8 AGRONOMY JOURNAL, VOL. 93, JANUARY–FEBRUARY 2001
Weed suppressing rice cultivars—Does allelopathy play a role? Rice, E.L. 1995. Biological control of weeds and plant diseases: Ad-vances in applied allelopathy. Univ. of Oklahoma Press, Norman. Weed Res. 39:441–454.
Olofsdotter, M., M. Rebulanan, A. Madrid, W. Dali, D. Navarez, and Rimando, A.M., M. Olofsdotter, and S.O. Duke. 2001. Searching for rice allelochemicals. Agron. J. 93:16–20 (this issue).
D.C. Olk. 2001. Why phenolic acids are unlikely allelochemicals
in rice. J. Chem. Ecol. (in press). Tanaka, F., S. Ono, and T. Hayasaka. 1990. Identification and evalua-tion of toxicity of rice root elongaevalua-tion inhibitors in flooded soils Pheng, S., S. Adkins, M. Olofsdotter, and G. Jahn. 1999. Allelopathic
effects of rice (Oryza sativaL.) on the growth of awnless barnyard with added wheat straw. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 36:97–103. Wu, H., J. Pratley, D. Lemerle, and T. Haig. 1999. Crop cultivars with grass [Echinochloa colona(L.) Link]: A new form for weed
man-agement. Cambodian J. Agric. 2(l):42–49. allelopathic capability. Weed Res. 39:171–180.
Barnyardgrass Growth Inhibition with Rice Using High-Performance Liquid
Chromatography to Identify Rice Accession Activity
John D. Mattice,* Robert H. Dilday, Edward E. Gbur, and Briggs W. Skulman
ABSTRACT weeding, and reduced rates or fewer applications of
herbicides may be required for weed control. Some accessions of rice (Oryza sativaL.) have been shown to
A useful tool for breeders would be an assay to screen inhibit the growth of barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli (L.)
Beauv.). Our objective was to determine if high-performance liquid accessions and individual plants within accessions for chromatography (HPLC) chromatograms from leaf extracts of differ- weed control activity. The assay would ideally be accom-ent accessions of rice correlated with weed control activity. Chromato- plished in a relatively short period of time, require a grams of extracts consisting of 10 mg of fresh leaf tissue per milliliter minimum amount of space, be relatively inexpensive, of methanol (CH3OH) were obtained from 40 accessions of rice. and could be done year-round in a greenhouse. We
Cluster analysis was performed using 20 peaks from the
chromato-report here an HPLC procedure that is showing promise grams. Three clusters were found, with one cluster being distinctly
toward meeting most of these criteria. separated from the other two. Although weed control data are not
available for all the accessions, the isolated cluster contains all of the
MATERIALS AND METHODS accessions that have been shown to inhibit growth of barnyardgrass
and none that do not. This indicates that the assay could be used
Rice Extraction year-round to screen accessions of rice for weed control potential to
determine which accessions should be further tested in the field. This Approximately 15 seeds were placed in 100 g of soil sieved
could be done in a relatively short time using a small amount of space through a 2-mm mesh in the rice growing region of Stuttgart,
in the greenhouse. Because the assay requires only 10 mg of tissue AR. The samples were grown in 474-mL (16 oz) plastic cups
per milliliter of methanol, it may potentially be used to test individual and thinned to 10 plants cup21, with three replications per plants within an accession for weed control potential in a nondestruc- accession. After 10 d, the leaves from each replication were
tive manner. removed, cut into approximately 1-cm lengths, and placed in Erlenmeyer flasks. A volume of HPLC grade methanol was added such that the ratio of fresh plant tissue/methanol was 10 mg mL21. The samples were placed in a refrigerator overnight.
D
ilday et al.(1989, 1991) first observed theinter-Then equal parts of the methanol extract and deionized water
ference of rice on the growth of ducksalad [Heter- were combined and analyzed by HPLC.
