HIGH SCHOOLS IN YOGYAKARTA
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements To Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree in
English Language Education
By:
GEORGE YUDONO HIDAYAT
Student Number
: 961214083
Student Reg. Number
: 960051120402120080
ENGLISH EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM
DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
YOGYAKARTA
this thesis successfully. I would like also to thank all of those who have supported me in
finishing this thesis, especially to Mr. P. Kuswandono, S.Pd., M.Ed., my first sponsor,
and Ms. Ch. Lhaksmita Anandari, S.Pd., my second sponsor because they have spent a
lot of time accompanying me in doing this thesis. Then, I also thank all of the PBI’s
lectures who have taught me in the previous semesters.
I would also like to thank all the respondents who have helped me. They
answered the questionnaire and gave it back to me on time so that I could write this
thesis successfully.
On this occasion, I would like to thank my father who had encouraged me a lot to
finish my study before he passed away and my mother who also supported me spiritually
and financially. “Father and Mother, finally I can make it.” Also, I would like to thank
all of those whom I cannot mention here by names.
I also thank to all of my classmates who encouraged me to finish this thesis.
They have supported me to finish my study.
At last, I would like to thank all my friends in ELTI who have encouraged me to
finish this thesis and the Branch Manager and Academic Manager of ELTI, who have
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS………. iv
1.1Background of the Problem………. 1
1.2Identification of the Problem………4
1.3Limitation of the Problem……… 5
1.4Problem Formulation……… 6
1.5Objectives of the Study………. 7
1.6Operational Definition of Important Terms……….. 7
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE………9
2.1 Review of Related Literature………..9
2.1.3 The second-year students of Junior High Schools………..15
2.1.4 English Teaching at Junior High School……….16
a. Reading……… 17
b. Listening……….17
c. Speaking……….17
d. Writing………17
2.1.5 The 1994 English Curriculum for Junior High Schools Students………...18
e. English Training for Job Seekers……….21
School………..32
2.1.10 English Materials for SLTP Students at ELTI………….34
2.2 Theoretical Framework……….. 38
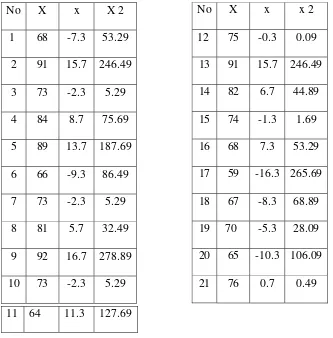
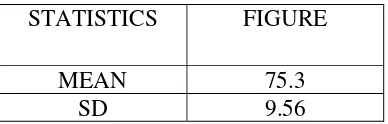
4.1 The English Learning Achievement of Student Who Took an English Course for More Than One Year……….52
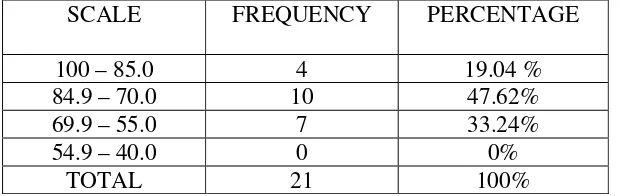
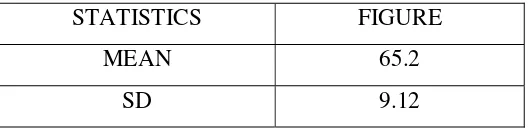
4.2 The English Learning Achievement of Students Who Took an English Course for Less Than One Year ……….53
4.3 The Difference Between the English Learning Achievement of Student Who Took an English Course for More Than One Year and Those Who Took an English Course for Less Than One Year………. 55
4.4 The Discussion of the Research Findings……… 56
4.4.1 The English Learning Achievement of Student Who Took an English Course for More Than One Year ………..………. 56
4.4.2 The English Learning Achievement of Students Who Took an English Course for Less Than One Year ……….58
4.4.3 The Difference Between the English Learning Achievement of Student Who Took an English Course for More Than One Year and Those Who Took an English Course for Less Than One Year………58
CHAPTER 5 CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION………..60
5.1 Conclusion………..61
5.2 Suggestion………..62
Took an English Course for Less Than One Year………..68 Appendix 3 The Computation of the Ideal Mean and Standard Deviation
of English Learning Achievement of Student Who Took
an English Course for More Than One Year………...69 Appendix 4 The Computation of the Ideal Mean and Standard Deviation
of English Learning Achievement of Student Who Took
an English Course for Less Than One Year……….70 Appendix 5 The Calculation of the t-test for the Significance of the
2. The English Learning Achievement of Second Year Students of Junior High Schools in Yogyakarta who Took An English Course at ELTI for
more than one year by Mean and Standard Deviation………50
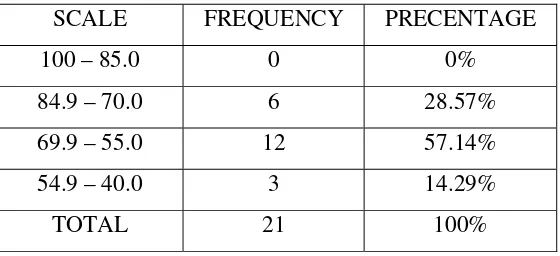
3. Distribution of Scores of Students who Took An English Course for
More Than One Year by Scale, Frequency, and Percentage………...50
4. The English Learning Achievement of Second Year Students of Junior High Schools in Yogyakarta who Took An English Course at
ELTI for less than one year……… ………. 51
5. The English Learning Achievement of Second Year Students of Junior High Schools who Took An English Course at ELTI for less than one
year by Mean and Standard Deviation………52
6. Distribution of Scores of Students who Took An English Course for
Less Than One Year by Scale, Frequency, and Percentage………52
7. The Results of the Analysis of Both Means of the Research by t-obtained
And t-table……… 54
Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta : Faculty of Teachers Training and Education, Department of Language and Arts Education, English Education Study Program.
English is a foreign language which is a very important language to learn because a lot of scientific books are written in English.due to the importance of English ,it becomes a subject which must be taught at school starting from junior high schools. Because English is an important subject, there are a lot of institutions which after English lessons .one of them is English Language Training international Which is located at Sabirin street number 6 Kotabaru Yogyakarta This institution offers English for any levels, they are English for kids and junior high school students ,general English course for senior high school, English for active communication for university student and employees who need English to support their English mastery which is needed at their places of work.
