THE EFFECTIVENESS OF NUMBERED HEAD TOGETHER
(NHT) TO IMPROVE FLUENCY OF SPEAKING ABILITY OF
THE 2
ndGRADE STUDENTS AT JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL
MDIA BONTOALA MAKASSAR
A THESIS
Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of SarjanaPendidikan in English Education Department of
Tarbiyah and Teaching Science Faculty of UIN Alauddin Makassar
By
RAHMADANI S. Reg. No. 20400113033
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TARBIYAH AND TEACHING SCIENCE FACULTY
UIN ALAUDDIN MAKASSAR
viii
COVER PAGE ... i
PERNYATAAN KEASLIAN SKRIPSI... ii
PERSETUJUAN PEMBIMBING ... iii
PENGESAHAN SKRIPSI ... ... iv
D. Research Significance ... 4
E. Research Scope ... 5
F. Operational Definition of Term ... 5
CHAPTER II REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURES ... 14
A. Review of Relevant Research Findings ... 14
B. Some Pertinent Ideas ... 16
1. Definition of Speaking ... 15
2. Definition of NHT (Numbered Head Together) ... 15
C. Theoretical Framework ... 18
D. Hypothesis ………... 19
D. Research Instrument ... 22
E. DataCollectingProcedure ... 22
F. Data Analysis Technique ... 23
CHAPTER IV FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION ... 27
ix
1. Result of the students’ pre-test in Experimental and Control
Class ... 27
2. Result of the students’ post-test in Experimental and Control Class ... 30
B. Discussion ... 35
CHAPTER V CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS ... 38
A. Conclusions ... 38
B. Suggestions ... 39 BIBLIOGRAPHY
APPENDICES
x
Table 1.3 The rate precentage of score control class in pre-test... 30 Table 1.4 The rate percentage of score control class in post test ... 32 Table 1.5 The mean score and standard deviation of experimental class
and control class in pre-test ... ... 33 Table 1.6 The mean score and standard deviation of experimental score
xi
LIST OF FIGURES
xii
Score of Students’ Pre Test and Post Test in Control Class
APPENDIX III The Mean Score of Experimental and Controlled Class ... 45
APPENDIX IV Standart Deviation of Experimental and Controlled Class ... 46
APPENDIX V The significance Difference ... 48
xiii
The Effectiveness of Numbered Head Together (NHT) to Improve Fluency of Speaking Ability of the 2ndGrade Students at Junior High School MDIA Bontoala Makassar
Dr. H. Abd. Muis Said, M.Ed. TESOL. Dr. H. Erwin Hafid, Lc, M.Th.I. M.Ed.
The objective of this research was to find out an empirical data, to see whether or not numbered head together method effective to improving students’ fluency of speaking ability. This research was held in August to September 2017 at Junior High School MDIA Bontoala Makassar.
The method used in this research was quantitative method in design of quasi experimental study.The sampling technique used in this study was purposive sampling. The subject of this research is second grade students and samplesare VIII A as experimental classand VIII B as controlled class. Instrument the used in this study is speaking test consist of pre-test and post-test.
The result of this research shows that using NHT method is effective in improving students speaking ability in fluency. It can be seen from mean of post test in experimental class (11,92) is higher than controlled class (7,5). The data analyzed by using T-test formula. The result of calculation showed that the value of test > t-table (8,5 >2,013).Therefore, it proves that alternative hypothesis (H1) which state there is a significant progress in using NHT method in improving students’ speaking ability in fluency is accepted.
1
English as a foreign language in Indonesia is taught at Junior High School (SMP/MTs) as a compulsory subject. The implementation of English teaching at present is based on the Content Standard. Its target is to have the students reach an informational level of literacy. It means that the students are expected to be able to access knowledge by using English.
English is also a need in this globalization area. The student are expected to have skills of the English Language such as reading, writing, listening and speaking because language is a tool of communication. Learning is the one of the most important activities in which human engage. It is at the very core of the educational process, although most of what people learn occurs outside of school x for example, giving a connection with the stranger.
2
a record of performance in the form written tests, speaking output is transient, with little record of it once the activities are over ( Christine C. M. Goh : 2007 ).
Speaking is one of the important and essential skills that must be practiced to communicate orally. By speaking people be able to know what kinds of situations the world. People who have ability in speaking will be better in sending and receiving information or message to another. Speaking is the process of building and sharing meaning through the uses of verbal and non verbal symbol in various contexts.
Speaking skill is very important thing and it must be developed. Since itcan be used in sharing ideas or information directly from one to other people through speaking or conversation, it can obtain ideas, messages and information.The goal of teaching speaking skills is to communicate efficiency. Learners should be able to make themselves understood, using their current proficiency to the fullest. So, it also must be supported by a good learning method.
model of Numbered Heads Together (NHT). This learning model focuses on specific
structure that is designed to influence students’ interaction pattern and have purpose
to increase academic achievement, which the students are divided into groups and every student in group has the different numbers, then teacher gives task and each group works on it by discussing, then teacher calls one of the students and the students report their group-work that would be respond by other groups members. (Ibrahim, 2000).
In reality of learning English especially to speaking is hard for some students because they only speak English. They do not pay attention to the sentence structure and correct pronunciation. The students are afraid of making mistake in speaking English. It indicates that the students have limited vocabulary. The teacher dominates
in teaching the students using Indonesian, so it can not increase students’ speaking
ability.The teachers usually use monotone technique, such as giving tasks, so the students are usually lazy to speak English with their teachers and with their friends. So, in order to get further causes why the students difficult to speak English in the classroom. It is needed a research dealing with the teaching and learning English especially in speaking. It can be seen in the following they do not have a self-confidence.
4
Based on the problem above, the researcher is interested in conducted a
research entitled “The Effectiveness of Numbered Heads Together (NHT) to Improve
Fluency of Speaking Ability of the 2nd Grade Students at Junior High School MDIA
Bontoala Makassar”.
B.Problem Statement and Research Questions
Based on the background and the phenomena on students learning achievement by using learning model of Numbered Heads Together (NHT), the problem of this research is identified in the following identification:
How is Cooperative Learning Model Numbered Head Together (NHT) effective to improve fluency of speaking ability at the 2nd grade Junior High School MDIA Bontoala Makassar ?
C.Research Objectives
To find out the effectiveness of using Numbered Heads Together (NHT) to improve fluency of speaking ability of the 2nd grade students at junior high school MDIA Bontoala Makassar.
D.Research sinificance
1. Theoritical Significant
The result of this research expected to become an empirical media to support the implementation theories using Numbered Head Together (NHT).
a. For student this research expected to help the stedent get a chance to speak in front of their friends.
b. For the teacher this researcher gave contrubution and information to English teacher about the effectiveness of Numbered Head Together (NHT) Method, that can improve their model of teaching in order that the students were not bored in learning English and can improve their fluency of speaking ability. c. For the next researcher this research expected to gave great contribution and
information to the other researcher as a reference for further studies on a similar topic.
E. Research Scope
To make the research clear, the researcher was scope the variables in this research. What the research attempt to find in this research was whether NHT can improve students’speaking ability or not, speaking ability that the researcher tend about fluency. For the place, the research conducted at the second grade of junior
high school MDIA Bontoala Makassar . The reseacher focuses in teaching fluency of
their idea by using NHT Method. The method that used in this research was Experimental Design in form Nonequivalen Control Group Design.
