i
THE USE OF
GRAB GAME VARIATIONS
TO IMPROVE
STUDENTS’ READING COMPREHENSION (A
CLASSROOM ACTION RESEARCH FOR THE FOURTH
GRADE OF MI SRUWEN 01 IN THE ACADEMIC YEAR
OF 2016/2017)
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board of Examiners in Particle Fulfillment of the Requirement for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd) in English Department of
Educational Faculty
SUTIKNO
NIM : 113-12-168
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TARINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES
(IAIN) SALATIGA
ii
DECLARATION
In the name of Allah the most gracious and merciful.
Hereby the writer fully declares that this graduating paper is written by the writer himself, and it is not containing materials written or has been published by other people and other peoples’ ideas except the information from the references.
The writer is capable to account to his graduating paper if in future it can be proved of containing others’ idea or in fact, the writer imitates others’
graduating paper.
Likewise, this declaration is made by the writer to be understood.
Salatiga, 3 April 2017 Writer,
Sutikno
MINISTRY OF RELIGIOUS AFFAIRS INSTITUTE OF ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
SALATIGA
Jl. Tentara pelajar 02 Telp (0298) 323433 Fax 323433 Salatiga 50724 Website: www.iainsalatiga.ac.id email: [email protected]
iii Hanung Triyoko, S.S.,M.Hum. M.Ed Salatiga, 3 April 2017
The lecturer of English Education Department State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
ATTENTIVE CONSELOR’S NOTE
Case : Sutikno’s Graduating Paper
Dear:
Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
Assalamu’alaikum Wr. Wb
After reading and correcting Sutikno’s graduating paper entitled “The use of grab game variations to improve students’ reading comprehension (A Classroom Action Research for the Fourth Grade of MI Sruwen 01 in the academic year of 2016/2017)”. I have decided and would like to propose that it could be accepted in the Education Faculty and I hope this graduating paper can be examined as soon as possible.
Wassalamu’alaikum Wr. Wb
Counselor
Hanung Triyoko, S.S.,M.Hum., M.Ed
MINISTRY OF RELIGIOUS AFFAIRS INSTITUTE OF ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
SALATIGA
Jl. Tentara pelajar 02 Telp (0298) 323433 Fax 323433 Salatiga 50724 Website: www.iainsalatiga.ac.id email: [email protected]
iv A GRADUATING PAPER
THE USE OF GRAB GAME VARIATIONSTO IMPROVE STUDENTS’
READING COMPREHENSION (A CLASSROOM ACTION RESEARCH FOR THE FOURTH GRADE OF MI SRUWEN 01 IN THE ACADEMIC
YEAR OF 2016/2017)
WRITTEN BY:
SUTIKNO
NIM: 113-12-168
Has been brought to the Board of Examiners of English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty at State Institute for Islamic Studies
(IAIN) Salatiga, on March 31th 2017, and hereby considered to complete the requirements for the degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd) in English Education.
Board of Examiners Head : Mashlihatul Umami, M.A
Secretary : Hanung Triyoko, S.S.,M.Hum., M.Ed. First examiner : Sari Famularsih, M.A
Second examiner : Faizal Risdianto,S.S.,M.Hum.
Salatiga, April 3 2017
Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty,
Suwardi,S.Pd.,M.Pd
v
MOTTO
“LIFE IS A COMPETITION”
“TOMORROW IS AN ADVENTURE THAT UNDISCOVER YET”
vi DEDICATION
This graduating paper is whole-heartedly decided to:
1. My dearest Father and Mother; Mr. Suparno and Mrs. Munjayanah, thanks a billion for your great affection, kindness, encouragement, education, and everything you have given to me.
2. My beloved sister and brother; Siti Aminah and Santoso, thanks a lots for your support. Your support gives confidence in my action.
3. Mr. Sukron makmun S.Pdi., as the English Teacher in MI Sruwen 01 for fourth grader who help and direct in the process of collecting data.
4. My best friends; Andri Triyono, Nanang dwi Setiawan, and Randika Dwi Wardana. Thank you for your support, I always manage to move on and be positive every time.
5. my friends in English department ’12, KKN posko 37, and karang taruna
“Eka Manunggal”.
vii ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Alhamdulillahirabbil’alamin, thanks to the almighty Allah. Because of Him, the researcher can complete this research as one of the requirements for getting the degree of Educational Islamic Studies (S,Pd.I) in English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga in 2016.
Secondly, peace and salutation are always given to our prophet Muhammad SAW who has guided us from the darkness to the lightness.
However, this success will not be achieved without support, guidance, advice, help, and encouragement from individual and institution, and I somehow realize that it is an appropriate moment to give my deepest gratitude for:
1. Dr. Rahmat Hariyadi, M.Pd., as the Rector of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga.
2. Suwardi, M.Pd., as the Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty. 3. Noor Malihah, Ph.D., as the Head of English Education Department. 4. Drs. Kastolani, M.Ag., as the Academic Counselor.
5. Hanung Triyoko, S.S.,M.Hum., M.Ed., as the research consultant who has educated, supported, directed and given the writer advices, suggestions, and recommendations for this research from beginning until the end. 6. Hanung Triyoko, S.S.,M.Hum., M.Ed., who supported the writer in
viii 7. All of the lecturers in English Education Department.
8. All staffs who helped the researcher in processing of graduating paper administration.
Finally this graduating paper is expected to be able to provide useful knowledge and information to readers. Moreover, the researcher is pleased to accept more suggestion and contribution from the reader for the improvement of the graduating paper.
Salatiga, April 3 2017
The researcher
Sutikno
ix ABSTRACT
Sutiko. 2017. The use of grab game variations to improve students’ reading comprehension (a classroom action research for the fourth grade of MI Sruwen 01 in the academic year 2016/2071) A Graduating Paper. English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga. Counselor: Hanung Triyoko, S.S.,M.Hum., M.Ed
The title of this research is THE USE OF GRAB GAE VARIATIONS TO IMPROVE STUDENTS’ READING COMPREHENSION (A CLASSROOM ACTION RESEARCH FOR THE FOURTH GRADE OF MI SRUWEN 01 IN teaching process in fourth grade of MI Sruwen 01. Total subjects of research are 38 students. Writer used Kemmis and Mc Tacggart model of CAR. Writer conducted two cycles in total to collect data. Each cycle writer gave pre-test and post-test. The result of this research showed that there was improvement in reading comprehension after researcher applied grab game variation in teaching process. The level of significance was set equal or less than 5%. The result from first cycle pointed out that t-test was 1.645 higher than the t-table. In the second cycle, t-test was 2.987 higher than the t-table.
