i
USING SONGS
TO TEACH PRONUNCIATION TO THE FIFTH GRADERS
OF SD NANGGULAN 1 KULON PROGO
ASARJANA PENDIDIKANTHESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain theSarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Mahatma Primandaru Student Number : 081214127
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
iv
This Undergraduate Thesis
Is dedicated to :
Allah SWT
Myself
My Beloved Mother
My beloved sisters
Anggoro suryo
Deliana Ciciliawati
My friends
vii ABSTRACT
Primandaru, Mahatma. 2013. Using Songs to Teach Pronunciation to the Fifth Graders of SD Nanggulan 1 Kulon Progo. Yogyakarta: Sanata Dharma University.
This research investigated the use of songs in teaching pronunciation to the fifth graders ofSD Nanggulan 1. The students did not accustomed to speak by using English language in their school and their daily life. This condition made them became hesitant to pronounce English. Moreover, they were afraid of making mispronunciation. As the result, most of the students faced difficulties in pronouncing some English words.
Therefore, the researcher intended to overcome that problem by conducting the experimental research. The researcher used songs as the treatment to improve the students’ pronunciation. The researcher formulated a question that should be answered through this research. The question was: What is the effect of teaching pronunciation through songs on the students’ pronunciation?
This research was based on experimental research. The participants of this research were 32 students. The researcher put the class into two groups, namely control group and experimental group. Then, the researcher conducted pre test for those two groups. In the following days, the researcher gave the treatment to the experimental group using two children songs, namely “Beautiful Day” and “Promise”. On the other hand, the researcher did not give any treatment to the control group. The researcher conducted the post test for those two groups in order to find out whether there was an improvement on the students’ pronunciation or not.
Based on the research result, there was significant difference between the pre test and post test on the experimental group. From the result of the test by using “Beautiful Day”, the mean value of T test was 3.78, and for the “Promise”, the mean value of T test was 15.6. From the result, the researcher inferred that there was a significant difference between pre test and post test because the mean number of T obtained was higher than the mean number of T critical (1.753). From the result of the control group, the mean value of T test on the “Beautiful Day” was 0.57 and the mean value of T test on the “Promise” was 0.65. Both of the mean value results were lower than T critical (1.753), it could be concluded that there was no improvement between pre test and post test on the control group. The results of this research showed that there was a significant improvement on the pronunciation of the students who had been taught through songs. It could be concluded that by using songs in teaching pronunciation gave the better improvement on the students’ pronunciation. Songs could be used as the teaching materials to improved the students’ pronunciation.
viii ABSTRAK
Primandaru, Mahatma. 2013. Using Songs to Teach Pronunciation to the Fifth Graders of SD Nanggulan 1 Kulon Progo. Yogyakarta: Sanata Dharma University.
Penelitian ini untuk mencari tahu mengenai penggunaan lagu dalam pengajaran pengucapan untuk siswa kelas lima SD Nanggulan 1. Para siswa tidak terbiasa untuk berbicara dengan menggunakan bahasa Inggris di sekolah mereka dan kehidupan sehari-hari mereka. Kondisi ini membuat mereka menjadi ragu-ragu untuk mengucapkan bahasa Inggris. Terlebih lagi, mereka takut membuat salah ucapan. Hasilnya, sebagian besar siswa mengalami kesulitan dalam mengucapkan beberapa kata dalam bahasa Inggris.
Oleh karena itu, peneliti bermaksud untuk mengatasi masalah tersebut dengan melakukan penelitian eksperimental. Peneliti menggunakan lagu sebagai perlakuan untuk meningkatkan kemampuan pengucapan siswa. Peneliti merumuskan sebuah pertanyaan yang harus dijawab dalam penlitian ini. Pertanyaan itu adalah: Apakah efek dari pengajaran pengucapan menggunakan lagu terhadap kemampuan pengucapan siswa?
Penelitian ini merupakan penelitian eksperimental. Responden dalam penelitian ini berjumlah 32 siswa. Peneliti membagi kelas tersebut menjadi dua kelompok, bernama kelompok kontrol dan kelompok eksperimen. Kemudian, peneliti melakukan pra tes di kedua kelompok tersebut. Di hari berikutnya, peneliti memberikan perlakuan kepada kelompok eksperimen dengan dua lagu anak-anak, bernama lagu “Beautiful Day” dan lagu “Promise”. Di sisi lain, peneliti tidak melakukan perlakuan apa-apa untuk kelompok kontrol. Peneliti melakukan tes akhir di kedua kelompok untuk melihat apakah ada peningkatan kemampuan pengucapan siswa atau tidak.
Dari hasil penelitian, terdapat perbedaan yang berarti dari pra tes dan tes akhir untuk kelompok eksperimen. Dari hasil tes untuk lagu “Beautiful Day”, nilai dari T tes adalah 3,78, sedangkan untuk lagu “Promise”, nilai T tes adalah 15,6. Kedua hasil tersebut berarti bahwa ada perbedaan yang menonjol antara pra tes dan tes akhir karena nilai T yang diperoleh lebih tinggi dari T kritis (1,753). Dari hasil pada group kontrol, nilai T untuk lagu “Beautiful Day” adalah 0,57 dan nilai T untuk lagu “Promise” adalah 0,65. Kedua nilai T tersebut kurang dari nilai T kritis yaitu 1,753. Hal ini berarti tidak ada peningkatan yang terjadi untuk grup kontrol.
Hasil dari penelitian ini menunjukkan bahwa ada peningkatan kemampuan pengucapan bahasa Inggris pada siswa yang mendapat pelajaran menggunakan lagu. Ini bisa disimpulkan bahwa penggunaan lagu dalam pengajaran pengucapan memberikan peningkatan yang baik pada pengucapan siswa. Lagu dapat digunakan sebagai bahan ajar untuk meningkatkan pronunciation pada siswa.
ix
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
First of all, I would like to express my gratitude to Allah SWT for His love and blessing in my life, especially during completing my thesis. Through weaknesses and strengths, happiness and sorrows, I could finish this thesis with His will. Secondly, I would like to express my gratitude tomy beloved mother. I dedicate my thesis to her as she always accompanied me and motivated me until I finished my thesis.
I would like to give my sincere thank to my supervisor, Drs. Barli Bram, M.Ed., Ph.D. for the time, advice, motivation and guidance during the research and the thesis writing process. I also address my gratitude to J.S.M Pudji Lestari, S.Pd., M.Humfor the time, advice, motivation, guidance, and support. I would thank to Drs. Sugengfor supporting and giving the permission to conduct the research inSD Nanggulan 1.
