A “Skripsi”
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers Training
in Partial fulfiment of the Requirements
for the degree of S.Pd (Bachelor of Arts) in English Language Education
By
Lia Aida
NIM. 1110014000054
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
A "SkiPsi"
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers Training in Partial fulfiment of the Requirements
for the degree of S.Pd (Bachelor of Arts) in English Language Education
By: Lia Aida
1110014000054
Approved by the Advisor
II
NIP.
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBTYAH AND TEACHERS' TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY JAKARTA
201s Approved by the Advisor I
ENDORSEMENT SIIEET
The Examination Committee
of
the Facultyof
Tarbiyah and Teachers, Training certifies that the "skripsi" (Scientific Paper) entitled ..An Investigationof the
Practice of Effective Teaching strategies in Three Islamic senior Irigh Schoolsin
South Jakarta"
written
by
Lia
Aida,
student's registration nurnber 1110014000054 was examined by the committee on February 4ft 2015. The ..skipsi', has been accepted and declared to have fulfilied oneof
the requirements for the degreeof
*S. Pd"
@achelorof
Arts)in
English Language Educationat
the Department of English Education.Jakarta, February 4h 2Ol5
EXAMINATION COMMITTEE
[I
\-raAIt!lvlAl\
SECRETARY
EXAMINERI
: Drs. Svauki.
ii.
Fd.NIP. 19641212 199103 1 002
: Zaharil Anasy, M. Hum. NIP. 19761007 200710 1 002
: Zaharil Anasy. M. IIum. NIP. 19761007 2007fi 1, 002
NIP.
Acknowledged By
t'll:---'--1
EXAMINER
II
: Ertin. MA. TESOLDean of T Facultv
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
In the name of Allah, The Beneficent and The Merciful
All praise be to Allah the Lord of the worlds for the blessing, the strength,
and the guidance to the researcher in completion of this research. Peace and
blessing from Allah SWT be upon to the Prophet Muhammad SAW, his families,
his companions, and his followers.
It is a valuable thing that the researcher finally accomplishes her “skripsi”
entitled “An Investigation of the Practice of Effective Teaching Strategies in Three Islamic Senior High Schools in South Jakarta” (Mixed-Methods in Islamic Senior High Schools in South Jakarta). It is presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah
and Teachers’ Training in a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
of Strata 1 (Bachelor of Art) in English Language Education.
First, the researcher would like to express her great honor and deepest
gratitude to her beloved parents, Asep Sugiar and Jubaedah. Further, her beloved
brother, Arif Anggi Wijaya. Furthermore, she thanks to all families in Bekasi,
Cilacap, and Ciamis who always give prayer, motivation, love, faith and support
for her to finish her study.
Furthermore, the researcher would like to give the deepest gratitude and
the greatest honor to:
1. All lectures in Department of English Education for the knowledge, the
motivation, and patience to the researcher during her study at State Islamic
Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta University.
3. Mr. Zaharil Anasy, M. Hum., the Secretary of Department of English
Education and the researcher’s academic advisor.
4. Nurlena Rifa’I, M. A., Ph.D., the Dean of Faculty of Tarbiyah and
Teachers’ Training.
5. Siti Nurul Azkiyah, Ph.D and Atik Yuliyani, MA. TESOL, the advisors
who have given guidance, advice, motivation and patience to the
researcher in accomplishment of this “skripsi”.
6. Mr. Zaharil Anasy, M. Hum., and Ertin, MA., TESOL, the examiners who
have given guidance and advice to the researcher in revision of this
“skripsi”. They decided how well the researcher had done in an
examination.
7. Dra. Hj. Isnadiar Dekok, M.M as the headmaster of MAN 4 Jakarta
Selatan who gave permission to do her research. Drs. Pursidi as the
headmaster of MAN 11 Jakarta Selatan who gave permission to do her
research. H. Ismail Nur, Lc. M.Ag as the headmaster of MAN 19 Jakarta
Selatan who gave permission to do her research.
8. Ten English teachers in MAN 4 Jakarta, MAN 11 Jakarta, and MAN 19
Jakarta. Thank you for giving the researcher permission to investigate their
teaching and learning process. They helped, advised, and supported the
researcher during the research.
9. All of students at tenth and eleventh grade at MAN 4, MAN 11, MAN 19
Jakarta Selatan, who participated in this research.
10.All of beloved friends of The Class of PBI B in Department of English
Education.
11.All of beloved friends of “PelatihanPenguatan Riset dan Bahasa”. 12.All of beloved friends of “Assalam, Cah Beddun, and “Petir”.
13.To any other persons who give contribution to the researcher and cannot
Finally, the researcher truly realizes that this “skripsi” cannot be considered as a perfect masterpiece. Therefore, it is a very precious thing for
her to get suggestion and criticism which can make this better.
And the researcher hopes this “Skripsi” can give the beneficent for all
people who are interested in it.
May Allah, the Almighty bless them all and give them more than what
they have given to the researcher. Amen.
Jakarta, January 2015
ABSTRACT
Lia Aida (NIM: 1110014000054). An Investigation of the Practice of Effective Teaching Strategies in Three Islamic Senior High Schools in South Jakarta (Mixed-Methods in Three Islamic Senior High Schools in South Jakarta). Skripsi of Department of English Education at Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training of State Islamic University Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, 2015.
Advisor I : Siti Nurul Azkiyah, Ph.D
Advisor II : Atik Yuliyani, MA. TESOL
Key Words: Effective Teaching, Effectiveness, Strategies
The objective of this study was to investigate the practice of Effective Teaching strategies in three Islamic Senior High Schools in South Jakarta. The sample of this study was consisted of ten English teachers at the first and the second grade of three Islamic Senior High Schools in South Jakarta such as MAN 4, MAN 11, and MAN 19.
The method used in this study was mixed-methods. The instruments of this research were questionnaires survey (quantitative) and classroom observation, documentation, and interview (qualitative). In analyzing the data, the researcher used triangulation.
