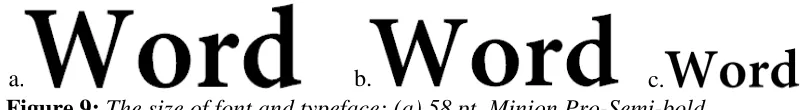A STYLISTIC ANALYSIS ON LINGUISTIC FEATURES
OF NEWS TITLES IN
THE JAKARTA POST
ON AUGUST 19, 2007 ISSUE
AN UNDERGRADUATE THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree ofSarjana Sastra
in English Letters
By
NANI TATO KAMBA
Student Number: 034214114
ENGLISH LETTERS STUDY PROGRAMME DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH LETTERS
FACULTY OF LETTERS SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
A STYLISTIC ANALYSIS ON LINGUISTIC FEATURES
OF NEWS TITLES IN
THE JAKARTA POST
ON AUGUST 19, 2007 ISSUE
AN UNDERGRADUATE THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree ofSarjana Sastra
in English Letters
By
NANI TATO KAMBA
Student Number: 034214114
ENGLISH LETTERS STUDY PROGRAMME DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH LETTERS
FACULTY OF LETTERS SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
ASarjana SastraUndergraduate Thesis
A STYLISTIC ANALYSIS ON LINGUISTIC FEATURES
OF NEWS TITLES IN
THE JAKARTA POST
ON AUGUST 19, 2007 ISSUE
By
NANI TATO KAMBA
Student Number: 034214114
Approved by
Dr. Fr. B. Alip, M.Pd., M.A. November 24, 2007
Advisor
Adventina Putranti, S.S., M. Hum November 24, 2007
Co-Advisor
ASarjana SastraUndergraduate Thesis
A STYLISTIC ANALYSIS ON LINGUISTIC FEATURES
OF NEWS TITLES IN
THE JAKARTA POST
ON AUGUST 19, 2007 ISSUE
By
NANI TATO KAMBA
Student Number: 034214114
Defended before the Board of Examiners on November , 2007
and Declared Acceptable
BOARD EXAMINERS
Name Signature
Chairman : Dr. Fr. B. Alip, M.Pd., M.A. Secretary : Drs. Hirmawan Wijanarka, M.Hum Member : Dr. Fr. B. Alip, M.Pd., M.A. Member : Adventina Putranti, S.S., M. Hum Member : J. Harris Hermansyah S, S.S., M.Hum
Yogyakarta, November 24, 2007 Faculty of Letters
Sanata Dharma University Dean
This thesis is dedicated to:
Jesus, my Lord, my Savior, my Father, and my Friend
My beloved parents
My beloved sister and brothers
My friends
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
In finishing this thesis, the writer should pass many processes and she realizes that they could not be passed if there were no help from others. How glad she is when this thesis was finished and she expresses her gratitude to all people that directly or indirectly have given a hand during her study in college for four and a half year even in finishing her undergraduate thesis. She would like to thank:
1. Her adoring Father and friend, Jesus Christ, who allows her to experience many
difficult processes in difficult time. However, in those processes and time, He never
leaves her alone. He always walks with her and controls her life. She thanks for His
blessing and all problems and joy that He allows to happen in her life.
2. Her advisor, Dr. Fr. B. Alip, M. Pd., M.A., for his time in guiding her in all
processes of finishing this thesis, for his advice in making this thesis better and
researchable.
3. Her co-advisor, Miss. Adventina Putranti, S.S., M. Hum., for giving her some
suggestions in this thesis.
4. Mr.Tatang Iskarna, S.S., M.Hum., for lending her some reference books.
5. Her beloved parents (Yohanis Tato KambaandHasyah Djabbar), sister (Neny),
and brothers (Rano and Andrew), for their love, prayers, care, and support that
make her strong to face many challenges and problems, and motivate her to finish
her study.
6. Her relatives in Yogyakarta, KakIta, MasIwan,Chandra,David, andYehuda, for
all support and prayers during her study in Yogyakarta.
7. Her little angel, for all supports and prayers that always comes in time and for
coloring her life. “You are the best!”
8. Ratnaand family, for their support, prayers, care, and kindness in giving a place to
take shelter for several months in the process of finishing this thesis.
9. Her friends in Gereja KIBAID Yogyakarta and Mr. Yerahmel B, S.Th, for their
prayers, support, and advice in every time.
10. Her friendSinta, for being her best friend for nearly 14 years.
11. Her friends in the 2003 English Letters especially Sastra Mungil Community.
Thanks to Ketut, Leni, Inop, Mey, Maya, Ike, Sondang, Dewi, Afrill, Yuni,
Agnes, Intan, Cisil, Cita, Clara, Wahyu, Abit, Tio, Demus, Muji, Daud, Mando,
Dean, Yacko,andBigar
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE... i
APPROVAL PAGE... ii
ACCEPTANCE PAGE... iii
MOTTO PAGE... iv
DEDICATION PAGE... v
ACKNOWLEDMENTS... vi
TABLE OF CONTENTS... vii
ABSTRACT... ix
ABSTRAK... x
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION... 1
A. Background of the Study ... 1
B. Problem Formulation ... 4
C. Objectives of the Study... 5
D. Research Benefit... 5
E. Definition of Terms ... 6
CHAPTER II: THEORITICAL REVIEW... 9
A. Review of Related Theories ... 9
1. The News Title ... 9
a. The Function of News Title ... 9
b. The Characteristics of News Title ... 10
2. Linguistic Features of News Titles... 13
a. Graphology ... 13
b. Phonology ... 20
c. Grammar ... 21
d. Lexis ... 26
B. Theoretical Framework ... 29
CHAPTER III: METHODOLOGY... 30
A. Object of the Study... 30
B. Approach of the Study... 31
C. Method of the Study ... 31
CHAPTER IV: ANALYSIS... 34
A. The Linguistic Features and the Most Common Linguistic Features in News Titles... 34
1. Graphology ... 35
2. Phonology... 49
3. Grammar... 54
4. Lexis ... 60
B. The Effects of Linguistic Features to the Texts ... 65
3. Grammar... 69
4. Lexis ... 70
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION... 72
BIBLIOGRAPHY... 74
APENDICES... 76
Appendix 1... 76
Appendix 2... 78
Appendix 3... 80
Appendix 4... 81
ABSTRACT
NANI TATO KAMBA. A Stylistic Analysis on Linguistic Features of News Titles inThe Jakarta Poston August 19, 2007 Issue.Yogyakarta: Department of English Letters, Faculty of Letters, Sanata Dharma University 2007.
There are many languages based on stylistic features. The most influential language is news media language. It is a language that is used in mass media. Newspaper is one of mass media to deliver news. Before reading the news the readers scan the title to choose which news that is going to be read. This title has a big role in giving an idea about the news and it has its own linguistic features that is different from literary text titles. The writer chose the news titles inThe Jakarta Post, the famous international newspaper in Indonesia,issued on August 19, 2007
to be analyzed. Analyzing these linguistic features in the news title can improve our knowledge about the news media language, its style, and help us predict the effect to the text.
In this thesis the linguistic features in news titles were analyzed. There are two problems that were formulated by the writer. First is to find out the linguistic features and the most common linguistic features of news titles in The Jakarta Poston August 19, 2007 issue, second is to find out the effects of these linguistic features to the texts.
