Recent Decisions in
Technologies for
Sustainable Development
Recent Decisions in
Technologies for Sustainable
Development
Selected, peer reviewed papers from the
3
rdInternational Conference on
Sustainable Technology Development
(ICSTD 2014),
October 30-31, 2014, Bali, Indonesia
Edited by
A. Ghurri, N.P.G. Suardana, N. N. Pujianiki,
I. N. Arya Thanaya, A.A. Diah Parami Dewi,
Copyright 2015 Trans Tech Publications Ltd, Switzerland
All rights reserved. No part of the contents of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without the written permission of the
publisher.
Trans Tech Publications Ltd Churerstrasse 20
CH-8808 Pfaffikon Switzerland
http://www.ttp.net
Volume 776 of
Applied Mechanics and Materials ISSN print 1660-9336
ISSN cd 1660-9336 ISSN web 1662-7482
Full text available online at http://www.scientific.net
Distributed worldwide by and in the Americas by
Trans Tech Publications Ltd Trans Tech Publications Inc. Churerstrasse 20 PO Box 699, May Street CH-8808 Pfaffikon Enfield, NH 03748
Switzerland USA
Preface
This volume was selected from papers presented at the 3rd International Conference on Sustainable Technology Development (ICSTD Bali 2014), which have been held in Udayana University Bali during October 30-31, 2014. The conference was organized by Faculty of Engineering, University of Udayana Bali Indonesia. This conference covered wide range of engineering issues toward the achievement of sustainablility.
In order to meet high standard of Applied Mechanics and Materials, the organization committee has made their efforts to do the following things. Firstly, all submitted papers have been reviewed by 2 anonymous expert reviewers, poor quality papers have been rejected after reviewing. Secondly, periodically review meetings have been held around the reviewers about three times for exchanging reviewing suggestions. Finally, the conference organization had several preliminary sessions before the conference. Through efforts of the scientific committee and Editors team, the volume will be the best collected papers.
We would like to thank the Faculty of Engineering, University of Udayana, the member of organizing and scientific committees, and also to TTP publisher.
Editors
Table of Contents
Preface
Chapter 1: Technologies of Sustainable Development in Civil
Engineering, Transportation and Urban Planning
Sustainable Development of Concrete Using GGBS: Effect of Curing Temperatures on the Strength Development of Concrete
G. Turu'allo 3
Properties of Sand Sheet Asphalt Mixture Incorporating Waste Plastic
I.N.A. Thanaya, I.G.R. Purbanto and I.G. Wikarga 9
Asphalt Pavement Temperature Profile for Tropical Climate in Indonesia
I.M.A. Ariawan, B.S. Subagio and B.H. Setiadji 17
The Development of Slurry Seal Design with Ordinary Portland Cement Replacement by Low Calcium Fly Ash
A. Setyawan, D. Sarwono and M.S. Adnan 24
The Structural Properties Assessment of Thin Hot Mixture Asphalt for Pavement Preservation
A. Setyawan, A.H. Mustafa Elshawesh and S. As'ad 30
Mechanical Strength of Hydraulic Binder Made by Blending Type I Portland Cement and Pozzolan
I.M.A.K. Salain 36
Laboratory Tests on Failure of Retaining Walls Caused by Sinusoidal Load
A.M. Hidayati, R.W. Sri Prabandiyani and I.W. Redana 41
Deformation Behavior of Concrete due to the Influence of the Steel Ring Width Variations as the External Confinement
E. Safitri, I. Imran, Nuroji and S. Asa'ad 47
Evaluation of High Grade Recycled Coarse Aggregate Concrete Quality Using Non- Destructive Testing Technique
N.N. Kencanawati, J. Fajrin, B. Anshari, Akmaluddin and M. Shigeishi 53
Experimental and Theoretical Investigation of Bolted Bamboo Joints without Void Filled Material
G.M. Oka, A. Triwiyono, A. Awaludin and S. Siswosukarto 59
The Significant Importance to Measure Road Safety
S.A. Caroline 66
Accessibility to Location of Activities in Denpasar City, Bali-Indonesia
P.A. Suthanaya 74
Travel Time Estimation Based on Spot Speed with Instantaneous and Time Slice Model
A.M.H. Mahmudah, A. Budiarto and S.J. Legowo 80
Port Location Selection Model: Case Study of Tourism Sector in Bali
R.M.N. Budiartha, T. Achmadi and D. Manfaat 87
