i THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Attainment of aSarjana SastraDegree in English Language and Literature
By
JANJANG KASTORI Student Number: 11211144022
ENGLISH LITERATURE STUDY PROGRAM
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF LANGUAGES AND ARTS
YOGYAKARTA STATE UNIVERSITY
vi
vii
the Most Merciful, and the Most Beneficent, for the best blessing, love, and
guidance given to me without which I would have never been able to finish
this thesis.
In accomplishing this thesis, I feel indebted to many people for their
guidance, assistance, and help. Therefore, I would like to express my special
gratitude to:
1. Drs. Suhaini M. Saleh, M.A., my first supervisor, and Paulus
Kurnianta, S. S., M. Hum., my second supervisor, for their hard work,
uncounted help, guidance, and patience, and for sharing ideas,
knowledge and time during my writing process, without which I
probably cannot finish this thesis well;
2. Erna Andriyanti, M. Hum., my academic advisor, for her guidance
during my years of study;
3. all lecturers, for teaching me well, and all staff members, for their help
during my study and my thesis accomplishment;
4. my beloved parents, Ibuk Tri Slamet and Bapak Kadiyono, for their
hard work, everlasting love, prayers, support, and understanding;
5. my sister Antaria Kurniati for her timeless prayers, support and
viii
8. last but not least, all people who sincerely helped me finish this thesis,
all of whom I cannot mention one by one.
Finally, I realize that this thesis is far from being perfect. Therefore, I
would be very grateful to accept constructive criticisms, comments, and
suggestions for the betterment of this thesis. Hopefully, this thesis will be
useful for everyone interested in language phenomena.
Yogyakarta, March 2017
ix
C. Limitation of the Problems ...4
D. Problem Formulation ...5
E. Objectives of the Study ...5
F. Significance of the Study ...5
x
B. Relevant Studies...19
C. Conceptual Framework ...20
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD A. Type of Research...23
B. Form, Context, and Source of Data...24
C. Research Instruments ...25
D. Technique of Data Collection ...26
E. Technique of Data Analysis ...26
F. Trustworthiness ...27
CHAPTER IV FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION A. Findings...30
B. Discussions...34
1. Types of Code Switching ...34
2. Functions of Code Switching ...44
CHAPTER V CONCLUSIONS A. Conclusions ...58
B. Suggestions ...59
REFERENCES...58
xi
Mario Teguh Golden Ways 2015...25 Table 3. Frequency of Occurrence of Types and Functions of Code Switching
xii
also finds out the functions of code switching used in the program.
This study employed a descriptive qualitative method with the use of the researcher and a data sheet as the research instruments. The data of this study were in the form of words, phrases, clauses, and sentences uttered by the speaker of Mario Teguh Golden Ways 2015 TV Program. This research applied triangulation technique to check and establish validity.
The results of this research show that there are three types of code
switching used by Mario Teguh as the speaker in the TV Program ‘Mario Teguh
Golden Ways 2015’. There are intersentential code switching (63%), tag switching (26%) and intrasentential code switching (11%). Intrasentential is the most appearing type in this TV program because it is considered to be the easiest type which does not need to consider the grammatical rule of the switched language. The most frequent occurrence of code switching function is reiteration (40%) and the least frequent is quotation (3%). Reiteration is the most appearing function in this TV program because the speaker uses code switching when he wants to emphasize the idea of his utterances so the audience can get the idea easier.
1 A. Background of the Study
Language is very important in our daily life. It cannot be separated from
our daily life. It is used as an instrument to communicate and deliver
message. People use language as a system to show their ideas, their
attitudes, and their thoughts. According to Palmer, if language is regarded as
an information system, or more strictly as a communication system, it will
associate the main message with a set of signs that means the sound of
language of the symbol of the written text (1997).
Nowadays, most people produce more than one language in
communicating for some considerations, such as to whom they speak to,
choice of topic, situation etc. When two or more people communicate to
each other, they produce some utterances. In the utterances used by people,
there is a system of communication called code. According to Wardaugh,
“code is a system used for communication between two or more parties”
(2006). They use code whenever they want to speak and they may decide to
change from one language to another language. This phenomenon is
involves two languages or linguistic varieties in the same utterance or
conversation (Hoffman, 1991).
Code switching is a part of sociolinguistics. Sociolinguistics is one of
the linguistics branches as defines by Aitchison (2003). Sociolinguistics is
the study of language and society (Aitchison, 2003). Through
sociolinguistics, people can have some understandings about the social
factors of the language variety.
This research is about code switching. Code switching exists in some
fields, for example, in social media, mass media and journals. It exists as
well in television programs like talk show, reality show, soap opera, etc.
Although code switching occurs in many fields, the researcher will only
focus in talk show because nowadays code switching appears more often in
conversational or spoken occasions than the other occasions. Talk show is a
part of television or radio show which is hosted by one person and the
speaker can be more than one person. According to Morissan, talk show is a
program that shows some persons to discuss about a certain topic and the
program is guided by a host (2008).
In this study, the researcher chooses Mario Teguh Golden Ways
English, Javanese and so on. It makes him sometimes change or mix the
languages on purposes.
The phenomenon challenges the researcher to conduct a research
entitled: ‘A Sociolinguistic Analysis of Code Switching in Mario Teguh Golden Ways’. The researcher focuses on what types of code switching are employed, and the functions of code switching in the show.
B. Identification of the Problem
People have their own purposes in changing their language. Those
purposes are based on the functions of the language use in the conversation.
In Mario Teguh Golden Ways, Mario Teguh mostly speaks in Indonesian.
He sometimes changes his language into English.In using two languages, he
conducts code switching. He switches his languages from Indonesian to
English or English to Indonesian. There are some problems that occur in
conducting code switching. The first problem which occurs is Mario Teguh
does not really know about code switching. It means that he sometimes does
not realize that he does code switching. He does not realize what types of
code switching he probably uses.
Second, every occurrence of code switching is certainly have the reason
that influences the occurrence of code switching uttered by the speaker in
the participants, the setting, and the topic that can define all kinds of code
switching that happen in the show.
The third problem is about the functions of code switching. The
functions of code switching used by Mario Teguh may vary in different
context. Therefore, analyzing the functions of code switching from Mario
Teguh utterances is very interesting.
The fourth problem is the effect of the use of code switching to the
audience in the show. Based on the audience perception, the effect of the
language switch can be vary from one person to another.
In addition, the fifth problem is how often Mario Teguh uses code
switching. As already known, Mario Teguh can speak English and
Indonesian as well. It is interesting to analyze the frequency of Mario
Teguh’s code switching in Mario Teguh Golden Ways.