F. Operational Definition of Terms
There are two components discussed in this research like speaking ability, and Numbered head together (NHT) method . The researcher would like to give definition
6
1) Speaking
Generally, speaking can be described as the ability of person to express their idea, feeling, or something in his or her mind to the other people by using the spoken language.Therefore, speaking is a productive skill.Speaking is one of the language skills and it is a tool of communication and the most important factor in teaching language well.
Speaking is a prominent skill among the others, it is the application after mastering other language skill such as listening, reading, and writing. These can not be separated each other, therefore it is important to practice speaking a lot to develop our ability, because no one can achieve the maximum goal without practicing.
a. Grammar
It is needed for students to arrange a correct sentence in conversation. It is in line with explanation suggested by Heaton (1978 ) that student’s ability to manipulate structure and to distinguish appropriate grammatical form in appropriate one. The utility of grammar is also to learn the correct way to gain expertise in a language in oral and written form.
Grammar is used to refer to a number of different things, it can be use to refer to books that contain descriptions of the structure of a language, it can be used to refer to the knowledge that a native speaker has of his or her language and to describtions of that knowledge, it can be used to refer to a set of rules developed to control certain aspects of the usage of native speakers, and it can be use to refer to a
set of rules typically taugh in school about “appropriate usage” and about writing.
(http://wsu.edu>Grammar_Book>Chapter1)
b. Vocabulary
8
c. Pronounciation
Pronunciation is the way for students’ to produce clearer language when they
speak. It deals with the phonological process that refers to the components of a grammar made up of the elements and principles that determine how sounds vary and pattern in a language. There are two features of pronunciation; phonemes and supra segmental features. A speaker who constantly mispronounces a range of phonemes can be extremely difficult for a speaker from another language community to understand.
d. Fluency
Fluency can be defined as the ability to speak fluently and accurately. Fluency in speaking is the aim of many language learners. Sign of fluency include a
reasonably fast speed of speaking and only a small number of pauses and “ums” or “ers”. These signs indicate that the speaker does not have to spend a lot of time
searching for the language items needed to express the message and idea.
the students level in this study. They are: Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair, Poor and Very Poor.
Based on the description above, the researcher concluded that ability is the power of understanding a matter that involves both mental and physical after they get some experiences through learning. Learning ability here refer to the ability of students in speaking English.
Many English students regard speaking ability as the measure of knowing a language. These students define fluency as the ability to converse with others, much more than the ability to read, write or comprehend oral language. They regard speaking as the most important skill they can acquire and they asses their progress in terms of their accomplishment in spoken communication.
2) Teaching Speaking
10
Speaking is a crucial part of second language learning and teaching. Despite its importance, for many years, teaching speaking has been undervalued and English language teachers have continued to teach speaking just as a repetition of drills or memorization of dialogues. However, today's world requires that the goal of teaching speaking should improve students' communicative skills, because, only in that way, students can express themselves and learn how to follow the social and cultural rules appropriate in each communicative circumstance.
Teaching speaking, in my opinion, is the way for students to express their emotions, communicative needs, interact to other person in any situation, and influence the others. For this reason, in teaching speaking skill it is necessary to have clear understanding involved in speech.
Teaching speaking is to teach English language learners to:
a. Produce the English speech sounds and sounds patterns.
b. Use words and sentence stress, intonation patterns and the rhythm of the second language.
c. Select appropriate words and sentences according to the proper social setting, audience, situation and subject matter.
d. Organize their thoughts in a meaningful and logical sequence. e. Use language as a means of expressing values and judgments.
which is called fluency. (Nunan, 2003) 3) Fluency
Hornby (2005: 165) said that “Fluency is able to speak a language easily and
well ”. According to Shamjaya, 2011 he assesst the fluency into smoothness and self-confidence.
a. Smoothness
Smothness is the ability of Speaking English through a good clustering and reducing forms (Brown, 1980:267). A good clustering is to speak English with phrasal fluently. It means that speaking English not word and reduce form are to use English with contaction, elosion and reduce vowels.
b. Self-Confidence
12
4) Numbered Head Together ( NHT )
NHT is a cooperative learning model where students in small groups divided into to 4-6 persons. Students learn and cooperate collaboratively with heterogenic group structure.
This structural approach is used as an alternative toward traditional class approach, where teachers ask question to students and then students answer after rise their hand or have been asked by teacher. The structural cooperative learning approach happens after students discuss the answer of the question, then teacher would call a certain number, students whose number is called have to raise their hand and answer the question for the class. This structure expects the students cooperate in small group and teacher give group appreciation than individual appreciation.
5) The Steps of Learning Numbered Heads Together (NHT)
Cooperative learning with structural Number Heads Together (NHT) is executed in four steps. First step Numbering. Teacher divides the students into groups consistingof 4-6 persons and each member of the group would have number among 1-6.Second step Submitting Question. Teacher asks the question to the students.The question can be varied, specific or in interrogative form. Third step Collective Thinking. Students elaborate opinion toward the answer of the question, and make
their hand. The teacher asks one of the students whose number has been called to present the result of his group. (Ibrahim, 2000)
14
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter divided into four main sections, namely review of related research finding, pertinent idea, theoretical framework, and hypothesis.
A. Previous of Related Findings
Sasli afandi (2011) conducted a research with a title “ The Effectiveness of Numbered Head Together (NHT) Toward Speaking Ability of the Student at the First
Year of Senior High School Selatpanjang Kepulauan Meranti Regency”, found that
teaching speaking use NHT (Numbered Heads Together) method in Emotion Expression Topic very helpful for increasing students’ speaking ability the first year
of Senior High School of Selat panjang Kepulauan Meranti Regency.
Identit Vigur Prasetyo (2015) in his research “Improving Speaking Skills of
Grade VIII B Students of SMP Negeri Jogonalan Through Numbered Heads Together
Strategy in the Academic Year of 2014/2015”, found that teaching speaking skills use NHT (Numbered Head Together) strategy very helpful for improving students’
speaking skill of Grade VIIIB of SMPN 1 Jogonalan in Academic Year of 2014/2015.
Ana Wahyu Dwi Andari (2012) in her research “ Teaching Speaking Skill Using Numbered Head Together to 8th Grade Student of SMP Negeri 2 Gatak
method is successful to make students more active in learning proccess at the 8th Grade student of SMP Negeri 2 Gatak 2011/2012.
Moh Lutfi Aziz (2016) on the research “The Effectiveness of Using Numbered
Heads Together (NHT) Technique Towards Students’ Achievement in Speaking of the
Eight Greaders At Mts N Ngantru Tulungagung”, found that teaching speaking use NHT (Numbered Head Together ) effective to get a significant score for speaking of the Eight Greaders at Mts N Ngantru Tulungagung.
Maria Videlis (2011) under the title “Implementing Numbered Head Together Stratey to Improve the Speaking Ability of the tenth Greaders of Marketing
Department in SMKN 1 Lumajang”, found that the numbered head together can help students to both students’ speaking ability and students’ speaking participation of the tenth greaders of marketing department in SMKN 1 Lumajang.
