EDUCATIONAL GUIDELINE OF
ENGINEERING FACULTY
CIVIL ENGINEERING
DEPARTMENT
ENGINEERING FACULTY
BRAWIJAYA UNIVERSITY
Academic Year 2017 - 2018
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... 3
VISION, MISSION PURPOSES OF ENGINEERING FACULTY ... 5
BRAWIJAYA UNIVERSITY DECISION OF THE DEAN OF ENGINEERING FACULTY BRAWIJAYA UNIVERSITY ... 7
EDUCATIONAL GUIDELINE OF ENGINEERING FACULTY ... 10
BRAWIJAYA UNIVERSITY CHAPTER I GENERAL PROVISION ... 10
CHAPTER II PURPOSES OF ENGINEERING EDUCATIONAL PROGRAM ... 12
CHAPTER III EDUCATIONAL SYSTEM... 13
CHAPTER IV ACADEMIC ADMINISTRATION ... 24
CHAPTER V CURRICULUM, SYLLABUS AND SPECIAL REGULATION OF . 31 DEPARTMENT/STUDY PROGRAM CHAPTER VI THESIS/ SKRIPSI AND FINAL EXAM ... 31
CHAPTER VII THESIS ... 35
CHAPTER VIII DISSERTATION ... 38
CHAPTER VIII ADDENDUM AND CLOSING ... 44
PREFACE ... 47
BACHELOR PROGRAM (S-1) INTRODUCTION... 51
I. Vision and Mission ... 53
II. Purposes ... 53
III. Learning Outcome ... 53
IV. Bachelor Degree... 55
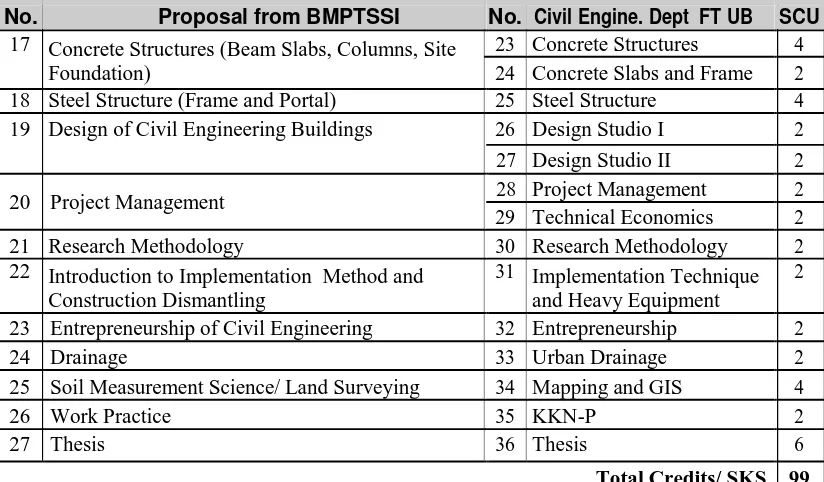
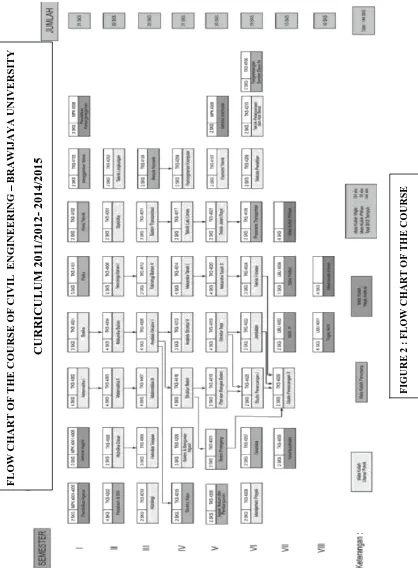
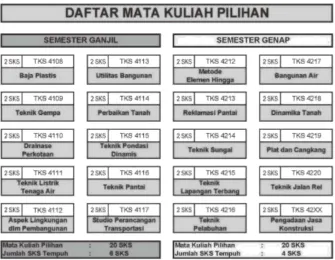
V. Curriculum ... 55
VI. Department Regulation ... 75
VII. Learning Facilities ... 80
VIII. Course Syllabus ... 86
MASTER PROGRAM (S-2) I. Vision and Mission ... 127
II. Purposes ... 127
III. Concentration (Interest) ... 127
IV. Study Load and Curriculum ... 128
DOCTORAL PROGRAM (S-3) I. Vision and Mission ... 159
II. Purposes ... 159
III. Curriculum and Study Load ... 159
IV. Course Syllabus ... 162
EDUCATIONAL GUIDELINE OF ENGINEERING FACULTY BRAWIJAYA UNIVERSITY 2017/2018
VISION, MISION AND PURPOSES OF
ENGINEERING FACULTY BRAWIJAYA UNIVERSITY
VISION
In 2020, Engineering Faculty of Brawijaya University becomes a leading higher education institution in the field of engineering in Asia, and able to actively participate in the national development through the process of education, research, and community service.
MISSION
1. Organizing education with high quality to produce graduates with a qualified academic ability in the field of engineering, have an entrepreneurial spirit, and have a noble character.
2. Conducting the research, development and dissemination of science and technology, as well as community service activities, especially in the field of engineering in order to improve the standard living of the people.
PURPOSES
1. Produces graduate in the field of engineering that superior, though, and able to compete at the national and international level, have an entrepreneurial spirit and noble character, and also fear of God Almighty.
2. Giving real contribution to the development of science, technology, and community service activities in the field of engineering, so that can play a role in determining the direction of national policy in order to improve the standard living of the people, the nation, and humanity.
DECISION OF THE DEAN OF
ENGINEERING FACULTY BRAWIJAYA UNIVERSITY
Number : 1066 The Year of 2017on
Educational Guideline of Engineering Faculty Brawijaya University Academic Year 2016 - 2017
Consider : a. Given that the Educational Guideline of Engineering Faculty Brawijaya University
the year of 2016/2017 – 2017/2018 need to be improved and adjusted to the developments of the needs of the
community for the personnel of Bachelor, Engineer and Doctor of Engineering
and with the regulations issued, either by the Ministry of Research and Technology and Higher Education or
by Brawijaya University and the Faculty of Engineering itself b. Given that to regulate the provision of educationon the basis of the credit system that has been adjusted to Indonesian National Qualification Framework / KKNI and National Standard
For Higher Education, then deemed necessary to improve the Educational Guideline of Engineering Faculty
Brawijaya University and published in the form of book of Educational Guidelines The Year of 2017/2018
Remember : 1. The Act of RI No 20 The Year of 2003 on the National Education System.
2. The Act of RI No 14 The Year of 2005 on Teachers and Lecturers.
3. The Act of RI No 12 The Year of 2012 on Higher Education. 4. Government regulations of RI No 66 The Year of 2010 on
Management and Implementation of the Education. 5. Government regulations of RI No 32 The Year of 2013 on
National Education Standards.
6. Regulation of the President of RI No 8 The Year of 2012 on Indonesian National Qualification Framework.
7. Regulation of the Minister of State Apparatus Empowerment and Bureaucracy Reformation of the RI No 46 The Year of 2013 on Amendment to the Regulation of the Minister of State Apparatus Empowerment and Bureaucracy Reformation No. 17 Year 2013 on Functional Position of Lecturer and the Credit Values.
