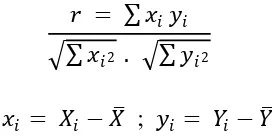AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY
A Research Paper
Submitted to the Department of English Education of the Faculty of Language and
Literature Education of Indonesia University of Education as a Partial Fulfillment
of the Requirement for Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
By
Selviani Vidya Lestari 1100061
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF LANGUAGE AND LITERATURE EDUCATION INDONESIA UNIVERSITY OF EDUCATION
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
An Analysis of Inte ie as a Te hni ue to Assess the Students’ Speaking A ility
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu| perpustakaan.upi.edu LEMBAR HAK CIPTA
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY
Oleh:
Selviani Vidya Lestari 1100061
Sebuah skripsi yang diajukan untuk memenuhi syarat memperoleh gelar Sarjana Pendidikan pada Fakultas Pendidikan Bahasa dan Sastra
©Selviani Vidya Lestari 2015
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia
Oktober 2015
Hak cipta dilindungi undang-undang.
PAGE OF APPROVAL
SELVIANI VIDYA LESTARI
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY
Approved by:
Main Supervisor Co-Supervisor
Prof. H. Fuad Abdul Hamied, M.A., Ph.D.Muhammad Handi Gunawan, M.Pd NIP. 195008211974121001 NIP. 197301132009121002
Head of Department of English Education Department of Language and Literature Education
Indonesia University of Education
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
ABSTRACT
Selviani Vidya Lestari (1100061). An Analysis of Interview as a Technique to Assess the Students’ Speaking Ability. Under the supervision of Prof. H. Fuad Abdul Hamied, M.A., Ph.D. and Muhammad Handi Gunawan, M.Pd.The research analyses the implementation and implication of interview as a
technique to assess the students’ speaking ability. Mix methods research design
was used to obtain the data. The data were gathered from 10 eleventh grade students and taken from observation and tests. The tests administered in this research were TOEIC speaking test and interview test. The qualitative data were taken from observation. The observation was conducted during the interview test to see the implementatation of interview. The quantitative data were taken from
the students’ TOEIC speaking test score and interview test score. The speaking
assessment criteria used to score the students’ speaking ability through interview was the combination of IELTS and Adam and Frith speaking assessment criteria.
The students’ TOEIC speaking test score and the interview score were computed
by using Pearson Product Moment Correlation formula to see the implication of interview. The findings showed that the implementation of interview was appropriate based on some steps by Underhill (1987). Besides, the interview had covered the components defined by Harris (1969) in the form of the IELTS-Adam and Frith speaking assessment criteria. In addition, the correlation coefficient
between the students’ TOEIC speaking test score and interview test score was 0,7.
It indicated thatthe correlation was strong and positive.This study brought to a
close that interview is a good and appropriate technique to assess the students’
speaking ability. However, some consideration should be made in the relation of time, setting, and the topic of the interview.
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PAGE OF APPROVAL ... i
STATEMENT OF AUTHORIZATION ... ii
PREFACE ... iii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... iv
ABSTRACT ... vi
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... vii
LIST OF TABLES ... x
LIST OF FIGURES ... xi
LIST OF GRAPH ... xii
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION ... 1
1.1Background ... 1
1.2Research Questions ... 3
1.3Aim of the Study ... 4
1.4Scope of the Study ... 4
1.5Significance of the Study ... 4
1.6Research Methodology... 5
1.6.1 Research Design ... 5
1.6.2 Site and Participants ... 5
1.6.3 Data Collection ... 5
1.6.4 Data Analysis ... 6
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
1.8Organization of the Paper... 7
CHAPTER II LITERATURE REVIEW ... 8
2.1 Speaking ... 8
2.2 Assessment in Speaking ... 11
2.3 Interview ... 13
2.4 Criteria of Assessing Speaking ... 17
2.5 TOEIC Speaking Test ... 27
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 37
3.1 Research Design ... 37
3.2 Site and Participants ... 39
3.3 Data Collection Techniques ... 39
3.3.1 Observation ... 39
3.3.2 Tests ... 40
3.4 Data Analysis ... 40
CHAPTER IV FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION ... 42
4.1 Implementation of Interview ... 42
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
4.3 Interview Test Result ... 63
4.4 The Implication of Interview ... 58
CHAPTER V CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS ... 63
5.1 Conclusions ... 63
5.2 Suggestions ... 64
REFERENCES ... xiii
APPENDICES ... xvi
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2.1 The Weighting Table ... 19
Table 2.2 IELTS Assessment Criteria: Speaking ... 21
Table 2.3 IELTS-Adam and Frith Speaking Assessment Criteria ... 25
Table 2.4 The Organization of TOEIC Task and Evaluation Criteria ... 32
Table 2.5 TOEIC Converting Table ... 33
Table 2.6 TOEIC Speaking Proficiency Level Descriptors ... 34
Table 4.1 TOEIC Speaking Test Scores ... 49
Table 4.2 TOEIC Speaking Test Proficiency Level Descriptors ... 50
Table 4.3 Interview Test Score ... 54
Table 4.4 Students’ Speaking Test Scores ... 58
Table 4.5 Calculation of Correlation Coefficient ... 59
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 3.1 Embedded Design Procedures ... 38
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
LIST OF GRAPH
Graph 4.1 The Relationship between TOEIC Speaking Test Score and
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
This chapter provides a brief description of the whole content of the
research. It covers background of the research, research questions, aims of study,
scope of the study, significance of the study, research methodology, and
clarification of terms. The organization of paper is also enlightened in this
chapter.
