i
THE USE OF BRAIN-BASED LEARNING METHOD
TO IMPROVE THE
STUDENTS’
READING
COMPREHENSION SKILL (A CLASSROOM ACTION
RESEARCH FOR THE 8
THGRADE STUDENTS
OF
SMP ISLAM SUDIRMAN 1 BANCAK SEMARANG
DISTRICT IN THE ACADEMIC YEAR 2016/2017)
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted
to
the
Board
of
Examiners
as
a
partial
fulfillment
of
the
requirements
for
the
degree
of
Sarjana
Pendidikan
(S.Pd) in
English
Education
Department
of
Teacher
Training
and
Education
Faculty State
Institute
for
Islamic
Studies
(IAIN)
Salatiga
Nita Susanti
113-12-141
ENGLISH
EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT
TEACHER
TRAINING
AND
EDUCATION
FACULTY
v MOTTO
“When one door closes, another opens, but we often look so long and so
regretfully upon the closed door that we do not see the one which has opened for
us”
vi
DEDICATION This graduation paper is whole heartedly dedicated to:
1. Allah SWT the Almigthy God for the everything to me.
2. My beloved parents Mr. Hamim and Mrs. Siti Asiyah, who always
educate me in doing good thing. And my beloved father Mr. Muhammad
Damuri (Alm) who teach me the real life from the distances. They are
my hero, thanks for all generosity, finance, and encouragement, and also
thanks for your love, trust, and everlasting praying. Allah bless you mom
and dad.
3. My beloved sisterRifa Izatun Nisfa, and my younger brother Ahmad
Rafie Zamzami thanks for your love and for support me.
4. My beloved grandfather and grandmother Mr. Sukeri and Mrs. Sugini
thanks for always being my inspiration.
5. Thank you so much to all of my uncles ( M.Syafii, M. Nur Solikin) and
my aunty (Endang, Neli) also all of my family members.
6. My beloved friends, YuNitAtik (Yuyun, Yunita, Atik) our togetherness
means a lot to me, love and peace gengs. I hope our friendship is never
end.
7. All my friends especially to TBI E class and generally to IAIN Salatiga
ix ABSTRACT
Susanti, Nita. 2017. The Use of Brain-Based Learning Method to Improve
Students’Reading Comprehension Skill ( A Classroom Action Research for Eighth Grade Students of SMP Islam Sudirman 1 Bancak, Semarang in
Academic Year 2016/2017. A Graduating Paper. English Education
Department. Teacher Training and Education Faculty. State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga. Counselor : Mashlihatul Umami, M.A
Keywords : Reading Comprehension, Brain-Based Learning Method.
This research is aimed to improve the students‟ reading comprehension skill through Brain-Based Learning Method. This research has three objectives of the study, there are 1) How is the implementation of Brain-Based Learning method in
improving students‟ reading comprehension skill for the 8th grade students of Smp Islam Sudirman 1 Bancak?. 2) Whether any improvements of the students‟ reading comprehension skill for the 8th grade students of Smp Islam Sudirman 1 Bancak by using Brain-Based Learning method or not? 3) How far is the improvement of Brain-Based Learning method in improving students‟ reading comprehension skill for the 8th grade students of Smp Islam Sudirman 1 Bancak?. This research was conducted at SMP Islam Sudirman 1 Bancak in academic year 2016/2017 especially in 8B class. The method of this research used Classroom Action (CAR). There were two cycles; each cycles comprised planning, implementing of the action, observing and reflecting. The techniques of collecting data are observation, test and documentation. The results show that the students‟ reading comprehension skill improves significantly. The T-calculation results of Cycle I is 2.89 and Cycle II is 3.98. the students who reach standarized score in cycle I, the percentage for Pre-test is 40.40 % and Post-test is 45.45 %. In cycle II, the percentage for Pre-test is 59.09 % and Post-test is 90.90%. So, it can be concluded
that there is significant improvement of students‟ reading comprehension by
x
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE OF PAGE ... i
DECLARATION ... ii
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR NOTES... iii
CERTIFICATION PAGE ... iv
MOTTO ... v
DEDICATION ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... vii
ABSTRACT ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... x
LIST OF THE TABLE ... xiii
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. Background of the study ... 1
B. Problem statements ... 4
C. Objectives of the study ...5
D. Limitation of the study ... 5
E. Benefits of the study ... 6
F. Clarification of the key terms ... 6
xi
CHAPTER II THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A. Review of the previous researches ... 9
B. Brain-Based Learning Method 1. Definition of BBL method ... 11
2. Procedure of BBL Method ... 20
C. Reading 1. Definition of Reading ... 23
2. Purpose of Reading ... 24
3. Techniques of Reading ... 26
D. Reading Comprehension 1. Definition of Reading comprehension ... 27
2. Components of Reading Comprehension ... 28
3. Levels of Reading Comprehension ... 29
4. Indicators of Students‟ Reading Comprehension ... 31
CHAPTER III METHOD OF RESEARCH A. Setting of the research ... 32
B. Method of the research ...33
C. Procedure of the research ... 34
D. Subject of the research ... 34
E. Data collection method ... 36
xii CHAPTER IV DATA ANALYSIS
A. Research findings ... 40
B. Discussion ... 50
C. Improvement ... 57
CHAPTER V CLOSURE A. Conclusion ... 59
B. Suggestion ... 60
REFERENCES ... 61
xiii
LIST OF THE TABLES
Tables 3.1 List of Research Samples of 8B class of SMP Islam Sudirman
1 Bancak
Table 4.1 The Result of Pre-test and Post-test Cycle I
Table 4.2 The Result of the Observation Sheet in Cycle I
Table 4.3 The Result of Pre-test and Post-test Cycle II
Table 4.4 The Result of the Observation Sheet in Cycle II
Table 4.5 The Result Analysis of Cycle I
Table 4.6 The Result Analysis of Cycle II
1 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the study
Every human was born with a high intelligence. They are able to
think and learn. The thing that distinguishes between each human being is
the speed in learning. Some of them are able to learn quickly and some
others learn somewhat slowly. But the certain fact, everyone is able to
learn because each of them was born with brains to understand how to
learn and think.
