THE EFFECTIVENESS OF USING PICTURES
IN TEACHING PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE
(An Experimental Study at the Seeond Year Students of SMP Perwira Ulujami Jakarta Selatau)
A PAPER
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers' Training in Partial Fulfillment of One of the Requirements
for the Degree of Strata 1 (81)
by
DewiMulia
102014023788
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS' TRAINING FACULTY
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH
JAKARTA
(An Experimental Stndy at the Second Year Students of SMP Perwira Ulnjami Jakarta Selatan)
A "Paper"
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Ieacher's Training in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
for the Degree of Strata-l (S.Pd) in English Language Education
By:
DewiMnlia
102014023788
Approved by Advisor
NIP. 150249910
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
TARBIYAH AND TEACHER'S TRAINING FACULTY
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY JAKARTA
ENDORSEMENT SHEET
The Examination Committee of the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers'
Training certifies that the Paper entitled "The Effectiveness ofUsing Pictures iu
Teachiug Present Continuous Tense" (An Experimental Study at the Second Year of SMP Perwira Jakarta Selatan), written by Dewi Mulia, student's registration number: 102014023788, was examined by the Committee on 6th June
2008, and was declared to have passed and, therefore, fulfilled one of the
requirements for the academic title of S.Pd. (Bachelor of Alis) in English
Language Education at The Department of English Education.
Jakarta, 6th June, 2008
CHAIRMAN
EXAMINATION COMMITTEE
n
I
Drs. Syauki M.Pd.
セGャGMセP
__
セ
NIP. 150246289
)
HセL
Jz4l--:-I. Drs. Baluul Hasibuan, M.Ed
L
!
)
セセ
-Neneng Sunengsih, S.Pd.NIP. 150293232
EXAMINERS SECRETARY
2. Dr. Atig Susilo, MA )
NIP. 150 182900
Acknowledged by:
Dean of Tarbiyah and Teachers' Training Faculty
ALL l'mlses be toallセィ Loyd of the "-",,,veyse, theセlBBMGPィエAZZj "1od foy ttls bLessl""0,
PBMャ、セBLL」・L hell'セBB、 Love whoィセウ bestowed "-1'0"" the wYlteyl""cO""-l'Letl""0thls SRxll'sL
pwceセBB、 bLessl""0ls;"-1'0"" O"-Yl'Y0l'hetOカ|BMィセBLLMLLLLMセ、 SAWセウ[ O"-Yl'Y0l'het, hls
、・ウ」・BB、セBBエウL hls 」oBBMャGセBBャッBBD セBBB hls foLLoweys;.
In this occasion, the writer would like to express her gratitude and her
honor to the. foUowing persons:
I. Prof. Dr. Dede Rosyada, M.A, The Dean of Faculty of Tm-biyah and
Teacher Training,UINSyarifHidayatuUah Jakarta. 2. Drs. Syauki, M.Pd, the chief of English Department.
3. Dra. Hj. Farida Hmnid, M.Pd as her advisor, thanks for her sincere and
generous help and professional advices.
4. Her beloved father (Mussholli H.S), mother (Mimin Rukmini almh.) and
also for her brother mld sister Ntmnala and Abd. Qadir Zailani who always
pray and suppOli me to finish this paper.
5. All lecturers of English Department who have taught and educated the
writer during her study atUINSyarif HidayatuUah Jakarta.
6. Mrs. Sulikah, B.A, the headmaster of SMP Perwira and stuff, who has
7. Drs. H. Mahyudin, M.M. who help, motivate and encourage me to finish this skripsi. Thank you!
8. Her beloved friends, Yova, Sofie, Nasriah and her husband, Ade Irma, Afrie and Latif. Thanks for your motivation, care and support! Also Mahdi Abdul Aziz, her beloved one. Thank you for your suppOli, spirit 'Ind affection.
May Allah guide them and give them all happiness throughout their lives. Amin.
May, 8 2008
TABLE OF CONTENTS... iii
LIST OF TABLES... v
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
A. Background of Study 1
B. Limitation of Problem... 3
C. Question of Research 3
C. Objective of Study. 3
D. Method of Study... 3
E. Organization of the Study... 4
CHAPTER II THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A. Picture... 5
B. Present Continuous Tense 8
1. Form of Present Continuous Tense 8
2. Usage of Present Continuous Tense 11
3. Verb Usually not used in Present Continuous Tense 12
C. Teaching Present Continuous Tense by Using Pictures .. 13
CHAPTER III THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE RESEARCH
A. Methodology of Research 15
1. Place and Time of Research ;.. 15
2. Objective of Research ; 15
3. Population and Sample ; 15
4. Data Collecting 16
5. Data Analysis /...16
6. General Procedure of' Teaching Present Continuous
.'
7. General Procedure of Teaching Present Continuous
Tense without Using Pictures 17
B. Research Findings 18
1. Data Description , 18
2. Data Interpretation 23
CHAPTER IV CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
A. Conclusion 24
B. Suggestion 24
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTON
A. Background of Study
Language is a way of expressing ideas, feelings, by using movements, symbols, and sounds.! As an international language, English has an important role in the world. Related to that case, Julian Edge in her book stated, "English as the International language serves to many people as a bridge into the worlds of higher education, science, international trade, politics, tourism or any other venture which interest them. 2
It is not enough for students to have proficient ability if students cannot develop and master the skill in understanding and expressing the language in both oral and written. In this sense, language teacher has a role as communication teachers and, indeed, as a teachers in broadest sense.
Teaching of English is stressed on mastering the four basic skills: listening, speaking, reading and writing. Besides, the knowledge of grammar is one of the impOltant factors that the students should master because grammar enables the students to make statements about how to use the language. Mastering grammar should be integrated with the language skills and the language factors in order to make the students easier to understand the language during the communication. Grammar is needed even in the communicative ways, as J. B. Gunawan said, " ... Even in real communicative activities, in which learners usually do not concentrate on language forms, grammar cannot be put aside.,,3
Some of the problems that bring out an obstacle for the learner to comprehend English are the influences of the structure and pattern from their
I A. S Hornby, Oxford Advanced Learner's DictionmyofCul'l'ent English, (Oxford:
Oxford University Press, 2000). p. 721
2Julian Edge,Essentialsof EnglishLanguage TeacMng:3rd Edmon"(London: Longnial1.
2003),p.25
3J. B. Gunawan, "The Teaching of Grammar inCLT. Oriented Ell\iirol1mcnt,"Tejlin
own language. Some students think of grammar as rather boring subject. When they learn English they try to avoid the grammar that for them is confusing and hard to be understood.
Present continuous tense as a part of grammar rules sometimes also makes students confused. The effect is that they cannot use and understand properly the present continuous tense.
Asking the children to memorize formula of grammar with their usage is usually ineffective methods, sometimes children remember their meaning for a short period of time, and more over they forget the meaning.
To solve the problems in teaching present continuous tense the teachers can use suitable and interesting methods or techniques that are suitable to the students. Techniques depend on the teacher, the imagination, his creativity and the condition of class, a certain problem can be solved with the various techniques.4
Teacher can use various visual sources in teaching language, for instance: teaching language by using tape-recorders, pictures-flashcard and television, by using a suitable method, because the method determines what and how much is taught (gradation), how the meaning and form are conveyed (presentation) and what is done to make the use of the language unconscious (repetition).5
The writer will give another alternative technique to enrich student's comprehension by using pictures. Pictures are 110t just an aspect of ihethod but through their representation of place, object and people essential parts of the overall experiences.6Because pictures can direct the students to speak, another reason is that using picture in teaching present continuous tense is effective and helpful in teaching learning process, so the students feel easy in understanding and studying English.
4Mulyanto Socmurdi,Pengajal'Gn Bahasa AsingSebuahTilljaucJ11dari Seglldet(]dologi,
(Jakarta: Bulan Bintang, (975), p. 14.