8. The Decision of Minister of National Education of RI No 232/U/2000 on Guidelines for Higher Education Curriculum Formulation and Assessment of Student Learning Outcomes. 9. The Decision of Minister of National Education of RI No
045/U/2002 on Core Curriculum of Higher Education 10. The Decision of Minister of National Education of RI No
080/O/2002 on Statute of Brawijaya University
11. The Regulation of Minister of technology research and higher education No. 44 The Year of 2015 on National Standards for Higher Education.
12. The Regulation of Minister of technology research and higher education No.4 The Year of 2016 on Organization and Working Procedure of Brawijaya University.
13. The Decree of the Directorate General of Higher Education No 28/DIKTI/Kep/2002 on The Implementation of Regular and Non Regular Program In State University.
14. The Decree of the Directorate General of Higher Education No 43/DIKTI/Kep/2006 on Implementation Benchmark of Course Group of Personality Development in Higher Education.
15. The Decree of the Directorate General of Higher Education No 44/DIKTI/Kep/2006 on Implementation Benchmark of Course Group of Social Life in Higher Education.
16. Form Letter of the Directorate General of Higher Education No 4071/D/T/2006 on Implementation of Benchmark of Study Materials implementation of Personality Development and Social Life.
17. The Decision of Rector of Brawijaya University No 74/SK/2006 on Organization and Working Procedure of Brawijaya University. 18. The Decision of Rector of Brawijaya University No 518/SK/2013
on The Book of Educational Guidelines of Brawijaya University. 19. The Decision of Rector of Brawijaya University No
208/PER/2010 on Institutional Curriculum of Brawijaya University.
20. The Decision of Rector of Brawijaya University No 221/PER/2010 on Guidelines for the Implementation of Competency in English, Technology and Communication Competencies, Sport/Art Activities and Intelligence Potential for the student of Brawijaya University.
21. The Decision of Rector of Brawijaya University No 223/PER/2010 on Guidelines for Implementation of Thesis/Skripsi as Final Task of Bachelor Education Program at Brawijaya University.
22. The Decision of Rector of Brawijaya University No 224/PER/2010 on Guidelines for Implementation of Thesis/Tesis as Final Task of Education Program of Master at Brawijaya University.
23. The Decision of Rector of Brawijaya University No 225/PER/2010 on Guidelines for Implementation of Dissertation as Final Task of Education Program of Doctor at Brawijaya University.
24. The Decision of Rector of Brawijaya University No 335/PER/2010 on Fast Track of Doctoral Program at Brawijaya University for The student of Master Education Program and Graduates of the Bachelor Programme With Outstanding Achievement.
25. The Decision of Rector of Brawijaya University No 336/PER/2010 on Recognition of Learning Outcomes from Another Higher Education to Brawijaya University.
26. The Decision of Rector of Brawijaya University No 337/PER/2010 on Students Transfer from Others Higher Education to Brawijaya University.
27. The Decision of Rector of Brawijaya University No 334/PER/2010 on the Implementation of Double Degree Program at Brawijaya University.
28. The Decision of Rector of Brawijaya University No. 22 The Year of 2015
on Guidelines for the Implementation of Judicium, The Issuance of Certificate and Certificate of Profession
Notice : 1. Results of Team Meetings of The Book of Educational Guidelines of Engineering Faculty Brawijaya University The Year of 2014/2015 - 2017/2018 during the period of
January - June 2017.
2. Input from the Executive of the Engineering Faculty at the Executive Meeting during the period of January – June 2017 3. Senate Meeting of Engineering Faculty Brawijaya University
during the period of January - June 2017.
4. Book of Educational Guidelines of Brawijaya University the Year of 2017.
5. Executive Meeting of Engineering Faculty Brawijaya University July - August 2017.
Enact : 1. Educational Guidelines of Engineering Faculty Brawijaya University Academic Year of 2017/2018 as attached, used as the main reference throughout the academic units
in the Faculty of Engineering Brawijaya University. 2. Educational Guidelines of Engineering Faculty Brawijaya
University Academic Year of 2017/2018 intended for students In the case of the determination of the acquisition credit for previous student class will be conducted transition in accordance with the Transitional Regulation in each Department / Study Program
3. The decision is valid from the date specified and will be held as necessary improvements, if there is a mistake in the
establishment
Enacted in : Malang On the Date of : August 2017 Dean,
Signed.
Dr. Ir. Pitojo Tri Juwono, MT NIP. 19700721 200012 1 001
EDUCATIONAL GUIDELINES OF ENGINEERING FACULTY
BRAWIJAYA UNIVERSITY
2016 - 2017
CHAPTER I GENERAL PROVISION
Article 1
In this Educational Guidelines what is meant by :
1. The Semester is a unit of time activity that consists of 16 (sixteen) weeks of lectures or other scheduled activities, with the following accompanying activities, including two (2) to three (3) weeks of the assessment activities.
2. Short Semester is a semester for a particular student which the implementation is shortened by referring to the provisions established by the Dean.
3. The Semester Credit System is a system of education implementation using a semester credit unit/ satuan kredit semester (sks) to express the study load of students, lecturer workload, the learning experience and the load of program implementation.
4. Semester credit unit/ Satuan kredit semester (sks) is a dose of appreciation for learning activities equivalent to 170 (one hundred and seventy) minutes of learning activities per week per semester.
5. Competency-Based Curriculum/ Kurikulum Berbasis Kompetensi (KBK) is curriculum that compiled based on elements of competencies which can deliver learners to achieve the main competencies, supporting competencies, and other competencies as a method of inquiry (a method of learning that fosters a great desire to want to know) that expected. 6. Competency is a set of intelligent action, full of responsibilities which owned by a
person as a condition to be considered capable by the community in carrying out the tasks in certain occupations.
7. Standards of graduates’ competencies is the qualification of graduate capabilities that include attitudes, knowledge, and skills.
8. Indonesian National Qualification Framework/Kerangka Kualifikasi Nasional Indonesia (KKNI) is the hierarchical arrangements framework of competency qualifications which can reconcile, equalize, and integrate between the education field and the field of job training and work experience in order to award the recognition of work competency in accordance with the structure of employment in various sectors.
9. Qualification is the mastery of learning outcomes which stated its position in Indonesian National Qualification Framework /KKNI.
10. The Credit score is a value that state the effort to complete the existing task in the lecture program, seminar, practicum/studio, work practices or other tasks
11. Lectures are an activity of tutorial/face to face, which conducted between lecturers and students that scheduled in the classroom or elsewhere specified.
12. Structured task is the learning activities in the form of material deepening for students, designed by lecturers to achieve the competency and task completion time is determined by the lecturer.
13. Independent (unstructured) task is the learning activities in the form of material deepening for students, designed by lecturers to achieve the competency. Task completion time is determined by students.
14. Seminar is a scientific meetings related to the course organized by students with the guidance of the lecturer.
15. Practicum/studio activities are a structured academic activity which conducted in a laboratory/studio or elsewhere specified.
16. Real Work Lecture-Practice/Kuliah Kerja Nyata-Praktek (KKN-P) is a structured academic activity which carried out in companies, projects and/or agencies approved by the Head of Department/Study Program.
17. The task of course is a structured academic activities undertaken by students with the guidance of lecturer/assistant and is one of the components of the assessment/evaluation. 18. Quiz and/or Middle Test of the semester/Ujian Tengah Semester (UTS) is the evaluation
activities conducted during the lecture takes place in the relevant semester.
19. Final Test of the semester/ Ujian Akhir Semester (UAS) is evaluation activities conducted at the end of the semester.