I would also like to thank Deliana Ciciliawati for always supporting me in my study. I thank her for the time, advice and love that she gave to me. I thank my best friends in my campus, Mia, Berlin, Mike, Saka, Bela, Aji, Pyta, Yeni, Dhian and Sandy for their laughter, cheer, help, concern, and love. Moreover, I thank my friends in my office, Ambar, Tulus, Pengky, Iwan, Mira, and Zully for always supporting me when I found many problems related to my thesis.
x
my study in PBI. I would also thank my friends in Dimas Diajeng Yogyakarta for giving me support in finishing my thesis. My thankfulness also goes to everybody whose name I could not mention one by one for always helping and supporting me in all aspects.
xi
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE... i
APPROVAL PAGES ... ii
DEDICATION PAGE ...iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ...v
PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI ...vi
ABSTRACT ...vii
ABSTRAK ...viii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ...ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS ...xi
LIST OF TABLES ...xiv
LIST OF APPENDICES ...xv
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Research Background………...1
1.2 Research Problem...………...3
1.3 Problem Limitation…………...………...4
1.4 Research Objective...4
1.5 Research Benefits...4
xii
CHAPTER II REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
2.1 Theoritical Description ...8
2.1.1 Young Learners...8
2.1.2 Pronunciation...……...9
2.1.3 Teaching Media...10
2.1.4 Children Songs...…...10
2.1.4.1 How to Present Educational Children Songs in Classroom…....11
2.1.4.2 Considerations and Principles in Choosing Children Songs…....11
2.1.4.3 The Benefits of Songs for Young Learners...13
2.1.4.4 Learning Pronunciation by Using Song...14
2.1.5 Review of Related Studies...16
2.2 Theoretical Framework...18
CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY 3.1 Research Method………...21
3.2 Research Setting………...24
3.3 Research Participants……….………...24
3.4 Instruments and Data Gathering Technique………...24
3.4.1 Test...24
3.5 Data Analysis Technique...27
3.6 Research Procedures...28
CHAPTER IV RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 4.1 Pre Test………...29
xiii
4.2.1 Experimental Group... .35
4.2.2 Control Group………...42
4.3 Post Test………..………...42
4.3.1 Experimental Group...42
4.3.2 Control Group...44
4.4 T test...46
4.4.1 T Test for Experimental Group...46
4.3.2 T Test for Control Group...49
4.5 Analysis...51
4.5.1 Pre test...51
4.5.2 Treatment...52
4.5.3 Post test...55
CHAPTER V CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS 5.1 Conclusions ………...58
5.2 Recommendations ………...60
REFERENCES...62
xiv
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
Table 4.1 Groups of the Research...30
Table 4.2 Pre-Test Result of “Beautiful Day”(Experimental Group)...31
Table 4.3 Pre-Test Result of “Beautiful Day”(Control Group)...32
Table 4.4 Pre Test Result of “Promise”(Experimental Group)...33
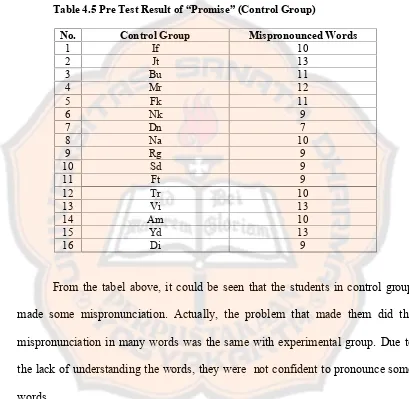
Table 4.5 Pre Test Result of “Promise”(Control Group)...34
Table 4.6 The Result of Tally Sheet of “Beautiful Day”...36
Table 4.7 The Result of Tally Sheet of “Promise”...37
Table 4.8 The Experimental Group’s Result of “Beautiful Day”-Post Test...42
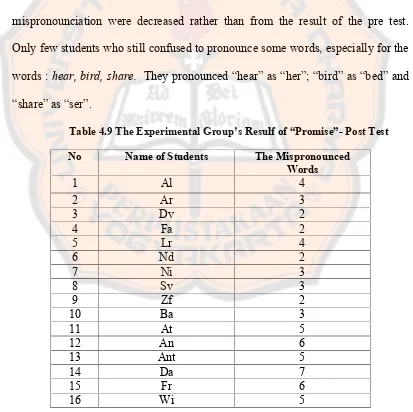
Table 4.9 The Experimental Group’s Resulf of “Promise”-Post Test...43
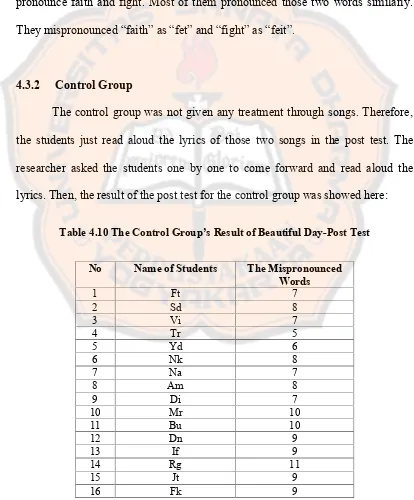
Table 4.10 The Control Group’s Result of “Beautiful Day”-Post Test...44
Table 4.11 The Control Group’s Result of Promise Song-Post Test...45
Table 4.12 T Test of “Beautiful Day” for Experimental Group...46
Table 4.13 T Test of “Promise” for Experimental Group...47
Table 4.14 T Test of “Beautiful Day” for Control Group ...49
xv
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix Page
Appendix 1. Covering Letter for the Head ofSD Nanggulan 1...64
Appendix 2. Lesson Plan...66
Appendix 3. Teaching Materials...79
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
In this chapter, the researcher presents the research background,
research problem, problem limitation, research objective, research benefits, and
definition of terms.
1.1 Research Background
The English language is one of the international languages which is
necessary to be learnt (Brewster, Ellis, & Girard, 2002, p. 1). Mastering the
English language can help us to communicate with so many people around the
world. Learning English can be started as early as possible. Since 1990s, most
people in Indonesia have learnt English since they were in elementary school.
According to the government’s instruction, English is taught in elementary school
starting from the fourth grade (Depdikbud, 1994:ii as cited in Sutiyono, 2001:1).
Therefore, inSD Nanggulan 1, the English subject is taught from the fourth grade.
Although the English subject is taught from the fourth grade, there were
many students in SD Nanggulan 1 who pronounced English words incorrectly. It
was because the students were not accustomed to practicing English in class or
their daily life. They did not have enough chance to speak in the English class. As
a result, the students became hesitant to speak in English as they were afraid of
producing incorrect sounds. In language learning, how to pronounce words is
really important. When the pronunciation is unclear, it may cause ambiguity in
is important in language learning to be learnt. Due to the problems, the teachers
need to make the students more active in speaking activities.
The teachers need to use the appropriate methods and teaching materials to
make the students active in the English class. Although the teachers have course
books as the guidance in teaching and learning process, the teachers might look
for another teaching materials (Brewster, Ellis, & Girard, 2002, p. 156). There are
many teaching materials that can be used, such as songs, rhymes, games, posters,
flashcards, CDs, the internet, and other CALL programmes (Brewster, Ellis, &
Girard, 2002, p. 156). One of those teaching materials is song. The teachers can
use song in the teaching and learning activities. In this study, the researcher chose
songs as the teaching material in teaching pronunciation to young learners.