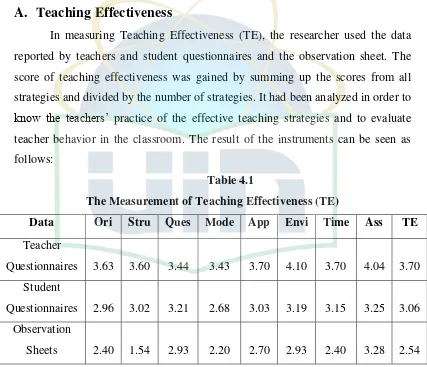
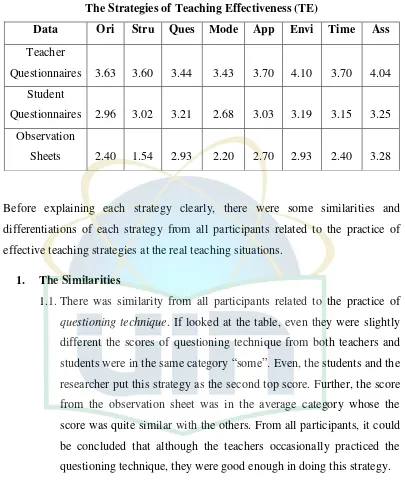
The result of this study showed that the teachers practiced the effective teaching strategies at their regular teaching practices. The teachers’ performance in practicing the strategies were included in the average category. It can be shown by the score of teaching effectiveness, which was gained by summing up the scores from all strategies and divided by the number of strategies, from the researcher which was 2.54. The score showed that the teachers were good enough in practicing the strategies. Although there was no strategy included in “excellent” category, there were four out of eight strategies included in “good” category. The strategies were classroom assessment, questioning technique, teacher role in making classroom a learning environment, and applications. The score of questioning technique was 2.93. The score of applications was 2.70. The score of teacher role in making classroom a learning environment was 2.93. The score of classroom assessment was 3.28. The scores showed that the teachers were good enough in practicing the strategies. However, the other four strategies such as orientation, structuring, teaching-modelling, and time management were included
ABSTRACT
Lia Aida (NIM: 1110014000054). An Investigation of the Practice of Effective Teaching Strategies in Three Islamic Senior High Schools in South Jakarta (Mixed-Methods in Three Islamic Senior High Schools in South Jakarta). Skripsi pada Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Ilmu Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, 2015.
Pembimbing I : Siti Nurul Azkiyah, Ph.D
Pembimbing II : Atik Yuliyani, MA. TESOL
Kata Kunci : Pengajaran yang efektif, Strategi, Keefektifan
Skripsi ini bertujuan untuk menyelidiki praktek penggunaan strategi-strategi pengajaran yang efektif di tiga Madrasah Aliyah Negeri di daerah Jakarta Selatan. Sampel pada penelitian ini adalah sepuluh guru bahasa inggris yang mengajar dikelas X dan kelas XI di MAN 4, MAN 11, dan MAN 19 Jakarta Selatan.
Metode yang digunakan pada skripsi ini ialah mixed-methods. Sementara itu, instrumen-instrumen yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini adalah kuesioner survei (kuantitatif) dan observasi kelas, dokumentasi, dan wawancara (kualitatif). Teknik triangulasi pun digunakan dalam penelitian untuk memeriksa keabsahan data dari keempat instrumen.
Hasil penelitian ini menunjukan bahwa para guru telah melakukan strategi-strategi pengajaran yang efektif dalam praktek pengajaran sehari-hari. Sikap para guru dalam mempraktekan strategi-strategi tersebut termasuk kedalam kategori
TABLE OF CONTENT
Page
TITLE
SURAT PERNYATAAN KARYA SENDIRI
APPROVAL ... ...i
ENDORSEMENT ... ...ii
ACKNOWLEDGE ... ...iii
ABSTRACT ... ...vi
TABLE OF CONTENT ... ....viii
LIST OF TABLES ... ...x
LIST OF APPENDICES ... ...xi
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION A. The Background of the Research... 1
B. The Identification of the Problem ... 4
C. The Scope of the Research ... 4
D. The Formulation of the Problem ... 5
E. The Purpose andSignificance of the Research ... 5
CHAPTER II: THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK A. Effective Teaching ... 6
1. The Concept of Teaching ... 6
2. The Concept of Effectiveness ... 7
3. The Concept of Effective Teacher...8
5. The Characteristics of Effective Teaching ...14
6. Strategies in Effective Teaching ...15
B. The Application of Effective Teaching Strategies...21
C. The Advantages of Effective Teaching Strategies ...23
D. Previous Studies...26
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY A. The Method of the Research ... 28
B. The Place and Time of the Research ... 29
C. The Sample and Population ... 30
D. The Instrument and Technique of Collecting Data ... 37
E. The Technique of Analysis Data ... 37
F. Trust Worthiness ...38
CHAPTER IV: RESULT OF THE STUDY A. Teaching Effectiveness ... 40
B. The Strategies of Teaching Effectiveness ... 42
1. The Similarities ... 43
2. The Differentiations ... 45
3. In Which Strategies were Teachers Good? ... 46
4. The Details of the Strategies in Teaching Effectiveness ... 47
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A. The Conclusion ... 64
B. The Suggestion ... 66
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... ...70
LIST OF TABLES
Page
[image:12.595.152.444.275.558.2]Table 4.1 The Measurement of Teaching Effectiveness (TE) ...40
LIST OF APPENDICES
Page
Appendix 1The Observation Sheet ...74
Appendix 2 The Mean Score of English Subject in UN (Ujian Nasional) ...78
Appendix 3 The Teacher Questionnaire ...79
Appendix 4 The Student Questionnaire ... ...83
Appendix 5 The Teaching Quality of The Teachers ... ...87
Appendix 6 The Interview Results...88
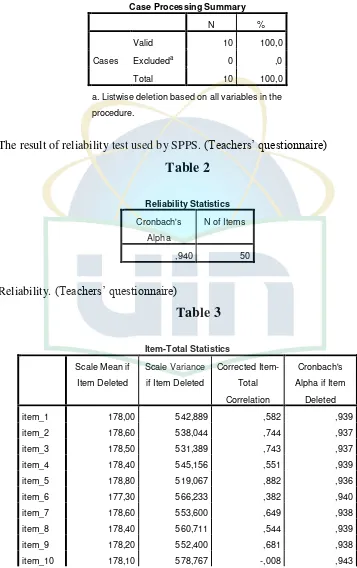
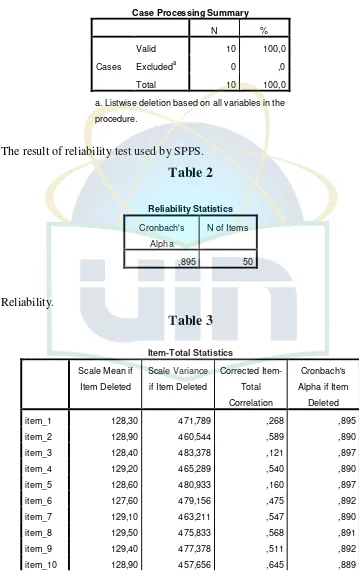
Appendix 7 The Result of Reliability of Questionnaires ...98
Appendix 8 The Assessments ... ...104
Appendix 9 ANABUT (Analisis Butir Soal)... ... ...106
Appendix 10 The Old RPP ... ...107
Appendix 11 The Current RPP ...110
Appendix 12 Surat Pernyataan telah Melakukan Penelitian... ...117
This chapter is an introduction which consists of the background of the
research, the identification of the problem, the scope of the research, the
formulation of the problem, the purpose and significance of the research.