The brain is the major controller of the body, similar to a
computer‟s CPU (Central Processing Unit). It is the information processor
of the human body. Jensen (2000) writes that the brain is capable of
multitasking. “It assembles pattern, composes meaning, and sorts daily life
experiences from extraordinary number of clues”. In addition, the brain is
being extremely complex, it is a dynamic and an adaptive system. The
brain contains hundreds of billions of neurons and interneuron that
produce the great number of neural nets, or groups of neurons working
together. From which, our daily experience is created (Lackney, 2004).
The brain‟s activity is controlled by genetics, development,
experience, culture, environment, and emotions. It is constantly under
2
had started to increase dramatically with new information about the brain.
Developments in technology have allowed researchers to see inside the
brain, and visualize how the structures in the brain communicate.
Nowadays, this condition shows that human becoming lazy to
develop the potential of the brain is increasingly. When the human stopped
to harness the potential of the brain, it makes the cells of the brain die over
the time. So, it is very important for every human to understand more
about the potential of their brains as much as possible to keep use it in full
potential. One way is through the process of reading. By reading, a human
is going to be able to find many things such as new knowledge more
broadly, as well as a way to maintain the ability of the brain to process
information, compare, analyze and then evaluate.
In addition, reading is one of the most important aspects of
language learning. Mastery of these aspects are very important to create
effective learning. There are many materials listed in the curriculum of
middle school (Junior High School) is like comprehensive reading
material. Reading material in a comprehensive manner is very important to
master, becauset is not only useful in learning English language.
Therefore, learning to read in a comprehensive manner need to be
improved so that students are able to increase their reading skill.
Prasetyono (2008:53) states that reading is a series of activities of the mind
that is done with great attention in order to understand information through
3
has meaning and significance. Reading in reality is a complex that
involves many things, not just recites the writing, but also involves a
visual activity, psycholinguistics, and Metacognition (Uterus, 2005).
In the practice of English language learning in the Junior High
School Of Islamic Sudirman 1 Bancak, it is able to be seen that the
students are passive in following activities, especially when they were
learning to read and solve problems related to the text read. Most of the
students are less familiar with learning reading intensive. In addition, the
confidences level of students was still low. This was caused by a lack of
student motivation in following the instruction. The students found that it
was hard to learn about reading comprehensive because of the teaching
and learning process. It happened because the teachers still using the
conventional nature way in the process of teaching and learning. On the
conventional learning patterns, teaching and learning activities more often
directed at the flow of information from the teacher to the students. The
characterization of conventional lecture was accompanied with an
explanation, as well as the division of tasks and exercises. The
conventional learning centered was on the teacher. It made the
conventional learning were more likely on how to memorize than
emphasizes the concepts of information, practice reserved, as well as his
judgement was still traditional in nature.
The new innovations of teaching are needed to increase the
4
implemented to be active, meaningful, and fun. One alternative solution is
to be attempted through the application of brain-based learning model.
Brain-based learning (BBL) model are the students‟ activity and learning
process which conducted based on stages of brain-based activity.
In the model of brain-based learning (BBL), students are required
to be active in learning. So the learning process is not only sourced from
the teacher. Then it is able to provide a variety of learning. Brain-based
learning (BBL) model, also directs students to carry out learning in
accordance with the existing rules. Students are directed to re-think the
early material that associated with the material covered. By the application
of brain-based learning (BBL) model, it is expected to provide the
student‟s comprehensive reading skill.
Based on the description, the writer wants to conducts a research
entitled “The Use Of Brain-Based Learning Method To Improve Students‟
Reading Comprehension Skill (A Classroom Action Research For 8th
1. Is there any improvements of the students‟ reading comprehension
5
using Brain-Based Learning method or not?
2. How far is the improvement of Brain-Based Learning method in
improving students‟ reading comprehension skill for the 8th grade
students of SMP Islam Sudirman 1 Bancak?
C. Objectives of the study
Dealing with the problem statements, the objectives of this
classroom action research are as follow:
1. To find out whether there is improvements of the students‟ reading
comprehension skill for the 8th grade students of SMP Islam Sudirman
1 Bancak by using Brain-Based Learning Method or not.
2. To find out how far the improvements of the students‟ reading
comprehension skill using Brain-Based Learning method for the 8th
grade students of SMP Islam Sudirman 1 Bancak.
D. Limitation of the Research
Some aspects are able to be examined in analyzing the problems.
Nevertheless, in this graduating paper, the writer needs to limit the
analysis in order to be more focused. The writer focuses on the using
Brain-Based Learning (BBL) method to improve students reading
comprehension skill. The writer only analyzes the 8th grade students of
SMP Islam Sudirman 1 Bancak in the academic year of 2016 as the
6 study effectively.
E. Benefits of the study
This research is expected to give theoretical and practical benefits.
1. Theoretical Benefits
The result of the study is able to support the writer to broaden
her knowledge in teaching reading and to be used as the reference for
those who want to conduct a research in English teaching and learning
process.
2. Practical Benefits
This study is expected to help teacher in applying Brain-Based
Learning (BBL) method instruction in the process of teaching reading.
For the students, it is expected to give solution in comprehend the
F. Clarification of the key terms 1. Reading
According to Beene (1992:12), “reading is the process of findig
7
text. Reading is the complement of writing”.
2. Comprehension
Comprehension is the ability to understand something (Oxford
University Press 2003:80).
3. Brain-Based Learning Method
Brain-Based Learning (BBL) is a concept that creates learning with
empowering oriented in the human brain. According to Tung
(2015:35), “Brain-Based Learning is learning that are aligned with the
natural workings of the brain in learning. The focus likes and loves
learning rather than focusing on the regularity”.
Brain-Based Learning (BBL) method refers to teaching
methods, lesson designs, and school programs that are based on the
latest scientific research about how the brain learns, including such
factors as cognitive development—how students learn differently as
their age, grow, mature socially, emotionally, and cognitively.
G. Graduating Paper Outline
This research is organized into five chapters as follows: Chapter I
presents the introduction. It explains the comprehensive background of the
research which discusses the reason of why the researcher wants to
analyze the use of Brain-Based Learning (BBL) method to improve
students‟ reading comprehension. This chapter also reveals statements of
8
the study, clarification of key terms, the previous research, and
organization of graduating paper. After that, describing of theoretical
framework of this research will be the main discussion in the second
chapter. The description includes the general concept of Brain-Based
Learning (BBL) method that use in learning and teaching English. The
third chapter, research methodology shows the required aspects in this
quantitative research. The first aspect is research design which explores
the quantitative approach. The object of the research is the 8th students
grade in Smp Islam Sudirmaan 1 Bancak in academic year of 2016/2017.