In teaching English to elementary school learners, the teachers need to
know their characteristics. Scott and Ytleberg (1990) explain that the children
have a great motivation to learn what they like. In line with their nature, they love
to play. The children will be enthusiactic in learning something they like. They
can easily learn something new from other people, that is why they need a
guidance to make them focus on what they need to learn (pp. 2-4). Based on Scott
and Ytleberg’s explanation, the researcher inferred that the children love to learn
something new which attract their attention. Furthermore, young learners like the
activities which can explore their body movements. Moreover, Slattery and
Willis (2001) explain that children usually like singing and performing (p.44).
They will enjoy learning songs and rhymes. They will be enthusiastic when they
the words until they can remember the lyrics of the songs. This activity will
increase the children’s ability in pronouncing English words.
Based on Brewster, Ellis, and Girard (2002), “Children love songs, rhymes
and chants and their repetitive nature and rhythm make them an ideal vehicle for
language learning” (p.162). In addition, Philip (1993) explains that music and
rhythm are an essential part of language learning for young learners (p. 100). It
means that music and rhythm can be used in teaching and learning activities,
especially in language learning. Music and rhythm will motivate and encourage
the children to learn language.
Using songs in learning pronunciation can bring a new atmosphere for
children. It can enourage them to learn pronunciation enthusiastically. According
to Lo and Li (1998), songs play an important role in motivating students to learn
English. By using songs, the teacher can develop the children’s abilities in
reading, writing, listening and speaking, as well as provide opportunities for
learning pronunciation, rhythm, grammar and vocabulary. There are many
activities which can do by using songs in the classroom. From the experts’
explanation, the teachers may use songs in teaching and learning activities to
improve children’s pronunciation.
1.2 Research Problem
The problem of the research can be stated as follows:
What is the effect of teaching pronunciation through songs on the
1.3 Problem Limitations
The researcher focuses on the use of songs in teaching English
pronunciation to the fifth graders of SD Nanggulan 1. The researcher wants to
find out the effect of using children songs in teaching pronunciation on the
students’ pronunciation. Moreover, the researcher will teach the students how to
pronounce vowels and consonants with the correct pronunciation through songs.
Then, the researcher will analyze their pronunciation in pronouncing English
vowels and consonants of the children songs.
Furthermore, the researcher will use simple songs which are appropriate
with the level of the students. In this research, the researcher will conduct tests to
answer the problem formulation. There will be two tests in this study, those are
pre test and post test. The tests are conducted in oral form because the researcher
will test the pronunciation ability of the fifth graders inSD Nanggulan 1.
1.4 Research Objective
The objective of this research is finding out the effect of teaching
pronunciation through songs on the students’ pronunciation. The researcher wants
to find out whether the use of songs in teaching pronunciation give the effect on
the students’ pronunciation or not. Moreover, the aim of this research is to know
the use of songs in classroom to help the fifth graders in SD Nanggulan 1 in
improving their pronunciation ability.
1.5 Research Benefits
Through this research, there are several benefits that could be
expected to give contribution for the English teachers, the elementary school
students, and other researchers.
a. English Teachers
The results of the study are expected to be the option used by the teachers
as the teaching materials to teach pronunciation for young learners. The teachers
might use songs in teaching pronunciation with various ways. In the teaching and
learning activities, it will be better if the teachers do not only explain the materials
all the time in front of the class and let students listen what they heard. The
teachers might use the appropriate teaching materials to support their teaching and
learning process. Using attractive teaching materials like songs can make the
teaching and learning process more lively and the students might have a new
optional way in learning pronunciation.
b. Elementary School Students
From this research, the students are expected to have a new spirit to learn
English pronunciation through songs. The researcher hopes that usings songs in
teaching and learning activities will break the boredom of old-fashioned way of
teaching. The students become more active in learning process. Moreover, the
students will be enthusiastic to learn English pronunciation. When the students are
well motivated, they will enjoy to learn and their pronunciation will be better.
c. Other Researchers
It is expected that the study will be useful for further research and enlarge
the readers’ knowledge in using the children songs as teaching materials. The
interested in conducting another research related to songs and its effects for young
learners.
1.6 Definition of Terms
There are several terms related to this research. The descriptions of those
terms are described below.
a. Song
According to Simms (1993), “a song is a short of piece in one concise
movement for the medium of solo voice and piano” (p. 29). Moreover, Parto
(1996) said that a song is a group of arrangements which consists of lyrics and
elements of music like rhythm, melody, harmony and expressions” (p. 99). All the
songs which are used in this study are children songs. It is because the object of
this study is elementary school students, aged 10-11. The songs which are used in
this study are related to the students’ level.
b. Pronunciation
According to Nunan (2003), pronunciation is sounds we make while
speaking. The sounds we produce are used as a communciation tool (p. 112).
Moreover, Jones (1958) describes pronunciation is the way people produce sound
using organ of speech. In this thesis, pronunciation is the act or manner of the
students in pronouncing English words.
c. The fifth graders ofSD Nanggulan 1 Kulon Progo
The fifth graders means the students who are in the fifth grade of
elementary school. Moreover, Nanggulan is the subdistrict of the Kulon Progo
8
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF LITERATURE
Chapter two presents the discussion of theories and research related to the
study in this thesis. The purpose of this chapter is to provide information of
theories used in answering the questions of this research. In this chapter, there are
two major areas of concern. The first part is the theoretical description and the
second part is theoretical framework.
2.1 Theoretical Description
In this part, the researcher disscusses the theories related to the use songs in
teaching English pronunciation. This chapter will also discuss young learners,
teaching media, and children songs.
2.1.1 Young Learners
According to Philips (1993), young learners are children from the first
year of formal schooling (five or six years old) to eleven or twelve years of age (p.
5). Children, especially young learners, have many unique characteristics that
make us interesting to discuss them. According to Scott and Ytlberg, young
learners are able to work with others and learn from others (Scott & Ytlberg,
1990, pp. 2-4). Young learners can learn from their friends, teachers, parents, etc.
Young learners are very active and also love to play (Scott & Ytlberg, 1990, pp.
sense of the world”. They will do something if their condition is good and they are
happy in doing it.
Based on the experts’ findings, the enthusiasm of the students is one of the
most important things. The teachers have to know the characteristics of the
students which really love to play. Moreover, the teachers need to use any
interesting media and teaching materials to support the teaching and learning
process.
2.1.2 Pronunciation
In communicating to other people, the way how to pronounce words is
really important. If the pronunciation is unclear, it may cause ambiguity in
understanding the meaning. According to Kenworthy (1997), in pronouncing the
words, intelligibility is really important to avoid ambiguity in communication.