x
Contents
DECLARATION ... ii
ATTENTIVE CONSELOR’S NOTE ... iii
CERTIFICATION PAGE ...iv
H. Graduation Paper Organization ... 6
CHAPTER II ... 7
LITERATURE REVIEW ... 7
A. Young learner ... 7
1. Definition of young learner ... 7
2. Characteristic of young learner ... 8
B. Reading ... 10
1. Definition of reading ... 10
C. Reading comprehension ... 12
1. Definition of reading comprehension ... 12
2. Developing comprehension in the classroom ... 13
D. Teaching reading comprehension ... 14
xi
2. General Procedures for improving comprehension ... 15
E. GRAB GAME VARIATION ... 18
1. Procedure of grab game variations ... 20
2. Caveats and options ... 21
CHAPTER III ... 24
METHODOLOGY OF RESEARCH... 24
A. Research method ... 24
1. Definitions of classroom action research... 24
2. Models of classroom action research ... 25
3. Data gathering ... 30
B. Place and time research ... 31
1. Place of research ... 31
CHAPTER IV... 37
ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION ... 37
A. Data presentation ... 37
1. First cycle ... 37
2. Second Cycle ... 54
3. Discussion... 70
CHAPTER V ... 72
CLOSURE ... 72
A. Conclusion ... 72
B. Suggestions... 75
xii LIST OF TABLE AND FIGURE
Figure 3.1 the action research spiral (base on kemmis and McTaggart) ……….26
Table 3.2 school facility in MI Sruwen 01………....32
Table 3.3 list of teacher in MI Sruwen 01……….33
Table 3.4 research date and description……….34
Table 3.5 Students list of fourth grade at MI Sruwen 01……….35
Table 4.1 the result pre-test and post-test first cycle………..40
Table 4.2 Accumulative of respondents score for standard deviation…………...42
Table 4.3 Distribution score of first cycle’s pre-test………..45
Table 4.5 distribution of first cycle post-test……….47
Table 4.6 Classification of respondents in first cycle’s post-test………..48
Table 4.7 sheet for classroom observation……….50
Table 4.8 Observation sheet in first cycle………..50
Table 4.9 the result pre-test and post-test second cycle ………57
Table 4.10 Accumulative of respondents score for standard deviation 2nd cycle..59
Table 4.11 Distribution score of second cycle’s pre-test………...61
Table 4.12 The result from distribution score of second cycle pre-test………….63
Table 4.13 post-test score distribution rank………...63
Table 4.14 The result of post-test score distribution rank………..65
Table 4.15 observation sheet for class observation………65
Table 4.16 Observation of students’ behavior in second cycle………..66
1 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of study
Suyanto (2010;23) said that learning English involves the four kinds of language skills; listening, speaking, reading, and writing. Teacher should develop four language skills in order that their students can use the skills to communicate or express their thought, feeling, and opinions in English. To master those skills, the students have to master some elements of language, for instance, grammar, pronunciation, vocabulary, etc. However, sometime the students get difficulties in reading mastery, whereas reading is a crucial element to master foreign language especially English.
Suyanto also explains that Teacher should apply appropriate teaching techniques or method to establish the effectiveness of English language teaching, and it make easier for students to enjoy and receive the lesson (2010;29). The use of appropriate technique is very important thing to make the student’s interested and motivated in learning English, so the
2 One of the techniques to teaching English is by using game. Khan as quoted by Suyanto (2010;117) said: game is activities that being carried out with specific rules. So, if teaching is conduct by game, they can have fun in learning and interact with other. In the interactions, language skill can be built.
In MI Sruwen 01 English lesson have not fully adapted to be primary subject in learning. English only became additional lesson such as Javanese language. English became primary lesson in sixth grade. More over English also determined students’ graduation. So, English lesson in fourth grade give great effect in students’ point of view in English lesson.
In fourth grade, students know for the first time about English lesson. If they have good impression on English, they likely do not have problem in the future when they have to learn it in the next grade.
Based on the explanations above, the writer is interested in conducting a research entitled “THE USE OF GRAB GAME VARIATIONS
TO IMPROVE STUDENTS’ READING COMPREHENSION (A
CLASSROOM ACTION RESEARCH FOR THE FOURTH GRADE OF MI SRUWEN 01 IN THE ACADEMIC YEAR OF 2016/2017).
B. Limitation of the problem
3 C. Research problems
To clarify the problems that are going to be analyzed, the statements of the problems are formulated as follows:
1. How do grab game variations improve students reading comprehension?
2. How far is the improvement of students’ reading comprehension after using grab game variations?
3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of using grab game variations in improving reading comprehension?
D. Objective
Objective of this research are:
1. To find out how grab game variations can give improvement in students’ reading comprehension.
2. To find out how far grab game variations is improve students’ reading comprehension.
4 E. The benefits of the study
1. Theoretical benefit
Theoretically, researcher hopes that this study can contribute to the science of language teaching, especially in using grab game variations to improve reading comprehension.
2. Practical benefit
Practically, researcher hopes, this study can improve the students or readers knowledge in understanding the benefit of using grab game variations to improve reading comprehension.
F. Definition of key terms
1. Grab Game Variations
Grab game variations is one of many teaching methods in Richard R. Day’s book (1993;50). Grab game variations are
activities to help young readers to increase their automatic decoding skills. Because it is played in form of game, students have an interest and their motivations are high. This game divides students into group, and then teacher spreads cards on the floor or table. Teacher reads a card and students should rush to grab it.
2. Reading Comprehension
5 effect, not a single skill, but a collection of skills. This process consist of determining what a source says literally (translation), what the author means by what he or she says (interpretation), and what the source mean to the reader (extrapolation), application, synthesis, or evaluation.
G. Methodology of Research
1. The Setting of Research
The Research was conducted in MI Sruwen 01 which is located in Sruwen 01 kec. Tengaran. The subjects of this research were the students of the fourth grade in the academic year of 2016/2017. There were 38 students who became the subject of research. They were students from class A and B. The writer took all students as subject of research based on the agreement which writer and homeroom teacher made before research being conducted.
2. The Methodology of the Research
6 pursue by systematic enquiry a reflective process, determine by the practitioners.
H. Graduation Paper Organization
In order to have guidance for researcher in writing the thesis or reader on the whole content of the thesis, the researcher sets up the organization of the thesis writing as follow:
7 CHAPTER II
LITERATURE REVIEW
In this chapter, the reference books and other relevant information will be discussed. They are very important to be the basic theory of teaching reading. Hence, the writer wants to deliberate about literature review of teaching reading for young learner and theoretical information about Grab game variations to improve reading comprehension.
A. Young learner
1. Definition of young learner
Looking at teaching English lesson for kids or English for young learners (EYL), we need to understand who the subject of matter is. Suyanto (2010;14) explains that Students of EYL are young learners who learn English lesson. They are children in elementary school who get English lesson as local content lesson. Commonly they are beginner at learning, so teacher cannot fairly treat them in the same condition by giving them the same task or lesson.
8 and older group in upper class (4th, 5th, 6th grader). Meanwhile, Scott and Ytreberg (1990) divide them in 2 groups; level one (5-7 years old) and level two (8-10 years old). Group of level two can be beginners if they recently learn English.
Nowadays, lots of preschool’s students have learned
English lesson. In this matter, it can be included in group of very young learners. In learning English, the achievement cannot be decided only by age or grade. There are other factors which can be considered such as; environment, culture, motivation, and parent’s influence. Thus, programs and kind of activities that teacher uses to teach mostly being decided by their understanding in environment, behavior, motivation, and student’s background.