5William Frances Mackey,Language Teaching Analysis,(London: Longman GrollpLtcl,
(965),p.xi
6Anclrc\v Wright, Pictures/or Language Learning:>.(Cambridge: Carnbridge University
3
In teaching present continuous tense the students are taught pattem of
verb to be, structure etc. In this paper the writer tries to use pictures in
developing their knowledge of present continuous tense. Visual aids are
important in teaching. Pictures can be used as teaching aids that can help the
students communicate in English. The aids are needed to develop their
language skill included grammar skill especially in present continuous tense.
B. Limitationof Problem
The limitation of the problem which will be discussed in this paper is
the teaching of present continuous tense using pictures at the second year of
SMP Perwira Jakarta Selatan.
C. Question of Research
The question of the research is: "Is there any significant difference in
the achievement of the students' English grammar especially in present
continuous tense taught by using pictures and without using pictures?".
D. Objective of Study
The objective of the study is find out whether there is a significant
difference in the achievement of the students' English grammar especially in
present continuous tense taught by using pictures and without pictures and
hopefully, this study will contribute many advantages to the English teacher in
implementing the teacher grammar teaching especially present continuous
tense. The result of the study hopefully can also assist students learning
grammar in an interesting way. Subsequently, it will assist the students in
upgrading their ability to communicate in English.
E. Method of Study
This research is done by usmg Experimental Method. The writer
conducted an experiment by teaching two different classes and then giving
them the test. In addition, the library study is also carried out by reading a
number of materials from books and other sources like magazine and journal
F. Organization of the Stndy
This sub chapter is intended to give a brief overview about the organization of the study from every chapter.
The first chapter is introduction. In this chapter there are seven sub chapters: (A) background of study, (B) limitation of the problem, (C) question of research , (D) objective of the study, (E) method of the study, (F)
organization of the study.
The second chapter is theoretical framework. In this chapter there are three sub chapters: (A) pictures, (B) present continuous tense, (C) teaching present continuous tense by using pictures.
The third chapter is the implementation of research. In this chapter there are two sub chapters: (A) research methodology and (B) research finding.
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A. Picture
According to Marianne Celce Murcia and Sharon Hills the meaning of
picture is that pictures are kind of visual instruction materials that might be
used more effectively to develop and sustain motivation in producing positive
attitudes toward English and to teach or reinforce language slalls. Picture can
also be used in various configurations to enhance leaming and practice. 1
Based on Webster New World Dictionary of American Englif.h
pictures are imagines or likeliness of an object, person or scenes on a flat
surface, especially by painting, drawing or photography.2
According to Andrew Wright picture is: Picture is the non-verbal
source of information. The non-verbal infonnation helps us to predict what the
next might be about, and this ability to predict helps us to recognize meaning
more quickly than if we had to sort it out solely from what we hear or read.
Picture can represent these non verbal sources of infonnation. Indeed, they
and what they represent are centrally bound up with the nature ()f
communication itself. What we see affects how we interpret what we hear and
vise versa.
From descriptions above, it can be said that picture has a lot of
meanings. Picture is defined as a drawing, a painting or photograph, an image
of someone or something. The meaning of picture can motivate presenting a
sequent of even, story and thing like the real life.
Picture plays an important role as an altemative teaching aid in
teaching English. The teacher gives a picture, then he/she asks the students
I Marianne Celce and Sharon Hills, Technique and Resources in Teaching Grammar,
(New York; Oxford University Press, 1998), p. 73
,
about them. By using pictures in teaching present continuous tense, the
students are expected to use it to communicate.
Picture is easy to be found by all people. Through picture the student
can practice to develop their ideas. We can make picture on the whiteboard,
cartoon etc.
There are many types of pictures can be used as visual aids and heip
the teacher bring the material easier for the student to understand. One of them
is pictures of situational pictures that show or suggest relationship between
object and or people can be perfect teaching aid, for introducing, practicing or
reviewing grammatical stmcture.
According to Betty Morgan, there are some types of pictures, as theirs:
Wall charts, wall pictures for whole class teaching, work card and flash card
word. Flash card with printed word or picture Call help in demonstrating what
the teacher wishes such as an object or action.3
Meanwhile, Noor Azlina Yunus writes inher book composite picture
is one of pictures type which is appropriate for class teaching because it enable
the students to see places, people and events that they would otheryvise not see
because of factor like distance, time alld cost.4
Some advantages of using pictures in teaching:
a. "Pictures can motivate the student and malce him or her want to pay
attention and want to take part.
b. Pictures contribute to the context in which the language is being used.
They bring the world into the classroom.
c. Pictures can cue responses to questions Orclle substitutions through
controll ed practiced
d. Pictures can stimulate and provide information to be referred to in
conversation, discussion and story telling.5
3Betty Morgan Bowen, Look Herel, Visual Aids in Language Teaching, (Lohdoll:
Essential Language Teaching Series, 1973), p. 13-31
7
In an article Edmundo1. Mora stated that "The pictures could be ustd to give students of English as a foreign language an opportunity to practice the
language in the real coutext or in situations which they can use it to
communicate their ideas.,,6
According to A.I.Romiszowski the uses of pictures are: I) Itis conveuieut to use the real thing
2) A model or chart can better explain the principle being taught
3) The real thing can be seen any way.?
A good picture can be the stimulus that generates the confidence '0
speak and a flow conversation. If this is its purpose, the picture can be
abandoned as soon as this warming-up has been achieved.8
Beside the advantages, pictures as teaching aids have disadvantages or
limitation, the writer assumed that it is difficult to make picture that explained
an abstract condition and the teacher has to prepare herself to make a picture
or to find a good picture. Because the students do not always know how to
read pictmes and the pictures often limits students' interpretation.9
From the theories above the writer synthesizes that the teacher should
make gradation in choosing the right pictures to convey the material in the
classroom because besides there are many advantages of teaching through
pictures, cmmot be avoided a case which the students sometimes find them
difficult to read the picture so they cau miss the point and have a little to say.
6Edmundo J.Mora, "Using Pictures Creatively". English Teaching Forum, Vol XXVI,
(Washington DC: Forum, October ,1988): p. 55
7 A. J. Romis2owski, The Selection and Use セイ Instructional Media: for Improved Classroom Teaching and IntCl'!Jctive, Individualized Instruction, (London: Kogen Page, 1988), p.
103 /
8Nick Underhill, Testing Spoken Language, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press,
B. Present Continuous Tense
1. Form of Present Continuous Tense
The Present Continuous Tense is formed with the presents tense of be,
verb be+ the present paliiciple.10
a. Affirmative Statements
To make an affirmative statement, we use the following formula:
BE (aIl1+are+is)+ PRESENT PARTICIPLE (ing-form)+(...)ll
EXaIl1ple:
Subject Form of be Base form of the verb+ing
I ... anl writing now
You are staying home today
He/she/it is sleeping
Yau/we/they al'e speaking English
Example of affirmative contraction with the form of Be
SubjectlBe Base form of the verb+ing contraction
I'm taking the day of today
You're staying home today
He's/she's/it's writing now
We're/you're/they're staying home today
b. Negative Statements
To make a negative statement, we put
not
aftel' [orIn ofbe+verb+ing+(....)
Formula:
Subject+Be+Not+verb+ing+ ( ...)
10 A.J. Thomson, A.V. Martinet, A Practical English Grammar, (Oxford: Oxford
University Press, 1986),p. 153
9
Example:
Subject Be not verb+illg Be contarction+not verb_ing
I am not waiting my I'm not waiting my girl
girl
You are not working You're not working
He/She/it is not speaking He's/She's/it's not speaking
You/we/They are not smiling We 'relYau' re/They' Ie not
smiling
c. Introgative Statements
To make an interrogative affirmative, we put the fOlm of Be before the
subject.
Formula: be+Subject+verb+ing+ (...)?
Example:
Be Subject Base form of the verb+ing
am I listening?
are You waiting?
is He/she/it playing?
are You/we/they watching television?
d. Interrogative Negative
To make an intel1'Ogative negative, we put contractive form of Be before
the subject.
Formula:
(Be+n't1contractive form ofbe)+subject+verb+ing+ (...)?
Example:
Be Subject Base form of the verb+ing
Isn't He/she/it listening?
Aren't You playing?