20. Grade Point/Indeks Prestasi (IP) is a score that indicates the student's achievement from the courses taken in one semester, which is calculated by the number of credits multiplying of each course multiplied with weight of value obtained divided by the number of credits taken.
21. Grade Point Average/Indeks Prestasi Kumulatif (IPK) is a score that indicates the student's achievement from all courses taken which is calculated by the number of credits multiplying of each course multiplied by weight of value obtained divided by the number of credits taken.
22. Bachelor Final Examination is a test that can be either Skripsi Exam or a Comprehensive Exam and Skripsi Exam.
23. Master Final Examination is a Thesis/Tesis Exam.
24. Doctoral Final Examination is Closed Exam and/Opened Exam.
25. Study Plan Card/Kartu Rencana Studi (KRS) is a record of students' academic program plans on one semester.
26. Study Results Card/Kartu Hasil Studi (KHS) is a record of a student's academic achievement which published every the end of the semester.
27. Year Transfer Program/Program Alih Tahun (PAT) is a matriculation program held by the master study program and doctoral study programs in the environment of the Engineering Faculty Brawijaya University for new student.
28. University is Brawijaya University.
29. Faculty is Engineering Faculty Brawijaya University. 30. Rector is the Rector of Brawijaya University.
31. Dean is the Dean of Engineering Faculty Brawijaya University.
32. Head of Department/Study Program is the Head of Department/Study Program in the environment of the Engineering Faculty Brawijaya University.
33. Student is the Student of Engineering Faculty Brawijaya University.
CHAPTER II
PURPOSES OF ENGINEERING EDUCATION PROGRAM Article 2
1. Purpose of engineering education program is to prepare students to become citizens that have the faith and fear of God Almighty, have the spirit of Pancasila, have high personal integrity, opened and responsive to change and advancement of the science, technology and problems faced by the community, particularly those related to their expertise with the following qualifications:
a. Have a high personal integrity.
b. Have the ability to conduct leadership development and the growth of sense of professional ethics.
c. Have the ability to work or continue their education to higher education after completing the undergraduate/bachelor education.
d. Have the motivation to keep up with technology and science with intellectual, social and cultural.
e. Able to deal with new situations in his profession as a bachelor of engineering, which is based on fundamental principles independently, with confidence and steady consideration.
f. Able to resolve the problem by applying the basic principles in engineering and analytical thinking in a discipline when formulating, planning, and simplify the problem without losing sight of specialization.
g. Able to conduct lifelong learning for themselves and others.
h. Able to be functioned themselves effectively not only as individuals, but also in the team of multi-disciplinary and multicultural, with the capacity as a leader effectively as a team member.
i. Able to communicate effectively not only in the technical field but with the larger society.
j. Able to understand the field of entrepreneurship creatively and innovative. k. Able to communicate both orally and in writing in a foreign language, especially
English.
2. Specific Purposes of Bachelor Education (level 6 of Indonesian National Qualification Framework/ KKNI) are as follows:
a. Able to apply and utilize their expertise in the field of science and technology in solving problems and able to adapt to the situation faced.
b. Mastering the theoretical concept of specific knowledge field in general and the theoretical concept of special section in these knowledge field in depth, as well as able to formulate a procedural problem solving.
c. Able to take the right decisions based on analysis of information and data, and able to provide guidance in selecting various alternative solutions independently and groups.
d. Responsible for own work and can be given responsibility for the achievement of the organization's work.
3. Specific Purposes of Engineering profession education (level 7 of Indonesian National Qualification Framework/ KKNI) are as follows:
a. Able to plan and manage the resources under their responsibility, and comprehensively evaluate the work by utilizing science and technology to produce the steps of organizational strategic development.
b. Able to solve the problems of science, technology, or art in their field through monodisciplinary approachment.
c. Able to conduct research and make strategic decisions with full accountability and responsibility for all aspects of which are under the responsibility of their expertise. 3. Specific Purposes of Master Education (level 8 of Indonesian National Qualification
Framework / KKNI) are as follows:
a. Able to develop knowledge, technology, and or art in the field of their scientific or their professional practice through research, until produce innovative works and tested.
b. Able to solve the problems of science, technology, and or art in their field through inter or multidisciplinary approachment.
c. Able to manage research and development that give benefit to society and science, and able to receive national and international recognition.
4. Specific purposes of Doctoral Education (level 9 of Indonesian National Qualification Framework/ KKNI) are as follows:
a. Able to develop knowledge, technology, and or the new art in the field of their scientific or their professional practice through research, until produce creative work, original, and tested.
b. Able to solve the problems of science, technology, or art in their field through inter, multi or transdisciplinary approachment.
c. Able to manage, lead and develop research and development that will give benefit to the science and mankind, and able to receive national and international recognition.
5. The Specific purposes of Engineering Education Program for each Department/Study Program is set in the Department curriculum section at this Education's Guidelines.
CHAPTER III EDUCATIONAL SYSTEM
Article 3
1. Faculty implement competency-based curriculum (KBK) with the Semester Credit System that produces learning outcomes in accordance with the qualifications specified in Indonesian National Qualification Framework/ KKNI.
2. Purposes of applying the competency-based curriculum with the Semester Credit System are as follows:
a. To prepare students to be members of society who have good morality, have the knowledge, skills, independence, and attitudes to discover, develop, and implement science, technology and art, which is beneficial to humanity.
b. To provide the opportunity for students to take courses that match with their interests and talents/abilities so that the competent and hard-working student can complete studies in the shortest possible time.
c. To provide the possibility for the system to evaluate students' learning progress could be organized as well as possible.
d. To allow transfer of credits between Department / Study Program, among faculty within the university and students transfer between universities.
e. To simplify the adjustment of the curriculum from time to time with the development of science and technology which is very rapid today.
3. The purpose of the application of Indonesian National Qualification Framework/ KKNI is in order the graduates receive recognition of work competency in accordance with the structure of employment in various sectors.
Semester Credit Unit Article 4
1. The study load of students, lecturer workload and the implementation of the Department/Study Program is expressed in semester credit units.
2. One unit of semester credit for the lecture is determined based on the load of activities covering the three forms of activity per week per semester as follows:
i. Events of scheduled face to face, namely the interaction between students and lecturer in the form of lectures, responsiveness, and tutorials for 50 (fifty) minutes; learning activities with structured assignment 60 (sixty) minutes; and self-learning activities 60 (sixty) minutes; or
ii. Seminars learning activities or other similar forms of learning which includes face to face learning activities 100 (one hundred) minutes and self-learning activities 70 (seventy) minutes; or
iii. Practicum learning activities, studio practice, workshop practice, field training, research, community service, and/or other equivalent form of learning for 170 (one hundred and seventy) minutes.
Student Study Load Article 5
1. Student study load of bachelor education program as a prerequisite for completing studies at the Faculty is a minimum of 144 credits.
2. Student study load of master education program as a prerequisite for completing studies at the Faculty is a minimum of 36 credits.
3. Student study load of doctoral education program as a prerequisite for completing studies at the Faculty is a minimum of 40 credits for participants which have an S2 education in the same field, and a minimum of 52 credits for participants which have S2 education not in the same field.
4. Included in this study load is institutions’ compulsory course (national content and University content) and expertise course for each study program.
