Linta Hayatunisa, 2013
STUDENT TEAMS ACHIEVEMENT DIVISIONS (STAD) IN TEACHING
WRITING NARRATIVE TEXT
A Research Paper
Submitted to the English Department of FPBS Indonesia University of Education in Partial
Fulfillment of the Requirements for Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
By:
Linta Hayatunisa
0906783
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
Linta Hayatunisa, 2013
Student Teams Achievement Divisions (Stad) In Teaching Writing Narrative Text
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
2013
STUDENT TEAMS ACHIEVEMENT DIVISIONS
(STAD) IN TEACHING WRITING NARRATIVE
TEXT
Oleh Linta Hayatunisa
Sebuah skripsi yang diajukan untuk memenuhi salah satu syarat memperoleh gelar Sarjana Pendidikan pada Fakultas Pendidikan Bahasa dan Seni
© Linta Hayatunisa 2013 Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia
Desember 2013
Hak Cipta dilindungi undang-undang.
Linta Hayatunisa, 2013
LINTA HAYATUNISA
STUDENT TEAMS ACHIEVEMENT DIVISIONS (STAD) TECHNIQUE IN TEACHING WRITING NARRATIVE TEXT
APPROVED BY:
First Supervisor,
Prof. Hj. Emi Emilia, M.ed., Ph.D.
NIP. 1966091619990012001
Second Supervisor,
Sri Harto, S. pd., M.pd.
NIP. 197205012006041004
Head of English Department
Prof. Dr. H. Didi Suherdi, M. Ed
Linta Hayatunisa, 2013
Student Teams Achievement Divisions (Stad) In Teaching Writing Narrative Text
ABSTRAK
Penelitian ini menginvestigasi keefektifan dari teknik Student Teams Achievement Divisions (STAD), yang diusulkan oleh Slavin (2005) dan kawan-kawan, dalam mengajar menulis teks naratif. Penelitian ini juga menginvestigasi respon-respon dari siswa untuk melihat potensi dari teknik ini jika dipakai dalam kelas. Penelitian ini menggunakan desain penelitian studi kasus kualitatif. Data dari penelitian ini diperoleh dari beberapa sumber dari kuestioner, observasi kelas (pada saat proses pembelajaran), dan contoh tulisan dari teks siswa yang dianalisis menggunakan systemic functional grammar (SFG) dalam segi struktur teks dan kebahasaan dari teks naratif. Hasil yang didapat menujukkan bahwa teknik Student Teams Achievement Divisions (STAD) efektif untuk digunakan dalam mengajar menulis teks naratif. Data dari observasi kelas dan teks-teks siswa menunjukan adanya perubahan dalam kemampuan menulis siswa dalam menulis teks naratif. Para siswa mampu menulis sebuah teks naratif yang baik dengan struktur teks yang jelas dan kebahasaan yang tepat. Terlebih lagi, data dari kuestioner menunjukan respon dari para siswa terhadap tekik STAD. Pertama, teknik STAD membantu siswa secara akademik dan social. Kedua, teknik ini juga memotivasi siswa untuk belajar. Akan tetapi, dalam kelas STAD, beberapa siswa tidak ikut berpartisipasi di dalam tim karena siswa yang lebih pintar lebih mendominasi di dalam diskusi kelompok. Berdasarkan hasil yang didapat, teknik STAD direkomendasikan untuk digunakan dalam mengajarkan bahasa Inggris, terlebih lagi untuk mengajar menulis teks naratif. Namun, untuk memaksimalkan teknik ini, beberapa aspek dari teknik ini diubah, misalnya, guru memerlukan pedoman yang jelas untuk diberikan kepada siswa, member dalam timnya harus diganti-ganti, dan aktivitasnya harus lebih bervariasi.