Intelligibility means “being understood by a listener at a given time in a given
situation” (p. 13).
In teaching and learning activities, the teachers have to be good models for
the students in pronouncing English correctly and clearly. The teachers need to
know and understand the problem faced by the students, so that the teachers can
give the best solution related with the problem. Most of students are not
accustomed to speaking English in their daily life. As a result, they feel less
confident to make mistake when they speak in English.
The teachers need to use the appropriate teaching materials to teach the
if the teaching materials contain the native language as they give clear example of
native language and the students would imitate the sounds precisely.
2.1.3 Teaching Media
According to Arsyad (2006), teaching media is used to convey teaching
messages (p. 4). In the view of National Education Association (in Arsyad, 2006,
p. 5), media is of communication either printed or audio visual and the tools.
Based on the above definition, it can be concluded that teaching media are needed
for the teachers to help them in teaching-learning activity. Teaching media can be
printed or audio visual and the tools. Teaching media is really important for the
teacher to convey the material for the students.
2.1.4 Children Songs
In understanding the definition of children songs, we need to know about
the definition of the song it self. According to Parto (1996), “a song is a group of
arrangements which consists of lyrics and elements of music like rhythm, melody,
harmony and expressions” (p. 99). In a song, there are harmony of lyric, music,
melody, rhythm and also expression. In this study, the researcher used the children
songs. Children songs are songs which related to the children’s characteristics.
Based on Hornby (1995), ”Child is an individual who has not reached puberty” (p.
192). Then, the researcher inferred that children songs are songs which really
attract the children’ enthusiasm to listen to them. The children songs consist of
beautiful words of which the melody is really cheerful. Moreover, the children
2.1.4.1 How to Present Educational Songs in Classroom
Knowing the procedure to present song in teaching and learning activities
is really important. Hubbard, Jones, Thornton, & Wheeler (1983) suggest some
procedures to present song. In using songs as the teaching materials, the teachers
need to explain the lyric of the songs carefully and patiently. Moreover, the
teacher explains the words clearly to make the students understand in pronouncing
the lyric and also the meaning. Then, the teachers play the whole songs to make
the students understand the rythm of the songs. When the students start to
understand the rhythm, they will imitate what they heard from the songs.
Furthermore, the teacher needs to bring the lively atmosphere into the
class. The teacher might use gesture activities related to the songs to attract the
students’ enthusiasm. If the students cannot understand clearly what they heard
from the cassete, the teacher might play the song verse by verse. After the
students start to understand the rythm and the pronunciation of the words, the
teachers let them to practice singing (Hubbard, P., Jones, H., Thornton, B., &
Wheeler, R., 1983, p.94).
2.1.4.2 Considerations and Principles in Choosing Children Songs
In using children songs in teaching and learning activities, the teachers
need to choose the appropriate children songs. According to Hubbard, Jones,
Thornton, & Wheeler (1983, pp. 93-94), there are some considerations and
principles in choosing educational children songs. First, the teachers need to make
sure if the songs are suitable for the language level of students (elementary,
students. When the songs are not appropriate with the age of students, the students
might not enjoy to listen and sing the song. Third, the songs should be more
appealing to the students. If the songs are interesting to them, they will pay
attention to the songs (Hubbard, P., Jones, H., Thornton, B., & Wheeler, R., 1983,
pp. 93-94).
In addition, Tassoni, Beith, Eldridge, and Gough (2002) explain some
principles in choosing children songs. First, the songs which are used in teaching
and learning for young learners should be fun and easy to be learnt. The teachers
need to choose the songs which have interesting rhytm so that the children will be
enjoy to listen and sing the songs. The teachers have to avoid the songs which are
too complicated for children, for example: the songs are too fast; the songs have
many difficult words for children. Second, the songs should have a relevance to
the children environment. The teachers might introduce the children’s
environment through songs. The children will be easy to draw their imagination
because what they heard from the songs are close to them. Third, the songs
should be linked to the theme. The teachers have to make sure if the songs are
related with the theme and the content of the learning materials. Furthermore, the
songs which will be used in teaching and learning acitivities should be bright with
clear image to attract children (Tassoni, P. , Beith, K. , Eldridge, H. & Gough, A.,
2002, pp. 424 – 428).
The teachers have to understand those considerations when choosing
songs as the teaching materials. If the songs are not appropriate to the children’s
songs. When the children are not interested to listen to the song, it will be difficult
for the teachers to teach English through songs.
2.1.4.3 The Benefits of Songs for Young Learners
Using songs in teaching and learning activities give many benefits for
children. Brewster, Ellis, and Girard (2002, pp. 162-163) explain that there are
some postive impacts due to the use of songs, rhymes, and chants in teaching and
learning activities. In linguistic resource, the use of songs can improve all aspects
of pronunciation. The students will imitate how to pronounce many English words
by singing and listening to the songs. The use of songs gives many benefits not
only for linguistic aspect of children but also for other aspects. When the
atmosphere of teaching and learning activities is enjoyable, it will affect on the
children’s mood. The children’s mood will be increased. It means that the
children’s psychological also obtain the positive impacts.
If the children are in a good mood, they will do the activities happily and
concentrate on what they do. After the listen to the songs, they will try to
remember the lyrics of the songs. This activity will sharpen their ability in
memorization. It means their cognitive aspect also obtain postive impacts.
Moreover, The children usually share what makes them happy to their friends. In
here, they will share what they have learnt by listening and singing to the songs.
The children will be happy to sing together with their friends. The teachers can
make a group discussion related to the songs which develop the social aspect of
2.1.4.4 Learning Pronunciation by Using Song
In learning pronunciation through songs, songs give some benefits to the
children. Based on Philips (1993), “the children can remember language easily by
listening to music and rhythm” (p. 94). According to Paul (2003), by listening and
singing song, the students’ feeling to learn language is increased (p. 58).
Moreover, Paul says that songs also help children to remember words and practice
language more easily. The children also get more deeply into a lesson. Based on
the explanation from Paul and Philips, the researcher inferred that song is a good
learning material for the students to increase their pronunciation. By listening to
the music and songs, the students will be easier to imitate the lyric of the songs.
Using songs in teaching and learning actitivities give many benefits for
children. Brewster, Ellis, and Girard (2002, pp. 163-164) explain the
pronunciation benefits of using songs. There benefits are in four aspects, those
are :
a. Individual sounds and sounds in connected speech
Songs and rhymes are useful for showing what happens to sounds in connected
speech, for example, the way that certain sounds run on together : You’re not IT!
Or All in together! Rather complicated consonant clusters in English are often
simplified, especially where a word which ends in /t/ or /d/ is followed by
consonant cluster (Brewster, Ellis,& Girard, 2002, pp. 163-164).
b. Stress and rhythm
Stress and rhythm can also be practiced in a very natural way by using songs or
help to develop a sense of rhythm in English. Weak forms, where the
pronunciation of a word differs according to wheter it is stressed or unstressed,
occur regularly in songs and rhymes (Brewster, Ellis,& Girard, 2002, pp.