Aren't You/we/they watching television ?
vie, vying13 tie, tying
Something must be noticed concerning with form of the Present
Continuous Tense that is the process of forming the infinitive form into
ing-fOlID because each verb has different forms. So process adding to
infinitive will undergo different.
There are some ways to spelling the present participle, like in a
practical English grammar book, written by A.J. Thomson and A.V.
Martinet explained as follow:12
a) When a verb ends in a single e, this e is dropped before ing: Argue,
arguing, hate, hating, love, loving. Except after age, dye and singe:
ageing, dyeing, singeing and verb ending ee: agree, agreeing, see,
seeing
b) When a verb one syllable has one vowel and ends in a single
consonant, this consonant is doubled before ing: hit, hitting, run,
running, stop, stopping
c) Verb of two or more syllables whose last syllable contains only
one vowel and ends in a single consonant double this consonant if
the stress falls on the last syllable: admit, admitting; Begin,
beginning prefer,prefelTing
d) lng can be added to a verb ending ywithout affecting the spelling
of the verb
Cany, carrying enjoy, enjoying huny, hUITying
e) The infinitive ends vowele preceded by vowelI,ie substituted
with y, then added ing
Die, dying lie, lying
12AJ. Thomson,A Practical English Grammar,p. 154
11
2. Usage of Present Continuous Teuse
Based on Raymond Murphy said, there are some usages of present continuous tense, as follow: 14
a. We use the present continuous tense when we talk about something that is happening at the time of speaking:
I) Please don't make so much noise. I'm studying (not study) 2) "Where is Peggy?" "She is taking a bath" (not she takes)
b. We also use present continuous tense when we talk about something that is happening around the time of speaking, but not necessarily exactly at tlle time of speaking, study this example situation:
Tom and Ann are talking and having coffee in Cafe. Tom says, "I'm reading an interesting book at the moment. I'll lend it to you whenI've finished it.
Tom is not reading the book at the time of speaking. He means that he has begun the book and hasn't finished it yet. He is in the middle of reading it
c. We often use the present continuous tense when we talk about a period around the present. For example today, this week, this season, etc: "You are working hard today," "Yes I have a lot to do"
d. We use the present continuous tense when we talk about changing situations:
I) The population of the world is rising very fast
'2) Is your English getting better?
e. We use the present continuous tense when we talk about a future
1-plan: )
I) Mike is coming here on Thursday 2) They are having a party next week
'4Raymond Murphy, Grammar in Use, (New York: Cambridge University Press, 1989),
p. 2
f. With always to criticize or complain about someone does:
I) You are always interrupting me!
2) My father is always losing his car keys
3. Verb Usually not used in Present Continuous Tense
Certain verbs are usually not usedincontinuous tense. Some of these
are verbs of preference, verb of knowing, linking verb, and verb that refer to a
mental state or to a permanent condition.16
The following verbs of preference are usually not used in present
continuous tense:
Agree Distrust Like
Appreciate Doubt Love
Care Fell Need
Detest Hate Prefer
Disagree Hope Want
Dislike Imagine Wish
The following verbs of knowing are usually not used in the present
continuous tense:
Believe Know Remember
Forget Recognize Suppose
Imagine Recollect Think
The following example with linking verbs:
He is (not is being) tall
His wife seems (not is seeming) happy
They look (not are looking) nice
And also, following verbs describe relatively permanent states rather
than events or actions. They are not usually used in the present continuous
13
Appear Deserve Own
Be Equal Posses
Belong to Fit Require
Concern Have Resemble
Consist of Involve Seem
Contain Look Sound
Cost Matter Sound
Depend on Owe Tend
C. Teaching Present Continuous Tense by Using Pictures
Pictures are versatile and useful resources for teaching aspects of grammar that require a structure meaning match. Pictutes can motivate students to respond in ways that more routine aid, such as textbook or a sentence on the board. Pictures can also be used in various configurations to enhance leaming and practice.I?
Teaching pictures at SMP is an impOitant role as alternative teaching aids in teaching English because most students like reading magazine or comic. By picture students are practiced to use their imagination and able to describe a picture is easy to be found anywhere. So that teaching using picture
is attractive for students.
The teacher points to the man and attempts to elicit the phrase He is
sWimming by saying can anybody tell me ... He is.... ? Or asking to the
questions if/hat's he doing? The teacher then models the sentence (He's
swimming) before isolating the grammar she wants to focus on (he's),
distorting, putting it back together again and then giving the model in a natural way once more (Listen ... He's swimming). She may accompany this demonstration of form rules by using some physical means such as bringing two hands (he and is)Jogether to show how the contraction works.18
CHAPTER
ill
THE IMPLEMENTATION
OF THE RESEARCH
A. Methodology of Research 1. Place and Time of Research
The field research the writer took at SMP Perwira Ulujami South Jakarta that is located on JI.H. Dilun No.4, Ulujami Jakarta Selatan. The research was held from January 7thto March 11th2008.
2. Objective of Research
As mentioned in the chapter one that the objective is to fmd out whether there is a significant difference in the achievement of the students' English grammar, especially in present continuous tense taught by using picture and without using picture
3. Population and Sample
The writer took an experiment in the second grade of SMP Perwira. The population of the second grade was 340 students and divided into eight classes, which consisted of VIII-l class until VIII-8. Each class consisted of 40 students. The writer took purposive cluster sampling technique, she chose VIIl-l as an experiment class and VIII-4 as control class. The writer chose those classes because she had more chance to conduct an experiment for more than two meetings before the students had school final test.
4. Data Collecting
The writer got the data by collecting the students' scores from both of
experiment class and control class. The scores were the result of learning present
continuous tense using pictures and without pictures.
5. Data Analysis
After getting the data from observation and evaluation using statistic
calculation of the t-test with
ウゥァョゥヲゥ」。ョエHoセPUI。ウ
follows:セNLLMセセLセNLN
MI-M2 =
クセ Kl^セ
N
I+N
2 )(N
I+N
2-2XN
I·N2 )M = The average of score the result of learning from each group
XI = Class with the picture test (experiment class)
X2 = Class without pictures test (control class)
N
=
Total studentsX = The value deviation of TIandT2
df = Degree of freedom
=N+N-2
6. General Procedure of Teaching Present Continuous Tense Using Pictures
The general procedure of teaching present continuous tense using pictures
as follows:
a. Teacher prepared some pictures to the students
b. Teacher sought some pictures to the students
c. Teacher explained function and form of present continuous tense based
on action picture provided
17
d. Teacher ordered students to look at and pay attention to the pictures
e. Teacher ordered students to say the name or an activity of the pictures
that seen, for example:
Teacher :"Look at the picture!, what is he doing?"
Students :"She is holding a cat"
f. The teacher asked the students in pair work to discuss about the
activity of the picture given and write some sentences in present
continuous tense form.
g. In the final step the teacher concluded what she had taught and asked
the students about their difficulties in learning present continuous tense
and found problem solving in the next meeting.
7. General Procedure of Teaching Present Continuous Tense without Using Pictures
In this activity the teacher did not used pictures as teaching aids in presenting present continuous tense, but she chose scrambled words exercise, the teacher followed the procedures:
b. Teacher prepared ten sentences on index cards (one word per index card). For example:
Sgャキ。ゥエゥョァャセblj
The teacher wrote a number on each card, either on the face of the card, or on the back. It is useful to keep various sentences from becoming mixed up.
c. Teacher shuffled the cards of each sentence and put them in about nine envelopes, which contained the same index cards.
d. Teacher divided the class into groups of 5 students, teacher gave each group an envelope
e. Teacher told each group to use all the cards to form a sentence by sticking the cards on a sheet of paper and do not forget to write the number of each sentence in front of it.
f. The teacher monitored the students' work and decided the group that reordering most of the sentences correctly is the winner.
g. The teacher concluded the material and asked the students about their difficulties in unscrambling words.