Determining Passenger Car Equivalent for Motorcycle at Mid-Block of Sesetan Road
I.G.R. Purbanto 95
Readiness Criteria: Indonesias’ New Initiative to Ensure Sustainable Development Program
A. Merthayasa 101
Conceptual Framework of Bidding Strategy in Order to Improve Construction Project Performance
I.N.Y. Astana, H.A. Rusdi and M.A. Wibowo 108
The Conceptual Framework of Design Change Effects in Some Project Delivery Systems
A.A.G.A. Yana, H.A. Rusdi and M.A. Wibowo 114
An Identification of Construction Project Overheads for Sustainable Cost Management and Controlling Practices (CMCPs)
N.M. Jaya and A. Frederika 121
Risk Analyses for Riau Regional Water Supply Projects (SPAM), Indonesia
b Recent Decisions in Technologies for Sustainable Development
Modeling Discharge of the Bangga Watershed under Climate Change
I.W. Sutapa, M. Bisri, Rispiningtati and L. Montarcih 133
Water Resources Management of Subak Irrigation System in Bali
I.N. Norken, I.K. Suputra and I.G.N.K. Arsana 139
Study of the Evolution of Sanur Beach Nourishment Project for Beach Enhancement
I.G.B.S. Dharma and S.S. Efendi 145
Numerical Simulation of Breaking Waves in a Wave Group by SPH
N.N. Pujianiki 151
The Study on Bore Piles Foundation of the Reinforced Concrete Arch Bridge Beams of Tukad Pekerisan and Tukad Penet
I.N. Sutarja and I.W. Wayan Redana 157
The Importance of the Physical Boundary Line onBali Coastal Tourist Resorts
A. Rajendra, N. Temple and R. Nicholls 163
Comparative Analysis of Traditional House at Taman Mini Indonesia Indah with Modern House
S.Purnawan, I.W. Sukania and L. Widodo 169
Chapter 2: Materials and Technologies for a Sustainable Development
The Property and Applicability to Auto Industry of Natural Fiber Reinforced Composites
R.H. Hu, Z.G. Ma, S. Zheng, C.L. Zheng and A.J. Jiang 179
Fracture Parameters of Short Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polycarbonate Composite Fabricated by Injection Molding Process
M.G. Hwang, G.H. Kim, H.J. Park, Y.G. Lee, C.M. Yang, J.K. Lim and H.Y. Kang 186
Effect of Polar Extract of Cocoa Peels Inhibitor on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Mild Steel Exposed in Hydrocloric Acid
Gunawarman, Y. Yetri, Emriadi, N. Jamarun, Ken-Cho, M. Nakai and M. Niinomi 193
Hardness Distribution and Effective Case Depth of Low Carbon Steel after Pack Carburizing Process under Different Carburizer
D.N.K.P. Negara, I.D.M.K. Muku, I.K.G. Sugita, I.M. Astika, I.W. Mustika and D.G.R. Prasetya 201
The Effect of Solidification on Acoustical of Tin Bronze 20Sn Alloy
I.K.G. Sugita and I.G.N. Priambadi 208
Morphological Analyses and Crystalline Structures of Anodic TiO2 Thin Film on Ti6Al4V
Alloy Using Phosphate and Calcium Containing Electrolyte under Different Voltage and Calcium Molarity
I.N.G. Antara, K.I.M. Gatot, I.M. Budiana and D.K. Choi 215
Determination of Optimal Clinker Factor in Cement Production by Chemical Grinding Aids Addition
T.Eryanto and E. Amrina 223
Wear of Carbon Steel (0.65%C) in Rolling-Sliding Contact with Creep Ratio
M. Widiyarta, T.G.T. Nindhia and H. Mudiastrawan 229
Hardness Prediction Based on P-h Curves and Inverse Material Parameters Estimation
I.N. Budiarsa 233
The Influence of Austenisation Temperature and Holding Time on Mechanical Properties, Scale Thickness, and Microstructure in Alloy Steel
A. Aziz, M. Hidayat and I. Hardiyanti 239
Hardness, Density and Porosity of Al/(SiCw+Al2O3p) Composite by Powder Metallurgy
Process without and with Sintering
K. Suarsana and R. Soenoko 246
Development of Fiberglass Woven Roving Composite as an Alternative Material for the Hull of Fishing Boat
Winarto, W. Eddy, R. Liza and H. Syamsul 253
Tensile Strength of Banana Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites Materials
A.P. Irawan and I.W. Sukania 260
Green Composites Based on Recycled Plastic Reinforced Local Sisal Fibers
N.P.G. Suardana, N.M. Suaniti and I.P. Lokantara 264
Cement Bonded Sol-Gel TiO2 Powder Photocatalysis for Phenol Removal
Applied Mechanics and Materials Vol. 776 c
Review on Zn-Based Alloys as Potential Biodegradable Medical Devices Materials
M.S. Dambatta, D. Kurniawan, S. Izman, B. Yahaya and H. Hermawan 277
Bone Implant Materials from Eggshell Waste
I. Sopyan 282