Then, data of the respondents, data of students„ reading comprehension are
the next needed aspects to conduct this research. Chapter IV reports the
findings of the research. It presents the result of the analysis of collecting
data. As the last chapter of this graduating paper, chapter V consists of
closure which will be divided into two parts. There are conclusion of the
9
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A. Review of Previous Researches
In this study, the writer takes three of previous research to
emphasize and support her research. The first, the previous research is
written by Muhammet Ozden and Mehmet Gultakin entitled “The Effects
Of Brain Based Learning On Academic Achievement And Retention Of
Knowledge In Science Course”. The aim of this study is to investigate the
effects of brain-based learning in a 5th grade Science course on academic
achievement and retention of previously acquired knowledge. It was
conducted in 2004-2005 academic year at Kütahya Abdurrahman Pasa
Primary School in Kütahya, Turkey. Two classes, namely 5-A and 5-B,
were determined as experimental and control groups respectively. During
the research process, the experimental group was administered a
brain-based learning approach, while the control group was administered a
traditional teaching approach. Analysis of post-test and retention level
tests revealed a significant difference between the groups favoring
brain-based learning.
The second is written by E. Akyürek & Ö. Afacan entitled “Effects
Of Brain Based Learning Approach On Students’ Motivation And Attitudes Levels In Science Class”. The purpose of the study was to
10
motivation levels in 8th grade students‟ science classes. The research was
conducted with one experimental group and two control groups in
2011-2012 academic years. Totally 57 students, 19 in experimental group, 19 in
each control groups participated in this research. As a result, using
brain-based learning approach the experimental group's success was found to be
significant differences in favour of the experimental group.
The other research is written by Maryam Haghighi entitled “The
Effects Of Brain Based Learning On Iranian EFL Learners’ Achievements
And Retention”. The aim of this study is to investigate the effects of
brain-based learning in sophomore students majoring in Aircraft Repair &
Maintenance on academic achievement and retention. This experimental
study was designed as pre-test and post-test control group model. It was
conducted in 2013 academic year at Civil Aviation Technology College in
Tehran, Iran. The study lasted 16 weeks for a total of 63 class hours.
During the research process, the experimental group was administered a
brain-based learning approach, while the control group was administered a
traditional teaching approach. Analysis of post-test achievement and
retention tests revealed a significant difference between the groups
favoring brain-based learning.
Some studies above shows that using brain based learning are
always success when conducted in the learning process. Such as the
increasing result of academic achievements, the retention and the students
11
out the effects of using brain based learning focusing on teaching reading
comprehension. Whether brain based learning can successfully through in
reading comprehension or not.
B. Brain-Based Learning Method
1.
Definition of Brain-Based Learning (BBL)The brain is an organ used by humans to acquire knowledge.
The brain is the center of all human activities, such as thinking,
remembering, understanding, imagination, logic and so on.
Basically, every human has a brain with the same potential.
Tung (2015:35), “Brain-Based Learning is learning that aligned with
the natural workings of the brain in learning. The focus likes and loves
the learning process rather than focusing on the regularity”.
As De Porter (1992) in quantum learning, someone is going to
learn all the ability. If he liked what he learned, he is going to feel
happy to be involved in the learning (Gardner:1993)
12
principles of Brain-Based Learning (Khoe Yao Tung :2015) :
a. Learning involves physiological processes
The brain is going to work well when available process
physiology that supports it. When the learning process is done, the
brain is going to affect all parts of the body. Some of the
physiological processes that are able to affect the learning process
are:
1). The availability of water in the body.
When the body dehydrated the concentration and
intellectual ability is able to be reduced. It would be good
if the teachers allow students to drink when learning
going to maintain balance in the child's brain.
4). The availability of essential minerals in the body can
increase concentration of the brain, such as:
- Boron (found in nuts, apples, broccoli, grapes and
legumes)
13 and whole grains)
- Chromium (found in red meat, eggs, cheese and
seafood)
- Calsium (present in dairy products, almonds,
apricot, grains and green vegetables, sardines).
5). Activities, lighting and disease.
Students desperately need activity or movement in
learning such as role play, stretching and change the sitting
position. The ideal lighting also important for the students in
accordance with the appropriate level of lumens (soft and
natural). The diseases is able to hinder the learning process
such as tonsillectomy and fever that can lower concentrations
of studied because of the pain.
6). Chemicals food and working memory in the brain.
According to Jensen (2008), “some food chemicals
may affect the working of the brain's memory, among other
things” (Khoe Yao Tung:2015) :
- Acetylcholine (helps the brain to form long-term
memory on neurotransmitters)
- Lecithin (lecithin derived from eggs, salmon and
meats without fat is able to produce a functioning
memory boost choline)
14 increase attention)
- Adrenaline (is able to protect and improve memory,
and also keep a pleasant memory or traumatic)
b. The brain or thoughts of the social
The original version of parallel processors is cerebrum.
The brain is always trying to distinguish and understand
existing events. When it felt meaningless then the brain is not
going to process it.
c. The brain is always looking for things that have meaning and
automatically going to react to information coming.
d. Meaningful learning, often through patterns
Comprehension and memory can occur via the pattern or
through natural ways. Information is able to be either learned new
things, which evokes the emotions and life safety. Learning about
life safety gets more attention and more meaningful.
There is the KWL term (what you Know, Want, and
Learn), integrated study, field trip, hands on learning, learning
math-generalization (pattern), visualization, communication
(implementation).
e. Emotions is the crucial part (specific part) to understand the
pattern.
Learning activities conducted the brain heavily influenced
15
atmosphere of pleasant and conducive learning, in positive
expectations. Here are some of the techniques of towing
emotions:
- Humor break.
- Drama, story telling, collaborative learning, dan
jigsaw.
- Celebration.
f. Brain partially and through processes simultaneously.
Brain work simultaneously to process parts per part and as
a whole. The left and right parts of the brain have different
functions and work simultaneously complementing each other.
g. . Learning demand focusing on considerate and peripheral
perception.
The brain is always absorbing information directly at the
time of our attentions wether focused or not. So it is need created
an environment that supports.
h. .Learning processes always consciously and subconscious.