C. Limitation of the Problem
As stated in the identification of the problem, this field of this study is
limited on the use of code switching by Mario Teguh in MTGW. This
research focuses on the types of code switching, and the functions of code
D. Problem Formulation
Based on the limitation of the problem, the research problems can be
formulated as follows.
1. What types of code switching occur in Mario Teguh Golden Ways
2015?
2. What are the functions of code switching appearing in Mario Teguh
Golden Ways2015?
E. Objectives of the Study The objectives of this study are:
1. to identify the types of code switching that occur in Mario Teguh
Golden Ways 2015, and
2. to describe the functions of code switching appearing in Mario
Teguh Golden Ways 2015.
F. Significance of the Study
The researcher expects this research can give a contribution to the field
of linguistics, especially Sociolinguistics. The result of this study is
expected to be valuable to increase the discussions of code switching. The
researcher also hopes that this research can be a valuable input to anyone
learning the result of the study, people are able to know about the kinds of
7
This chapter explores the literature review containing several
theories that are used to guide the process of this research. The discussion
covers sociolinguistics, bilingualism, and code switching. This research also
describes Mario Teguh Golden Ways 2015as the object of the research and
previous studies that have been conducted related to the topic of this
research. Moreover, the conceptual framework and analytical construct of
the research are also provided.
A. Literature Review 1. Sociolinguistics
The study of language used by society is called sociolinguistics. This
idea is supported by Hudson (1980) “sociolinguistics is the study of
language in relation to society”.
Sociolinguistics is one of the branches of linguistics as defined by
Aitchison (2003). It is about the study language and society. There is a
relationship between language and society. A language used in certain
Wardaugh (2006) also states that sociolinguistics is focusing on the
relationship between language and society with the purpose to have a better
understanding of the structure of the language and of how languages
function in communication.
According to Trudgil as cited by Wardaugh, sociolinguistics also
covers some works such as structure of discourse and conversation, speech
acts, studies in the ethnography of speaking, investigations of such matters
as kinship systems, studies in the sociology of language such as
bilingualism, code switching, and diglossia and certain practical concerns
such as various aspects of teaching and language behavior in classroom
(2006).
In short, sociolinguistics is a branch of linguistics that concerns with
the relationship between the languages used in a society. To understand
language, people should understand the elements involved in the
conversation.
2. Bilingualism
Most people as speakers usually use more than one code and require
a selected code whenever they choose to speak with other people. The
phenomenon of people having more than one code (language) is called
Spolsky (1998) defines a bilingual as “a person who has some functional ability in the second language.” This may vary from a limited ability in one or more domains, to very strong command of both languages.
Related to speech community, Hamers and Blanc (1987) define
bilingualism as “the state of a linguistic community in which two languages
are in contact with the result that two codes can be used in the same
interaction and that a number of individuals are bilingual”. In addition, Gumperz (1982) also mentions that bilingual people usually use their own
idioms for in-group communication and the common language for their
interaction and communication with outsiders. In this case, the bilinguals
have a repertoire of domain-related rules of language choice (Spolsky, 1998:
46) meaning that bilinguals are able to choose which language that he is
going to use.
There are three reasons why someone becomes a bilingual, i.e.
membership, education, and administration (Hoffman, 1991). The example
of membership reason is the use of French by all European aristocracy to
signal the membership of the elite. The example of education and
administration reason is the use of English by Indonesians, Scandinavians,
Germans, and Dutches in discussing their technologies, academics, or
business. In many countries and communities, bilingualism is a normal
requirement for daily communication and not a sign of any particular reason
In other words, since the members of a bilingual community vary in
the capacity of mastering the languages used in the community, they have to
be able to set a condition where they can communicate effectively. This
condition leads them to do code switching and code mixing.
3. Code
According to Wardhaugh (2006) code is a particular dialect or
language which is chosen on any given occasion and the communication
system used between two or more parties.
Code as a language means the system agreed by people to
communicate one with another. It refers to some languages used by
bilingual or multilingual members of the society. However, code as a variety
of language refers to style shifting in one language, for example: the use of
speech level in Javanese language. There are three kinds of speech level.
They are krama, ngoko, and madya. Their use depends on some social and
cultural dimensions, such as age, sex, social class, and relationship between
speakers.
4. Code Switching
There are several definitions of code switching viewed by some
linguists. They have different ways in describing code switching. Thus, in
order to have a deeper understanding related to code switching, this research
Code switching occurs among people who can speak more than one
language and this is also agreed with the idea from Chana that “code
switching is the juxtaposition within the passage of someone’s speech which
involves items of two different languages” (1984). This can be understood
that code switching occurs when the speaker inserts two different languages
in his utterance.
The other linguist, Akmajian, states that code switching is language
mixture. He states, “Code switching refers to a situation in which the
speaker uses a mixture of distinct language varieties as discourse proceeds”
(2001). It means that code switching is a situation when the speaker
combines two different languages in a speech.
Code switching relies on the meaningful juxtaposition of what
speakers must consciously or sub-consciously process as strings formed
according to the internal rules of two distinct grammatical systems
(Gumperz, 1982). It means that code switching occurs when the speaker
mixes two different languages in a speech.
Hoffman (1991) states that code switching includes two languages or
linguistic varieties in the same utterance or conversation. Therefore, code
switching is a situation when the speaker uses two different languages to
Furthermore, there is code mixing that also relates to code switching.
According to Wardaugh (2006) “code mixing occurs when conversants use
both languages together to limit that they change from one language to the
other in the course of a single utterance”. It means that code mixing is also
combination of two languages that occurs in a single sentence. According to
Muysken, Poplack, and McLaughin as cited by Hoffman, code mixing refers
to intrasentential switch (1991). The difference between code mixing and
code switching can be seen from their occurrences. Code mixing occurs at
the lexical level within sentence. Code switching occurs within phrases or
sentences including tags and exclamations at the end of the sentence
(Hoffman, 1991).
The example of code mixing can be seen is from an English native
speaker who speaks Spanish and has lived in Spain for many years: “I was
speakando with Steve the other day”. In this case, the speaker uses the
Spanish morpheme ‘ando’ rather than the English ‘ing’. The mixing occurs in the lexical level within the sentence. On the other hand, code switching
occurs within phrases or sentences (We‟re going to Nicki‟s house at nine
and maybe to the night club afterwards.Kristina bleibt allerdings zu Hause
a. Types of Code Switching
There are two types of code switching. They are situational
switching and metaphorical switching. According to Wardhaugh (2006),
situational switching occurs when people employ changes according to the
situation. It means that people start a conversation with certain language and
certain situation. When people feel uncomfortable in their conversation,
they will use another language which is more appropriate to the situation.