Boiling Phenomenon of Tabulate Biomaterial Wick Heat Pipe
W.N. Septiadi and N. Putra 289
Fluidization Characteristic of Sewage Sludge Particles
I.N.S. Winaya, R.S. Hartati and I.N.G. Sujana 294
Design of Fluidized Bed Co-Gasifier of Coal and Wastes Fuels
I.N.S. Winaya, R.S. Hartati, I.P. Lokantara, I.G. Subawa and I.M.A. Putrawan 300
Chapter 3: Advanced Decisions in Mechanical Engineering
Magnetic Camera and its Applications in Aging Aircraft, Express Train and Pipelines for Green Technology
J.Y. Lee and J.M. Kim 309
Buckling Analysis on Pechiko Field of Fixed Offshore Platform in Makassar Strait
M.Z.M. Alie, Y.R. Palentek and D.G. Sesa 313
Simulation of a Differential-Drive Wheeled Mobile Lego Robot Mindstorms NXT
I.W. Widhiada, C.G.I. Partha and Y.A.P. Wayan Reza 319
Design and Simulation of Five Fingers Gripper for Dexterous Pick-Up Various of Components
I.W. Widhiada, E. Pitowarno, C.G.I. Partha and Y.A.P. Wayan Reza 325
Tar Balls Collector for Mechanical Recovery in Combating Oil Spill on the Marine Environment
C.P. Mahandari, M. Yamin and D.S.A. Asandi 331
Three Wheel Bike as Physical Therapy Equipment for Post-Stroke Patient
I.M.L. Batan, Rodika and M. Riva'i 337
Geometric Progression Application in Design Transmission Gear Ratio
A.A.I.A.S. Komaladewi, I.G.A.K. Suriadi and I.K.A. Atmika 343
Role of Risk Management in Effective Maintenance
H.A. Yuniarto and P.F. Paristiawati 349
Redesign Combustion Air Shelter of the Furnace to Improve the Performance in Melting Bronze for Manufacturing Gamelan
I.G.N. Priambadi, I.K.G. Sugita, A.A.I.A.S. Komaladewi, K. Astawa and I.W.B. Adnyana 355
Model of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Emission from Motorcycle to the Manufactures, Engine
Displacement, Service Life and Travel Speed
A.M. Mulyadi and S. Gunarta 361
Experimental Study of Heat Transfer Characteristics of Condensed Flow on the Vertical Wave Plates
W.H. Piarah and Z. Djafar 371
Forces Analysis on a Spherical Shaped Delivery Valve of Hydram Pump
M. Suarda 377
The Influence of Distance Variation between Rings with Sloping Position on the Cylinder Surface to Drag Coefficient
S.P.G.G. Tista, A. Ghurri and H. Wijaksana 384
Auto PID Tuning of Speed Control of DC Motor Using Particle Swarm Optimization Based on FPGA
H. Tayara, D.J. Lee and K.T. Chong 390
Mobile Robot Motion Planning to Avoid Obstacle Using Modified Ant Colony Optimization
N. Habib, A. Soeprijanto, D. Purwanto and M.H. Purnomo 396
Mobile Robot Motion Control Using Laguerre-Based Model Predictive Control
M. Chipofya, D.J. Lee and K.T. Chong 403
Applied Mechanics and Materials Vol 776 (2015) pp 289-293 Submitted: 2015-02-17 © (2015) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Accepted: 2015-04-10 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.776.289
Boiling Phenomenon of Tabulate Biomaterial Wick Heat Pipe
Wayan Nata Septiadi
1,a, Nandy Putra
2,b1
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Udayana, Kampus Bukit Jimbaran, Bali - Indonesia
2
Heat Transfer Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Indonesia Kampus UI-Depok 16424 Indonesia
a
wayan.nata@gmail.com, bnandyputra@eng.ui.ac.id
Key Words: heat pipe, wick, biomaterial
Abstract. This research purposed to know the performance of heat pipe using wick made from biomaterial. Biomaterial (Coral) is the porous media which has the relative homogenous and small porous structures. The homogenous structures and the small biomaterial have the better capillarity and could be used as wick to circulate condensate in heat pipe. The heat pipe made from copper pipe with 50 mm in length and the inside and outer diameter was 25 mm and 24 mm in each, with the wick as thick as 1 mm made from Tabulate. Heat sink was adhered to the condenser part of heat pipe as wide as 637.5 cm2. The study was the observation of phenomena in porous media boiling between biomaterials with solid copper, in which the observations were made by using High Speed Video Camera (HSVC). Tabulate biomaterial has the porous structure which quite homogeny and the best capillary energy. The biomaterial as wick heat pipe could keep the condition of heat pipe from easily reachs the transition condition.
