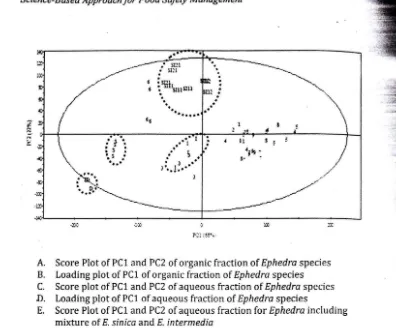
A. Score Plot of PCl and PC2 of organic fraction of Ephedra species
B. Loading plot of PCl of organic fraction of Ephedra species
C. Score plot of PCl and PC2 of aqueous fraction of Ephedra species D. Loading plot of PCl of aqueous fraction of Ephedra species
E. Score Plot of PCl and PC2 of aqueous fraction for Ephedra including mixture of E. sinica and E. intermedia
(S=E. sinica; I=E. intermedia; D=E. distachya var. distachya. 1-9, commercial
Ephedra herbs, SI12=mixture of E. sinica and E. intermedia (1 : 2, wjw),
SI11=mixture of E. sinica and E. intermedia (1 : 1, wjw), SI21=mixture of E. sinica
[image:13.610.169.565.25.353.2]and E. intermedia (2 : 1, w jw)
Figure 1. (adapted from (Kim et 01.,2005), with permission)
The solvent mixture of CHCb-MeOH-HzO-NH40H was used to extract metabolites from Ephedra species. Organic and aqueous fractions were measured by NMR separately. The most alkaloids were present in the organic solvent phase. The PCA score plots and loading plots for each fractions are presented in Fig. 1.A-D. Figure 1.A. shows that the three species of Ephedra are separated from each other. The loading plot of PCl was analyzed further since it is the main PC for the separation. It was found that characteristic NMR signals for ephedrine alkaloids such as CH3 at 8 0.9-0.8 ppm, N-CH3 at 8 2.60 ppm, and the aromatic signal at 8 7.3 ppm were responsible for the separation. These alkaloids are higher in E. sinica while ephedrine was not detected
in E. distachya var. distachya, therefore this species was located
Proceeding oj internatIOnal ')'emtnar Lurrem I ... ue .... UTIU lMBオエNエZZBセエZZウ@ III rood Sajety
outside of the 95% Hotelling T2 confidence eclipse. Analysis of aqueous fractions was also performed since there was no clear separation between commercial Ephedra samples. From fig. LC-D, it is obvious that all commercial samples clustered close to E.
intermedia except sample number 6. Analysis of the aromatic
area showed typical signals of benzoic acid analogues at 8.08 (d, 1-7.2 Hz), 7.70 (t, 1-7.5 Hz), and 7.56 (t, 1-7.8 Hz) and monosubstituted phenolic compounds like phenylalanine at d 7.46 (m) which are higher in E. intermedia. Sample 6 was located between E. sinica and E. intermedia. PCA analysis of a mixture of
E. sinica and E. intermedia (fig.1.E.) confirmed that sample 6 was
indeed the mixture of both species.
This study showed that standardization by focusing on alkaloids content alone is not efficient and it is not possible to detect if synthetic ephedrine alkaloids were added to the commercial herbs. This is the advantage of applying NMR spectroscopy coupled to MVA since the analysis is based on total metabolic fingerprinting.
2. Classification of !lex Species Based on Metabolomic Fingerprinting Using NMR and Multivariate Data Analysis (Choi
et al., 2005)
I1ex paraguariensis var. paraguariensis, or yerba mate, is a
popular beverage in South America, besides it is also used as tonic, diuretic, to reduce fatigue and to improve gastric function (Gonzalez et al., 1993). This study was conducted to see the differentiation between !lex paraguariensis var. paraguariensis.
and some other I1ex species which are commonly used as adulterants or substitutes, (Le. I. argentina, I. brasiliensis, I. brevicuspis, I. dumosa var. dumosa, I. dumosa var. guaranina, I.
integerrima, I. microdonta, I. pseudobuxus, I. taubertiana, and I.