Basically, teacher should remember that the main purpose in teaching English in elementary school is to grow student’s
motivation or interest in learning English. To achieve this purpose, teacher needs to understand students’ characteristic to make good
method and learning material, and also enough knowledge about their students. So, in the end EYL class can be fun experience for them.
2. Characteristic of young learner
9 fact that they do not have inhibitions about learning which older children and teenagers often bring to school. Young learners are able to respond to meaning even if they do not understand the meaning of individual words. Harmer also mentions that young learners “find abstract concepts such as grammar rules difficult to
grasp” (2007;82). So, intonation, gestures, facial expressions,
10 The other matter that young learner also have short span of attention and concentration. That is why, teacher should make a class that can make them active and far from boredom. The activity should be as attractive as possible. Because another features on young learner is their instinct for fun and play. Halliwell said that children take great pleasure in finding and creating fun in what they do (1992;3). That is why, young learner always love to play.
Other than that, young learner commonly takes seriously anything they are doing. They cannot distinguish between fiction and reality. Halliwell explains that reality for young learners still includes imagination and fantasy as well (1992;7). Finally, young learner easily learns by using themselves to be the object of learning by making their life as the main topic in the classroom.
B. Reading
1. Definition of reading
11 There are some explanations about reading from many experts:
DeBoer and Dallmann (1960:19) consider that reading involves the comprehension and interpretation of ideas symbolized by the written or printed page. Dalmann also mention that reading as a process involving meaningful reaction to printed symbols in the other book (Dalmann, Rouch, Char, and DeBoer 1978:33). Bond and Tinker (1967:22) said that reading contain the recognition of printed or written symbols which serve as incitement for interpretation of meaning through the reader’s past
experience. Haris and Sipay (1975:5) defined reading as “the
meaningful interpretation of written or printed verbal symbols.”
Dechant (1970:19) also defined reading as the process of giving the significance intended by the writer to the graphic symbols by relating them to one’s own fund of experience.
12 brings to the page is at times as significant to reading as what is actually written on it. In the process of reading give instruction should be done both to assist an individual in the acquisition of reading skills and concurrently to help him acquire the reading habit of value to him as an individual and as a member of society.
C. Reading comprehension
1. Definition of reading comprehension
13 Comprehension includes the correct association of meanings with word symbols, the selection of the right meanings suggested by the context, the organization and retention of meanings, the ability of reasoning way through smaller ideas segments and the ability to grasp the meaning of a large unitary idea (Barry, 1979:95).
Comprehension is a thinking process, it is through reading. As such, it is dependent upon the learner’s basic cognitive and
intellectual skills upon the background of experience (vocabulary, knowledge, concepts and ideas) and upon their language skills (knowledge of morphology, syntax and grammar).
2. Developing comprehension in the classroom
Two widely accepted requirements for the development of comprehension in the classroom are (1) establishing a purpose error to reading and (2) asking question before during and after reading. Other technique for developing comprehension includes (Lee. T. T, 1998):
a. Having pupils show by an illustration of the event by retelling the story, or by demonstration.
b. Having pupils identify and state the topic sentence, write a little for the paragraph or story on sequence of material read.
14 e. Having pupils provide the ending for a story which has not
been read to completion.
f. Having pupils match the pictures with sentences or phrase. D. Teaching reading comprehension
1. The teacher’s Role in Teaching Reading Comprehension
Smith (1982:181) argues that teachers have a critical role in helping students learn to read. The primary roles are to ensure that the students have adequate demonstration of reading being used for evident meaningful purposes, and to help them to fulfill such purposes. For instance, the teachers must provide a model when the students see little relevance in reading. Otherwise, they must create more interesting situation when the students find little interest in reading. When the students have difficulty in reading, they must also help the students to read what they would like to read.
15 reading skill is the ability to recognize relations of meanings through the use of cohesive devices such as co-reference and pronouns.
Smith (1982:182) elucidates that teaching reading comprehension is a bit difficult. The teachers should strive to ensure the students that reading is comprehensible. However, the thing that should be considered by the teachers is to understand the factors that make reading difficult including materials or activities used in the teaching process. It frequently happens that unsuitable material is given to the students, consequently, they will not understand. Thus, the teachers can give any material as long as the students are expected to read because they can never learn to read by not reading.
2. General Procedures for improving comprehension
16 a. Improvement through Incidental Means
Reading comprehension can be improved through incidental means that includes all types of reading situations. A creative teacher probably creates many ways to develop comprehension during the regular reading period. Most common means is giving the students questions deal with a story. In order to answer the questions, they will read the story that indirectly it helps them to develop their comprehension. In addition, asking the students to make a drama, puppet show, or movies based on books also encourages them to read with more comprehension.
b. Improvement through practice exercises
17 see the importance of the skill to be developed by means of a given exercise; and 4) with the students knowing what, if any, progress is being made.
c. questioning as a Technique for Improving
Comprehension
Questions can serve as one of the most effective means of improving comprehension which is commonly employed during the school day. In fact, questioning has been over-used as a teaching tool, rather that under-used. However, the teacher must know that questions should be on all levels of comprehension. Besides that, questions should interest people in reading a selection, increase comprehension, and check the comprehension. Moreover, questions should be within the learner’s capability to answer and adapted to individual differences within a group.
d. Use of Close Procedure
18 E. GRAB GAME VARIATION
Before writer explain about grab game variation, writer want to try to explain a little about game. Ioannou (2010;1) said that Games are a valuable activity for language learning, especially for very young learners. Children enjoy games and participate without anxiety. Games can motivate children greatly and they are activities which are usually familiar to children as regards structure, rules etc. Games are mostly inclusive activities in that they involve all the children and they can cater to different learning styles and different personalities.
Fleta as quoted by Ioannou (2010;1) said that Games are simple structured activities which may involve little language but are meaningful to students. It also involves the whole self (cognitively and emotionally) that creating strong associations with the language used.
19 participate fully in all the activities without being pressured to produce language.
Finally game is a good tool to make young learner to know how to work in group or to associate with their friend in class.
There are some example of game that often teacher use in English class. For example:
• Simon says
The teacher asks the students to perform actions. Teacher: “Simon says sit down”
• Question-Answer
This game help student to think fast in understanding a question and try to answer quickly base on the clues which have been given. Example:
Guess what fruit!
Teacher : it is yellow, it is long, it is sweet. Student : it is banana.
• Whisper game
Students sit in row or enclose. Teacher will whisper to the first student. Next, the student will also whisper the words to students next to him, and it will move on until the last student. The last student should state the words that have been passed to him.
20 happy. Player should enjoy the time in game. A good game is game that can make children have fun. In other side, they also learn something from it.
Now, the writer would like to explain about grab game variation which he useed in teaching reading comprehension.
Grab game variations is a game helps young readers increase their automatic decoding skills. Because it is played in form of a game, student interest and motivation are high. This game is made by Jack C. Richard and has been used by Matthew Taylor in Nagoya, Japan for many years and has recently obtained an MA TESOL degree from Columbia University Teachers College, Tokyo.