In relation to this research paper, English for junior high school students was presented .this study tried to see the contribution of English courses towards the achievements of the student at school, especially the second year students who took an English course at ELTI. in this study ,two kinds of research methods were employed. They were library research and survey research .library research was done to obtain any necessary data related to this study.
This study dealt whit the difference between the English learning achievements of second-year junior high school students who took an English course at ELTI for more than one year and those for less than one year. In order to see the difference ,score data of both groups of second-year students who took an English course for more and less than one year at ELTI were gathered .after gathering the data ,calculation using t-test was conducted to see the whether the difference of both achievements were significant ,or in doubt.
The result of the calculation of the means of both group indicated that there was a difference .the means of the student who took an English course at ELTI for more than one year .to see whether the mean of the students who took an English course at ELTI for less than one year. To see whether the mean of the student who took an English course at ELTI for more than one year was significantly higher, t-test was conducted.
Yogyakarta
.Yogyakarta :Fakultas keguruan dan ilmu keguruan jurusan pendidikan Bahasa dan seni ,program studi Pendidikan bahasa inggris
Bahasa inggris merupakan bahasa yang sangat penting untuk dipelajari sebab banyak buku ilmiah ditulis dalam bahasa inggris mengigat pentingnya Bahasa Inggris ,Bahasa inggris menjadi mata pelejaran yang harus diajarkan di sekolah-sekolah mulai dari sekolah tingkat lanjutan pertama.karena Bahasa Inggris merupakan mata pelajaran yang penting maka banyak institusi yang menawarkan Pelajaran Bahasa Inggris.salah satunya adalah English Language Training International (ELTI)yang terletak di jalan Sabirin 6 kotabaru Yogyakarta.ELTI menawarkan Pelajaran Bahasa Inggris Untuk semua kelas yaitu Bahasa Inggris untuk Sekolah Dasar dan Sekolah Menengah Tingkat Pertama,General English Course untuk sekolah menengah atas,English for activeCommunication untuk pera maha siswa dan para karyawan yang membutuhkan Bahasa Inggris untuk mendukung penguasaan Bahasa Inggris Yang diperlukan di tempat mereka bekerja
Sehubungan dengan skripsi ini, Bahas Inggris untuk siswa-siswa Sekolah lanjutan menengah tingkat pertama dibahas.studi ini mencoba melihat kontribusi lembaga bahasa inggris terhadap nilai yang diperoleh siswa disekolah,terutama sekolah menengah lanjutan pertama kelas dua. Dalam studi ini,dua macam metode penelitian yang dipakai yaitu studi pustaka dan surfei. Study pustaka dimaksudkan untuk mendapat informasi yang penting berkenaan dengan skripsi ini.sedangkan surfei dimaksudkan unuk memperoleh data data penting yang berhubungan dengan studi ini
Studi ini membahas perbedaan tentang antara kemampuan bahasa inggris siswa sekolah lanjutan tingkat pertama kelas Dua yang telah belajar di ELTI selama lebih dari Satu tahun dan yang kurang dari satu tahun.untuk melihat perbedaan tersebut,data nilai di ambil dari dua kelompok tersebut di atas.setelah memperoleh data penghitungan menggunakan t-test dilakukan untuk melihat apakah perbedaan antara keduanya itu signifikan,tidak signifikan atau meragukan.
Hasil perhitungan nilai rata-rata dari kedua kelompok menunjukan adanya perbedaan.nilai rata-rata dari siswa yang belajar di ELTI lebih dari satu tahun ternyata lebih tinggi dari pada nilai rata-rata siswa yang belajar kurang dari satu tahun.untuk melihat apakah nilai rata-rata siswa yang balajar di ELTI secare signifikanlebih tinggi atau tidak, t-test dilakukan.
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
1.1. Background of the problem
English is an important language because English is an international language
and it is the most-widely-use language (Quirk,1985:3).People in the world use English
not only as a mans to communicate and interact with one another but also as a man to
follow the development of science and technology since most science books are written
in English.
In Indonesia, English is formally taught at junior high schools. in conjunction
with the development of science and technology, there are many elementary schools
which provide English as their subjects. Muslich (1994:62 ) says that English teaching
at elementary high school is known as a local content ( muatan lokal ).this is an
additional subject which school provide in order to give certain knowledge or skills to
their students. at junior high school and senior high schools, English is a compulsory
subject which must be taught .at the university level ,English is also taught to students to
support their English mastery.
At school, English learning may have limited time of meetings so many students
find it difficult to learn English . To over come this situation, many people or institutions
develop English courses in order to help students to increase their English skills and
ability .By the development of English institutions, there is a question on whether
Learning English can be carried out on many ways. People can learn in a formal
education or in a non-formal education. Husain (1995:19)says that the realization of
education uses two ways, they are formal education and non-formal education. A formal
education is one which is managed at school through teaching learning activities which
are not done continuously and gradually. The types of a formal education are elementary
schools, junior high schools, and vocational schools. The types of a non-formal
education are courses, private courses, study groups, workshops, seminar, and so on.
Recently, there are many kinds of a non-formal education. One of them is
English institution. Those institutions offer programs to increase the English ability of
learners, for example, English for children, English for job interview, English for
banking, English for businesswomen, English for secretaries and so on.
In teaching learning processes, a lot of students still have difficult to speak, to
write, to pronounce, of to understand words and sentences so they sometimes receive
low marks on their English subject .this fact can be seen in their English scores which
they receive from their insertive tests. Due to this fact many students take English course
to overcome their weaknesses in English because the allocated time for English lesson at
school is limited. Thus, they need more time to study English outside school. Event
some students, who are already good at English, also take English courses because they
wont to improve their English mastery and they also realize that English will be useful
for their future education and life.
Baradja (1990:61) adds that the failure of teaching foreign languages may be
languages. He also explains that the principles of successful foreign languages teaching
are small classes, professional and experienced teachers, high frequency of meetings,
suitable learning resources, environmental support, and students’ motivation
From the explanation above, there are two questions which motivate the
researcher to write this thesis. First, can English courses support the English learning
achievement of students? Second, how do English learning achievements of the students
who took English course for more than one year differ from those who only took English
course for lees than one year?
