IMPROVING THE STUDENTS’ ABILITY TO WRITE
HORTATORY EXPOSITION TEXT THROUGH PICTURE
WORD INDUCTIVE MODEL
(Classroom Action Research at the Eleventh Grade of SMA N 1
Tuntang in the Academic Year of 2017/2018)
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board of Examiners as a partial fulfillment of the requirements for
The degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd)
By:
TIKA LUTFIA NINGSIH
NIM. 11314035
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
IMPROVING THE STUDENTS’ ABILITY TO WRITE
HORTATORY EXPOSITION TEXT THROUGH PICTURE
WORD INDUCTIVE MODEL
(Classroom Action Research at the Eleventh Grade of SMA N 1
Tuntang in the Academic Year of 2017/2018)
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board of Examiners as a partial fulfillment of the requirements for
The degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd)
By:
TIKA LUTFIA NINGSIH
NIM. 11314035
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
DECLARATION
In the name of Allah,
Hereby, the writer declares that this graduating paper is written by the writer. This paper does not contain any materials published by other people and it does not cite any other people’s ideas except those quoted overtly. The thing
related to other people’s work are written in quotation and included in the
bibliography.
Salatiga, July 27th 2018
Faizal Risdianto, S.S., M.Hum
The Lecturer of English Education Department State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR’S NOTE
Case: Graduating Paper of Tika Lutfia Ningsih
Dear,
Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty Assalamu’alaikum Wr. Wb
After reading and correcting the graduating paper of Tika Lutfia Ningsih, entitled “IMPROVING THE STUDENTS’ ABILITY TO WRITE HORTATORY EXPOSITION TEXT THROUGH PICTURE WORD INDUCTIVE MODEL
(Classroom Action Research at The Eleventh Grade of SMA N 1 Tuntang in the Academic Year 2017/2018)”, I have decided and would like to propose that this paper can be accepted by the Teacher Training and Education Faculty. I hope this paper will be examined as soon as possible.
MOTTO
“Thoughts give birth to actions, actions
spawned a habit, habit bore the
character, and the character created
fate”
-Aristoteles-
DEDICATION
The writer dedicated this graduating paper to:
1. My beloved mother (Kasniyati) and father (Suwarno Utomo) who always love, pray and support me.
2. My beloved brother Nugroho Adi Utomo thanks for your kindness. 3. All members of Edi Mancoro Islamic Boarding House.
4. All members of LPM Dinamika IAIN Salatiga, especially for members of Lpm Dinamika 2015.
5. My friends all members of TBI 2014, especially for class TBI A 2014 thanks for your support.
6. My roomates of Edi Mancoro Islamic Boarding House; Bunda Fajar, Dek Surya, Masitoh, Bunda Mar’ah, Mbak Asya, Dek Ajeng, Dek Nanik, Mbak Isma, Dek Riski, Dek Riris, and Dek Novita. Thanks for your support and spirit.
7. My big family that supported for my education and finishing this graduating paper.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Bismillahirrohmanirrohim.
Assalamu’alaikum Wr. Wb.
In the name of Allah, The Most Gracious and The Most Merciful, The Lord of Universe. Because of Him, the researcher could finish this graduating paper as one of the requirements for Sarjana Pendidikan in English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga.
Secondly, peace and salutation always be given to our prophet Muhammad SAW who has guided us from the darkness to the lightness. However, this success would not be achieved without supports, guidance, advice, helps, and encouragements from individual and institution, and the researcher somehow realize that an appropriate moment for him to deepest gratitude for:
The writer would like to express her deepest gratitude and appreciation to:
1. Drs. Rahmat Hariyadi, M.Pd, the Rector for State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga.
2. Mr. Suwardi, M.Pd, the Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty in the State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga.
4. Mr. Faizal Risdianto, S.S., M.Hum., as the writer’s counselor. Thanks for your advice, suggestion and correct to my graduating paper.
5. Mr. Kastolani, Ph.D., as my academic consultant.
6. All lecturers and staffs of IAIN (Salatiga), the writer deeply thanks all for your advice, knowledge, and kindness.
7. Almaghfurlah K.H. Mahfudz Ridwan and Hj. Nafisah as the founder of Edi Mancoro Islamic Boarding House (PPEM).
8. Muhamad Hanif, M.Hum, as the patron of Edi Mancoro Islamic Boarding House (PPEM).
9. My parents and my big family who always support and advice me.
10.All of my friends in Edi Mancoro Islamic Boarding House (PPEM), thanks for your support and togetherness.
11.All my friends in TBI 2014, thank you for giving a sweet moment. 12.All my friends in LPM Dinamika IAIN Salatiga.
Finally, this graduating paper is expected to be able to provide useful knowledge and information to the readers.
ABSTRACT
Ningsih, T. L. (2018). Improving The Students’ Ability to Write Hortatory Exposition Text through Picture Word Inductive Model for Eleventh Grade Students of SMA N 1 Tuntang in The Academic Year of 2017/2018. A Graduating Paper. English Education Department. Teacher Training and Education Faculty. State Institute for Islamic Studies Salatiga. Counselor: Faizal Risdianto, S.S., M.Hum.
Keywords : Writing; Hortatory Exposition Text; Picture Word Inductive Model; Classroom Action Research.
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1.1: Students’ List of XI IPA 1 ... 12
Table 1.2: Reseach Schedule ... 13
Table 1.3: The Students’ Observation Check List ... 15
Tabel 1.4: The Teacher’s Observation Check List ... 15
Table 2.1: The Analytical Scoring Rubric ... 31
Table 2.2: Example of Hortatory Exposition Text ... 41
Table 4.1: The Students’ Observation Check List of Cycle I ... 66
Table 4.2: The Teacher’s Observation Check List of Cycle I ... 68
Table 4.3: The Result of Students’ Observation of Cycle I ... 70
Table 4.4: The Score of Pre-Test in Cycle I ... 72
Table 4.5: The Score of Post-Test in Cycle I ... 73
Table 4.6: Difference Square of Pre-Test and Post-Test Score of Cycle I ... 75
Table 4.7: Descriptive Statistics Cycle I ... 76
Table 4.8: Paired Samples Test Cycle I ... 77
Table 4.10: The Teacher’s Observation Check List of Cycle II ... 85
Table 4.11: The Result of Students’ Observation of Cycle II ... 87
Table 4.12: The Score of Pre-Test in Cycle II ... 90
Table 4.13: The Score of Post-Test in Cycle II ... 91
Table 4.14: Diifference Square of Pre-Test and Post-Test Score of Cycle II ... 92
Table 4.15: Descriptive Statistics Cycle II ... 93
Table 4.16: Paired Samples Test Cycle II ... 94
LIST OF FIGURES
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Research
Language is an important tool to communicate with each other in the world. According to Brown (1980: 5), language is a set of arbitrary symbols which used for communication. Gentner and Goldin-Meadow (2003: 17) state that “Although we use language every day to talk about experience, language itself is far from being an exact representation of our experience. When we understand and produce language, we always have to take into account the fact that language does not offer us exact maps of the experiences we may wish to recount to someone or interpret from
someone else.” In short, language is an instrument to convey information which is used to express ideas, feelings, purposes, thoughts, and opinion in written or spoken way.