B. Research Findings
1. Data Description
Table I
Individual Seore for e1ass VIII-lUsing Pietures
(Experiment Class)
19
Student Correct answer Incorrect answer Scorc
1 20 10 66
2 30 0 100
3 14 16 46
4 25 5 83
5 30 0 100
6 24 6 80
7 20 10 66
8 30 0 100
9 21 9 70
10 30 0 100
11 27 3 90
12 26 4 86
13 30 0 100
14 28 2 93
15 29 1 96
16 23 7 76
17 30 0 100
18 30 0 100
19 29 1 96
20 18 12 60
Table II
Individual Score for Class VIII-4 without Using Pictures
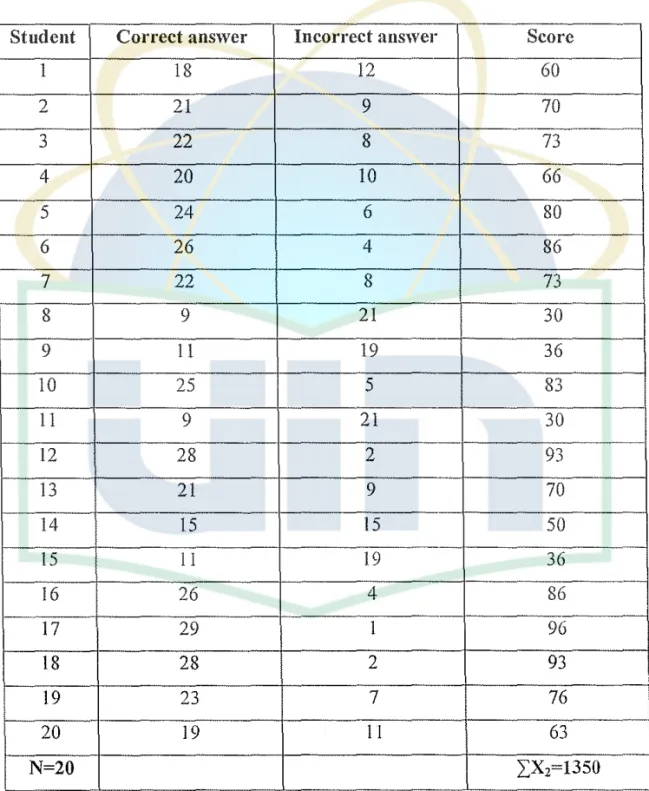
(Control Class)
Stndent Correct answer Incorrect answer Score
I 18 12 60
2 21 9 70
3 22 8 73
4 20 10 66
5 24 6 80
6 26 4 86
7 22 8 73
8 9 21 30
9 II 19 36
10 25 5 83
11 9 21 30
12 28 2 93
13 21 9 70
14 IS IS 50
IS 11 19 36
16 26 4 86
17 29 I 96
18 28 2 93
19 23 7 76
20 19 11 63
21
TableID
Comparison of the Score of Each Student of Class VIII-l (Experiment Class)
and VIII-4(Control Class)
-No XI X2 XI X2 x/
xl
I 66 60 -19.4 -7.5 376.36 56.25
2 100 70 14.6 2.5 213.16 6.25
3 46 73 -39.4 5.5 1552.36 30.25
4 83 66 -2.4 -1.5 5.76 2.25
5 100 80 14.6 12.5 213.16 156.25
6 80 86 -5.4 18.5 29.16 342.25
7 66 73 -19.4 5.5 376.36 30.25
8 100 30 14.6 -37.5 213.16 1406.25
9 70 36 -15.4 -31.5 237.16 992.25
10 100 83 14.6 15.5 213.16 240.25
I I 90 30 4.6 -37.5 21.16 1406.25
12 86 93 0.6 25.5 0.36 650.25
13 100 70 14.6 2.5 213.16 6.25
14 93 50 7.6 -17.5 57.76 306.25
15 96 36 10.6 -31.5 112.36 992.25
16 76 86 -9.4 18.5 88.36 342.25
I
l7 100 96 14.6 28.5 213.16 8l2.25
I
18 100 93 14.6 25.5 213.16 650.25 I
I
19 96 76 10.6 8.5 112.36 72.25
20 60 63 -25.4 -4.5 645.16 20.25
N=20 IXI= 1708 IX2-1350 IXt-O IxrO ixQRセUャPVNX Ix/=8521
After comparing between the score of the experiment and control class, the analysis of data from the result both of classVIII-I and VllI-4 and the result of calculation as follow;
MI
M2
1708 20 = 1350
20
= 85.4
=67.5
= ---ri'========i7====e=2MI-M2
= MMョ]]]]]ョ]]セ
to 17.9
-J358.62xO.1
17.9 to
-J35.862
17.9 to
-5.988 to = 2.98
tt =5% = 2.02 1% = 2.71 df = (N1+N2)-2 = (20+20)-2 = 40-2 = 38
23
Thus, the score of class using picture is better than class without pictures. The result of the class using picture cセZZZxャ]QWPXI and the result of the score without sing pictures O':X2=1350)
The obtained statistical result to is 2.98 and the degree of freedom (df)=38.
The result oft, significant 0.05=2.02, so to>t, or 2.98>2.02.It means that experiment hypothesis (Ha) is accepted.
2. Data Interpretation
A. Conclusion
From the statistic result above, it is obtained the value of to is 2.423 and the degree of freedom (dt)= 38. The result oft, on significant 0.05 is 2.02, so to>t, or 2.423>2.02. Itmeans that hypothesis is accepted, or there is significant difference between teaching present continuous tense using picture than without pictures
B. Suggestions
The teacher should give motivation for students in learning English by visual aids such as picture, because the result of study shows that teaching present continuous tense using pictures is better than teaching without picture. The writer would like to suggest English teachers in junior high school to use
BIBLIOGRAPHY
IXBadalamenti, Victoria Carolyn Henner-Stachina. Grammar Dimension. Boston:
Heinle-Heinle Piblisher, 1993: p. 191
",Bing, Janet Mueller. Grammar Guide; English Grammar in Context. New Jersey: Prentice Hall Engliwood Cliff, 1989: p. 75
Bowen, Betty Morgan. Look Here!, Visual Aids in Language Teaching. London:
v Essential language teaching series, 1973: p. 13-31
\.- Celce, Murcia and Sharon I-Hils. Technique and Resources in Teaching Grammar.New York: Oxford University Press, 1998.
... Edge, Julian. Essentials of English Language teaching: 3rd Edition, London: Longman, 2003: p. 25
セ Gerlach, Vemon S. and Donald P .Elly. Teaching and Media Systematic Approach.New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 1980 p. 273
Gunawan, J. B. "The teaching of Grammar in CLT. Oriented Environment,"
Teflin Journal. volume Vll. (September 1993) p. 34
I-Im'tanto, Jhon S., S. Koentjoro, Manaf Asmoro Saputro. Accurate, Brief and Clear, English Grammar. Surabaya: Indah Publisher, 1996: p.255
Hanner, Jeremy. The Practice of English Language Teaching. Kuala Lumpur: Second Impression, 2002
vHeinch, Robert, Michael Molendan and James D. Russel. Media. Singapore: Mc Millan Publishing Company, 1990: p. 76
Hornby, A. S.Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary ofCurrent English.Oxford: Oxford university Press, 2000: p. 721
Mackey, William Frances. Language Teaching Analysis. USA: Indiana University Press, 1965: p. xi
Mora, Edmundo J. "Using Pictures Creatively". English Teaching Forum. Vol XXVI. Washington DC: Forum,October,1988: ]J.S5
Romiszowski, A. J. The Selection and Use of Intructional Media: for Improved Classroom Teaching and Interactive, Individualized Instruction. London: Kogen Page, 1988: p. 103
Schutcher and Simon. Webster's New twentieth Centwy dictionwy: Second Edition.London: William Collin's Publisher inc, 1979: p. 1352
Soemardi, Mulyanto. Pengajaran Bahasa Asing Sebuah Tinjauan dari Segi Metodologi. Jakarta: Bulan Bintang, 1975: p. 14.