No topic change is involved. On the other hand, in metaphorical switching,
the topic is the driving factor in determination of the change of languages.
Another linguist defines the types of code switching in to three
types. There are three types of code switching according to Stockwell
(2002) that are described as follow:
1) Tag switching
This type of code switching only switches an interjection, a tag, or
sentence filler in the utterances of the interlocutor. It is easily inserted at a
number of points in monolingual utterance without violating syntactic rule.
Tag switching is code switching with tags that follow a sentence.
This contains the insertion of a tag in one language into an utterance of the
other language. Examples of common tags in English include ‘you know’, ‘I mean’, and ‘right’. A Japanese-English example might be: “I’m a good
friend, neh?” Where the Japanese particle, ‘neh’ (‘no?’ or ‘is not that
2) Intersentential Switch
Intersentential switch occurs between sentences made by the
speaker. The topic of the conversation may be switched by pause employed
by one of the speaker. The pause employed here shows a brief suspension of
the voice to indicate limits or relations of sentences. Intersentential switch
occurs between more than one sentence. The example of intersentential code
switching is below:
We‟re going to Nicki‟s house at nine and maybe to the night club
afterwards. Kristina bleibt allerdings zu Hause sie muss noch arbeiten.
(Unfortunately Kristina is staying at home because she still has to do some work).
Based on the example, the first sentence of the speaker uses English
and in the second sentence, he changes into the other language.
3) Intrasentential Switch
Intrasentential switch occurs within a sentence or a clause. The form
of code in this switching can be in the form of a single word, a phrase, or
clause.
In addition, intrasentential switch has the same occurrence with tag
switching but intrasentential switch is not a sentence filler. If the
intrasentential switch is omitted, the sentence will produce the ambiguity
and often violate grammatical or syntactical rule of certain language.
An example is from an English native speaker who speaks Spanish
and has lived in Spain for many years: “I was speakando with Steve the
rather than the English ‘ing’. The grammatical boundaries for this are similar in English and Spanish and so the code switching ‘works’.
b. Functions of Code Switching
There are three functions of code switching according to Holmes
(2001: 34-40). They are participant’s solidarity and status, topic switch, and
affective functions. On the other hand, another linguist defines functions of
code switching into six functions. According to Gumperz (1982:75-81),
there are six functions of code switching that explained as follows.
1) Quotation
People sometimes quote or say well-known expression. Those
quotes may from different language so they will switch the language. Here
is the switch from Slovenian to German. The conversation from an informal
business discussion among neighboring farmers, called to discuss the
sharing of farm machinery. The speaker is reporting on a conversation with
a German speaking businessman:
Pa prawe (then he said) wen ersi nit caltgib I si nit (If he does not pay for it, I will not give it).
A: (Speaking to B) Nceabaprisu, vokisuvaitar (it wil not come, it will pass by)
B: (Speaking to A) Yakitekena Basanzapkama pa ye zieciu stem ye pastrane (it is so overloaded with apples and the entire tree is bent already). B: (B continues turning to C sitting apart) Regenvert so ainvint is drausen (It will rain, it is so windy outside).
Based on the example above, after speaking to A, B switches his
language in speaking to C. It seems like B does not agree with A, so that he
gives his opinion to C by switching his language. Therefore, the switch from
B is functioned to direct the message to C.
3) Interjection
Interjection is an exclamation that the language is used to express
sudden emotions or feeling. It can be in the form of words or even a
morpheme. Interjection is usually not in the full sentence but it can represent
the whole meaning of sentence. For instance, here the main message is in
Spanish and the speaker switches into English.
Perocomo (but how) you know la Estella y la Sandi relistas en el telefon(Stella and Sandi are very precocious on the phone).
Based on the sentence above, the switch “you know” is the sentence
filler. The function of the sentence filler is to signal to other addressee.
4) Reiteration
Frequently a message in one code is repeated in the other code either
literary or in somewhat modified form. It means to clarify what is said or to
Baju-me jao beta, andar mat (go to the side son, not inside)Keep to the side.
The switch “keep to the side” here has the same meaning with “Baju-me jao beta” or go to the side. The speaker reiterates his calling by
switching to English. Then, the function of the switch here is to clarify what
has been said in the beginning.
5) Message qualification.
The function of the language switch is to qualify the message or to
convey the main message. The form of switch here such as sentence, verb
complements, predicates following a copula.
The example from college student conversation:
A: Bina vet kiyeap a gae(without waiting you come)
B: Nehi. I came to the bus stop peccis per (about nine twenty-five). According to the example above, B switches Hindhi to English. The
switch of English is functioned to convey B’s main message.
6) Personalization or objectification.
The function of code switching can be used to mark personalization
or objectification. By switching to the other codes, a speaker tries to express
his knowledge or expertise about the discussed topic.
personal involvement. B shift back to Hindi in talking about what she
personally intended to do.
5. Mario Teguh Golden Ways
Mario Teguh Golden Ways (MTGW) is an interactive talk show TV program which air on Metro TV. This program air live on Metro TV every
Sunday at 19.00 WIB with 60 minutes duration in every show. The first
show of Mario Teguh Golden Ways was air on December 2008. The
shooting processes of the show take place in The Grand Studio of Metro TV
with audience around 300 people. However, sometime the shooting
processes take place outside the studio; it depends on the topic of the show.
The format of the program is interactive talk show. Talk show is a
program that shows some persons to discuss about a certain topic and the
program is guided by a host. Interactive talk show means that the audience
can ask or interact with the speaker, Mario Teguh. This program concept is
inspirational and motivational program. The characteristic of the program is
the choice of topic. The choice of the program topic depends on the fans of
Mario Teguh who always post their feeling or their concern in their life in
B. Relevant Studies
There are several previous studies with code switching as the topic
of investigation. The researcher takes two of them as references in
conducting this research:
1. An Analysis of Code Switching Used by Hashim as a Character in the
FilmJava Heat( Sukma Oktavian, 2013)
In this research, Oktavian focused on code switching which were
produced by the main character in a film entitled Java Heat. The researcher
chooses this film as the object of study because this film has unique topic
and contains the beauty of Indonesia culture about Javanese culture that
exists in this world. The objectives of the research were to investigate the
types and functions of code switching in Java Heat.
The results of the research show that in terms of types code
switching, inter sentential occurred the most among other types. Then, intra
sentential term took the second position. For the function of code switching,
the researcher found that code switching in the films are used as terms of
expressing of group identify.