There are many languages to communicate with each other in the world. Learning English is so necessary for every people in this era. According to Harmer (2001: 5), English is a number of future possibilities, all of which question the certainty of English as the number one in the world.
production, they are productive skills. On the other hand, listening and reading involve accepting the message, so they are as receptive skills.
The students have to learn all of the skills above because the government had been arranged the curriculum of English lesson. But, not all of them are capable of those skills. One of those skills above is writing skills. According to Arumi (2015: 1), writing as one of language skill considered very difficult. It is due to the fact that writing needs to produce and organize ideas using appropriate vocabulary, language use, paragraph organization, and mechanism. It also needs to turn the ideas into a readable text and for foreign language learners; they should also transfer ideas from their native language into the target language (foreign language).
In fact, Indonesian students have many difficulties in learning English. Actually, in writing skill they have difficulties to practice because to write a good text, students have to follow the rules of the target language. The students have to learn the grammar, mastering the vocabulary, elaborate their ideas to achieve writing form, and arrange the paragraphs. They are difficult to change their ideas to become the text that easy to read.
argues that X should or should not be the case. In short, hortatory exposition is a type of spoken or written text that persuade the listeners or readers that something should or should not happen or be done.
There were some problems occurring in SMA N 1 Tuntang. Based on the interview with Mrs. Surti Harjanti who is the English teacher of eleventh-grade students on March, 26th 2018 students’ difficulties in writing for eleventh-grade students of SMA N 1 Tuntang. The researcher asked some questions. The first question is about the Standardized of Minimum Score (KKM) of English subject is 70 and SMA N 1 Tuntang uses curriculum 2013. The next question is about the most difficult skills in writing the subject for the students. The eleventh-grade students at SMA N 1 Tuntang are difficult to write the text. There are caused some factors. The factors were the students and teaching techniques used in the writing teaching and learning process.
attention to how to organize their idea into a good organization. As the result, their sentences and paragraphs were not well sequenced.
Suharmi (2015: 3) states, “To be a good writer must have good capabilities in writing. The writer has to be able to organize the ideas, to construct the sentences, to use punctuation and spelling well. Besides that, they must be able to arrange their writing into a cohesive and coherent
paragraph.” However, the students did not master grammar well. They often made mistakes in writing sentences. They also were confused about using pronouns and articles in their writing. Furthermore, they often ignored the writing mechanics such as spelling, punctuation, and capitalization. They thought that English is a difficult subject.
The next factors were the activities used in the teaching and learning process. When the researcher observed the class in the teaching and learning process, the students were talking to each other. They did not pay attention to the teacher explanations. When they had a topic to write, it is difficult for them to arrange the sentences into good writing. There was no strategy that helped them to arrange text using the correct generic structure. The teacher had given an example and the vocabulary below the text, but many students did not understand if they have to arrange the sequence sentences.
Picture Word Inductive Model (PWIM) to improve students’ ability to write hortatory exposition text. According to Calhoun (1999: 21)
“Developed the Picture Word Inductive Model (PWIM), which uses pictures containing familiar objects, actions, and scenes to draw out words
from children’s listening and speaking vocabularies. It is be effective for the students who want to expand their writing skill. This model helps the students add words to their sight-reading vocabulary, as well as their writing vocabulary, and also discover phonetic and structural principles present in those words.”
The reasons for conducting the research is as to give the teachers appropriate teaching, especially in hortatory exposition text in the eleventh-grade students. Then, they are willing and able to make writing hortatory exposition text easily. It can solve students difficulty in understanding a hortatory exposition text paragraph by using PWIM. The students will be easy to arrange the words become sequence sentences and paragraphs.
Based on the explanation above the researcher is inspired to conduct a research entitled Improving The Students’ Ability To Write Hortatory Exposition Text through Picture Word Inductive Model
B. Problems of the Research
Based on the background of the research, there are some problems with the research are as follows:
1. How is the implementation of Picture Word Inductive Model (PWIM) to improve the students’ writing ability in hortatory exposition text at the eleventh-grade students’ of SMA N 1 Tuntang in the academic year of 2017/2018?
2. What is the significant improvement after using the Picture Word Inductive Model (PWIM) in students’ writing ability in hortatory exposition text at eleventh-grade students of SMA N 1 Tuntang in the academic year of 2017/2018?
C. Objectives of the Research
1. To describe the implementation of the Picture Word Inductive Model (PWIM) in improving the students’ ability in writing hortatory exposition text at eleventh-grade students of SMA N 1 Tuntang in the academic year of 2017/2018.
D. Significances of the Research
This research is expected to be used theoretically and practically: 1. Theoretically
This research is expected to give an explanation about the use of the Picture Word Inductive Model (PWIM) to improve students’ writing ability in hortatory exposition text.
2. Practically
The result of this research is expected to be useful for the students, English teachers, and institution:
a. For the Students
1) Help the students to comprehend the hortatory exposition text easily.
2) Improve the students’ writing ability which is taught by the Picture Word Inductive Model.
b. For the English teachers
The finding of this research can be a new knowledge for the English teachers to teach writing skill in hortatory exposition text. Picture Word Inductive Model (PWIM) is effective to improve the students’ writing ability.
c. For the Institution
E. Hipotesis and Success Indicator
Based on the student's observation result in hortatory exposition text as illustrated in chapter 1, the researcher tries to overcome those problems by implementing the Picture Word Inductive Model (PWIM). By conducting this research, the researcher proposes a hypothesis: the implementation of Picture Word Inductive Model (PWIM) can improve the students’ ability in writing hortatory exposition text.