Based on previous research which related to the method examined by the researcher, all of that showed effective results in give NHT method to improve student’s speaking ability. All reviewer that the researcher showed to discuss about
improvement of student’s speaking ability with NHT method but in another aspect
16
B. Some Pertinent Ideas
1. Definition of speaking
Speaking is a complex skill because it is concerned with component of grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation, fluency ( Syakur, 1987 ). Speaking is one of the important and essential skills that must be practiced to communicate orally. By speaking people are able to know what kinds of situations the world. People who have ability in speaking will be better in sending and receiving information or message to another. Speaking is the process of building and sharing meaning through the uses of verbal and non verbal symbol in various contexts.
Speaking is the one of the important parts in English skills that should be mastered by students besides reading, writing and listening. The fuction of speaking skill are to express and idea, some feeling, thought and it express spontaneously by orally. Speaking is the one of the language art of talk as communication interaction with someone, and it is very difficult to master it. Speaking skill is have a closely relationship with listening skill, in speaking act, the students must be listening and then speak up, because speaking is not only remembering and memorizing the sentences in written but speaking is spontaneous to show the students idea by orally.
2. Definition of Numbered Heads Together ( NHT )method.
pattern and have purpose to increase academic achievement, which the students are divided into groups and every student in group has the different numbers, then teacher gives task and each group works on it by discussing, then teacher calls one of the students and the students report their group-work that would be respond by other groups members. (Ibrahim, 2002).
18
C. Theoritical Framework
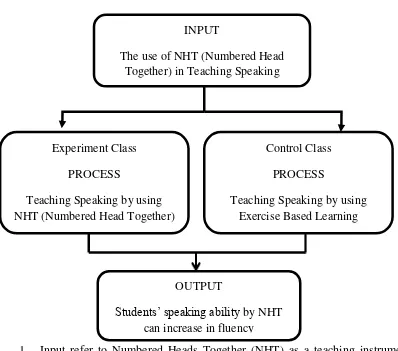
The theoritical framework in this research presented by the following diagram : FIGURE 1.1
1. Input refer to Numbered Heads Together (NHT) as a teaching instrument that was expected to be a good way to teaching Speaking Ability.
2. Process was which works through treatments in Speaking Ability that use two classes were experimental class and controlled class. In experimental class the researcher will teach Speaking Ability by using Numbered Heads Together (NHT), while in controlled class teach by the teacher using Exercise based Learning. When the researcher observed in controlled class
INPUT
The use of NHT (Numbered Head Together) in Teaching Speaking
Students’ speaking ability by NHT can increase in fluency
Control Class PROCESS
the teacher teach speaking by giving task to the students after that the student must collect the task and reading a loud by the teacher’s point.
3. Output, refers to students’ improvement on speaking ability by using Numbered Head Together (NHT).
D. Hypothesis
H1: Numbered Heads Together (NHT) method can improve fluency of students’ speaking ability in the second grade of junior high school MDIA Bontoala Makassar.
H0: Numbered Heads Together (NHT) method can not improve fluency of students’speaking ability in the second grade of junior high school MDIA
20 CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD
This chapter deals with research method, population and sample, variables and instrument, data collection procedures, data analysis techniques and statistic procedures.
A.Research Design
The design of this research was Quasi Experimental Design. In this case the researcher wants to know the effectiveness of NHT method to improve the students’
fluency of speaking ability.
This is a model of Quasi-Experimental design, exactly Non-equivalent Control Group design :
FIGURE 1.2
Where :
O1O2 : Pre-test
X : Treatment for experimental class by using Numbered Head Together Method O3O4 : Post-test
( Sugiyono, 2010) This method was appropriate in the research because it can describe whether Numbered Heads Together (NHT) method effective to improve students’ speaking ability in fluency or not. Besides that, the researcher can easly conduct this method
O1 X O2
because the researcher can use purposive sampling because only pre-experimental and quasi-experimental design can use it.
B.Research Variable
There are two variables in this research, they were independent variable and dependent variable :
a. Independent variable
The independent variable was Numbered Heads Together (NHT) method, which the teaching aids that help the students to get a chance to speak up in front of their friend. Independent variable affected to dependent variable. It was show how the use of the NHT method can improve students’ fluency.
b. Dependent variable
The dependent variable was students’ fluency in speaking ability. Dependent variable was affected by independent variable.
C.Population and Sample
1. Population
22
2. Sample
In this research, the sample only two classes the researcher was apply the total sampling. In this case, the researcher choosed class VIII A as a experimental class and class VIII B as a controlled class. Each of the classes consist of 24 students in VIII A and 24 students in VIII B, therefore the total number of sample is 48 students. D.Research Instrument
To obtain the data, the researcher will use test of speaking, namely pre-test and post-test. The test used to find out the students’ beable to speakingby using NHT method. The speaking will be administered in the pre-test and post-test. The pre-test will be intended to assess the students’ speaking before use NHT method and the post-test will administered to know the result of the application of the use of NHT method. Both of the pre-test and post-test become inventory test.
E. Procedure of Collecting Data
1. Pre-test
To collect the data, the researcher was administer a pre-test to both classes. It tested to the students and assessed by the researcher based on speaking rubric.
2. Treatment
3. Post-test
After gave the treatments, post-test was given to the students. It aim to know whether the implementation of Numbered Heads Together(NHT) method improve the students’ speaking ability or not. Like pre-test, post-test also assessed based on
speaking rubric.
F. Technique of Data Analyses
After conducting pre-test and post-tests in the experimental class and
thecontrolled class, the results both of the tests in the each class was analyzed together. to see if there is any constructing from one another (O2-O1) – (O4-O3) (Sugiyono, 2010). To calculate the mean score of the students’ answer of pre-test and
post-test, the researcher used the formula as follow:
1. Classifying the score answer of speaking test into the following : a. SmoothnessAssessment
Classification Score Criteria
Excellent 12 Speech on all professional and general topics as effortless and smooth as a native speaker’s
Very Good 10 Speech was effortless and smooth, but perceptively non-native in speed and evenness
24
some unevenness caused by rephrasing and grouping for words
Fair 6 Speech was frequently hesitant and jerky, sentences may be left uncompleted Poor 4 Speech was very slow and uneven except
for short or routine sentences
Very Poor 2 Speech was so hairing and fragmentary that conversation was virtually impossible
(Adam in Hughes, 2003 : 132-133) b. Self – Confidence Assessment
Classification Score Criteria
Excellent 6 Thier speech is very understandable and high of self-confidence
Very Good 5 Their speaking is very understandable and very good of self-confidence
Good 4 They speak effectively and good of smoothness
Fair 3 They speak sometimes hasty but fairly good of self confidence
Very Poor 1 They speak hasty and more sentences no self confidence
( Adam in Hughes, 2003 :133)
2. Scoring the students’ correct answer of pretest and postest
∑
= mean score ∑ = sum of all scores
N = total number of the respondents
(Sugiyono, 2010) 3. The formula used in calculating the standard deviation is:
SD = √ , where SS= ∑X2 ∑
SD = standard deviation SS = the sum of square
N = total number of the subjects ∑x2
= the sum of all square; each score is squared and all thesquares are added up
(∑x)2
= the square of the sum; all the scores are added up and the sum is square, total.