5. Institutions compulsory course for the students of bachelor education program are consist from:
a. National Content:
i. Religious education (2 credit) ii. Pancasila Education (2 credit) iii. Citizenship (2 credit)
iv. Indonesian Language (2 credit) b. University Content:
i. Thesis/ Skripsi (6 credits)
ii. Real Work Lecture -Practice (KKN-P) (3 credits)
iii. Entrepreneurship (3 credits)
iv. English Language (minimum 2 credit) c. Faculty Content :
i. Ethics of Profession (minimum 1 credit)
6. Information and Communication Technology Competency, (minimum 1 modules/ similar programs in accordance with the needs of the study program) at least 1 (one) type of computer applications recognized by the University.
7. Study load for the student of education program of engineer profession is as follows: a. Course:
b. Field Work Practice :
8. Study load for the student of the postgraduate education program (master) are as follows: a. Brawijaya University Compulsory Course:
i. Research Methods and Scientific Writing (3 credits) ii. English Language (2 credit)
iii. Computer science and its applications (2 credit) b. Study Program Compulsory Course (12-18 credits) c. Elective courses (6-15 credits)
d. Research and Thesis Writing (12-15 credits)
Total of study load at least 37 credits. Lectures study load a maximum of 18 credits per semester. The things related to the changes in the curriculum prescribed in the education guidelines of each Study Program.
9. Study load for the student of doctoral education program consist of: a. Brawijaya University Compulsory Course:
i. Research Methods and Scientific Writing (3-4 credits) ii. Computer science and its applications (2 credit) b. Study Program Compulsory Course (9-12 credits), c. Elective courses (0-12 credits)
d. Research and Dissertation Writing (28-32 sks)
Total of study load at least 44 credits. Lectures study load a maximum of 18 credits per semester.
10. The results of the competency test or assessment of students learning outcomes toward the institution compulsory course are set in the Guidelines Book of University
Education.
11. The requirements for the course of Information and Communication Technology Competency is set in the Guidelines Book of University Education.
12. Expertise Course is set in the Guidelines Book of each Department/ Study Program. 13. The study load in one semester is the number of credits that can be taken by a student in
the relevant semester.
14. Study load in the first year for the new student of the Bachelor program determined by each of Department/Study Program ranges between 12-24 credits/semesters.
15. Study load in the first semester for the new student of master education program and doctoral education program determined by each of Study Program ranges between 12-18 credits which is based on a package of courses or Grade Point/IP of Year Transfer Program/ PAT Program.
16. The study load that can be taken by a student for each semester is determined based on the Grade Point (GP) previous semester as far as it complies requirements prescribed with the following calculation:
Grade Point (GP) at previous
The maximum study load that can be taken in the following semester
semester
S1 Program S2 and S3 Program
GP 3,50 24 credits
3,00 GP 3,50 24 credits 18 credits
2,50 GP 3,00 21 credits 15 credits
2,00 GP 2,50 18 credits 12 credits
1,50 GP 2,00 15 credits -
GP < 1,50 12 credits -
Prerequisites may in the form of courses, tasks, Practicum, internship/work practice or seminar. The definition of Grade Point (GP) can be seen in Article 1 and regulated in Article 9.
Teaching Implementation Article 6
1. The Teaching Implementation refers to Semester Learning Plan/Rencana Pembelajaran Semester (RPS) which compiled by lecturers, approved by the Department/Study Program and openly communicated to students at the beginning of the lecture.
2. Implementation of the teaching emphasized on efforts of increasing the willingness and ability of students in finding, obtaining and processing science and technology.
3. Implementation of teaching can be conducted in the form of lectures, speeches, seminars, tutorials, discussions, practicum, studio, the working on independent and group task, field studies or undertake work practices.
4. To increase the quality of the teaching implementation, then at the faculty level is assisted by the Cluster of Quality Assurance/ Gugus Jaminan Mutu (GJM) and at the level of the Department/Study Program is assisted by Quality Assurance Unit/ Unit Jaminan Mutu and Group of Expertise Lecturer/ Kelompok Dosen Keahlian (KDK) and/ or Laboratory.
Assessment of Student Study Results Article 7
1. Assessment of the success of a student's study intended to assess the attitudes, understanding and the mastery of the material presented in the course.
2. Assessment of the success of a student's study conducted in a way by getting information about how far the students have achieved the objectives outlined in the curriculum through the implementation of examinations, task assessment and other activities.
3. To obtain information that approaches the precision needed to assess the ability of a student, conducted summative and formative evaluation which can be conducted with the following procedure:
a. Quiz/ task, at least twice in one semester.
b. Middle Test of the semester/Ujian tengah semester (UTS), written test conducted in the classroom in the middle of semesters and can be replaced in the form of test/ another task.
c. Final Test of the semester/ Ujian akhir semester (UAS), written test conducted in the classroom in the end of semesters and can be replaced in the form of test/ another task.
d. On certain courses, the assessment can be added from practicum implementation. e. Supporting Lecturers is obliged to deliver in a transparent way the details of the
evaluation to students.
4. Implementation method of the Quiz, Middle Test, and Final test can be conducted as follows:
a. Written test b. Oral test c. Task provision d. Preparation of papers e. Seminar
Assessment Guideline Article 8
1. Assessment of the success of a student's study for each course is based on three alternative assessments, as follows:
a. Using the system of Benchmark Reference Assessment/ Penilaian Acuan Patokan (PAP) namely by determining the pass mark/batas kelulusan.
b. Using the system of Normal Reference Assessment/ Penilaian Acuan Normal (PAN), namely by comparing the grade of a student with the grade of the group. c. Using a combination system of PAP and PAN, namely determine the grade of the
pass mark first, then compare the grade which relative passed with the group. It is suggested in the assessment system used PAN or a combination of PAN and PAP. d. The Results of the final assessment of the course expressed by Quality Letter /Huruf
Mutu (HM) and Quality Score/Angka Mutu (AM) as in the following table:
Quality Letter Quality Score Category
A 4 Very good
B+ 3,5 Between Very Good and Good
B 3 Good
C+ 2,5 Between Good and Sufficient
C 2 Sufficient
D+ 1,5 Between Sufficient and Less
D 1 Less
E 0 Very Less
e. Scoring in every activity can be conducted with Quality Letter (E-A) which is then converted to a Quality Score (0-4).
f. The Weight of the course assessment activities determined by the material balance of activities with the overall course material in one semester
2. The results of the evaluation mentioned in Article 7 of this Regulation can also be expressed in terms of a number between 0-100. This score includes an assessment of the attitudes and the responsibility of students.
3. As a guideline, Final score/Nilai Akhir (NA) of each course can be determined by the formula:
with :
NA : The achievement scores of students with rounding up to two digits behind the decimal point.
n : The number of quiz events. Bk : Weight of quiz grades. Bm : Weight of middle test grades. Bp : Weight of practicum grades. Bt : Weight of tasks grades. Ba : Weight of final test grades. Bs : Weight of activity.
Nk : Quiz grades. Nm : Middle test grades. Np : Practicum grades. Nt : Task grades. Na : Final test grades. Ns : Activity grade.
4. The final grade specified in section 2 may in the form of number grade and converted into a Quality Letter with the equality provisions as follows :
Number Grade Letter Grade
80 < N 100 A
75 < N 80 B+
69 < N 75 B
60 < N 69 C+
55 < N 60 C
50 < N 55 D+
44 < N 50 D
0 < N 44 E
5. Final grades of the Course is said valid if the student qualifies as follows: a. Officially registered as a student for the current semester.
b. Has fulfilled the requirements of academic administration prescribe. c. Has attended a minimum of 80% from lectures given by the lecturer.
d. Specific to the bachelor program, if the students programmed KKN-P, then the permission of KKN-P is recognized as a lecture with the duration appropriate with permissions of KKN-P, and follow the activities which there is a permission letter issued by minimum of Head of Department/Study Program.