A.
The Background of the Research
Nelson Mandela once said that “Education is the most powerful weapon
which you can use to change the world.”1
The important idea is that the country
which has good quality in education can certainly be a developed country such as
Finland. Started from an agricultural country which was not well-known, today
Finland goes forward in technological aspect. For instance, the product of Nokia
is spread in the world market. The excellence of Nokia which has varied
innovation, commercial enterprise, and technological improvement makes this
country as a developed country like Germany, Japan, and the United States.2 Not
only is the improvement supported by research and technological industry, but it
is also supported by education.
The education in Finland is categorized best because the country produces
high quality generations. For example, in 2013, 93% the citizens in Finland
graduated from Senior High School which was 17.5% higher than those in the
United States of America. Then, more than 66% students attended the university
which has the best quality in Europe.3
In addition, the international survey of Organization for Economic
Cooperation and Development (OECD) in 2012 reported that Finland was
1
http://www.brainyquote.com (retrieved on December, 26th 2014).
2
SAINS Indonesia, Budaya Inovasi di Finlandia Patut Ditiru, www.sainsindonesia.co.id. (retrieved on December, 26th 2014).
3
included in one of high-performing countries besides China and South Korea. For
instance, in 2012, the Program for International Student Assessment (PISA) which
stands for testing literacy in three competence fields like mathematics, science,
and reading shows that Finland was ranked first out of 65 countries for
mathematics and science. Further, it was also ranked first out of 65 countries for
reading.4 The evidence supported the assumption that teacher quality was high
because the achievement of each subject indicated a positive effect from teacher’s
educational coursework. In line with this, the teaching process was assumed
effective because of high student achievements.
Unlike Finland, student achievement in Indonesia has been considered
low. In 2012, the Program for International Student Assessment (PISA) showed
that Indonesia was ranked 64 out of 65 countries for mathematics and science
respectively. In addition, it was also ranked 61 out of 65 countries for reading.5
The low achievement was likely to be related with the low quality of most
teachers. As we all may know, teacher is the crucial factor that determines
students’ achievement. Teachers have a powerful, long-lasting influence on their students. They directly affect how students learn, what they learn, how much they
learn, and the ways they interact with one another and the world around them.
Unfortunately, Indonesian government has low standard in selecting the
qualification of teachers. For instance, the Asian Development Bank (ADB) in
2006 reported that more than 90% teachers in Madrasah taught lessons which
were not in their field such as biology, chemistry, English, and math.6 This fact
indicated that Madrasah teachers in Indonesia had low quality in teaching because
of low competency and qualification.
Moreover, James H. Strong states in his book that some studies from
Darling-Hammond and Fidler about “Teacher Quality” conclud that the teachers
who teach a subject for which they are not prepared do not provide student needs
4
Andreas Schleicher, PISA 2012 Results in Focus, www.oecd.org/pisa., p. 12 (retrieved on November, 6th 2014).
5
Ibid., pp. 3 – 5.
6
as good as certified teachers.7 Based on the explanation, it can be said that
teachers who are well-qualified in their own fields become ineffective in teaching
a subject for which they are not prepared. Consequently, this problem causes low
students achievement.
On the other hand, there are three Islamic Senior High Schools in South
Jakarta, which are considered good by public such as MAN 4 Jakarta, MAN 11
Jakarta and MAN 19 Jakarta. The student achievement in those schools is
categorized high because of high mean scores of Ujian Nasional (UN), especially
for English subject. For instance, in 2013, the mean score of English subject at
MAN 4 Jakarta for IPA was (7.70), IPS (7.47), BAHASA (7.14) and
KEAGAMAAN (6.49). Based on the result, it can be assumed that the English
teaching process in those schools are effective because of high student
achievement.
The above explanations emphasize the idea that effective teaching affects
high student achievement. For that reason, creating an effective teaching becomes
an important aspect for Indonesia as a developing country to produce future
generations who can compete with other people in the world. However, designing
an effective teaching is not easy because the teachers have to apply some
strategies that lead to effective teaching. Therefore, in this study, the researcher
conducted a research about An Investigation of the Practice of Effective Teaching
Strategies in Three Islamic Senior High Schools in South Jakarta.
Meanwhile, in conceptualizing the effective teaching strategies, the
researcher used dynamic model. The model developed by Creemers and
Kyriakides was used because it relates teacher behavior in the classroom with
student achievement gains. The model refers to eight effectiveness strategies that
describe teachers’ instructional role. The strategies are orientation, structuring, questioning, teaching modeling, applications, teacher role in making classroom a
learning environment, management of time, and classroom assessment.8
7
James H. Stronge, Qualities of Teachers, (Alexandria: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development ASCD, 2007), 2nd Edition, p.8.
8
In summary, there is a fact that teacher quality in Indonesia has been
considered low due to low student achievement gains. However, there are three
Islamic Senior High Schools in South Jakarta which are categorized good by
public because of high student achievement gains, especially English subject in
UN (Ujian Nasional). For that reasons, the researcher is interested in checking
whether the teachers in those schools practice the effective teaching strategies.
Moreover, there are not many studies especially “skripsi” that look at whether the
teachers practice effective teaching strategies.
B.
The Identification of the Problem
Referring to the background above, there are four factors that cause the
teaching process in Indonesia is not effective.
1. Students’ achievement in Indonesia has been considered low. Based on
PISA in 2012, the country was ranked 64 out of 65 countries for
mathematics and science respectively. Further, it was also ranked 61 out of
65 countries for reading.
2. Based on the data from Asian Development Bank (ADB) in 2006,
Indonesian government still accepted the teacher’s candidates who do not
appropriate in their field.
3. Low student’s achievement in Indonesia proves that the teachers still do
not practice the effective teaching strategies.
4. It was assumed that teachers in three Islamic Senior High Schools in South
Jakarta had practiced the effective teaching strategies since student
achievement in those schools had high achievement in Ujian Nasional.
However, there has not been any study that looks at this practice.
C.
The Scope of the Research
There is an assumption that teachers in Indonesia do not practice the
effective teaching strategies because of low student achievement gains. Further, as
previously mentioned, there is no “skripsi” that look at whether teachers practice
Schools in South Jakarta which are known good by public because of high student
achievement gains in UN (Ujian Nasional), especially in English subject.
Therefore, this study investigates whether the teachers in three Islamic Senior
High Schools practice the effective teaching strategies.
D.
The Formulation of the Problem
The formulation of the problem in this study is: “Do the teachers in three
Islamic Senior High Schools in South Jakarta practice the Effective Teaching
Strategies at their regular teaching practices?”