26
4. The formula will be used in finding out the difference between students’ score in Pre-Test and in Post-Test is:
̅ ̅
√( ) ( )
Where:
t = test of significance
̅1 = mean score of experimental group
̅2 = mean score of controlled group
SS1 = sum square of experimental group SS2 = sum square of controlled group
n1 = number of students of experimental group n2 = number of students of cotrolled group
27
A. Findings
The findings of this research were based on the result of the data analysis. The data analysis used to collect the data. The researcher took the data by using speaking test about described familys’ name. The test consisted of pre-test and post-test. The pre-test was given to find out the students’ background knowledge on speaking ability before applying NHT (Numbered Head Together) method and the post-test was given to find out the enhancement of the students’ speaking ability after gave the
treatment.
The effectiveness of NHT method to students’ speaking ability after applied
can be seen from the result of students’ speaking score in the rate percentage in
experimental class, which used smoothness and self-confidence assessment.
1. The Classification of Students’ pre-test scores in Experimental Class This page the table show the distribution of frequency and percentage of final score of students’ speaking ability at the second grade of junior high school MDIA
28
Table.1.1
The rate percentage of score experimental class in pre-test a. Smoothness Assessment
No Classification Score Frequency Percentage
1 Excellent 12 0 0%
2 Very Good 10 0 0%
3 Good 8 0 0%
4 Fair 6 0 0%
5 Poor 4 7 26%
6 Very Poor 2 17 74%
Total 24 100%
b. Self Confidence Assesment
No Classification Score Frequency Percentage
1 Excellent 6 0 0%
2 Very Good 5 0 0%
3 Good 4 6 25%
4 Fair 3 3 12,5%
5 Poor 2 12 50%
6 Very Poor 1 3 12,5%
Table 1.1 shows that the rate percentage and frequency of the students’ experimental class in the pre-test7 (26%)students got poor score,17 (74%) students got very poor score in smoothness assessment and 6 (25%) students got good score, 3 (12,5%) got fair score, 12 (50%) got poor score, and 3 (12,5%) got very poor score in self confidence assessment.
Table 1.2
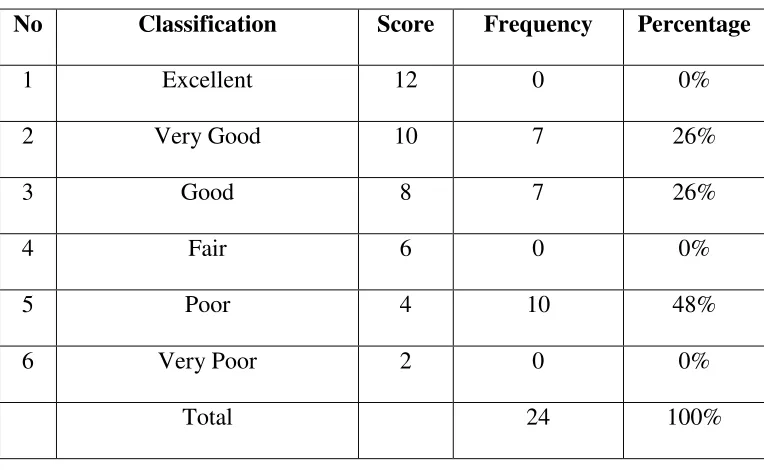
The rate percentage of score experimental class in post test a. Smoothness Assessment
No Classification Score Frequency Percentage
1 Excellent 12 0 0%
2 Very Good 10 7 26%
3 Good 8 7 26%
4 Fair 6 0 0%
5 Poor 4 10 48%
6 Very Poor 2 0 0%
Total 24 100%
b. Self Confidence Assesment
No Classification Score Frequency Percentage
30
Table 1.2 shows that in the post test there were students 7 (26%) got in Very Good and Good score, 10 (48%) students got poor score in smootheness assessment and 14 (52%)students got very good, 10 (48%) got good score in self confidence
MDIA Bontoala Makassar in pre-test and post-test scores in control class. Table 1.3
The rate precentage of score controlled class in pre-test a. Smoothness Assessment
No Classification Score Frequency Percentage
1 Excellent 12 0 0%
3 Good 8 0 0%
4 Fair 6 0 0%
5 Poor 4 3 12,5%
6 Very Poor 2 21 87,5%
Total 24 100%
b. Self Confidence Assesment
No Classification Score Frequency Percentage
1 Excellent 6 0 0%
2 Very Good 5 0 0%
3 Good 4 0 0%
4 Fair 3 0 0%
5 Poor 2 6 25%
6 Very Poor 1 18 75%
Total 24 100%
32
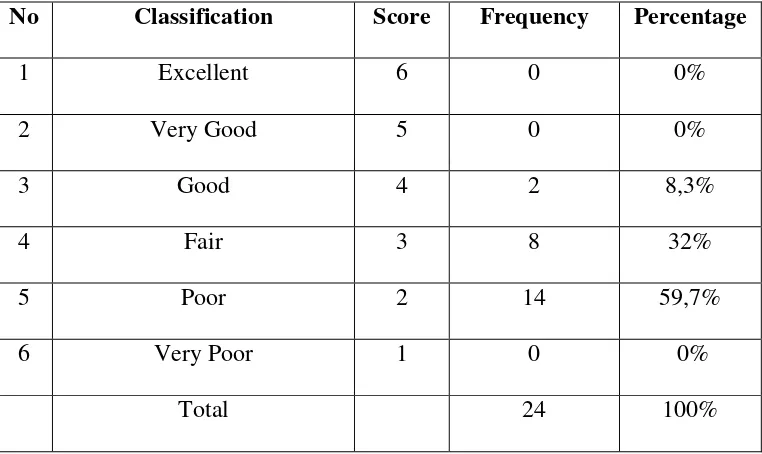
Table 1.4
The rate percentage of score control class in post test a. Smoothness Assessment
No Classification Score Frequency Percentage
1 Excellent 12 0 0%
2 Very Good 10 0 0%
3 Good 8 2 8,3%
4 Fair 6 8 32%
5 Poor 4 14 59,7%
6 Very Poor 2 0 0%
Total 24 100%
b. Self Confidence Assesment
No Classification Score Frequency Percentage
1 Excellent 6 0 0%
2 Very Good 5 0 0%
3 Good 4 2 8,3%
4 Fair 3 8 32%
5 Poor 2 14 59,7%
6 Very Poor 1 0 0%
Table 1.4 shows that in the post test there were students 2 (8,3%) got in Good score, 8 (32%) students’ got in Fair score, 14 (59,7%) students got poor score in smootheness assessment and in self confidence assessment.