1. Procedure of grab game variations
Based on Richard’s book (1993;250), the procedures of
teaching process with grab game variations as follows:
a. Set 3-10 students around a table, or several desks moved together, or a section of floor.
21 2. Caveats and options
a. Spread out the cards of either half of a matching group. Instead of calling out one of the cards, simply show a card from the other matching half. Students rush to find and grab the card that matches the one shown. For instance, in the case of pictures and words, all of the word cards are laid out. As you show the picture cards one by one, students try to grab the matching words. This is, of course, reversible; the picture cards could be spread out, and the word cards could be spread out, and the word cards could be shown one by one.
22 c. This is a somewhat more involved version of the previous option, but definitely worth trying. Students are in two teams. Each team has caller(s) and grabber(s). Half of a matching group of cards is spread out face up on one side of the room. The other half is in one stack, face down, on the other side of the room. Calles of both teams draws from this one stack and call out the drawn card to their team members on the other side of the room. These grabbers grab the card that matches the one called and run to the callers to hand it over to them. When the callers have a matching pair in their hand, they can draw another card, which they in turn call out to their grabbers on the other side of the room. After about 5 minutes of yelling and dashing back and forth across the room, one team will end up with the most correctly matched pairs.
d. For the simple grab game and option 1, sharp students can easily dominate, so it is good to periodically remove them from the competition somehow (for example, by making them callers instead of the teacher).
23 card, in Japanese on another, and an illustration of the expression on another. Option 3, in particular, works well with the game focused on three different parts of the room and three different kinds of cards.
Levels students: young learners who already know the alphabet and some basic phonics
Aims : make finding and recognizing the written form of already familiar items rewarding through fun and competition.
Class time : 5-10 minutes
24 CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY OF RESEARCH
A. Research method
1. Definitions of classroom action research
In this research, the researcher used Classroom action research as research method. So, the researcher would like to provide some reference relate to the method in order to give a little picture about it.
Classroom action research or in short (CAR) is a method that teacher, lecturer, or student of educational department used to solve problem in class. It is used to try a new method in teaching. By this, they can find the advantage, disadvantage, or the compatibility of the teaching method to the class.
Action research combines as substantive act with research procedure; it is action disciplined by enquiry, personal attempt at understanding while engaged in process of improvement and reform.
Here are some definitions of action research. It is taken from Robert Rapoport (1970), he said that”. . . aims to contribute both to the
practical concerns people in an immediate problematic situation and the goals of social science by joint collaborating within a mutually acceptable ethical framework.”
25 So, it can help in the improvement of their activity on it. It can show the compatibility of their action. This can be done by group or individually. CAR can give more accurate result if it is been done with collaborative between participant. Even so, mostly it is done by individuals and some time with help from outside.
This research had been used in school to curriculum development, teacher development, testing school program, and in the planning policy and new system.
In the Dave Ebbutt (1985) paper, he emphasizes that action research help them to reflect on their action. So, they can improve their learning by experience it. As john Elliot (1991:69) says” action research is the study of a social situation with a view to improving the quality of action within it”. By doing this, the result can be proven more dependable
on the result of practice and not to the scientific test of trust. 2. Models of classroom action research
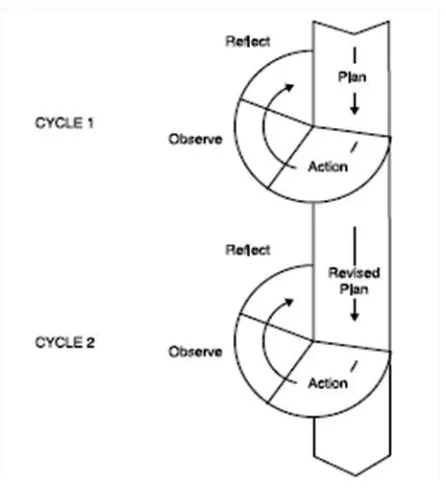
26 refined a formalized the concept of action research and how it apply to education. Kemmis and his college produce a series of publications and courses and materials on action research curriculum development and evaluation at Deakin University in Australia. His articles of action research (Kemmis 1982, 1983) are useful review on how educational action research has been developed from work of Lewin and established its own character. Kemmis summarizes his approach to act research in the model shown in figure 3.1:
Figure 3.1 the action research spiral (base on kemmis and McTaggart (1988: 14) ) Method which Kemmis and McTacggart used was the improvement from Kurt Lewin’s method. In Kemmis’s method they do
27 A number of other similar models are recently developed and mostly are developed by using Lewin or Kemmis’s idea. For example, James McKernan (1991) proposes, a method that call a ‘time process’
model. This method emphasize the important of not allowing an action research ‘problem’ to become too rigidly fixed in time, and of rational
problem solving and democratic ownership by the community of researchers.
To make easy in the way researcher conducts the research, the method which researcher used was the Kemmis and McTacggart’s
method. The steps that researcher follows are: planning, acting, observing, and reflecting.
a. Planning
The activities in planning are:
• Prepare materials, make lesson plan, and design the steps in
doing the action
• Prepare list of object (students name/ participants)
• Prepare teaching aids. Prepare sheets for classroom
observation.
• Prepare a test.
b. Action
• Give pre-test.
28
• Make team study (self-learning by group).
• Give occasion to students to ask any difficulties or
problems.
• Give post-test.
c. Observation
This research used observation to provide data in order to answer the problems within this research. There were several steps that researcher did in doing observation. So, researcher did not move to judgments too quickly.
1) Joint planning
There is a need to establish at the connection between observer and observed so they can focus on the agreement that both party agree on. Likewise, to discuss the context of the lesson, to sort out the basic rule, time, and place of the observation, how to interact with pupils, or how much time to spend in the classroom, etc. the more focus and specific the observation, the more essential for joint planning. By the way, researcher asks the teacher to help and be partner in observation.
2) Focus
29 less subjective judgment, researcher also asks the teacher to do observation in the process. By doing this the researcher and teacher can learn and observe to improve their selves. 3) Establishing criteria
This is important to come on agreement in what criteria that researcher’s want to observe. Some time teacher is not always agree or maybe teacher has better idea in what criteria should be cover. This act can be use as a ‘road map’ for development as well as providing standards
by which to discuss the outcomes of an observation. 4) Observation skills
In the process, observer should not jump too quickly to conclusion. Always respect people privacy. That is why observer should not step too far in person’s space. Even if it
should be done, always remember to get permission from the object of observation. The other skill is more technical: It knows how to design schedules that allow the observer to gather appropriate information.
d. Reflection
Based on the data which was collected, researcher concluded the activities are given effect to student’s reading comprehension. Researcher
30 3. Data gathering
a. Test
The way to get some data with test in this research, the researcher uses two steps. They are: pre-test and post-test. According to David (1969:112) Pre-test is one form may be used at the beginning of a course of study or training program. The researcher uses pre-test to know the student’s ability before the teaching learning process.