A conscious and subconscious learning process which is
done by the brain takes place continuously. Therefore, we are able
to give sufficient time for students to consolidate what they have
learned by using a different intonation, different speeds, and
different volumes.
16
of spatial memory) and recollections (rote learning).
Setting up the memory in the human brains are meaningful
and meaningless. It is need how to recite effectively . As well as it
gives some skills in students to recalling something, for example
by means of:
- Mnemonic : for example, mejikuhibiniu
- Chunking information : for example, by using the
hand that is lumped to calculate the number of days
in a month.
needs exposure, repetition, meaning and practice are important to
students.
k. Complex Learning are enhanced through the challenges and is
inhibited by the threat.
Learning is able to occur maximum when there is an
appropriate challanges. Not to be too easy or too difficult. There
are some tips in teaching:
- No test or quiz surprising because it would threaten
17
- Create the clear agenda when beginning lessons.
- Create a conducive climate when learning process
occurs.
- Use the clear assessment criteria.
- Avoid the statement that make the children
concentrations lower.
l. Every brain has a unique Setup.
Brain-based learning instruction would be better if it uses a
variety of learning or makes an applications of multiple
intelligences or Bloom's taxonomy.
According to Caine (1994), “a teacher who applies the
principles of brain-based learning must pay attention to the
following components”:
- Orchestrated immersion: Setting up the learning
environment to incorporate students into a learning
experience.
- Relaxed alertness: an attempt was made to eliminate
the fear when in a challenging environment.
- Activate processing: students incorporate and
internalize information by actively process. This
information is linked to previous learning so that
more attached to this new information.
18
learn in a safe and comfortable situation.
As Dave there are several things must attend to brain based
learning (Aminudin,2015:18) :
(focusing dimension), stimulate the system associated
with feelings / emotions mid brain (limbic) and cerebrum
(the dimensions of convergence).
c) Choices
19
to increase the students comfortable. For example, the
freedom to choose the seat position and the sitmate. It
is able to increase the level of students' understanding
Teachers are always responsible for guiding students in
setting goals, such as determining the learning objectives related
to real life.
though the music was inadvertently heard.
h) Questioning
A question addressed to students is going to make them
more active and feel appreciated.
i) Rewards
Giving compliment is a reward that can motivate students.
20
It means the technologies appropriately to support the
learning process.
k) Water
Water is one of the main components of the brain.
Because the brain consists of 80% water, the brain will be
sensitive to changes in pH. Therefore, in BBL a good teacher
instructs students to bring drinking water and drink it when
thirsty.
2.
The Procedure of BBL in Learning ProcessAccording to Jensen (2008), there are 7 stages in the brain
based learning process (Aminudin:2015:20) :
a. Pre-exposure
This stage helps the brain build a better conceptual map.
Here are the things to do:
1). Teachers showing a concept map of the new
material to be learned.
2). Master condition exciting learning environment.
3). Teachers convey learning objectives.
4). Students are required to bring drinking water /
21 b. Preparation
In this stage teachers create the curiosity and the
enjoyment of students. Here are the things to do:
1). Students are briefed in advance of the material to be
studied.
2).Students are encouraged to respond to whether or not
the material is relevant to what is real life.
c. Initiation and acquisitions
This stage is the stage of the creation of understanding,
connection or when neurons interconnected 'communicate'
each other. Here are the things to do:
1). Presenting the material with the help of audio-visual
media such as by using power point.
2).Starting active learning, for example by guiding
students into the discussion of the task group, filling
out the students worksheets to reinvent the concept.
d. Elaboration
This stage provides an opportunity for the brain to sort,
search, analyze, test and deepen learning. Here are the things to
do:
1). Students present the results of group discussions in
22
2). Conducting an open question and answer regarding
the outcome of the discussion or the material being
studied.
3). Students are asked to create a concept map
individual or group about what they have learned.
e. Incubation and insert the memory.
This phase emphasizes that the rest time and to repeat
an important thing. Here are the thingsto do:
1). Teachers give the stretches and relaxation by Brain
Gym.
2). Teachers show up the video that can train the brain
concentration and focus.
3). Teachers provide exercises.
f. Verification and checking of confidence.
In this stage, the teacher checks whether the student
already familiar with the material they have learned or not.
Students also need to know if he had understood the material or
not. Here the things to do:
1). The teacher checks whether the student is already
familiar with the material they have learned.
2). Teachers conduct a quiz to students either verbally
23 g. Celebrations and integration.
In this phase of the celebration, it is very important to
involve emotions. Here are the things to do:
1). Giving awards to students
2). Time sharing or telling stories exciting experience.
3). In closing the teachers along with students doing a
small celebration like cheering and clapping.
C. Reading
1. Definition of Reading
Reading is a verbal process interrelated with thinking and with all
other communication abilities-listening, speaking and writing.
Specifically, reading is a process of reconstructing from the printed
patterns on the page ideas and information intended by the author
(Dallman, Rouch, Char and Deboer, 1982:23)
According to Carrell (1988), Reading is a receptive language
process in hat it stars with linguistic surface representation encoded by
a writer and ends with meaning which the reader constructs
(Istikhayatun,2015:14). Thus, there is an essential interaction between
language and thought in reading. The writer encodes thought as
language and the reader decode language to thought.
24
communication process, it means that the process of putting the reader
in contact and communication with ideas”. Reading always involves an
interaction between the writer and the reader. It is culminating act of
the communication process, initiated by the thoughts of the writer and
expressed through symbols on the page.
Reading also as an interaction by which meaning encoded in visual
stimuli by author becomes meaning in the mind of the reader.
From the definition above it can be concluded that reading is an
effort to understand the content of the texts and the result of interaction
between the perception of graphic symbols and the readers‟ language
skills and the knowledge of the world. Besides that, reading is used to
get an idea, pleasure, or feeling that is expressed by the writer.
Reading is also interaction between the reader and the author‟s ideas.
2. Purposes of Reading
Grabe (2009: 8-10) stated that, “there are at least six main purposes
for comprehensive reading”. These purposes include:
1. Reading for information
The combination of scanning (identifying a
specific graphic form) and skimming (building a simple
quick understanding of the text) allow a reader to search
information.
25
Reading for quick understanding used for
variety of other reasons or it may be seen as a
superordinate purpose. The readers use skimming when
they want to determine what a text is, about and
whether or not they want to spend more time reading it.