In the analysis, the approach that was used is stylistics which is the most appropriate approach because it studies linguistic features. The writer did several steps in analyzing the data. First, the data was collected from The Jakarta Post
issued on August 19, 2007 and classified based on its news column. Second, the writer found out the linguistic features that news titles have based on their graphological features, phonological features, grammatical features, and lexical features. After that, the writer counted the total number of news titles having those features to determine the most common features that occur in news titles. Lastly, the writer found out the effects that the linguistic features have when they are applied in the news titles.
ABSTRAK
NANI TATO KAMBA. A Stylistic Analysis on Linguistic Features of News Titles inThe Jakarta Poston August 19, 2007 Issue.Yogyakarta: Jurusan Sastra Inggris, Fakultas Sastra, Universitas Sanata Dharma, 2007.
Berdasarkan stilistika, ada beberapa macam bahasa. Yang paling berpengaruh adalah bahasa media berita. Bahasa ini adalah bahasa yang digunakan dalam media massa. Koran adalah salah satu media massa yang menyebarkan berita. Sebelum membaca isi berita, pembaca membaca judul berita secara sepintas untuk memilih berita mana yang akan dibaca. Judul berita ini mempunyai peranan besar dalam memberikan gagasan tentang isi berita dan judul berita ini mempunyai karakteristik bahasa tersendiri yang berbeda dengan judul-judul karya sastra. Penulis memilih judul-judul-judul-judul berita di koran The Jakarta Post, koran internasional yang terkenal di Indonesia, yang diterbitkan pada tanggal 19 Agustus 2007 untuk dianalisa. Menganalisa karakteristik bahasa dalam judul berita dapat menambah pengetahuan kita tentang bahasa media berita, gaya penulisannya, dan membantu kita untuk memprediksi pengaruhnya pada teks.
Karakteristik bahasa dianalisis dalam skripsi ini. Ada dua masalah yang diteliti oleh penulis. Pertama adalah menentukan karakteristik bahasa apa saja yang dimiliki judul berita The Jakarta Post yang diterbitkan pada tanggal 19 Agustus 2007dan menentukan karakteristik bahasa yang paling banyak digunakan oleh judul berita, yang kedua adalah menentukan pengaruh yang ditimbulkan karakteristik bahasa itu pada teks.
Dalam analisis ini, pendekatan yang digunakan adalah stilistika yang merupakan pendekatan yang paling tepat karena stilistika mempelajari karakteristik bahasa. Penulis melakukan beberapa tahap dalam menganalisa data. Pertama, data dikumpulkan dari The Jakarta Post yang diterbitkan pada tanggal
19 Agustus 2007 dan diklasifikasikan berdasarkan kolom beritanya. Kedua, penulis menentukan karakteristik bahasa yang dimiliki judul berita berdasarkan karakteristik grafika, fonologi, gramatikal, dan leksisnya. Setelah itu, penulis menghitung jumlah judul berita yang memiliki krakteristik-karakteristik tersebut untuk menentukan karakteristik bahasa yang paling banyak muncul dalam judul berita. Terakhir, penulis menentukan pengaruh karakteristik bahasa tersebut saat digunakan dalam judul berita.
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Study
In this world, we live with other people and we need to communicate with them. To communicate with other people, we use language. Language cannot be separated from human life.
Based on stylistic features, there are many kinds of language variety. Related to occupational groups, there are religious language, scientific language, news media language, etc. These languages are “taken up as we begin to work and put down as we end it” (Crystal, 1994: 370). Moreover, those languages have their own linguistic features that make them lexically and grammatically different.
News media language is the most influential language for people because what is written in, for example; newspapers, is the most believable language for people although the use of language is sometimes wrong or it does not follow the rule of language. In Dari Katabelece sampai Kakus published by Penerbit Buku Kompas, it is said that “idioms, new words, and the utterance grow and come from mass media” (Nuradjiet al, 2003: xiv, translated by the writer). Also, “mass media is a communication media that is very influential in the development of language” (2003: xxi).
a conversation on one issue which involves at least two persons, it is called as a direct communication. When we communicate using media such as newspaper, television, letter which deliver messages to the receivers, we use indirect communication.
One of examples of indirect communication tool is the newspaper. Every day many people read a newspaper. Newspapers provide not only news but also comments, analysis, advertisements, and entertainment.
The term newspaper suggests that the content of newspaper will be primarily devoted to the news of the day, and some analysis and comment on this news. Newspapers however contain a range of items: news, comment, and analysis, advertising, entertainment. (Reah, 2002: 2)
Most nations have at least one newspaper that circulates throughout the whole country: in Indonesia, a national newspaper like Kompas, as contrasted with a local newspaperserving a city or region, likeKedaulatan Rakyat. There is also aninternational newspaper, likeThe Jakarta Post.
newspaper provides not only news but also comments, analysis, advertisements, and entertainment.
Reah defines newspapers as “ephemeral text, that is, they are intended only for the day they are delivering news” (Reah, 2002: 13), so it can be said that a newspaper is a medium to spread news for a day. “News is information of recent events that are of interest to a sufficiently large group, or that may affect the lives of sufficiency large group” (Reah, 2002: 4). News or information provides the reader an enormous amount of information in very short sentences.
In addition, people select which news that is going to be read by reading the news title first. Not all of the news in a newspaper are read by the readers. They read the news that makes them curious and they search the news that they want to know by reading the title first. From these facts the writer can make a preliminary assumption that the linguistic features of news title have a big influence for the quality of the news.
A news title has its own linguistic features that make it special. The linguistic features that are meant here are divided into four main parts namely, graphological, phonological, grammatical, and lexical features. These features are applied to the news titles to give several effects.
reader. This practice applies commercial trick that cannot be approved. The reader will become accustomed to read news titles only and it will not be effective (Rivers, Peterson, and Jensen, 2004: 329-330).
However, a news title has a big effect to the quality of the news. A good news title will be easily remembered by the reader and can attract people’s attention. For example, there are some columns in newspapers that sometimes people never read because they are not interested in those topics. Nonetheless, actually, the way the newspaperman or newspaperwoman forms the title can persuade people to read the news in those columns. From that fact, it is interesting and challenging to observe the linguistic features of news’s title which make the news titles special.
In this study, the writer uses The Jakarta Post for the source of the data.
The Jakarta Post is the only popular international newspaper from Indonesia (http://en.wikipedia.org, accessed on February 23, 2007). The Jakarta Post has gained many readers time to time. Moreover, it is easy to find this newspaper because it is in every where, like at the bookshop, circle K, newspapers distributors, etc.
B. Problem Formulation
In this research the writer has formulated two problems, they are: 1. What are the linguistic features and the most common linguistic features of
C. Objectives of the Study
There are two objectives of study in this paper. First is to find out the linguistic features of news titles and the most common linguistic features of news titles inThe Jakarta Poston August 19, 2007 issue. Based on the data, the writer will find out some of linguistic features that are used in news titles and there will be some levels of the linguistic features that are found in this data based on their quantity. The linguistic features will give some effects to the news titles. Therefore, the last objective study in this paper is to find out the effects of these features to the texts.
D. Research Benefit
E. Definition of Terms
There are five key terms that will be used in this analysis to give the reader ideas about what are going to be analyzed and to avoid misunderstanding on certain terms, they are:
1. Stylistics is “the study of varieties of language whose properties position that language in context” (http://en.wikipedia.org, accessed on February 23, 2007).
For example, the language of advertising, politics, religion, individual authors, etc., or the language of a period in time, all belong in a particular situation. In other words, they all have ‘place’.
Barry in his book, An Introduction to Literary and Cultural Theory, definesstylistics as “a critical approach which uses the methods and findings of the science of language in the analysis of literary texts” (2002: 203).