Sudjiono, Anas.Statistik Pendidikan. Jakarta: Raja Grafindo Persada, 2006
Szyke, Grazna. "Using Pictures as Teaching Aids",English Teaching FOrUlll. Vol. XIX No.4. October, 1981: p. 45
Thomson, AJ., A.V. Martinet. A Practical English Grammar. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1986
Underhill, Nick. Testing Spoken Language. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1993, p. 76
Willes, Dave and John Wreight. Basic Grammar: Classroom Edition. Cambridge: Harper Collins Publisher Ltd, 1995: p. 6
Wright, Andrew. Pictures for Language Learning. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1989
APPENDIX 1
PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSEtャセst USING PICTURES
FOR EXPERIMENT CLASS
Multiple choices : 30 questions
Choose the best answer and put(X) on your answer sheet!
I, Look at the pictures carefully and answer questions no 1-4!
What is the boy doing?
a, He is playing football
b, He is sitting on a bench
c. He is sweeping the ground
d. He is holding a book
2.
What is the teacher doing?a, He is playing football
b. He is sitting on a bench
c. He is sweeping the ground
c. Yes, she is
d. No, she is
4. Where does the situation in the picture take place?
I
a. In the supermarket
b. In the school
c. In the library
d. In the laboratory
5.
He is ... the plantsa. cutting
b. putting
c. watering
d. flowering
6. Look at this picture! This boy is ...
a. planting
-'-"---"---""-------.._."..,..
b.. sweeping the courtyard
.c. watering the plants
d. No, they are c. No, they aren't 7. Look at the pictures carefitlly and answer questions110 7-10f
',... ,
セゥ
What is the boy doing?
a. He is swimming
b. He is singing
c. He is climbing the coconut tree
d. He is eating the coconut
8.. Are the boys playing ball?
a. Yes, they are .
b. Yes, they aren't
9. What is the girl doing?
a. She is climbing the coconut tree
b. She is playing ball
c. She is playing sand
d. She is swimming
10. Where does the situationinthe picture take place?
a.
In
the garden c.In
the zooc, they are diving
d. he is diving
12. Look at this picture! What are they doing? ...
a. they are cooking
b. they are playing
c. they are planting
d. they are eating
13. Look at this ーゥセエオイ・A What is she doing? She is .,.
a. mopping the floor
b. doing the pattern
c. washing the clothes
d. cleaning the door
14. Anton: Is the boy flying the kite?
Rudy
a. No, he isn't
b. Yes,heis
c. 'Yes, she is
d. No, she isn't
セャ
0,: .:
',,'
,
, ' ,QLZセZ .; _ .
セZG
.-l/A,
",",",
=:,.• 'J" LLセW[NNIGZᄋ "','
セDLLMLセMBH
_
G[ェyLMLGセセLMMB
",', ]•
>11 , , , ,
ZセZA . , , \'.;
15. Look at the picture carefidly and ans,I'er questions no 15-191
Where does the situation in the picture take place?
a. In the library
b. In the supermarket
c. In the canteen
d. In the classroom
16. What is the girl no.1 doing?
a. She is typing
b. She is going up stair
]}. Are the girls no. 3, 5, 6 reading books?
a. Yes, they are
b. No, they aren't
18. What is the boy no. 2 doing?'
a. He is reading a book
b.. He is expressing a speech
19. Who is going up stair?
a. Student no. 5
b. Student no. 3
c. She is reading a book
d. She is writing
c. Yes, they aren't
d. No, they are
c. He is going
up
staird. He is typing
c. Student no.2
c. Reading
d. cutting
21. She is ... because herュッエィ・セ leave her
a. laughing
b. crying
c. playing
d. shouting
22. Look at the picture carefully and answer questions no 22-241
What is grandmother holding?
a. She is holding a stick
b. She is holding a fish
c. She is holding a ruler
23. What is the girl doing?
a. She is feeding a chicken
b. She is feeding a cat
24. Is the fish jumping?
a. Yes,itis
b. Yes, it isn't
25. The boy scouts are ....
a. camping and sightseeing
b. camping and cooking
c. camping and singing
d. camping and smoking
26. Itso hot in her room. She is ...
a. turning on the fan
b. turning off the fan
c.
burning the fand. throwing the fan
c. She is feeding a frog
d. She is feeding afish
c.No, it isn't
d. No, it is
c. In the school canteen
d. In the library
28. What is she selling?
a. She is selling a book
b. She is seIling cakes
c. She is selling souvenirs
d. She is seIling toys
29. Are the students going to buy some books?
a. No, they aren't
b. Yes, they are
30. Look at the picture!
c. Yes, they aren't
d. No, they are
What are they doing?
a. They are having a birthday party
.
.b. They are eflting cakes
c. They are blowing the balloons
1. A 2. D 3. C 4. B 5. C 6. B 7. C 8. A 9. C 10. B
11.B 12. A
l3.A
14.B 15.A 16.A 17.A 18. B 19. D 20.B
21. B 22. A 23.D 24.A 25. C 26.A 27.C 28. B 29.A 30.A
Mata Pelajaran
Kelas/Semester
Pertemuan
: Bahasa 1nggris
: VIII (delapan)/ II
:1
Standar Kompetensi :
8. memahami makna dalam teks lisan fungsional dan monolog pendek sederhana
berbentuk
narrative
dan unfuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar.10. Mengungkapkan makna dalam teks lisan fungsionaldan monolog pendek
sederhana untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar.
11. Mengungkapkan malma dalam teks twis fungsional dan esei pendek sederhana
berbentuk
narrative
untuk nerinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar.Kompetensi Dasar
8.2. Merespon makna yang terdapat dalam monolog pendek sederhana secara
aknrat, lancar, dan berterima untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar
dalam teks berbentuk narrative.
IO.l.Mengungkapkan makna dalam teks lisan fungsional pendek sederhal1a
dengan menggunakan ragam bahasa lisan secara akurat, Iancar dan berterima
untuk berinteraksi denganlingkungan sekitar.
11.1. Mengungkapkan makna dalam bentuk teks tulis fungsionalpendek
sederhana dengan menggunakan ragam bahasa tulis secara aknrat, Ian car dan
berterima yang berkaitan dengan lingkungan sekitar.
Indikator
Siswa dapat menjawab pertanyaan secara lisan
Siswa dapat merespon monolog pendek
Siswa dapat melafalkan kalimat-kalimat
Present Continuous Tense
berdasarkan gambar yang diberikan oleh guru
Alokasi Waktu : 2 x 40 menit
Tujuan Pembelajaran:
Pada alchir pembelaj aran
Siswa dapat menjawab pertanyaan secara lisan
Siswa dapat merespon mono log pendek
Siswa dapat melafalkan kalimat-kalimatFnsenl Continuous Tense
berdasarkan gambar yang diberikan oleh guru
Materi Pembelajaran
Vocabulary For Language Master:
READING
WAITING
I
CAL.L.ING
SHAKING
HANDS
L.EAVING
SHOWING
ARRIVING
TALKING
a. Script untuk writing
Gambm' apartmen dengan aktivitas yang berbeda
PART A
Apt. I C : The family is watching TV
Apt. IB : The woman is eating ice cream and watching TV Apt IA : The man is sleeping
Apt. 2C : The teenage is ironing his pants
Apt 2B : The mother is holding her baby
Apt 2A : The couple are leaving the apartment
c. Kosakata terkait tema : leaving, arriving, exercising, holding, shaking,
waiting, calling, reading, etc,
d. Action verbs : leaying, arriving, exercising, holding, shaking,
waiting, calling, reading, etc,
Media pembelajaran
Metode : Individual, group and whole class
SKENARIO PEMBELAJARAN
NO KEGIATAN WAKTU
I PENDAHULUAN 5
1.1. Guru mengncapkan salam 1
1.2. Guru mengabsen siswa 2
1.3.
Tanyaiawab mengenai hal terkait kondisi siswa 2II KEGIATAN POKOK , 65
2.1.Guru memberikan pertanyaan kepada murid mengenai 20 kegiatan dengan jawaban present continuous tense dan siswa ". menulis jawaban tersebut di papan tulis serta membahasnya. 2.2.Guru membagikan kelas menjadi 9 kelompok yang terdiri . 5
dari $5 siswa, sertaュセュ「。ァゥォ。ョ hand out mengenai gambar apartment.