6. If a student does not meet the requirements as mentioned in item 4, then the student given the grade of K (Equivalent to zero) for the lecture concerned and will be used in the calculation of grade point (GP) and considered not taking this course.
Grade Point Calculation Article 9
1. The success of a student's study is expressed with a Grade Point (GP)/ Indeks Prestasi (IP).
2. To calculate the Grade Point (IP), a letter grade is converted into the weight value with the following conditions:
Letter Grade Weight
A 4
B+ 3,5
B 3
C+ 2,5
C 2
D+ 1,5
D 1
E 0
Grade Point calculations conducted as follows:
with :
IP : Indeks Prestasi/ Grade Point
n : The number of course. K : Course credit grades.
NA : The final grade of the course in the form of a weighted grades (Article 8, section 2).
4. If a student has cancelled a course, then the course is not calculated in calculating the grade point.
5. In calculating the Grade Point Average/Indeks Prestasi Kumulatif (IPK), each course from all semesters that have been followed by the student is only counted one time and taken the best grade in the course, including the grade obtained in the short semester for the students of the bachelor education program.
Evaluation of Study Success Article 10
1. Evaluation of the study success of bachelor education program student conducted at: a. The end of the first year (two semesters).
c. The end of the second years (four semesters). d. The end of the third years (six semesters). e. The end of the fourth years (eigth semesters).
f. The end of the bachelor study program (after reaching 144 credits). g. The time limit for the study (fourteen semesters).
2. Evaluation of the success of master education program student and doctoral education program student conducted as follows:
a. For the students of master education program the evaluation conducted at the end of the first year and the end of the study/ (eight semesters).
b. For the students of doctoral education program the evaluation conducted at the end of the first year and the end of the fifth year/ deadline of the study (ten semesters for linear and eleven semesters for nonlinear).
3. Evaluation of the study success of bachelor education program student at the end of the first year:
a. Evaluation of the study success of bachelor education program student at the end of the first year (starting from the moment the student for the first time registered) is used to determine the continuation at the Faculty.
b. Students are allowed to continue their studies at the Faculty if meet the requirements as follows :
i. Collect at least 24 passed credits (without E grade and in accordance with the requirements of passing courses) with GPA > 2,00.
ii. If already accumulated more than 24 credits with GPA <2.0, then take the best 24 credits (without E grade) with GPA > 2,00.
c. If the student can not meet the requirements mentioned in Article 10 Section 3 Item b, the student is dismissed as the students of the Engineering Faculty.
4. Evaluation of the study success of bachelor education program student at the end of the second year:
a. Evaluation of the study success of bachelor education program student at the end of the second year (starting from the moment the student for the first time registered) is used to determine the continuation at the Faculty.
b. Students are allowed to continue their studies at the Faculty if meet the requirements as follows:
i. Collect at least 48 passed credits (in accordance with the requirements of passing courses) with GPA > 2,00.
ii. If already accumulated more than 48 credits with GPA <2,0, then take 48 passed credits with GPA> 2,00.
c. If the student can not meet the requirements mentioned in Article 10 Section 4 Item b, the student is dismissed as a student of the Faculty.
5. Evaluation of the study success of bachelor education program student at the end of the third year:
a. Evaluation of the study success of bachelor education program student at the end of the third year (starting from the moment the student for the first time registered) is used to determine the continuation at the Faculty.
b. Students are allowed to continue their studies at the Faculty if meet the requirements as follows :
i. Collect at least 72 passed credits (in accordance with the requirements of passing courses) with GPA > 2,00.
ii. If already accumulated more than 72 credits with GPA <2,0, then take 72 passed credits with GPA> 2,00.
c. If the student can not meet the requirements mentioned in Article 10 Section 5 Item b, the student is dismissed as a student of the Faculty.
6. Evaluation of the study success of bachelor education program student at the end of the fourth year:
a. Evaluation of the study success of bachelor education program student at the end of the fourth year (starting from the moment the student for the first time registered) is used to determine the continuation at the Faculty.
b. Students are allowed to continue their studies at the Faculty if meet the requirements as follows :
i. Collect at least 96 passed credits (in accordance with the requirements of passing courses) with GPA > 2,00.
ii. If already accumulated more than 96 credits with GPA <2,0, then take 96 passed credits with GPA> 2,00.
c. If the student can not meet the requirements mentioned in Article 10 Section 6 Item b, the student is dismissed as a student of the Faculty.
7. A student of the bachelor education program stated to have finished attending a lecture at one Department/ Study Program if already accumulated the amount of the credit score as many as 144 credits, with the terms as follows:
a. GPA > 2,00, b. None of E grade.
c. Total credits of the courses which has a grade of D and D +, not exceeding than 10% from the credits of courses that must be taken.
d. Has completed a thesis/skripsi.
e. Has completed the other academic task.
f. Already passed the Bachelor final exam and completed the revision of the thesis/skripsi.
g. Has met the administrative requirements.
8. In order to be able to graduated the student of bachelor education must be: a. Had the score of the certificate in English (TOEIC, IELTatau TOEFL).
b. Had a computer application program certificate value (IC3 minimum 1 modules/ similar programs in accordance with the needs of the study program) At least one (1) type of computer applications that recognized by the Faculty / University).
9. Completion time for bachelor education program study:
a. Completion time of the study provided the longest 14 (fourteen) semesters starting from the time the student first registered as a student.
b. If after fourteen (14) semesters a student has not met the conditions specified in Article 10 Section 7, students is dismissed as a student of the Faculty.
10. Evaluation of the study success of master education program student conducted as follows:
a. At the end of the second semester collect a minimum of 16 credits with GPA >2,75.
b. At the end of the fourth year has completed the entire load of lecture credits, thesis and scientific publications in national journals.
c. Students at the end of the first semester has not achieved GPA = 2,75 for the eight best credits will be given a warning.
d. If the student cannot meet these requirements in Article 10 Section 9 Items a and b, the student is dismissed as a student of the Faculty.
11. Evaluation of the study success of doctoral education program student conducted as follows:
a. At the end of the second semester collect a minimum of 16 credits with GPA >2,75. b. At the end of the fifth year (participants with the same field of education) or at the
end of the eleventh semester (participants with the different field of education) has completed the entire load credits of lectures, dissertations and scientific publications in international journals recognized by Higher Education.
c. If the student can not meet the requirements mentioned in Article 10 Section 10 Item a and b, the student is dismissed as a student of the Faculty.
12. A student during the lecture at a department/ study program was given the opportunity to fix the grade of the course during the study time limit allowed for him/her that has not to be surpassed. What is meant by fixing the value is with programing and retake the lecture with the following conditions:
a. Grade used for evaluation is the best grade.
b. The courses which received a D grade must be reprogram and C grade can be reprogram.
Special Exam Article 11
1. For the bachelor education program, Special exam is given to students who will be facing the Bachelor Final Exam, but the Grade Point Average (GPA) obtained less than 2,00 and or the grade of D/D+ more than 10% and or there is an E grade. Special exam only conducted once during the study period with terms as follows:
a. The courses that ever been followed the exams; b. Has completed all other academic prerequisites; c. The maximum tested 10 credits;
d. The maximum grade is A.
e. The mechanism of implementation determined by each of Department/ Study Program. 2. For postgraduate programs (master and doctoral), the implementation of special exam
along with the terms determined by the relevant Study Program.