E.
The Purpose and Significance of the Research
Based on the statement above, the purpose of the study is to investigate
whether the teachers in three Islamic Senior High Schools in South Jakarta
practice the effective teaching strategies at their regular teaching practices. The
result of the study will be useful for:
1. The researcher herself, to know the eight effective teaching strategies that
lead to an effective teaching. Further, observable attributes of effective
teaching is one step toward helping the researcher better understand what it
takes to be a good teacher.
2. Every teacher, to provide valuable data based on the teachers’ practice of
effective teaching strategies at the first and the second grade of three Islamic
Senior High Schools in order to evaluate their teaching activities for
creating an effective teaching.
3. Undergraduate students, to conduct the related issues on the practice of
effective teaching strategies.
4. Other people and everyone who reads this study can take benefit from this
and know the eight effective teaching strategies in increasing student
achievement gains.
The researcher wants to get an answer whether the teachers in three Islamic
Senior High Schools really apply the eight effective teaching strategies in their
This chapter presents theoretical framework. It is divided into four parts.
Part A discusses about effective teaching. Part B discusses about the application
of effective teaching strategies. Part C discusses the advantages of eight effective
teaching strategies; and part D discusses about previous studies related to the
effective teaching.
A.
Effective Teaching
1. The Concept of Teaching
Teaching is frequently considered as a simple process for those who
master their subjects. However, the idea of teaching is related to a complex
process which is fulfilled with varied people in a complicated social institution.1
In line with this, Brown said that as a complex process, teaching requires
teachers not only to deliver the material, but also to guide and facilitate learning,
to enable the learner to learn, and to set the condition for learning. Indirectly, this
process provides teachers to create an academic cooperative environment in the
school.2
The content of learning may be facts, procedures, skills, ideas and values
which are applied in the learning activities. Moreover, the content is useful in
some activities such as comprehending the material, providing student needs, and
solving the learning problem which are included in the teaching objectives.3
1
Bruce R. Joyce and Berj Harootunian, The Structure of Teaching, (Chicago: Science Research Associates, 1967), p. 1.
2
H. Douglas Brown, Principles Of Language Learning And Teaching Classroom, (New York: Oxford University Press, 1987) p. 44.
3
In addition, Moore explains that teaching is an activity which provides
students to maximize their abilities in all aspects of development.4 Meanwhile,
Nathaniel Gage argues that:
As an instrumental art, teaching is something that departs from recipes, formulas, or algorithms. It requires improvisation, spontaneity, the handling of hosts of considerations of form, style, pace, rhythm, and appropriateness in ways so complex that even computers must, in principle, just as they cannot achieve what a mother does with her five-year-old or what a lover says at any given moment to his or her beloved.5
Related to the statement above, Gage states that not only is an art regarded
as a component of teaching, but science is also included as the other one.
Teaching has a scientific basis which its applications are derived from research.
Further, it is called as an art because it depends on the teachers’ intuition
combined with teacher’s experiences at the real teaching practice. Thus, teaching
can be viewed as having both artistic and scientific components.6
Based on the opinions given by the experts, the researcher can conclude
that teaching is a complex process which involves students’ diverse ability and
backgrounds in terms of linguistic, cultural, racial, and ethnic diversity. Teaching
is also called as an intentional activity concerned with student learning.
Moreover, teaching is a combination between science and art. It requires
best practice to help students learn essential skills and attitudes. Further, teaching
has aspects that cannot be learned by scientific knowledge alone but instead
depend on an individual belief based on personal experiences.
2. The Concept of Effectiveness
Defining the effective teacher, effective teaching and teaching
effectiveness can be complex and controversial. Effectiveness can elicit strong
feelings because it is sensed connections with ideas of professional competency
4
Keeneth D. Moore, Effective Instructional Strategies, (London: SAGE Publications, Inc, 2012), pp. 3 – 5.
5
Nathaniel Gage, an Unpdate of the Scientific Basis of the Art of Teaching (mimeographed), (Palo Alto, CA: Stanford University, 1984), p. –.
6
and high stakes responsibility in some systems. Personal teachers’ credibility
about professional autonomy may be questioned by the term of effectiveness.7
According to Moore, he argues that effectiveness covers the area of study,
pupils, and learning environment. Mastering the subject, analyzing student needs,
and managing classroom environment are important aspects that can support the
effectiveness of the teaching practices. These activities must be applied by the
teachers because it is related to the teaching objectives. 8
In line with this, Arrends states that the ultimate goal of teaching is that
providing students to become autonomous learners. In this part, students are
expected to provide their learning strategies and use the strategies in solving their
learning problems. The teachers’ role is that facilitating and guiding them to be an independent learner.9
Based on the above explanations, it can be concluded that effectiveness in
this study is focused on successful teaching process which can help students
achieving learning objectives and create students to become autonomous learners
by combining teacher’s competency and accountability.
3. The Concept of Effective Teacher
It has been recognized generally that teachers bring significant effect that
influence on student learning and achievement. The increasing the overall
numbers of effective teachers will automatically lead to the improvement of
effective teaching. Actually, the term of effectiveness gives multiple contributions
inside of the teaching work. For example, it is related to the basic goal of teacher
educational programs which provide the same learning environment to all diverse
students. Further, it also assists students to solve their learning problems. Related
to this goal, the future teachers have to master multiple teaching strategies to be
applied in the class. Furthermore, the teachers have to manage learning
7
James Ko, Effective Teaching: A Review of Research and Evidence, CfBT Education Trust, 2013, p. 5.
8
Moore, op. cit., p. 28.
9
environment by using those strategies. These goals can lead teachers to become
effective teachers.10
Effective teacher is a major component that affects on students learning. It
brings more effect if compared with the other components included in school
systems like the measurement of teaching and learning environment and the
standard of after-school programs.11
In line with this, effective teacher is called as a major component because
of the quality of them who has characteristics of the teacher as a personal; teacher
preparation; classroom maintenance; and the way teachers manage their teaching
process started from the previous, after, and during the lesson. According to
James H. Strong, there are eight characteristics of effective teacher such as:12
a. The Role of Caring: effective teachers always pay attention to the
student needs and let their students know about that.
b. The Role of Fairness and Respect: effective teachers keep on showing
the equitable honor and knowledge to diverse students.
c. Social Interactions with Students: effective teachers use multiple
strategies to communicate with their students. It is addressed to create
supportive learning environment and improve student outcome.
d. Promoting Enthusiasm and Motivating Learning: teachers’ interest for
teaching, learning, and their lesson has been demonstrated to become a
crucial part of effective teaching, both providing the interaction
between students and enhancing student outcome.
e. A Teacher’s Attitude toward the Teaching Profession: effective teachers
operate their own education. They become a model that encourages
students to involve actively in the classroom activities. In line with this,
the teachers are active in improving their knowledge by attending
teacher training programs.