The success indicator of this research is taken from the students’ Basic Competence ability shown in Lesson Plan (RPP). The students’ success and failure in conducting the activities in cycle I and II will be assessed by referring to the criterion of a passing grade (KKM). The passing grade of English lesson in SMA N 1 Tuntang is 70. The teacher and the researcher expect that there are at least 85% of the students who pass the passing grade.
F. Research Methodology 1. Research Design
Type of this research is using Classroom Action Research (CAR). Classroom Action Research (CAR) is a similar systematic process aimed at gathering information on teaching and learning problems in the classroom and working toward a solution.
time. It is related to the ideas of reflective-practice and the teacher as researcher. Action research involves taking a self-reflective, critical, and systematic approach to exploring teacher own teaching contexts.
Burn (2010: 2) states that in the teaching-learning, the teacher has to take a questioning and problematizing stance towards the teaching. Problematizing doesn’t apply to look at the teaching as if it is ineffective and full of problems. Rather, it means taking an area you feel could be done better, subjecting it to questioning, and then developing new ideas and alternatives. So, in Classroom Action
Research (CAR), a teacher becomes an ‘investigator’ or ‘explorer’ of
his or her personal teaching context, while at the same time being one of the participants in it.
Figure 1.1: Four Activities in Each Cycle
The spiral Model by Kemmis and Mc Taggart
Based on Arikunto (2008: 75), there are four steps in each cycle for conducting classroom action research, which can be explained as follows:
a. Planning
In this step, the researcher focusses on who, what, when, where, and, how the action is conducted.
b. Action
In this step conducted to implement the strategies prepared in the planning.
c. Observation
result of the action. The researcher prepares the observation paper to know class condition when the action is done, then the researcher (as the observer and collaborator) and the English teacher (is the teacher in the research) discuss about the result of observation, what the problem faced when teaching-learning process and look for good solution to solve the problem. In this phase, the researcher observes and takes notes during the teaching-learning process.
d. Reflection
Reflection means to analyze the result based on the data that have been collected to determine the next action in the next cycle. In this phase, the researcher could observe the activity that results in any process, the progress happened, and also about the positives and negatives sides.
2. Subject of the Research
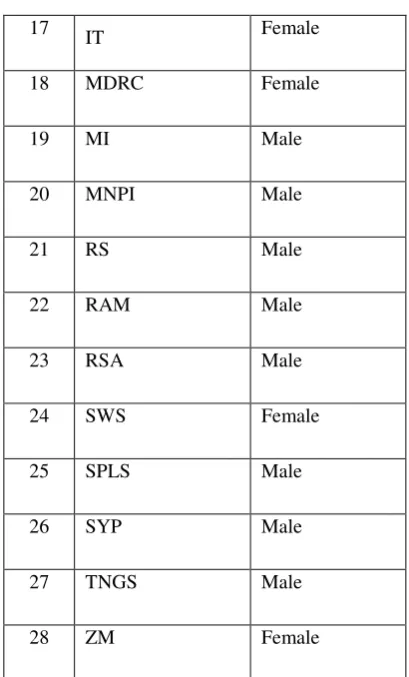
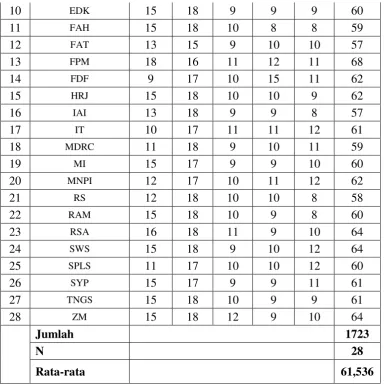
The subject of research is students of the eleventh grade from XI IPA 1 at SMA N 1 Tuntang in the academic year of 2017/2018. There were 28 students in that class.
Table 1.1: Students’ List of XI IPA 1
No Name Gender
1 AF Female
2 AS Male
3 AS Male
4 AKW Female
5 DK Female
6 DSR Female
7 DSN Female
8
DSW Female
9 DP Male
10 EDK Female
11 FAH Male
12 FAT Male
13 FPM Female
14 FDK Female
15 HRJ Male
17
IT Female
18 MDRC Female
19 MI Male
20 MNPI Male
21 RS Male
22 RAM Male
23 RSA Male
24 SWS Female
25 SPLS Male
26 SYP Male
27 TNGS Male
28 ZM Female
3. Steps of the Research
In conducting the research, the researcher carries out the steps which summarized in the following research schedule. The research schedule is shown in table 1.2.
Table 1.2: Research Schedule
No Activities Time Allocation
1 Preparing the research proposal March
2 Conducting observation April
4 Analysis data April
5 Writing research result May
6 Continuing writing the graduating paper May
4. Data Collection Method and Research Instrument
The techniques of collecting data are ways to acquire data in a classroom action research. The act old collecting data will be presented as follows:
a. Observation
According to Arikunto, (2010: 272) observation is a method which effectiveness with complete the observation sheet as an instrument. The form that arranged items which explain the occurrences, behaviors or actions which is described. Write the data of observation is not just to write, but also have to consider the case then assessing the level of scale.
In short, in the action and observation steps, the observation guide was used to see the implementation of the actions and success of the research. In the reflection steps, the field notes were used to evaluate the actions that have been done.
checklist observation to make it more systematic. It consists of student It consists of students’and teachers’ observation checklist. In filling the observation checklist, the researcher use the mark “√”. The students’ observation checklist is written below:
Tabel 1.3 The Students’ Observation Check List
No Indicator Yes No Descriptions Obstacles Solutions
1 Paying attention
2 Asking Question
3 Responding to Question
4 Accomplishing task
5 Being enthusiastic of
Picture Word Inductive
Model
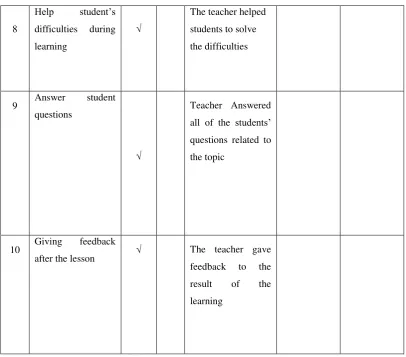
The form observational field note for a teacher is shown in table 1.4 Table 1.4: The Teacher’s Observation Check List
No Aspect Yes No Descriptions Obstacles Solutions
1 Greeting students before the lesson begin
2 Praying before the lesson begins
3 Checking student attendant
4 Reminding previous material
material
6 Use of Picture Word Inductive Model in accordance with the material
7 Giving opportunity for asking a question
8 Help student’s difficulties during learning
9 Answer student questions
10 Giving feedback after the lesson
b. Test
To get the data, the researcher conduct the test that consists of a pre-test and post-test. Each meeting consists of several teaching activities a pre-test and post-test.