theezans). Moreover, the difference between these 10
adulterants/substitutes was analyzed as well. An Extraction method similar to the one used in the Ephedra study was performed and NMR analysis was carried out for both organic and aqueous fractions
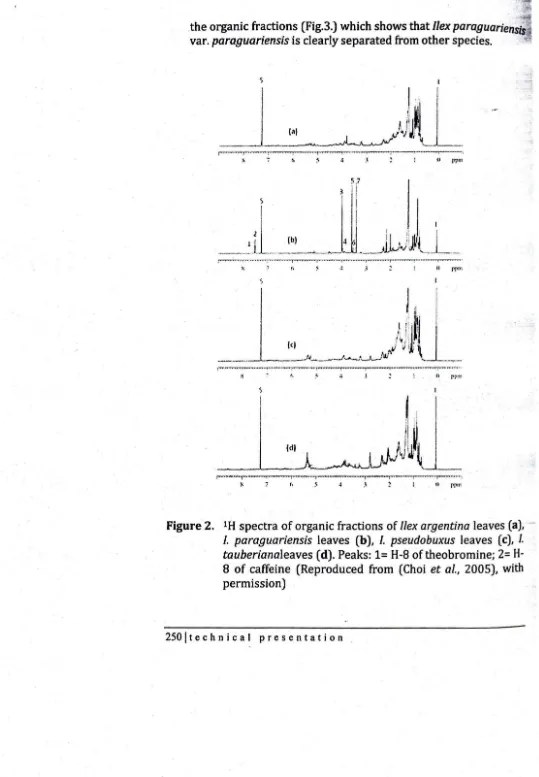
From visual observation of the IH-NMR spectra (Fig. 2), only
!lex paraguariensis var. paraguariensis was observed to contain
caffeine and theobromine. This was confirmed by score plot of
.l(;It::nce-uasea ApprOaCnJor rooa OlaJety m。ョ。ァ・ュ・ョエ セ エ@
セセ ャセ@
GゥBゥ セ@ the organic fractions (Fig.3.) which shows that
/lex
ー。イ。ァオ。イゥ・ョウゥ セ Gェ@var.
paraguar;ens;s
is clearly separated from other ウー・」ゥ・ウN \ セ@r-.... ' .. MMイMセNNLNNNNLNNNNMQG@ .... - -... ..,--.-.... セMセ@ ... Mセ@ •. - ... MBAMセMMMMMN I@
.s j (, 5 ,t 2 l .) wm
; ... Mᄋᄋセセ ᄋ ᄋ ᄋ G ᄋᄋᄋᄋM ᄋ ᄋ セ ᄋ ᄋ Wᄋ ᄋ@.. · .. - ... ·-·T ... · ... •· ... · .. ·.-···..-.. · .... r ... · ... ·-... ! -... · ··T .. - .. ·• ... Gイ ᄋセ@ .. - - -.. ·!' ... • ... - ·
セ@ エセ@ . : " , : ! o ppm
... ..-._
..--_.---
...-_
.... . .
t.