The aim of using stylistic to analyze the linguistic feature is to show how the technical linguistic features of the news titles, such as grammatical structure, contribute to overall meanings and effects. Therefore, stylistic can be defined as the study of language in defining linguistic feature of particular text in context and the effect of particular linguistic features to the text.
purpose or function of a piece of writing that distinguishes one type of writing from one another” (Nunan, 1999: 280).
Linguistic features are applied in particular text to give the text its own characteristics that can distinguish it from another text. It can be in its typography, grammar, sound, etc.
3. In Webster dictionary title is defined as “the name of poem, essay, chapter book, picture, statue, piece of music, etc. Reah defines news as “information of recent events that are of interest to a sufficiently large group, or that may affect the lives of sufficiency large group” (Reah, 2002: 4).
Therefore, news title is the name of information of recent events that are of interest to a sufficiently large group, or that may affect the lives of sufficiency large group. Moreover, the term ‘news title’ refers to the words in the leading position of news that will be read first by the reader because it is attractive in its form.
4. Issueis “all copies of the day’s paper and its edition” (Keeble, 2001: 248).In this study the writer chose the news titles in Sundayissueas the data.
“A daily newspaper is issued every day, often with the exception of Sundays and some national holidays. Saturday, and where they exist Sunday, editions of daily newspapers tend to be larger, include more specialized sections and advertising inserts, and cost more. Typically, the vast majority of these newspapers' reporters work Monday to Friday, so the Sunday and Monday editions largely depend on content done in advance or content that is syndicated.” (http://en.wikipedia.org, accessed on February 23, 2007).
5. There are several meanings of the wordeffect in Verdonk’s books,Stylistics;
(2002: 6), and effect is “interpretation and intention of the reader toward particular verbal features” (2002: 9)
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL REVIEW
This chapter covers two parts; review of related theories and theoretical framework. The first part contains the review of some theories that will be applied in analyzing the object of study. The last or the second part is the theoretical framework that is concerning with the contribution of the theories in answering the problems of the study and the way they are applied in answering the problems in this study.
A. Review of Related Theories
1. The News Title
A news title is the name or the head of news. Most of news titles are written in the form of sentence. It is different from novels whose titles commonly are written in the form of phrases. These news titles have a job to advertise their stories or news.
a. The Functions of News Title
fact; if the story is tragic, the news title should be tragic in tone (Mulligan, 1943: 232).
b. The Characteristics of News Title
The news titles have a big role in attracting the reader to read the news even to give the reader an idea about the news. They are different from other literary text titles like poems or novels because they are written in different functions from literary text. The titles in literary text are generally written for the beauty of the work so that phrases are commonly used whereas the news titles written to bring main points of news and advertise it. Here are some characteristics of news titles as written in Experiences in Journalism (Mulligan, 1943: 232-244):
i. Using short and sharp words
As the news titles should give a vivid summary of the facts in its story so short and sharp words are used as much as possible in preference to longer synonyms.
e.g. Police vow to speed up probe into Munir’smurder
The wordmurderhas two synonyms namely, assassination and kill. However, the wordmurder is used because it is shorter than the wordassignationand it is a common word and commonly used.
ii. Articles are commonly omitted
e.g. 1) Sutiyoso talks trash at recycling plant launch
The complete sentence: Sutiyoso talks trash attherecycling plant launch 2) Turkish government condemns army threat on poll dispute
The complete sentence: Turkish government condemns anarmy threat on poll dispute
iii. Verbs are essential
The news titles that do not contain verbs, either expressed or clearly understood, are really not heads at all but mere labels.Verbs are used to make a complete statement.
e.g. Japan’s PMbeginsThree-day visit (sentence form with verbbegin) PM Abe’s trust mission (noun phrase form without verb)
iv. Using present tense for past event
The use of historic present or the present tense used for referring past event is commonly used in news titles and it is used as vivid as possible.
e.g. Donald takes one-shot lead into last round of Byron Nelson (The title is in Present Tense)
England’s Luke Donald maintained his one-shot lead in the 6.3 million-dollar Byron Nelson Championship on Saturday with a three-under 67 in the third round. (The first sentence in the first paragraph that is represented directly in the title is in Past Tense)
(The Jakarta Post,April 30, 2007) (The Jakarta Post,April 30, 2007)
v. Using active voice than passive voice
The active voice in a news title unless the passive is necessary to get the main idea of news into the opening words of the news title. However, when it is necessary to use the passive voice, to be is omitted before verb.
e.g. Fergie hails his ‘have –a-go’’ heroes (active voice) Bike courier robbed in North Jakarta (passive voice)
(The Jakarta Post,April 30, 2007) vi. Using positive statements
A positive statement is more emphatic than a negative statement which is also weak.
e.g.Senior debate postponedis better than
Senior debate will not be held Friday.
vii. Using familiar or common abbreviation or acronyms
The abbreviations or acronyms that are used in the news titles are the common abbreviations that are generally known by all readers so that the readers will understand them at once when read them.
e.g. JonesJr.beats Hanshaw in 12-round decision (Jr. forJunior)
U.S.defies pressure to expand Blair’s Mideast mandate (U.S. forUnited State) (The Jakarta Post,July 16, 2007) viii. Usingflush-left head
e.g.
ix. Often require punctuation
Punctuation sometimes used to replace certain words or to give a stress to the title. For example, to separate two independent statements, a semicolon or a dash is used.
2. Linguistic Features of News Title
Linguistic features are applied in particular text to give the text its own characteristics that can distinguish it from another text. It can be in its graphology, phonology, grammar, and lexis.
a. Graphology
In A Dictionary of Stylistics, graphology is meant as the study of a grapheme, the smallest distinctive unit in the writing system of a language. The graphological features are size of print and capitalization in newspaper and advertising lay-outs; and different typefaces (Wales, 2001: 182-183).
i. Typography
Typography is “system of letters” (Woods, 1987: 98). Marking copy with type specifications should cover a number of elements (Woods, 1987: 103-104):
Poor sanitation causes return of diarrhea outbreak
Poor sanitation causes return of
diarrhea outbreak
Poor sanitation causes return of diarrhea outbreak
(a) (b) (c)
1) Type style or styles to be used for specific components of the copy, including body type, major and secondary headline type, subheads or running headlines, and quoted material.
2) Type point sizes for each of these components. 3) Column width of copy, headlines, or quoted material.
4) Leading or spacing between lines of text, paragraphs, or headlines and paragraphs.
5) Indentations of text, headlines, and subheadlines.
Sometimes it is confusing when we want to select the right typeface for a job, because literally thousands of styles and families of type are available. They are broken down into four general categories: roman (serif), sans serif, script, and ultrabold sans serif (Woods, 1987: 108).
These typefaces are only the general categories. There are still many typefaces which are used for several importances. However, there are many typefaces that have too many indentation that make them difficult to read and with their 3-demension style. These typefaces are usually used for brochure and advertisement.
a.
History book still not closed on Fujimori
b.
History book still not closed on Fujimori
c.
History book still not closed on Fujimori
d.History book still not closed on Fujimori
Figure 2:Sample of four categories of type: (a) roman / serif; (b) sans serif; (c) script; (d) ultrabold sans serif.