2. Code Switching in Indonesia Song Lyrics Composed by Melly Goeslaw
(Rosa Delima Witasitakusuma Widaya, 2015)
This thesis talked about types and functions of code switching
presented in the song lyrics composed by Indonesia singer, Melly Goeslaw.
switching using the theory from Stockwell and theory of the reason of code
switching using the theory from Malik.
For the type of code switching, intersentential occurred the most
among other types followed by intrasentential and tag switching. For the
reasons of code switching, the researcher found that the reasons are because
of lack of facility, difference audience, and semantic significance.
Both of the previous studies focus on code switching. It is interesting
to investigate the same topic by using a different object. By using a different
object, the research can show different results as it takes a different context.
Unlike the previous studies, the object of this research is a talk show. It will
give difference result from the others.
C. Conceptual Framework
The objectives of this study are to identify the types and the
functions of code switching that occurs in Mario Teguh Golden Ways in
2015. The first problem is the identification of the types of code switching
that occur in Mario Teguh Golden Ways in 2015. In answering the first
problem, the researcher uses the theory of type of code switching from
Stockwell (2002). There are three types of code switching namely tag
switching, intrasentential, and intersentential. Tag switching is code
switching with tags that follow a sentence. Intersentential code switching is
Another is intrasentenstial code switching. Intrasentential code switching
happens in the word level.
The second problem is the analysis on the functions of code
switching which occur in in Mario Teguh Golden Ways in 2015. In
discussing the functions of code switching, the researcher uses the theory of
conversational function of code switching from Gumperz (1991).The
functions of code switching are classified into six: quotation, addressee
specification, interjection, reiteration, message qualification, and
Figure 1. Analytical Construct
Ways 2015
Sociolinguistics
Bilingualism
Code Switching
SSwitching
Functions
Types
Quotation
Addressee
Interjection
Reiteration
Message Qualification
Personalization vs. Objectivication
Tag
Intersentential
23
In this chapter, the researcher presents all elements regarding the
research method applied in conducting this research. The discussion in this
chapter includes the type of study, research instrument, form, context and
source of data, technique of data collection, technique of data analysis, and
triangulation.
A. Type of research
This research used a descriptive qualitative method which produced
descriptive data. Vanderstoep and Johnson (2009:167) say that a qualitative
method focuses on cultural, social, personal identity and its goal is more
descriptive than predictive. It can give complex detail about particular
phenomena which are difficult to be expressed with quantitative method.
Therefore, the findings of qualitative research will not be in the form of
statistic data which usually belong to quantitative research. In this research,
qualitative method was chosen as the appropriate method because it
Besides descriptive data, the researcher also used quantitative
method to support the interpretation of data. Vanderstoep and Johnson
(2009: 7) state that quantitative method brings statistical work to a certain
phenomenon under study. By providing statistical work in the form of
percentage, the researcher could easily describe the phenomenon that the
researcher wanted to investigate by giving fixed percentages to make a clear
explanation.
B. Form, Context, and Sources of Data
Dey (2005) states that qualitative data deal with meanings. The
meanings come from the combination between language and action. The
data may be created from sources such as interview transcript, documents,
photographs, sketches, video, and tape recording. The data in this research
were spoken language captured from Mario Teguh Golden Ways in 2015.
The form of the data was utterances which contained code switching
performed by the speaker, Mario Teguh. The context of the data was
dialogues between the host, the audience, and the speaker. Meanwhile, the
sources of data in this research were limited because only three episodes
were investigated. They were episodes entitled “Rating Pribadi”, “Salah
C. Research Instrument
In qualitative approach, the researcher becomes the main instrument
(Moleong, 2001). In this research, the researcher considered himself as a
primary instrument. The researcher was the planner, data collector, data
analyzer, and data reporter. In addition, this research used secondary
instruments such as data sheet and computer. The data sheet was functioned
to write down the classified data. The data sheet was in the form of a table
for presenting two objectives which became the focus of the study. The
format of the data sheet could be illustrated in the table below.
Table 1: Sample Data Sheet of Types and Functions of Code Switching
inMario Teguh Golden Ways 2015
D. Technique of Data Collection
In conducting this research, the researcher collected the data through
three steps. First, the researcher watched the videos. It was necessary to do
because it was important to get the background knowledge of the story and
the attitude of all the characters. Second, the researcher transcribed the
recorded data that contain code switching. Because the data sources were in
the form of recorded media, the researcher wrote the transcriptions based on
the dialogue spoken by the speaker. Third, after finishing transcribing the
data, the researcher analyzed the data through some procedures.
E. Technique of Data Analysis
After finishing the processes of data collection, finally the raw data
were ready to be analyzed. The relation between data collection and data
analysis was inseparable (Bungin, 2007). It means that when the researcher
collected the data, the process of data analysis started. Then the remaining
steps of data analysis were described as follows:
1. Data Classifying
After the data were collected, they were classified. The classification
was about the types and the functions of code switching found in the talk
2. Data Analyzing
After the classification was completed, the collected data were ready
to be analyzed. The classified data in the table were analyzed to describe the
types and the functions of the code switching in the dialogues. Moreover, in
this research, the data analysis employed quantitative method since it
involved number to get the percentage of each phenomenon in the table.
Then, those fixed percentages were used to support the interpretation of the
data.
3. Data Discussing
The researcher confirmed the findings with the theories that were
employed in the analysis. After that, the researcher also explained the
findings in order to answer the objectives of the research.
4. Data Reporting
The last step was reporting the findings and finally the researcher
also added some points of conclusions and suggestions.
F. Trustworthiness
The trustworthiness of this research was gained by doing
triangulation and discussion. Moleong (2001) states that triangulation is a
technique for checking the trustworthiness of data by utilizing something
In this research, the researcher used a triangulation by theory.
Triangulation by theory was done by using the thoeris from Stockwell and
Gumperz about code switching. Besides, the researcher had peer reviewers
from English Department students majoring in linguistic as his triangulation
This chapter presents the results of the research. As mentioned in the
first chapter, this research has two objectives, i. e.: 1) types of code
switching used by Mario Teguh inMario Teguh Golden Ways 2015, and 2)
functions of code switching used by Mario Teguh in Mario Teguh Golden
Ways 2015.
Moreover, this chapter is divided into two sections: findings and
discussion. The first section, the findings section, shows the data about
types of code switching and functions of code switching used by Mario
Teguh in Mario Teguh Golden Ways 2015. Then, the second section, the
discussion section, talks about detailed analysis and explanation of the
findings of this research.