10
James H. Stronge, Qualities of Teachers, (Alexandria: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development ASCD, 2007), 2nd Edition, p p. 99.
11
Bill & Mellinda, Empowering Effective Teachers, (Chicago: Gates Foundation, 2010), p. 1.
12
f. The Role of Reflective Practice: effective teachers always analyze their
teaching practices in order to provide effective teaching.
g. Teachers of At-Risk Students: effective teachers of at risk-students are
always curious about student needs. Further, they are attempted to
support students reach the learning goals.
h. Teacher of High-Ability Students: effective teachers of gifted students
master multiple strategies that is useful to control diverse characteristics
of gifted students.
Effective teacher is a personality who typically focuses on the teacher’s
roles and the practices of teaching and learning process that can lead to the
improvement of student achievements. However, it can widely be explained
because rarely is the teachers’ role limited to direction only. At the real situations, teachers should promote their team teaching, involve them in wider leadership
roles in the school, and improve their teaching competence by join in the teachers
training programs.13
In addition, effective teachers are people who master their subject matter,
who get a permission to teach, and who deal with well-being of students. They
can generate students who success achieving their learning objectives. These
characteristics are needed for teaching, but they are not enough without four
higher-level attributes:14
a. Individual competence: Effective teachers are allowed to evolve
authentic human relationship by using their individual competences in
order to provide a democratic interaction between the learners and the
stakeholder in the school.
b. Positive characters: Effective teachers have positive characters that
influence on student development. Further, they use the characters to
lead the science and art of their teaching practices.
c. Teaching repertoire: Effective teachers manage a teaching repertoire to
encourage students to become an autonomous learner.
13
Ko, op. cit., p. 6.
14
d. Evaluation: Effective teachers analyze every single teaching practice in
order to create an effective teaching by finding student needs, solving
the learning problems, and improving student outcomes.
Moreover, effective teacher understands that effective teaching is not a
simple process which just teaches the material itself. At the real teaching process,
effective teacher must be creative to create new atmospheres that are managed
orderly. According to Danielson, four major skill areas are needed for effective
teaching.15
a. Quality Planning and Preparation
Before teaching in the classroom, effective teachers must take the time
for preparing the materials and activities which is related to the teaching
objectives. They have to (a) master the subject matter, (b) know student needs, (c)
use learning strategies, (d) know multiple teaching and learning strategies, (d)
create supportive application tasks, (d) evaluate student outcomes.
b. The Classroom Environment
Effective teachers can provide and manage a supportive learning
environment. In line with this, Danielson states that this process needs the abilities
to design a positive learning environment, to develop learning intelligence, to
organize the classroom, to control student attitude, and to arrange physical space.
c. Instructional Technique
Effective teachers have to master multiple teaching strategies that can
encourage student to be participated actively in the learning activities. Effective
teachers plan and use strategies that, convey the material clearly and accurately,
use effective questioning and discussion technique, engage students in learning,
provide feedback to students, and are flexible and responsive.
15
d. Professional Behavior
Effective teachers apply the professional attitudes that can lead to the
significant improvement to their school and community. They interact well with
people who contribute in the teaching and learning process.
Effective teacher helps students to do multiple tasks easily. They manage
diverse students to learn the material effectively.16 Moreover, they combine the
teaching strategies with more responsive approach to their students. Actually, to
be an effective teacher, not only do the teachers have to emphasize on the teaching
strategies but they also have to develop their qualities.17 In line with this, the
research which was done by Linda Darling Hammond states that there are five
qualities needed by teachers:18
a. Applying appropriate verbal ability during the teaching process.
b. Mastering the subject matter.
c. Promoting higher-order thinking skills.
d. Evaluating the teaching and learning process.
e. Flexible, provide easily new creative learning environments that deal
with student needs.
Based on the above definitions, it can be concluded that effective teacher
is an individual who combines teaching instructional procedures and teachers’
effective characteristics to achieve the learning objectives. Further, effective
teacher is a crucial component that determines student outcomes inasmuch as
he/she directly interacts with all students in the teaching and learning process.
4. The Concept of Effective Teaching
According to Chirs Kriyacou, effective teaching can be defined as a
teaching process that successfully accomplishes the student activities of obtaining
16
Arthea J.S Reed, Verna E. Bergemann, and Mary W. Olson, In The Classroom, (Boston: The McGraw-Hill Companies, 1998), p. 42.
17
Peter Westwood, Effective Teaching, Australian Journal of Teacher Education, 1996, p. 15.
18
knowledge designed by the teacher. It concerns on the importance of learning
activities and the causes of the effectiveness. At the real teaching situation,
teachers apply effective teaching strategies that lead to the effective learning.
Further, mastering the lesson and comprehending the effective teaching strategies
can lead to the basic for effectiveness.19
Teaching effectiveness can be comprehended by learning the strategies
that can lead to the definition of effective teachers; effective teachers behaviors
applied at the real teaching situations. These activities require a deep inside of
subject matter, learning theory of diverse students, designing, teaching strategies,
student needs, and evaluation of student outcomes. Further, the activities also
involve a teacher’s competence to reflect, work with team teaching, and keep on
establishing professional teaching in order to create students’ achievement which
can perform at high levels of success.20
On the other hand, not only does effective teaching focus on success but it
also concerns with appropriate values. It is related to behaviorist values which
focus on what teachers did in using strategies which can produce positive
long-lasting effects on student understanding. Thus in considering research on effective
teaching, it is important to consider successful teaching strategies.21
Based on the above definitions, it can be concluded that effective teaching
is a complex teaching process which involves a set of behaviors that effective
teachers include in daily professional practice that successfully leads to the
improvement of student progress.
Further, not only does effective teaching need the teaching strategies, but
effective teaching also requires human abilities, instinct, and intelligence to
maximize teaching and learning process. Furthermore, effective teaching is
defined as a teaching process that successfully achieves the teaching objectives by
producing autonomous learners and high student outcomes.
19
Chirs Kyriacou, Effective Teaching in Schools: Theory and Practice, (Cheltenham: Stanley Thornes, 2009), p. 8.
20
Robert A. Barry, Teaching Effectiveness and Why It Matters, (Oregon: Marylhurst University, 2010), pp. 3 – 4.
21
5. The Characteristics of Effective Teaching
There have been some experts proposing the characteristics of effective
teaching. All of them have similar ideas in the characteristics. The first is that
Richard Dunne and Ted Wragg who state that two characteristics are essential for
effective teaching. The first characteristic is teacher behavior which focuses on
facilitating students’ learning in order to create high student achievement gains. The other one is teacher competencies that include intelligence, communication,
teaching experiences, and teacher’s educational background.22
The second expert is Cheryll M. Adams and Rebecca L. Pierce who state
that teacher competencies are also important to provide effective teaching.