Figure 3: Two kinds of typeface in 24 pt: (a) Inertia BRK; (b) Unicode 0024
In making news titles, there many typefaces that are provided and they should be chose to make the news titles more highlighted than the body. In
Printing and Production for Promotionals, it is said that “heads should be of similar or heavier weights than the body type, using boldface or even just a larger size version of the body type” (Woods, 1987: 108). The bigger the sizes of font the easier to read it. Therefore, the size of font shows the importance of the news. Because the big size of font that is used in news titles can be more attractive than the smaller one (see figure 4 that has been minimized for 41.4 %).
ii. Punctuation
“Punctuation is the action or system of dividing writing into sentences, phrases, etc by using special marks” (Hornby, 1995: 941). InPunctuation written Figure 4: The news titles in various size and typeface: (a) Optima-Bold, 14 pt; (b) Minion Bold, 58 pt; (c) Minion Bold, 30 pt; (d) Minion Pro-Semi-Bold, 36 pt
a.
b.
by G.V. Carey (1957: vi), there are two main principles in use punctuation. First, the punctuation should serve the eye before the tongue and the ear, i.e. that it is concerned more with reading silently than with reading aloud. Therefore the best punctuation is based on the structure, or syntax, of the sentence, not on the need to pause for breath; the pause for effect is a different matter, of which punctuation must of course take account. The second principle is: subject to the demands of lucidity, the fewer stops the better.
In writing there are many punctuation marks, such as full stop (.), question mark (?), comma (,), exclamation mark (!), quotation marks or inverted commas (“ “ or ‘ ’), semicolon (;), colon (:), dash (—) , hyphen (-), apostrophe (`), and brackets [( )].
Here is the usage of punctuation marks based on the book Write Well
written by Barli Bram (1995: 93-103). 1. Full Stop or Period (.)
a. It is often used to mark the end of initials or abbreviations; sometimes it is optional, as in:
1) JonesJr.beats Hanshaw in 12-round decision 2) Asian financial crisis helpedU.S.economic growth 2. Question Mark (?)
a. As its name suggests this function mainly to signal that a message or an utterance is in a direct question form.
b. Although rarely, it can also be used to show doubt, to show something we are unsure about, as in:
1) Open space? Jakarta? Look inside and you’ll see (The Jakarta Post, April 30, 2007)
3. Comma (,)
a. We use commas to separate series of items from the same category, such asnouns,phrases, andclauses, as in:
1) BlackBerry 8707 v: Efficient, functional and friendly (The Jakarta Post, August 20, 2007)
b. To add non-defining phrase or clause or comment clause to a sentence, we need the comma(s) too. See the below usage:
1) More TNT, detonators found after bomb blast 2) Bosowa, Chinese firm star power project
(The Jakarta Post, August 20, 2007) 4. Exclamation Mark (!)
This punctuation is useful to show strong emphasis, as in: 1) How delicious the soup is!
2) Do not cheat!
5. Quotation Marks or Inverted Commas (“ “ or ‘ ’)
a. As the terms implies, this kind of punctuation functions to mark quotation or others’ speech. The single mark pair (‘ ‘) is more common in British English. The combination of the two pairs is also possible. Here are a number of sample uses:
1) “I don’t care,” he shouted angrily.
2) ‘If necessary,’ the editors stated, ‘we will edit your article.’
b. In addition, quotation marks are used to give more attention to a certain word or term. They can also be used to show that a word in a certain context has a particular meaning, a meaning that is different from the common one (The single-quotation mark pair is the more common). 1) ‘Cooper’ or ‘Copper’? The choice is yours (The Jakarta Post, April
29, 2007). 6. Colon (:)
a. We use this punctuation to introduce along list or a series or things. The colon is often preceded by the phrase in the following, as follows, or as in, to mention three examples, as in:
1) The prefix in- meaning not can be found in the following: inexpensive, intolerable, and incurable.
7. Dash (—)
a. The function of the dash is to make a certain piece of information more highlighted or more dramatic, as in:
1) Do not forget — once again do not forget — to post the letter today 2) Now she wants to be free — to live her own life.
b. A dash is also used to introduce additional details in order to make a previous piece of information clearer or more vivid. In this case, a dash is similar tothat is,vizornamely.
2) Indonesia lies between two oceans — the Pacific and the Indian Oceans
8. Hyphen (-)
a. The function of hyphen is to connect words in order to create or form words or new phrases.
1) TNI troops keep the place in war-torn Lebanon (The Jakarta Post, August 20, 2007)
9. Apostrophe (‘)
a. In formal writing and in written dialogue, the apostrophe functions to indicate that one, or more than one, letter has been deleted. Quite often, the apostrophe represents the omitted letter. Since most of auxiliary verbs can be shortened, we use the apostrophe to realize the contracted auxiliaries which are usually combined with personal pronouns, as in: 1) How’s life?
2) She’s sent the message.
b. The apostrophe can replace the letteroinnotto form a contraction, as in: 1) “No, it isn’t,” answered Ouda shortly.
2) Don’t stand so close to me! c. It is also used to mark possesion.
10. Ampersand
Ampersand is the sign (&) meaningand that is often used in names of companies (Hornby 1995:37).
e.g. Brown, Brown & Walkins b. Phonology
Phonology is “the study of the ways in which speech sounds form systems and patterns” (Fromkin, Rodman, and Hyams, 2003: 273). The phonological knowledge gives us information how to combine sounds, which sounds should be at the beginning or at the end of a word, and which sounds can appear next to each other.
i. Alliteration
Alliteration is “the repetition of an initial sound in words that follow each other” (Hicks, 1998: 62). Alliteration occurs in initial sounds of a word, it can be a consonant or a vowel which is repeated in a line of a poem or in a sentence or in a close succession.
fishandphysics
sing asong ofsixpence
InStylistics, written by Verdonk, it is said that alliteration pleases the ears of readers and the sense of rhythm, such as sound effects add to the attention-drawing aspect and memorability of the news titles (Verdonk, 2002: 5). In addition, A Dictionary of Stylistics, it is said that alliteration can be used for emphasis, and to aid memorability (Wales, 2001: 14).
ii. Rhyming Consonance
In Exploring Poetry written by Frank Madden, consonance is defined as “repeated consonant sound” (2002: 70). It is horizontal rhymes; means that the repeated consonant sound is in one line or one sentence and at the end of words. It is not like rhyme that is in one stanza or vertical.
e.g. shortandsmart strutsandfrets c. Grammar
Grammar is “the set of rules and conventions that are the basis of the language” (Hicks, 1998: 3). This definition shows that in learning a language we have to understand its grammar first. “The grammar of a language consists of the sounds and the sound patterns, the basis units of meaning such as words and the rules to combine all of these to form sentences with the desired meaning” (Fromkin, Rodman, and Hyams, 2003: 273).
becomes the skill that can help them in their work. It also helps the sub-editor in correct the copy, headlines, etc.
i. Tense
Tense shows us “the correspondence between the form of the verb and our concept of time” (Quirk and Greenbaum, 1985: 40). Tenses in news titles show the time of the news which is present, future, and sometimes in past times but is written in present that is called Historic Present. News titles are different from other literary texts whose titles sometimes are formed in phrase only. Since most of news titles are formed in a sentence with several linguistic features are applied so they need tenses.
1. Simple Present Tense
InA Communicative Grammar of Englishwritten by Geoffrey Leech and Jan Svartvik (1994: 66-67), the use of simple present tense is for present state, present event, and present habit. For examples:
1) The sunrisesin the east. (General Truth) 2) Ilikecoffee.
3) Ideclarethe meeting closed. 4) Weworkfor a major company.
