2. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE 2.1 The Definition of Semantics
The history of linguistics shows periods in which semantics received more or less attention. In the nineteenth century linguists concentrated more on phonology and morphology and semantics suffered from comparative neglect. With the advent of structuralism at the beginning of the 20th century, it looked as if semantics might achieve the status it deserved. However, the development of American structuralism between the two world wars did nothing to further linguistic interest in semantics. Such prominent linguists as Leonard Bloomfield (active in the 1920s and 1930s) regarded semantics as too difficult to deal with scientifically and left it to one side. The same is true of early transformational grammar in the 1950s. Only in the mid 1960s did the interest of linguists turn to semantics once more. Since then there have been many works on semantics both within models of grammar and outside. Despite these efforts there are no coherent theories of semantics on a par with those in syntax and phonology.
conditions under which they are true or false. This type of semantics goes back to Classical Greece, to the three main philosophers Socrates, Plato and Aristotle. In the sphere of logic, semantics is important as a system of logical analysis where it is not so much the relation between language and the outside world which is of concern but rather the internal formal relationships between terms in a logical system.
According some linguists, semantic can be defined as follows :
1) Semantic is the study of the meaning. It concerned with what sentences and other linguistics object express, not with the arrangement of their syntactic parts of their pronounciation (Katz, 1972:2)
2) Semantic is generally defined as the study of meaning (Lyons, 1977:2)
3) Semantic is the study of meaning communicated through language (Saeed, 1997:1)
4) Semantic is a mayor branch of linguistics devoted to the studyof meaning in language (Crystal, 1980:315)
5) Semantics is the technical term used to refer to the study of meaning (Palmer, 1976:1)
2.2 The Scope of Semantics
language structure and have distinguished between different types of meanings and also semantic structure of sentences. The second is philosophical approach. Philosophers have investigated between linguistic expression such as the words of language, and persons, things and events in the world to which these word refer.
Although there maybe different approaches to semantics, three basic terms have been widely mentioned in this approaches, namely meaning, sense, and reference.
2.2.1 Meaning
According to Oxford Learner‟s Pocket Dictionary, meaning is defined as
the thing or idea that sound, word, sign, etc represents. There are some definitions of meaning from some Linguist, such as :
1) Meaning is a complex pheomenon involving relationship between a language and the mind of its speaker and the practical use which it is put (Nikelas, 1988: 231)
2) Meaning is a word of ordinary , everyday vocabulary in English (Lyons, 1977: 4)
The term meaning is derived from the word mean. It is fact that the verb to mean and the noun meaning have many distinguishable meaning. In everyday
English, we use the word mean in a number of different ways : 1) They are so mean (cruel) to me
2) That was no mean (insignificant) accomplishment
5) I mean (intend) to help if I can
6) Keep off the grass, this means (refers to) you
7) His loosing his job means (implies) that he will have to look for another job. 8) Lucky Strike means (indicates) fine tobacco
9) Those clouds mean ( are a sign of) rain 10)She doesn‟t mean (believe) what she said 11)Procrastinate means (?) to put this thing off 12)In saying that, he meant (?) that we would leave,
The word mean in (1) to (10) has their “equivalence‟ in another word, while in the same word in (11) or (12) does not. The last two sentences, in fact, exemplify two importantly different sorts of meaning, i. e. linguistics meaning and speaker meaning. In (11) procrastinate has a linguistics meaning of to put thing off while in (12) meant refers to speaker intention or what message the speaker intends to say in his word.
In general, the linguistics meaning of an expression is simply the meaning or meanings of that expression in some form of language. For example, in one form of language, known as standard British English, the word run means something different in each of the sentences:
1) I like to run
2) The engines run well
There are two different sort of meanings, linguistic meaning and speaker meaning. In general, linguistic meaning is meaning of that expression in some from of language. Speaker meaning is what a speaker means in producing an utterance.
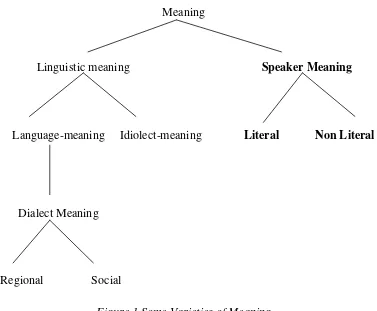
The following figure can show how meaning can have several distinctions : Meaning
Linguistic meaning Speaker Meaning
Language-meaning Idiolect-meaning Literal Non Literal
Dialect Meaning
Regional Social
Figure 1 Some Varieties of Meaning
2.2.2 Sense and Reference
says He saw Paul or She bought a dog, the underlined nominals identify, pick out or refer to specific entities in the world. However words also derive their value from their position within the language system. The relationship by which language hooks on to the world is usually called reference. The semantic links between elements within the vocabulary system is an aspect of their sense or meaning.