ABSTRACT
This study investigates the effectiveness of Student Teams Achievement Divisions (STAD) technique, proposed by Slavin (2005) and his colleagues, in teaching writing Narrative text. This study also investigates students’ responses to see the potential of the technique to be applied in the classroom. The study employs a qualitative case study research design. The data were obtained from several sources, including questionnaire, classroom observation (teaching process), and collection of
samples of students’ texts in every meeting, which were then analysed using systemic
functional grammar (SFG) in terms of generic structures and linguistic features of Narrative text. The findings reveal that Student Teams Achievement Divisions (STAD) technique is effective in teaching writing Narrative text. Data from
classroom observation and students’ texts show the improvement in students’ writing
skill in writing narrative text. The students write a good narrative text with clear generic structures and appropriate linguistic features. Moreover, the data from the questionnaires shows some responses from the students toward STAD technique. Firstly, STAD technique is found to be helpful for the students academically and socially. Secondly, the technique is also proven to motivate the students to learn more. However, to some extended some students did not want to participate in the team because the higher achiever students tended to dominate more in the discussion. Based on the findings, it is recommended that STAD technique should be used in teaching English, especially in teaching writing Narrative text. However, in order to achieve maximum benefits of the technique, it is suggested that some aspects of the method should be improved, for example, the teacher needs a clearer guidance to be given to the students, the team should be shuffled, and the activity should be more varied.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHAPTER I : INTRODUCTION 1 1.1 B CHAPTER II : THEORETICAL FOUNDATION... 5 2.1 Writing...
2.1.1 The Nature of Writing ...
Linta Hayatunisa, 2013
Student Teams Achievement Divisions (Stad) In Teaching Writing Narrative Text
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
2.1.2 The Aspect of Writing ... 2.2 Student Teams Achievement Divisions (STAD) ....……… 2.2.1 The Nature of STAD ... 2.2.2 Main Concept of STAD ... 2.2.3 Implementing STAD in the Classroom ... 2.2.4 Procedures of STAD in Classroom ... 2.2.5 Advantages an Disadvantages of STAD ... 2.3 Finding from Previous Studies ... 2.4 Narative ... 2.4.1 Definition of Narrative ... 2.4.2 Generic Structure of Narrative ... 2.4.3 Language Feature of Narrative ... 2.5 Conclusion ...
CHAPTER III : RESEARCH METHODOLOGY... 16
3.1 Site and Participants …………...………...……… 3.4.1 Data Analysis of the Classroom Observation ... 3..4.2. Data Analysis of the Students’ Texts ... 3.4.3 Data Analysis of the Questionnaire ... 3.4.3.1 Likert Scale ...
4.1 Data from Observation ... 4.2 Data from Students’ Te.. ... 4.2.1 Analysis of High Achiever Student’s Text ... 4.2.1.1 First Draft ... 4.2.1.2 Second Draft ... 4.2.1.3 Third Draft ... 4.2.1.4 Final Writing ... 4.2.2 Analysis of Middle Achiever Student’s Text ... 4.2.2.1 First Draft ... 4.2.2.2 Second Draft ... 4.2.2.3 Third Draft ... 4.2.2.4 Final Writing ... 4.2.3 Analysis of Low Achiever Student’s Text ... 4.2.3.1 First Draft ...
CHAPTER V : CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS …………..…….. 67
5.1 Conclusions……… 67
5.2 Suggestions……… 68
REFERENCES ……… 69
Linta Hayatunisa, 2013
Student Teams Achievement Divisions (Stad) In Teaching Writing Narrative Text
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter provides a brief description of whole contents of the research including background, research questions, research aims, the scope of the research, the significant of the research, the clarification of terms, and the organization of the paper.
1.1Background
Writing is seen as the most difficult skill to be learned among the four skills in English:
listening, speaking, reading, and writing because writing is “a complex skill that engages the
writer in physical as well as mental effort” (Constantine, 2007, p. 7). Writing is “not only how
people produces some words” (Alwasilah, cited in Alwasilah, 2007, p. 42), but it also requires a
long and complex process. This statement is also supported by Myles (2002, p. 1) who states
“…writing in a second language is a complex process involving the ability to construct a text in
order to express one’s idea effectively in writing.” Moreover, Byrne (1993, p. 4) says, usually, writers face “psychological problems, linguistic problems and cognitive problems” in writing
which is why writing is tend to be seen as a difficult skill to be learned.
The difficulties in writing have been one of the reasons why students see writing as a difficult skill to be learnt. Teachers need to find a suitable method in teaching writing in order to make the students improve their writing skill. One method that can be applied in teaching writing is Student Teams Achievement Divisions or STAD.