anthera limosa (Sw.) Willd.] in field tests evaluating
accessions of rice for tolerance to alachlor
[2-chloro-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography 29,69-diethyl-N-(methoxymethyl)acetanilide]. Since 1987,
Conditions laboratory and field tests have been performed to
iden-Analyses were performed using a 25-cm by 4.6-mm
Pheno-tify accessions that inhibit the growth of several weed
menex Prodigy C18 column. The HPLC system consisted of a
species, including barnyardgrass. Growth inhibition of
Hitachi L-7450A diode array detector, L-7200 autosampler,
barnyardgrass has also been reported by Navarez and
L-7100 pump, and the Hitachi HSM software for data
proc-Olofsdotter (1996), Hasan et al. (1998), and Kim and
essing. Solvent was degassed with an ERC model 3415a
de-Shin (1998). We have also observed it routinely in green- gasser, and the column was held at 35
8C with an Eppendorf
house bioassays. TC-45 heater. The gradient used 1% acetic acid (vol./vol.) Although the interference may be due to allelopathy, and HPLC grade acetonitrile (acet). The program was 10% there is also the possibility that it may be due to competi- acet (vol./vol.) at 1.5 mL min21for 3 min, increased to 50% acet tion or a mixture of competition and allelopathy. Either (vol./vol.) over 27 min at 1.5 mL min21, increased to 80% acet way, if the trait can be incorporated into agronomically (vol./vol.) at 2 mL min21over 0.1 min and held for 1.9 min,
decreased to 10% acet (vol./vol.) over 0.1 min and held for 7.9
useful varieties, fewer hours may be required for manual
min, and decreased to 1.5 mL min21over 0.1 min. The total
run time was 40 min, and data were collected for the first 30 J.D. Mattice, E.E. Gbur, and B.W. Skulman, Dep. of Crop, Soil, and
min. The first and last portions of the chromatogram contained Environ. Sci., Univ. of Arkansas, Fayetteville, AR 72704. R.H. Dilday,
only peaks that were essentially background. The injection USDA-ARS, Dale Bumpers Natl. Rice Res. Cent., Stuttgart, AR
volume was 30mL and quantitation was at 320 nm. 72160. E.E. Gbur, Agric. Statistics Lab., Univ. of Arkansas,
Fayette-ville, AR 72701. Received 29 Nov. 1999. *Corresponding author ([email protected]).
Abbreviations: acet, acetonitrile; HPLC, high-performance liquid chromatography.
MATTICE ET AL.: INHIBITION OF BARNYARDGRASS GROWTH WITH RICE USING HPLC 9 zation of the sum of squared errors in an analysis of variance Cluster Analysis
by the least-squares estimators.
The peaks that were considered to be above background Using the clusters defined by theK-means procedure, the were used for data analysis. This resulted in 20 peaks being first two canonical variables were calculated and plotted to used. The chromatograms from some accessions contained all show the separation among the clusters as clearly as possible 20 peaks; for other accessions, some peaks were absent. in two dimensions (Krzanowski and Marriott, 1994, p. 91). All The set of peak heights from each sample was considered analyses were carried out using SAS (Version 7, SAS Inst., as a point in 20-dimensional space. The peak height data were Cary, NC).
subjected toK-means clustering (Hand, 1981, p. 174) for K5 2 to 7 clusters.K-means clustering is a nonhierarchical iterative
Rice Accessions Used clustering method in which the centroids of theKinitial
clus-ters are determined. If any point within a cluster is determined The rice accessions that were used, and information regard-to be closer regard-to the centroid of a different cluster, then that point ing the pedigree, clustering, and weed control activity, when is reassigned to the different cluster. The cluster centroids are known, are listed in Table 1.
then recalculated, and the procedure is repeated until there are no changes in the clusters. TheK-means procedure
mini-RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
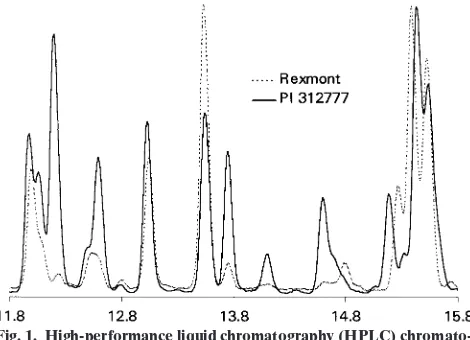
mizes the sum of squared distances of the observations fromtheir assigned cluster centroids and is analogous to the minimi- The chromatograms were of two main types, as shown
in Fig. 1. The chromatogram for PI 312777 is
representa-Table 1. The accessions studied, weed control activity (if known), tive of those from accessions showing activity while the cluster containing accession, and pedigree as listed in the chromatogram for Rexmont is representative of those USDA-ARS Germplasm Resource Information Network
showing little or no activity. The peaks in the PI 312777
(GRIN).