A. Findings
This section describes the findings of the research on code switching
uttered by Mario Teguh in Mario Teguh Golden Ways 2015. From the
analysis process, the total data collected in this research are 62 data. The
data are displayed in Table 1. The table shows the frequency of the
inMario Teguh Golden Ways 2015. The results are various and they will be
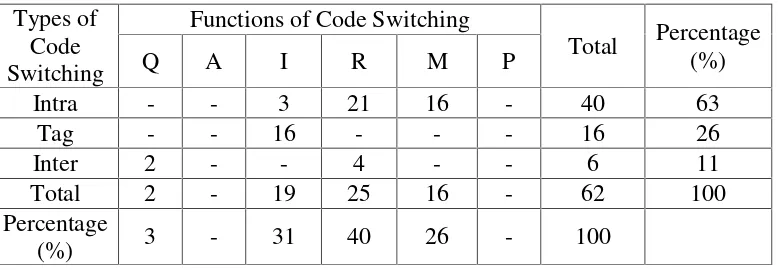
There are three types of code switching, i.e. tag switching, intersentential
switching, and intrasentential. All of them appear in the conversations spoken by
Mario Teguh. From the table above, it can be noticed that the most dominant type
used by the speaker, Mario Teguh, is intrasentential switching, which appears 39
times (63%). Then, the second highest frequency is tag switching which appears
16 times (26%). Finally, the least to occur is intersentential switching which
appears 7 times (11%).
Intrasentential switching and tag switching are more frequently found in
Mario Teguh Golden Ways than intersentential switching. The 2 types of code switching are the dominant types because they are easily to appear in
conversation. Because intersentential switching is the switch occurs between
sentences, the speaker need to consider the grammatical rule of the switched
of word or phrase which makes them easily appear in conversation because the
speaker does not need to think about the grammatical rule of the switched
language.
Table 2 above shows that all functions of code switching are found in the
talk show. However, each of them has a different frequency. There are six
functions of code switching, namely quotation, addressee specification,
interjection, reiterations, message qualification, and personalization vs.
objectification. From the finding, there are just four functions found in Mario
Teguh Golden Ways 2015. Among them, the highest frequency of functions of code switching is reiteration which appears 25 times (40%). Interjection is in the
second position with 19 occurrences (31%). The third position is message
qualification with 16 occurrences (26%). The last position is quotation which only
occurs twice and reaches 3%. There are 2 functions of code switching not found in
Mario Teguh Golden Ways 2015. They are Addressee and Personalization vs. Objectification.
Reiteration is the most function of code switching that occurs in Mario
Teguh Golden Ways 2015. The researcher assumes that reiteration is the most frequent function because the speaker of the show, Mario Teguh, wants to make
the audience get the point of the utterance easily. In order to make the audience
get the point easily, the speaker uses code switching. He switches his language to
repeat or to emphasize of the idea.
There are 2 functions of code switching that not appear in the show. They
a talk show TV program and the audience of the show is general people. Because
of that, the speaker does not speak something specific or speak to specific person.
He always speaks in general in the show.
B. Discussion
In this section, the researcher discusses the findings in depth to answer the
problem formulation stated in Chapter I. To provide a complete explanation, some
data from the appendix are taken as the examples. This section consists of two
parts. The first part is related to the types of code switching in Mario Teguh
Golden Ways 2015, which is presented to answer the first formulation of the problem and the second part is about the functions of code switching, which is
presented to answer the second formulation. The discussion starts from the types
of code switching.
1. Types of code switching inMario Teguh Golden Ways 2015
There are three types of code switching uttered by Mario Teguh inMario
Teguh Golden Ways 2015. They are tag switching, intersentential switching, and intrasentential switching. Each of them is explained one by one and followed by
some examples.
a. Intrasentential switching
Intrasentential switching becomes the most dominant type used by Mario
Teguh in Mario Teguh Golden Ways 2015. Intrasentential switch means that the
switch occurs within a sentence or a clause. It occurs within the clauses or
sentences by the insertion of words or phrases from one language into another.
switch. These are some evidences of Intrasentential switching that occur in Mario Teguh Golden Ways 2015.
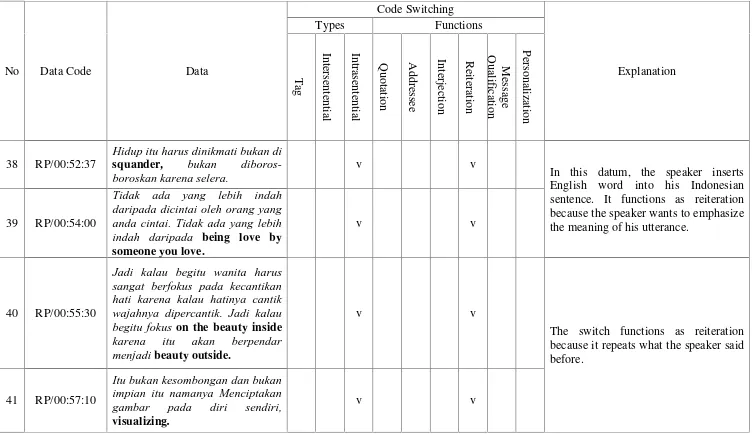
RP/00:52:30 Hidup itu harus dinikmati bukan disquander, bukan
diboros-boroskan karena selera.
The main idea of the utterance above is that Mario Teguh tells to the
audience that life must be enjoyable, not squandered. Mario gives an advice to the
audience that many people feel sad but they are not aware of their sadness.
Because ofpeople’s awareness oftheir sadness, people leave their sadness behind
and they try to find something to cover their sadness. They follow their desire that
they think can give them happiness. They are not aware of the happiness that they
feel is just a temporary happiness. After the temporary happiness is gone, they
will face the bigger sadness that they leave behind.
Mario Teguh produces the sentence in Indonesian and he inserts the
English word “squander” within the sentence in his Indonesia utterance. It is
categorized as intrasentential switching. The switch occurs as a single word. The
switch “squander” is categorized into intrasentential switch because it occurs as a
single word within the sentence. The utterance “Hidup itu harus dinikmati bukan
disquander, bukan diboros-boroskan.” shows that Mario Teguh inserts English word into his Indonesian sentence.
RP/00:23:50 Jadi katakan apa yang Ibu inginkan, yang sweet but not too
The idea of the utterance is about Mario Teguh who tells to the woman if
she wants to have a partner for her life, she should find the one who is sweet but
not too sweet. In the last clause, Mario tells that she should not be too amazed by
the man she found. The point of the utterance is that Mario wants to tell the
audience of the Mario Teguh Golden Ways that they should not put so much
affection in one thing because when someone put too much attention to
something, he/she will ignore other things around him.