1.1 Background
There are four essential skills of language; listening, speaking, reading,
and writing. Students must have a great mastery in all skills. Nowadays, school
and institution are only focusing on the students’ writing skill. They always
administer an assessment that can only assess the students’ writing ability and
neglect the students’ speaking ability. Whereas the speaking skill plays an important role in students’ mastery of language.
Speaking is arguably used for education and business field. Someone’s
mastery of language can also be seen from the speaking ability. The teaching and
learning process often forget the urgency of speaking skill. Regarding that, the
speaking assessment is always neglected. Teaching, learning, and testing speaking
are rarely focusing on the production of spoken discourse because it was easier for
teachers, methodologists, applied linguists and linguists to focus on written
language than spoken language (Carter and Nunan, 2001). Egan (1999) argued
that speaking is at the heart of second language learning but has been somewhat
ignored in teaching and testing for a number of logistical reasons. It is in line with
Clifford’s argument (as cited in Egan, 1999) that speaking is also absent from testing because of the difficulty in evaluating it objectively and the time it takes to
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
Students’ speaking ability is rarely assessed because there are some difficulties in administering the spoken test. Speaking is probably the most
difficult skill to assess—even with the aid of recording technology—given its
real-time and typically interactive nature (Thornbury in Burns and Richards,
2012).The most common difficulties in administering the spoken test are the time
management and the technique used. The spoken test will take longer time than a
written test. For that matter, teachers tend to hold a written test which is easier to
administer than the spoken test.
Teachers need a special technique to assess students’ speaking ability
properly and objectively. Several techniques can be used to assess students’
speaking ability such as interview, pictures, role play, interpreting, prepared
monologue, reading aloud, and discussion (Hughes, 2003). In the relation to
choosing the relevant technique to assess students’ speaking ability, teachers also
need to plan and structure the testing carefully. These are the guidelines, adopted
from Hughes (2003), for teacher to conduct the speaking assessment, (1) make
oral test as long as feasible; (2) plan the test carefully; (3) give the candidates as
many “fresh start” as possible; (4) use a second tester for interview; (5) set only
tasks and topics that would be expected to cause candidates no difficulty in their
own language; (6) carry out the interview in a quiet room with good acoustics; (7)
put candidates at their ease so that they can show what they are capable of; (8)
collect enough relevant information; (9) do not talk too much; (10) select
interviews carefully and train them.
Several researches on the topic of speaking assessment have been
conducted. Kormos (1999) employed a conversation analysis of role plays and
non-scripted interviews in language exams. The result showed that certain control
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
proficiency reliably, but they do not provide candidates with adequate
opportunities to display their conversational competence.
Most recently, a study by Plough, Briggs, and Bonn (2010) provides
insight into a multi-method analysis of evaluation criteria used to assess the
speaking proficiency. There are several methods used to assess the speaking
proficiency on this research; the general interview, the lesson, the office hour role
play, and the video questions. The focus on the general interview lasts
approximately 5 minutes and the prospective GSI candidate is asked a few general
questions about his or her background and educational interests. The result on the
general interview shows that the focus of the general interview are on listening
comprehension, pronunciation, and responding to questions which are significant
and appropiate with the evaluation criteria to assess speaking proficiency.