163-164).
c. Intonation
Intonation can also be practiced in songs and rhymes (Brewster, Ellis,& Girard,
2002, pp. 163-164).
d. Ear training
By using songs and ryhmes, the teachers can use ear training to help the
children distinguish between different aspects of English pronunciation. To do
this activity, the teachers might ask the children to listen and count how many
times an individual sound or word occurs in a song or rhyme (Brewster, Ellis,&
Girard, 2002, pp. 163-164).
Based on the experts’ explanation above, there are four aspects related to
pronunciation that get the good impacts of using songs in teaching and learning.
By using songs, the teachers can teach the children about connected speech. Songs
are useful for showing what happens to sounds in connected speech. The teachers
might use songs to teach about stress, rhythm and also intonation. In here,
repetition is really needed so that the students will be accustomed to pronounce
words in a good stress and intonation.
Intonation is really important, according to Brewster, Ellis, and Girard
(2002, p. 77), there are some functions of intonation in English. The first function
function is to show the grammatical function of what is beid said, for example,
wheter something is a statement or question. The last function of intonation in
English is to show feelings and emotions.
Due to the importance of teaching intonation for students, songs can be
used as a teaching material which can attract the students’ enthusiasm. In the
lyrics of children songs, there are so many expressions which have different
intonation. The teachers might use them to be taught in attractive ways so that the
children will be enthusiastic to learn. In addition, the teacher might do ear training
to the students through songs. This activity will encourage the children to be
focused on what they heard.
2.1.5 Review of Related Studies
There was a research which investigated the implementation of the use of
songs for teaching vocabulary to kindergarten students. This research had been
conducted by Apsari (2012). This research was also an attempt to investigate the
students’ response toward the use of songs in teaching and learning process. An
English teacher and fifteen students of TK Kartika XV-5 Batujajar, Bandung
Barat were selected to be the respondents of this study. The results of the study
revealed that songs can be used effectively to improve students’ English
vocabulary. Finally, media such as picture is required in order to convey the
meaning of songs. The study also showed that the majority of students were
interested in learning English vocabulary through songs. This results indicates that
by using songs the students tend to be more active in the teaching and learning
Moreover, there was a journal which discussed that songs play an
important role in the development of young children learning a second language.
This research was conducted by Millington (2011). This study will discuss how
songs can help learners improve their listening skills and pronunciation, and how
they can be useful in the teaching of vocabulary and sentence structures.
Millington also discussed how songs can reflect culture and increase students’
overall enjoyment of learning a second language. Finally, the paper explored how
songs for children can be adapted to suit a particular theme or part of the
curriculum a teacher might wish to teach (Millington, N., 2011, pp. 134-141).
Based on a journal named “The Value of Songs and Chants for Young
Learners” by Forster (2006, p. 63-68), using songs in the teaching-learning for the
children can increase their English vocabulary, intonation and pronunciation. The
use of songs, music and rhythm in teaching pronunciation will help the teachers in
doing teaching and learning process. In using songs, the first thing that the
teachers need to do is determining the age of the students. Then, the teachers have
to make sure whether the songs and chants are appropriate for their age or not.
Basically, children love music and songs. It will be better if the teachers
include music and songs in basic communication acts or classroom situations. For
the example, the teachers can lead the students to sing a children song or chant.
The teachers need to give the example how to pronounce the lyric of the songs.
Repetition is really good to improve the students’ memorization. From this
activity, the children can improve their pronunciation and their vocabulary is also
Those three studies proved that songs can be use in teaching and learning
activities. The children who had been taught through songs obtain the positive
effects on their pronunciation, vocabulary mastery, and other aspects of language.
Moreover, the students’ interest to learn language was also increased. In line with
those three studies, in this research the researcher conducted a study through
songs. The researcher focussed to find the effect on the students’ pronunciation
when the students obtained the treatments through songs.
2.2 Theoretical Framework
In learning language, there are four skills that need to be developed. Those
skills are speaking, listening, reading and writing. The teachers have to teach
those skills to make the students understand clearly about the language. One of the
important skills in mastering the language is speaking. Ability to speak fluently
and clearly are really needed to avoid miscomunication. The stundents also have
to pay attention on their pronunciation. If the pronunciation is unclear, it may
cause ambiguity in understanding the meaning. According to Kenworthy (1997),
in pronouncing the words, intelligibility is really important to avoid ambiguity in
communication. Intelligibility means “being understood by a listener at a given
time in a given situation” (p. 13). From the expert’s explanation, we can
understand that speaking with the good pronunciation is really important.
In teaching English to the children, the teachers need to know the
children’s characteristics due to the appropriate teaching materials that will be
have a great motivation to learn what they like. The elementary students will be
enthusiactic in learning something which attract their attention. Based on Scott
and Ytleberg’s explanation, we can understand that the teachers need to use the
appropriate teaching materials to be taught. The teachers have to choose the
teaching materials which can attract the students’ attention so that the students
will enjoy to join the teaching-learning activities.
In this research, the researcher focused on the teaching pronunciation to
young learners. The researcher found that the fifth graders ofSD Nanggulan 1had a problem in pronunciation. They pronounced English words incorrectly and some
of words were influenced by Javanese accent. One of the problems that made the
young learners felt difficult to improve their speaking ability, especially in their
pronunciation was because the students were not accustomed to practice English.
The teachers needed to use the appropriate media and teaching materials to make
the students more active in speaking activities.
The researcher offered the use of songs as the teaching materials to attract
the students to learn English pronunciation. The reason why the researcher used
songs in teaching pronunciation was because basically the students love songs,
rhymes and chants. According to Brewster, Ellis, and Girard (2002), “Children
love songs, rhymes and chants and their repetitive nature and rhythm make them
an ideal vehicle for language learning” (p.162). Moreover, the use of songs in
teaching pronunciation will improve the students’ linguistic aspect, especially on
In addition, Philip (1993) explains that music and rhythm are an essential
part of language learning for young learners (p. 100). Based on a journal named
“The Value of Songs and Chants for Young Learners” by Forster (2006, pp.
63-68), using songs in teaching-learning for the children can increase their English
pronunciation. Based on the experts’ explanation, the researcher inferred that
songs, musics and rhythm could be used in teaching and learning activities,
especially in language learning. Songs, music and rhythm would motivate and
21
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter discusses several things such as research method, research
setting, research participants, instuments and data gathering technique, data
analysis technique, and research procedure. Those things are very important for
the researcher in conducting the study and obtaining the empirical data as the
results of the study.
3.1 Research Method
The researcher used the analysis of results from an experimental research
to answer the research problem of this thesis. Experimental research has long been
employed by linguists and educational researchers to discover whether one
teaching or learning technique or other variables is more effective than another
when applied to one or two groups of participants. According to Gay (1992, p.