Student Teams Achievement Divisions (STAD) is “a cooperative learning method developed by Slavin and his colleagues which has been influential in bringing positive effects in multiple
grades and subjects” (Alijanian, 2012, p. 1). STAD is the “easiest technique” (Palmer, 1998, p.
1) to be applied in the classroom among the other cooperative learning techniques. In STAD
approach, “students are divided into some small group consisting four or five members who has
heterogeneous grouping of high, average, and low achievers of diverse ethnic backgrounds and
different genders” (Palmer, 1998, p. 1). Alwasilah (2002, cited in Alwasilah, 2007, p. 44) states,
Many researchers have conducted some studies related to this technique. Although a lot of research has been conducted and shows the effectiveness of STAD, research on the implementation of STAD in writing class is rare especially in the research site. In order to fill the gap in the study about STAD, this study aims to find the effectiveness of STAD technique in
teaching writing narrative text, and to identify students’ responses toward STAD technique.
1.2Research Questions
As informed in the background of the study above, there are two problems that will be investigated in this study. The problems are formulated in the following questions:
1. Is Student Teams Achievement Divisions (STAD) effective in teaching writing narrative text?
2. What are students’ responses toward Student Teams Achievement Divisions (STAD)?
1.3Research Aims
Based on the background of the study above, the aims of the research are:
1. To find out the effectiveness of Student Teams Achievement Divisions (STAD) technique in teaching writing narrative text.
2. To identify students’ responses toward Student Teams Achievement Divisions (STAD) technique in writing class.
1.4Scope of the Study
The scope of this study is limited to two concerns. First, this study focuses on analyzing the effectiveness of Student Teams Achievement Divisions (STAD) technique in teaching writing narrative text, in terms of schematic structures and language features. Second, it also tries to
investigate the students’ responses towards STAD technique in teaching writing narrative text.
1.5Significance of Study
Linta Hayatunisa, 2013
Student Teams Achievement Divisions (Stad) In Teaching Writing Narrative Text
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
1. Provide useful information for the reader especially English teacher about Student Teams Achievement Divisions (STAD) technique that can be used in teaching writing and teaching English generally.
2. Provide additional informative input for the other researcher who intends to carry on research in the same field with certain interest.
1.6Clarification of the Main Terms
Student Team Achievement Divisions (STAD) is a cooperative technique where a whole class is divided into some small heterogeneous groups consist of four or five members in each group (Palmer, 1998, p. 1; Slavin, 2005; Aljanian, 2012, p. 1).
Narrative text aims to amuse or entertain reader and to deal with actual or vicarious experience in different ways (Gerot and Wignell, 2004, p. 18).
1.7Paper Organization
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter provides the explanation about the procedures of the research in order to find out the answer to the research question which is stated in previous chapter. This chapter covers research participants, research method, data collections, techniques for analyzing the data and teaching program.
3.1. Site and Participants
The research was conducted in one senior high school in Serang. The reason of choosing the school was the school is accessible. One class of XI consisting of 30 students was chosen as the participants of this study. They were chosen purposively in order to develop an in-depth understanding related to the topic. It gives benefits for the researcher to obtain access easily, gather more useful data, and enhance understanding of the context based on prior knowledge (Duff, 2008) regarding the analysis of narrative text in terms of general structures and linguistic features. The class was also recommended by the teacher since the students were considered active and highly motivated compared to other classes.
3.2. Research Design
Linta Hayatunisa, 2013
Student Teams Achievement Divisions (Stad) In Teaching Writing Narrative Text
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
This research was descriptive because the researcher analyzes the data descriptively and the presentation of the result was in form of explanation of words. Suryana (2010) said that descriptive study has aim to make a description systemically and accurately which is based on facts about certain object.
3.3. Data Collection
There are three data collection techniques that used in this study. They are classroom observation, document analysis, and questionnaire in the last day of the research.
3.3.1 Classroom Observation
The classroom observation was conducted for four meetings from August 22nd to September 11th, 2013. The classroom observation was conducted twice a week, every Wednesday and Thursday for 90 minutes in each meeting. Classroom observation was employed in the study because the data from classroom observation gave detailed descriptions of learners and the observation was made at “periodic intervals for an extended period of time” (Mackey & Gass, 2005, p. 171).