Starting from those two question, the researcher writes this thesis which is
related to the contribution of English language training international Yogyakarta Branch
towards the English learning achievement of second-year students of junior high schools
in Yogyakarta in the academic year 2001/2002 who took an English courses at English
Language Training International (ELTI) Yogyakarta Branch
1.2. Identification of the Problem
According to educational Basic Course Outline (Depdikbud 1994 :1) English is
the first foreign language which is taught at school. It is important for the development
of the science, technology, art and culture and the development of the relationship with
order nations. It develops students’ understanding in science technology, art and culture,
so students will grow and develop into educated and skillful citizens and be ready to
At the junior high schools, English covers reading, writing, speaking and
listening skills. Those skills are presented integratively although the emphasis is on
reading skill. Language elements, such as structure, vocabulary, pronunciation, and
spelling are taught to support the development of the four language skills state above.
Language skills are presented in a scope which is called the theme in educational Basic
course outline.
There are some factors which influence teaching learning processes. Slameto
(1995:54) states that there are two general factors which influence teaching learning
processes and learning achievement. They are internal and external factors. The internal
factors consist of physiological and psychological factor includes IQ (intelligence),
attention, interest, aptitude, motivation, readiness,and maturity.
The external factors consist of family, school and society ones . the family
factors consist of parents education, relationship between members of family, family
situation, Family‘s finances ,parents’ cultural background the school factors consist of
methods ,curriculum, relationship between teachers and students, relation ship among
students, school discipline, lesson instruments school schedule, home assignments and
building of the school. the society factors include students’ activities in the society, such
as taking course joining group discussions, making use of mass media available in the
1.3. Limitation of the Problem
From the identification of the problem above, the researcher will limit to one of
the students’ activities in the society as one of the external factors which influence
teaching learning processes and learning achievement, that is, talking an English course.
The reason for the limitation is that the students’ activities in the society take longer time
than their activities in the society are assumed to have greater effect on their learning
achievement. Slameto (1995: 70) writes that students’ activities in their society can
support their personal development and their learning. For example, an English course
they take can support their English mastery.
Starting from the statement above, junior high school students who took an
English course both for more than one year are and less than one year are treated as
independent variables of the study. This independent variable is supposed to have an
effect to the dependent variable, that is the students’ English learning achievement at
junior high schools. Student who took an English course for less than one year are
treated as a control group and students who took an English course for more than one
year are treated as an experimental group
The phrase “English learning achievement” here refers to the English learning
achievement of second-year students of junior high schools in Yogyakarta in the
academic year 2001/2002. The reason for choosing second year students of junior high
schools is that they are assumed to have learned English at their schools for at least one
any psychological burden in their learning processes which might affect their learning
achievements.
1.4. Problem formulation
To make the study more operational, three problems are stated below
1. What grades are achieved by second-year students of junior high schools who
took an English course at ELTI for more than one-year?
2. What grades are achieved by second –year students of junior high schools who
took an English course at ELTI for less than one-year?
3. How do the English learning achievements of the second-year students of junior
high school who took an English course at ELTI more than year differ from
those who took an English course at ELTI for less than one year?
1.5. Objectives of the Study
Three objectives are proposed. These there objectives are related to the first ,the
second and the third problems stated above in the formulation of the problems .those
there objectives of the study are stated below.
1. To describe the English learning achievement of the second-year study of junior
high schools who took an English course at ELTI for more than one-year
2. To describe the English learning achievement of the second-year study of junior
3. To fine out the difference between the English learning achievement of
second-year students of junior high schools who took an English course at ELTI for
more than one-year and those who took an English course at ELTI for less than
one year
1.6. Operational Definition of Important Terms
In order to have the same frame of reference of terms used in this thesis, it is
necessary that the same understanding of the terms be established. in this thesis, there
are seven important terms, namely courses, English courses, learning achievement,
English learning achievement, and English Language Training International .
1. A course is a kind of non-formal education which is managed by people or
institutions and which offer a certain subject in order to help learners to develop their
ability (Husain, 1995:155).
2. English courses are the types of non-formal education which are managed by people
or institutions and offer English program as their subject (Husain,1995:155).
3. Learning is the change of behavior as a result of experience and practice.
4. Achievement is the progress a learner makes in learning, often measured by either
standardized or teacher-made tests (Atkinson, 1964:870). In this study, achievement
is the result of learning of the students which is measured with a test.
5. Learning achievement is the progress of learners’ behavior of how much learners
study , learning achievement is the progress of students’ learning which the score
represents.
6. English learning achievement is the score of the progress of learners’ behavior of
how well and how much learners have learned English by experience and practice.
7. English language training international Yogyakarta Branch is one of the institution in
Yogyakarta which offers English training for its customers. It is located at Jalan
Sabirin 6 Kotabaru ,Yogyakarta .In the following chapters, English Language
CHAPTER 2
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
In this chapter, two topical issues will be discussed. The first topic is the review
of related literature which consists of theorist of learning achievement, the second year
students of junior high school, the 1994 English teaching at junior high schools, English
courses, language testing , the English materials taught in ELTI ’s contribution to junior
high school students, and theories of learning . The second topic is theoretical frame
work to note the difference between English learning achievement of second-year
students of junior high schools who took an English course at ELTI for more than one
year and those who took an English course at ELTI for less one year .At the end this
chapter ,hypothesis will be formulated.
2.1. Review of related literature
In this section, the researcher presents the theorist of learning ,achievement, the
English learning achievement , learning theorist, the second year student of junior high
schools, English teaching at junior high schools, the English curriculum for junior high
school students, English course, English teaching at ELTI for junior high school
students, the English materials for junior high schools, and materials for junior high
2.1.1 English learning achievement
The world ‘learning’ has some definitions. According to Silverman (in Masyhuri,
1990:130 ), learning is a process in which past experiences or results of practice change
the individual repertory of response. Similarly, Suryabrata (1983: 181) defines that
learning is shown by a change in behavior as a result of experience. In edition, Travers
(1977: 28) states that learning involves a relatively permanent change in behavior as
result of exposure to conditions in the environment. Wood worth ( 1955:491) adds that
’a learned act is something newly added to the individual and reappears in his or her
activities.
Cronbach, ( 1957:47) defines that if a person makes a different response this
month from the one he or she made a month ago, it is said that he or she has learned
some thing. Or more precisely, learning is shown by a change in behavior as a result of
experience. In other words, Mouly (1968:298) defines that “learning” is the
improvement in behavior in the sense that a person becomes more proficient at whatever
he or she is learning”.