298), in conducting experimental research, the researcher will have to manipulate
at least one independent variable, control over relevant variables, and observe the
effect on one or more dependent variables.
According to Fraenkel and Wallen (2009) , “Experimental research is
the only type of research that directly attempts to influence a particular variable,
and when properly applied, it is the best type for testing hypotheses about
cause-and-effect relationships” (p. 261). The independent variable in experimental
known as the outcomes of the study (Fraenkel & Wallen, 2009, p. 261).
Moreover, Fraenkel and Wallen (2009) explain that the researchers can
manipulate the independent variable (p. 261). In other words, the researchers who
conducts an experimental research decides what will happen to the subjects. The
researchers can manipulate the methods if instruction, type of assignment,
learning materials, rewards given to students, and types of questions asked by
teachers. At the end of the research, the researcher observe or measure the groups
receiving differents treatments. The researchers will see whether the treatment
made a difference or not (Fraenkel & Wallen, 2009, pp. 261-262).
In an experimental research, three variables must be taken into account.
The first one was the starting point, the second was the treatment, and the last
was the outcome. After that, the researcher would compare between the starting
point and the result point to see the effect after the researcher gave the treatment
to the samples. Commonly, an experimental research has two or more groups of
samples to be compared, although having only one group is possible (Fraenkel &
Wallen, 2009).
In this research, the researcher wanted to know the effect of using songs
in the classroom activities to the students’ pronunciation. That was the reason the
researcher used the experimental method to answer the research problem.
Through the experimental research, the researcher would find out the difference
between the students who were given the treatment by using songs and those who
In this reseach, the researcher used static-group pretest-posttest design.
According to Fraenkel and Wallen (2009, p. 266), the static-group pre test-post
test design is a design that involves at least two nonequivalent groups. The groups
which will be compared are already formed. There will be a pretest for those two
groups. Moreover, one group will receive a treatment and the other one will not.
The result of pre test and post test from those two groups will be analyzed to see
the difference (Fraenkel&Wallen,2009, p. 266).
The Static-Group Pre test-Post test Design
Treatment group O X O
Control group O O
(Fraenkel & Wallen, 2009, p. 266).
In this research, the research put the class into two groups, namely
experimental group and control group. Both of groups being measured or
observed twice. The first measurement was the pre test, the second was the post
test. The measurements were collected at the same time for both groups. In the
pre test, the researcher asked both of groups did the pre test by reading aloud the
pre-test paper. Then, the researcher analyzed the result of the pre test. After that,
the researcher gave the treatment by using songs for the experimental group. On
the other hand, the researcher did not give any treatment for the control group.
After the treatment was given, the researcher conducted post test for both of
groups. Then, the researcher compared the result between pre test and post test
for those two groups and analyzed whether the treatment made a difference or
3.2 Research Setting
The experimental research of this study was conducted in SD Nanggulan 1, Jatisarono, Nanggulan, Kulon Progo, Yogyakarta. The condition of the school
was fairly quite and condusive to conduct a research. The researcher chose the
fifth graders ofSD Nanggulan 1. The class was quite condusive and it supported
for the process of study.
3.3 Research Participants
The participants of the study were the fifth graders of SD Nanggulan 1in
the academic year 2012/2013. There were 32 students. It consisted of 15 males
and 17 females. They were around 10-11 years old. Moreover, they had learnt
English since they were in the fourth grade. Most of the students faced difficulties
on pronouncing some English words.
3.4 Instruments and Data Gathering Technique
An instrument plays an important role in a study in the sense that the
reliability of the instrument will influence the reliability of data obtained. The
instrument used in this experiment was intended to measure the students’
achievement in English pronunciation. Therefore, the instrument used in this
study is test.
3.4.1 Test
Test is valuable measuring in a research. As Ary wrote (1979) “a test is a
set of stimuli presented to an individual in order to elicit responses on the basic of
which a numerical score can be assigned” (p. 179). Therefore, tests are very
achievement in mastering English pronunciation through songs. The songs which
were used in this tests were “Beautiful Day” and “Promise”. In choosing the
songs, the researcher referred to the theories from Hubbard, et al. (1983) and
Tassoni, et al. (2002). According to the explanation from Hubbard, et al. (1983)
and Tassoni, et al. (2002), there are some considerations in choosing children
songs (see chapter 2, p. 12). In using songs as the teaching materials, the songs
must be suitable for the language level and the age of the students (Hubbard, et
al., 1983). “Beautiful Day” and “Promise” contained words which were common
for the children. The children already known those words from their English
teacher and English books.
The songs which are used as the teaching materials should be more
appealing to the students (Hubbard, et al., 1983). Moreover, the teachers need to
choose songs which are fun and easy to learn (Tassoni, et al., 2002). Both of
songs which were used by the researchers were easy to learn and fun.
Furthermore, the lyrics of “Beautiful Day” and “Promise” contained words which
were related to the children’s environment. In line with the theory from Tassoni,
et al. (2002), the songs which are used in the teaching and learning activities
should have a relevance to the children environment.
In this research, the researcher conducted pre test and post test. The
result of the achievement tests were used to indicate the students’ progress of
English pronunciation by using English children songs. In the pre test, the
researcher asked the students to read aloud the lyrics of “Beautiful Day” and
lyrics. It refered to the Basic Competence of reading aspect for the fifth graders of
Elementary School: “Reading aloud words, phrases, simple sentences and texts
using the appropriate pronunciation, stress, intonation”. Based on the basic
competence, the lyrics of those two songs contained simple sentences which
appropriate with their level. All of the students came forward one by one to read
the lyrics of those two songs. The researcher recorded their voice to analyze their
pronunciation in pronouncing those words.
As it had been explained previously, the researcher put the class into two
groups, named experimental group and control group. The next four activities
were teaching pronunciation to the students in experimental group using children
songs. The last activity was a post test. The post test was to know the progression
of the students in English pronunciation before and after getting a treatment by
using English children songs.
In the post test, the researcher asked all of the students in the
experimental group to came forward one by one to sing the songs. Due to the
control group was not given any treatment through songs, in this post test all of
the students in control group just read aloud the lyrics of those two songs. The
researcher recorded their voice to analyze their pronunciation in pronouncing
those words.
In line with the objectives of experimental research, the researcher used
T test to make comparison of the mean between pre test and post test. Based on
difference or not.The result of the T test would support in answering the research
problem of this study. The T test formula was described as follows.
d =∑ Sd = ∑ (∑ ) /
t = d - µd Sd/√n
Source: Fraenk, Wallen, and Hyun (2012)
3.5 Data Analysis Technique
In this research, the researcher collected the data both of pre test data and
post test data of the respondents. In the pre test , all of the students came forward
one by one to read the lyrics of those two songs. The researcher recorded all of
their voice to analyze their pronunciation in pronouncing those words. The
researcher counted how many mispronounced words made by the students.