Words other than proper names both have a meaning and can be used to refer to things and objects. The German philosopher and mathematician Gottlob Frege proposed a distinction between the reference of a word and the sense of a word. The reference of a word and the sense of a word. The reference of a word is the object designated, while the sense of a word is the additional meaning. On the other hand F.R. Palmer (1976: 30) says that reference deals with the relationship between the linguistic elements, word, sentences etc, and the nonlinguistic world of experience. Sense relation is the complex system of relationship that hold between the linguistic elements themselves (mostly the words) ; it is concerned only with intralinguistic relations
Phrases, like words, normally both have sense and can be used to refer. Thus, the phrase “The woman who is my mother” refers to a certain individual and
has a certain sense which could be different from that of “The woman who
married my father”, although both expression usually have the same reference.
2.3 Varieties of Meaning
expression in some form of a language. While, speaker meaning is what speaker means in producing an utterance. Speaker meaning consist of literal meaning and non literal meaning.
2.3.1 Literal Meaning
If we are speaking literally, then we mean what our words mean, the meaning of the utterance is the lexical meaning or literal meaning. There will be no important difference between the linguistic meaning and the speaker meaning. There is no hidden meaning and misinterpretation between the speaker and hearer. For more details about literal meaning, look at these examples :
1) I‟m hungry 2) He goes to school 3) She is my lecturer 4) They are having lunch
All the sentences above are literal meaning. We know clearly about the meaning of the sentence.
2.3.2 Non Literal Meaning
In using the langugage, a speaker may sometimes use a word to mean something different from what it means literally or what the words mean. The words, phrases, and the sentences have another different meaning than literal meaning. For more details about non literal meaning, look at these examples : 1) I could eat a horse
2) I am starving
All those examples above are non literal meaning. All the meaning f them are same. It means someone who feels very hungry.
According to Saeed (2003: 15) Non literal uses of language are traditionally called figurative and are described by a host of rhetorical terms including metaphor, simile, metonymy, synecdoche, hyperbole, litotes and personification.
1) Metaphor
Wren and Martin (1981: 489) says that a metaphor is an implied simile. It does not, like the simile, state one thing is like another or acts as another, but takes that for granted and proceeds as if the two things were one. Based on that statement, if we say He fought like a lion, that means we use simile. While if we say He was a lion in the fight, that means we use metaphor. 2) Simile
Simile is figure of speech in which there are two different things compared because they appear to be similar in at least one character. Simile is
introduced by the word like or as. A simile must compare two basic things that are found to be alike in an aspect. For the example :
1) His temper was as explosive as a volcano 2) He runs like a cheetah
3) Metonymy
Metonymy is a figure of speech characterized by the use of the name of one thing in place of the name of something that is symbolized. For example He bought a new chevrolet. Chevrolet is the one of the brand name of car.
4) Synecdoche
The word of synecdoche is derived from a Greek word “syneckdechestai”
which means “to take up”. Siswantoro (2002: 39) says, “synecdoche
merupakan gaya bahasa yang manifestasinya tercermin dalam kemasan
sebagian tetapi yang mewakili keseluruhan. Synecdoche is a figurative expression which its manifestation reflected a part is used to designate the whole. For example He has many mouths to feed that in literal meaning this statement means „He feeds many mouths‟. In this case, mouth is people who
are fed. 5) Hyperbole
Wren and Martin (1981: 491) says that in hyperbole, a statement is made emphatic by overstatement. In daily language, hyperbole appears in student circle when they will have an examination by saying I’ll die if I don’t pass this course. The word of die is overstatement because there is no people
who will get die due to not pass an examination. The others example are : 1) I carry you heart with me
2) My heart feel dead before 3) On a great horse of gold
6) Litotes
Litotes is an understatement in which an affirmation is expressed by the negative of its contrary, often used for emphasis or ironically. To make it clear look the example: please come to my hut. From the sentence, as we know hut is very simple. Nevertheless, in this situation hut is not the hut, but actually, he has a big house. He does not want to tell the truth, he just trying to be low profile.
7) Personification
The word personification derives from Latin word „persona‟ means person,
actor or mask and „fic‟ means to make. Then, personification is a figurative
speech that giving human characteristics to an object. For example, the trees are afraid to put forth bud. This word trees in the sentence figure as a human being that has been afraid represent for fear or being frightened. Indeed such emotional feelings are shown as a natural reaction from human when they feel something wrong or being shocked. The others example of personification are :
1) The pen is dancing on the paper
2) Every night, the moon comes by just to say goodnight to me