Therefore, there are five key characteristics of effective teaching:23
1. Understanding pedagogic theory
2. Designing supportive classroom environment
3. Teaching experience
4. Self-reflection and modification of techniques
5. Flexibility
In addition, Chirs Kyriacou state that not only teacher’s competencies that
should be emphasized, but teaching strategies must also be used to provide
effective teaching. Therefore, the process-product studies which have dominated
research on effective teaching result ten characteristics of effective teaching that
focus on teacher behaviors to produce high student achievements:24
1. Clear explanation
2. Providing authentic tasks
3. Maximizing learning activities
4. Managing time on-task activities
5. Encouraging students to be participated actively in the classroom
6. Understanding student needs and evaluating student outcomes
7. Delivering the material orderly
22
Richard Dunne and Ted Wragg, Effective Teaching, (New York: Taylor&Francis e-Library, 2005), p. 4.
23
Cheryll M. Adams and Rebecca L. Pierce, Characteristics of Effective Teaching, p. 1.
24
8. Giving positive feedback to students
9. Reaching the learning objectives
10. Using appropriate questioning techniques
In line with this, high-level of student performances cannot be reached
without five Characteristics of Highly Effective Teaching and Learning
(CHETL).25
1. Learning Climate: a supportive learning environment that encourages
students to be participated actively in the classroom.
2. Classroom Assessment and Reflection: a teacher always evaluates
student outcomes and acts as a good model that is followed by the
students.
3. Instructional Rigor and Student Engagement: a teacher provides student
critical thinking and finds student needs to solve the learning problems.
4. Instructional Relevance: creating authentic learning tasks that can be
applied by students in their daily activities.
5. Knowledge of Content: a teacher has to master the subject matter and
multiple teaching strategies.
Based on the explanations given by the experts, it can be concluded that
the characteristics of effective teaching are typical quality of successful teaching
process that can lead to effective teaching. The characteristics which are required
for effective teaching are based on teacher’s competencies and teaching strategies
applied by the teachers.
6. Strategies in Effective Teaching
Instructional strategies are decisions about organizing people, materials,
and ideas to produce learning. They determine the objectives of classroom
instruction, the means that will be employed, and the ways results will be
evaluated. Teaching strategies encompass both decisions about instructional goals
and decisions about the means of achieving those goals with particular students.
25
Further, the reason that the teacher must posses a range of teaching strategies is
simply because different styles of teaching behavior are useful for different
educational purposes, and every teacher seeks educational ends that demand more
than one way of teaching.26
There have been some experts proposing the strategies for effective
teaching. All of them have similar ideas on the strategies for effective teaching.
First, Daniel Muijs and David Reynold describe the effective direct instructions,
such as:27
1. Clearly structured lessons: the lesson should have a clear structure, so
pupils can easily understand the content of the lesson and how it relates
to what they already know.
2. Clear, structured presentations: within this overall structure, it is
recommended that material should be presented in small pitched at the
pupils’ level, which are then practiced before going on to the next step.
3. Pacing: it is recommended by teacher effectiveness researchers that
lessons designed to teach basic skills are paced in such a way that during
weekly or monthly reviews pupils are able to respond correctly in 90-95
per cent of cases.
4. Modeling: a useful procedure to follow when teaching certain topics is to
explicit model a skill or procedure. Modeling means demonstrating a
procedure to learners.
5. Use of conceptual mapping: a conceptual map is a framework that can be
presented to pupils before the topic of the lesson is presented.
6. Interactive Questioning: it is an effective and important part of the
lesson. It can lead to interactive teaching.
In line with this, another expert, Peter Westwood adds that there are some
selected forms of effective teaching:28
26
Joyce and Berj Harootunian, op. cit, p. 94.
27
Daniel Muijs and David Reynolds, Effective Teaching, (London: SAGE, 2001), pp. 30 – 32.
28
a. Presentation and explanations: presenting information to children and
providing explanations are two of the main activities in which teachers
engage. Effective teaching requires clarity in presentation and
explanation.
b. Questioning: effective teaching must involve careful attention to
classroom questioning.
c. Teaching Task-Approach Strategies: effective instruction must include a
focus on teaching students efficient ways of approach in the tasks they
are set.
d. Adapting instruction: adaptive instruction is defined as instruction geared
to the characteristics and needs of individual students.
In addition, Creemers and Kyriakides develop a dynamic model which
relates teacher behavior in the classroom with student achievement gains. The
model refers to eight effectiveness strategies that describe teachers’ instructional
role.29
1. Orientation
It refers to the teacher behavior in providing the objectives for which a
specific task, lesson, or series of lessons takes place and challenges students to
identify during the lesson the reason why a particular activity takes place.
2. Structuring
A structuring task may refer to the achievement of a single objective or to
the relation of the elements of the lesson in relation to multiple objectives.
Moreover, schools and teachers can structure learning activities to emphasize their
intrinsic value so students become totally involved and experience the type of
flow described earlier.30
29
Bert P.M. Creemers, and Leonidas Kyriakides, The Dynamics of Educational Effectiveness, (New York: Routledge, 2008), p.104 – 117.
30
3. Questioning Techniques
Questioning is an important part of the teaching-learning process because
it enables teachers and students to establish what is already known, use and extend
this knowledge, and then develop new ideas. Good questioners must be skilled in
formulating good questions: Question must be asked at the appropriate level. They
must be of the appropriate type and must be worded properly. Moreover, the kinds
of questions asked, the way they are asked, and the responses given affect both the
self-esteem of the students and their participation.31
Effective teachers usually raise questions that few students can answer
correctly or that have no single correct answer at all. Questions may be
categorized as being “narrow” or “broad”. Narrow questions usually ask for only
factual recall or specific correct answer, whereas broad questions seldom can be
answered with a single word. Moreover, broad questions do not have one correct
answer and call on students to reach beyond simple memory. Broad questions
prompt students to use the thinking process in formulating answers. Both narrow
and broad questions contribute to the learning process.
As an effective teacher, you must ask the right types of questions. There
are three types of questions:32
a. Focusing questions, which may be factual, empirical, productive, or
evaluative, are used to direct student attention. Focusing questions can
determine what has been learned by students, motivate and arouse
student interest at the start of a lesson or during the lesson, stimulate
involvement and check understanding during a lesson, and check
students’ understanding of lesson material at the close of a lesson.
b. Prompting Questions use clues that help students answer questions or
correct initially inaccurate responses. Thus, a prompting question is
usually a rewording of the original question-with clues added.
c. Probing Questionsaim at correcting, improving, or expanding a student’s
initial response. They compel the students to think more thoroughly
31
Moore, op. cit., p. 303.