2. The mean score and standard deviation of Experimental Class and Controlled Class
After calculated the result of the students score, the mean score and standard deviation of both classes can be presented in the following table :
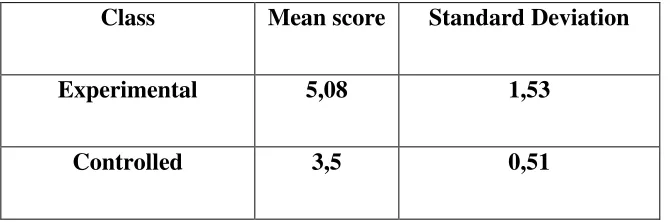
Table 1.5
The mean score and standard deviation of experimental class and controlled class in pre-test
Class Mean score Standard Deviation
Experimental 5,08 1,53
34
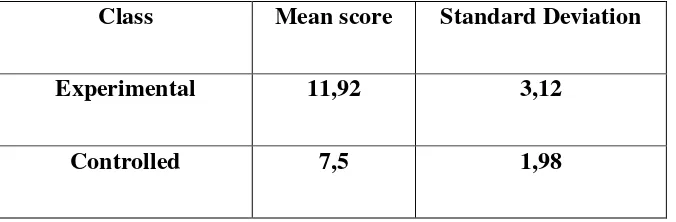
Table 1.6
The mean score and standard deviation of experimental score and controlled class in post-test
Class Mean score Standard Deviation
Experimental 11,92 3,12
Controlled 7,5 1,98
The table 1.5 shows that, the mean score of experimental class in pre-test was (5,08) and the standard deviation of experimental class was (1,53) and the mean score of the controlled class in the pre-test was (3,5) and the standart deviation was (0,51). While the mean score of the experimental class in post-test was (11,92) and the standard deviation was (3,12) and the mean score of controlled class in post-test was (7,5) and the standard deviation was (1,98). It can be concluded from both of the classes that the experimental class obtained the higher mean score in the post test than the controlled class.
3. Test of significance Testing
Table 1.7
Distribution the value test of t-test and t-table in post-test Variable t-test value pre-test and post-test t-table value
X₁ - X₂ 7,5 < 8,5 2,013
The table 1.7 showed the result from test of significance testing. The table showed that the value of the t-test in post test was higher than t-test in pre-test and the t-test in post-test higher than t-table value. The result of the test in post test clearly showed that there was a significant difference between the students’ score in the experimental and controlled class before and after the treatment NHT (Numbered Head Together). It indicate that the NHT (Numbered Head Together) was effective in
improving students’ Fluency of Speaking Ability. It meant H0 was rejected and H1
was accepted because the t-test was higher than t-table (8,5>2,013). Therefore, the hypothesis of the research was accepted.
B. Discussion
36
different number for each group. Group learning outcomes are brought individually in front of the students according to the number that calls by the teacher randomly. So it could be that they were more confidence to speak in front of their friends and have a chance for each students to show their knowledge by randomly number called.
In this study, several things have been logically concluded. First, for both classes, they tend to have the same problem, they have difficulty in speaking ability. For example when they do a pre-test, most of them are difficult to speak up in front of the students. Second, subjects in the experimental class indicate that they have a great desire in the learning process. For example, they are enthusiastic to speak related to the topic. Third, experimental class students showed improvement after applying Numbered Heads Together (NHT) method.
Analysis of the mean score gap in the post-test between the experimental and control ensured if the approach used was effective. The mean score of the experimental class was 11,92 and 7,5 for control class. It means the gap of the students’ score of the experimental and control class was 4,42. The explanation of the
gap between the two classes indicated that the experimental class showed higher improving than the control class while the control class scores were decreased.
Based on the result of the study, the researcher concluded that the students’
was also proven by the result of T-test. The result of T-test was higher than T-table (8,5> 2,013). Based on the hypothesis testing, it means that H0 (Null hypothesis) was rejected and H1 (Alternative Hypothesis) is accepted. Therefore, the hypothesis in this research (H1) stated that “ The use of NHT (Numbered Head Together) method was effective to improve students’ speaking ability in fluency of second grade students at
Junior High School MDIA Bontoala Makassar is accepted.
38 CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
This chapter presents the conclusions as well as few suggestions of this study. Suggestions were taken based on findings and conclusions obtained in this research.
A.Conclusion
The findings of the research are :
1. Numbered Head Together method used in teaching speaking and improving speaking ability at the 2nd grade Junior High School MDIA Bontoala Makassar. The result of data analysis showed that the total score of the experimental class students in post test is 276 and 180 for the control class. In addition, the post test average score for the experimental class was 11,92 and 7,5 for the controll class. The data indicates that the students’ grade in the experimental class is higher than control class. This
means that NHT method is more effective than conventional methods of teaching.
2. There is a significant difference between speaking ability of students by using NHT method and conventional method in second grade of Junior High School MDIA Bontoala Makassar. The result of analysis data showed that the students’ competence in the experimental class is higher
hypothesis (H1) is accepted. This means that theNumbered Head Together ( NHT ) applied in the Experiment class effectively to improve Students’ Speaking Ability.
B.Suggestions
In relation to the conclusion above, the researcher proposes the following offers:
1. For the teacher
It is important for the teacher to make the class situation especially in teaching speaking more interesting rather than having stressful atmosphere. The teacher can use NHT to make students enjoy learning and improving their speaking ability. NHT gives students chance to develop their ideas, promote effective team work, learn to criticize, exchange ideas, and learn to speak in front of the people, and be fluence in speak english by their idea. Thus, NHT not only develop students’ academic skill but also social skill.
2. For the student
40
3. To the other researcher
41
BIBLIOGRAPHY
A Murni., Ervi Yenni., Natalina and Irianti. 2009. Model-ModelPembelajaran Inovatif dan Media. Pekanbaru : DepartemenPendidikan Nasional, Panitia Sertifikasi Guru (PSG) Rayon05 FKIPUniversitas Riau.
Afandi, Sasli. 2011. The Effectiveness of Numbered Head Together (NHT) Toward Speaking Ability of the Student at the First Year of Senior High School SelatpanjangKepulauanMeranti Regency.
Arikunto, Suharsimi. 2006. Prosedur Penelitian Suatu Tindakan Praktek. Jakarta : PT. Rineka Cipta.
Aziz, Moh Lutfi. 2016. The Effectiveness of Using Numbered Heads Together (NHT) Technique Towards Students’ Achievement in Speaking of the Eight Greaders At MtsNNgantruTulungagung.
Babbie, Earl R. 2010. The Practice of Social Research. 12th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Cengage.
C.M Goh, Christine. 2007. Teaching Speaking in the Language Classroom. Republic of Singapore : SEAMEO Regional Language Centre.
Dwi Andari, Ana Wahyu. 2012. Teaching Speaking Skill Using Numbered Head Together to 8th Grade Student of SMP Negeri 2 Gatak 2011/2012.
Gordon, Lynn. 2008. English Grammar. Washington State University.
Heaton, J.B. 1978. Writing English Language Tests (Longman Handbooks for Language Teachers).
Herdian. 2009. ModelPembelajaran NHT. http://www.google.co.id/amp/s/
herdi07.wordpress.com/-2009/04/22/modelpembelajaran-nht-numbered-head-together/ amp diakses tanggal 23 oktober 2017.
Hornby, AS. 1995. Oxford Advance Learners Dictionary of Current English. Oxford : Cambridge University Press.
Hughes, Arthur. 2003. Testing For Language Teacher Second Edition. England: Cambridge University press.
Ibrahim, M. & Nur, M. 2000.Pembelajaran Kooperatif. Surabaya: University Press. Mujis, Daniel. 2010. Doing Quantitative Research in Education with SPSS 2nd
edition. London : SAGE Publication.