2.3.Siswa berdiskusi di kelompoknya masing-masing untuk. )5 menemukan perbedaan antara gambar Pm:t A dml Part B serta menuliskan alctivitas tersebut dalam Present Continuous Tense.
2.4.Guru memberikml satu gambar kamm' apartmen berbeda 20 pada setiap kelompok dan kelompok lain menebalc no kamar apartmen tersebut secara bergantian
III PENUTUP
10
3.1. Guru memberikan kesimpulml dml menanyakan hmubatan 5 yang dialanli siswa selama proses pembelaj aran
3.2.guru memberikan kegiatan tindak lanjut berupa pekerjaan 5 rurnal1
3.3.Guru menutup pelajaran dmlleave taking
Sumber pembela)aran
1. Sumber bahan syllabus
Skyline resource pack I, published by Macmillan Publisher limited
Whiteboard
Marker
Hand out
Gambar
'"
!
i
Aspek penilaian A. penilaian proses
Penilaian proses dilakukan selama proses beajar mengajar berlangsung
Sekolah
Mata Pelaj aran
Kelas/Semester
Pertemuan
: SMP Perwira Jakarta
: Bahasa Inggris
: VIII (delapan)/ II
:II
StandarKompetensi :
11. Memahami makna dalam esei pendek sederhana berbentuk narrative untuk
berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar.
12. Mengungkapakan malma dalam teks tulis fungsional dan esei pendek sederhana
,
berbentnknarrativeuntuk berinteraksi dengan IiIngkungan sekitar
Kompetensi dasar
11.1. Membaca nyaring bennakna teks fungsional dan esei pendek sederhana dengan
ucapan, tekanan dan intonasi yang benerima yang berkaitan dengan Iingkungan
sekitar
12.l.Mengungkapkan malma dalam bentnk teks tnlis fungsianal pendek sederhana
dengan menggullakan ragam ballasa tnlis secara akmat, lancar dan berterima
untuk berillteralcsi dengan Iingkungan sekitar.
Indikator
Siswa dapat menj elaskan isi bacaan sederhana dengan menj awab pertanyaan
berdasarkan teks yang diberikan gmu
Siswa dapat menemukan kalimat dengan paJaPresent Continuous Tense
Siswa dapat membaca nyaring dengan intanasi yang benar dan lancar
Jenis teks :Teks fungsional /esei pendeknarrative
Tema :Teenage Life
Aspek : reading and writing
Tujuan Pembelajaran Pada akhir pembelajaran
Siswa dapa! menjelaskan isi bacaan seclerhana c1engan menjawab pertanyaan berdasarkan teks yang diberikan guru
Siswa dapat menemllkan kalimat dcngan polaPrese!1f Continuuus Tense
Siswa dapat membaca nyaring dengan intonasi yang benar clan lancar
Materi Pembelajaran
a. Seript untuk Readiug
Rearrange the/allowing pictures according10the st()!:}'!
How frogs are coming into the world? Here is a story about frogs. Two beautiful sisters, lippi and Indra are taking a bath I a pool in the forest. Suddenly, a crocodile called Wilar comes to the pool to clrink. When he sees the girls, he is going to catch onc of thcm for his wifc. Suddcnly he is jumping and catching Indra. lippi is very afraid and runs away for help. Wilar, the crocodile is bringing Indra home. His house is a cave. lnclra becomes his wife. When Wilar is going out for food, he shuts the cave with the big stones. lndra moves the Slones with her long hair and goes out. She meets her siSler again, but when she is going out her stomach is big and many eggs come out of her stomach. The people strike the eggs, when the people are striking the eggs many frogs come out of the eggs.
a,
セ
//l!:J),
j
. d.
c.
The Present Continuous Tense is used for actions which are happening at the
time of speaking, or for a limited period of time.
The present Continuous Tense is constructed as follows, example:
Notes that:
a. There are certain verbs which drop the 'e' before adding the 'ing' at the
end
b. Sometimes the last letter has to be doubled before adding the 'ing'
Examples:
a. dance - dancing
b. swim - swimming
Negative Form : The negative is formed by adding the word 'not' between the
verb to be and the verb ending in 'ing.'
Example: He is not swimming
Interrogative Form: The interrogative is formed by inverting the positions
of the pronoun and the verb to be.
Do Ihe lasks bellow!
1. Is the man running?Answer: No, he isn'l, he's swimming
2. Make questions based on the pictures!
Answer:
Is she wearing sung!asses? Is he swimmingjclsl?
I. Is he reading a newspaper?
2.' Make question based on the pictures!
I, Is he riding a motorcycle?
2. Makc qucstions based on thc pictures!
I. Is she holding a dog?
2. Make questions based on the pictures!
I. Are they dancing?
Hand out, pictures, OHP, whiteboard, marker, etc.
Strategi, Model, Pendekatan dan Metode Pembelajaran
Strategi : two ways communication
Model
Pendekatan
Metode
: face to face
: Communicative
: Individual, group and whole class
SKENARIO PEMBELAJARAN
NO KEGIATAN WAKTU
I PENDAHULUAN
5
1.1. Guru mengucapkan salam I
1.2. Tanya jawab mengenai hal terkait kondisi siswa dan topik 2
yang sedang in. 2
II KEGIATAN POKOK
65
2.I.Siswa membaca nyaring teks 10
2.2.Siswa memahami makna teks dan mencari kalimat yang 10
mengandung polaPresent Continuous Tense:
...
2.3.Siswa menyusun gambar sesuai dengan cerita tel'sebut 110 2A.Guru memberikan pelianyaan kepada siswa dan siswa 20
menjawabnya dengan yes/no answer serta menulisnya di papan tulis. Guru membahas sedikit tentang pola (,,7) present continuous tense.
2.5.Siswa menjawab pertanyaan yang ada pada hand out gambar
15
III PENUTUP
10
Sumber pembelajaran 1. Sumber bahan
Syllabus
Effective English 2, Soegeng B.S., PT Tiga Serangkai pustaka l\1andiri, Solo
2. Media OHP Whiteboard Marker I-land out Gambar
a. ,
セ
//J:JJ,
j
d.
'1
GᄋᄋᄋセᄋBGᄋGGGᄋGMGGGGGGGGGGGセnエNャャiZiャセGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGG __'''_"'''_
Aspek penilaian C. penilaian proses
Penilaian proses dilakukan selama proses beajar mengajar berlangsung D. penilaian hasil
Penilaian hasil diambil dari hasil jawaban siswa atas pertanyaan yang diberibm
Sekolah
Mata Pelajaran
FCelas/semester
Pertemuan
: SMP Perwira Jakarta
: Bahasa Inggris
: VIII (delapan)!II
: III
Standar Kompetensi :
7. Memaharni makna dalam percakapan transaksional dan interpersonal pendek
sederhana untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar.
12. Mengungkapkan malma dalam bentuk teks tulis fungsional pendek sederhana
dengan menggunakan ragarn bahasa tulis seCal'a akurat, lancal' dan berterima
untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar.
Kompetensi Dasar
7.2. Merespon makna yang terdapat dalarn percakapan transaksional (to get things
done) dan interpersonal (bersosialisasi) pendek sederhana secara akurat, lancar,
dan berterima untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan terdeka.t yang melibatkan
tindak tutU!'; meminta, memberi persetujuan, merespon pemyataan, memberi perhatian terhadap pembicara, mengawali, memperpa.njang, dan menutup
percakapan, dan mengawali, memperpanjang, dan menutup percakapall telepon.
12.I.Mengungkapkan makna dalam bentuk teks tulis flmgsional pendek sederhana
dengan menggunakan ragarn bahasa tulis secara akurat, lancar dan berterima
untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar.
Indikator
Siswa dapat melengkapi leks dialog yang rumpang
Siswa dapal merespon malma dalarn leks dialog dengan menjawab pertanyaan
Siswa dapat membaca leks esei pendek dengan intonasi yang benar danlancar.