There are many news titles in newspaper use present tense both of in passive and active voice. In passive voice,to be is omitted before the main verb or_ed verbor past participle (Mulligan, 1943:234).
e.g. Jailstoldto include schools
Foldable, bendable batterymadefrom paper
PRESENT STATE
PRESENT EVENT
PRESENT HABIT
2. Historic Present Tense
Generally, the news titles are written in present tense for past event; the news is in past tense and the title is in present tense. This tense is called ‘historic present’.
e.g. Thai army-backed government hails referendum (The Jakarta Post, August 20, 2007)
3. Simple Future Tense
There are five chief ways of expressing future time in the English verb phrase. The most important future constructions are those which use
will(orshall) andbe going to(1994: 76-77). a. Will / shall
We usewillwhen we decide to do something at the time of speaking. The speaker has not decided before (Murphy, 1990: 16).
e.g. A: Dian left his bag.
B: Really! I’ll bring it to her. b. Be going to
We usebe going towhen we have already decided to do something (1990: 16). News titles that are in future tense always written in the form of
be going toandbe going is omitted like in the second example below. e.g. 1) A: We run out of milk.
B: I know. I am going to buy it.
ii. Ellipsis
Ellipsis is “grammatical omission” (Greenbaum and Quirk, 1990: 255). Strict ellipsis requires that when we insert the missing words we do not change the meaning of original sentence.
Based on the position where the ellipsis occurs within a construction, we distinguish ellipsis in three categories (Greenbaum and Quirk, 1990: 256).
1. Ininitialellipsis e.g. (I) hope he’s there. 2. Inmedialellipsis
e.g. Jill owns a Volvo and Fred (owns) a BMW. 3. Infinalellipsis
e.g. I know that we haven’t yet set the record straight, but we will (set the record straight).
There are some recoverability types of ellipsis, such as situational ellipsis, structural ellipsis, and textual ellipsis.
1. Situational ellipsis
In situational ellipsis, the interpretation may depend on knowledge of the extralinguistic context. Typically situational ellipsis is initial. Here are some examples of situational ellipsis:
1) (I’m) Sorry I couldn’t be there. 2) (It’s) Good to see you.
3) (Is there) Anybody in?
2. Structural ellipsis
In structural ellipsis, the interpretation depends on knowledge of grammatical structure.
1) I believe (that) you are mistaken.
2) We’re staying there (for) another weeks. (informal) 3. Textual ellipsis
In textual ellipsis, the interpretation depends on what is said or written in the linguistic context. According to the relative positions of ellipsis and its antecedent, there are two kinds of ellipsis, they are:
1) Anaphoric ellipsis, the interpretation depends on what comes before. e.g. I’m happy if you are (happy).
2) Cataphoric ellipsis, the ellipsis depends on what comes after. e.g. Those who prefer (to stay indoors), can stay indoors.
In Anwar’s book there are some opinions about that, they are: (Anwar, 1991: 17, translated by the writer)
1) Fenelou: “The more you say, the less be remembered. The less words, the more advantage”
2) Walt Whitman: “Simplicity is the rich of expression.” 3) Gustave Flaubert: “The best sentence is the shortest
sentence.” d. Lexis
Lexis means word. The American linguist, Bloomfield defined a word, cited in Linguistics written by Jean Aitchison, as “a minimum free form, that is, the smallest form that can occur by itself” (Aitchison, 1978: 65). Words can be combined to create phrases, clauses, and sentences. A word consisting of more than one morpheme is called a compound.
In making news title, the journalist selects words that carry particularly strong connotations that carry an emotional loading beyond their literal meaning. There are some suggestions told by Anwar to select words, they are:
1) “use common word that can be understood by people” (Anwar, 1991: 13, translated by the writer)
2) “use simple and clear words” (Anwar, 1991: 13, translated by the writer) 3) “use affirmative sentence not negative one” (Anwar, 1991: 14, translated
by the writer)
In the news titles, there are many uses of acronyms or abbreviation idiom, antonym and synonym, and personification. The number of words also affects the use of space. Here are the explanations of each.
i. Acronym and Abbreviation
The meaning of the word acronymin A Dictionary of Stylistics is “a very popular twentieth-century method of word formation, by which words and especially names are formed from the initial letter of a group of words” (Wales, 2001: 4). Moreover, in thejakartapost.com there is a page that shows the Indonesian Acronyms that are used in newspaper. For Example:
ABRI : Indonesian Armed Forces Bulog : State Logistics Agency DPR : House of Representatives
The abbreviation that is used in news titles is so generally known so that the reader understands it.
ii. Idiom
In Dictionary of Idioms and Their Origins, it is said that “the very word
e.g. Alpha and Omega : the beginning and the end; the first and the last; God
Drive something in: Explain repeatedly; get into one’s head iii. Antonyms and Synonyms
Antonyms and synonyms sometimes are used in making news title but they rarely occur. Antonyms or the words that have opposite meaning and synonyms or words that have similar meaning are used to create irony (antonyms) and avoid repeated word (synonyms).
e.g. ManandBoy(synonyms)
RichandPoor(antonyms) iv. Personification
Personification is “a figure of speech or trope in which an inanimate object, animate non-human, or abstract quality is given human attributes” (Wales, 2001: 294). Personification is often used in literary text.
e.g. Slowly, silently, now the moon Walks the night in her silver shoon; this way, and that, she peers, and sees Silver fruit upon silver trees.
Walter de la Mare –Silver v. Word Number
At the present time, a newspaper uses flush-left head or the news titles whose lines starts flush at the left of the column. The word number is needed to form news titles whether it is in one line or in two or three lines offlush-left head
B. Theoretical Framework
This part explains, one by one, the contribution of the theories in solving the problems mentioned in Chapter I. It is important to include the related theories as foundation for the writer to analyze the object of the study.
CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
A. Object of the Study
The news titles ofThe Jakarta Postare going to be analyzed in this thesis.
The Jakarta Post is one of newspapers in Indonesia that uses English. It consists of 24 pages and commonly it is divided into 13 to 14 news columns in Monday to Saturday editions and 16 to 17 news columns in Sunday edition.
The Jakarta Postis a famous international newspaper in Indonesia. It was established in 1982 after Indonesian Times and Indonesian Observer (both of these newspapers used English) were established. On April 25, 1983, 5.474 copies of the first edition of The Jakarta Post were sold out (http://en.wikipedia.org, accessed on February 23, 2007). However, today total daily average paid circulation ofThe Jakarta Postis around 40,000 copies (www.thejakartapost.com, accessed on July 18, 2007)
There are 50 news titles that are going to be analyzed. They are taken from August 19, 2007 issue. This issue is chosen because it is considered up to date and the most relevant to the time of analysis. Moreover, Sunday edition is the special edition in a week.
The news titles in every column are taken as data, except in Classifieds, Image, and Entertainment Guide column because these three columns contain advertisements and images only. The data are not advertorial and sharing-story or testimony news.
B. Approach of the Study
In analyzing the linguistic features that are applied in news titles, stylistics will be used as approach. Stylistics is “a critical approach which uses the methods and findings of the science of language in the analysis of literary texts” (Barry, 2002: 203). Moreover, stylistics studies linguistic features and their effects so that stylistics is the most appropriate approach to this analysis. Moreover, stylistics can be used in both of literary and non-literary texts. In this thesis, the data that are going to be analyzed are non-literary ones. They are news titles which are the hard data and the object of stylistic analysis.
C. Method of the Study
This study is an empirical research. The writer gathered the data from written text. This study is also descriptive. It means that only descriptions were the result that was found from the analysis. The source in this study isThe Jakarta Poston August 19, 2007 issue.
and Entertainment Guidecolumn and the news titles of advertorial, sharing-story or testimony news.