(dl
セMNNNL@ ... イセNNNMMMM ... QセGNNNMNNLNNMMBェMMイMMNMMセMMM .. · ... ro--... - .... セ@
セ@ -; ヲセ@ 5 . a ., ! 1 o ppm
Figure 2. IH spectra of organic fractions of
!lex argentina
leaves (a),-I. paraguar;ens;s
leaves (b),I. pseudobuxus
leaves (e), J.tauberianaleaves
(d). Peaks: 1= H-8 of theobromine; 2=H-8 of caffeine (Reproduced from (Choi
et al.,
2005), with permission) [image:15.612.36.575.37.814.2]r
Science-Based Approach for Food Safety m。ョ。ァ・ュセョエ@-I -2
II)
-3L-_ _ MMセ@ _ _ MMセ@ _ _ MMセ@ _ _ MMセ@ _ _ - - + _ _ _ - -_ _ _ _ - -_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ __J
0.60 0 .50 040 0 .30 0.20
セ@ 0 . 10
-0.10
-4 -3 - 2 -I o pe2 (18.2%)
1_24 DDm
5.36 ppm
___ -At
セ\MZMM BjjィG@
"[:"" 0"" _ .III
iJ.'!I
v 0_5 _ 1
セ@ イセセj LゥGゥャエ NA@
-0.20 :;
-0.30
I
-OAO lMMiMMM⦅MMMMセ@ _ _ _ >--_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ --__t_----__ MセMMMM __ - _ . J
o 100 200 300 400 soo
[image:16.618.31.600.22.786.2]Num
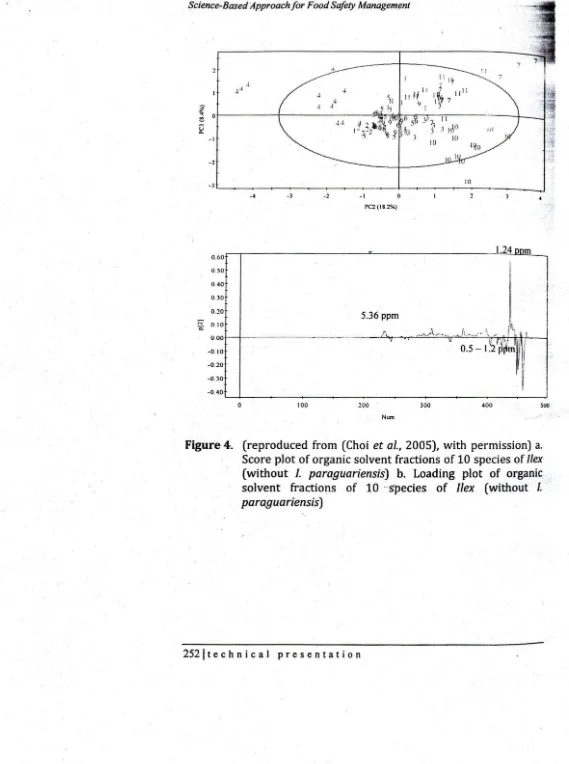
Figure 4. (reproduced from (Choi et al., 2005), with permission) a.
Score plot of organic solvent fractions of 10 species of /lex (without /. paraguariensis) b. Loading plot of organic solvent fractions of 10 "s'pedes of /lex (without I. paraguariensis)
Proceeding of International Seminar Current Issues and Challenges in Food Safety
1.0
0.5
0.0
,...
セ@
セ@ -0.5
e
'"
u -1.0 "'"
-1.5 -2 .0
... 'rr----·."'cc""'ro ... - - - ,
11.211 i
....
セ@ fUll
.. (1.10
-tun
,. \
", L セ@:
.. , ':( - " ' ;" i"
.rbulln セヲ@ .
Ii
,
..
,,
...
. . BLィ、 ᄋ NLHLセ@
(b)
(a)
n .. W
0 .211
セ@ NZZセセNョセセセQイQセ」n、セ
L@
d,ij'"' \ ; .',,'I!
0
0.20°'-+ _ _ _ _ ' _ _ ___ _ _ _ _
.1110 '00
....
(c)
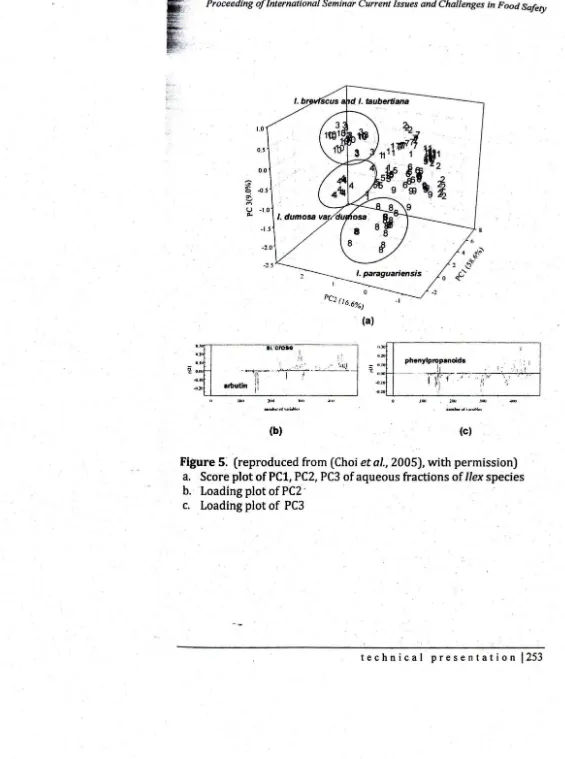
Figure 5: (reproduced from (Choi
et al.,
2005), with permission) a. Score plot of PCl, PC2, PC3 of aqueous fractions of Jlex species h. ' 'Loading plot of PC2 'c. Loading plot of PC3
-' ....