3. Reading to learn
Reading to learn is often carried out in academic
and professional settings. Reading to learn places more
processing demands on the reader because the reader is
expected to remember the main ideas and many
supporting ideas and be able to recall this information
as needed.
4. Reading to integrated information
This type of reading requires that the reader
synthesize and learn information from multiple texts or
bring together information from different parts of a long
text.
5. Reading to evaluate, critique, and use information
It often represents an increasing level of demand
and a more complex interaction of reading processes.
6. Reading for general comprehension
26
common purpose for reading among fluent readers. It is
the default assumption for the term reading
comprehension.
3. Techniques of Reading
According to Wright (1989: 159), there are some
techniques of reading, such as:
a. Skimming
decide on the basis of the examination whether to read the
selection more intensively or not."
b. Scanning
Scanning is reading to locate specific information.
For example, locating a telephone number in a directory,
being able to search through material rapidly with given
purposes in mind in order to find a specific fact or an
answer to particular question plays a large role in much of a
27 c. Extensive Reading
Extensive reading is reading longer text, usually for
one‟s own pleasure. This is a fluent activity, mainly
involving global understanding. For example, reading
novel, newspaper, and short story.
d. Intensive reading
Intensive reading is reading shorter to extract
specific information. This is more an accuracy activity
involving reading for detail. For example, reading dosage
instruction of medicine.
D. Reading Comprehension.
1. Definiton of Reading Comprehension
Reading is not able to be separated from comprehension,
because reader has to comprehend what he/she reads to get information
from a text or a book. According to Scanlon et al (2010: 276),
Comprehension is an active and constructive process in which the
ultimate understanding of the text is determined by a combination of
what is stated directly in the text and the reader‟s preexisting
knowledge related to the topic of the text.
McGuinne (2004: 234) as quote by Istikhayatun, says that
28
but as an active one that engaged the reader. Reading came to be seen
as intentional thinking during which meaning is constructed through
interactions between text and reader. Reading comprehension was seen
as the construction of the meaning of a written text through a
reciprocal interchange of ideas between the reader and the message in
a particular text.
Comprehension includes the correct association of meanings
with word symbols, the selection of the right meaning suggested by the
content, the organization and retention of meanings, the ability to
reason one‟s way through smaller idea segments, and the ability to
grasp the meaning of a larger unitary idea (Dechant, 1982: 311)
Based on the above explanation, the writer concludes that
reading comprehension is a process of understanding written text,
integrate new ideas and generalize from what is read.
2. Components of Reading Comprehension
A study by Davis (in Heilman, Blair, & Rupley, 1961:241) as
quote by Istikhayatun (2015) is generally regarded as the significant
attempt to delineate separating comprehension skills. His analysis
showed the following five comprehension skills:
a. Recalling word meaning (vocabulary knowledge)
b. Drawing inferences from the content
29
d. Recognizing a writer‟s purpose, attitude, tone and mood.
e. Finding the answers to questions answered explicitly or in
paraphrasing.
3. Levels of Reading Comprehension
According to Heilman, Claire, & Rupley (1961), there are
three levels of reading comprehension: literal, interpretative, and
critical .(Istikhayatun:2015)
a. Literal Comprehension
Literal comprehension is an understanding the ideas and
information explicitly state in the passage. The abilities are:
1). Knowledge of word meaning.
2). Recalling of details directly stated and paraphrased in
own words.
3).Understanding of grammar clues-subject, verb,
pronouns, conjunctions, and so forth.
4). Recalling of main idea explicitly stated.
5). Knowledge of sequence of information presented in
passage.
b. Interpretative comprehension
Interpretative comprehension is an understanding of
ideas and information not explicitly stated in passage. The
30
1. Reason with information presented to understand
theauthor‟s tone, purpose, and attitude.
2. Infer factual information, main ideas, comparisons,
cause-effect relationship not explicitly stated in the
passage.
3. Summarization of story content.
c. Critical Comprehension
Critical comprehension includes analyzing,
evaluating, and personally reacting to information
presented in the passage. The abilities are:
1) Personal reacting to information in a passage
indicating its meaning to the reader.
2) Analyzing and evaluating the quality of written
information in terms of some standards.
In the other hand, Dechant as quote by Istikhayatun
explains that learning to comprehend involves a complex of
skill. Various writers have attempted to categorize these
into three or four levels. Lanier and Davis in Dechant
(1982:313) summarise comprehension skills and categorize
them as:
1) Literal skill (recognizing and recalling facts, details,
sequence, main idea, directions, and organization).
31
generalizing, deriving meaning from figurative
language, predicting, anticipating, and summarizing).
3) Critical skills (judging, detecting propaganda, analyzing,
checking validity, checking the author‟s biases and
purpose)
4) Creative skills (applying information, responding
emotionally).
4. Indicators/ the nature of Students’ Reading Comprehension
There are some indicators of students‟ reading comprehension:
a. The students are able to understand the function of
narrative/recount text.
b. The students are able to find the difficult words from narrative
/ recount text.
c. The students are able to answer the questions about
narrative/recount text.
d. The students are able to identify the important information on
the text.
e. The students are able to give opinions about the text that they
32 CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter pointed out the place, time and research methodology.
This research was conducted in SMP Islam Sudirman 1 Bancak Kab.
Semarang. This chapter consisted of general information of SMP Islam
Sudirman 1 Bancak which dealed with vision and mission; the situation of
teaching and learning activities; the teachers; students; staffs, and the
facilities of that school. The research method contained the types of the
research; population; sample; data sources; technique of data collection
and technique of data analyzes. The explanation of each point was
discussed further into detail explanation.
A. Setting of the Research
1. General Information of SMP Islam 1 Bancak Kab. Semarang
The research was conducted at SMP Islam Sudirman 1
Bancak. SMP Islam Sudirman 1 Bancak is located in Sultan
Agung street 172, Boto Kec.Bancak Kab. Semarang.
2. Vision and Mision
1) . Vision
The vision of this school was “to excelled in academics and
non academics achievement based on science technology and
33 2). Mision
a. To realize an adaptive curriculum development;
b. To enhance the development of educators and educations;
c. To pursue the implementation of active, innovative;
creative, and effective learning
d. To realize the improvement of education facilities;
e. To realize the increased competence of graduates;
f. To pursue a school-based management formidable;
g. Empower the community participation in the improvement
of the education funding is adequate, reasonable and fair;
h. To promote the development of assessment.
i. To improve the quality of faithfully and akhlakul karimah
B. Method of Research
The writer used classroom action research (CAR) in this
research. The definition of CAR according to Tampubolon, 2014 :
classroom action research is a research that to do by teacher in own
class by means of self-reflection. According to Tampubolon, 2014 :
in (Lewin, 1946) the procedures of classroom action research there
are 4 steps : (1) planning, (2) acting, (3) observing, (4) reflecting in
cycles.