1) Pre-Test
Before conducting the cycle I and cycle II, the researcher give the pre-test for each cycle. The purpose tried to know the
students’ writing ability before the teacher implementing the Picture Word Inductive Model (PWIM). The forms of the test were an essayed test. In this test, the teacher give some grade based on some aspect. Those aspects are grammar, content, organization on form and, punctuation.
2) Post-test
needed to write the hortatory text based on the picture. The purpose of conducting the post-test was to know the improvement of the students’ writing ability after implementing Picture Word Inductive Model (PWIM).
c. Documentation
The researcher also used the documentation as the method of collecting data in this research. The documentation also is a method used to find the data related, by picture and video. According to Arikunto (2010: 274), documentation is finding the data about variables as a note, transcript, book, newspaper, magazine, agenda, picture, video, voice record, etc.
5. Data Analysis Techniques
The researcher conduct the Classroom Action Research (CAR) in improving the students’ ability to write hortatory exposition text through Picture Word Inductive Model (PWIM) for the eleventh-grade students of SMA N 1 Tuntang. In analyzing the data, the researcher used the mixed method. It means that the research involved mixing of qualitative and quantitative data. The researcher would like to analyze the data using the mixed method as follow:
a. Qualitative data
humanity. This research applies an inductive way of looking at the research, focusing on the meaning of the individual, and translating the complexity of a problem.
The most important data in the action research is the description behavior of the students. The analysis of qualitative data is taken from observation, test, and documentation.
b. Quantitative data
Based on Creswell (2016: 5) the quantitative data is a method for testing certain theories by examining relationships between variables. Variables are measured, usually with research instruments so that data composed of numbers can be analyzed based on statistical procedures. The quantitative data is processed by the teacher and the researcher gets the score of the students. The maximum score is 100.
1) Score the Students’ Test
There are five components present in the analytical scoring rubric for writing, are content, organization, grammar, punctuation, and vocabulary (Brown, 2004: 244-245). The researcher uses an analytical scoring rubric to analyze the data
related to the students’ paragraph writing test of writing ability. 2) Calculate the Result of the Test
significant difference in cycle I and cycle II. This research uses the Statistical Package for the Social Science (SPSS) for analyzing the data. According to Landau and Everitt (2003: 1), said that SPSS is manipulating, analyzing, and presenting data program which is used in the social and behavioral science. In practice, the researcher use SPSS Base. SPSS Base has a number of add-on modules that extend the range of data entry, statistical, or reporting capabilities. That also provides methods for data description, simple inference for continuous and categorical data and linear regression.
G. Graduating Paper Outline
This research is organized into five chapters. Chapter I present the introduction. It contains the background of the research, research question, objectives of the research, significance of the research, hypothesis and success indicator, research methodology, and graduating paper outlines. Chapter II describe the supporting theories and preevious studies. It consists of the definition writing, the requirement of a good writing, type of texts, the definition of hortatory exposition text, Picture Word Inductive Model (PWIM), how to implementing the Picture Word Inductive Model (PWIM) in writing hortatory exposition text.
findings and the data analysis. It contains the result of the research the use
of PWIM in improving students’ ability in writing hortatory exposition
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF LITERATURE
A. Supporting Theories 1. Writing
a. The Definition of Writing
There are some experts who define writing, based on Lado (1983: 143), says that writing is a partial representation of units of language expression. To write is to put down the graphics symbols if they know the language and the graphic representation.
Brown (2001: 334) states that learning writing is like learning to swim. Learning to swim can only be practiced if there is a body of water available and usually only if someone teaches too. People learn writing if they are a member of a literate society and usually only if someone teaches too. If someone wants to be able to swim, he can not just master the theories to swim, but he has to get into the water to practice and apply the theories, but instead, he must plunge into the real writing world where he would practically involve in writing.
b. The Purpose of Writing
According to Nunan (2003: 88), the purpose of writing is express and impress. Writers typically serve two masters; themselves, and their own desires to express an idea or feeling, and readers, also called the audience, who need to have ideas expressed in certain ways. Writers must then choose the best form for their writing, shopping list, notes from a meeting, a scholarly article, a novel, or poetry are only a few of the choices. Each of these types of writing has a different level of complexity, depending on its purpose.
c. Types of Writing
According to Brown (2004: 220), the type of writing contains four categories. Each category resembles that categories defined for the other three skills, but these categories, as always, reflect the uniqueness of the skill area. The types of writing, as follows:
1) Imitative
this stages, from is the primary if not exclusive focus, while content and meaning are of secondary concern.
2) Intensive (controlled)
Beyond the fundamentals of imitative writing skill in producing appropriate vocabulary within a context collocation, idioms and correct grammatical features up to lengths of a sentence. Meaning and contexts are of some importance in determining connectors and appropriateness, but most assessment tasks are more concerned with a focus on form and are rather strictly controlled by the test design.
3) Responsive
Here, the assessment task requires learners to perform at a limited discourse level, connecting into a paragraph and creating a logically connected sequence of two or three paragraphs. Tasks respond to pedagogical directives, first criteria outline, and other guidelines. Genres of writing include brief narratives and descriptions, short report, lab reports, summaries brief responses to writing and interpretations of the chart of graphs under specified conditions, the writer begins to exercise some freedom of choice among alternative forms of expressions ideas.
that will achieve the objectives of the written text. From focus attention is mostly at the discourse level, with a strong emphasis on context and meaning.
4) Extensive
Extensive writing implies successful management of all the processes and strategies of writing for all purposes, up to the length of an essay, a term paper, a major research project report, or even a thesis. Writers focus on achieving a purpose, organizing and developing ideas logically, using details to support or illustrate ideas, demonstrating syntactic and lexical variety, and in many cases, engaging in the process of multiple drafts to achieve a final product. Focus on grammatical form is limited to occasional editing or proofreading of a draft.
d. Effective Writing
According to Langan (2004: 13), paragraph is a series of the sentence about one main idea, or point. A paragraph typically starts with a point, and the rest of the paragraph provides specific details to support and develop that point. There are goals of effective writing as follows:
1) Make a point
2) Support the point
To support the point in the first paragraph, there is a need for a support sentence or supporting details.