Video recording was not used in this study, therefore, the researcher made observation notes right after every meeting finished, when “the memory of observation is still fresh” (Van Lier, 1988; cited in Emilia, 2008, p. 43) to avoid missing information from the study. The overall classroom observation will be elaborated and discussed in Chapter IV.
3.3.2 Document Analysis
The document analysis was carried out during the research, specifically on students’ writing products (draft and final writing) and the English curriculum for senior high school grade XI.
The last analysis and also the important data to be analyzed was students’ writing product consisting draft and final writing. The draft and the final writing products were collected from the teaching-learning process using STAD technique and will be discussed in data finding and discussions in Chapter IV.
3.3.3 Questionnaire
Questionnaire as the supplementary instruments in this study was distributed in the last meeting. Questionnaire was distributed to 15 students. The questionnaire consisted of 15 questions in a form of multiple choices. The questionnaire was employed to explore students’ responses toward STAD.
3.4 Data Analysis
3.4.1 Data Analysis of the Classroom Observation
The analysis of the classroom observation was done during and after teaching-learning process in every meeting using teacher’s field notes since the analysis was used as the guiding plan for next learning process. The analysis of observation is presented in Chapter IV.
3.4.2 Data Analysis of the Students’ Texts
Students’ final writing product was analyzed using SFG in terms of the schematic structures and linguistic features of Narrative text adapted from Joyce & Feez, 2004; Christie & Derewianka, 2008; and Gibbons, 2009 (cited in Emilia, 2010, p. 168-169). The analysis of the students’ text is presented in Chapter IV
3.4.3 Data Analysis of the Questionnaire
Linta Hayatunisa, 2013
Student Teams Achievement Divisions (Stad) In Teaching Writing Narrative Text
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Table 3.1 following presents the formula to calculate the percentages. (Ningrat, 2000 cited in Nurlaila, 2013).
p
=3.5 The Teaching Programs
In conducting the treatments, the researcher acted as the teacher and the observer. The teacher used Student Teams Achievement Divisions (STAD) technique during teaching-learning process in teaching narrative texts. The steps of STAD technique can be seen in table 3.2.
Table 3.2 meeting. The lesson plan using this technique can be seen in the appendix. The steps of STAD technique in writing narrative text will be systematically interpreted below:
P = Percentage
F o = Frequency
N = The number of Respondent
Step 1: Class Presentation
In the class presentation step, teacher delivered the material through lecturing (Aljanian, 2012, p. 1). The class presentation was done to build students’ knowledge to do the quiz. The material given in this study was about narrative text. Narrative text was chosen as the material of this study because it was appropriate with the SKKD. The class presentation was done in the first and the fourth meeting. The success of the class presentation steps can be seen from the students’ text in the analysis of students’ text part in Chapter IV.
Step 2: Team
In the team step, students were divided into groups consist of four or five students (Norman, 2005, p. 7; Slavin, 2005, p. 11). In order to make a heterogeneous group, the group was chosen by the teacher based on table 3.2. In this step, students were asked to work in the groups. The second step was given in every meeting. On the first and fourth day, teacher asked them to do a worksheet (see in the lesson plan in the appendix) together with their own team to see whether or not all of them has already understood about the material. Then, on the second meeting, the teacher asked them to make their own draft about one legend from Indonesia. The students were asked to brainstorm their idea helped by their own team. On the third, fifth and sixth day, the team’s job was to review the members’ texts by giving some feedbacks to the members’ texts in order to help their own team members to revise their own text. The feedback from team was used to do better in the quiz. The success of the team can be seen from the students’ text in the analysis of students’ text part in Chapter IV.
Step 3: Quiz
Linta Hayatunisa, 2013
Student Teams Achievement Divisions (Stad) In Teaching Writing Narrative Text
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
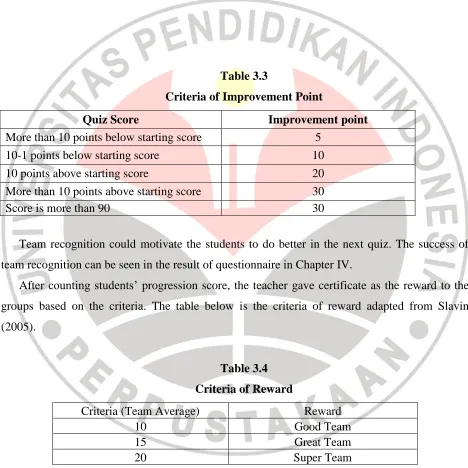
After doing the quiz, the teacher gave individual progression score to each team. The team recognition was done after the quiz was conducted. The individual progression score was counted based on their individual score (Slavin, 2005).