chromatogram are substantially higher for compounds Accession Activity† Cluster Pedigree whose retention times are 12.2, 12.6, and 13.8 min. PI 1053RU960153 U 1 NA‡ 312777 also contains compounds producing peaks at Alan U 1 Labelle/L-201 14.1, 14.6, and 15.15 min, which are essentially absent
Cocodric U 1 NA
in the extracts from Rexmont. Additionally, there are Cypress U 1 L-202/Lemont
Dellmont U 1 Della-X2/5*Lemont peaks at 13.6, 14.8, and 15.3 min that are larger in the
Delrose N 1 NA
chromatogram of the Rexmont extract. Figure 2 shows Dixiebelle N 1 (Newrex/Bellemont)RU830
3181/CB801 the expanded section of the chromatograms from 15.0 Drew U 1 Newbonnet/Katy to 15.7 min. Rexmont, and to a lesser extent PI 312777, GuiChao Y 3 developed. From China
both contain a compound whose retention time is ap-Jackson U 1 RU7603015/L-201
Jasmine Y 3 developed 1998. From the proximately 15.3 min. However, only the chromatogram United States from PI 312777 contains a peak at 15.15 min. Most of Jefferson U 1 Rosemont/B82-761
the chromatograms from the 40 accessions investigated Katy N 1 Bonnet
73/CI9722//Starbon-net/Tetep/3/Lebonnet were similar to either the Rexmont or PI 312777 chro-Kaybonnet N 2 Katy/Newbonnet
matograms. Koshihikari U 1 Norin 22/Norin 1
L204 U 2 Lemont//Tainung-sen-yu 2414/ Allelopathy is commonly thought to be a result of L-201 the action of several compounds rather than just one. Lacassine U 2 Newbonnet/Lemont
This creates a problem when comparing chromatograms
Laffite U 2 NA
Lagrue N 2 Bonnet 73/Nova 76//Bonnet from a set of samples that show activity with a set that 73/3/Newrex does not show activity. One or more of the compounds Lemont N 1 Lebonnet/CIor 9881/PI 331581
may be unique to the set showing activity, but it is more
Litton U 2 NA
M204 U 1 M201/M7/3/M7//ESD7-3/ likely that the same compounds are present in both sets Kokuhorose
PI 350468 Y 3 2*IR8//Yuhkara/TN 1 PI 366150 Y 3 developed. From Taiwan PI 338046 Y 3 2*IR8//2*B5894a4-18-1/TN 1 PI 312777 Y 3 2*T65/TN 1
Teqing Y 3 collected from Zhejiang, China
TN-1 Y 3 Tie-cha-oo-chien/Tsai-yuan-chung
Truebonnet U 2 NA
ZHE733 Y 3 developed. From China
† Y, yes; N, no; U, unknown.
Fig. 1. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) chromato-‡ NA, not available.
grams of methanol extracts of rice leaf tissue from PI 312777 and § Two replications were in the group without parentheses, and one
10 AGRONOMY JOURNAL, VOL. 93, JANUARY–FEBRUARY 2001
the inactive set. If a peak were found to be significantly higher in the allelopathic set, it might be related to the effect. The problem with this approach is that there may be numerous peaks in the chromatograms that need to be compared. At a level of significance ofP50.05, the risk of falsely finding a significant difference when there is none is approximately one minus (0.95)n, where n is the number of peaks being compared. If, as in our case, 20 peaks were being compared, we would falsely find significant differences 64% of the time even if there were no difference in the size of any of the pairs of peaks. To avoid this problem, our approach has been to use all 20 peaks in the chromatogram to determine a point in 20-dimensional space, and then use cluster analysis to see if the points are in different clusters.
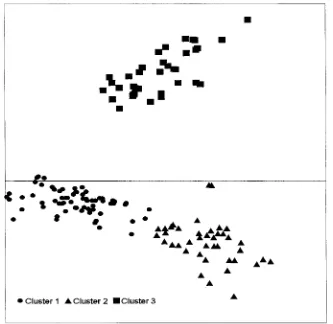
K-means clustering for two clusters did not separate Fig. 2. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
chromato-accessions showing weed control activity from those that grams of methanol extracts of rice leaf tissue from PI 312777 and
Rexmont from 15.0 to 15.8 min. did not. The results forK53 clusters are shown in Fig. 3 where the isolated Cluster 3 contains those accessions that so far have shown activity. The other two clusters in differing amounts. The chromatograms in Fig. 1 and
represent more of a division of a cloud of data points 2 show that there may be up to nine peaks that appear
rather than two well-separated groups. The results for to differentiate the chromatograms of the PI 312777
K54, 5, and 6 clusters showed further division of the extracts from those of Rexmont. However, there is some
latter into smaller, relatively nondistinct groups. The variability in the peak heights from sample to sample,
isolated Cluster 3 containing the accessions showing and the peaks that are responsible for the clustering
activity remained intact through K 5 6 clusters. For may not be obvious from simple inspection.