Thus, this study analysed the appropriateness of interview as the
assessment technique to measure the students’ speaking ability considering the result, objectivity of the assessment and time consumed to administer the test.
1.2 Research Questions
This study is conducted to answer the following questions:
1. How is the implementation of interview to assess the students’
speaking ability?
2. What is the implication of interview as a technique to assess the
students’ speaking ability?
1.3 Aims of the Study
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
1. Analysing the implementation of interview to assess the students’
speaking ability.
2. Analysing the implication of interview as a technique to assess the
students’ speaking ability. 1.4 Scope of the Study
This study focuses on the analysis of interview as a technique in assessing
students’ speaking ability. Futhermore, the study investigates the use of interview
to assess students’ speaking ability in senior high school.
1.5 Significance of the Study
The findings of this study are expected to contribute and give some
informative inputs in assessing students’ speaking abillity in terms of theory, profession and practice.
From the theoretical perspective, the result of this study can enrich theories
related to speaking assessment for senior high school students. Thus, this study
will be a reference of study which investigates the similar variables.
Professionally, the result of this study is expected to inspire English
teachers about techniques in assessing senior high school students’ speaking
ability. Therefore, teachers will improve their professionalism.
Moreover, from the practical perspective, this study can motivate English
teachers to use the proper technique in assessing students’ speaking ability. As a
result, students can improve their speaking ability based on the assessment made
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
1.6 Research Methodology 1.6.1 Research Design
This study is in form of mixed methods research because this study is
aimed at describing the analysis of speaking assessment techniques, interview.
Creswell (as cited in Heigham and Croker, 2009) defined mixed methods as a
procedure for collecting, analyzing, and mixing quantitative and qualitative data at
some stage of the research process within a single study in order to understand a
research problem more completely. The embedded design is used in this research.
In line with Creswell, this present research will observe the students’
behaviour on speaking assessment and analysing the students’ speaking ability
through the result of interview.
1.6.2 Site and Participants
Research participants in this present study are students of a senior high
school in Cimahi. This is because the students who are taking a study in the senior
high school are expected to have a good ability in speaking. The students who
became the participants of this research had accomplished the first grade of senior
high school.
1.6.3 Data Collection
The data of this study are gathered through observation and interview.
a. Observation. Records the students’ interview and transcribes it into a
written form.
b. Interview. The interview is conducted to participants who related to the
study in order to support the data collection. The interview is
administered along with the spoken test. Structured interview is used
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
1.6.4 Data Analysis
The data obtain from the observation and interview are presented in the
form of transcription. The systems of transcription seek to capture every aspect of
speech that might indicate something about the way verbal interaction operates
and what it achieved (Horrocks and King, 2010).
1.7 Clarification of Terms
In order to avoid misunderstanding, some terms are clarified as follows:
1. Assessment
Assessment is the process of the data analysis that teacher uses to get
evidence about their learners’ performance and progress in English (Pinter, 2006).
2. Speaking
Speaking is physically situated face-to-face interaction; usually
speakers can see each other and so can refer to the physical context and
use a number of physical signals to indicate attention to interaction,
their attention to contribute and their attitute towards what is being said
(Bygate in Carter and Nunan, 2001).
3. Interview
Interview is unequal social encounters in which the interviewer retains
most of the rights in the interaction and in which turns are
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
1.8 Organization of the Paper
This paper is presented into five chapters. The chapters are divided into
subtopics that elaborate the given issues.
CHAPTER I Introduction
This chapter introduces the present study. It includes the background of the
study, research question, aims of the study, scope of the study, significance of the
study, research design, clarification terms, and organization of the paper.
CHAPTER II Literature Review
This chapter provides the theoretical foundation of the topic related to
assessment, speaking, speaking technique assessment, and criteria of assessing
speaking.
CHAPTER III Research Methodology
This chapter consists of research procedures which explain how the
research is conducted. It includes research design, site and participants, data
collection, and data analysis.
CHAPTER IV Findings and Discussion
This chapter will explain findings and discussion. This chapter describes
the result of the instrument analysis such as the result of observation and
interview. This chapter will also explain the interpretation of the findings from the
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
CHAPTER V Conclusions and Suggestions
This chapter draws conclusion which describes the result of the study as
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter deals with aspects of methodology used to guide the present
study. Some points to discuss are the explanation of the research design, site and
participants, data collection technique, and data analysis.