42
Shamjaya. 2011. Improving Students’ Speaking Ability through Community Interaction Activities (A Classroom Action Research at the Second Year Students of SMA Negeri 1 Sinjai Selatan Kabupaten Sinjai).
Sugiyono. 2010. Metode Penelitian Pendidikan Pendekatan Kuantitatif, kualitatif, dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Sugiyono. 2014.Skripsi, Tesis, dan Disertasi, Yogyakarta : IKAPI.
Syakur. 1987.Language Testing and Evaluation. Surakarta : Sebelas Maret University Press.
Videlis, Maria. 2011. Implementing Numbered Head Together Stratey to Improve the Speaking Ability of the tenth Greaders of Marketing Department in SMKN 1 Lumajang.
43 APPENDIX I
Score of Students’ Pretest and Posttest in Experimental Class
45
APPENDIX III
The Mean Score of Experimental Class and Controlled Class
A. Experimental Class 1. Pre-test
̅1 =
̅1
2. Post-test ̅1 =
̅1
B. Controlled class 1. Pre-test
̅2 =
̅2
2. Post-test ̅2 =
48
APPENDIX V The significant Difference
̅1 = 5.083 SS1 = 53.83
̅2 = 3.5 SS2 = 6
1. T-test in pre – test
̅ ̅
√(
) (
)
√(
) (
)
√(
) (
)
√( )( )
√
49
̅1 = 11,92 SS1 = 224
̅2 = 7,5 SS2 = 90
2. T-test in post - test
̅ ̅
√(
) (
)
√(
) (
)
√(
) (
)
√( )( )
√
t
hitung =8,53. T-table
For level of significance (D) =0,05
50
APPENDIX VI Distribution of t-Table
Df
Level of Significance for two-tailed test
0,5 0,2 0,1 0,05 0,02 0,01
Level of Significance for one-tailed test
51
56
A.
KOMPETENSI INTI
Mata Pelajaran : Bahasa Inggris Kelas / Semester : VIII/GanjilMateri Pokok :(a) meminta perhatian, (b) mengecek pemahaman,
(c)menghargai kinerja yang baik, dan (d) meminta / mengungkapkan pendapat serta responnya
Chapter 1 May I Have Your Attention, Please? ( LKS )
Asking for and giving attention
Checking understanding,
Giving appreciation
Asking for and giving opinion. Alokasi Waktu : 8 x 40 Menit (4 TM)KI 3 : Memahami dan menerapkan pengetahuan (faktual, konseptual, dan prosedural) berdasarkan rasa ingin tahunya tentang ilmu pengetahuan, teknologi, seni, budaya terkait fenomena dan kejadian tampak mata.
57
B.
Kompetensi Dasar dan Indikator
No Kompetensi Dasar Indikator
1. 1.1 Mensyukuri kesempatan
dapat mempelajari bahasa
Inggris sebagai bahasa
pengantar komunikasi
internasional yang
diwujudkan dalam semangat belajar.
1.1.1 Mengungkapkan rasa
syukur atas kesempatan dapat belajar bahasa Inggris
2. 2.2 Menunjukkan perilaku jujur,
disiplin, percaya diri, dan
bertanggung jawab dalam
melaksanakan komunikasi
transaksional dengan guru dan teman.
pada saat mengerjakan tugas
2.2.3 Berani mengakui
kesalahan yang telah dilakukan
2.3 Menunjukkan perilaku
tanggung jawab, peduli,
kerjasama, dan cinta damai,
dalam melaksanakan
komunikasi fungsional
2.3.1 Berani mengakui
kesalahan yang telah dilakukan
2.3.2 Bertanggung jawab atas
tindakan anggotanya
saat menjadi pemimpin kelompok.
58
unsur kebahasaan untuk
melaksanakan fungsi sosial
dari ungkapan meminta
perhatian, mengecek
pemahaman dan menghargai
kinerja yang baik, dan
meminta dan
mengungkapakan pendapat,
serta responnya, sesuai
dengan konteks
penggunaannya
penggunaan ungkapan meminta perhatian serta responnya secara lisan
dan tulis dengan
struktur teks yang
runtut degan unsur
kebahasaan yang benar
yang sesuai dengan
secara konteks.
3.1.2Menjelaskan tentang
ungkapan menghargai kinerja yang baik serta responnya secara lisan
dan tulis dengan
struktur teks yang
runtut degan unsur
kebahasaan yang benar
yang sesuai dengan
pendapat serta responnya
untuk melakukan
komunikasi secar
interpersonal degan
59
struktur teks yang runtut
dengan unsur
kebahasaan yang benar
yang sesuai dengan
secara konteks .
4. 4.1 Menyusun teks sederhana
untuk mengucapkan dan
merespon ungkapan meminta
perhatian, mengecek
pemahaman ,dan mengecek kinerja yang baik meminta
dan mengungkapkan
pendapat dengan
memperhatikan fungsi sosial, struktur teks yang dan unsur kebahasanaan yang benar dan sesuai konteks
4.1.1Mengungkapkan
pendapat dengan
memperhatikan fungsi
sosial, struktur teks yang dan unsur kebahasanaan yang benar dan sesuai konteks
4.1.2Mendemonstrasikan penggunaan ungkapan mengecek pemahaman serta responnya secara lisan dan tulis dengan
struktur teks yang
runtut degan unsur
kebahasaan yang benar
yang sesuai dengan
60
D. Materi pembelajaran
Setelah mengikuti serangkaian kegiatan pembelajaran;
Melalui pengamatan siswa terampil memahami , menyatakan , dan menanyakan teks lisan dan tulis untuk meminta perhatian mengecek pemahaman ,menghargai kinerja yang baik dan meminta atau menggungkapkan pendapat serta responnya, untuk melaksanakan komunikasi interpersonal dengan guru dan teman.
Melalui diskusi siswa dapat mnggunakan ungkapan dengan struktur teks yang runtut dengan unsur kebahasaan yang benar dengan unsur kebahasaan yang benar dan sesuai konteks, secara jujur, disiplin, percaya diri, bertanggung jawab, peduli, kerjasama, dan cinta damai. (sikap, pengetahuan, keterampilan)
Melalui pengamatan siswa dapat memperagakan atau memodelkan berbagai ungkapan dengan struktur teks dan unsur kebahasaan yang benar dengan percaya diri dan kerjasama
Misalnya :
a) Attention please , excuse me. b) Understood , is it clear. c) That’s great, excellent.
62
F. Media, Alat dan sumber
pembelajaran
G. Langkah – Langkah Pembelajaran
Pembelajaran
1. Pendekatan : Scientific
2. Model : Cooperative learning
3. Metode : Numbered Head Together (NHT)
1. Media : Gambar
2. Alat/bahan : Spidol and paper
3. Sumber belajar : Buku LKS
Pertemuan Pertama
No Langkah-Langkah Kegiatan Pembelajaran
1. Pendahuluan (10 menit )
Menyapa Peserta didik (greeting) Mempersiapkan kelas oleh leader Memeriksa lingkungan belajar
Mengecek kehadiran dan memotivasi Peserta didik Menjelaskan tujuan pembelajaran
2. Kegiatan inti (60 menit)
Guru membagi siswa dalam beberapa kelompok dengan masing
masing kelompok terdiri dari 4-5 anggota dan setiap anggota diberi nomor (sebagai acuan dalam presentasi).