While Chaplin ( 1995: 89) states that “learning is acquisition of any relatively
permanent change in behavior as a result of practice and experience” while Hinzman
(1995:89) defines that “learning is a change in organizing due to experience which can
affect organism’s behavior”. Reber (1995:90) adds that “ learning is a permanently
change is response which occurs as a result of reinforced practice”
Page and Thomas ( 1977:203) Devine that “learning is a relatively permanent
trough institutional learning like teaching“. Similarly good (1945:237) explains that
“learning is a change in responses or behavior (such as innovation , elimination, or
modification or response which involve some degree of permanence caused partly or
wholly by experience”.)
From those theories above, it can be concluded that the meaning of the word
“learning” is a change of behavior which is caused by experience and practice and it is
an act to add the individuals repertory. This means that there is a different response a
letter made in the past and a letter makes today.
The following section includes some definition of the world “achievement is
Performance in schools or collages in a standardized series of educational tests”. The
term is used more generally to describe one performance in the subjects of the
curriculum. They also say that an achievement test is a test designed to measure the
effects of specific teaching or training in the area curriculum.
From the definition of learning and achievement can be explained and
achievement can be explained as the progress of learner’s behavior of how well and how
much learners have learned English which are caused by experience and practice.
2.1.2 Theories of Learning
According to Fraenkel ( 1980:107) a learning theory is a carefully worked out set
of interrelated prepositions that attempt to explain how people learn. He describes the
learning process based on some theories of learning as follows:
a. Mental Discipline
This theory believes that individual’s mind contains a number of basic capacities
such as imagining, reasoning, and remembering which grow and remembering which
grow and develop in a learning process, those capacities a stated above are developed
trough knowledge acquisition. The more difficult the knowledge is to acquire, the better,
because the mind will be trained more effectively. Thus, practice and drill are the
appropriate ways which will develop someone mind.
b. Conditioning Theory
This theory sees learning as a change in behavior. The easiest way to explain the
change in behavior is by seeing the connection between stimuli and responses
( Bohannon and Leubecker, 1965: 177). Meanwhile, the Russian psychologist, Ivan
Pavlov, says that a learning process consist of the information of association between
stimuli and reflexive responses. These associations can be viewed from the ideas or
things which are associated in someone’s minds because they were related in some ways
c. Gestalt – field Psychology
It views learning as the discovery of meaning or insight within a given situation.
Some theorists assume that insight, intelligence, and other cognitive process are the
fundamental characteristics which are involved in the responses of human beings to
know the connection. For instance, the connection between two things on how they work
and how they are related to each other. Thus, a person will come to a certain action, that
is to understand or get knowledge by himself or herself and not by being told by
someone else. In this case, he or she discovers meaning or knowledge.
Skinner ( 1957: 87) and Richards and Rodgers ( 1986: 50 ) explain another way
of learning process, that is , behaviorism or usually known as stimulus-response (S-R)
theory. In this learning theory, he describes the relations among stimulus, organism,
response/ behavior and also reinforcement.
The stimulus is used to elicit behavior, whereas the human beings are the
organism. The response is elicited from the stimulus, and the reinforcement used to mark
the response as being appropriate or inappropriate and to encourage repetition of the
responses in the future. The relationship between the stimulus and the response above is
connected by reinforcement.
According to Skinner (1957: 87), if a particular response is reinforced, it will
become a habit. Therefore, teachers must select stimuli and the responses until they get
the desired behavior from the students which is called a habit. After becoming the habit,
In ELTI, teaching learning processes are conducted in such a way that students
will maintain the response as expected by teachers. For example, a student must answer
the teacher’s question with a complete sentence and not merely with a single word or
some words only. When a teacher asks “What time do you get up?”, the expected answer
from the student is “I get up at 5 o’clock” and not merely “At 5 o’clock”. If a student
answer with only a single word or some words only as the example above, the teacher
should reinforce him/her to answer in a complete sentence become a habit.
Thus, the theory of behaviorism is controlled by reinforcement. If the
reinforcement are rewarding (positive reinforcements), the behavior may be maintained
or even increased. Yet, if the reinforcements are punishments, mockery, and any other
negative reinforcements or if there is lack of reinforcements, the habit may be weakened
or even disappeared.
At school, mental discipline and behaviorism learning theories are applied. The
students, according to mental discipline, need a lot of practices in order to face semester
tests and national final examination when they are in the third grade. In the learning
process, the students are motivated to get good marks in doing exercises or tests. As a
result, they are accustomed to doing exercise or test with great efforts in order to achieve
their best. In behaviorism learning theory, the students, as the organism, are given the
stimulus. The student’s reaction toward the stimulus is called response, in which they
regularly practice many exercises and answer question in order to get accustomed,
especially, in doing tests. A lot of practices will relatively make them better.
2.1.3 The Second -Year Students of Junior High School
Educational system in Indonesia includes three stages or levels. There are three
levels of education in Indonesia. The first is primary education which involves
elementary schools (Sekolah Dasar or SD). The second is secondary education which
involves junior high schools (Sekolah Menengah Lanjutan Tingkat Pertama or SLTP)
and senior high schools (Sekolah Menengah Umum). The third is tertiary education
which involves universities, academies and other tertiary educational institutes (Tanlain,
1995).
The second- year students of junior high schools belong to students of secondary
education. They are at the ages of twelve until fourteen years old. Junior High School
students receive four sessions of English teaching a week over a period of three years
with the duration of 45 minutes in each meeting. Thus. The total number of teaching
sessions which students get in each grade is 136 sessions. (GBPP 1994: 10)
2.1.4 English Teaching at Junior High School
As stated in the previous sub-unit, the allocation time of English subject is one
hundred and thirty six teaching hours with forty five minutes each teaching hour during
the second-year study. Within that time the students are expected to be able to master
English with about two hundred and fifty new words at the level of about one thousand
a. Reading
Students are able to read text in narration, description and conversation such as
in leaflets, personal letters of about two hundred words in order to find certain
information, to get general description of the content of the texts, to find the main ideas,
to find the hidden messages, to find detailed information, to get the implied information,
to interpret the meaning of words, phrases, sentences of the texts and to get pleasure
from reading.
b. Listening
Students are able to answer oral question, to ask for information from texts
presented orally (conversation, narration, description) which are suitable with themes
and topics, to get information, to complete forms, diagrams or maps and to find implied
information of simple and short conversations.
c. Speaking
Students are able to ask and answer questions, to make short conversations, to
give information and explanation of things, people, places or events, to express simple
feelings, ideas and opinion.
d. Writing
Students are able to arrange random sentences into a good paragraph, to
sentences) in narration and description of simpler topics and to write message and
simple letters.