[image:17.611.12.577.27.786.2]Science-Based Approach for Food Safety Management
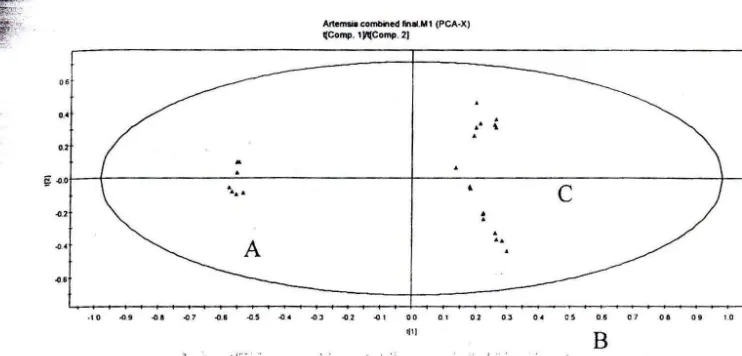
3. Metabolomic quality control of claimed anti-malarial Artemisia afra herbal remedy and A.afra and A. annua plant extract (van der Kooy et al., 2008)
Artemesia annua L. has been used for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine to treat malaria and fever with artemisinin as
active constituent (Klayman, 19'85). Artemisia afra jacq. Ex Willd. is originally from South Africa and commonly used as a medicine for a wide range of illness such as cough, colds, fever, loss of appetite, and also malaria, although there is no report that A. afra
contains artemisinin or its derivetives (van der Kooy et al., 2008).
In this study, a commercial anti-malaria capsule, which was claimed to contain 400 mg of pure A. afra without any additives or excipients, was investigated. The producer claimed that artemisinin is the active ingredient in these capsules. For NMR analysis, 100 g of each sample (plant material removed from capsules, powder of A. annua, powder of A. afra) were extracted with deuterated chloroform, sonicated, filtered, then transefered to NMR tubes. The lH NMR data was subjected to PCA analysis, to determine whether the capsule contained A. annua, A. afra, or a combination of the two.
From the PCA score plot ゥセ@ is clear that A. annua and A. afra are separated from each other in PC1, but the commercial sample could not be differentiated as A. annua or A. afra The loading plot
revealed that artemisinin is an important marker for the differentiation in PCl (methyl signals at 0.99 ppm, 1.21 ppm, 1.44
ppm). LC-MS analysis of three samples, confirmed that A. annua
contains 0.078 - 0.84% artemisinin but it is not present in A. afra
or the commercial sample. It could be concluded that the commercial capsules contain A. afra.
Proceeding o/International Seminar Currene issues unu LIIUtlell[;eCi In rood Sqjety
go D.' D' §: .(1.0
セ N L@
セ@
..
セL@
.
.
'.,
A
Arternsil;combinedfin"."'" (PCA-X)
1{Comp. '}1(Comp. 21
.'
,c
. 10 .0.9 .0.1 .0.7 .0.' .o.S Nッ セ@ .0_3 .02 .01 00 0. 1 02 0 .1 oセ@ os 0 .15 0 7 08 09 1.0
[image:19.617.186.557.55.233.2]'"
BFigure. 6. Score plot of the Artemisia samples showing the clear differentiation in PC 1 between the A. annua (A) samples and the A. afro (B) and commercial herb (C) (reproduced from (van der Kooy et al., 2008), with permission)
CONCLUSION
NMR based metabolomics in combination with multivariate data analysis can be applied as a finger printing tool for the quality control of herbal medicine. Adulterants or substitutes in commercial herbal preparations can be identified very quickly with a simple sample preparation.