32
about the initial response. Probing questions can be used for correcting
an initial response, eliciting clarification, developing critical awareness,
or refocusing a response.
Certain techniques associated with asking questions tend to increase the
quantity of and enhance the quality of the students’ responses.33
a) Redirecting
Redirecting is a technique that is useful for increasing the amount of
student participation. It allows you to draw students into a discussion by asking
them to respond to a question in light of a previous response from another student.
b) Wait Time
Students need time for thinking and pondering the responses they will
give to your questions. Research by Rowe (1974a, 1974b, 1978), however, has
shown that teachers wait, on average, only about 1 second for students to give an
answer. Rowe’s research also revealed that when teachers learned to increase wait
time from 3 to 5 seconds, the following results occurred such as student response
time increased, failure to respond tended to decrease, students asked more
questions, unsolicited responses tended to increase, and student confidence
increased.
c) Halting Time
When presenting complex material, you need to learn to halt in what you
are saying and give students time to think. This pause is referred to as halting
time.
d) Reinforcement
Your reinforcement-that is, your pattern of positive reaction- will have a
powerful effect on the direction of the interaction in the classroom. Rewards and
praise often encourage students to participate. Phrases such as “Fine answer,”
33
“Great,” “What an outstanding idea,” and “Super” may be used when rewarding students’ correct answers. Reinforcement is often a good idea, but the too -frequent application of reinforcement can negate the benefits of using wait time.
You should allow as many students as possible to respond to the question, then
reinforce all of them for their contributions. You can always return to the best
answer for further comment.
4. Teaching-modeling
The term teaching model is used to describe an overall approach to or
plan for instruction. The attributes of teaching models are a coherent theoretical
framework, an orientation toward what students should learn a specific teaching
procedures and structures.34
Modeling is a powerful motivational technique in which people whom
students admire demonstrate (nonverbally) the values and behaviors they want
students to acquire.35 The most notable model in most classrooms will be the
teacher. The enthusiasm and sense of wonder you show for learning will often be
passed on to students. Consequently, if you appear interested and excited about a
lesson, students often become transfixed, eager to find out what is so interesting.
Indeed, research suggests that enthusiastic teachers produce higher academic
achievement by students.
Effective teachers may either present a strategy with clarity or invite
students to explain how they solve a problem and subsequently use that
information for promoting the idea of modeling.
5. Application
This strategy focuses on learning activities that students are expected to
perform. It refers to some parts of the lesson, to the whole lesson, or even to a
series of lessons. Actually, in this part the students are expected to perform.
34
Arends, op. cit., p. 25.
35
6. Teacher role in making classroom a learning environment
This strategy looks at different strategies that the teacher uses in order to
keep different groups of students involved in the classroom interactions. It refers
to the teacher’s contribution in creating a learning environment in his or her
classroom, and five elements of the classroom as a learning environment are taken
into account: teacher-student interaction, student-student interaction, students’
treatment by the teacher, competition between students, and classroom disorder.
7. Management of time
Management of time is one of the most important indicators of a
teacher’s ability to manage the classroom in an effective way. Effective teachers are expected to organize and manage the classroom environment as an efficient
learning environment and thereby to maximize engagement rates.
8. Classroom Assessment
Assessment is seen as an integral part of teaching; formative assessment,
especially, is one of the most important factors associated with effectiveness at all
levels, especially at the classroom level.
Based on the opinions given by some experts, the researcher prefers to
use the effective teaching strategies from Creemers and Kyriakides because the
eight strategies of the dynamic model relate teacher behavior in the classroom
with student achievement gains.
B.
The Application of Effective Teaching Strategies
The importance of teaching, and of how teachers teach in their classroom,
is being recognized as of key importance in many ways. In this part, the
researcher will explain the application for each effective teaching strategy based
on Creemers and Kyriakides in the practice of teaching and learning process.36
36
1. Orientation
a. Starting the lesson with a review,
b. Practice of what was learnt during the previous lesson,
c. Refers to the purpose of the activities,
d. Refers to the stage at which an activity takes place,
e. Take other perspectives into account during the orientation tasks,
f. Encourage students to identify the teaching objectives.
2. Structuring
a. Beginning with overviews and/or review of objectives,
b. Outlining the content to be covered and signaling transitions between
lesson parts,
c. Calling attention to main ideas,
d. Reviewing main ideas at the end of the lesson.
3. Questioning techniques
a. Support the student to know something,
b. Suggest the students to get information,
c. Asses students’ skills of critical thinking,
d. It teaches the students to think critically.
4. Teaching-modeling
a. emphasize on applying a single strategy for a group of students,
b. emphasize on using multiple strategies for a group of students,
c. develop different strategies for a group of students,
d. Demonstrate the teacher’s opinion,
e. Demonstrate how the teacher wants the students to learn,
f. Demonstrate what the teacher want the student can do it too.
5. Applications
b. Emphasize the immediate exercise topics taught during the lesson,
c. Provided direct feedback at either individual or a group level,
d. Examine the number of purposes that have to be achieved,
e. Monitor and supervise during application activities.
6. Teacher role in making classroom as a learning environment
a. Refer to the number of interactions between teacher and students,
b. Attempt of teachers to create a businesslike and supportive
environment for learning,
c. Teacher’s ability to establish rules,
d. Persuade students to respect and use the rules,
e. Maintain them in order to create a learning environment.
7. Management of time
a. Opportunity to learn,
b. Time on task,
c. Organize the classroom environment,
d. Take into account the time allocated to different phases of the lesson.
8. Classroom assessment
a. Evaluate with various ways and from many sources,
b. Measure the knowledge and the student skill,
c. Require of applying the knowledge or experience,
d. Contextual assignment and relevant,
e. Process and product can measure.
C.
The Advantages of Effective Teaching Strategies
The advantages are specifically based on each factor of the Dynamic
Model which is related to the practice of teaching and learning process.37
37
1. Orientation
This strategy provides students to participate actively in the classroom. It
also may encourage students to identify the purposes that can be achieved by
carrying out a task and therefore increase their motivation towards a specific task,
or lesson, or series of lessons. Further, not only do the students get some benefits,
but the teacher also can find out to what extent pupils have grasped the content of
previous lessons, and therefore to what extent this content will need to be
re-taught.