2.1.5 The1994 English Curriculum for Junior High School Students
English is the first foreign language which is taught formally as a subject in
junior high schools. English is considered a very important language because it used for
understanding and developing knowledge, arts, technology, and relationship with other
countries. Based on this consideration, English lesson is a compulsory subject which
must be given to every junior high school student as the first foreign language.
The curriculum used in Indonesia have experienced four successive changes,
beginning from the 1968 curriculum, the 1975 curriculum, the 1984 curriculum, and
newest one, which is used up to now, the 1994 curriculum. A.M. Shaw (1977) in Yalden
(1971:569) quotes Robertson that
… the curriculum includes goals, objectives, contents, processes, resources, and means of evaluation of all the learning experience planned for pupils both in and out of school and community through classroom instructions related programs…(Yalden, 1971:569).
Curriculum, therefore, is generally explained as the planned guidance to teach
certain subject or programs of teaching- learning processes which are supposed to be
conducted in the classroom.
the analysis on education, the teaching -learning evaluation and the input of the society
about the quality of the graduate students.
Today, the 1994 curriculum is the curriculum which every schools refers to. This
curriculum is used today because of a new regulation about educational system in
Indonesia, that is Indonesian Regulation no.2 year 1989 on National Educational
System. Because of this new regulation, the decision of Minister of Education and
Culture was set on February 25th, 1993. (Kurikulum Pendidikan Dasar Lamp. I, GBPP
1994:5)
2.1.5 English Course
Husain (1995:115) says that a non-formal education is education manage by
people or institutions. People who study in a non-formal education are called learning
people. The purposes of a non-formal education are to serve learning people so they get
knowledge and skills from the education that they take, to increase their educational
quality, to continue to the text education, and so on.
An English Curse is one kind of a non-formal education. It serves learning
people to develop their English language proficiency. In an English course, there are a
lot of programs which they offer. For example, ELTI offers programs as follows:
a. General English Course
General English Course is one of the programs which is offered by ELTI. This
language elements are taught equally. In this program, students will study for twenty
sessions, including two sessions for written overall revision, which is administered on
the 17th meeting and verbal overall revision which is administered on the 18th meeting.
The last two meetings, that is the 19th and 20th meetings are used to administer final
tests. There are two kinds of final tests. They are final written test and final verbal test.
The final written test covers grammar (20 items), reading (10 items) and writing. The
final verbal test covers all the materials taught in level students belong to. The final
written test is administered on the 19th meeting and the final verbal test is administered
on the 20th meeting. The passing score for final written test is 60 and the final verbal test
is C.
b. English for Active Communication
English for Active Communication is the other program which is offered by
ELTI. This program helps learning people to communicate in English. Thus, the
emphasis of this program is on conversation, although grammar, vocabulary,
pronunciation and skills like reading, writing and listening are not neglected. In this
program, there are three kinds of final tests, they are written test, verbal final test, and
listening final test. Written final test is administered on the 19th meeting while final
listening and verbal test are administered on the 20th meeting. In English for active
students have the change to get feedback on what they have learned and achieved from
the teacher during their study at ELTI. The 21st meeting is called the graduation day.
c. TOEFL Preparation Course
TOEFL Preparation Course is a program which is offered to answer the social
needs. People need to learn TOEFL for many purposes, for example to continue their
education to master’s degree, to get a job in a foreign company or increase their English
language knowledge.
d. English for Specific Purposes
This program is held to answer the social needs for this program. This program
offers English for Banking, English for Hotels, English for Secretary, English for Taxi
drivers, in – company training and soon.
e. English Training for Job Seekers
This new program is held to answer the social needs towards this program. In
this program, people will learn how to face job interviews, how to answer questions in
job interview, and how to write a good application letter. There are twenty sessions in
this program with ninety minutes each meeting.
This program is held to help elementary students and junior high school students
to learn English. In this program, students will study grammar, writing, listening and
speaking. Those four things are taught integratively. In this program, students will have
twenty five meetings, including three meetings for written, oral and second test, with
one hour each meeting. For elementary students, they are six levels which they have to
pass, they are Kids level 1, Kids level 2, Kids level 3, Kids level 4, Kids level 4, Kids
level 5, Kids level 6 and one Kids Maintenance Class (KMC). For junior high school
students, they are six levels they have to pass, they are English for SLTP level 1, English
for SLTP level 2, English for SLTP level 3, English for SLTP level 4,English for SLTP
level 5, English for SLTP level 6 and three more levels of SLTP- maintenance Class
level 1, SLTP-Maintenance Class level 2 and SLTP-Maintenance Class level 3.
In this program, the students will study for 25 meetings. Including 3 meetings for
the final tests, with one hour duration in each meeting.
Supporting the description of English for Kids and SLTP program which is
related to this paper, the writer presents basic course outline for English for SLTP
materials which students learn in class in the section 2.1.9. The explanation about how
the English for SLTP materials at school will be presented after the discussion of the
English materials for junior high school students used in ELTI, that is in section 2.1.10.
ELTI is an English language institution which has a purpose of helping people
learn and understand English. ELTI also helps junior high school students master
English. In the teaching-learning processes in the classroom, teaching media is often
used. The purpose of using teaching media is to motivate students and to make them
interested in the lesson being taught. The teaching media available in ELTI are cards ,
toys, board game and soon.
In ELTI the focus of learning is on speaking. Speaking in considered very
important since the students do not practice speaking much at schools. So, it is expected
that students who have passed SLTP-Maintenance class level three can understand
English and express their ideas orally.
2.1.7. Language Testing
Heaton asserts that (1975:1) learning cannot be separated from testing. Testing is
important since it can reinforce learning and motivate students, or primarily it can
measure students’ performance in the languages he or she learns.
In teaching and learning, the effect of teaching is known as ‘backwash’.
Backwash can be harmful or beneficial. The effect of testing is harmful if it fails to
measure what is intended to measure and it is beneficial if the result of the test is not at
variance with what is intended to measure.
1. To measure languages proficiency regardless of any language courses that candidates
may have followed. Such a test is called a proficiency test.
2. To discover how far students have achieved the objectives of the courses of a study.
This kind of test is called achievement test.
3. To diagnose students’ strengths and weaknesses, to identify what they know and what
they do not know. This is called a diagnostic test.