3) Organize the support
Organizing the support in a paragraph is important. The students have to list the order, time order, and, attention about the transitions.
4) Write error-free sentences
The students have to keep a good dictionary and grammar handbook nearby to correct the error-free sentences.
In another hand, according to Oshima & Hogue (1988: 57-63), the good writing has some components. There are:
(a) Topic sentence
The students have to write down the topics sentences in a paragraph. The topics sentences usually in the first sentences that is mention deductive paragraph. Sometimes, in the last paragraph that is mention an inductive paragraph
(b) Supporting Sentence
(c)The concluding sentence
The concluding sentence is a general statement that introduces the topic to be discussed in the paragraph. The concluding sentence can be written like the topics sentence but in other words.
e. Writing Process
Based on Langan (2004: 16-25) as follows: 1) Prewriting
In the prewriting, there are several strategies before writing the draft of the paper, as a freewriting, questioning, clustering, and making a list.
2) Making an outline
Making an outline is a brief plan for a paragraph. It shows at a glance the point of the paragraph and the main support for that point. It is the logical backbone on which the paper is built.
3) Writing the first draft
sentence. According to Rafida (2017: 4), the sentence should be arranged based on the correct rules include:
(d) The elements in a sentence
(e) The application of the correct spelling (f) Selecting the right word in a sentence 4) Revising
Revising is as much a stage in the writing process as prewriting, outlining, and writing the first draft. Revising means rewriting a paper, building on what has been done.
5) Editing and proofreading
Editing and proofreading are checking a paper for mistakes in grammar, punctuation, usage, and spelling. The students often find it hard to edit a paper carefully. Eliminating sentence-skill mistakes will improve an average paper and help ensure a strong grade on a good paper.
f. Teaching Writing
On another hand, there some roles of the teacher to teach writing, Based on Harmer (2001: 261) as a follows:
1) Motivator
One of the principal roles in writing tasks is a motivator. The teacher has to motivate the students. Motivation is a purpose to create the right conditions for the generation of ideas, persuading them of the usefulness of the activity, and encouraging them to make as much effort as possible for maximum benefit. This may require special and prolonged effort on the process of teaching-learning part for longer process-writing sequences.
2) Resource
After giving the motivation, the teacher should be ready to supply information and language where necessary. The teacher should tell to their students that the teacher is available and be prepared to look at their work as it progresses. For example, there is usually time for discussion with individual students, or students working in pairs or groups.
3) Feedback provider
and how much to focus on based on what students need at this particular stage of their studies, and on the tasks they have undertaken.
g. Assessing Writing
Assessing of writing is an important point in teaching writing. According to Brown (2004: 241), there are three scoring that can be applied by the teacher to assess the students’ writing.
The first scoring method is holistic scoring. Holistic scoring is given a systematic set of descriptors, and the reader-evaluator matches an overall impression with the descriptors to arrive at a score. This scoring method is done by assigning a single score to a piece of writing. It views the written product without paying too
much attention to the details. Teachers cannot diagnose students’
writing skills since five aspects of writing such as content, organization, vocabulary, language use, and mechanics are not rated specifically.
The second scoring is primary trait scoring. This scoring focuses on how well students can write within a narrowly defined range of discourse. This type of scoring emphasize the task at hand
and assigns a score based on the effectiveness of the text’s
washback for any of the aspects of the written punctuation that enhance the ultimate accomplishment of the purpose.
The third method is an analytic scoring or analytic
assessment. The scoring is done by assessing students’ writing
based on the aspects such as content, organization, vocabulary, language use, and mechanics. According to Brown (2004: 243), analytic scoring is the most appropriate scoring method to apply in the classroom since teachers can get more details information of
students’ writing ability in each aspect.
Based on the reviews of the three types of scoring methods, the researcher decided to use the analytic scoring method. It was
easier for the researcher to analyze the students’ lacks and needs
since this method provides details information about students’ ability in each aspect of their writing.
information, as in expository writing. Then, the dominant intention or purpose is to learn, to convey emotions, to inform, to convince or persuade, to entertain/delight, and to keep in touch.
Table 2.1 The Analytical Scoring Rubric adapted By Brown (2004, 244-245)
1. Organization;
introduction,
Body, and
Conclusion
Appropriate title effective introductory paragraph, the
topic is stated, leads to the body; transitional
expressions used; arrangement of material shows plan
(could be outlined by the reader), supporting evidence
given for generalizations; conclusion logical and
complete
20-18
Excellent to Good
The adequate title, introduction, and conclusion body
of the essay is acceptable, but some evidence may be
lacking some ideas aren't fully developed; the
sequence is logical but transitional expressions may
be absent or misused
17-15
Good to Adequate
Mediocre or scant introduction or conclusion;
problems with the order of ideas I body; the
generalizations may be not fully supported by the
evidence given; problems of organization interfere
14-12
Adequate to Fair
Shaky or minimally recognizable introduction; the
organization can barely be seen; severe problems with
the ordering of ideas, lack of the supporting evidence.
Conclusion weak or illogical, inadequate effort at
effort to organize the composition (could be outlined
concrete and thoroughly developed; no extraneous
material; essay reflects the thought
20-18
Excellent to Good
The essay addresses the issues but misses some
points; ideas could be more fully developed; some
extraneous material is present
17-15
thinking or was hurriedly written; inadequate effort in
the area of content
11-6
Unacceptable
The essay is completely inadequate and does not
reflect college-level work; no apparent effort to
consider the topic carefully
5-1
Not College-level
work
3. Grammar Native-like fluency in English grammar; correct use
of relative clause, prepositions, modal, articles, verb
forms, and tense sequencing; no fragments or run-on
sentences
20-18
Excellent to Good
Advanced proficiency in English grammar, some
grammar problems don’t influence communication,
although the reader is aware of them; no fragments or
run-on sentences
17-15
Good to Adequate
Ideas are getting through to the reader, but grammar
problems are apparent and have a negative effect on
communication; run on sentences or fragments
presents
14-12
Adequate to Fair
Numerous serious grammar problems interfere with
communication of the writer’s ideas; grammar review
of some areas clearly needed; difficult to read
sentences
Unacceptable
Severe grammar problems interfere greatly with the
message; reader can’t understand what the writer was trying to say; unintelligible sentence structure
5-1
right margins, all needed capitals, paragraphs
intended, punctuation and spelling; very neat
20-18
Excellent to Good
Some problems with writing conventions or
punctuation; occasional spelling errors; left margin
correct; paper is neat and legible
17-15
Good to Adequate
Uses general writing conventions but as errors;
spelling problems distract reader; punctuation errors
interfere with ideas
14-12
Adequate to Fair
Serious problems with the format of paper; parts of
easy not legible; error n sentence punctuation and
final punctuation; unacceptable to educated readers
11-6
Unacceptable
Complete disregard for English writing conventions;
paper illegible; obvious capitals missing, no margins,
severe spelling problems
Precise vocabulary usage; use of parallel structures;
concise; register well
20-18
Attempts variety; good vocabulary; not wordy;
register OK; style fairly
17-15
Good to Adequate
Some vocabulary misused; lacks awareness of
register; may be too wordy
14-12
Adequate to Fair
Poor expression of ideas; problems in vocabulary;
lacks a variety of structure
11-6
Unacceptable
Inappropriate use of vocabulary; no concept of
register or sentence variety
5-1
Not College-level
work
2. Text
a. Definition of Text
According to Gerrot Wignel (1994: 15), a genre can define as a culturally specific text-type which results from using language (written or spoken) to (help) accomplish something.