Next step was analyzing the data. The data were analyzed to answer the problems. The first problem was answered by finding out the linguistic feature(s) that the data have. The data were classified and analyzed based on their news columns. First step to answer the first problem was reading the news of the data to find out sentence (s) that is (are) directly represented in news title or similar to the news title.
e.g.:
News title : Iraq war pushed without ‘serious debate’
The sentence that is represented directly in the title:
…Vice President Dick Cheney and other administration officials
pushedthe country to invadeIraq withouta“serious debate”…
(The Jakarta Post, April 28, 2007)
After finding the related sentence of news title, the data were analyzed to see the change of news title (the grammar) from the related sentence and linguistic feature (s) that were applied to the data. For example is the size of font (typography), the writer measured the font manually by printing various sizes of font after that comparing to the font of news titles to find the size. To find out the typeface, the writer copied the news title from the internet and put it to the
and then determined the length based on the column width conversion in
www.thejakartapost.com.
Then, the data were classified based on the linguistic features they have to see the most common features. It was true that the amount of the frequency of occurrence of each linguistic feature was needed to find out which linguistic feature occurred the most frequent. This step was done after the data were classified according to their linguistic features.
The frequency of occurrence for each linguistic feature was counted by this formula;
From the presentation, the most common linguistic features that are applied on the news titles were determined.
Then, the second problem was answered by applying theories in chapter II to show the effects of linguistic features to the text. Theory of linguistic features also gives explanation to the effect of linguistic features to the text. For example is the theory of typography. In size of font, the bigger the font the easier to read it. The last step was drawing a conclusion from the result of analysis.
X 100 %
% X= Y
Z
X: linguistic feature
CHAPTER IV
ANALYSIS
News titles as other literary work titles, speech titles, or song titles have their own styles. Moreover, news titles have a persuasive function when they are designed to attract the attention of the readers and they are scanned to get an idea of the news. News titles have their own linguistic features that become the character of news titles.
In this thesis, the data are taken from the Sunday edition of The Jakarta Postwhich is a special edition in a week. It is designed for lazing at that day after six-day working. However, it also includes analytical news and the latest news of the weekend. The data in this analysis are classified based on their news column. There are 50 data in this analysis.
In this chapter, the writer divided the data that were analyzed based on the news columns. Moreover, this chapter is divided into two main parts, namely the linguistic features and the most common linguistic features in news titles, and the effects of linguistic features to the texts.
A. The Linguistic Features and the Most Common Linguistic Features in
News Titles
1. Graphology
In graphology, the linguistic features that were analyzed are the typography and the use of punctuation. Typography includes the size of font, the length of news title, and the typeface of news title. Moreover, punctuation is about the usage of certain marks to form a news title with certain purpose. The data were analyzed based on the news columns.
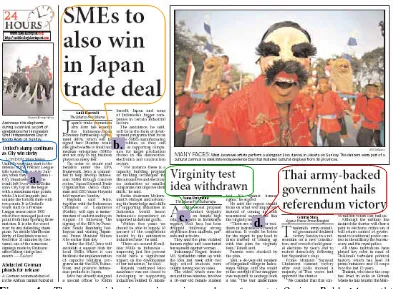
a. Front Page
This column is the column of the cover of newspaper. There are four news titles in this column, but only three of them are taken because the other one is just a testimony or sharing-story.
No. Front Page
lament frictions 64 pt 94 4
Minion first king of Elvis
pretenders 36 pt 241 1
Minion
Pro-Semi-Bold
-3.
Sony a step away from winning world
The longest news title is “Graceland anoints first king of Elvis pretenders”. It is in five columns long or 241 mm and in one line that is called
five-column line.
“One-line heads beginning flush at the left and running entirely across a page or a major part of a page sometimes are used over big stories. … . They may also be called five-, six-, or seven-column lines, the number indicating the length of the head” (Mulligan, 1943:237).
The two or three-line news title is the most common. However, the “Religious leaders lament frictions”is in four lines. This title is the only one that is in four lines. Moreover, all of news titles in this column use Minion Pro-Semi-Bold, one of three typefaces that are used for news title inThe Jakarta Post.
In “Sony a step away from winning world c’ship”, the usage of apostrophe is to indicate that some letters have been deleted to shorten. The word c’ship
means championship. The word c’ship is familiar for the reader so that it can be used.
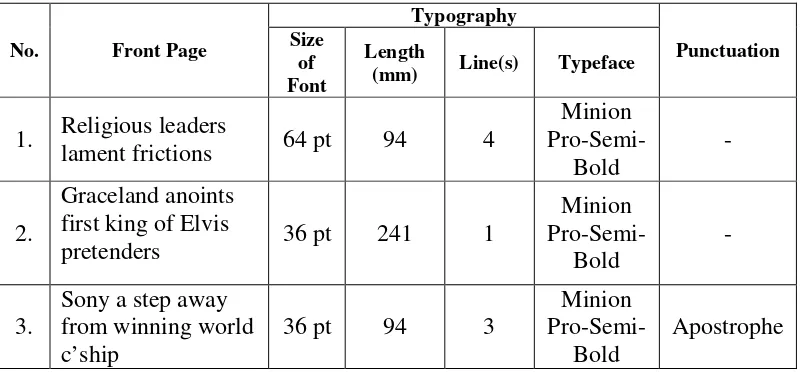
b. News
This column is a news column that consists ofNews Highlightscolumn in it. It is on second page and there are six news titles in this column and two of them are inNews Highlightscolumn.
Figure 5:The size of font and typeface: (a) 64 pt, Minion Pro-Semi-bold (b) 36 pt, Minion Pro-Semi-bold
No. News
over murder fugitive 48 pt 143 2
Minion Pro-
Semi-Bold
-5. RI workers in Taiwan
find solace on Aug.17 36 pt 241 1
Minion
7. Scholarship opens up
doors to art & culture 30 pt 94 2
Minion Pro-
Semi-Bold
Ampersand
8. 5,400 chickens culled
in Bali 14 pt 94 1
The news titles that have the smallest font are the short news in News Highlights column. They also use different typeface. Moreover, the use of apostrophe in “Death’s stench rises in quake town” is to show the possession, the ampersand in “Scholarship opens up doors to art & culture” has a meaningand, and the use of full stop in “RI workers in Taiwan find solace on Aug.17”to mark abbreviation. The use of ampersand here is aimed to economize the use of word and space.
Figure 6:The size of font and typeface: (a) 48 pt, Minion Pro-Semi-bold (b) 34 pt, Minion Pro-Semi-bold, (c) 30 pt, Minion Pro-Semi-bold, (d) 14 pt, Optima-Bold Table 2:The graphological features of news titles in News column
d. c.
c. Current Issues
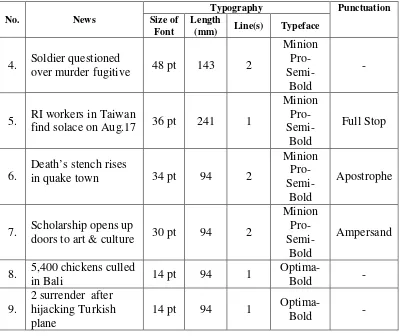
This column is on page three and there are three news titles in this column and all of them are taken as data.
No. Current Issues — and feed doubts
34 pt 94 3 Minion Full Stop,
Dash
12. Quitting Iraq no easy
task for UK troops 36 pt 241 1
From the size of font, we can see that “U.S. citizens warned of mounting homegrown terrorist threat” is the most important news in this column because the size of font is the biggest in this column and the size of font shows the importance of news. Moreover, the use of full stop in this title and in “W. House criticism could boost Clinton — and feed doubts” is to show acronym; W for White and U.S for United State. The use of dash is to make a certain piece of information more highlighted.
d. People
This column contains news of famous people. It is on page four and there are two news titles in this column and they are taken as data.