3.1 Research Design
This research deals with analysing the technique of speaking assessment,
that is, interview. Besides, this research will also analyse the implication of
interview as a technique to assess the students’ speaking ability. In conducting the
research, the researcher applies mixed methods research as the research methodology. This is in line with Creswell’s explanation, in Heigham and Croker (2009), that mixed method is defined as a procedure for collecting, analysing, and
mixing quantitative and qualitative data at some stage of the research process
within a single study in order to understand a research problem more completely.
Johnson defined mixed method in Kumar (2014) as the type of research in which
a researcher or team of researchers combine elements of qualitative and
quantitative research approaches (e.g., use of qualitative and quantitative
viewpoints, data collection, analysis, inference techniques) for the purposes,
breadth, depth of understanding, and corroboration. In mixed method research, a researcher collects both numeric information and text to better answer a study’s research questions (Heigham and Croker, 2009).
In conducting the mixed method research, the researcher applies the
embedded design. Heigham and Croker (2009) argued that the embedded design
is used when a researcher needs to answer a secondary research question that
requires the use of different types of data within a traditional quantitative or
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
the use of the embedded design. The data were collected qualitatively through
interviews, classroom observations, and teacher narratives. Meanwhile, the
quantitative data were taken in the form of test scores. Figure 3.1 presents the
visual diagram of the Embedded Design procedures in this research.
Figure 3.1 Embedded Design Procedures
In this research, the researcher obtained the qualitative data from
interviews and observation. Meanwhile, the quantitative data were obtained from the students’ TOEIC speaking test score and interview score. The scores from the tests mentioned were produced by using Pearson Product Moment Correlation
formula to see the correlation between the scores, whether the correlation was
positive or negative. The Pearson Product Moment Correlation formula, adapted
from Susanti (2010), is presented as follows.
� = � �
�2 . �2
� = �− ; � = � −
Figure 3.2Pearson Product Moment Correlation Formula
QUAL
Observation Interpret
Interpretation based on QUAL and Quan results Quan
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
In this research, there was no cause-effect relationship between the TOEIC
speaking test score and the interview score. Douglas (2010) believed that in
language performance, correlation is based on the assumption that when people
perform similarly on two different tasks, similar abilities must be required for the
performance. In this research, the correlation coefficient only showed the degree
of relationship of TOEIC speaking test score and the interview score. The range of
correlation coefficient would vary from -1 to 0 to +1. Hatch and Farhady (1982)
argued that A +1 correlation coefficient indicates a perfect positive correlation, a
-1 correlation coefficient indicates a perfect negative correlation, and a 0
correlation indicates no relationship between the variables.
Therefore, this research used mixed methods reasearch method by
applying the embedded design, because it generated data both qualitative and
quantitative. The data were obtained in the form of observation, and students’
speaking test score.
3.2 Site and Participants
The eleventh grade students of a public senior high school in Cimahi were
selected as sample of this study. This was because students’ speaking proficiency
was considered adequate, as presented on students’ speaking score in the tenth
grade, and the materials covered in the eleventh grade of senior high school were
comprehensive. The sample were choosen randomly. The students taken as
sample are 10 students.
3.3 Data Collection Techniques
In collecting the data, two techniques were employed: observation and
tests. Each of these data collection techniques will be discussed below.
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
Heigham and Croker (2009) stated that observation is the conscious noticing and detalied examination of participants’ behavior in a naturalistic setting. This is in line with Kumar (2014) that observation is a purposeful,
systematic and selective way of watching and listening to an interaction or
phenomenon as it takes place. The emphasis during observation is on
understanding the natural environment as lived by participants, without altering or
manipulating it (Gay, Mills, and Airasian, 2009).
In this research, the observation was used to analyse students’ speaking
ability while being interviewed by the teacher. The steps in interview were also be
the focus on the observation. The type of non-participant observation was used. In
this case, the researcher did not get involved in the activities of the group but
remained a passive observer, watching and listening to its activities and drawing
conclusions from the activity (Kumar, 2014). The observation was only conducted
during the assessment and was purpose to observe the behaviour or personality
traits of each student.
3.3.2 Tests
Brown (2001) defined a test as a set of techniques, procedures, and items
that constitute an instrument of some sort that requires performance or activity on the part of the test taker. Brown (2001) added that a test measures a person’s ability and competence.