Table 3.3
Criteria of Improvement Point
Quiz Score Improvement point
More than 10 points below starting score 5
10-1 points below starting score 10
10 points above starting score 20
More than 10 points above starting score 30
Score is more than 90 30
Team recognition could motivate the students to do better in the next quiz. The success of team recognition can be seen in the result of questionnaire in Chapter IV.
After counting students’ progression score, the teacher gave certificate as the reward to the groups based on the criteria. The table below is the criteria of reward adapted from Slavin (2005).
Table 3.4
Criteria of Reward
Criteria (Team Average) Reward
10 Good Team
15 Great Team
20 Super Team
3.6 Conclusion
Linta Hayatunisa, 2013
Student Teams Achievement Divisions (Stad) In Teaching Writing Narrative Text
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
5.1 Conclusions
This study was concerned with the effectiveness of STAD technique in teaching writing narrative texts to eleventh-graders. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether or not this technique is effective in teaching writing narrative text. Furthermore, this study also aimed to discover students’ responses toward the technique.
The research found that STAD technique was effective in teaching writing skill. Additionally, the technique was found to be potential to provide better. This was proven by the
analysis of the students’ texts and several responses from the students toward the technique.
First, STAD technique could help the student academically. One of main concepts of STAD was team. Here, the students shared their knowledge about narrative text and also gave some
feedback about the members’ writing. This could help the students to understand the material
well and in the end the students could write a good narrative text. Second, STAD technique
motivated the students to improve their writing skill. This could be seen by the students’
responses that they said they were motivated to have a good score in every quiz. The team also
motivated the students to do their best because each member’s score participate in recognition
team stage. So, each member motivated him/herself to do him/her best in order not to disappoint
him/her team members. Third is STAD technique helped students’ social life. Based on the
findings, the students felt that they become closer to their classmates, especially their team
members. In addition, they also said that they learnt to appreciate or respect others’ opinion
through this technique. Working in a group asked them to participate more in the team, moreover, in STAD technique, each group consists of heterogeneous members which can help them to socialize with each member of the team well.
5.2 Suggestions
There are some suggestions that can be recommended for the follow-up study. For any English teacher, it is suggested to apply the Student Teams Achievement Divisions (STAD) technique to help students improve their writing ability in writing Narrative texts, as well as other genres such as Descriptive, Procedural, Recount or News item.
Linta Hayatunisa, 2013
Student Teams Achievement Divisions (Stad) In Teaching Writing Narrative Text
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
REFERENCES
Abbot, H. P. (2009). The Cambridge Introduction to Narrative 2nd Edition. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Al-Munawwarah, S. F. (2013). The Implementation of Student Teams Achievement Divisions Technique in Teaching Reading Comprehension. FPBS UPI Sarjana Degree: Unpublished paper.
Aljanian, E. (2012). The Effect of Student Teams Achievement Division Technique on English Achievement of Iranian EFL Learners. In Theories and Practice in Language Studies [Online], Vol. 2(9), 5 pages. Available at: ojs.academypublisher.com[December 26, 2012]
Alwasilah, A. C. & Alwasilah, S. S. (2007). Pokoknya Menulis: Menulis Dengan Metode Kolaborasi. Bandung: Kiblat Buku Utama.
Arikunto, S. (1998). Prosedur Penelitian Suatu Pendekatan Proses. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Bernard, H. R. (2006). Research Methods in Antropology. Lanham, MD: Altamira Press.
Brown, H. D. (2001). Teaching by Principles: An Interactive Approach to Language Pedagogy. San Francisco: Addison Wesley Longman, Inc.
Byrne, D. (1993). Teaching Writing Skills. London: Longman.