According to David (1969:112) Post-test is another form at the conclusion of the program to determine degree of improvement. The researcher uses post-test to know the student’s improvement after teaching
learning process is conducted. David (1969:7) multiple-choice item is generally can be answered fairly rapidly and scoring can be done quickly and involves no judgments as to degrees of correctness. Both the pre-test and post-test are considered 20 items for every test. The forms of multiple-choice type and four alternatives answer a, b, c, or d, in every number. If the students answer 20 items of questions correctly, they get score 100.
b.Observation
There are some ways in doing observation: 1) Field note
31 Researcher uses this technique to record his impression in the process of research, from beginning to the end.
2) Videotape recorder
Researcher uses recorder to obtain visual material of the total teaching procedure. It is also act as an aid to diagnosis. 3) Questionnaires
Researcher provides some questions that are filled by teacher to help in observation.
B. Place and time research
1. Place of research
The research was conducted at MI SRUWEN 01 that located on JL. Kementrian no. 1 Ds. Sruwen, Kec. Tengaran, Kab. Semarang.
a. General information of the school
School name : MI Sruwen 01
NSM (statistic school number) : 111233220018
School address : Jl. Kemetiran no. 1 Ds. Sruwen
: (village) sruwen : (sub-district) tengaran : (district) semarang : (province) central jave
32 Institute address : Butuh, tengaran
: semarang Institute’s phone number : 0298-3405188
No. certificate foundation date : no 6 21th July 2011 Ownership land property : personal
Building status : institute’s property
Land scale : 1251 + 825 = 2076 m2
Building scale : 915 m2
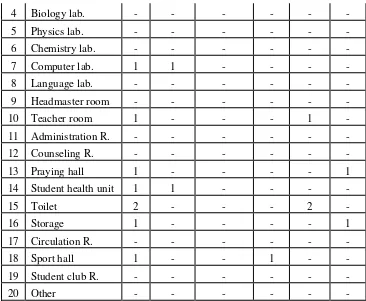
b. The profile of education facilities
33
Table 3.3 list of teacher in MI Sruwen 01
NO Description Total
Teacher
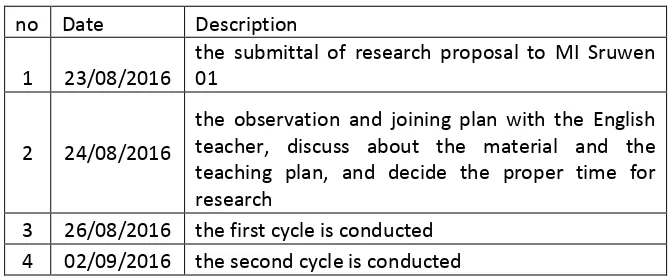
34 Table 3.4 research date and description
no Date Description
3 26/08/2016 the first cycle is conducted 4 02/09/2016 the second cycle is conducted
3. Subject of research
The subject of this research was the fourth grader of MI Sruwen 01. This class was handled by a teacher.
More detailed can be see in the resume below:
Name : SUKRON MAKMUN
Birth date :KAB. SEMARANG, 17 OKTOBER 1985
Address : GUDANG SAKTI RT 29 RW 10
No. Hand phone : 089669605621
EMAIL : [email protected]
Last education : S1 PGMI IAIN WALISONGO SEMARANG Teaching history : 2005-2007 teach class 1
35 Mr. Makmun take care the entire students of fourth grade of MI Sruwen 01. The list of the students is:
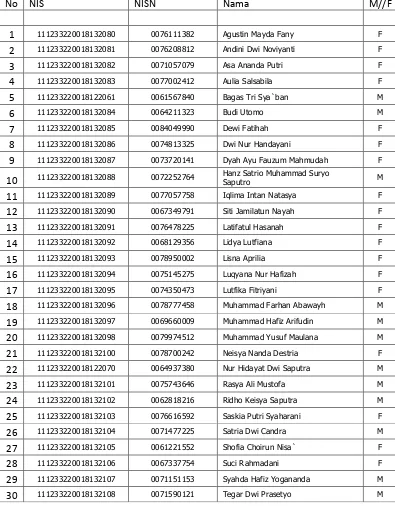
Table 3.5 Students list of fourth grade of MI Sruwen 01
No NIS NISN Nama M//F
1 111233220018132080 0076111382 Agustin Mayda Fany F 2 111233220018132081 0076208812 Andini Dwi Noviyanti F 3 111233220018132082 0071057079 Asa Ananda Putri F 4 111233220018132083 0077002412 Aulia Salsabila F 5 111233220018122061 0061567840 Bagas Tri Sya`ban M
6 111233220018132084 0064211323 Budi Utomo M
36 Researcher and homeroom teacher made discussion; both of them decided that this research was conducted to the entire members of fourth grader, 38 students in total. Therefore for this matter, Mr. makmun as homeroom teacher of fourth grade in MI Sruwen 01 agree to help in the observation process. So, with this researcher can move forward with the schedule that both of party is agree in the early discussion
37 CHAPTER IV
ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
A. Data presentation
1. First cycle
There were several data that researcher collected during the first cycle. Both of the researcher and homeroom teachers as observer collected data. Homeroom teacher conducted observation to the class activity and researcher directly did the research by teaching the class with the method that has been described in the chapter 2.
a. Implementation of the action
The first cycle was held on Friday, 26 Augustus 2016 in fourth grader in MI Sruwen 01. It started at 8.30 am. Actually, The class was follows by 38 students but one of the students absents that day. So, only 37 students followed the first cycle. In this cycle, researcher was helped by Mr. makmun as the observer. He helped to fill the observation sheet as the researcher taught the class. For this cycle researcher used color as the subject material in class. The material can be seeing in appendix.
Researcher started the class by giving greeting.
38 Students : waalaikum salam w.b. good morning pak(sir). I am fine
sir.
Teacher : “seperti yang kemarin sudah terangkan, hari ini kita akan belajar tentang warna. Tapi sebelumnya kita akan ada pre-test tentang warna”.(as I told yesterday, today we will learn about colors. But before that, we will do pre-test about the materials).
The pre-test took 20 minutes to finish. Meanwhile, researcher prepared the material for the class activity, wrote some material on blackboard, and made ready the card that is used. After that, researcher waited until all students finished their pre-test.
He asked if there was any difficulty in the pre-test. Then he tried to solve it. After that, researcher started the main activity. He explained the material that he wrote on blackboard. He told the variety of colors and how to read it. After a while, researcher moved to the next activity. Researcher divided class into 8 groups. Researcher explained the rules of grab game variations.
Each group got an envelope which contained a bundle of card. It was a card with word of color in each card but had different color as the word mean. The task was; each group spread the card on the table. Each time researcher called a card, they had to find it immediately. Teacher : anak-anak. Sekarang kalian sebar kartu yang ada di
39 inside the envelope on the table). Pastikan tiap kartu terbuka.(make sure each card face up)
students : iya pak. Yes sir
Teacher : kalau sudah, sekarang perhatikan bapak. Bapak akan mengucapkan ciri-ciri sebuah kartu dan kalian harus mencari kartu mana yang sesuai. Perhatikan kartu mana yang sesuai dengan ciri-ciri yang bapak sampaikan. Apakah itu tentang warnanya atau tentang tulisannya. Finished? if yes, now pay attention to me. I will tell the specific of a card and your job is to find the right card. Make sure to find the card that match with the characteristic. Is it about the card’s color or the word in the
card?)