In the post test, the researcher asked the students in experimental group
one by one to sing the songs . The researcher recorded all of their voice and
counted how many mispronounced words made by the students. For the control
group, the researcher asked them one by one to read aloud the lyrics of the songs.
The researcher recorded all of their voices and counted how many mispronounced
words made by the them. Furthermore, the researcher analyzed the data by
comparing the result between pre test and post test for those two groups. The
researcher did the T test for the pre test and post test in order to show whether the
3.6 Research Procedures
The researcher conducted this research by planning several steps to do as
follows:
First, the researcher put the class into two groups, namely experimental
group and control group. There were 16 students in experimental group and 16
students in control group. Before doing the pre test, the teacher taught them how
to read the words correctly. Then, the researcher did the pre test for those two
groups. Moreover, the researcher recorded all of their voice and analyzed the
result of the pre test.
Second, the researcher conducted the treatment for the experimental
group. The treatment was using the children songs. There were four times of
treatment by using songs. The objective on conducting the treatment was to
increase students’ ability in pronouncing English. On the other hand, the
researcher did not give any treatment for control group. Moreover, the researcher
wanted to measure the difference of pronunciation between pre test and post test
for those two groups.
Third, the researcher conducted a post test to measure the students’
achievement in mastering English pronunciation through songs. The researcher
recorded all of the students’ voice and analyzed the result. Then, the researcher
did the T test for the pre test and post test in order to show whether the treatment
made a difference or not.The result of the achievement tests are used to indicate
29 CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter will discuss the results of the research, the comparison between
control group and experiment group and the analysis of research. As mentioned in
the previous chapter, the research was conducted to 32 students at SD 1
Nanggulan, Kulon Progo, Yogyakarta. The researcher put the students into two
groups, namely experimental group and control group. Then, the researcher made
a treatment for experiment group and did not make treatment for control group.
The researcher analyzed the data by comparing the result between pre test and
post test for those two groups. The research was conducted through several steps
as follows:
4.1 Pre Test
The researcher conducted the research on March 16th, 2013. The
researcher opened the teaching learning activities by introducing himself. After
that, the researcher asked the students to introduce themselves in English. After all
of the students introduced themselves in English, the researcher knew that
students’ pronunciation was weak and they mispronounced many words. They
applied Javanese accent and their mother tounge in pronouncing English words.
They often made sound substitutions and sound deletions when they pronounced
The researcher put the class into two groups, namely experimental group
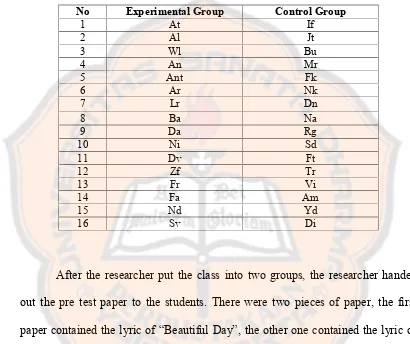
and control group. Those two groups were listed as follows:
Table 4.1 Groups of The Research
No Experimental Group Control Group
1 At If
2 Al Jt
3 Wl Bu
4 An Mr
5 Ant Fk
6 Ar Nk
7 Lr Dn
8 Ba Na
9 Da Rg
10 Ni Sd
11 Dv Ft
12 Zf Tr
13 Fr Vi
14 Fa Am
15 Nd Yd
16 Sv Di
After the researcher put the class into two groups, the researcher handed
out the pre test paper to the students. There were two pieces of paper, the first
paper contained the lyric of “Beautiful Day”, the other one contained the lyric of
“Promise”. After all students got the paper, the researcher gave the examples of
how to pronounce the words on the pre-test paper. After that, the researcher asked
them to read aloud the words together.
Then, the researcher asked all of the students one by one to come forward
reading the first pre test paper which contained the lyric of “Beautiful Day”. The
to analyze their pronunciation in pronouncing those words. In the pre test, the
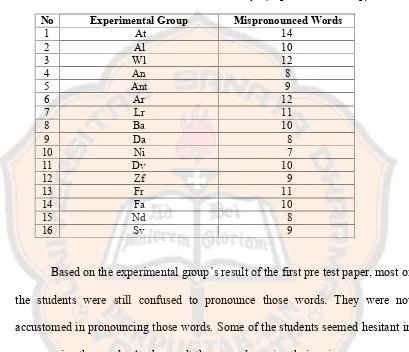
researcher obtained the result as follows:
Table 4.2 Pre-Test Result of “Beautiful Day” (Experimental Group)
No Experimental Group Mispronounced Words
1 At 14
2 Al 10
3 Wl 12
4 An 8
5 Ant 9
6 Ar 12
7 Lr 11
8 Ba 10
9 Da 8
10 Ni 7
11 Dv 10
12 Zf 9
13 Fr 11
14 Fa 10
15 Nd 8
16 Sv 9
Based on the experimental group’s result of the first pre test paper, most of
the students were still confused to pronounce those words. They were not
accustomed in pronouncing those words. Some of the students seemed hesitant in
pronouncing the words. As the result they were lowering their voice.
From the tabel above, the student who made the most mispronunciation
was At. At mispronounced 14 words out of 82 words. Meanwhile, the student who
made minimum mispronunciation was Ni. Ni mispronounced 7 words. Ni was
quite confident in pronouncing the words. On the other hand, At was not really
confident of what he said. Furthermore, some of words were influenced by
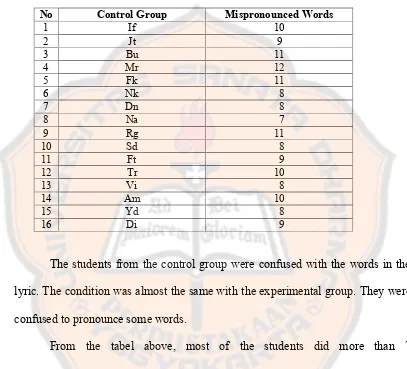
The researcher also did the pre test for the control group. In the first pre
test paper, the researcher obtained the result as follows :
Table 4.3 Pre-Test Result of “Beautiful Day” (Control Group)
No Control Group Mispronounced Words
1 If 10
2 Jt 9
3 Bu 11
4 Mr 12
5 Fk 11
6 Nk 8
7 Dn 8
8 Na 7
9 Rg 11
10 Sd 8
11 Ft 9
12 Tr 10
13 Vi 8
14 Am 10
15 Yd 8
16 Di 9
The students from the control group were confused with the words in the
lyric. The condition was almost the same with the experimental group. They were
confused to pronounce some words.
From the tabel above, most of the students did more than 7
mispronunciation, except Na who only made 7 mispronunciation. Meanwhile, the
student who made the most mispronunciation was Mr. In here, Mr mispronounced
12 words out of 82 words.