Introduction
Since the earlier of invention of electronic technology, the production of heat flux is on the increase and this trend is expected to increase provided that the development of the electronic is always occurred (Chein et al., 2004). The high amount of heat flux was produced by electronic equipment give vast challenge to researchers in thermal area to manage this problem (Solomon et al., 2012). The use of cooler systems which set to work through two phases is greatly used because the heat transfer through these two phases is better than another cooler system with mono phase such as heat sink, heat sink fan and liquid cooling block. The combination of porous media in cooler equipment with two phase also become to use especially as the capillary porous to circulate the working fluid. Heat pipe it has excellent ability of dissipating heat through the working fluid phase change.
In addition to working fluid, material, dimension, and form, one of the determinations of heat pipe performance is wick (Reay et al., 2006). Wick plays important rules in working fluid circulation especially when condensate process returns to the evaporator site. Wick in heat pipe is a capillary structure and an artery which function as a returning canal from the working fluid of condenser to the evaporator site through adiabatic site (Mudawar, 2001). Therefore, wick plays an important role in heat pipe (Weibel et al., 2010). There are variety of wick, starting from screen mesh, sintered powder, groove, and wire which all made from metal, composite, ceramic and biomaterial (Harris, 2008; Li et al., 2010; Deng et al., 2013; Kempers et al., 2008; Putra et al., 2013).
290 Recent Decisions in Technologies for Sustainable Development
level from wick. K.C Leong et al. (1997) also had characterized the effect of sintering temperature (800oC and 1000oC) and sintering time to the porosity of wick. There are also lots of researches have been done relating to wick heat pipe (Mishra et al., 2010; Tang et al., 2010; Holley et al., 2006; Lago et al., 2001).
Biomaterial (Coral) is the porous media which has the relative homogenous and small porous structures. This homogenous structures and the small biomaterial have the better capillarity and could be used as wick to circulate condensate in heat pipe. The proposed of this research is to study the performance of heat pipe in applying biomaterial as the base material of wick.
Methods
The preparation of biomaterial and solid cupper wick
Wick heat pipe made from tabulate biomaterial and the average of the mean pour diameter ± 52.95 µm obtained from the test results of SEM, as it could be seen from figure 1. Figures show that the pore structure of tabulate biomaterials quite homogeneous with the pore diameter range is from 20 µm to 60 µm. Wick had 50 mm in length, and 15 mm and 14 mm in diameter respectively. Wick also made with solid copper which is formed of the same size.
Fig 1. (a) Biomaterial wick and (b) The picture of SEM biomaterial
Experimental set-up
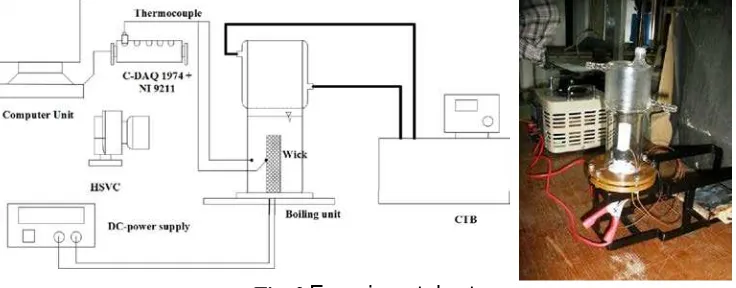
[image:11.595.116.484.569.713.2]Boiling phenomena observed using boiling tubes made of phyrex and using water distillated as the working fluid. The cathride heater is submerged in water used as a heat source with load variation is set by using a DC-power supply.