Cohen, L. & Manion, L. (1994). Research Methods in Education. London: Routledge. Constatine. (2007). Writing Under The Competency-Based Approach: The Case Of Second Year Middle School Pupils. Dissertation of Magistere degree to Department of Foreign Languages [Oline], available at:
http://www.google.com/ [May 4, 2013]
Coolidge, F. L. (2000). Statistics: A Gentle Introduction. London: Sage Publication Ld.
Emilia, E. (2008). Pendekatan Genre-Based dalam kurikulum Bahasa Inggris tahun 2006: Penelitian Tindakan Kelas di Sebuah SMP Negeri di Bandung. Bandung: Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris FPBS UPI.
Emilia, E. (2010). Teaching Writing: Developing Critical Learners. Bandung: Rizqi Press.
Emilia, E. (2011). Pendekatan Genre-Based dalam Pengajaran Bahasa Inggris: Petunjuk untuk Guru. Bandung: Rizqi Press.
Erlinah, E. (2012). The Implementation of Student Teams-Achievement Divisions (STAD) in Teaching Reading Descriptive Text. FPBS UPI Sarjana Degree: Unpublished paper.
Firdaus, R. B. (2010). The Effectiveness of Student Team Achievement Division
Technique in Improving Students’ Reading Comprehension. FPBS UPI
Sarjana Degree: Unpublished paper.
Gerot, L. (1995). Making Sense of Functional Grammar: An Introductory Workbook. Sydney, Gerd Stabler.
Gillham, B. (2000). Case Study Research Methods. London: Wellington House. Hutchinson, E. (2005). Narrative Writing: Plot, Characters, Dialogue, Setting,
Conflict, Climax. Irvine: Saddleback Educational Publishing.
Knapp, P. & Watkins, M. (2005). Genre, Text, Grammar: Technologies for Teaching and Assessing Writing. Sydney: University of New South Wales Press Ltd.
Machey, A. & Gass, S. M. (2005). Second Language Research: Methodology and Design. New Jersey: Lawrence Elbaum Associaties Publishers.
Murray, D. M. (1972). Teaching Writing as a Process Not Product. Retrieve from e-book. Accessed on September 26, 2013.
Myles, B. (2002). Second Language Writing and Research: The Writing Process and Error Analysis in Student Text. In TESL-EJ [Online], Vol. 6(2). Available at:
http://tesl-ej.org/ej22/a1.html [May 4, 2013]
Linta Hayatunisa, 2013
Student Teams Achievement Divisions (Stad) In Teaching Writing Narrative Text
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Norman, D. G. (2005). Using STAD in an EFL Elementary School Classroom in South Korea: Effects on Student Achievement, Motivation, and Attitudes Toward Cooperative Learning. In Asian EFL Journal [Online] Available at: http://www.google.com/ [March 7, 2013]
Nudee, N. et al. (2010). Cooperative Learning and Writing Ability Improvement. In The 2nd International Conference on Humanities and Social Sciences [Online], 14 pages. Available at: sv.libarts.psu.ac.th/ [December 26, 2012] Nurmalasari. (2011). The Use of Student Team-Achievement Divisions (STAD)
Method to Improve Students’ Reading Comprehension. FPBS UPI Sarjana
Degree: Unpublished paper.
Palmer, S. A. J. (1998). Student Teams Achievement Divisions (STAD) in a twelfth grade classroom: Effect on student achievement and attitude. [Online] Available at: http://findarticles.com/ [March 7, 2013]
Peha, S. (2002). The Writing Process Notebook. Retrieve from e-book. Accessed on September 26, 2013.
Slavin, R. E. (2005). Cooperative Learning: Teori, Riset, dan Praktik. Bandung: Nusa Media.
Sugiyono. (2008). Teknik Analisis Regresi dan Korelasi Bagi para Peneliti. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Sukmana, F. W. D. (2012). How Teachers Teach and How Students Perceive Teaching Writing Descriptive Text Using STAD Technique. FPBS UPI Sarjana Degree: Unpublished paper.
Suryana. (2010). Metode Penelitian Model Praktis Penelitian Kuantitatif & Kualitatif. Buku Ajar Perkuliahan Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia. Bandung: Unpublished.
Susanti, R. (2011). The Use of Student Teams Achievement Divisions (STAD) in Teaching Reading Comprehension. FPBS UPI Sarjana Degree: Unpublished paper.