CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED STUDY
This thesis focuses on modalities found in expressed by Hillary Clinton in a
speech that deals with the concepts of Discourse Analysis, the concepts of Systemic Functional Linguistic (SFL), and the concept of Modalities of functional grammar. The explanation of each field of study is as follows:
2.1 THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
2.1.1 An overview of Discourse Analysis
A discourse is not simply an organized collection of words, it is the distillation in verbal form of the thoughts and outlook of the communicator (Mann and Thompson, 1992:5). In understanding of a discourse does not tell about the
structure of the text or language system only, but primarily know about the meaning which is the meaning mostly use verbal form. Man and Thompson state that verbal
forms are signals, signals of the meaning which the speaker or writer wishes to convey.
In discourse studies, the focus has been solely on the written or spoken forms
for too long (Renkema, 2009:2). In this case of description, the writer will be analyzing a text such a speech as an object description which is produced as spoken discourse. The text is often seen as unproblematically given but this is misleading, as
a spoken discourse shows particularly well: one has to produce a ‘text’ by transcribing speech, but there are all sorts of ways found in one might transcribe any
transcribes it (Fairclough, 1989:26). Halliday as cited in Webster (2002:4) states that
a text as an instance of social meaning in a particular context of situation.
Trapes and Lomax: state that the discourse analyst’s particular contribution to
this otherwise mundane activity is to do the noticing consciously, deliberately, systemactially, and as far as possible, objectively, and to produce accounts (descriptions, interpretations, explanations) of what their investigations have
revealed.
Discourse analysis is concerned with the study of the relationship between
language and the contexts found in it uses written texts of all kinds and spoken data, from conversation to highly institutionalized forms of talk such as newspaper articles, letters, stories, recipes, instructions, notices, comics, billboards, leaflets
pushed through the door, speech, debate, and so on (McCarthy, 1991:5).
Renkema (2004:282-285) as cited in Renkema (2009:277) states that the method of discourse analysis is developed into context of critical discourse analysis.
Moreover, the term of discourse is central to critical discourse analysis.
Critical discourse analysis as a framework to explain how discourse is
influenced by the social, economic and political world (Van Leeuwen as cited in Renkema, 2009:8).
In critical discourse analysis (CDA), the broader ideas communicated by a text are referred to as discourses and the process of doing CDA involves looking at choices of words and grammar in texts in order to discover the underlying discourses
Van Dijk (1993:252) as cited in Renkema (2009:277) states that critical
discourse analysis is methodologically electic: it chooses and elaborates theories, methods and empirical work as a function of their relevance for the realization of socio-political goals.
2.1.2 Systemic Functional Linguistic (SFL)
Systemic Functional Linguistic (SFL) is very useful descriptive and
interpretive framework for viewing language as a strategic, meaning making resource (Halliday as cited in Eggins, 2004:2). Obviously, in learning about language refers to
know about what the system. Language is as one of the semiotic system that represents a resource to create meaning. A language is a resource for making meaning, and meaning resides in systemic patterns of choice (Halliday and
Matthiessen, 2004:23).
SFL is that the ways in which we can create meaning through language are organized through patterns of use (Fontaine, 2013:5). Halliday (1994:xxix) as cited
in Eggins (2004:2) states that SFL is the one which will provide the framework to understand the quality of texts; why a text means what it does, and why it is valued
as it is. Therefore SFL can be determined through the meaning potentials of language as emphasize the code of language, utterances of the language and specify of all the text which have all the meaning potentials.
2.1.3 Metafunction
In analyzing of Systemic Functional Linguistic (SFL) is the notion of
terms of metafunctions, it concludes that the one of metafunction term consist as
modality and mood. The term of metafunction is interpersonal function. The interpersonal function is called as clause exchange. For interpersonal function embodies all uses of language to express social and personal relations. In
interpersonal options, those in the systems of mood, modality, person, key, intensity, evaluation, comment and the like, tends to be determined by the role relationships in
the situation (Halliday, 2002:56). So this is quite different from the expression of content mainly in language, such as both interactional and personal: there is, in other words, a component in language which serves at one and the same time to express
both the inner and the outer surfaces of the individual, as a single undifferentiated area of meaning potential that is personal in the broadest sense (Halliday, 2002:92).
In addition, interpersonal function is concerned with enacting interpersonal relations through language, with the adoption and assignment of speech roles, with the negotiation of attitudes, and so on - it is language in the praxis of intersubjectivity, as
a resource for interacting with others (Halliday and Matthiessen, 1999:7).
2.1.4 Modality
These intermediate degrees, between the positive and negative poles, are known collectively as modality (Halliday, 1994:88). In a statement the modality is an
2.1.4.1 Functional Account of Modality
2.1.4.1.1 Modalization
Modality may be categorized as the area of meaning that lies between yes and
no (Halliday, 1994:356). In determining the intermediate ground between positive and negative polarity can be found into category of modality such as modalization and modulation. Modalization refers to the modality of propositions as information,
for instance: statements and questions.