Fig. 2 Experimental set-up
Applied Mechanics and Materials Vol. 776 291
each of pieces on the surface and the working fluid. Data measured from the thermocouple was recorded using c-9174 DAQ and NI module 9211. The pattern and diameter size of the bubbles was recorded by using High Speed Video Camera (HSVC), as show in the figure 2.
Result and Discussion
The phenomenon of bobble and nucleic form could be seen at Figure 3. The comparison between heaters without wick biomaterial is studied to analyze the boiling phenomenon in heat pipe owing to the use of this biomaterial wick. The occurrence of heat flux and the bobble condition and boiling nucleic is the observation aspect in this study. Heater without the porous layer of biomaterial wick could be a data base that was observed to compare the difference of the temperature between the heater wall and heater with the water temperature at the saturation condition with the use of the quiet homogenous porous media. It also could be seen from the picture that the bobble structure was small and relative similar to the use of wick biomaterial, compared to without the use of biomaterial wick at the heater surface. At the same heat flux, the boiling at the heater without biomaterial wick was about to fuse and form the big bobble. The fuse of this bobble became bigger and this condition was not effective because the temperature of the wall surface will increase so that the difference of temperature between wall temperature and saturation temperature would also increase.
292 Recent Decisions in Technologies for Sustainable Development
Fig 4. The comparation of calor flux and the different temperature between heater without and with wick biomaterial
Figure 4 shows the deviation of temperature (∆T) decreased when the boiling nucleic start to appear and detach from the wall surface. In this heat transfer, the transient condition could be prevented. This is a condition which the deviation of temperature was considerable high but the heat flux was the lowest. The figure shows that with the addition of a porous media in tabulate biomaterial, the heat flux was relative to the smooth metal surface can be achieved in the temperature difference between the wall and the temperature saturation of the smaller working fluid. The The small and uniform bubbles are formed continuously on the biomaterials due to a fairly homogeneous pore structure. The existence of bubbles that relatively uniform and easily detached to the surface results the heat from the evaporator can be transferred quickly to the condenser.
Thus, the addition of porous media like biomaterial which has the homogenous porous could keep the heat pipe from easily reach the transition condition. The same view was also conducted by Justin A et al. (2012) which tried to study the boiling from the heater using sintered powder at its surface.
Conclusion
Wick is one of the crucial factor in increasing the performance of heat pipe. The homogenous and the refined porous structure could increase the capillary energy of the porous media which is used as the wick heat pipe. Tabulate biomaterial has the porous structure which quite homogen and the best capillary energy. The biomaterial as wick heat pipe could keep the condition of heat pipe from easily reach the transition conditon.
Acknowledgements
[image:13.595.162.438.72.303.2]Applied Mechanics and Materials Vol. 776 293
References
[1] Brusly Solomon, K. Ramachandran (2012). Thermal performance of a heat pipe with nanoparticles coated wick, Applied Thermal Engineering, Vol. 36 10 6e11 2.
[2] A. J. R. R. Kempers, D. Ewing, C.Y. Ching. (2008) "Characterization of evaporator and condenser thermal resistances of a screen mesh wicked heat pipe," International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol. 51, 6039-6046.
[3] Brian Holley, Amir Faghri (2006). Permeability and effective pore radius measurements for heat pipe and fuel cell applications. Applied Thermal Engineering 26 448–462.
[4] D. Deng, D. Liang, Y. Tang, J. Peng, X. Han, and M. Pan. (2013) "Evaluation of capillary performance of sintered porous wicks for loop heat pipe," Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science.
[5] D.K. Mishra, T.T. Saravanan, G.P. Khanra, S. Girikumar, S.C. Sharma, K. Sreekumar, P.P. Sinha (2010). Studies on the processing of nickel base porous wicks for capillary pumped loop for thermal management of spacecrafts, Advanced Powder Technology, Vol.21 658–662.
[6] J. A. Weibel, S. V. Garimella, and M. T. North, (2010) "Characterization of evaporation and boiling from sintered powder wicks fed by capillary action," International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol. 53, 4204-4215,.
[7] J. R. Harris, (2008) "Modeling, Designing, Fabricating, and Testing of Channel Panel Flat Plate Heat Pipes," Logan, Masters Thesis.