Guru memberikan materi tentang asking and giving attention kepada siswa untuk di diskusikan.
63
Guru memberikan siswa lembar percakapan asking and giving attention.
Siswa bekerjasama dalam kelompoknya untuk menyelesaikan lembaran yang diberikan, guru membimbing dan mengarahkan siswa dalam menyelesaikan tugasnya.
Guru membahas hasil kegiatan tersebut dengan memanggil
siswa satu nomor tertentu untuk menjawab
pertanyaan/masalah yang dibahas.
3. Penutup (10 menit)
Setelah mengikuti kegiatan pembelajaran pada pertemuan ini, Peserta didik ditanya bagaimana perasaannya (REFLEKSI).
Guru memberikan pertanyaan untuk mengetahui apakah
Peserta didik sudah memahami topik tentang “penggunaan ungkapan attention.”
Peserta didik diminta membuat kesimpulan pembelajaran pada pertemuan ini
64
Menyapa Peserta didik (greeting) Mempersiapkan kelas oleh leader Mereview materi sebelumnya
Mengecek kehadiran dan memotivasi Peserta didik Menjelaskan tujuan pembelajaran
2. Kegiatan inti (60 menit)
Mengamati
Peserta didik mengamati dialog yang guru berikan pada siswa.
Menanya (Disampaikan secara lisan tentang langakahnya)
Dengan bimbingan dan arahan guru, Peserta didik menanyakan ungkapan pengecek pemahaman siswa.
Mengumpulkan informasi
Peserta didik diperlihatkan 2 dialog tentang percakapan mengenai mengecek pemahaman (to check understanding).
Guru menjelaskan secara singkat penggunaan ungkapan
mengecek pemahaman (to check understanding). dan responnya.
Mengasosiasi
Peserta didik dibagi 4 kelompok besar, dengan cara membagikan nomor kepada masing masing siswa sebagai penanda saat akan mempresentasikan hasil diskusi mereka. Setiap kelompok mendiskusikan kemudian membuat dialog
terkait dengan ungkapan mengecek pemahaman (to check understanding) dengan mengisi bubble teks.
Guru membimbing setiap kelompok sesuai dengan
permasalahannya.
Mengomunikasikan
65
Guru memberikan refleksi dengan memberikan koreksi
terhadap struktur teks dan unsur kebahasaan dari ungkapan attention.
3. Penutup (10 menit)
Setelah mengikuti kegiatan pembelajaran pada pertemuan ini, Peserta didik ditanya bagaimana perasaannya (REFLEKSI).
Guru memberikan pertanyaan untuk mengetahui apakah
Peserta didik sudah memahami topik tentang “ungkapan
mengecek pemahaman (to check understanding).”
Peserta didik diminta membuat kesimpulan pembelajaran pada pertemuan ini.
66
Menyapa Peserta didik (greeting) Mempersiapkan kelas oleh leader Mereview materi sebelumnya
Mengecek kehadiran dan memotivasi Peserta didik Menjelaskan tujuan pembelajaran
2. Kegiatan inti (60 menit) Mengamati
Peserta didik mengamati penjelasan yang guru berikan.
Menanya (Disampaikan secara lisan tentang langakahnya)
Dengan bimbingan dan arahan guru, Peserta didik menanyakan ungkapan menghargai kinerja yang baik.
Mengumpulkan informasi
Peserta didik diperlihatkan dialog tentang percakapan mengenai menghargai kinerja yang baik (giving appreciation) oleh guru.
Guru menjelaskan secara singkat penggunaan ungkapan
menghargai kinerja yang baik (giving appreciation) dan responnya pada peserta didik .
Mengasosiasi
Peserta didik dibagi 6 kelompok kecil, dengan cara membagikan nomor kepada masing masing siswa sebagai penanda saat akan mempresentasikan hasil diskusi mereka.
Setiap kelompok berdiskusi kemudian membuat dialog terkait dengan ungkapan menghargai kinerja yang baik (giving appreciation).
Guru membimbing setiap kelompok sesuai dengan
permasalahannya.
Mengomunikasikan
Setiap kelompok mempresentasikan hasil kerja dan dialog yang mereka buat di depan kelas dengan di wakili oleh siswa yang di sebut nomornya oleh guru.
67
3. Penutup (10 menit)
Setelah mengikuti kegiatan pembelajaran pada pertemuan ini, Peserta didik ditanya bagaimana perasaannya (REFLEKSI).
Guru memberikan pertanyaan untuk mengetahui apakah Peserta
didik sudah memahami topik tentang “ungkapan mengecek
pemahaman (to check understanding).”
Peserta didik diminta membuat kesimpulan pembelajaran pada pertemuan ini.
68
Menyapa Peserta didik (greeting) Mempersiapkan kelas oleh leader Mereview materi sebelumnya
Mengecek kehadiran dan memotivasi Peserta didik Menjelaskan tujuan pembelajaran
2. Kegiatan inti (60 menit) Mengamati
Peserta didik mengamati penjelasan yang guru berikan tentang asking for and giving opinion.
Menanya (Disampaikan secara lisan tentang langakahnya)
Dengan bimbingan dan arahan guru, Peserta didik menanyakan ungkapan tentang memberi dan menerima pendapat.
Mengumpulkan informasi
Peserta didik diperlihatkan dialog tentang percakapan mengenai memberi dan menerima pendapat(asking and giving opinion) oleh guru.
Guru menjelaskan secara singkat penggunaan ungkapan
memberi dan menerima pendapat (asking and giving opinion) pada peserta didik .
Mengasosiasi
Peserta didik dibagi 5 kelompok besar, dengan cara membagikan nomor kepada masing masing siswa sebagai penanda saat akan mempresentasikan hasil diskusi mereka.
Setiap kelompok berdiskusi kemudian membuat dialog terkait dengan ungkapan memberi dan menerima pendapat (asking and giving opinion).
Guru membimbing setiap kelompok sesuai dengan
permasalahannya.
Mengomunikasikan
Setiap kelompok mempresentasikan hasil kerja dan dialog yang mereka buat di depan kelas dengan di wakili oleh siswa yang di sebut nomornya oleh guru.
69
struktur teks dan unsur kebahasaan dari giving appreciation. 3. Penutup (10 menit)
Setelah mengikuti kegiatan pembelajaran pada pertemuan ini, Peserta didik ditanya bagaimana perasaannya (REFLEKSI).
Guru memberikan pertanyaan untuk mengetahui apakah Peserta
didik sudah memahami topik tentang “ungkapan mengecek
pemahaman (to check understanding).”
Peserta didik diminta membuat kesimpulan pembelajaran pada pertemuan ini.
70
B.
Kompetensi Dasar dan Indikator
A.
KOMPETENSI INTI
Mata Pelajaran : Bahasa Inggris Kelas / Semester : VIII/Ganjil
Materi Pokok : Teks lisan dan tulis mengenai (a) mengungkapkan dan menanyakan tentang kemampuan, (b) mengungkapkan dan menanyakan tentang memampuan keinginan.