The tests conducted in this research were TOEIC speaking test and
interview test. The TOEIC speaking test was conducted by asking students using
TOEIC sample questions to gain students’ speaking proficiency level. Meanwhile,
the interview was conducted after the TOEIC test to see the students’ speaking
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
ETS (2012) argued that TOEIC speaking test is a valid assessment of a
person’s ability to speak in English. In the relation with interview, Kvale in
Dörnyei (2007) defined interview as a one-to-one ‘professional conversation’ that
has a structure and a purpose to obtain descriptions of the life world of the
interviewee with respect to interpreting the meaning of the described phenomena.
3.4 Data Analysis
After collecting the data through observation and interview, the data were
analysed to draw the conclusion. The analysis of data was elaborated below.
There were several steps conducted in analysing the data collected in this
research. The analysis was intended to answer the research questions stated in the
previous chapter.
The first data analysis conducted was data analysis from observation. The
observation was conducted during the interview. The analysis was based on what
the researcher had been observed and noted. After that, the conclusion was drawn
to answer the research question on the implementation of interview.
The second data analysis was the data from test. The first test conducted
was TOEIC speaking test. The testwas audio recorded. The students’ answerfrom
the test were transcribed, scored, and interpreted to see the speaking proficiency level of the students. The students’ answers were scored based on the criteria of speaking assessment by ETS. The second test conducted was the interview test.
The students’ answer were also transcribed based on the video recording. Then,
the researcher scored the students’ answer based on the combination ofthe
speaking assessment criteria by Adam and Frith and IELTS.The speaking
assessment criteria included fluency and coherence, lexical resource, grammatical
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
After that, the score for each student was obtained based on the result of
TOEIC speaking test and interview test. Then, the correlation between students’
TOEIC speaking test score and the students’ interview score was computed by
using Pearson Product Moment Correlation formula. Finally, the interpretation of
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
This chapter is proposed to depict the summary of the study. The
conclusions and suggestions for further studies on the findings and discussions
from the previous chapter will be elaborated in this chapter.
5.1 Conclusions
The aims of this study were to analyse the implementation and implication
of interview as a technique to assess the students’ speaking ability. The findings
and discussions in Chapter IV have elaborated the data related to the study.
The implementation of interview had been proper based on the stages
suggested by Underhill (1987). The interview had followed the stages started from
introduction and warm-up until the feedback and wind-up level. Interview had
also covered the components of speaking as stated by Harris (1969) in the form of
the IELTS-Adam and Frith speaking assessment criteria. The interview lasted for
115 minutes. It covered the time for giving instruction, asking and answering
questions, and giving compliments.
Regarding the result of TOEIC speaking test, it showed that the speaking
proficiency level of students were at the scale of 3 to 6. One student obtained the
score of 3 and two students gained the score of 4 in TOEIC speaking test.
Furthermore, four students obtained the score of 5 in TOEIC speaking test and the
highest score was gained by three students. From the result, it could be stated that
the students’ proficiency level was adequate and the students were able to
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
After conducting the interview test, the score of students were obtained.
The interview test scores were at the scale of 3 to 5. Generally, most of the
students obtained the score of 5. Meanwhile one student obtained the score of 3
and two students gained the score of 4 in the interview test.
The implication of interview was based on the computation of the
correlation coefficient between the students’ TOEIC speaking test score and the
interview test score, it was found that the correlation was 0,7. It indicated that the
correlation was strong and positive.
Therefore, this study showed that interview is a proper technique to be
administered in order to assess the students’ speaking ability. However, some
consideration should be made in the relation of time, setting, and the topic of the
interview.
5.2 Suggestions
From the findings that have been elaborated, some suggestions are drawn
to the teachers in general, as well as to the future researchers who conduct a topic
related to the speaking assessment technique. The suggestions are listed in the
following.
1. The teachers should prepare the time to administer the spoken test. The
teacher must pay attention to not only the time for asking and answering
questions, but also the time to give instructions and comments. For that
matter, the spoken test will take a longer time than the written test. It
means that with the amount of students in Indonesian class, the school
should prepare more than a day to conduct the spoken test.
2. The teachers should take notes during the students’ performance instead of
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
performance based on what the teachers have felt and witnessed and what
the teachers have written during the students’ performance.