4. To assist placement of students by identifying the stage or part of a teaching program
most appropriate to their ability. It is called a placement test.
People use tests to obtain information. Thus information will, of course, vary
from situation to situation. It is possible to categorize tests according to a small number
of kinds of information being sought. This categorization will be useful in deciding
whether a test is suitable for particular purpose or not.
In relation to the problem of this research, the kind of test which is suitable to
measure the competence of students is that of an achievement test. The result of the test,
as would be expected, can give information about their language ability. He term
‘ability’ used here simply refers to what people can do in, or with, a language. It could,
for example, include the ability to converse fluency in a language, as well as the ability
to recite grammatical errors.
To measure the students, competence in the English language, achievement test
is used both at school and at ELTI. However, there is one different, that is, at school
Information about people’s language ability is often very important and
sometimes necessary (Hughes,1989:4). This information is important since it can be
used to decide whether students from overseas, for example, are accepted to study in
British or American universities. Without some knowledge of their proficiency in
English, it is impossible to accept them. The same is also applicable for organization or
institutions who hire interpreters and translator. They certainly need dependable
measurement of languages ability.
Although the researcher did not test the students, the researcher included
languages testing in this thesis because the English learning achievement of the students
was taken from the result of how well they did the test, that is written test.
2.1.8. The English Materials for Junior High School
The materials which are started in the Education Basic Course Outline of the
1994 curriculum for junior high schools cover the materials for the first grade, second
grade and the third grade. The discussion of the English materials for junior high school
is important in order to see whether the English materials taught at ELTI are in line with
those taught at school or not. Those materials can be seen in the following sections.
2.1.9. The Materials for the First Grade
The following sections presents the themes and topics of the reading texts in the
GBPP, the functional skills taught for the first grade of junior high schools and
a. The Themes and Topics of the Reading texts in the GBPP (1994:11-12)
In the GBPP, the themes and topics of the reading texts for the first grade is
explained below.
1. Identify : Introduction, physical description, character description, in the canteen, in
the laboratory, the school garden, the school activities, scouting activities, and the rulers
of the school.
2. Jobs : At work, kind of jobs, and level of jobs.
3. Hobbies : Pet, gardening, collecting stamps, camping reading, cooking, sports and
art.
4. Shopping : Going to the market, department store, and merchandise.
5. Family Life : Family members, house and furnishing, family activities, daily
activities, neighbors, and possession.
6. School Life : At school, I the classroom, and in the library.
7. Daily Needs : Food and Drink, clothes and recreation.
8. Games : Modern games, traditional games , and children’s games.
b. The Functional Skills (GBPP 1994 : 13-14)
In this part, the students are expected to be able to:
1. Understand and express self-introduction.
2. Understand and express how to introduce someone to some else.
5. Understand and express like and dislike.
6. Understand and express apologizing.
7. Understand and express commands.
8. Understand and express factual information.
9. Understand and express want
10.Understand and express abilities and disabilities.
11.Understand and express possession
12.Understand and express choices
13.Understand and express profession
14.Understand and express adverbial of places
15.Understand and express the existence of things or persons
16.Understand and express the quantifiers for uncountable nouns
17.Understand and express evens which are still in progress
18.Understand and express habit in doing something
19.Understand and express events that happened in the past
20.Understand and express events which will happen in the future
21.Understand and express a must.
c. Vocabulary
Vocabularies are listed according to the themes. Teachers may add vocabularies
from other sources for their students which are related to the themes, considered
2.1.9.2. The Materials for the Second Grade
The themes and topics of the reading texts and the functional skills taught for the
second grade of junior high school are explained in the following sections.
a. The Themes and The Topics of Reading (GBPP:33-34)
. In GBPP, the themes and topics of the reading texts for the second grade of the
junior high school can be explained as follow:
1. Sports: Sports facilities, doctor and paramedic, kinds of sports, sport match, and
athletes.
2. Health: Our body, doctor and paramedic, hospital, medicine, and sickness
3. Clothes: Kind of Clothes, making clothes, materials for clothes
4. The Live of Village/ City: Occupations, transportation, and society
5. General Services: Hotel, post office, bank, telecommunication office, entertainment
places, restaurant, clinics, and place of worship
6. Indonesian Geography: Ocean, Indonesian nature, national resources, land and space
7. Entertainment: Dance, music, film, and drama
8. Animals: Pet, wild animals, livestock animals, and protected animals
9. Recreations: at the beach, in the zoo, in the mountain
b. The Functional Skills
In this part, the students are expected to be able to:
1. Understand and express factual information
4. Understand and express request and the responses
5. Understand and express how to ask, give reject permissions
6. Understand and express hopes
7. Understand and express choices
8. Understand and express sympathy
9. Understand and express how to invite and respond
10. Understand and express a condition and feeling
11. Understand and express quantity
12. Understand and express the description of something or someone
13. Understand and express the information about the position of something
14. Understand and express comparison of two things or persons
15. Understand and express the frequency of an event or an activity
16. Understand and express how something is done
17. Understand and express plans or events in the future
2.1.9.3 The Materials for the Third Grade
The following are and themes and topics of reading texts and the functional skills which
are taught for the third grade of junior high school students.
a. The Themes and The Topics of Reading (GBPP,1994:49-50)
In GBPP, the themes and topics of the reading texts for the third grade of junior
high school can be explained as follows:
1. Light Technology: Agricultural equipment, household equipment, health equipment,
2. Transportation; Land transportation, sea transportation, and air transportation.
3. Flora and Fauna: Parts of the plant, flower garden, nature preserves, botanical garden
and dense forest.
4. Culture: Traditional Houses, costumes and traditions, dance, folk songs, religion
industry, traditional clothes, traditional ceremonies, and folk tale.
5. Mass Media: Newspaper, magazines, radio and television.
6. Word Geography: Natural condition, natural resources, and demography.
7. Tourism: Planning/preparing, accommodation, equipment, and traveling.
8. International Sports: The national games, The Olympic games, and The SEA games.
b. The Functional Skills (GBPP, 1994: 51-57)
In this part, the students are expected to be able to:
1. Understand and express abilities/ disabilities.
2. Understand and express the feeling of like and dislike.
3. Understand and express possibilities and impossibilities.
4. Understand and express surprise.
5. Understand and express certainly or uncertainly.
6. Understand and express agreeing and disagreeing.
7. Understand and express denying.
8. Understand and express satisfaction and dissatisfaction.
9. Understand and express disappointed.
12.Understand and express the comparison of someone’s health.