In RP/00:23:50, Mario Teguh states Indonesia utterance and he inserts
English phrase “sweet but not too sweet”. The switch is categorized as
intrasentential switching. The switch occurs as a phrase. The switch “sweet but
not too sweet” is categorized into intrasentential switch because it occurs within
the sentence. The utterance “Jadi katakan apa yang Ibu inginkan, yangsweet but
not too sweet gitu lohh, yang kagum tapi tidak terlalu kagum”shows that Mario Teguh inserts English phrase into his Indonesian sentence.
CAD/00:23:30
Kalau baru mengurusi dirinya sendiri sudah kerepotan bagaimana dia bisa bertanggung jawab atas kesejahteraan banyak orang. Memang menilai dari face value memang mudah, dari tampilan luar itu mudah.
The main idea of the utterance above is about Mario Teguh who tells the
audience about judging people. Many people think that successful men have an
responsibility that can give a hard life. In this utterance, Mario Teguh wants to
gives an advice to the audience that they should not judge the others from what
they see from his appearance. People can never judge the lives of others, because
each person knows only their own pain and renunciation.
According to CAD/00:23:30, the switch occurs as an English phrase. The
switch “face value” is categorized into Intrasentential switch because it occurs
within sentence the sentence. The utterance “Kalau baru mengurusi dirinya
sendiri sudah kerepotan bagaimana dia bisa bertanggung jawab atas kesejahteraan banyak orang. Memang menilai dari face value memang mudah, dari tampilan luar itu mudah...” shows that Mario Teguh inserts English phrase into his Indonesian sentence.
SF/00:52:00
Mereka adalah pewarna dalam kehidupan anda. Bukan untuk anda hakimi, bukan untuk anda judge. Tetapi untuk menjadi pelajaran.
The idea of the first sentence is that failure of people around you is the
paint for your life who can give you variation of live. In the second sentence,
Mario tells that the audience does not have the right to judge people who failed.
The last sentence idea is about taking value from the failure of other people. From
this utterance, Mario Teguh wants to give an advice to the audiences that failure
can give experience. Experience can have ability to teach someone to face the
problems of life.
In RP/00:52:00, Mario Teguh produces utterance in Indonesia and he
categorized as intrasentential switching. The switch occurs as a word. The switch
“judge” is categorized into intrasentential switch because it occurs within the
sentence. The sentence “Bukan untuk anda hakimi, bukan untuk anda judge”
shows that Mario Teguh inserts English word into his Indonesian sentence.
b. Tag switching
Tag switching means the switch of language which occurs as a tag or
sentence filler. The occurrence of this type of code switching will not change the
main point of the sentence because it does not violate the syntactic rule of a
sentence. This type of code switching occurs almost anywhere. Based on the
findings, there are 16 data which are categorized as tag switching, as follows:
RP/00:01:00
Sahabat saya yang baik hatinya selamat malam, silahkan duduk. So, Rating Pribadi, kita semua harus menjadi pribadi yang bernilai, yang mahal, yang dihormati, yang didengarkan saat berbicara, yang tidak diperlakukan dengan sembarangan oleh orang lain.
The main idea of the utterance is about introduction of the show. Mario
Teguh tells to the audience the topic of the show. He gives the audience an advice
that they should be a valuable person, respectable person who always listen by
others. It is important to be a respectable person because people will not treat a
respectable person with unrespectable action.
In RP/00:01:00, the switching language exists at the beginning part of the
sentence. The word “So” is tag switching because it occurs as a tag and its
“So, Rating Pribadi, kita semua harus menjadi pribadi yang bernilai”. In this
case, the point of sentence is about introducing the topic of the show. When the
word is omitted, it will be “Rating Pribadi, kita semua harus menjadi pribadi
yang bernilai”. Therefore, the point of sentence is stillthe same.
RP/00:23.20 Okay, 30 detik pertama Ibu temukan apa yang akan Ibu
lakukan.
The utterance is a part of conversation between Mario Teguh and one of
the audience invited to the stage. In that situation, Mario Teguh tells the woman
who he was invited if she found a man. In the first 30 seconds, she needs to think
about her next move. The woman should think before she moves to make the
action more memorable.
In RP/00:23.20, the switching language exists on the beginning part of the
sentence. The word “okay” is a tag switching because it occurs as a tag and its
occurrence will not change the meaning of the sentence. It can be seen from
“Okay, 30 detik pertama Ibu temukan apa yang akan Ibu lakukan.” In this utterance, the main point of sentence is about what the woman will do in the first
30 second when she is meeting a new man. When the word “Okay”is omitted, it
will be “30 detik pertama Ibu temukan apa yang akan Ibu lakukan”. Therefore,
the main point of sentence is still the same. The word does not change the main
RP/00:48:20 Good,Saya ambil satu lagi.
In this utterance, Mario wants to invite one of the audience to join him in
the stage. He has invited one of the audience to the stage and he wants to invite
one more audience to be in the stage.
In RP/00:48:20, the switch appears in the beginning of the sentence. The
word“Good” is tag switching because it occurs as a tag, “Good, Saya ambil satu
lagi (I pick one more)”. Whether it does exist or not, it does not change the point
of the sentence. The idea of the sentence is about that Mario Teguh wants to pick
one more of the audiences to the stage. When the word “Good” is omitted, the
idea is still similar. “Saya ambil satu lagi(I pick one more)”.
SF/00:05:00 So, kehidupan itu masalah keputusan. Kalau prasangka kita
buruk terhadap kehidupan kita mudah berharapan buruk.
The datum above is an advice about life. Life is about decision. When
people decide to have negative thinking about their life, they will make bad
expectation with their life. With this advice, Mario hopes the audience can have a
good prejudice for their life. Good prejudices can have ability to give a good
expectation. When people have a good expectation, they will make a good
decision for their life.