Siswa dapat mencocokan gambar sesuai dengan leks
JenisteI{S
Tema Aspek
Alokasi Waktu
: Dialog dan esei pendek
: Teenage Life
: Listening/reading
: 2 x 40 menit
Tujuan pembelajaran
Siswa dapat melenglcapi teks dialog yang runlpallg
Siswa dapat merespon makna dalam teks dialog clenganluenjawab pertanyaan
Siswa dapat membaca teks esei penclek del1gan intonasiyang benar clan lancar.
Siswa dapat mencocokan gambar sesuai clengan teks
Siswa clapat merespon makna teks esei pendek denganmenjawab pertanyaan
Materi Pembelajaran a. Script untuk listening
Listen to the teacher carefully and complete the missing words!
John : Excuse me, (1) for Albert
Andrew : He isn't in the classroom now
John Anclrew John Anclrew John Anclrew
: Where (2) ?
: Hmm.. I think (3) in the school yard
: Oh, I see. Okay.. would you please send my regard to Albert?
: Sure, Hey Look! That Albeli! He is outside the teacher's
room. (4) with Mr. Brown
: (5) approach him. Thank you
: You are welcome.
Answer Key
1. I'm looking for
2. Is he going
3. He is playing basketball
4. He is talking
5. I'm going to
b. Scriptuntuk reading
Thios is the picture of Mr. Hasan family, write a story based on the picture in
pair and
Mr Htl\;Vllhiーャ。ャ|エィャAセ It
pllpayailZcセN
h.
·\di \, \,,)c>I.nIrC) \\'r
How'T
c. Kosakata terkait terna : working, looking for, planting, helping
d. Action verbs : working, looking for, planting, helping
Media Pembelajaran:
Hand out, pictures, whiteboard, marker etc.
Strategi, Model, Pendekatan dan Metode Pembelajarlln
Strategi
Model
Pendekatan
. Metode
: two ways communication
: face to face
: Communicative
SKENARIO PEMBELAJARAN
NO KEGIATAN WAKTU
I PENDAHULUAN 10
1.1. Guru mengucapkan salam 1
1.2. Guru memotivasi siswa dengan membuat games BINGO, 2 siswa menuliskan sembilan Verb-ing (kata kerja yang biasa 2 dilakukan murid di kelas)
II KEGIATAN POKOK 60
"
2.1. Guru memberikan hand out dan membacakan teks dialog 10 dengan lengkap, siswa melengkapi teks yang rumpang
2.2. Siswa membaca nyaring dialog dan mempl'aktekannya di 10 depall kelas
2.3. Siswa memahami teks dialog dan menjawab pertanyaan 10 berdasal'kan teks.
2.4. Guru memberikan pertanyaan beI'dasaI'kan gambar yang 10 diberikan guru
2.5. Siswa dapat menyusun gambaI'-gambaI' tel'sebut menjadi 20 sebuah cerita
III PENUTUP 10
1.1. Guru memberikan kesimpulan dan menanyakan hambatan 9 yang dialami siswa selama proses pembelaj aran
1.2. Guru mellutup pelajaran dan leave taking I
Sumber pembelajaran
1. Sumber bahan
Syllabus
Effective English 2, Soegeng H.S., PT Tiga Sel'angkai pustaka Malldiri, Solo
2. Media
OHP
Whiteboard
Marker
Hand out
セセ
(D·.··
Plll'ht""
Aspek penilaian E. penila.ian proses
Penilaian proses dilakukan selama proses beajar mengajar berlangsung" ,
F. penilaian hasil
Peni/aian hasil diambl! dari hasi/'jawaban siswa atas pertanyaan yang diberikan
Sekolah
Mata Pelajaran Kelas/semester Pertemuan
RENCANAPELAKSANAANPEMBELAJARAN
(RPP) UNTUK EXPERIMENT CLASS
: SMP Perwira : Bahasa Inggris : VIII (delapan)/II : IV
Standar Kompetensi :
10. Mengungkapkan makna dalam teks lisan fungsional dan monolog pendek sederhana untuk berinteraksi dengan lingknngan seldtar.
12. Mengungkapkan makna dalam teks tulis fungsional dan esei pendek sederhana berbentukdescriptiveuntuk berinteraksi denganlingknngan sekitar.
Kompetensi Dasar :
10.1. Mengungkapkan makna dalam teks lisan fungsional pendek sederhana dengan menggunakan ragam bahasa lisan secara akurat, lancar dan berterima untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar.
12.1. Mengungkapakan makna dalam bentuk teks tulis fungsional pendek sederhana dengan menggunakan ragam ballasa tulis secara akurat, lancar, dan berterima untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar.
Indikator
Siswa dapat mengungkapkan kalinlat present continuous tense yang diperagakan secara akurat dengan lancar
Siswa dapat menuliskan berbagai aktivitas yang ada pada gambar dalarn bentuk present continuons tense.
Tujuan pemhelajaran
Siswa dapat mengungkapkan kalimat present continuous tense yang diperagakan
secara akurat dengan lancar
Siswa dapat menuliskan berbagai aktivitas yang ada pada gambar dalarn bentuk
present continuous tense.
Siswa dapat mendeskripsikan aktivitas pada gambar di depan kelas
Materi Pembelajaran
ING HAIR
PLAYING FOOTBALL
.-..セL ...""".,..•...
lG THE <>(""uND
NGING
SLEEPING
OPENING THE WINDOW
COOKING IN THE KITCHEN
WRITING A BOOK
READING NOVEL
. S'ervPI
",c.-
A LGTHJLI. A boyis sitting on the ground 2. A girl is sitting ona bench
3. A girl is sweeping the ground
4. etc.
Look at the pictures carefully and then write at lest5sentences about the situations in the pictures!
!Lセ⦅NLMMBMB⦅NM •••.⦅N⦅N⦅LN⦅Nセ ...セMMMセNセ •._.•"..- ...⦅MNLLBMMセGBMGGGMGGGセG|ャ
i
I
I
i
"I
c. Kosakata terkait tema
d. Action Verb
: cutting, catching, typing, blowing
: cutting, catching, typing, blowing
Media Pcmbelajaran
Plash card, hand out, OHP, whiteboard, marker
Strategi, model, pendelcatandanmetode pembelajaran
I
Strategi : Two ways communication
NO KEGIATAN WAKTU
I PENDAHULUAN
10
1.1. Guru mengucapkan salam I
1.2.Tanya jawab menegenai topik yang sedang berkembang, 2 contohnya banjir, jika mereka berada di lingkungall tersebut 2 apa yang sedang mereka lakukan saat itu.
II KEGIATAN POKOK
60
2.1. Guru memberikan amplop yang berisi flashcard pada setiap 20 kelompok yang telah dibentuk sebelumnya dan menugaskan ketua kelompok untuk memperagakan kalimat yang ada pada gambar tersebut menggunakan present continuous tense sementara peserta yang lain menebaknya.
2.2. Siswa menuliskan kalimat present continuous tense 10 berdasarkan hal yang sedang diamati di kelas
2.3. Guru menampilkan sebuah gambar dengan berbagai kegiatan 10 dan menunjuk beberapa siswa untuk menyebutkan salah satu aktivitas tersebut dalam bentuk present continuous tense
2.4. Siswa menuliskan berbagai kegiaatn yang ada pada gambar 20 dalam bentuk present continuous tense
III PENUTUP
10
3.l.Guru memberikan kesimpulan dan menanyakan hambatan 9 yang dialarni siswa selama proses pembelajaran
3.2.Guru menutup pelajaran dan leave taking 1
Sumber pembelajaran 1. Snmber bahan
Syllabus
Effective English 2, Soegeng H.S., PT Tiga Serangkai pustaka Mandiri, Solo 2. Media
OHP
RENCANA PELAKSANAAN PEMBELAJARAN (RPP)
UNTUK CONTROL CLASS
Sekolah
Mata Pelajaran Kelas/Semester
: SMP Perwira Jakarta : Bahasa Inggris
: VIII (delapan)/ II
Standar Kompetensi :
8. memahami malcna dalam teks lisan fungsional dan monolog pendek sederhana berbentuknarrativedan untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar.