Program of Short Semester/Semester Antara at S1 (Bachelor) Program
Article 12
1. Program of Short Semester is a program of lectures held at the break time of even semester/semester genap adjusted to the academic calendar of the Faculty. The implementation of Short Semester is set by each of the Department/ Study Program.
2. Program of Short Semester at the Faculty aims to increase the grade point average and shorten the study period and avoiding dropping out the study. Therefore the Short semester program has an alternative to:
a. Giving the opportunity to the student to improve the grade of the courses that have been taken.
b. Special program (summer course program) which provides an opportunity for outstanding students to graduate faster (3-3,5 year).
3. The implementation of the short semester program includes activities of face-to-face, structured task, independent task and a final test which is equivalent to a regular lectures study load.
4. Study load of the student of short semester equivalent to a study load of the regular semester.
5. Short semester implemented in the form of face to face at least 16 times, including Middle Test/UTS and Final Test/UAS.
6. Student load at most 9 credits with a maximum grade of Course taken is A. 7. Short Semester not taken into account in the calculation of the study period.
8. Particularly for the short semester program in order to improve the grade of the courses that have been taken are required:
a. The courses which can be programmed by the students in the Short semester is a courses that ever be taken by following all processes.
b. Curriculum and academic regulations in lectures of short semesters still refers to the curriculum and academic regulations applicable at that time, with the additional provision that the practice that has been passed is not necessary to repeat.
c. The maximum grade for the repeated courses is A.
Dual Degree Program
Article 13
1. The Dual degree education program is an educational programs which provide graduate degree from the two (2) different study programs for students who have qualified. 2. Students must have two (2) main competency from the two (2) study program in which
the student registered by completing the core curriculum in the form of the courses of: The Courses of Science and Skills/ Mata kuliah Keilmuan dan Keterampilan (MKK), The Courses of Work Skills/ Mata kuliah Keahlian Berkarya (MKB) and The Courses of Work Behavior/ Mata Kuliah Perilaku Berkarya (MPB) for each of study programs. 3. Students must have a supporting competency and other competency by completing the
institutional curriculum and other academic obligations by taking the courses which included in the group of Personality Development Courses/ Matakuliah Pengembangan Kepribadian (MPK) and Social life Courses/ Matakuliah Berkehidupan Bermasyarakat (MBB).
4. Compulsory courses which included in the group of Personality Development Courses/ MPK and Social life Courses/ MBB can be taken on one of two (2) study program in which the student registered.
5. The curriculum is assigned by Rector upon the recommendation of the Faculty / Program / Post Graduate Program.
6. Degree from the 2 (two) different study program given to students after completing the entire curriculum of dual degree program legally and in accordance with the provisions.
Double Degree Program Article 14
1. The Double degree education program is an educational program which provides a graduate degree from the same two (2) study program from the two (2) different institutions.
2. This program in its implementation should be based on the MOU from the two (2) institutions and obtain permission from the Ministry of education and culture.
3. The participating student of double degree studying at two (2) Higher Education in full-time and must meet the requirements set by the two (2) Higher Education in accordance with the agreement that has been agreed by the two (2) Higher Education.
4. The participating student of double degree eligible to receive an academic transcript that is a combination of the courses taken in two (2) Higher Education, the student is also eligible for receiving certificates from the 2 (two) Higher Education.
CHAPTER IV
ACADEMIC ADMINISTRATION
Implementation of Academic Administration Article 15
1. To carry out the academic activities required the administration which includes : a. Carry out the re-registration at the beginning of the semester.
b. Determination of the semester study plan of the student. c. The changes in student's study plan.
d. Lectures, assignments/task, seminars, practicum/studio activities and work practices. e. Quiz, Semester Middle Test/Ujian Tengah Semester (UTS) and Semester Final Test/Ujian
Akhir Semester (UAS).
f. Filling and validation of Study Results Card/ Kartu Hasil Studi (KHS).
g. Validation of student study result in the Report of Study Results and the form of Control Card.
2. The executing of academic administration carried out by the Faculty.
Student Registration Article 16
1. To be eligible for the academic activities, all students are required to enroll in the form of the administration and academic registration orderly. The administration and academic registration of new and old students the time is arranged in accordance with the academic calendar in the relevant year.
2. Specific for the new student of Bachelor program of Electrical Engineering, Department must have a certificate of not color blind before re-registration, specifically for Department of Architecture and Urban and regional planning, if declared partial color blindness then it is necessary to have an interview and specific tests at the Department concerned.
3. Specific for prospective students of master education program must have a Bachelor degree certificate (S1) in the same field, have a Grade Point Average 2,75 (on a scale 0-4) or 6,25 (on a scale 0-10). Having a Certificate of TPA OTO Bappenas with a administrative requirements must follow the Year Transfer Program/ Program Alih Tahun (PAT). Furthermore the GPA grade from this Year Transfer Program/ PAT program is used to determine study load in the first semester by considering the bachelor background.
5. Specific for prospective students of doctoral education program must have a certificate of Master of Engineering (for regular program) or Bachelor of Engineering (for fast track participants) which is in the same field with the selected study program at Doctoral Program of Engineering Faculty Brawijaya University, have a Grade Point Average 3,50 (on the scale 0-4); or have a GPA = 3.00 - < 3,50 and accompanied by at least four scientific work (journals, books, proceedings or similar). All the students candidate are obliged to follow Year Transfer Program/ PAT. Furthermore the GPA grade from this PAT program is used to determine study load in the first semester by considering the bachelor background. Background of Master education which considered in the same field is determined by each of the Doctoral Study Program.
6. For prospective students of doctoral education obliged to have a Certificate of TPA OTO BAPPENAS minimum 400 and Certificate of English equivalent TOEFL with a minimum score of 500/IB TOEFL minimum 60/ IELT minimum 5,5.
7. Prospective students of doctoral education program obliged to make draft plan of the dissertation research that will be taken during the doctoral education program.
8. Specifically for students from abroad for master education program and doctoral education program must have a certificate and the amount of credit equivalent to S1 program (for master prospective students) and equivalent to S2 (for doctoral education program) and have a certificate of English equivalent TOEFL with a minimum score 500/IB TOEFL minimum 60/ IELT minimum 5,5.
9. The terms of administration registration that must be fulfilled by the student following the requirements set by the University and the Faculty.
10. Students that not conducted or too late conduct re- registration for a semester without getting the approval of the Rector, declared inactive at that semester.
11. Inactive status taken into account in the determination of students study period and the tuition fees (UKT of each semester).
Academic Advisor Article 17
1. Academic Advisor/Penasehat Akademik (PA) is a lecturer assigned to guide students in accordance with the Department/Study Program in which he/she served.
2. Academic Advisor/Penasehat Akademik (PA) has the duties, authorities and responsibilities as follows:
a. Give explanations and instructions about the plan of the study taken by students under his/her guidance.
b. Provide guidance and advice in selecting several courses that accordance with a student's study plan under his/her guidance.
c. Provide guidance and advice on issues of academic and non-academic in connection with a student's study plan under his/her guidance.
3. Academic Advisor/ Penasehat Akademik (PA) directly responsible to the Head of Department/ Study Program concerned.
Study Plan Card and The Changes of Study Plan Article 18
1. Every registered student must fulfill Study Plan Card/Kartu Rencana Studi (KRS) each semester with the guidance and approval of the Academic Advisor.