Murid : iya pak. Yes sir.
Teacher : sekarang cari kartu dengan warna red.(now, find the card with red color.)
Murid : ini pak !!!(this is it sir!!!).
Teacher : bagus, sekarang cari kartu yang bertuliskan kata warna biru.(good, now find the card with word biru).
40 The activity carried on until students were understood. Then researcher evaluated by asking each student one by one. He called students name and asked them to find card which researcher described.
After that, he asked if they got any difficulty in the process. Did they get problem in memorize the color and the word? Next activity was doing post-test. They got post-test after took break for snack time.
The post-test took 20 minutes differ to each student. After they finished, they submitted the paper. In the end, researcher closed the class.
b. The result from collecting data:
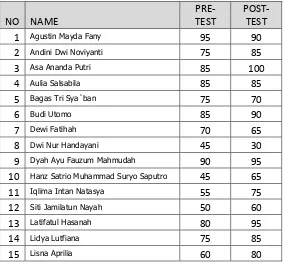
Tables 4.1 shows the result of pre-test and post-test each student.
Table 4.1 the result pre-test and post-test first cycle
NO NAME 10 Hanz Satrio Muhammad Suryo Saputro 45 65
11 Iqlima Intan Natasya 55 75
12 Siti Jamilatun Nayah 50 60
13 Latifatul Hasanah 80 95
14 Lidya Lutfiana 75 85
41
1) Pre-test and post- test average
The score can be obtained by the formula below:
𝑆 =𝑁 ×100𝐵
S : score
B : the right answers N : total of items
The average of the pre-test and post-test are:
42
As the data shown above, the average from the first pre-test is 71.892, the lowest score is 30 and the highest score a 100. The average of post-test is 78.378. The lowest score is 30 and the highest is 100.
∑D = total differences between pre-test and post-test ∑D2 = total the raised 2 of D
Table 4.2
Accumulative of respondents score for standard deviation
44
𝑆𝐷 = √178.373 − 42.068
𝑆𝐷 = √136.31
SD= 11.675 3) Figure out the T-test
𝑡𝑜 = [∑ 𝐷𝑆𝐷𝑁 ] √𝑁 − 1
To= T-Test
∑D= total difference between pre-test and post-test
SD= standard deviation N= total number of students
𝑡𝑜 = 11.675[24037 ] √37 − 1
𝑡𝑜 = 11.6756.486 6
𝑡𝑜 =6.4861.946 = 3.333
4) t-table
The calculation of the t-table (df= N-1) The number of participant is 37, so:
45 5) distribution of rank
From first cycle, researcher collects some data about the pre-test and post-test. This data is used to show how many students who passed minimum score in English lesson. These data are distributed and sort out as the table 4.3 shows:
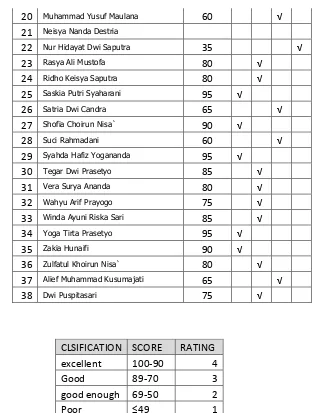
Table 4.3 Distribution score of first cycle’s pre-test
NO NAME SCORE CLASIFICATION
46
The result from the distribution of pre-test can be seemed in the table 4.4:
Table 4.4 Classification of respondents in first cycle’s pre-test
CLSIFICATION SCORE RATING FREQUENCY PERCENTAGE
Excellent 100-90 4 5 13.50%
Good 89-70 3 20 54%
good enough 69-50 2 7 19.00%
Poor ≤49 1 5 13.50%
CLSIFICATION SCORE RATING
Excellent 100-90 4
Good 89-70 3
good enough 69-50 2
47 Table 4.4 points out the respondents’ pre-test in first cycle.
From 37 respondents, there are 5 respondents (13.5%) get excellent score. There are 20 respondents (54%) get good score. There are 7 respondents (19%) get good enough score and 5 respondents (13.5%) get poor score. As the minimum pass score for English lesson is 70.00, there are 25 respondents (67.5%) who pass It. as for the rest is failed.
Researcher tried to do the same to the post-test score. The data can be seen in table 4.5:
Table 4.5 distribution of first cycle post-test
NO NAME SCORE CLASIFICATION
48
Table 4.6 Classification of respondents in first cycle’s post-test CLSIFICATION SCORE RATING FREQUENCY PERCENTAGE
Excellent 100-90 4 11 30%
Good 89-70 3 17 46%
good enough 69-50 2 7 19%
Poor ≤49 1 2 5%
CLSIFICATION SCORE RATING
excellent 100-90 4
Good 89-70 3
good enough 69-50 2
49 Table 4.6 points out the total respondents’ classification
score in first cycle post-test. With the minimum pass score (KKM) is ≥ 70, There are 11 respondents (30%) get excellent
score. 17 respondents (46%) get good score. 7 respondents (19%) get good enough score and 2 respondents (5%) get poor score. Total 28 respondents (76%) pass the minimum pass score. Only 9 respondents (24%) are failed.
Comparing the result from pre-test and post-test, there is improvement. Respondents who are passed the minimum pass score (KKM) is increase. The result from pre-test is 67.5% and from post-test is 76%.
6) observation
The observation was held by the researcher and the English teacher. Researcher used field note and camera to record. As the teacher, he filled the observation sheet that researcher provided.