3. The future researchers can focus on other issues in speaking assessment
techniques, such as analysing role-play or presentation to assess the
students’ speaking ability, analyse the discourse of speaking assessment,
and so on. In addition, the future researchers can also analyse the
implementation and implication of interview to assess the students’
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
REFERENCES
Brown, H. (2001). Teaching by principles: An interactive approach to language pedagogy. New York: Longman
Burns, A., & Richards, J. (2012). The Cambridge guide to pedagogy and practice in second language teaching. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
Carter, R., & Nunan, D. (2001). The Cambridge guide to teaching English to speakers of other languages. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
Cohen, A. (1994). Assessing language ability in the classroom. Boston: Heinle & Heinle Publishers
Davies, A., Brown, A., Elder, C., & et.al. (1999). Studies in language testing 7: Dictionary of language testing. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
Dörnyei, Z. (2007). Research methods in applied linguistics. Oxford: Oxford University Press
Douglas, D. (2010). Understanding language testing. London: Hodder Education
Egan, K. (1999). Speaking: A critical skill and a challenge. CALICO Journal. Federal Language Learning Laboratory
ETS. (2010). User guide: Speaking and writing. Retrieved from https://www.ets.org/s/toeic/pdf/toeic_sw_score_user_guide.pdf&sa=U&ved =0CA4QFjAAahUKEwjEslPhmf3HAhXGVI4KHVHFAeA&usg=AFQjCN ED1jr6NbcFI5DxyAd0MR25EbTdag
ETS. (2012). Examinee handbook: Speaking and writing. Retrieved from https://www.ets.org/Media/Tests/TOEIC/pdf/TOEIC_Speaking_and_Writin g_Examinee_Handbook.pdf&sa=U&ved=0CBIQFjABahUKEwjEsIPhmf3 HAhXGVI4KHVHFAeA&usg=AFQjCNFsr3vxOq85ZfPXu6Qr7gZ7jtnC1 Q
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
Gay, L., Mills, G., & Airasian, P. (2009). Educational research: Competencies for analysis and applications. New Jersey: Merrill
Halliday, M. (2004). An introduction to functional grammar. London: Arnold
Harris, D. (1969). Testing English as a second language. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company
Harmer, J. (2001). The practice of English language teaching. London: Longman
Hatch, E., & Farhady, H. (1982). Research design and statistics for applied linguistics. Rowley: Newbury House Publishers, Inc
Heigham, J., & Croker, R. (2009). Qualitative research in applied linguistics: A practical introduction. London: Palgrave Macmilan
Horrocks, C., & King, N. (2010). Interviews in qualitative research. London: SAGE Publications Inc.
Hughes, A. (2003). Testing for language teachers. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
IELTS. (2012). Guide for teachers. Retrieved from: www.ielts.org
Irianto, A. (2009). Statistik: Konsep dasar dan aplikasinya. Jakarta: Kencana
Kormos, J. (1999). Simulating conversations in oral proficiency assessment: a conversation analysis of role plays and non-scripted interviews in language exams. Language Testing, 16, 163–188.
Kranzler, G., & Moursund, J. (1999). Statistics for the terrified. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Kumar, R. (2014). Research methodology: A step-by-step guide for beginners. London: SAGE
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
Leech, G.& Svartvik, J. (1975). A communicative grammar of English. London: Longman
Louma, S. (2004). Assessing speaking. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
McNamara, T. (2000). Language testing. Oxford: Oxford University Press
Murray, D., & Christison, M. (2011). What English language teachers need to know: Volume II. New York: Routledge
Nation, I.& Newton, J. (2009). Teaching ESL/EFL listening and speaking. New York: Routledge
Oller, J. (1979). Language tests at school: A pragmatic approach. London: Longman
Pikulski, J.,& Templeton, S. (2004). Teaching and developing vocabulary: Key to long-term reading success. USA: Houghton Mifflin Company
Pinter, A. (2006). Teaching young language learners. Oxford: Oxford University Press
Plough, I., Briggs, S., Bonn, S. (2010). A multi-method analysis of evaluation criteria used to assess the speaking proficiency of graduate student instructors. Language Testing, 27, 235–260. doi: 10.1177/0265532209349469
Saville-Troike, M. (2006). Introducing second language acquisition. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
Sugiyono. (2013). Statistika untuk penelitian. Bandung: Alfabeta
Susanti, M. (2010). Statistik deskriptif dan induktif. Yogyakarta: Graha Ilmu
Suskie, L. (2009). Assessing student learning: A common sense guide. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass
Selviani Vidya Lestari, 2015
AN ANALYSIS OF INTERVIEW AS A TECHNIQUE TO ASSESS THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | \.upi.edu perpustakaan.upi.edu
Trew, G. (2010). Tactics for TOEIC®: Speaking and writing tests. Oxford: Oxford University Press