2. Study load taken by students for each semester is set accordance with Article 5 Section 14.
3. Specific to master education program and doctoral education program the number of credits that can be taken for the first semester depends on the GP of Year Transfer Program/ PAT program namely:
GP of PAT Program The amount of credit that can be taken
GP ≥3,00 18 credits
2,75 GP 3,00 15 credits
GP < 2,75 12 credits
4. Every student who has been filling the Study Plan Card/ Kartu Rencana Studi (KRS) in accordance with Article 18 Section 1, with the approval of the Academic Advisor/ Penasehat Akademik (PA) can change the study plan with the deadline of the changes in accordance with academic calendar in the relevant year.
Semester Final Test Article 19
1. The assessment of Semester Final Test/Ujian Akhir Semester (UAS) is the responsibility of the lecturer concerned.
2. The implementation of Semester Final Test/ Ujian Akhir Semester (UAS) conducted by the Department / Study Program respectively in accordance with Faculty academic calendar.
3. The schedule of Semester Final Test/ Ujian Akhir Semester (UAS) must be carefully planned and announced to students and lecturers simultaneously with the announcement of the schedule of lectures.
4. Students must show all the requirements of the Final Test to Recording Section at the specified time.
5. The Supporting Lecturer of the course/ Dosen pengasuh mata kuliah must submitted a Final Grade to the Head of the Study Program in accordance with the prescribed time limit and maximum one week after Final Test/ Ujian Akhir Semester (UAS) conducted.
6. If supporting lectures of the courses not submitted the grades in accordance with the prescribed time limit after the Semester Final Test/ Ujian Akhir Semester (UAS), then the decision of Final Grade will be determined by the Dean upon the proposal of the Head of the Department/ Study Program.
7. If the student cannot follow the Semester Final Test/Ujian Akhir Semester (UAS) because of something that can be proven with real, then the department can organize supplementary Test with the time limit specified by the Head of Department/ Study Program.
Study Result Card Article 20
1. Head of Study Program after receiving the results of Final Grade for a course from the lecturer immediately sent it to the Head of Academic Affairs of the department for the record. The delivery of the assessment result should conducted immediately in order sooner could issued Study Result Card/ Kartu Hasil Studi (KHS) at the relevant semester, so that the academic schedule that has been set can be met.
2. Study Result Card/ Kartu Hasil Studi (KHS) each semester made in 4 (four) duplicate. One sheet is given to the academic Advisor to be used in guidance and counseling of the students, one sheet given to the students, one sheet submitted to the parents/ guardians of students, and one sheet again to be saved by academic recording.
Academic Leave Article 21
1. A student is allowed to apply for academic leave maximum of two years cumulative. Academic leave application conducted at least two weeks after the re-registration. 2. Academic leave of the student must obtain written approval from the Rector. To be
eligible for the academic activities again, the students must make a petition letter to the Rector to be active and register again in accordance with the provisions of applicable academic.
3. Time of academic leave is not calculated in the determination of the duration of the study. 4. During the time of academic leave, students not allowed to conduct the registered
academic activities.
5. Student has the right to submit academic leave since the first semester.
6. The deviation from Article 21 Section 1 may only be carried out with the written approval from the Rector.
Transfer Student Article 22
1. Transfer student is students who move/entrance into one of the Department/ Study Program in the Faculty that comes from :
a. Other universities,
b. Other faculties at the University,
c. Other Department/Study Program at the faculty.
2. Requirements to be met to apply for transfer to the Faculty are as follows:
a. Not a dropped out students and never get and/or currently undergoing academic sanctions from the previous department/study program.
b. The previous field/study program in accordance with in the Faculty.
c. The previous Study Program accredited by the National Accreditation Agency/BAN at least with B ratings.
d. Has been studying continuously at a previous university for:
i. Bachelor Program : minimum 2 (two) semester and maximum 3 (three) semester, under the condition:
- 2 (two) semester: has achieved at least 40 credits with GPA ≥ 3,00 or - 3 (three) semester: has achieved at least 60 credits with GPA ≥ 3,00. ii. Master Education Program : minimum 1 (one) semester and maximum 2 (two)
semester, under the condition:
- 1 (one) semester: has achieved at least 15 credits with GPA ≥ 3,00 or - 2 (two) semester: has achieved at least 30 credits with GPA ≥ 3,00.
iii. Doctoral Education Program: minimum 1 (one) semester and maximum 2 (two) semester, under the condition:
- 1 (one) semester: has achieved at least 15 credits with GPA ≥ 3,00 or - 2 (two) semester: has achieved at least 30 credits with GPA ≥ 3,00. e. Get permission/ approval to transfer from the previous universities, and submit
evidence of other legitimate academic activities.
f. Have a valid certificate for the results of Academic Potential Test/ Tes Potensi Akademik (TPA) issued by the competent institutions with a score ≥ 500 for the Bachelor and score ≥ 550 for master and doctoral education program.
g. Passed the Test of Equality.
3. The cost of Equality Test implementation and recognition of students learning outcomes from other universities is the responsibility of the transfer students.
4. Student submit a petition letter to the Rector of the University with a copy of a letter to Dean and the related Head of Department/ Study Program.
5. Transfer of Credit and Probation
a. Transfer of credit due to the transfer carried out by taking into account course’s completion at previous Higher Education / Faculty/ Deartment/ Study Program and consideration of the Department/ Study Program that accepts. The amount of credit that is transferred set by the Dean based on the proposal of the Head of Department/ Study Program.
b. For Bachelor Program, student transfer put on probation for two semesters, namely must collect at least 32 credits with GPA 2,00. If fails in probation, the student is dismissed.
c. Evaluation on the transfer student in accordance with applicable regulations by
considering the study period at previous Higher Education /Faculty/ Department/Study Program.
Recognition of Learning Outcomes from Other Higher Education Article 23
1. Based on Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between the Faculty/ University with other higher education institutions that have obtained the approval from the Director General of Higher Education, Students of the Faculty allowed to study in other universities to complete the part of activities/ the academic load.
2. Studying in other universities is the student participation in learning activities within a certain time at other universities, either inside and outside the nation, which has cooperation with the Faculty.
3. Activities/ academic load that can be achieved through learning activities in other universities is limited not more than 50% from academic load from applicable curriculum at the Department/ Study Program.
4. Studying in other universities, as mentioned in Article 24, Section 3 includes the participation of students in the form of activities :
a. Double Degree Program. b. Twinning Program. c. Sandwich Program.
d. Student Exchange Program.
e. Other academic programs that equal.
5. During the taking of learning activities in other universities legally, the student is exempt from tuition fees at the University.
6. The other terms related to the student's participation in the program as described in Article 24, Section 4 is set by the Rector.
7. The learning result from the activities/ academic load which taken legally, institutionally and qualified the academic requirement from other universities can be equalized after through verification.
8. The Dean formed a committee upon the recommendation of the Head of Department/ Study Program for verification tasks as mentioned in Article 24, Section 7.
9. All costs related to learning activities and the recognition of learning outcomes in other universities is the responsibility of the respective student.
10. Students who complete study load partially at other universities legally and passed the verification can be given a degree of graduation in accordance with the study program and levels of study that he/she passes.
Fast Track Doctoral Education Program Article 24
1. Fast track doctoral education program is an education program of strata 3 (S3) intended to obtain the highest academic degree for student participants of Bachelor program or master degree program with special or extraordinary intelligence potential and academic achievement.