According to Halliday (2004: 3), the text is a rich,
many-faceted phenomenon that ‘means’ in many different ways. It can be explored from many different points of view. But we can distinguish two main angles of vision: one, focus on the text as an object in its own right; two, focus on the text as an instrument for finding out about something else. Focusing on the text as an object, a grammarian will be asking questions such as: Why does the text mean what it does (to me, or to anyone else)? Why is it valued as it is? Focusing on the text as an instrument, the grammarian will be asking what the text reveals about the system of the language in which it is spoken or written.
b. Type of Texts
There are some types of text based on Gerrot and Wignel (1994: 152), as follows:
1) Spoof
2) Recount
A recount text is used to retell events, to state what happened for the purpose of informing or entertaining which usually proceeds through an orientation, sequence of events in time order, and re-orientation or conclusion.
3) Report
The report is a factual text which provides to describe the ways things are and give the information about what is or what happened. Reports can be written about an object, animal, person, place, event or thing. It usually proceeds through a classification and description.
4) Analytical Exposition
An analytical exposition is a text which functions to persuade the reader or listener that something in the case. It usually proceeds through a thesis, arguments, and re-iteration. 5) News item
The news item is a text which functions to inform readers, listeners, or viewers about events of the day which are considered newsworthy events, background events, and sources.
6) Anecdote
generic structures are abstract, orientation, crisis, reaction, and coda.
7) Narrative
The narrative is a text that has a function to amuse, entertain and to deal with actual or vicarious experience in different ways. Narrative deal with problematic events which lead to a crisis or turning point of some kind, which in turn finds a resolution.
8) Procedure
Procedure text is a text to describe how something that accomplished through a sequence of actions or steps. The generic structures of this text are goal, materials, and steps. 9) Description
Description text is a text to describe a particular person, place or thing. There is generic structure as identification to identifies phenomenon to be described. Then, description the parts, qualities, characteristics.
10)Hortatory exposition
should not happen or be done. A hortatory exposition text consists of these following structures as thesis, arguments, and the recommendation.
11)Explanation
An explanation text is a factual text used to explain the process of how something works. It usually proceeds through a general statement, explanation, and conclusion.
12)Discussion
The discussion is a text which used to present information about the different sides of an issue or topic. It usually proceeds through the issue, arguments, and recommendation.
13)Reviews
Reviews is a text which contains any critiques of an work or event for a public audience. It usually proceeds through the orientation, interpretative recount, evaluation, and evaluative summation.
3. Hortatory Exposition Text
a. Definition of Hortatory Exposition text
a type of spoken or written text that persuade the listeners or readers that something should or should not happen or be done.
In short, hortatory exposition text is kind of texts that designed to give information to readers about opinion or argument which we make as a result from the analysis from the problems as nature, environment, society, culture, politics, economy, etc.
b. Generic Structure of Hortatory Exposition Text
A hortatory exposition text consists of these following structures (Gerrot and Wignell, 1994: 166-167):
1) Thesis
The thesis is the announcement of the issue of concern. It is a statement about the truth or the fact the cases that occurred based on our conviction, moreover, there are invited other person to be contradicted the truth of our conviction about the problems that have been occurred.
2) Arguments
3) Recommendation
The recommendation is the statement of what ought to or ought not to happen. In the hortatory text, there is any recommendation about this problem that has been discussed from thesis and argument.
c. Language Features of Hortatory Exposition Text
There are language features of hortatory exposition text according to Gerrot and Wignel, 1994: 210):
1) Focus on generic human and non-human participants, except for speaker or writer referring to self.
2) Use of:
(a) Mental Processes: to state what the writer thinks or feels about the issue. For example: realize, feel, appreciate.
(b) Material Processes: to state what happens. For example: is polluting, should be treated.
(c) Relational Process: to state what is or should be. For
example: doesn’t seem to have been, is.
Table: 2.2 Example of Hortatory Exposition Text
Generic Structure Example Note
Thesis Now we can live in the global
era. We can find anything
from different concerns of the
world easily. Through the
internet, we can get any
information about anything in
the world easily.
The thesis is using the present
tense (modal verb: can)
Argument 1 The Internet is very useful for
junior highs school students,
as long as the students can use
this sophisticated media
properly On the internet, we
a. Nominal sentence:
is/are
Example: it is very useful
for us.
b. Verbal sentence: find,
like, use, etc.
Example: we can find any
material.
Argument 2 There are many different
kinds of people in the market;
different characteristics,
different professions, different
ages, different sexes, different
purposes, etc. We can see
these all on the internet too.
On the internet, there are
many kinds of learning
materials which help students
learn better. On the other hand,
good purposes may lead the
students into the wrong places
if they are not very careful
The argument is using the
present tense.
a. Nominal sentence:
is/are
enough with them.
Recommendation To be effective in using the
internet, Junior High School
students need to be
supervised when using this
sophisticated media.