After the researcher recorded the students’ voice in reading the first pre
test paper, the researcher asked all of the students from both groups to come
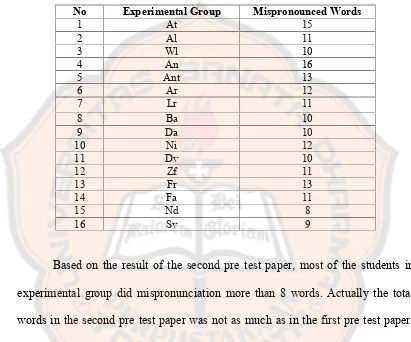
The total words in the lyric were 55 words. In the second pre test paper, the
researcher obtained the result as follows :
Table 4.4 Pre Test Result of “Promise” (Experimental Group)
No Experimental Group Mispronounced Words
1 At 15
2 Al 11
3 Wl 10
4 An 16
5 Ant 13
6 Ar 12
7 Lr 11
8 Ba 10
9 Da 10
10 Ni 12
11 Dv 10
12 Zf 11
13 Fr 13
14 Fa 11
15 Nd 8
16 Sv 9
Based on the result of the second pre test paper, most of the students in
experimental group did mispronunciation more than 8 words. Actually the total
words in the second pre test paper was not as much as in the first pre test paper,
but the students were not accustomed in pronouncing those words. Some words
which considered as difficult words for the students to be pronounced were: pal,
nice, faith, we’ll, fight, crossed, fingers, and leap.
From the tabel above, the student who made the most mispronunciation
was At. At mispronounced 15 words out of 55 words. On the other hand, the
student who made minimum mispronunciation was Nd. Nd mispronounced 8
The researcher also asked the control group to come forward and reading
the second pre test paper. In the second pre test paper, the researcher obtained the
result as follows :
Table 4.5 Pre Test Result of “Promise” (Control Group)
No. Control Group Mispronounced Words
1 If 10
2 Jt 13
3 Bu 11
4 Mr 12
5 Fk 11
6 Nk 9
7 Dn 7
8 Na 10
9 Rg 9
10 Sd 9
11 Ft 9
12 Tr 10
13 Vi 13
14 Am 10
15 Yd 13
16 Di 9
From the tabel above, it could be seen that the students in control group
made some mispronunciation. Actually, the problem that made them did the
mispronunciation in many words was the same with experimental group. Due to
the lack of understanding the words, they were not confident to pronounce some
words.
There were three students who mispronounced 13 words, they were Jt, Vi,
and Wd. Meanwhile, Dn only mispronounced 7 words out of 55 words. Other
students in control group mispronounced more than 7 words and less than 13
Based on the pre test result, all students of those two groups almost did the
similar mistakes in pronouncing the words. The students were not accustomed to
those words. Therefore, they were not confident enough to pronounce those
words. As the result, they were lowering their voice. This result of pre test would
be compared to the result of the post test.
4.2 Treatment
Based on the pre test result, the researcher made several treatments to the
experimental group by giving the special class for learning English pronunciation.
On the other hand, the researcher would not give any treatment to the control
group.
4.2.1 Experimental Group
In learning English pronunciation, the researcher chose to teach the
students by using songs. The researcher arranged four times class by using
English children songs. The first meeting was conducted on March 21st March,
2013. The songs were played to help them grasp the correct pronunciation.
a.First Treatment on March 21st, 2013 (the allocation time : 60 minutes)
The researcher gave the lyric of “Beautiful Day” to the students. Then,
the researcher taught the students how to pronounce the lyric of the songs clearly.
The researcher repeated the word by word patiently while the students were
imitating what they heard from the researcher. The researcher did this action three
times. When the students were getting bored of this action, the researcher put the
lyrics of “Beautiful Day” and his friend listened to him while making tally sheet
for the mispronounced words (see appendix 2, p. 71). They took turn doing the
activity. Then, the result of the first meeting treatment was as follows:
Table 4.6 The Result of Tally Sheet of “Beautiful Day”
No Name of students The mispronounced words
1 At 9
2 Al 10
3 Wl 10
4 An 11
5 Ant 9
6 Ar 10
7 Lr 9
8 Ba 9
9 Da 10
10 Ni 8
11 Dv 9
12 Zf 10
13 Fr 9
14 Fa 10
15 Nd 8
16 Sv 9
Based on the tally sheet of the students, most of the students
mispronounced more than 8 words. The researcher analyzed and discussed the
result of the tally sheet together with the students. The students were very active
to ask for the correct pronunciation.
On the first day, there were several words of “Beautiful Day” which were
considered as difficult words. Those words were shining, start, hear, we’re, bird
and share. The students faced difficulties in pronouncing those words because
they were not accustomed with those words. Their Javanesse accent also
Then, in the same day the researcher also conducted treatment by using
“Promise”. The researcher gave the lyrics and taught them how to pronounce the
lyric of the songs. The researcher repeated the word by word patiently while the
students were imitating what they heard from the researcher. Then, the researcher
also asked the students to work in pair and analyze their friends’ pronunciation.
The result of the first treatment by using the “Promise” was as follows :
Table 4.7 The Result of Tally Sheet of “Promise”
No Name of the students The mispronounced words
1 At 10
2 Al 9
3 Wl 9
4 An 11
5 Ant 10
6 Ar 9
7 Lr 10
8 Ba 10
9 Da 10
10 Ni 9
11 Dv 10
12 Zf 10
13 Fr 11
14 Fa 11
15 Nd 8
16 Sv 9
The researcher analyzed and discussed the result of the tally sheet
together with the students. The situation of the class became more lively because
the students were supporting each other in understanding for the right
pronunciation. The researcher pronounced the words for few times while the
Based on the result, the students did mispronounciation in some words.
Then, the number of the mistakes in pronouncing the lyrics were still high. There
were several words of “Promise” which were considered as difficult words. Those
words were pal, crossed, leap, faith, we’ll, fight, nice. The students were not
accustomed with those words.
In the end of the class, the researcher played the “Beautiful Day” and the
“Promise”. The students were surprised and enthusiastic to listen those two songs.
The students tried to sing the songs. Moreover, they enjoyed to sing the songs.
Based on the result of both songs in the first meeting treatment, the
researcher did not find high improvement of the students’ pronunciation. The
researcher had to explore the activity through songs. Then, the researcher decided
to conduct the second meeting on March 23, 2013.
b.Second Treatment on March 23th, 2013 (the allocation time : 60 minutes)
The researcher reviewed what the researcher had taught from the
previous meeting. The researcher played those two songs to make the students
remembered the songs. The researcher taught the students how to sing the songs,
especially the rhythm of the songs. The students imitated what they heard from
the researcher. Moreover, the students sang happily and they were so enthusiastic
to sing the songs. Then, the researcher asked the students to make a group of four
and they had to listen to the songs carefully. Then, each group had to sing the
songs in front of the class. After all the groups sang in front of the class, the