The definition of classroom action research according Iraís,
34
out by teachers in their context, in their classrooms. Teachers
identify a problem or an area they wish to improve and based on
theory or experience or a hypothesis they think of an intervention.
They document the intervention and results of it. If the results are
positive they could lead to the dissemination of the information. If
not, the cycle may be started again.
C. Subject of the Research
In this research, the writer choose SMP Islam Sudirman 1
Bancak as subject of the study.Especially eighth grade students that
consist of two classes, but the writer took one class 8B. Their native
language is Bahasa Indonesia. They have been taught English since
the first year of school. They have English lesson at least two
meetings in a week which are each meeting along with two hours
lesson: one hour lesson is 45 minutes.
D. Data Collection Method
The writer would presented the data collecting as follows:
1. Observation.
Observation method was the most effective way to
complete the format or list of observations as instruments
(Arikunto: 2014:272). In this research, the writer observed the
35
process used check list. The observation noticed classroom
events and classroom interaction. The writer used field note.
David (1989:116) Keeping field notes was a way of reporting
observations, reflections, and reactions to classroom problems.
2. Test.
According to Arikunto (2014:266) test is used to
measure the basic capabilities and achievements. Especially for
learning achievement, tests commonly used in schools can be
divided into two general categories:
a. Tests Created by Teacher
Tests made by the teacher with a particular
procedure, but no trials have repeatedly then is not yet
known features and benefits.
b. Standardized Test
Tests that usually already provided in the testing
agencies, which are already guaranteed quality. And
Standardized Test trials has experienced repeatedly so it
can be said to be good. Writer prefers tests made by
teachers. Because teacher could measured students
difficulties in learning English, especially in teaching
reading comprehension. The writer used pre-test and
post-test. Pre-test was given to students at the very
post-36
test was given after students receiving the method from
teacher. Pre-test and post-test were to know the
differences between the students‟ reading
comprehension skill before and after the teacher used
the method.
3. Documentation.
Method of documentation that is looking for data about
things or variables in the form of notes, transcripts, books,
newspapers, magazines, etc.(Arikunto: 2014:274). In this case,
the writer made a note and took photographs as proof of
teaching learning activity, which was by using camera (photo)
and fill note.
E. Procedure of the Research
The writer applying classroom action research in her study.
It consisted of two cycles, each cycle consists of 4 steps, and they
are presented below:
1. Planning
In this stage, the writer did some activities, they
were:
a. Making the schedule of the research
b. Preparing material and making a lesson plan
37
d. Preparing list of the students‟ name and scoring
e. Making an observation sheet
f. Making pre-test and post test each cycle.
2. Action.
a. Giving pre-test
b. Teaching reading using Brain-Based Learning
Method.
collecting data. The writer as the teacher and helped by
a collaborator, researcher‟s partner, she observed the
learners‟ activity in teaching learning activity by using
observation sheet. The writer knew the students‟
activities and something occured during the teaching
learning process through observation sheet. Besides
using observation sheet, the observer also took pictures
as the image of documentation during teaching learning
process.
4. Reflection
38
test, she used the observation sheet. That would be used
to revise the steps in Cycle I in order to be better than
before. The writer as a teacher also did self evaluation;
it was expected to reform next cycle.
F. Techniques of Data Analysis
The writer would like to analyze the data by the action
research. The data was attained from teaching-learning process and
evaluation. The data will be analyzed in two ways;
1. Descriptive Qualitative Technique
Descriptive qualitative technique was used to know
students participation and their activities in classroom. In this
case the writer would used field note in which record all of
activities in classroom. It described the process and the result of
students‟ improvement in reading comprehension using Brain
Based Learning method.
2. Statistical Technique
Beside descriptive technique, the writer used a statistical
technique. In scoring the test, the students score was counted
with the following formula:
a. Mean calculation
Mean is formula to know the average of the students‟
score. The formula is:
39 Explanation :
M = Mean of the student‟s score
ΣX = the sum of student‟s score
N = the total number of students
b. Standard Deviation Calculation
The formula is:
= √∑2 − (∑)
2
Explanation :
SD : Deviasion Standart for one sample t-test
D : Different between pre-test post-test
N : Number of observation in sample
c. T-test
After calculating the SD, the writer did a test
to know is there any significant differences or not
between pre-test and post-test, the formula is:
=
(∑) (
√−1) Explanation :
to : T-test for the differences of pre-test and post-test
SD : Deviation Standart for one sample t-test
D : Different between pre-test and post-test
40 CHAPTER IV
DATA ANALYSIS
This chapter focused on analyzing the data collected. The writer gave
the details of the findings. It displayed the finding of the data collected since
in the begining until the end of the research. The findings consisted of the
results of the cycle I and cycle II. The two cycles were treatments for the
implementation of the Brain-Based Learning Method in the teaching reading
comprehension.
A. Research Findings
1. Cycle I
a. Score of the test of cycle I
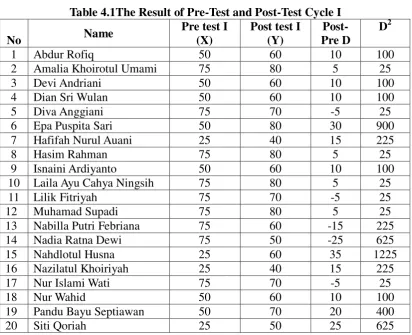
Table 4.1The Result of Pre-Test and Post-Test Cycle I
41
21 Sutarni 25 40 15 225
22 Syaiful Anwar 50 70 20 400
∑= 1200 1390 190 5750
1) Calculating Mean of Pre-Test and Post-Test cycle I
a) Mean of Pre-Test I
e) Mean of Pre-Test < Mean of Post-Test
f) There was improvement of reading comprehension skill
through Brain-Based Learning Method between Pre-Test I
(before the action) and the Post-Test I (after the action).