In the proposition, the meaning of the positive and negative poles are asserting and denying. There are two kinds of intermediate possibilities in
proposition such as degree of probability and degree of usuality. It is as follows:
2.1.4.1.1.1 Probability
Probability is degree of intermediate possibilities. The degrees of possibilities in probability are possibly, probably, and certainly (Halliday, 1994:89). So the
degree of probability can be determiner to analyse modality. Probability can be expressed through three ways (Halliday, 2004:147), as follows:
1. By a finite modal operator in the verbal group.
2. By a modal adjunct. 3. By both together.
2.1.4.1.1.2 Usuality
The degree of possibilities began from low up to high. Usuality can be expressed in
the three ways, as follows:
1. By a finite modal operator in the verbal group.
2. By a modal adjunct. 3. By both together.
2.1.4.1.2 Modulation
In while, in proposals (goods-&-services), for instance: offers and commands. In the proposals the meaning of positive and negative poles are prescribing and proscribing. There are two kinds of intermediate possibilities in proposals depend on
the case of speech function such as command (the intermediate points represent degrees of obligation) and offer (that represents degrees of inclination). It refers to
categorized as modulation (Halliday, 1994:222). It is as follows:
2.1.4.1.2.1 Obligation
Obligation is the kind of intermediate possibilities. In proposal, the intermediate degree of command represents as obligation. The kind of intermediate degrees of obligation are allowed to, supposed to, and required to (Halliday, 1994:
89). Obligation can be expressed in either of two ways, as follows:
1. By a finite modal operator
2. By an expansion of the predicator: (i) typically by a passive verb and
(ii) typically by an adjective.
2.1.4.1.2.2 Inclination
The intermediate points of offer in proposal represent degrees of inclination in modulation. The kind of intermediate degrees of inclination are willing to, anxious
to, and determined to (Halliday, 1994:89). To analyse modality through intermediate degrees of inclination can be expressed in two ways, as follows:
1. By a finite modal operator
2. By an expansion of the predicator: (i) typically by a passive verb and (ii) typically by an adjective.
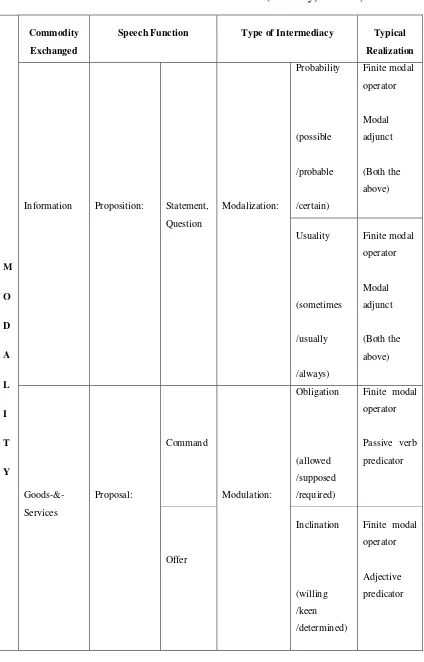
Based on the explanation above, the modality has four kinds of intermediate
possibilities found in modalization and modulation. It is as representative the meaning of the positive and negative poles in proposition and proposal. To
Table 2.1: Modalization and Modulation (Halliday, 1994:91)
In modalization, the speaker is making opinion about information through
statement or question for the listener. In the statement, the modality is an expression of speaker’s opinion, whereas in the question it is a request for listener’s opinion (Halliday, 1994:89). In modulation, the speaker is making command or offer for the
listener such as offering to do something, requesting the listener to do something, and suggesting that they both do something. Modulation regularly implicates third
person; it is a statement of obligation and inclination in respect of others. In this case they function as propositions, since to the person addressed they convey information rather than goods and services. But they do not thereby lose their rhetorical force to
the third person (Halliday, 1994:89).