In SF/00:05:00, the switched language exists at the beginning part of the
sentence. The word “So” is tag switching because it occurs as a tag and its
“So, kehidupan itu masalah keputusan. Kalau prasangka kita buruk terhadap
kehidupan kita mudah berharapan buruk”. In this case, the point of sentence is about introducing the topic of the show. When the word is omitted, it will be
“Kehidupan itu masalah keputusan. Kalau prasangka kita buruk terhadap
kehidupan kita mudah berharapan buruk.” Therefore, the point of sentence is still the same. There is no meaning change in the utterance.
c. Intersentential switching
Intersentential switch is the switch that occurs between sentences made by
the speakers. The topic of the conversation may be switched by pause employed
by one of the speaker. The pause employed here shows a brief suspension of the
voice to indicate limits or relations of sentences. Intersentential switch occurs
between more than one sentence. Based on the findings, there are 7 data that
belong to intersentential switch. Below are four examples of Intersentential switch
that occur in Mario Teguh Golden Ways 2015:
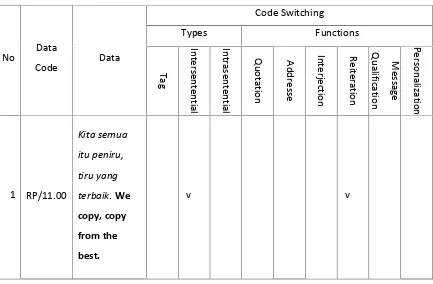
RP/00:11.00 Kita semua itu peniru, tiru yang terbaik.We copy, copy from
the best.
The idea of the datum above is about Mario Teguh who tells to the
audience that we are an imitator. The first Indonesian sentence idea is to tell the
audience that we are an imitator and we need to imitate the best to be a good
imitator. In the second sentence, Mario Teguh repeats his Indonesian sentence
Based on RP/00:11.00, the switch “We copy, copy from the best” is categorized into intersentential switch because it occurs after pause employment.
It is shown from, “Kita semua itu peniru, tiru yang terbaik (pause) We copy, copy from the best.” The pause occurs to indicate the boundary of the sentences.
In this case, it indicates the boundary between the two sentences “Kita semua itu
peniru, tiru yang terbaik.” and the switch “We copy, copy from the best”.
RP/00:40:10 Jangan tergesa-gesa untuk tampil, tunggulah waktu yang
tepat.When the time is right. Jepret masuk.
The idea of the utterance is about showing people’s potential. Mario tells
to the audience that when they want to show their potential, they need to be
patient. They should not show their potential or capability in a rush. They need to
wait until the time is right to show their potential. If they fail to get a timing, the
people around will not really appreciate their potential. Mario tells that many
youngsters fail because they are in a rush and they cannot read the situation
around them.
According to RP/00:40:10, the clause “When the time is right” is the
evidence of intersentential switch because it occurs after pause employment. It is
seen from, “Jangan tergesa-gesa untuk tampil, tunggulah waktu yang tepat.
(pause)When the time is right. Jepret masuk”. The occurrence of the pause here
is to indicate the limits between the sentences “When the time is right.” The
clause is also the evidence of intersentential switch because it occurs within
CAD/00:46:00
Lakukan yang terbaik untukmu atau kamu tidak akan menjadi baik untuk siapapun. Do what good for you or you are not good for anyone.
The idea of the utterance above is Mario Teguh who tells the audience to
do something good for their self. If they do something good for them it will good
for anyone around them, but if it is not good for them it is not good for anyone.
The first consideration when someone want to do something is the benefit of the
action for himself. If someone do something good, it will be good for anyone
because God will take care of what people think about it.
In CAD/00:46:00, the clause “Do what good for you or you are not good
for anyone” is intersentential switch because it occurs after pause employment. It
is shown from; “Lakukan yang terbaik untukmu atau kamu tidak akan menjadi
baik untuk siapapun (pause) Do what good for you or you are not good for anyone.” In this case, the pause occurs to indicate the boundary between the
sentences “Lakukan yang terbaik untukmu atau kamu tidak akan menjadi baik
untuk siapapun” and the switch “Do what good for you or you are not good for anyone.”
SF/00:52:00 Itu akhir dari hubungan kita. Kalau dalam bahasa inggris.
This is the end of our relationship.
The main idea of the datum above is about an advice about a bad
keep his relationship. He needs to be resolute to end his relationship and does not
hold it. If it bad for his life, it is bad. It needs to be end.
In SF/00:52:00, the sentence “This is the end of our relationship” is
intersentential switch because it occurs after pause employment. It is shown from :
“Itu akhir dari hubungan kita. Kalau dalam bahasa inggris. (pause) This is the end of our relationship”.In this case, the pause occurs to indicate the boundary
between the sentences “Itu akhir dari hubungan kita. Kalau dalam bahasa
inggris” and the switch “This is the end of our relationship”.
2. Function of code switching inMario Teguh Golden Ways 2015
According to the theory mentioned previously, there are six functions of
conversation code switching. After analyzed the data, the researcher finds that
code switching that are employed by Mario Teguh in Mario Teguh Golden Ways
2015 only have functions as Reiteration, Interjection, Message Qualification,
Quotation.
a. Reiteration
Reiteration means the switch serves to clarify what is said or to emphasize
the message. In the findings, the researcher finds that there are 25 data function as
reiteration inMario Teguh Golden Ways 2015.
RP/00.11.00 Kita semua itu peniru, tiru yang terbaik. We copy, copy from
The main message of the sentences above is about Mario Teguh who tells
to the audience that we are an imitator. The first Indonesia sentence idea is Mario
Teguh who tells the audience that we are an imitator and we need to imitate from
the best to be a good imitator. The second sentence Mario Teguh repeats his
Indonesian sentence uses English to emphasize the idea of his utterance.
In RP/00.11.00, there is intersentential switching found in the utterance.
The switch happens between the sentences. The sentence “We copy, copy from
the best” is as reiteration: “Kita semua itu peniru, tiru yang terbaik. We copy,
copy from the best.” The sentence “We copy, copy from the best”in this case has the same meaning with the first sentence. In this case, Mario Teguh reiterates his
statement by switching to English in order to emphasize what he wants to state.
The switch here is to emphasize the main meaning of the statement.
RP/00.12.00 Kita itu sebenarnya hanya penyalur. You never own. Saya
Mario Teguh tidak pernah memiliki ilmu.
The main message of the utterance above is about telling the audience that
people are just messenger and people never own knowledge. The speaker wants to
advice the audience that they do not need to be miserly with their knowledge.
They do not own the knowledge. They are just messenger who needs to deliver
the knowledge to the others.
Mario Teguh uses Indonesian to convey the main idea of his utterance and
he inserts an English sentence in the middle of his utterance “You never own” to
In this data, the sentence“You never own” is categorized to intersentential
switching because the switch happens between the sentences of the utterance. The
reseacher also finds that the utterance is categorized as reiteration function: “Kita
itu sebenarnya hanya penyalur.You never own. Saya Mario Teguh tidak pernah memiliki ilmu.” The sentence “You never own”in this case has the same meaning with the first and third sentence. In this case, Mario Teguh reiterates his statement
by means of switching to English in order to emphasize what he wants to state.
The switch here is to emphasize the main meaning of the statement.