[8] K.C. Leong And C.Y. Liu, (1997) Characterization of Sintered Copper Wicks Used in Heat Pipes, Journal of Porous Materials Vol. 4, 303–308.
[9] Mudawar. (2001) "Assessment of high-heat-flux thermal management schemes," Components and Packaging Technologies, IEEE Transactions on, Vol. 24, 122-141.
[10] Marcelo Lago, Mariela Araujo (2001). Capillary rises in porous media. Physica A 289 1– 17.
[11] N. Putra, W. N. Septiadi, and R. Irwansyah, (2013) "Effect of Concentration and Loading Fluid of Nanofluids on the Thermal Resistance of Sintered Powder Wick Heat Pipe," Anvanced Material Research.
[12] N. Thuchayapong, A. Nakano, P. Sakulchangsatjatai, and P. Terdtoon, (2012) "Effect of capillary pressure on performance of a heat pipe: Numerical approach with FEM," Applied Thermal Engineering, Vol. 32, pp. 93-99.
[13] Reiyu Chein, Guanming Huang. (2004) Thermoelectric cooler application in electronic cooling, Applied Thermal Engineering, Vol. 24, 2207–2217.
[14] Justin A. Weibel, Suresh V. Garimella (2012). Visualization of vapor formation regimes during capillary-fed boiling in sintered-powder heat pipe wicks. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.55 3498–3510.
Boiling Phenomenon of
Tabulate Biomaterial Wick Heat
Pipe
by
Wayan Nata Septiadi
FILE
T IME SUBMIT T ED 10- JUL- 2015 06:12AM
SUBMISSION ID 554907040
WORD COUNT 2046
CHARACT ER COUNT 10750
9
%
SIMILARIT Y INDEX
1
%
INT ERNET SOURCES
9
%
PUBLICAT IONS
0
%
ST UDENT PAPERS
1
3
%
2
1
%
3
1
%
4
1
%
Boiling Phenomenon of Tabulate Biomaterial Wick Heat
Pipe
ORIGINALITY REPORT
PRIMARY SOURCES
Putra, Nandy, Wayan Nata Septiadi, Rosari
Saleh, Rardi Artono Koestoer, and Suhendro
Purbo Prakoso. "The Effect of CuO-Water
Nanofluid and Biomaterial Wick on Loop
Heat Pipe Performance", Advanced Materials
Research, 2014.
Publicat ion
Pan, Z.A., and J.X. Zhu. "Context Awareness
on Mobile Devices", Applied Mechanics and
Materials, 2015.
Publicat ion
Putra, Nandy, Rosari Saleh, Wayan Nata
Septiadi, Ashar Okta, and Zein Hamid.
"Thermal performance of biomaterial wick
loop heat pipes with water-base Al2O3
nanofluids", International Journal of Thermal
Sciences, 2014.
Publicat ion
Putra, Nandy, Wayan Nata Septiadi, Ranggi
Sahmura, and Cahya Tri Anggara.
5
1
%
6
1
%
7
1
%
8
<
1
%
9
<
1
%
10
<
1
%
Copper-Powder Vapor Chamber for
Electronic Cooling", Advanced Materials
Research, 2013.
Publicat ion
Uranus, Henri P.. "Computational Study on
Modeness of Silicon on Insulator Photonic
Wire with Water Cladding", Procedia
Engineering, 2012.
Publicat ion
Putra, N.. "Application of nanofluids to a heat
pipe liquid-block and the thermoelectric
cooling of electronic equipment",
Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science,
201110
Publicat ion
Putra, Nandy, Wayan Nata Septiadi, and
Ranggi Sahmura. "Analysis of CuO-Water
Nanofluid Application on Heat Pipe", Applied
Mechanics and Materials, 2014.
Publicat ion
www.waset.org
Int ernet Source"High-Heat-Flux Distributed Capillary Artery
Evaporators", Handbook of Porous Media
Third Edition, 2015.
Publicat ion
11
<
1
%
EXCLUDE QUOT ES OFF
EXCLUDE BIBLIOGRAPHY
ON
EXCLUDE MAT CHES OFF
Electronic and Photonic Packaging Electrical
Systems Design and Photonics and
Nanotechnology, 2005.
Publicat ion
Li, J.. "Experimental study on capillary
pumping performance of porous wicks for
loop heat pipe", Experimental Thermal and
Fluid Science, 201011