13.Understand and express the comparison about the quantity of something.
14.Understand and express the quality which is exaggerated.
15.Understand and express the comparison about how to do something or how
something happens.
16.Understand and express contrary.
17.Understand and express confirmation.
18. Understand and express two positive things are the same.
19.Understand and express two negative things are the same.
20.Understand and express reasoning.
21.Understand and express two choices.
22.Understand and express admiration.
23.Understand and express habits.
2.1.9.4. Examples of the Functional Skills Taught at Schools
The following is the examples of functional skills taught at junior high schools.
They are:
1. The students are able to understand and express:
a. Comparison of someone‘s health (e.g. Billy was ill this morning and he is
worse now.),
b. Comparison of the quantity of things (e.g. Can I have some more information
c. Superlative degree (e.g. Bali is the most interesting island in Indonesia),
d. Comparison of how something is done (e.g. She always dances gracefully but
yesterday she danced more gracefully.),
e. Comparison of quality of a person, thing or event (e.g. The air in small cities is
cleaner and fresher than that in big cities.),
2. The students are able to understand and express:
a. Ability and disability (e.g. “Is your daughter taking piano lessons?” The
answer: “No, but she can play violin.”),
b. Happiness and unhappiness (e.g. I am very pleased with it),
c. Possibility and impossibility (e.g. “ I cannot find my glasses”. The answer:
“Perhaps they are in the living room”.),
d. Wondering (e.g. Are you serious?”),
e. Certainty or uncertainty (e.g. I am sure he has forgotten to come.),
f. Agreeing or disagreeing (e.g. I agree.),
g. Denial (e.g. “You are telling me a lie”. The answer: “ I’m not”.),
h. Satisfaction or dissatisfaction (e.g. “What do you thing of the food?” The
answer: “ I like it very much”.),
i. Disappointment (e.g. That’s very bad.),
j. Warning ( e.g. Look out!)
3. The students are able to understand and express confirmation (e.g. Traveling by
4. The students are able to understand and express ellipsis using to, so, neither and
either. (e.g. Andi likes the story and so do I ; He doesn’t like it and neither do I)
5. The students are able to understand and express the answer of a Yes? No
question. (e.g. “Do you like it?” The answer: “ Yes, I do”.)
6. The students are able to understand and express qualitative statement. (e.g. I like
this hotel. It is quite nice.)
7. The students are able to understand and express an event relating to uncertain
persons, things or places (e.g. What happened to everybody in that village?)
8. The students are able to understand and express a statement which shows quantity
(e.g. All of road users should obey traffic regulations)
9. The students are able to understand and express a statement related to pressure
(e.g. I have a mistake. I am so sorry.)
10. The students are able to understand and express admiration (e.g. Marry’s work is
excellent. What a clever girl!)
Those examples about are some of the functional skills taught at junior high
schools. There are many other examples which are taught at junior high schools which
are not mentioned above.
2.1.10. English Materials for SLTP Students at ELTI
According to the syllabus of the English lessons for SLTP classes, in level 1
students will learn how to ask someone’s name and how to answer it, numbers, things in
the house, things in the classroom, phone numbers, greetings, fruits and vegetables, jobs,
Those are the materials which are taught in ELTI in level 1. In level 1, the grammar
which are taught to the students is only simple presents tense.
In level 2, students will learn, adverb of frequency, imperative, warning and
apologies, possessive adjective and possessive pronouns, likes and hates, ordinal and
cardinal numbers, dates, numbers (100-1,000,000,000), preposition, some and any,
countable and uncountable nouns, how much, how many, quantifiers, irregular plural
nouns, abilities, obligations and necessities, school ruler and traffic signs. The grammar
learnt in this level are simple present tense and presents continuous tense.
In level 3, the students will learn present progressive tense with future meaning,
how to ask permission , present future tense, how to make suggestions, simple past tense
of be, regular verbs, irregular verbs, future predictions based on presence evidence,
holidays, changes, how to make polite request, childhood, accidents, inventions, how to
say goodbye and farewell, shapes, indoor directions. In this level, simple past tense and
present future tense are introduced to the students. Some revisions about the materials
taught in the previous level are also given in order to remind the students on this things
they have learnt before. For example, revision on obligations and necessities, present
continuous tense and simple present tense and also the differences among the three
tenses.
In level 4, students will learn the experience of visiting other countries or cities,
actions which were continuing in the past and were interrupted by another action,
form, how to make a polite enquiry, adverb of manners, expressing someone’s age,
height and weight, going shopping, and health. Some revisions about the materials in the
previous level are on simple past tense, simple present tense warning. The new grammar
points given in this level are present perfect tense and past continuous tense.
In level 5, students will learn future predictions using will, quantities of food,
how to apologize, collections and collectors, passive voice, ability and lack of ability in
past, agreement and disagreement, expressing advice using should and should not,
expressing satisfaction and dissatisfaction, future possibility, relative pronouns to
identify persons or things, medical equipment, and traveling. The new grammar points
discussed in this level are passive voice, the use of could and was/ were able to, the use
of might, should and should not, relative pronouns ( which and who).
In level 6, students will learn past form of must, expressing choices/preference,
the use of used to, entertainment, question tags, how to make polite refusal, probability
that something will or won’t happen, recipes, expressing deductions, conditional type 1,
and present perfect continuous tenses, and expressing thanks and surprise,. The new
grammar points discussed during this level are past form of must, the use of would
rather and would prefer for preferences, question tags, conditional type1, and present
perfect continuous tenses.
After students have passed level 6, it is expected that they continue their study in
to SLTP Maintenance Class Level 1, SLTP Maintenance Class level and SLTP
Maintenance Class Level 3. The purpose of taking SLTP Maintenance Classes is that
English Course which is meant for senior high schools students because usually after
they have passé level 6, they have not graduated from their junior high schools, yet.
In SLTP Maintenance Class level 1, students will learn a lot of materials which
they have learnt before in the previous levels. However, in this maintenance classes, the
students are expected to have more discussions and to be more confident when
expressing their ideas in speaking. The materials in SLTP Maintenance Class Level 1
are simple present tense to talk about general truths, routines and habit, imperatives used
for instructions, the use of will for prediction, the use of each other, the use of could for
potential choice, the use of should to make advise, relative clauses, conditional sentence
type 1, defining relative clause, conditional sentence type 2, and giving indoor direction.