SF/00:52:00 Itu akhir dari hubungan kita. This is the end of our
relationship, kalau dalam bahasa inggris.
The main message of the first sentences above is the end of relationship.
Mario Teguh uses Indonesian in the first sentence and he changes to English for
the second sentence to give repetition of the idea of the first sentence. From this
utterance, the speaker wants to gives an advice about relationship. He tells the
audience that they should not hold someone who brings something bad for their
life.
In this particular object, there is intersentential switching found in the
uttearance. The switch that happens in the utterance categorized as intersentential
switching because it happens between the sentences. In the datum SF/00.52.00,
the researcher also finds that the sentence “This is the end of our relationship” is
categorized to have the function as reiteration. The sentence “This is the end of
case, Mario Teguh reiterates his statement by switching to English in order to
emphasize what he wants to state. The switch here is functioned to emphasize the
main meaning of the statement.
CAD/00:07:10
Kebetulan pemula, Beginner's luck, Para pemula sering beruntung karena memulai yang dicobanya dari mental yang terbuka bagi semua kemungkinan.
The main idea of the sentence above is about why some beginners can get
a good result when they try something in the first try. Mario tells the audience that
happens because beginners have an open mind. With their open mind and
meantal, they can have an ability to learn something new. Beginners who try
something in the first try have nothing to lose. They do not afraid to lose because
that is the first time they try. Because of that mentality, they can do something
without pressure.
In CAD/00:07:10, the researcher finds intrasentential switching. Mario
Teguh uses Indonesian to explain the idea of the utterance. In the middle of his
sentence, he inserts the phrase “Beginner luck”. The phrase is categorized as
intrasentential switching. The researcher also finds that the phrase “Beginner’s
luck” is classified as the function as reiteration: “Kebetulan pemula, Beginner's
luck, Para pemula sering beruntung karena memulai yang dicobanya dari mental yang terbuka bagi semua kemungkinan.” The phrase “Beginner’s luck” in this
case has the same meaning with thefirst phrase “Keberuntungan pemula”. In this
emphasize what he wants to state. The switch here is functioned to emphasize the
main meaning of the statement.
b. Interjection
Interjection serves to mark an interjection or sentence filler. Based on the
findings, there are 19 data of code switching of interjection. The example of
interjection in Mario Teguh Golden Ways 2015 can be seen as follows:
RP/00:01:00
Sahabat sayq yang baik hatinya selamat malam, silahkan duduk. So, Rating Pribadi, kita semua harus menjadi pribadi yang bernilai, yang mahal, yang dihormati, yang didengarkan saat berbicara, yang tidak diperlakukan dengan sembarangan oleh orang lain.
Based on the data above, the idea in the first sentence is a greeting from
Mario Teguh to the audience in the beginning of the show. The idea in the second
sentence is to introduce the topic of the show. Mario Teguh gives the introduction
and a short explanation about the title of the show. He says that the audience
should be a valuable, respectful person who not allowing people to insult them.
In RP/00:01:00, the researcher finds that the word “So” is tag switching
because it occurs as a tag and its occurrence will not change the main point of the
sentence. The switch “So” is regarded as interjection because it serves to mark
sentence filler. In this case the switch occurs in the second sentence which is the
actual main point of the utterance above. Theswitch “So”is functioned to fill the
RP/00:44:10 Very good, kita berikan tepuk tangan.
The main idea of the sentence is about Mario Teguh who asks the
audiences to give applauses to the one of the audience who stands in the stage. It
is a common situation to give applause to the one of the audience who is invited to
the stage of Mario Teguh Golden Ways. Mario Teguh always gives applause to
the audience because he wants to show to the audience that they need to
appreciate every good thing that someone do. Even though, it is a very little thing
if it is a good thing they must appreciate it.
In RP/00:44:10, there is tag switching found in the utterance and its
occurrence will not change the main point of the sentence. The switch happens in
the beginning of the sentence. The phrase “Very good” functionsas interjection. It
is an interjection because it is one of the phrases to express emotion.
RP/00:23:20 Okay, 30 detik pertama Ibu temukan apa yang akan Ibu
lakukan.
The main idea of the sentence above is about Mario Teguh who gives an
advice to the woman what she should do when she meets a man for the first time.
From this utterance, Mario wants to tell the audience that the first 30 second of
introduction is important. The first 30 second of introduction can impress the
In this case, there is a tag switching found in the utterance and its
occurrence will not change the main point of the sentence. “Okay” is regardedas
interjection because it serves to mark sentence filler. In this case, the switch
occurs in the beginning of the sentence which is the actual main point of the
utterance above. The switch “Okay” is to fill the time when Mario Teguh thinks
about the main point that he wants to say.
SF/00:05:20
So, mudah-mudahan dari sekarang kita berprasangka baik dari penampilan orang. Kita bilang gini "Jangan beli buku berdasarkan sampulnya"
The main idea of the utterance above is about Mario Teguh’s advice on
prejudice. Mario tells the audience that they should not judge people from their
appearance. Sometimes people who wear good dresses are not always good
people. Many bad people have the ability to cover their badness with very good
covers. That is why Mario Teguh gives an advice to the audience why they should
not judge people by their appearance.
In SF/00:05:20, there is tag switching found in the utterance and its
occurrence will not change the main point of the sentence. The switch “So” is
regarded as interjection because it serves to mark sentence filler. In this case, the
switch occurs in the beginning of the sentence which is the actual main point of
the utterance above. The switch “So”functions to fill the time when Mario Teguh
c. Message Qualification
Message qualification means that the switch serves to convey the main
message or to qualify the message in someone’s uterrance. According to the
findings, there are 16 data functioning as message qualification in Mario Teguh
Golden Ways 2015;
RP/00:39:00
Istilahnya ya kebaruan, dalam marketing disebut newness. Orang yang punya sesuatu yang lebih baru dari kita membuat kita terusik.
The function of the switch occurs in this data is closely related to the main
idea of the sentence. The main idea of the first sentence is about Mario Teguh
who tells the man that in the future time people need to do something new. The
second sentence main idea is about telling to the audience that someone who does
not do something will be disturbed by the other. In this utterance, Mario Teguh
wants to give an advice to the audience that everyone needs to do something new
and fresh. Everyone is getting old every time. Everyone in the world is getting old
but there is always someone new. If the old people are not creative and they do
not do something fresh and new, they will lose the competition from the people
who have fresh ideas.
In RP/00:39:30, the researcher finds there is intrasentential switching. The
speaker, Mario Teguh, inserts an English word into his Indonesian sentence. The
main message is in Indonesian and the switch “newness” is considered to be
message qualification which means that the switch functions to convey additional