2) Calculating of Standart Deviation
SD= √∑2− (∑)2
SD = √575022 − (19022)2
42
b) Consult with t-table value
With df = 21, the value of t-table with level of
significant 5% is 2.079.
c) Comparing t-test with t-table
T-test = 2.89, therefore test was higher than
43
If T-test similar or higher than t-table, so null
hypothesis (H0) is rejected. H0 is no significant difference
between pre-test and post-test. T-table with n= 21 is 2.079.
The comparing result of t-test and t-table is 2.89 > 2.079.
So, t-test calculating is higher than t-table. Therefore, H0 is
rejected, it meant that there is a significant difference
between pre-test and post-test.
From the calculation above, the writer concluded
that between pre-test I and post-test I had significant
difference, where the students‟ score of post-test was higher
than pre-test. It showed that using Brain-Based Learning in
teaching reading could improved the reading
comprehension skill.
The improvement also could be calculated in
percentage by calculating students‟ Pre-Test and Post-Test
score. The calculation could be showed below :
P = 21−1
The calculation which showed the class percentages
44
passing grade. So the writer wanted to take a second cycle
to be able to improve the students‟ reading comprehension
skill.
b. Students‟ Observation sheet in Cycle I
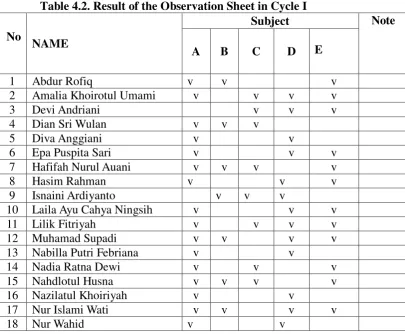
Table 4.2. Result of the Observation Sheet in Cycle I
45
B : Activeness in Learning Process
C : Understanding new vocabulary
D : Answer the question
E : Comprehend the material
2. Cycle II
a. Score of the test of Cycle II
Table 4.3 The Result of Pre-Test and Post-Test Cycle II
46
1) Calculating Mean of Pre-Test and Post-Test Cycle II
a) Mean of Pre-Test II
e) Mean of Pre-Test II < Mean of Post-Test II
f) There was improvement of reading comprehension skill
through Brain-Based Learning Method between Pre-Test II
(before the action) and the Post-Test II (after the action).
2) Calculating of Standart Deviation
SD= √∑2− (∑)2
SD = √917522 − (29522)2
SD = √417.04−179.56
47
b) Consult with t-table value
With df = 21, the value of t-table with level of
significant 5% is 2.079
c) Comparing t-test with t-table
48
From this calculation, the writer concluded that
between Cycle I and Cycle II had significant difference,
where the students‟ score of Cylce II was higher than score
of Cycle I. It showed that using Brain-Based Learning in
teaching reading could improved the reading
comprehension skill.
The percentage of students‟ score of Pre-Test II and
Post-Test II. The calculation could be showed below :
P = 21−1
The calculation which showed the class percentages
of students who pass the passing grade was :
49
b. Students‟ Observation sheet in Cycle II
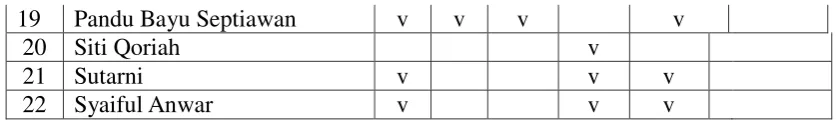
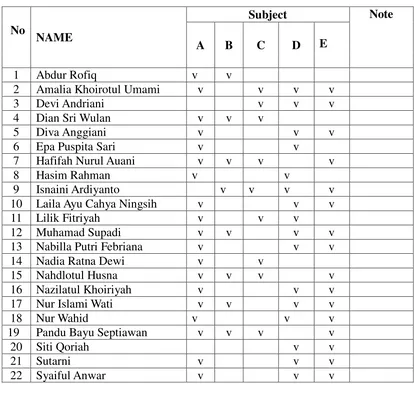
Table 4.4. Result of the Observation Sheet in Cycle II
No
B : Activeness in Learning Process
C : Understanding new vocabulary
D : Answer the question
50 B. Discussion
In this research, the writer acted as the teacher and learning process
was observed by her collaborator, Yuyun Azizah. The writer arranged two
cycles, each cycle consisted of planning, action, observation and
reflection. The whole step of this research were explained in this
description below:
1. Cycle I a. Planning
Before conducting the research, the writer prepared the
instrument of research, in the following :
1) Preparing the schedule of the research
2) Preparing material and making lesson plan
3) Designing the steps doing the action
4) Preparing list of the students‟ name and scoring
5) Preparing an observation sheet (to know the situation of
teaching learning process when method was implemented)
6) Preparing a test (to know whether the students‟ reading
comprehension skill was improved or not when the method is
applied). Pre-Test was given to the students before applying of
Brain-Based Learning Method and Post-Test was given to the
students after applying the method.
b. Implementation of the Action
51
the observer entered classroom. The situation was so crowded.
Some student still talked to their friends and the other students
was outside of the class.
Before the lesson, the teacher conducted the pre-test for
students in 15 minutes. She divided the sheets and walked around
the class in order to check students along do the test. After
students finished the pre-test, she began the teaching learning
process. The teacher introduced the model of discussion in
studying English especially reading through Brain-Based
Learning method and explained the role of Brain-Based Learning
method. She gave a text about “My Adolescence” to the students
to stimulate the students‟ curiosity.
After the teacher explained about recount text to the
students, she explained about the role of Brain-Based Learning
method in order to improve students‟ reading comprehension.
Then the teacher gave the students a chance to drink mineral
water to gave the nutrition for their brain. After that, the teacher
gave the students “Coconut Dance” as the Brain gym to reconcentrated their brain. Then the teacher and students did some
celebration with clapping hands.
Finally, the teacher summarized the recount text and
giving homework to the students. The students felt more enjoy
52
condusive. Then, the teacher conducted the post-test for students in
15 minutes. After finishing the Post-Test, students submitted the
answer sheet and teacher closed the meeting.
c. Observation
In the first cycle, the writer obtained the field note from
her partner. By monitoring the students‟ activity in this action,
the teacher (writer) could see that the students were not ready
yet when the teacher (writer) came to the class. It could be seen
from the situation of the class was crowded, because it was the
first time for them in using Brain-Based Learning method and
monitored by observer.
d. Reflection
After analyzing the result of the action in cycle I, the
students‟ reading comprehension was improved. It could be seen
by average of post-test, which was higher than the average of
pre-test.