2. The requirements for applicants from the Bachelor Program are as follows:
a. Graduated from universities and study program accredited by National Accreditation Agency/ BAN with rated minimum B.
b. Comes from the study program/field of science that the same field with doctoral studies program that will be taken.
c. For the graduates of S1 program, candidates must graduate with cum laude predicate with length of study is not more than 4 (four) years and three (3) months, or predicated Highly Satisfactory with GPA> 3,75 with length of study of not more than five (5) years and already have 1 (one) publications in international scientific journals in the appropriate field.
d. Obliged to follow the education program of enrichment/ stabilization for at least 1 (one) semester and graduated with GPA> 3,75.
3. The requirements for applicants from the master degree program are as follows: a. Have completed all courses (theory), without thesis, in accordance with the
provisions within not more than 1 (one) year with GPA >3,75.
b. At the time of graduates from Bachelor Program at least predicated Highly Satisfactory with GPA > 3,50 and the study period is not more than five (5) years. c. Have a valid certificate for the results of Academic Potential Test/ Tes Potensi
Akademik (TPA) from authorized institutions with score > 600 and English language proficiency with a score of Internet Based Test (IBT) TOEFL>73.
d. Meet other administrative requirements set by the master and doctoral education programs.
4. Study period of Fast track doctoral education program at least five (5) semesters, but not more than eight (8) semesters, calculated since graduated from Qualification Test. 5. Further provisions on the curriculum, Qualification Test and study period of Fast track
doctoral education program is set in the book of Educational Guidelines of each Department.
6. Student of master education program that switch status into Fast track doctoral education program obliged to pay all fees during registered as students in the master degree
8. Student of Fast track doctoral education program that comes from bachelor obligated to pay all costs of education since semesters 1 (one) in accordance with applicable regulations.
9. Student of Fast track doctoral education program which at the same time also taking a master degree program charged education fees as applicable to the double degree program education.
Academic Sanction Article 25
1. The types of fraud of academic administration are : a. Forgery of academic documents and signatures.
b. Falsify the Satisfied Letter, bribing, and falsify the data in the practicum and task processing.
c. Changing the content of Study Plan Card/Kartu Rencana Studi (KRS) and Study Result Card/Kartu Hasil Studi (KHS) illegally.
2. The types of fraud in academic activities is:
a. Cheated, take the work of other participants, cooperation during quizzes/ exams. b. Plagiarize the report of KKN-P (Bachelor study program), practicum/studio,
community service, tasks processing and thesis/skripsi, thesis/tesis and dissertation. 3. Determination of fraud established by the official report at the time of incident happened. 4. Student who commits fraud of academic administration, then all courses that
programmed in the relevant semester can be aborted.
5. Student who commits fraud in academic activities, namely quizzes, exams, practicum, processing the results of the task, KKN-P, then all the relevant semester study plan can be canceled according to the book of University Educational Guidelines.
6. Student who commits fraud on a course that is intended to be fixed the grades, then the aborted besides the courses that are programmed in the semester, as well as courses that will be fixed.
7. Student or alumnus who is convicted of fraud in the thesis (skripsi) / thesis (tesis) / dissertation (including plagiarism) then the academic degree is canceled and / expelled as a student of the Faculty.
8. Student who commits fraud twice as referred to in Article 26 Section 1 and 2 can be dismissed as a student.
9. Academic sanctions issued by the Dean after passing the process in the shortest possible time.
10. If the academic sanction in the form of a temporary suspension of the academic
activities, then the temporary suspension time is taken into account within the time limit of the study period.
11. Students who perform actions that may be defamatory almamater, may be subjected to the academic sanction which the type is determined by the Dean.
CHAPTER V
CURRICULUM, SYLLABUS AND SPECIAL REGULATIONS OF THE DEPARTMENT / STUDY PROGRAM
Article 26
Vision, Mission, Purpose, curriculum, syllabus and specific regulations of the Department/ Study Program set by each of the Department/ Study Program and submitted in another section of this Educational Guidelines
CHAPTER VI
THESIS/ SKRIPSI AND FINAL EXAM
Thesis/ Skripsi Article 27
1. Thesis/skripsi is a scientific paper based on research/ planning/ design/ survey/ literature study/ comparative study/ case study/ feasibility study in the field of engineering in accordance with the department/ study program.
2. Skripsi is the final project/task that must be prepared/ conducted by each student of Bachelor Program.
3. The requirement of skripsi taking determined by the Department /Study Program. 4. The thesis/skripsi topics chosen by the students or given by the lecturer, and approved by
the Head of Department/ Study Program.
5. The format of thesis/skripsi prepared according to the provisions set by the Faculty in the Writing Guidelines for Thesis/ Skripsi, Thesis/Tesis, and Dissertation.
Thesis/ Skripsi Purpose Article 28
The Skripsi processing is intended to provide basic provisions to students in preparing a written scientific work to poured the critical power, analysis and synthesis of students to a phenomenon or problem with regard to the development of science and technology on the study program concerned.
The Amount of Study Load and Time Limit of Thesis/ Skripsi Article 29
1. Skripsi has the amount of study load of 6 (six) credits.
2. The deadline for the completion and submission of thesis/skripsi to be tested is six (6) months from the date of the issuance of Assignment Letter. Extension is only allowed with the approval of the Head of Department/Study Program with consideration of the Supervisors/ Dosen Pembimbing.
Qualification, Provision, Rights and Obligations of Supervisor/ Dosen Pembimbing Article 30
1. In the preparation of thesis/ skripsi the student is guided by one or more the Supervisors. 2. Preparation of thesis/ skripsi guided by one lecturer or more which at least has the Assistant Professor/Lektor positions with Master academic qualifications, or Instructor/Asisten Ahli with Doctoral academic qualifications in an appropriate field of science, or in one clump of science that in accordance with the study program in which the student is registered.
3. The Duties of Supervisors/ Dosen Pembimbing:
a. Assist the students in finding the problems that can be used as the topic of the thesis/skripsi.
b. Assist the students in the preparation of the thesis/ skripsi.
c. Giving the thesis/ skripsi grades for the students under his/her guidance. d. Accompanying the students during final exams.
4. Supervisors of thesis/ skripsi determined by the Dean upon the recommendation of the Head of Department/ Study Program.
5. The deviation from Article 31 Section 2 is determined by the Dean upon the recommendation of the Head of Department / Study Program.
Assessment of Learning Outcomes for Thesis/ Skripsi Article 31
1. The results of student learning on the implementation of the skripsi are assessed starting from the process of proposal preparation, implementation, reporting and examination. 2. Thesis/ skripsi is tested by Board of Examiner Lecturer/ Majelis Dosen Penguji which
shall be a minimum of 3 (three) persons, including Supervisors.
3. Qualification of Examiner Lecturer/ Dosen Penguji at least equal with the qualification of Supervisors/ Dosen Pembimbing.
Equality of Students Written Creative Scientific Work with Thesis/ Skripsi
Article 32
1. In the case of substance /Thesis material written by the student become 1 (one) articles in accredited national scientific journals /international journal (indexed by Scopus, ISI Thomson Reuters, Microsoft Macromedia, Ebsco, Proquest and others that recognized by the Ministry of Education and Culture in the appropriate field of science can be recognized equally with Thesis), the students remain obliged to compile the thesis but without the exam and stated the Thesis/ skripsi passed with A grade.