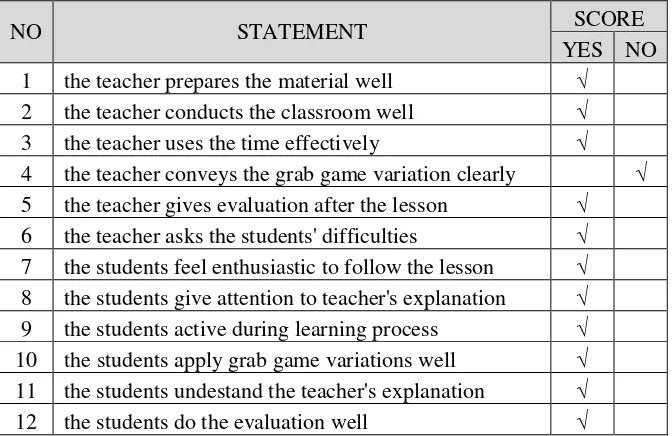
50 Table 4.7 sheet for classroom observation
NO STATEMENT SCORE
YES NO 1 the teacher prepares the material well √ 2 the teacher conducts the classroom well √ 3 the teacher uses the time effectively √ 4 the teacher conveys the grab game variation clearly √ 5 the teacher gives evaluation after the lesson √ 6 the teacher asks the students' difficulties √ 7 the students feel enthusiastic to follow the lesson √ 8 the students give attention to teacher's explanation √ 9 the students active during learning process √ 10 the students apply grab game variations well √ 11 the students undestand the teacher's explanation √ 12 the students do the evaluation well √
The second was observation on students’ behavior. This
observation was about students’ behavior in the middle of
class. There were some actions which researcher gathers which may occur during activity. The result is shown in table 4.8:
Table 4.8 Observation sheet in first cycle
51
Scan code: 1. Talk unrelated to task assigned 2. Doodling
3. Daydreaming, 4. Wandering around 5. Do something else 6. Bothering friend
7. Attempting to draw attention 8. Play with stationery
52 The result:
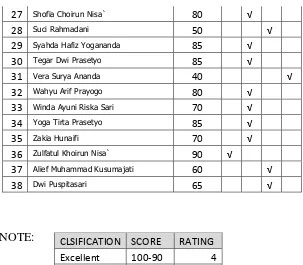
There were five students that talked unrelated to task, there were: Dwi Nur Handayani, Dyah Ayu Fauzum Mahmudah, Muhammad Farhan Abawayh, and Ridho Keisya Saputra, five students that wandered around, there were: Andini Dwi Noviyanti, Asa Ananda Putri, Dwi Nur Handayani, Lidya Lutfiana, and Muhammad Yusuf Maulana. Three students did something else, there were: Bagas Tri Sya’ban, Budi Utomo, and Satria Dwi
Candra. Four students played with stationery, there were: Siti Jamilatun Nayah, Muhammad hafiz Arifudin, Nur Hidayat Dwi Saputra, and Syahda Hafiz Yogananda. Three students did other thing. There were: Muhammad Farhan Abawayh, Nur Hidayat Dwi Saputra and Wahyu Arif Prayogo. Total numbers from students who included in the description were 18 students from 37 total populations.
53 There are many reasons why students do that. Like the compatibility between the ways (method) which teacher uses and student’s type of learning. As for them who is kinesthetic type,
they hardly to stay till when they are learning. That is why some students wandering around in meddle of class. They only learn when they move their body; practice directly. There is another type: like visual type and auditory type. Each student has different type. So, this not something that teacher should force to student about how they have to learn. In contrary, teacher should match the learning process to students’ type learning. Even so, there should
be limit to the process so there is no discrimination. In the way that one character get better attention than other character.
54 After seeing the result from first cycle, researcher knows that there is improvement between before and after researcher uses grab game variations as the learning method. It can be seen in the improvement of average score which students get. The average pre-test score is 71.892 and the average post-test score is 78.378.
Result from T-test shows that T-table with significant 5% with 37 respondents is 1.688 and result for T-test is 3.333. The significance difference between T-table and T-test was 1.645.
The number for students who passes in the first cycle is increase. The result from pre-test is 67.5% and from post-test is 76%. There is 8.5% improvement.
Even there is improvement in the first cycle; researcher still decides to do the second cycle. Hopefully in the second cycle there is more high result than the first cycle in the T-test result.
2. Second Cycle
a. implementation of action
55 Mostly there were similarities in the process of teaching between first and second cycle. In the beginning, researcher started with greeting. Then he gave pre-test before main activity. After that he gave the material. The last he gave post-test.
The difference was in the material and the card that was used in main activity. For second cycle researcher made the card with word of English stationery and the picture about it separately. So they had to match it.
Teacher : baik anak-anak, sekarang kita akan belajar tentang stationery, ada yang tau apa itu stationery? Stationery itu peralatan tulis/ alat-alat tulis. Sekarang lihat ke papan tulis. Ada yang tahu apa itu pen?.(ok kids, now we will learn about stationery, anyone know what is stationery? Stationery is any equipment which helps in writing process. Now look at the blackboard. Anyone know what is pen?)
Students : bolpoin pak. (it’s a Pen sir) Teacher : kalau eraser? (and eraser?) Students : penghapus pak. (eraser sir)
56 berisi gambar dan bahasa inggris nya. Tugas kalian untuk mencocokkannya. Apa kalian mengerti?(now, after all of you knew what is stationery, you will be divide into some groups. Each group will get an envelope which contains pictures and words. Your job is to match it. Do you get it)
Students : ya pak.(yes sir)
Teacher : sekarang kalian susun gambar dan kata2nya. Bapak beri waktu 5 menit. . . .time is up. Sekarang tunjukkan gambar dan kata bahasa unggrisnya sesuai dengan yang bapak minta. (Now all al of you arrange the picture and words. I give you five minutes. . . . Time is up; now show me the arrangement as I ask to you.) Teacher/researcher asked one by one to each student. He asked students to show the stationery which he called randomly. He asked several times until he was sure that the students were understood. Researcher stopped the activity. Then, he asks if they got problem. After that he gave post-test.
b. The result from collecting data:
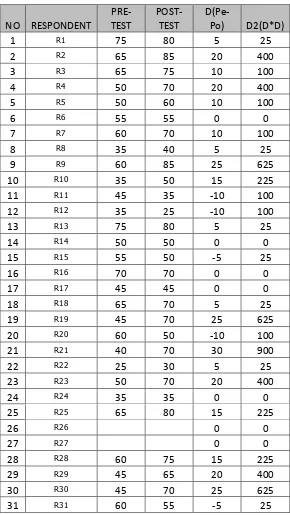
57 Table 4.9 the result pre-test and post-test second cycle
NO NAME PRE-TEST 10 Hanz Satrio Muhammad Suryo Saputro 35 50
58
Total 1855 2185
1) pre-test and post-test
The score can be obtained by the formula below:
𝑆 = 𝑁 ×100𝐵
S : score
B : the right answers N : total of items
The average of the pre-test and post-test are:
𝑝𝑟𝑒 − 𝑡𝑒𝑠𝑡 𝑎𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒 = 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑝𝑜𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑟𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒 𝑝𝑟𝑒 − 𝑡𝑒𝑠𝑡
=185535 = 53
𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑡 − 𝑡𝑒𝑠𝑡 𝑎𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒 =𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑝𝑜𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑟𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑠𝑟𝑜𝑟𝑒 𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑡 − 𝑡𝑒𝑠𝑡
= 218535 = 62.429
As the data is shown above, the average from the first pre-test is 53, the lowest score is 25 and the highest score a 75. The average of post-test is 62.429. The lowest score is 25 and the highest is 85.