It was stated in the previous paragraph that the materials in SLTP Maintenance
Classes have been learnt before. Thus , in one section (60 minutes), students will have
the explanation of the grammar points in a certain meeting from the teacher for about 15
minutes. Then, students will have discussion or practice on the grammar points given by
the teacher for about 15 minutes. The rest 30 minutes is used for student’s presentation,
that is, one of the students go to the front of the class to present his/her topics. The topics
are the simple ones, for example, my favorite food, my teacher, my hobby, my school,
my house and soon. After he/she has finished with his/her presentation, his/her
classmates ask questions to him/her related to his/her topic.
In SLTP Maintenance Classes , the students also learn how to make wall
In SLTP Maintenance Classes Level 2 and 3, the programs are similar to those
given in SLTP Maintenance Class Level 1. They have to give presentation and make
wall magazines. However, the topics of the presentation and wall magazines are not the
simple ones, for example , drugs, teenagers’ life , smoking and its effects and soon. In
SLTP Maintenance Classes Level 2 and 3 , they are not any new grammar points but
there are a lot of a new words introduced to the students can express those new words in
the grammar they have learnt before.
ELTI is said to contribute a lot to the development of junior high school students
in terms of their English mastery. The contribution can be seen from the examples of the
English materials for SLTP- students at ELTI which are in lines to those taught at
school.
Beside ELTI’s contribution to the development of junior high school students,
ELTI also gives the students more chances to practice speaking in the classroom.
Practicing speaking can be carried out by many activities, like playing games using
cards, group discussions, mingling, and soon.
2.2. Theoretical Framework
From the theoretical review, it is known that English courses support students’
English mastery. The materials of English Courses are in line with those in English
teaching at school. One of the successful English teaching principles is frequency of
meeting( Baradja, 1990: 61). It is realized that English is foreign language and it cannot
must be learned from the base because it is not the same as a first language. Three or
four times or meeting with one-hour duration each meeting are not enough to master
English. It is expected that the higher the frequency of English learning, the better the
result which the might achieve. Theoretically, students who take an English course have
higher frequency of learning English than those who do not. They often have situations
in which they have to face English materials. If they do not understand a certain topic
explained by their teachers at school, they can get detailed information for English
courses that they take.
In this study, the word ‘achievement’ is very important because this study deals
with the English learning achievement of second-year students. The word achievement
here simply means the progress which the learner makes during his/her study and the
progress is usually measured by a test, either standardized or teacher-made test. Thus ,
the English learning achievement here means the progress which the learner makes in
English during his/her study.
2.3. Hypotheses
According to the explanation in the conceptual framework on dependent and
independent variables, the hypotheses of this research are formulated as follows:
1. The English Learning Achievement of students who took an English course for more
than one year at ELTI is higher than whose who took an English course for less than
2. There is a significant difference between the achievement of students who took an
English course at ELTI for more than one year and those who took an English
CHAPTER 3
RESEARCH METHOD
This study in intended to estimate the effect of independent variable on the
dependent variable. The independent variable is the second-year students of junior high
school in Yogyakarta in the academic year 2001/2002 who took an English course at
ELTI and the dependent variable is the English learning achievements. The dependent
variable is defined as the scores of the progress of how well and how much students
have learned English (Y). The independent variable is divided into two sub variables.
The first sub-variables (X1) is second year students of junior high schools in Yogyakarta
in academic year 2001/2002 who took an English course at ELTI more than one year.
The second sub-variable (X) is the second-year students of junior high schools in
Yogyakarta in academic year 2001/2002 who took an English course at ELTI for less
than one year.
In this chapter, the researcher will describe the kind of research, population and
sample of research, research design, research instrument, procedures of the research and
technique of data analysis.
3.1. Kind of Research
To answer the questions which are stated in problem formulation, two methods
Library research was done in order to obtain any necessary information related to
this study. Data analysis research was done to see the difference between the English
learning achievements of students who took an English course at ELTI for more than
one year and the English learning achievements of students who took an English course
at ELTI for less than one year.
According to Brown (1988: 3) a survey research is one which often takes the
form of a questionnaire that is sent to a group of people. The advantage of survey
research is that information can be collected in a relatively short time.
3.2. Population and sample Research
The population of this research was a group of second-year students of junior
high schools who took an English course at ELTI. There were some reasons why this
population was chosen as the sample. First, ELTI is a reputable English course in
Yogyakarta. Second, the second-year students of junior high schools were assumed to
have adapted themselves to the school atmospheres, so that they did not have any
psychological burden in their learning process which might affect their learning
achievements. Last, the location of ELTI was easy to reach, so that the researcher found
it easy to conduct this research. Samples are drawn from the population by random
sampling whish aims at creating accurate samples, that is, representative to the
populations. Thus, the researcher used random sampling by taking 110 respondents as
the samples of the research. All of the respondents returned the questionnaire to the
3.3. Research Design
Nachmias and Nachmias (1987:103) define a research as a program that guides
an investigation in the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting observations.
The design of this study is non-experimental study. The researcher only took the data
from the result of two kinds of learning achievements. They were the learning
achievements of students who took an English course at ELTI for more than one year
and the learning achievements of students who took an English course at ELTI for less
than one year. The scores of the two groups of achievement were used represent one of
the research variables, that is dependent variable.
The research design can be seen in figure 1
X1
Y
X2
Figure 1 : The Illustration of Research Design
Where:
X1= the group of students who have taken an English course at ELTI more than
one year
X2= the group of students who taken an English course at ELTI less than one
3.4. Research Instrument
There were two kinds of research instruments which were used by the researcher
in conducting this research. They were questionnaire and English score data.
3.4.1. Questionnaire
According to Ary et.al. (1979: 24), questionnaire are classified into two types.
They are structured questionnaire is a questionnaire which contains some questions with
alternative answers for each item of question. An unstructured questionnaire is a
questionnaire which contains some questions without any suggested answers. In
conducting this research, the researcher used a structured questionnaire. The reason for
choosing this kind of questionnaire was that it would be much easier for the researcher
to classify the samples into groups needed for this research. The questionnaire can be
seen in Appendix 6
3.4.2. English Scores Data
Score data is data which described students’ performance at their school in a
trimester. This score data was classified into two groups. They were score data of the
students who took English course at ELTI for more than one year and score data of the
students who took an English course at ELTI for less than one year.
3.5. Research Procedures
There were four main activities in conducting this research. The first activity was