As presented of Halliday’s table of modalization and modulation above the
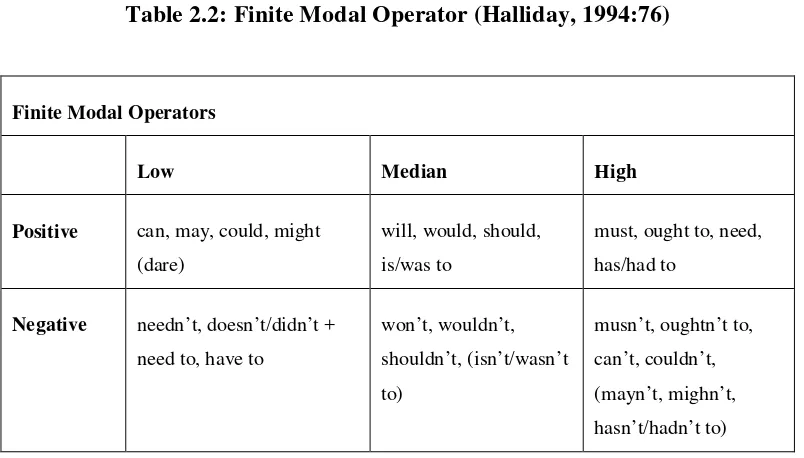
typical realizations of the four of degrees in modalization and modulation will be described in value of modal as modal operators and in degree of assertiveness are
high, median, and low. It is explained based on modalities theory by M.A.K Halliday (1994), as follows:
Table 2.2: Finite Modal Operator (Halliday, 1994:76)
Finite Modal Operators
Low Median High
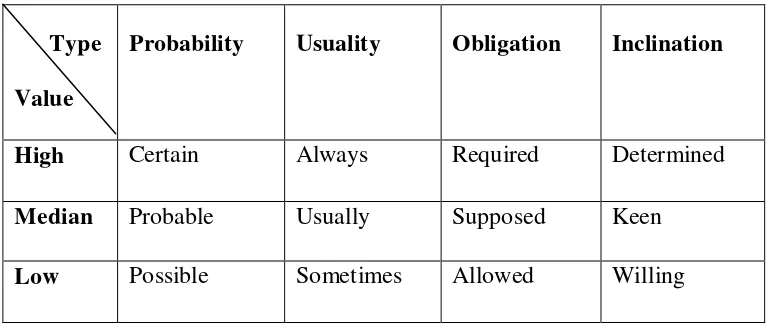
In other explanations modality particularly in type and value of modality in
which presented above also classifies as modal adjunct. To determine type of modality found in look out for what kinds of value are used in modality. They are as follows:
Table 2.3: Three Values of Modality (Halliday, 1994:358)
Type Value
Probability Usuality Obligation Inclination
High Certain Always Required Determined
Median Probable Usually Supposed Keen
Low Possible Sometimes Allowed Willing
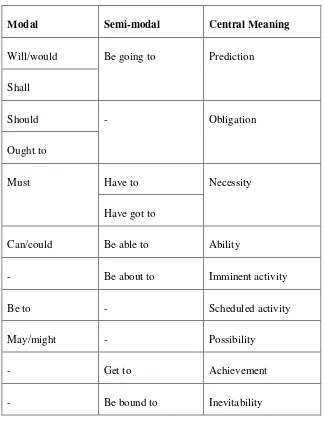
The type of modality above is classified in four kinds of types in modality (probability, usuality, obligation, and inclination). The value of modality is not
classified into modal only but can be classified into semi-modal. Dixon (2005:173) states that the value of modality classifies modal and semi-modal in certain central
Table 2.4: Modality Expressed by Modals and Semi-modals (Dixon, 2005:173)
Modal Semi-modal Central Meaning
Will/would Be going to Prediction
Shall
Should - Obligation
Ought to
Must Have to Necessity
Have got to
Can/could Be able to Ability
- Be about to Imminent activity
Be to - Scheduled activity
May/might - Possibility
- Get to Achievement
- Be bound to Inevitability
In analyzing about modality does not analyse by modal adjunct or semi-modal only but semi-modality can be analyzed by uses the category of mood adjuncts, mood adjunct of temporality time, clauses, semi – modal (finite non-modal tense),
finite verbal operators, modal adjunct, adverb of modality, adverb serving as comment adjunct, typically by an adjective, projection type as manner (as an idea),
Because Halliday (1994) states that clause is used to exchange information and
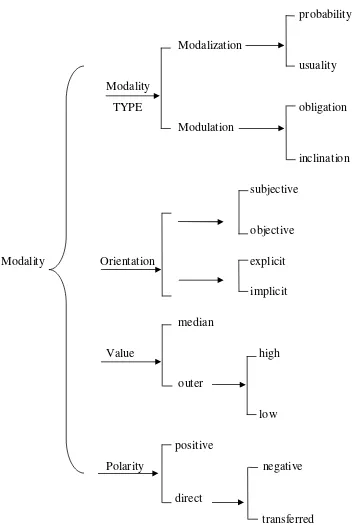
modality involved in clause as exchange. In the below is the schema of system of modality in clause as exchange in Halliday’s theory as follows:
Figure 2.1: Sytems Network of Modality (Halliday and Matthiessen, 2004:150)
probability
Modalization
usuality Modality
TYPE obligation
Modulation
inclination
subjective
objective
Modality Orientation explicit
implicit
median
Value high
outer
low
positive
Polarity negative
direct
2.2 RELEVANT STUDIES
There are some relevant studies in analyse modalities in speech or in debate as the object of study to support this thesis. It is analysis on modalities in political debate mainly in language of politics as the object of study. The analysis on
modalities is used by Rabiatul Adawiyah (2014) has investigated modalities used in political debate discourse. She was analyse the two debate as the purpose to know the
modalities used by speakers. The study is analyse the presidential debate from U.S and Indonesia. The U.S presidential debate was between Obama and Romney. In whilst, Indonesia presidential debate was between Mega and SBY. So the
Indonesia presidential debate knew as “Beda Mega Beda SBY”. Temporary in other relevant studies find out in thesis of Santi Siti Aisyah (2012) was analyse the