2. Structuring
Structuring elements not only facilitate memorizing of the information but
allow for its apprehension as an integrated whole, with recognition of the
relationship between parts. It is expected that structuring tasks not only are clear
for students but also help them understand the structure of the lesson.38 Further,
this allow pupils to gain a sense of mastery over the content and will stop pupils
getting bored or losing the thread of the lesson. All this ensures not only that
pupils will remember better what they have learnt, but will help them to
understand more easily the content as an integrated whole, with recognition of the
relationships between the parts.39
3. Questioning techniques
This is the best way of checking pupils’ retention of material taught
earlier. Questioning allows the teacher to check her/his pupils’ understanding of
the lesson. Then, questioning allows pupils to practice and master the topic taught
before having to go on the next topic. The last one, answering questions allows
pupils to clarify their own thinking and understanding of the concept taught, and
makes them verbalize their thinking, especially if they are asked to explain the
method or knowledge they used to work out a particular answer. This will help
38
Ibid.
39
them develop verbal skills they will need not only in school but in the workplace
as well.40
4. Teaching-modeling
This strategy can help students to solve different types of learning
problems. This strategy may encourage students not only to use but also to
develop their own strategies for solving problems.
5. Applications
Application tasks can develop student’s learning by giving some activities
related to the teaching objectives.
6. Teacher role in making classroom as a learning environment
This strategy can help the teacher to solve a specific problem (e.g
classroom disorder, fights between students) or create an atmosphere that avoids
further existence of similar problems. Further, it can help teacher deals with
negative effects of competition. Furthermore, it can help students to see the
positive aspects of competition and avoid the negative one.
7. Management of time
This strategy can help the teacher to guide and maximize the learning time.
Not only is this strategy useful for the teacher, but it can provide students to do
and finish the application tasks on time.
8. Classroom assessment
This strategy is useful to find the students’ needs and to evaluate the teacher’s teaching practice. It can also create positive implications for teaching and learning by providing constructive feedback.
In general, it can be concluded that if the teachers practice the strategies of
effective teaching, it will make the teaching and learning process become more
40
interesting. Further, the students can be more motivated to involve in the process.
Furthermore, by applying those strategies, it can easier for both teachers and
students achieve the teaching objectives such as increasing the student
achievement and helping students to become autonomous learners. Consequently,
the teaching and learning process will be effective.
D.
Previous Studies
Related to the practice of effective teaching strategies, there are three
studies from Muhammad Yusup, Sukadi, and Reza Karimi, Fawzy Elbarbry with
Jeff Fortner which discussed the effective teaching in different ways.
First, the study came from Muhammad Yusup about “Strategi Efektif Pembelajaran Fisika: Ajaran Konsep”.41
In this paper, he was intended to explain
effective strategies applied in teaching physics which gave a conceptual
understanding before explaining mathematics formulas. As a result, he presented
three strategies which could help students developing their conceptual
understanding by using multi-representation, exploring broader context, and using
comparing and contrasting process. These strategies were based on the research in
terms of physics education.
Second, the study came from Sukadi about “Efektivitas Pengajaran Dalam Mencapai Kompetensi Siswa Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan”.42
In this paper, he
was intended to find out the relationship between insight teacher’s profession,
educational background, teaching experiences, teaching and learning task with the
effective teaching and students’ competence. In summary, the hypotheses showed
that there was a positive and significance connection between insight teacher’s
profession, educational background, teaching experiences, teaching and learning
task with the effective teaching and students’ competence.
Third, the study came from Reza Karimi, Fawzy Elbarbry, and Jeff Fortner
about “Integrative Student Learning: An Effective Team Learning Activity in a
41
Muhammad Yusup, “Strategi Efektif embelajaran Fisika: Ajaran Konsep”, Skripsi pada Program Studi Pendidikan Fisika FKIP Universitas Sriwijara, pp. 1 – 4.
42
Learner-Centered Paradigm”.43 The purpose of this study was that an Integrative
Student Learning (ISL) activity was developed with the intent to enhance the
dynamic of student teamwork and enhance student learning by fostering
critical-thinking skills, self-directed learning skills, and active learning. As a result, the
ISL activity was proven to be an effective learning activity that promotes
teamwork and integration of didactic pharmaceutical sciences to enhance student
learning of didactic materials and confidence in searching online library resources.
It was found that all of this can be accomplished in a short amount of class time
with a very reasonable amount of preparation.
Based on the studies above, it could be concluded that this study had
different intention with the three studies. The three studies just specifically
focused on strategies in teaching physics, pharmaceutical, and the relationship
between teacher’s background and teaching and students’ competence. However,
this study focused on the investigation of the practice of effective teaching
strategies of Dynamic Model such as orientation, structuring, questioning,
teaching-modeling, applications, teacher role in making classroom a learning
environment, management of time, and classroom assessment in the schools
which were categorized good by public because of the high mean score of English
subject in UN. The purpose of this study was that investigating whether the
teachers in three Islamic Senior High Schools in South Jakarta practice the
effective teaching strategies in their regular teaching practices. Therefore, the
researcher conducted the research about “An Investigation of the Practice of
Effective Teaching Strategies in three Islamic Senior High Schools in South
Jakarta”.
43
BAB III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter presents about the method of the research, the time and place
of the research, the sample and population, the instruments and techniques of
collecting data, the techniques of data analysis, and trust worthiness.
A.
The Method of the Research
Mix methods were used in this study, in which a survey (quantitative) and
classroom observation, documentation, and interview (qualitative) were
conducted. A mixed methods study involves the analysis of both quantitative and
qualitative data in a single study in which the data are collected sequentially, are
given a priority, and involve the integration of the data at one or more stages in
the process of research.1 There were four common mixed-methods designs such as
convergent designs, embedded designs, exploratory designs, and explanatory
designs.
Embedded designs were used in this study. In embedded designs, a
researcher collects both qualitative and quantitative within the same general time
frame. One general approach dominates, perhaps a qualitative approach, but more
often a quantitative one with the other approach serving in a secondary,
supplementary role.2 However, in this study, qualitative approach dominated and
quantitative one served as a supplementary role. Moreover, to make more
convincing conclusions, the researcher used triangulation that would be explained
clearly in part F.
1
Uwe Flick, Introducing Research Methodology, (London: SAGE, 2011), p. 189.
2
B.
The Time and Place of the Research
The researcher conducted the research from May, 7th up to June, 7th 2014,
in three Islamic Senior High Schools in South Jakarta. They were MAN 4 Jakarta,
MAN 11 Jakarta, and MAN 19 Jakarta.
C.
The Sample and Population
The sample of this study was ten English teachers at the first and the
second grade of three Islamic Senior High Schools in South Jakarta. The sample
was chosen by using proportional stratified sampling. This technique selects a
random sample from each stratum after identify the members of each stratum.3 In
this situation, the researcher took 6 out of 8 English teachers in MAN 4 Jakarta.
The researcher also took 3 out of 5 English teachers in MAN 11 Jakarta. In MAN
19 Jakarta, the researcher took 1 out of 3 English teachers. So, there were