Chapter 1 May I Have Your Attention, Please? ( LKS )
Stating and asking about ability
Stating and asking about willingness Alokasi Waktu : 4 x 40 Menit (2 TM)KI 3 : Memahami dan menerapkan pengetahuan (faktual, konseptual, dan prosedural) berdasarkan rasa ingin tahunya tentang ilmu pengetahuan, teknologi, seni, budaya terkait fenomena dan kejadian tampak mata.
KI 4 : Mengolah, menyaji, dan menalar dalam ranah konkret (menggunakan, mengurai, merangkai, memodifikasi, dan membuat) dan ranah abstrak (menulis, membaca, menghitung, menggambar, dan mengarang) sesuai dengan yang dipelajari di sekolah dan sumber lain yang sama dalam sudut pandang/teori.
No Kompetensi Dasar Indikator
1. 1.1 Mensyukuri kesempatan
dapat mempelajari bahasa
Inggris sebagai bahasa
1.1.1 Mengungkapkan rasa
71
bertanggung jawab dalam
melaksanakan komunikasi
transaksional dengan guru dan teman.
pada saat mengerjakan tugas
2.2.3 Berani mengakui
kesalahan yang telah dilakukan
2.3 Menunjukkan perilaku
tanggung jawab, peduli,
kerjasama, dan cinta damai,
dalam melaksanakan
komunikasi fungsional
2.3.1 Berani mengakui
kesalahan yang telah dilakukan
2.3.2 Bertanggung jawab atas
tindakan anggotanya
saat menjadi pemimpin kelompok.
2.3.3 Tidak menyalahkan
orang lain atas
tindakannya sendiri
3. 3.1 Menerapkan struktur teks dan
unsur kebahasaan untuk
melaksanakan fungsi sosial dari ungkapan kemampuan dan keinginan , sesuai dengan
3.1.1Mendeskripsikan
penggunaan ungkapan
kemampuan serta
responnya secara lisan
dan tulis dengan
72
3.1.2Menjelaskan tentang
ungkapan keinginan
serta responnya secara lisan dan tulis dengan
struktur teks yang
runtut degan unsur
kebahasaan yang benar
yang sesuai dengan
secara konteks.
4. 4.1 Menyusun teks sederhana
untuk mengucapkan dan
merespon ungkapan
kemampuan dan keinginan dengan memperhatikan fungsi sosial, struktur teks yang dan
unsur kebahasanaan yang
benar dan sesuai konteks
4.1.1Mengungkapkan
kemampuan dengan
memperhatikan fungsi
sosial, struktur teks yang dan unsur kebahasaan yang benar dan sesuai konteks.
4.1.2Mendemonstrasikan penggunaan ungkapan keinginan secara lisan
dan tulis dengan
struktur teks yang
runtut degan unsur
kebahasaan yang benar
yang sesuai dengan
73
C. Tujuan pembelajaran
D. Materi pembelajaran
Setelah mengikuti serangkaian kegiatan pembelajaran;
Melalui pengamatan siswa terampil memahami , menyatakan , dan menanyakan teks lisan dan tulis untuk menyatakan kemampuan, serta keinginan, untuk melaksanakan komunikasi interpersonal dengan guru dan teman.
Melalui diskusi siswa dapat mnggunakan ungkapan dengan struktur teks yang runtut dengan unsur kebahasaan yang benar dengan unsur kebahasaan yang benar dan sesuai konteks, secara jujur, disiplin, percaya diri, bertanggung jawab, peduli, kerjasama, dan cinta damai. (sikap, pengetahuan, keterampilan)
Melalui pengamatan siswa dapat memperagakan atau memodelkan berbagai ungkapan dengan struktur teks dan unsur kebahasaan yang benar dengan percaya diri dan kerjasama
Materi Pokok :
Teks lisan dan tulis mengenai (a)mengungkapkan dan menanyakan kemampuan , (b) mengungkapkan dan menanyakan keinginan.
74
E. Metode pembelajaran
F. Media, Alat dan sumber
pembelajaran
G. Langkah
–
Langkah Pembelajaran
Pembelajaran
- Ucapan , tekanan, dan intonasi.
- Ejaan dan tanda baca
Struktur Teks :
(ungkapan hafalan, tidak perlu dijelaskan tata bahasanya)
a. Nina, can you help me ?, can you teach me ? dan semacamnya.
b. will uou marrie me ?, will you go ?, will you drink ? dan semacamnya.
1. Pendekatan : Scientific
2. Model : Cooperative learning
3. Metode : Numbered Head Together (NHT)
1. Media : Gambar
2. Alat/bahan : Spidol, and paper 3. Sumber belajar : Buku LKS
Pertemuan Pertama
No Langkah-Langkah Kegiatan Pembelajaran
1. Pendahuluan (10 menit )
75
Mengecek kehadiran dan memotivasi Peserta didik Menjelaskan tujuan pembelajaran
2. Kegiatan inti (60 menit)
Guru membagi siswa dalam beberapa kelompok dengan masing
masing kelompok terdiri dari 4-5 anggota dan setiap anggota diberi nomor.
Guru memberikan materi tentang stating and asking about ability kepada siswa untuk di diskusikan.
Dengan aktif siswa mencermati dan mengamati penjelasan dari guru.
Guru memberikan siswa lembar percakapan stating and asking about ability.
Siswa bekerjasama dalam kelompoknya untuk menyelesaikan lembaran yang diberikan.
Guru membimbing dan mengarahkan siswa dalam
menyelesaikan tugasnya.
Guru membahas hasil kegiatan tersebut dengan memanggil siswa
dengan satu nomor tertentu untuk menjawab
pertanyaan/masalah yang dibahas.
3. Penutup (10 menit)
Setelah mengikuti kegiatan pembelajaran pada pertemuan ini, Peserta didik ditanya bagaimana perasaannya (REFLEKSI).
Guru memberikan pertanyaan untuk mengetahui apakah Peserta didik sudah memahami topik tentang “ungkapan kemampuan.” Peserta didik diminta membuat kesimpulan pembelajaran pada
pertemuan ini
76
Menyapa Peserta didik (greeting) Mempersiapkan kelas oleh leader Memeriksa lingkungan belajar
Mengecek kehadiran dan memotivasi Peserta didik Menjelaskan tujuan pembelajaran
2. Kegiatan inti (60 menit)
Guru membagi siswa dalam beberapa kelompok dengan masing
masing kelompok terdiri dari 4-5 anggota dan setiap anggota diberi nomor.
Guru memberikan materi tentang stating and asking about willingness kepada siswa untuk di diskusikan.
Dengan aktif siswa mencermati dan mengamati penjelasan dari guru.
Guru memberikan siswa lembar percakapan stating and asking about willingness.
Siswa bekerjasama dalam kelompoknya untuk menyelesaikan lembaran yang diberikan, guru membimbing dan mengarahkan siswa dalam menyelesaikan tugasnya.
Guru membahas hasil kegiatan tersebut dengan memanggil siswa satu nomor tertentu untuk menjawab pertanyaan/masalah yang dibahas.
3. Penutup (10 menit)
Setelah mengikuti kegiatan pembelajaran pada pertemuan ini, Peserta didik ditanya bagaimana perasaannya (REFLEKSI).
Guru memberikan pertanyaan untuk mengetahui apakah Peserta didik sudah memahami topik tentang “penggunaan ungkapan keinginan.”