No. People
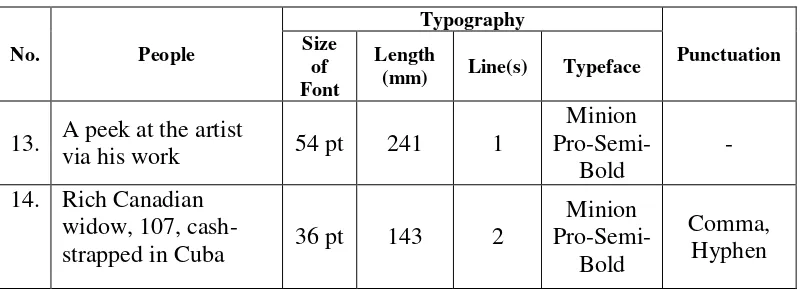
13. A peek at the artist
via his work 54 pt 241 1
strapped in Cuba 36 pt 143 2
Minion
Pro-Semi-Bold
Comma, Hyphen
The usage of comma in “Rich Canadian widow, 107, cash-strapped in Cuba” is to indicate the missing relative pronoun and to be, and to add non-defining clause and the hyphen (-) is to indicate new phrase. The Minion Pro-Semi-Boldthat is used is the most common typeface for big size titles.
e. On the Town
This column is on page five and it contains two other columns,Metro Mad
that is about sharing-story, and Take Your Pick that is advertisements about the good place to get delicious food. In this column, the writer took only one news title of seven, because five of them are advertorial and the other one is just a testimony.
Table 4:The graphological features of news titles in People column
No. On the Town
15. Delicious food at
affordable prices 50 pt 192 1 Minion
-The typeface of this news title is Minionand it is in one line that is called
four-column line. The size of font is 50 point and the length is four columns or 192 mm. There is no punctuation used in this news title.
f. Lifestyle
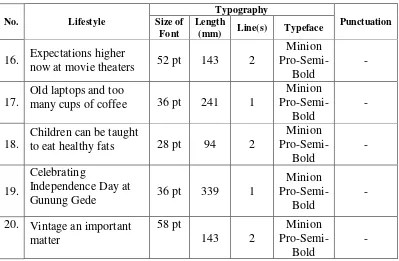
This column is on page six and seven. There are three other columns in it, namely Personal Technology, Shopping Basket, and Walking Home. Personal Technology is about sharing- tips about technology from the expert. Shopping Basket is advertorial. Walking Home is about the story of someone in certain region in Indonesia, and in this edition the person is a Balinese. There are five news titles taken from this column, the others are just advertisements.
No. Lifestyle
now at movie theaters 52 pt 143 2
Minion
Pro-Semi-Bold
-17.
Old laptops and too
many cups of coffee 36 pt 241 1
Minion
Pro-Semi-Bold
-18.
Children can be taught
to eat healthy fats 28 pt 94 2
Gunung Gede 36 pt 339 1
Minion
Pro-Semi-Bold
-20. Vintage an important
matter Table 5:The graphological features of news title in On the Town column
The title “Old laptops and too many cups of coffee” uses the wordand not the ampersand (&) to fit the news title to the space provided. It is in one line that is called five-column line. Furthermore, the title “Celebrating Independence Day at Gunung Gede” uses seven columns, the maximum column in the newspaper and it is 339 mm long.
g. Art
This column is on page eight. There are three news titles in this column and all of them are taken as data.
No. Art
forgotten past 58 pt 192 1
Minion
puzzle of identities 40 pt 192 1
Minion Pro-
Semi-Bold
-23. History largely a
question of culture 30 pt 94 2 Minion
-From the table above we can see that the size of font are different each other. Although there are two news titles are the same in length but they are different in the typeface.
Figure 10:The size of font and typeface: 40 pt, Minion Pro-Semi-Bold Table 7:The graphological features of news titles in Art column
Figure 9:The size of font and typeface: (a) 58 pt, Minion Pro-Semi-bold (b) 52 pt, Minion Pro-Semi-bold, (c) 28 pt, Minion Pro-Semi-bold
h. Home & Family
This column is on page nine. It has columns of recipe and it contains two news titles that become the data.
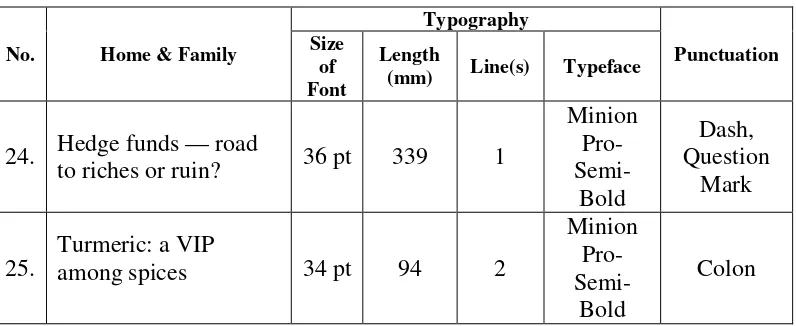
No. Home & Family
Typography
24. Hedge funds — road
to riches or ruin? 36 pt 339 1
among spices 34 pt 94 2
Minion indicate that there are missing words (isand the) and the use of question mark is to signal that a message or an utterance is in a direct question form. The use of colon (:) in “Turmeric: a VIP among spices” is to take the position of is. All of the news titles that are in more than one line areflush-left headbut this title is the only one that ispyramid-head.
i. Sports
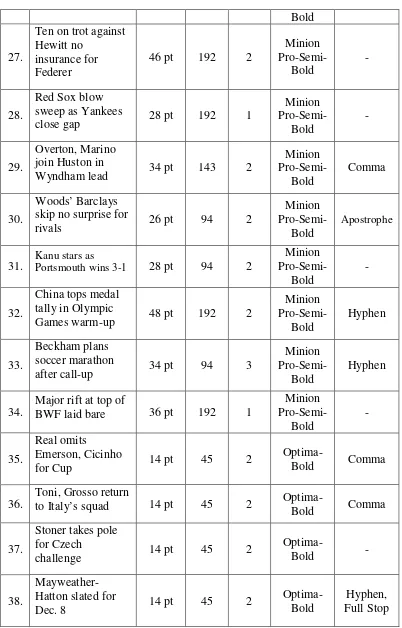
This column is on page eleven and twelve. There are two columns in this news column, namelyScore Boardthat provides score of some sport tournaments, and Putting It Briefly that provides brief short news of sport. There are thirteen news titles in this column and all of them are taken as data.
No. Sports
26. Sony ready to fillTaufik’s shoes 30 pt 94 2 Minion
Bold
27.
Ten on trot against Hewitt no
Wyndham lead 34 pt 143 2
Minion skip no surprise for
rivals 26 pt 94 2
Portsmouth wins 3-1 28 pt 94 2
Minion
Games warm-up 48 pt 192 2
Minion
after call-up 34 pt 94 3
Minion
Pro-Semi-Bold
Hyphen
34.
Major rift at top of
BWF laid bare 36 pt 192 1
to Italy’s squad 14 pt 45 2 Optima-Bold Comma
37.
Stoner takes pole for Czech
challenge 14 pt 45 2
The news titles in Putting It Briefly column use one column only (or 45 mm long) because they are short news. In addition, the size of font is the smallest one (14 pt). The use of comma in those titles is to substitute the wordand,the use of hyphen in “Mayweather-Hatton slated for Dec. 8” is to substitute the wordand, whereas in other news titles, the hyphen is used to show a verb phrase, the use of apostrophe is to indicate apposition, and the use of full stop is to mark abbreviation.