K 5 7 clusters, the cluster split, but the two newly One analytical approach is to compare each peak
from the set showing activity with the same peak from formed clusters were not well-separated. Hence, three
MATTICE ET AL.: INHIBITION OF BARNYARDGRASS GROWTH WITH RICE USING HPLC 11 clusters appear to be sufficient to separate these 40 raphy is not an inexpensive technique but is widely
available. accessions into those showing activity and those that
Because the procedure requires only 10 mg of tissue do not.
per milliliter of methanol, it can be done in a nondestruc-For our accessions, we have determined that those
tive manner on a rice plant. It remains to be seen if the with known activity are in a cluster by themselves.
How-procedure could be used to identify which plants within ever, for any given set of accessions, there is no
guaran-a cross between two guaran-accessions would be most likely to tee that the separation would be so clearly defined
be-have the highest weed control activity, and would thus cause the range of activity may not be as great as was
be the most useful to breeders. found in our group. Moreover, if there is more than one
mechanism for growth inhibition, the set of defining
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
chromatographic peaks would not necessarily be the
same as ours. We acknowledge the contribution of the USDA, Arkansas
Rice Research and Promotion Board, and IRRI for support
The next step in our research is to determine which
of this project.
peaks, and ultimately which compounds, are primarily responsible for the clustering. This step must necessarily
REFERENCES consider peak heights as well as missing peaks.
Dilday, R.H., P. Nastasi, J. Lin, and R.J. Smith Jr. 1991. Allelopathic
It is important to remember that correlation does not
activity in rice (Oryza sativaL.) against ducksalad [Heteranthera
imply causality, and we do not imply that the compounds limosa(Sw) Willd.]. p. 193–201.InJ.N. Hanson et al. (ed.) Proc. producing the larger peaks in the PI 312777 extract Sustainable Agric. for the Great Plains, Beltsville, MD. USDA-would be allelochemicals; they USDA-would, however, be can- ARS.
Dilday, R.H., P. Nastasi, and R.J. Smith Jr. 1989. Allelopathic
observa-didates for identification and testing. Differences in the
tion in rice (Oryza sativaL.) to ducksalad (Heteranthera limosa).
peak size, regardless of which chromatogram it is in,
Proc. Arkansas Acad. Sci. 43:21–22.
may be useful in differentiating accessions according to Hand, D.J. 1981. Discrimination and classification. John Wiley & their ability to inhibit barnyardgrass growth. Whether Sons, New York.
Hasan, S.M., I.R. Aidy, A.O. Bastawisi, and A.E. Draz. 1998. Weed
or not the compounds are allelochemicals, and whether
management using allelopathic rice varieties in Egypt. p. 27–38.
or not the observed effect is allelopathy or competition,
InM. Olofsdotter (ed.) Allelopathy in rice. Proc. Workshop on
the procedure shows promise for predicting which acces- Allelopathy in Rice, Manila, Philippines. 25–27 Nov. 1996. IRRI, sions are likely to show a weed control effect toward Makati City, Philippines.
Kim, K.U., and D.H. Shin. 1998. Rice allelopathy research in Korea.
barnyardgrass and perhaps other weed species. The
pro-p. 39–44.InM. Olofsdotter (ed.) Allelopathy in rice. Proc.
Work-cedure allows assaying of 7- to 10-d-old samples, so
shop on Allelopathy in Rice, Manila, Philippines. 25–27 Nov. 1996.
screening can be done on a series of samples during IRRI, Makati City, Philippines.
late summer through early spring to identify promising Krzanowski, W.J., and F.H.C. Marriott. 1995. Multivariate analysis.
Part 1. Distributions, ordination, and inference. Edward Arnold,
accessions to take to the field for further testing. This
London.
meets the objectives of being accomplished in a
rela-Navarez, D.C., and M. Olofsdotter. 1996. Relay seeding technique
tively short period of time (#10 d), using a minimum for screening allelopathic rice (Oryza sativa). p. 1285–1290.InProc. amount of space (≈1 m2for 30 accessions), and can be
Int. Weed Control Congr., 2nd, Copenhagen, Denmark. 25–28 June 1996.