However, there was weakness that happened in the
teaching learning process in cycle I. Some students still asked to
the other students when did the individual task. So, the writer
has to encourage the students to do the task by themselves. She
needed to ask the students to bring dictionary to help their
vocabulary difficulties and bring mineral water to give their
53
reading with the different topic for the next meeting to get better
result.
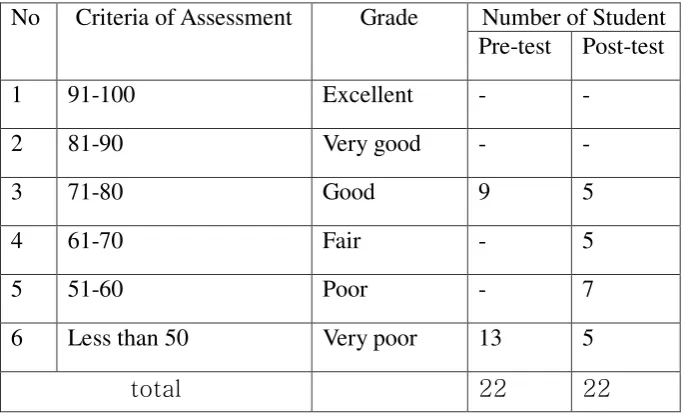
Table 4.5 Criteria of Students’ Achievement in Cycle I
No Criteria of Assessment Grade Number of Student Pre-test Post-test
From the result in the cycle 1, based on the passing
grade it was 70, the writer wanted to get 75% of total
students who got score approach the passing grade. The
students who got the score approach with the passing grade
was 45.45 % of the total students. It meant that the target of
the writer was not suitable.
So the writer wanted to take a second cycle to look
out the improvements of the students who passed the
passing grade.
2. Cycle II
Based on the result of cycle I, it was better to the teacher to
54 a. Planning
Before conducted the research, the writer prepared the
instrument of research, in the following:
1) Preparing lesson plan
2) Preparing material
3) Preparing list of the students‟ name and scoring
4) Preparing an observation sheet (to know the situation of
teaching learning process when method was
implemented).
5) Preparing a test (to know whether students‟ reading
comprehension was improved or not when the method
was applied).
b.Implementation of the action
On Friday, February 24th 2017, the teacher (writer) and the
observer entered classroom. In action 2, the teacher revised the
teaching learning process in cycle I to get better result in cycle II.
The teacher waited for a minute because some students were still
outside the class. Then teacher opened the lesson.
Before the lesson, the teacher conducted the pre-test for
students in 15 minutes. Then teacher started the lesson.
The students submitted their homework, then the teacher
55
After the teacher read the text, the students started to
identify the general structure of recount text. Before the teacher
made a discussion to solve the problem, the teacher asked the
students to drink mineral water. After that, the teacher and students
made a discussion tocheck the correct answer, then teacher gave
the students “Stand Line Game” as a brain gym. And finally, the teacher asked the students to do celebration with clapping hands.
Finally, the teacher summarized recount text to the
students. Then, the teacher gave students 15 minutes to do the
Post-Test. After finishing the Post-Test, students submitted the
answer sheet and teacher closed the meeting.
c. Observation
In the cycle II, the writer obtained the field note from her
collaborator. By monitoring the students‟ activity in this action, the
teacher could measure the students‟ understanding about Recount
Text. Based on the observation, most of students were active in
cycle II. They gave more attention to the teacher‟s explanation and
asked some questions when they did not understand about the
material.
d. Reflection
After analyzing the result of cycle I and cycle II, the writer
concluded that using Brain-Based Learning method could
56
by comparing the result of test between cycle I and cycle II. There
was significant improvement between the result of testing in Cycle
I and Cycle II
Table 4.6 Criteria of Students’ Achievement in Cycle II
No Criteria of Assessment Grade Number of Student Pre-test Post-test
1 91-100 Excellent - 7
2 81-90 Very good - 3
3 71-80 Good 5 6
4 61-70 Fair 12 4
5 51-60 Poor 4 -
6 Less than 50 Very poor 1 2
total 22 22
From the result in the cycle II, based on the passing grade
it was 70, the writer wanted to get 75% of total students who got
score approach the passing grade. The students who got the score
approach with the passing grade was 90.90%. Finally, the writer
get the results of this cycle was suitable with her target. It was
successful based on the percentage in the cycle I and cycle II. So,
57 C. Improvement
From the result of analyzing in Cycle I and Cycle II, there was
significant improvement on the students‟ reading comprehension skill,
it would be explained in the table below :
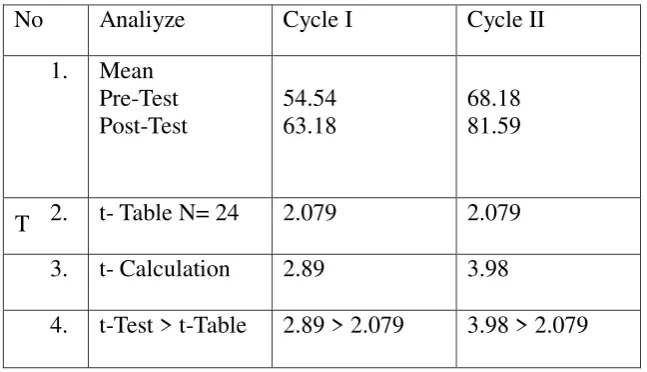
Table 4.7. The Mean And T-Calculation Of Students’ Score
T
The table shows that T- Calculation was higher than T- Table,
which meant there was significant improvements to the students‟ reading
comprehension skill from Cycle I and Cycle II. The result of T-
Calculation in Cycle I was 2.89 and Cycle II was 3.98 it meant that the
application of Brain-Based Learning methods could improved the
students‟ reading comprehension skill. From the finding research above, it
could be showed that Brain-Based Learning Method encourages the
students‟ motivation to study harder.
The result showed that the finding in cycle I were lower than the
passing grade in score 70. In the cycle II, the mean of post test was 81.95,
58
result could happen because there were some problems occurred. In cycle
I, the students were not familiar with the vocabulary in the text. In cycle II,
only two student who got score less than the passing grade, it was 45.