11. Mengungkapkan makna dalam teks tulis fllngsional dan essei pendek sederhana berbentuk narrativeuntuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar. 12. Mengungkapakan malGla dalam teks tulis fungsional dan essei pendek
sederhana berbentllknarrativeuntuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar
Kompetellsi Dasar:
8.2. Merespon makna yang terdapat dalam monolog pendek seclerhana seCaI'a akurat, lancar, dan berterima untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkllngan sekitar dalam teks berbentuknarrative.
I1.1.Membaca nyaring bermakna teks fUlIgsional danessei pendek sederhana dengan ucapan, tekanan dan intonasi yang berterima yang berkaitan dengan lingkungan sekitar
12.1. Mengungkapkan makna dalam bentuk teks tulis fungsional pendek sederhana dengan menggunakan ragam bahasa tulissecara akurat, lancar dan berterima llntllk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar.
Illdikator
Memahami makna clalam essei penclek seclerhana Mengllngkapkan makna dalam teks tulis fungsional
SkimmingkalimatPresent Continuous Tense
Tujuan Pembelajaran
Pada akbir Pembelajaran siswa dapat:
- Memahami makna dalam essei pendek sederhana - Mengungkapkan makna dalam teks tutis fungsional
- Menyusun kalimatPresent Continuous Tense dengan bentuk yang baik - Membaca nyaring
7. Those patients _ for the dentist 8. Students _ _ a very sad story 9. Rina _ _ a baby's diapers 10. You _ _ to catch a mosquito Materi Pembelajaran
a. Script untuk Listening
I. She _ _ ajar 2. Vou _ a busy road 3. Mother _ a cup of tea 4. Ade _ very spicy food
5. That boy _ a race car 6. We for a bus
( is opening) (are crossing) (is making) (is eating) (is driving) (are waiting) (are waiting) (are reading) (is changing) (are trying) b. Script untuk Speaking
1. Sally is selling sea shells by the sea shore.
2. So if she is selling shells on the seashore,
3. I'm sure she's selling seashore shells.
4. The shells she's selling are surely seashells
1. who fished for a fish in a fissure.
2. Pulled the fisherman in;
3. Now they're fishing the fissure for Fischer
4. The fish with a grin,
Task
I. Unscramble those sentence to make agood poem II.Answer these questions based on the text above!
2.Find the present continuous form in the text! 3.What are we watching?
4.What is Sally selling? 5.Where is she selling it?
6.What is the young man fisher's name?
c. Kosakata terkait tema/jenis teks selling, crossing, fishing, crossing changing, trying
d. Action verbs selling, crossing, fishing, crossing
changing, trying
Media Pembelajaran
Hand out, pictures, OHP, whiteboard, marker etc.
Strategi, model, pendekatan dan metode pembelajaran Strategi : Two ways communication
Model Pendekatan
Metode
: Face to face : Communicative
: Individual and whole class
SKENARIO PEMBELAJARAN
NO KEGIATAN WAKTU
I PENDAHULUAN 5
1.1 Guru mengucapkan salam I
1.2.Guru mengabsen siswa 2
dengan menyimpulkanjawaban tersebut
2.3.Siswa menuliskan beberapa eontoh Present Continuous
Tense di whiteboard 5
2A.Guru menampilkan reading script pada OHP dan l11emandu anak untuk mel11baca nyaring 10 2.5.Siswa menyusun kalil11at yang aeak l11enjadi puisi yang
baik dan menjawab pertanyaan yang ada pada teks. 15
10 dan l11enanyakan 5
selama proses 5 kesimpulan
dialami siswa PENUTUP
3.1. Guru mel11berikan hal11batan yang pembelajaran
3.2. Guru memberi kegiatan tindak lanjut berupa pekerjaan rumah
III
Sumbel' Pembelajaran I. SUl11ber Bahan
- Syllabus
- Article; Teaching Grammar in your Class: Activities & Strategies, presented by Dr. BradleyC. Gilpin University of California Irvine, Extension. 2. Media
- OHP - Wh iteboard - Marker
Aspek pellilaiall a. pellilaiall proses
Penilaian proses dilakukan selama proses beajar n1eng:Jjar berlangsung b. pellilaian hasil
RENCANA PELAKSANAAN PEMBELAJARAN (RPP)
UNTUK CONTROL CLASS
Sekolah
Mata Pelajaran Kelas/Semester
: SMP Perwira Jakmta : Bahasa Inggris : VIII (delapan)/II
Standar Kompetensi
12. Mengungkapkan makna dalam teks tulis fungsional dan essei pendek sederhana berbentuknarrativeuntuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar
10. Mengungkapkan makna dalam teks lisan fungsional dan monolog pendek sederhana berbentuknarrative untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar
Kompetensi Dasar
10.2. Mengungkapkan makna dalam monolog pendek sederhana dengan menggunakan ragam bahasa lisan seem'a akurat, lanear dan belterima untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar dalam teks berbentuknarrative.
12.1. Mengungkapkan makna dalam bentuk teks tulis fungsional pendek sederhana dengan menggunakan ragam bahasa tulis secara akurat, lancar dan berterima untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar.
Indikator
Mengungkapkan makna dalam monolog pendek Mengungkapkan makna dalam teks tulis fungsional Mengungkapkan secm'a lisan teks monolog pendek Melakukan monolog pendek sederhana
Bertanya dan menjawab seem'a lisan info dalam teks Jenis teks : monolog pendek
Tema : Teenage Life
Mengungkapkan seCaI'a Iisan teks monolog pendek Melakukan monolog pendek sederhana
Bertanya dan menjawab secm'a Iisan info dalam teks
Materi Pembelajarall
a. Script untuk speaking
Amplop yang berisi kalimat-kalimat dengan polaPresent Continuous form, setiap kelompok secara bergiliran memperagakan kalimat tersebut dan kelompok lain menebaknya.
GUES!! WHAT ARE THEY DOING???
I. buying fruit 2, reading newspaper 3. catching the mosquitoes 4. listening to music 5. sweeping the floor 6. teaching the students 7. running fast
8. swimming slowly 9. laughing loudly 10. calling on the phonc 11. flying in the sky 12. walking
b. Script untuk writing
The Present Continuous Tense is used for actions which are happening at the time of speaking, or for a limited period oftime.
The present Continuous Tense is constmcted as follows, example:
Notes that:
a. There are certain verbs which drop the 'e' before adding the 'ing' at the end
b. Sometimes the last letter has to be doubled before adding the 'ing' Examples:
a. dance - dancing b. swim - swimming
Negative Form : The negative is formed by adding the word 'not' between the verb to be and the verb ending in 'ing.'
Example: He is not swimming
Interrogative Form: The interrogative is formed by inverting the positions of the pronoun and the verb to be.
Example: Is he swimming?
Amplop berisi potongan-potongan kata dan siswa menyusunnya
IS SHE THROWING THE PAPER?
I AM NOT EATING HAMBURGER
ARE YOU GOING TO
thesuperセarォet_THE POLICE ARE STANDING IN THE MIDDLE OF
THE ROAD
SHE IS WEARING A BLUE DRESS
c. Kosakata terkait tema/jenis teks d. Action verb
: learning, wearing, going, taking : learning, wearing, going, taking
Media Pembelajarall:
Hand out, OHP, whiteboard, marker, etc.
Strategi, Model, Pendekatan dan Metode Pembelajaran: Strategi : TPR, Games
Model : face to face Pendekatan : Communicative Metode : Group and whole class
SKENARIO PEMBELAJARAN
NO KEGIATAN WAKTU
I PENDAHULUAN 5
1.l.Guru mengucapkan salam 1
1.2. Guru mengabsen siswa 2
1.3.Tanyajawab mengenai hal terkait kondisi siswa 2
II KEGIATANPOKOK 65
2.1.Guru membagi kelas menjadi 9 kelompok dan 5 memberikan amplop yang berisi . kalimat Present Continuous Tenseberbeda pada setiap kelompok
2.2.Setiap kelompok memeperagakan kalimat yang teliera