The recommendation is using
suggestion sentences. Verb:
should to, must be, need to,
4. Picture Word Inductive Model
a. Definition of Picture Word Inductive Model
According to Calhoun (1999: 21), Picture Word Inductive Model (PWIM) is an inquiry-oriented inductive model language arts strategy that uses pictures containing familiar objects and actions to lead students in acquiring words to improve their vocabulary mastery, to discover phonetic and structural principles, and to observe and analyze text in their study of reading and writing. PWIM contains writing techniques such as brainstorming, listing, clustering, and free-writing. Teachers apply those techniques in a sequence ste
words are written surrounding the pictures, the chart can be used as an illustrated dictionary to facilitate students’ writing process.
According to Joyce, Weil, & Calhoun (2009; 148), Picture Word Inductive Model have arranged based on the research of
students’ ability of reading and writing. Picture Word Inductive Model is appropriate for the cognitive and metacognitive curriculum. This model has been implemented approximately 20 years ago, and the application of this model could improve the student's ability in reading and writing, especially to improve their vocabulary.
According to Huda (2016: 78) inductive model based on
the beginning assumption that every human is the nature concept.
They always do the conceptualization every time. The human can
distinguish the object, cases, and emotion. The teacher should take
this opportunity to design the effective environment
teaching-learning. The teacher can give the students to improve their
Figure 2.1: The Steps of Thinking Inductively by Huda (2016)
According to Yuniarsih & Saun (2014: 4), the Picture Word Inductive Model contains a familiar object, actions, and scenes, the students can hear and see the words spelled correctly and directly, then they will analyze word by word, for example: phonetic, synonym, antonym or how to spell it. The students also can read the vocabulary, so it can make the students understand and make it easier to memorize the vocabulary.
In conclusion, PWIM, as an integrated writing technique is essential for the ongoing English teaching and learning process, since it enables students to improve their vocabulary and to explore their writing ability. Picture Word Inductive Model (PWIM) can improve the students from passive learning into active learning by
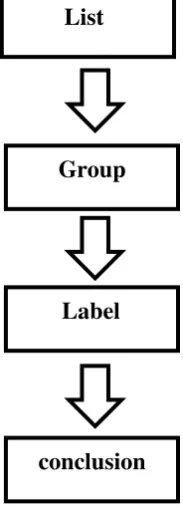
List
Group
Label
applying the provided writing activities, and help students write up paragraphs step by step by planning, drafting, revising, and publishing.
b. Advantages and Disadvantages of Picture Word Inductive Model
There are some advantages and disadvantages based on Calhoun (1999: 55-65). The first advantages of PWIM is an effective to use in all level, low level-middle-and advanced level. Then, PWIM emphasizes phonics, grammar, mechanics, and usage of Standard English. In another hand, the picture provides concrete referents for the learning of new words, phrases, and sentences. Furthermore, the students feel a part of a classroom community and can participate in class activities. Then, Supporting all learning opportunities.
In another hand, the Picture Word Inductive Model has disadvantages. The first, this model needs a teacher who competence in questioning, so this model can be a success if the teacher can explore the illustration to the students. The teacher can divide the students to be a heterogeneous group, so the teacher will not difficult to set the activities of teaching-learning. Then, the teacher has to guide the students in the teaching-learning, so the students can understand more.
The teacher has to prepare the material and the picture in teaching PWIM. The teacher has to explore the new issues to
adapted the students’ generation. The teacher has to get off the best
situation to illustrate the issue form the picture, This model is depending on the picture, new issues, an illustration from the teacher. The teacher can prepare well the media before teaching the students in the classroom.
c. The Benefits of Picture Word Inductive Model
In implementing the Picture Word Inductive Model (PWIM), the students have to be supported to read, explore the vocabulary, analyze the phonetic, and understanding about the content of the texts. According to Huda (2016: 89), there some benefits of Picture Word Inductive Model, as follows:
2) The students are able to learn about the structure of words and sentences.
3) The students are able to write the title, sentences, and paragraph.
4) The result of the Picture Word Inductive Model is understanding the correlation between writing and reading. 5) The students are able to explore their ability in phonetic and
syntax.
6) The students are able to explore their ability to express their ideas in writing.
7) Picture Word Inductive Model can improve reading nonfiction text.
8) The students can develop their ability to cooperation with another person in reading or writing.
d. The Steps of Implementing Picture Word Inductive Model There are steps of implementing the Picture Word Inductive Model (PWIM) based on Calhoun (1999: 67-80), as follows:
1) The teacher selects the picture
2) The students have to identify and label what they see in the pictures
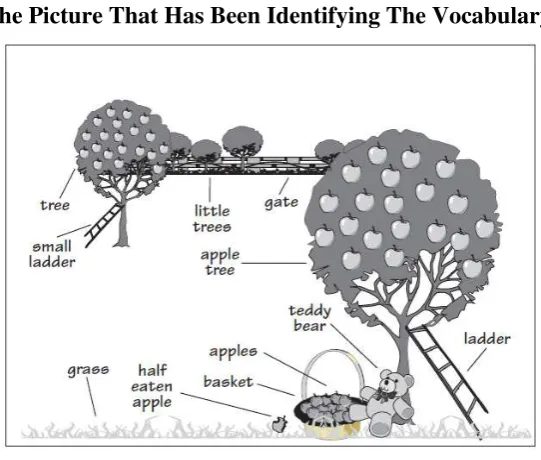
The next steps include a clustering technique which the students are asked to draw a line from an identified object in the picture. The words or phrases are put down in the paper or board in a pattern which connects to a keyword in each picture.
Figure 2.2
The Picture That Has Been Identifying The Vocabulary
Source: Calhoun (1999: 3)
3) Read and review the picture word chart
considering the grammatical rules. It helps students to form a good sequenced text based on the list of ideas.
4) Lead students into creating a title for the picture word chart Teachers ask students to think about information on the pictures and ask them about what they want to say about the pictures. The students can look at the title of the textbook as an example of how to arrange a good title. Generate all the collected words or phrase into sentences, and arrange sentences into paragraphs The technique which is used in this step is free-writing. In this technique, the students generate words, sentences, and paragraphs to express their ideas. The words and phrases that have been written in the previous step aim to help students to write easily and make them being comfortable in the writing process.
5) Read and review the sentences and paragraphs
The students checked their writing whether it has been qualified as a good, text or not. The reviewing process includes checking the purpose of writing and the generic structure of the
texts. Teachers can present some students’ final drafts to give
e. The Use of Picture Word Inductive Model in Writing Hortatory Exposition Text
In practice teaching-learning, the teacher is using a picture. Picture Word Inductive Model is effective to use because according to Wright (1989; 2-3), the picture is verbal language that only a part of the way to get meaning from context. The students are not only hearing, reading but also remembering what they having seen. The picture is not just an aspect of the method but through their representation of places, objects, and people they are an essential part of the overall experiences. Especially, the picture contributes to interest and motivation; a sense of the context of the language; a specific reference point or stimulus. There are some reasons to use a picture in English language teaching, as follow: easy to prepare; easy to organize; interesting; meaningful and authentic; sufficient amount of language.
identify the word, phrases, sentences based on the picture. The students write down many words after they observe the picture.