References
Calfee, R. and Fadale, P. (2006). "Popular ergogenic drugs and supplements in young athletes." Pediatrics 117(3): eS77-S89. Calixto,
J.
(2000). "Efficacy, safety, quality control, marketing andregulatory guidelines for herbal medicines (phytotherapeutic agents)." Brazilian TournaI of Medical and Biological Research 33: 179-189.
Choi, Y. H., Kim, H. K, Hazekamp, A., Erkelens,
c.,
Lefeber, A. W. M. and Verpoorte, R. (2004). "Metabolomic differentiation of Cannabis sativa cultivars using IH NMR spectroscopy and PrincipalScience-Based Approach/or Food Safety Management
Component Analysis." lournal of Natural Products 67(6):
953-957.
Choi, Y. H., Sertic, S., Kim, H. K., Wilson, E. G., Michopoulos, F., Lefeber
A W. M., Erkelens,
c.,
Prat Kricun, S. D. and Verpoorte, R. (200S): i"Classification of Ilex species based on metabolomic GセゥゥZ@
fingerprinting using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and
Multivariate Data Analysis." Journal of Agricultural and Food
Chemistry 53(4): 1237-1245.
-Elvin Lewis, M. and Steve, L. T. (2005). "Safety issues associated with
herbal ingredients." Advances in Food and Nutrition Researcll
50: 219-313.
Eriksson, L., Johansson, E., Kettaneh-Wold, N. and Wold, S. (2006) .
Multi-and Megavariate Data Analysis. Umea, Sweden, Umetrics
AB.
Gonzalez, A, Ferreira, F., Vazquez, A, Moyna, P. and Paz, E. A (1993).
"Biological screening of Uruguayan medicinal plants." lournal of
Ethnopharmacology 39(3): 217-220.
Haller, C. A and Benowitz, N. L. (2000). "Adverse cardiovascular and
central nervous system events associated with dietary
supplements containing Ephedra alkaloids." New England
Journal of Medicine 343(25): 1833-1838.
Jahangir, M., Kim, H. K., Choi, Y. H. and Verpoorte, R. (2008).
"Metabolomic response of Brassica rapa submitted to
pre-harvest bacterial contamination." Food Chemistry 107(1):
362-• 368.
Kim, H. K., Choi, Y. H., Erkelens,
c.,
Lefeber, A W. M. and Verpoorte, R.(2005). "Metabolic fingerprinting of Ephedra species using
lH-NMR spectroscopy and Principal Component Analysis."
Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 53(1}: 105-109.
Klayman, D. (1985). "Qinghaosu (artemisinin): an antimalarial drug
from China." Science 228(4703): 1049-1055.
Ong, E. S. (2004). "Extraction methods and chemical standardization
of botanicals and herbal preparations." lournal of
Chromatography B 812(1-2): 23-33.
E:""
. . Proceeding of International Seminar Current Issues and Challenges in Food Safety
r
セ [Z@ Schripsema,J.
and Verpoorte, R. (1991). "Investigation of extracts ofセ ZG@
plant cell cultures by proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy." Phytochemical Analysis 2(4): 155-162.
van der Kooy, F., Maltese, F. and Choi, Y. (2009). "Quality control of herbal material and phytopharmaceuticals with MS and NMR based metabolic fingerprinting." Planta Medica 75(7): 763-775.
van der Kooy, F., Verpoorte, R. and Marion Meyer,
J. J.
(2008). "Metabolomic quality control of claimed anti-malarial Artemisia afra herbal remedy and A. afra and A. annua plant extracts." South African Journal of Botany 74(2): 186-189.van Herweghem,
J.-L.
(1998). "Misuse of herbal remedies: The case of an outbreak of terminal renal failure in Belgium (Chinese Herbs Nephropathy)." Journal of Alternative Complementary Medicine 4(1): 9-13.