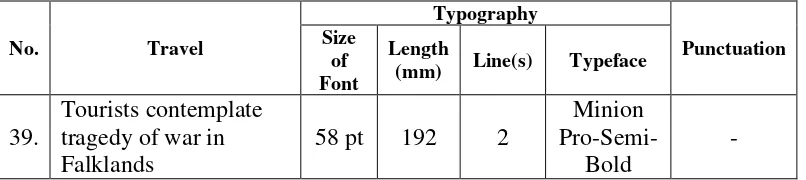
j. Travel
This column is on page thirteen. There is only one news title in this column and it is taken as data.
No. Travel tragedy of war in Falklands
As this news is the only one news in this column, so the size of font is big and it isflush-lefthead in two lines.
k. Art & Music
This column is on page fourteen. There is one other column in it that is namedOn the Record. It is about the music album. Moreover, in this column there are only two news titles and they are taken as data.
Figure 11:The size of font and typeface: (a) 46 pt, Minion Pro-Semi-bold (b) 26 pt, Minion Pro-Semi-bold
Table 10:The graphological features of news title in Travel column
No. Art & Music
with thinking’ 56 pt 339 1
Minion
Success all round at
Brisbane Powerhouse 38 pt 241 1
Minion
Pro-Semi-Bold
-These two sizes of font are used only once in this edition and the length which is 339 mm or seven columns long is the maximum length. Therefore, the title “‘Dance culture starts with thinking’” is calledseven-column lineand the title “Success all round at Brisbane Powerhouse” is called four-column linebecause it is in one line and in four columns. Furthermore, the usage of inverted comma is to give more attention to the news title.
l. Screen
This column is on page fifteen. There are two other columns in it that contain the synopsis of movies and the list of movie that is still playing. The names of these columns are Now Showing and Still Playing. Moreover, this column provides the news of movie and in this column there are only two news titles that are taken as data.
Figure 12:The size of font and typeface: (a) 56 pt, Minion Pro-Semi-bold (b) 38 pt, Minion Pro-Semi-bold
Table 11:The graphological features of news titles in Art & Music column
No. Screen
This column is on page eighteen and nineteen. There are five news titles in this column and only three of them are taken as data because the other two are advertorial.
Vying for slice in logistics service
business pie 50 pt 339 1
Minion
warehousing business 50 pt 339 1
Minion
Pro-Semi-Bold
-n. Mosaic
This column is on page twenty and twenty one. There are two other columns in it, namely Design Brief that is about critical analysis in certain topic and Keeping Mum that is about sharing-story. There are five news titles in this column and only four of them are taken as data because the other one is just a testimony and consultation column.
Table 12:The graphological features of news titles in Screen column
No. Mosaic Berlin Wall 46 years
on 50 pt 241 2
The table below shows the total number of news titles that have each of linguistic features that were analyzed. There are sixteen sizes of font that are used inThe Jakarta Post issued on August 19, 2007 and there are only three typefaces that are used. Furthermore, The Jakarta Post consists of seven columns or 339 mm long.
o. 58 pt
From the table above we can see that the most common size of font that is used is 36 pt, with the percentage of the occurrence is 20 % and the most common typeface that is used is Minion Pro-Semi-Bold, with the percentage 82 %. Also, the most common length of the news title is94 mm, with the percentage 30 %, the most common line-use is 2 lines, with percentage 50 %, and the percentage of the data that use punctuation is 42 %. These percentages are gained from this formula:
a. Percentage of 36 pt
10 50
X 100 %
% 36 pt = = 20 %
Table 15:The total number of the use of graphological features
X 100 %
% X= Y
Z
X: linguistic feature
b. Percentage of Minion Pro-Semi-Bold
c. Percentage of 94 mm
d. Percentage of the Punctuation-Use
e. Percentage of News Titles that Use 2 Lines
2. Phonology
In phonology, the linguistic features that were analyzed are the use of alliteration and the use of rhyming consonance. The total numbers of news titles that have rhyming consonance or alliteration were classified based on news column.
No. News Column (total news title) Alliteration Rhyming Consonance
8. Home & Family (2) -
-9. Sports (13) 3 5
10. Travel (1) 1
-11. Art & Music (2) -
-12. Screen (2) 1
-13. Focus (3) 1 1
14. Mosaic (4) 3 1
Total 15 11
Not all of the news titles that were analyzed have alliteration and rhyming consonance. Some of them have alliteration and rhyming consonance; some of them have alliteration or rhyming consonance only even some of them have not alliteration and rhyming consonance. Here are the news titles that have rhyming consonance and alliteration and those that have rhyming consonance or alliteration only.
a. Front Page
1. Religious leaders lament frictions
Alliteration leadersandlament
Rhyming Consonance leadersandreligious 2. Graceland anoints first king of Elvis pretenders
Rhyming Consonance Elvisandpretenders 3. Sony a step away from winning world c’ship
Alliteration Sonyandstep
winningandworld
b. News
4. Soldier questioned over murder fugitive
Rhyming Consonance soldier,over, andmurder c. Current Issues
10. W. House criticism could boost Clinton — and feed doubts Alliteration criticism,could, andClinton
d. People
13. A peek at the artist via his work
Alliteration a,at, andartist
14. Rich Canadian widow, 107, cash-strapped in Cuba
Alliteration Canadian,cash, andCuba
e. Lifestyle
17. Old laptops and too many cups of coffee
Rhyming Consonance laptopsandcups
18. Children can be taught to eat healthy fats
Alliteration taughtandto
f. Sports
27. Ten on trot against Hewitt no insurance for Federer
Alliteration tenandtrot
Rhyming Consonance trotandHewitt 28. Red Sox blow sweep as Yankees close gap
Rhyming Consonance asandYankees 29. Overton, Marino join Huston in Wyndham lead
Rhyming Consonance Overton,Huston, andin 30. Woods’ Barclays skip no surprise for rivals
Alliteration skipandsurprise
Rhyming Consonance Woods,Barclays, andrivals 31. Kanu stars as Portsmouth wins 3-1
Rhyming Consonance stars,as, andwins
g. Travel
39. Tourists contemplate tragedy of war in Falklands Alliteration touristsandtragedy h. Screen
43. Promising psychological drama spoiled by foggy script
Alliteration promisingandpsychological spoiledandscript
i. Focus
45. Trapping an elephant in one’s own home
Rhyming Consonance an,in, andown 46. Lucrative logistic warehousing business
j. Mosaic
48. Mustang Ranch survives sordid past for rebirth
Alliteration Ranchandrebirth
survivesandsordid
49. Bike trail follows Berlin Wall 46 years on
Alliteration bikeandBerlin
Rhyming Consonance Berlinandon followsandyears trailandWall 50. Understanding the busway’s brutal design
Alliteration busway’sandbrutal
Here, we will see the percentage of each linguistic feature that was analyzed. The total number of news title that have alliteration or rhyming consonance are gained from the answer of problem one.
No. Phonology Total
1. Alliteration 15
2. Rhyming Consonance 11
From the table above, we can see the percentage of news titles that have alliteration is 30 % and the percentage of news titles that have rhyming consonance is 22 %.
a. Percentage of Alliteration
b. Percentage of Rhyming Consonance
3. Grammar
In grammar, the linguistic features that were analyzed are the use of tense; whether it is historic present tense or present tense or future tense, the use of ellipsis, and the form of news title; whether it is in a sentence or in a noun phrase form and whether it is in a passive voice or active voice. These features were analyzed on the data and presented in the table below.