After brainstorming ideas, the students can begin writing the sentences. The students can use the word that has been identifying from the picture. The students are not difficult to arrange the sentences. They can write the simple sentences using the vocabulary from the picture to collect their ideas.
After completing the draft, the students are guided to the revising stage. Picture Word Inductive Model provides an opportunity for conducting a task in groups, so the students have a collaborate with their friends to give a comment and suggestion, then revise their writing. The students must be careful to read the draft again. The activity focuses on checking whether the social purpose of the text has been delivered or not and whether the generic structure is corrected or not.
PWIM also provides activities to spell words correctly and to use correct punctuation and other mechanical aspects such as commas and capital letter. After checking all the details of the draft, the students can publish their hortatory exposition text. Their draft may be different from the first plan because it has been revised. In short, PWIM has the strength to keep the students engage in the writing process of hortatory exposition text and it deals with the aspect of writing ability such as generating ideas, an organization of the text, vocabulary, language use, and mechanics.
B. Review of Previous Studies
In this chapter, the writer will explain the previous studies. The writer takes a review of related literature from the other research. The first research was done by Apiah (2016) in her graduating paper entitled “The Effectiveness of Picture Word Inductive Model (PWIM) on Students’
Ability in Writing Recount Text (A Quasi-Experimental Research at the
Eighth Grade Students of SMPN Tangerang Selatan in Academic Year
of 2015/2016)”. The objective of this research was to know the empirical evidence concerning whether Picture Inductive Word (PWIM) strategy is
gives a score on the students’ writing pre-test and post-test. The result of the calculation showed that students taught by using the PWIM strategy have higher achievement than those who were taught without PWIM.
The third research was done by Louise (2007) in her annual GRASP Symposium entitled, “The Picture Word Inductive Model and
Vocabulary Acquisition”. The purpose of this quasi-experimental research
was to determine if students’ vocabulary acquisition is enhanced with the
picture word inductive model (PWIM), a research-based method of vocabulary instruction. During instruction with the PWIM, students were shown a picture and were asked to identify items in the picture, eliciting
words from the children’s listening and speaking vocabularies. This
process essentially created a picture-word dictionary which the students could employ to connect words with corresponding pictures. The results indicated that statistically significant differences were achieved between the control and experimental group participants on the final assessment.
The last research was done by Anne (2010) in her graduating paper entitled, “The Picture Word Inductive Model: An Effective Model for
CHAPTER III
IMPLEMENTATION OF RESEARCH
A.Procedures of the Research in Cycle I
In this research, the researcher conducted the research into two-cycle: cycle I, and cycle II. The researcher collaboration with the English teacher who taught in XI IPA 1.The researcher use picture to explore the vocabulary that appropriates with the topic, which it can improve student understanding of the hortatory exposition text. The procedure as below:
1. Planning
In this step, the researcher plans the following below:
a. Preparing the picture (poster) that planned appropriately with the material b. Preparing the teaching material of cycle I
c. Make lesson plan of the cycle I
d. Preparing field note observation of cycle I e. Preparing students attendance list
f. Preparing pre-test and post-test of the cycle I
2. Action
In this section, the learning process is led by the teacher. a. The teacher gives a pre-test.
b. The teacher explains the generic structure of hortatory exposition text and gives a stimulant to the students about the hortatory text.
c. The teacher selects the picture that appropriates to the topic.
d. Giving some examples of hortatory exposition text that are represented to the picture.
e. The teacher asking the students to write a draft about the vocabulary of the picture that has been showed by the teacher. Example: “What is the
activity in the picture?”
f. The students have to read (pronunciation) and review the picture word chart.
g. The teacher leads students into creating a title for the picture word chart. h. The teacher leads the students to find out the argument based on the
picture.
i. The students have to read and review the sentences and paragraphs.
j. Made some sentences related to the picture that repairs to their friends (cooperation in the group).
3. Observation
The researcher observed students and teacher activity by using field note.
4. Reflection
a. The researcher evaluated the activities that have been done.
b. The classroom teacher and the researcher discussed to make a reflection about what should they do to repair the problems.
c. Analyzing the data from the observation checklist and test of the cycle I.
B.Procedures of the Research in Cycle II
The second cycle does base on the result of reflection from the first cycle. If the result from observation shows that the quality of the students was still low, it is needed for another action in order to make improvement of the quality for the next cycle. The topic is same with cycle I. The procedures are as follow:
1. Planning
a. The researcher identifies the problem and makes the solution to the problems
b. Preparing picture of cycle II c. Preparing material
d. Designing lesson plan of cycle II
g. Preparing post-test of cycle II. 2. Action
In this section the learning process is led by the teacher, as follow: a. The teacher asked students about the generic structure of hortatory
exposition text that have already discussed at the previous meeting. b. Explain again about the generic structure of hortatory exposition text that
has already discussed at the previous meeting.
c. Give some examples of hortatory exposition text based on the picture that has been selected by the teacher.
d. The teacher checking the students’ mastering vocabulary. e. The students have to read and review the picture word chart. f. The students divided into some groups to identify the picture.
g. Each group is a different picture, the students have to identify the picture and write down the word chart.
h. The teacher leads the students to find out the argument based on the picture.
i.The students have to write sentences that appropriate with their title to arranged the paragraph.
j.The sentence must be grammatically correct and accurately depict what is happening in the picture.
l. At the end of the lesson, giving post-test.
m.The students have to read and review the sentences and paragraphs. n. Made some sentences related to the picture that repairs to their friends
(cooperation in the group).
o. Giving correction and feedback to the student’s answer. p. At the end of the lesson, giving post-test.
3. Observation
The researcher observes students and teacher activity by using field note.
4. Reflection
a. The researcher evaluates the activities that have been done.
b. The classroom teacher and the researcher discuss to make a reflection what will they do to repair the problems.
c. Analyzing the data from the observation checklist and test of cycle II. d. Next cycle III will happen when the cycle II is fall.
C.The Minimum Passing Grade