2) Standard deviation
Based on the second cycle, researcher also calculates standard deviation as follows:
59 SD = standard deviation
∑D = total differences between pre-test and post-test ∑D2= total the raised 2 of D
Table 4.10
60
32 R32 75 70 -5 25
33 R33 55 85 30 900
34 R34 40 70 30 900
35 R35 50 60 10 100
36 R36 0 0
37 R37 65 75 10 100
38 R38 50 60 10 100
Total 1855 2185 330 7950
𝑆𝐷 = √795035 − [33035 ]2
𝑆𝐷 = √227.142 − 88.887
𝑆𝐷 = √138.255
SD= 11.758
3) Figure out the T-test
𝑡𝑜 = [∑ 𝐷𝑆𝐷𝑁 ] √𝑁 − 1
To= T-Test
∑D= total difference between pre-test and post-test
SD= standard deviation N= total number of students
𝑡𝑜 = 11.758[33035 ] √35 − 1
61
𝑡𝑜 =9.4292.016 = 4.677
4) t-table
Calculation of the t-table (df= N-1) The number of participant is 35, so:
df =35-1= 34, the value of t-table with level of significant 5% is distributed and sort out as the table 4.11 shows:
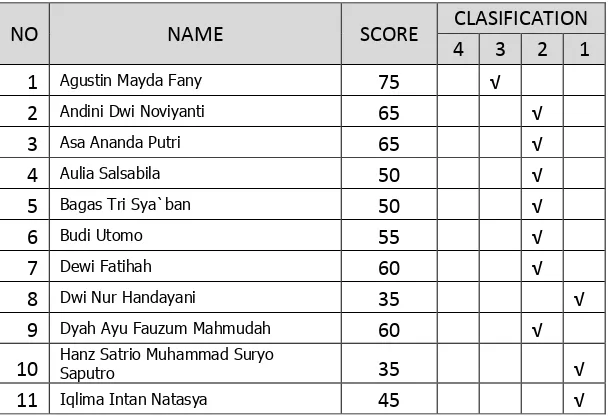
Table 4.11 Distribution score of second cycle’s pre-test
NO NAME SCORE CLASIFICATION
62
CLSIFICATION SCORE RATING excellent 100-90 4
Good 89-70 3
good enough 69-50 2
63 : The result from distribution of second cycle pre-test can be seen in table 4.12:
Table 4.12
The result from distribution score of second cycle pre-test
Table 4.10 shows the result from the distribution of pre-test rank in second cycle. There are 4 respondents (12%) get good score, 19 respondents (54%) get good enough score, and 12 respondents (34%) get poor score. There is no respondent who get excellent score.
Next, researcher does the same think as the pre-test to the post-test. This can be used to compare the result of pre-test and post-test. Post-test score distribution rank can be seen in table 4.13:
Table 4.13 post-test score distribution rank
NO NAME SCORE CLASIFICATION
4 3 2 1
CLSIFICATION SCORE RATING FREQUENCY PERCENTAGE
Excellent 100-90 4 0 0%
Good 89-70 3 4 12.00%
good enough 69-50 2 19 54%
64
CLSIFICATION SCORE RATING Excellent 100-90 4
Good 89-70 3
good enough 69-50 2
Poor ≤49 1
65 The result could be seemed in table 4.14:
Table 4.14 The result of post-test score distribution rank CLSIFICATION SCORE RATING FREQUENCY PERCENTAGE
Excellent 100-90 4 0 0%
Good 89-70 3 19 54%
good enough 69-50 2 10 28.50%
Poor ≤49 1 6 17.50%
Table 4.14 shows there is significant improvement in the result. There are 19 respondents (54%) get good score, 10 respondents (28.5%) get good enough score, and 6 respondents (17.5%) get poor score. This is good sign that the method which researcher uses can give improvement.
6) Observation
Researcher still used the same observation sheet as first cycle. First sheet was about the class observation. The second was observation for students’ behavior. This observation was to see
students’ behavior in the process. The result of class observation
can be seen in table 4.15:
Table 4.15 sheet for class observation
NO STATEMENT SCORE
66 3 the teacher uses the time effectively √ 4 the teacher conveys the grab game variation clearly √ 5 the teacher gives evaluation after the lesson √ 6 the teacher asks the students' difficulties √ 7 the students feel enthusiastic to follow the lesson √ 8 the students give attention to teacher's explanation √ 9 the students active during learning process √ 10 the students apply grab game variations well √ 11 the students understand the teacher's explanation √ 12 the students do the evaluation well √
The second observation is about students’ behavior. The result can be seen in table 4.16:
Table 4.16 Observation of students’ behavior in second cycle
67
Scan code: 1. Talk unrelated to task assigned 2. Doodling
3. Daydreaming, 4. Wandering around 5. Do something else 6. Bothering friend
7. Attempting to draw attention 8. Play with stationery
9. Other thing beside above.
68 saputra, and Syahda Hafiz Yogananda. There were 3 students who wandering around; Bagas Tri Sa’ban, Ridho Keisya Saputra, and
Yoga Tirta Prasetyo. Even in the second cycle there were 3 students (Dwi Nur Handayani, Siti Jamilatun Nayah, Lidya lutfina) who did other thing. There were 2 students (Iqlima Intan Natasya, Muhammad Hafiz Arifudin) who played with their stationery. Also a student (Muhammad Farhan abawayh) just attempted to draw attention.
Researcher assumes that students start to feel less interest. There are more students who talk unrelated to task assigned. Although, in total number of students who misbehavior in the middle class is decrease. There were only 15 students in total. It is worth to get attention for better result in the future. Teacher can make each class activity different and exciting.
In the end of observation, researcher asked some questions to teacher about the method which researcher proposed. The questions and the answer can be seeing below:
• What is your opinion about the method that being used?
Answer: metode cukup menarik hanya saja kurang penjelasan sesuai dengan langkah pembelajaran. The method is interesting enough, only there were no enough explanations as on the lesson plan.
69 Answer: mengkombinasikan dengan metode lain. To combine
with other methods.
• What is the advantage if teacher uses the method?
Answer: keuntungannya anak lebih aktif, giat, serta senang dalam menerima pelajaran sehingga prestasi meningkat. The advantage is students more active, energetic, also happily in receiving the learning process so the archievement is increase.
• Did teacher will consider this method to be used in the teaching
in the future?
Answer: bila memungkinkan akan digunakam apabila sesuai dengan materi juga waktu.if there is an opportunity, it will be use as long as compatible with the material and the time.
These questions are answered by Mr. Sukron Makmun as the English teacher.
Researcher concludes that there is improvement before and after researcher used grab game variations as the learning method from second cycle,. It can be seen in the improvement of average score which students get. The average pre-test score was 53 and the average post-test score was 62.429.
70 significance difference between T-table and T-test was 2.987. It is better than first cycle which only got 1.645.
The number for students who pass in the second cycle is increase. The result from pre-test is 12% (4 students) pass the KKM and from post-test is 54% (19 students) pass the KKM from 35 students in total. There is 42% significant improvement.
That is all data which writer collects during the second cycle.
3. Discussion
The table 4.17 is the summary for the first and second cycle calculation.
Table 4.17 summary for pre-test and post-test first and second cycle
No Result cycle 1 cycle2
1
mean of
pre-test 71.892 53
post-test 78.378 62.429
2 standard deviation 11.675 11.758
4 T-table vs. t-test 1.688≤
3.333
1.690≤ 4.677
Based on the data which researcher collects during first and second cycle, the writer is able to clarify that there is an improvement of students’
72 CHAPTER V
CLOSURE
A. Conclusion
In this chapter researcher presents the conclusion of this research which is entitled “the use of Grab Game Variations to improve students’
reading comprehension (a class action research of fourth grader of MI
Sruwen 01 in academic year 2016/2017)”. After conducting the research, presenting the data, analyzing the data, it can be conducted as follows:
1. Grab game variations make students more active in learning. It changes the class condition that make students can learn
reading comprehension more effective.