Grammatical Cohesion Used in
Nawal El-
Sadawi’s
Woman at Point Zero
A THESIS
Submitted as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Bachelor Degree of English Department Faculty of Arts and Humanities State Islamic
University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya
By:
Hodairiyah
Reg. Number : A03212006ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF ARTS AND HUMANITIES
ABSTRACT
Hodairiyah. 2016. Grammatical Cohesion Used in Nawal El-Sadawi’s Woman at
Point Zero. Thesis, English Department. Faculty of Arts and Humanities. The State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya.
The Advisor : Dr. A. DzoulMilal, M. Pd.
Key words : Discourse, Grammatical Cohesion, Woman at Point Zero novel.
The researcher uses novel to be object of research. The novel is taken from Nawal El-Saadawi’s Woman at point Zero. This thesis presents the types of grammatical cohesion that is used by Nawal El-Saadawi’s in her novel “Woman at Point Zero”. Furthermore, the researcher has two research problems. Those are what are the types of grammatical cohesion found in Nawal El-Saadawi Woman at Point Zero and what are the functions of grammatical cohesion found in Nawal El-Saadawi Woman at point Zero.
Based on the explanation above, this research focuses on the types of grammatical cohesion used by Nawal El-Saadawi’s novel and the function of types of grammatical cohesion in Nawal El-Saadawi’s novel. The researcher uses the types of grammatical cohesion theory by Halliday (1976) to analyze the types of grammatical cohesion and describes the function of types of grammatical cohesion. To supporting this research of types of grammatical cohesion used in Nawal El-Saadawi’s novel, the researcher uses the qualitative methods to analyze each word, phrase, and sentence in this novel. Then the researcher describes the conclusion from each word, phrase, and sentence. The data is taken from fragment of sentences that contains the types of grammatical cohesion in Nawal El-Saadawi’s novel. The discussion in this analysis includes the types of grammatical cohesion. They are reference, substitution, ellipsis, and conjunction that found in Nawal El-Saadawi’s novel. Then the researcher also describes about the function the types of grammatical cohesion based on Halliday’s theory.
xv
Hodairiyah. 2016. Grammatical Cohesion Used in Nawal El-Sadawi’s Woman at
Point Zero. Thesis, English Department. Faculty of Arts and Humanities. The State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya.
The Advisor : Dr. A. DzoulMilal, M. Pd.
Key words : Discourse, Grammatical Cohesion, Woman at Point Zero novel.
Peneliti menggunakan novel sebagai objek penelitian. Novel tersebut adalah karya dari Nawal El-Saadawi yang berjudul “Woman at point Zero”. Skripsi ini berisi tenang “the types of grammatical cohesion” yang digunakan oleh Nawal El-Saadawi dalam novelnya yang berjudul “Woman at Point Zero”. Penulis mempunyai dua permasalahan penelitian. Permasalahan tersebut yaitu, apa jenis “grammatical cohesion” yang ditemukan dalam novel Nawal El-Saadawi yang berjudul Woman at Point Zero dan apa fungsi dari grammatical cohesion yang ditemukan dalam novel Nawal El-Saadawi yang berjudul Woman at point Zero.
Berdasarkan penjelasan diatas, fokus penelitian ini terletak pada jenis-jenis grammatical cohesion yang digunakan oleh Nawal El-Saadawi’s dalam novelnya serta fungsi dari jenis-jenis of grammatical cohesion dalam novelnya Nawal El-Saadawi. Dalam penelitian ini, penulis menggunakan teori types of grammatical cohesion dari Halliday (1976) untuk menganalisis jenis-jenis grammatical cohesion serta menggambarkan jenis-jenis fungsi grammatical cohesion. Untuk mendukung penelitian ini, peneliti menggunakan metode kualitatif untuk menganalisis kata, frasa, dan kalimat di novel ini. Kemudian penulis menggambarkan dalam bentuk kesimpulan. Data tersebut diambil dari potongan kalimat yang berisi types of grammatical cohesion dalam novelnya Nawal El-Saadawi’s. Pembahasan dalam analisis ini meliputi jenis-jenis grammatical cohesion. Diantaranya adalah reference, substitution, ellipsis, dan conjunction yang ditemukan dalam novelnya Nawal El-Saadawi. Kemudian, peneliti juga menggambarkan fungsi dari jenis grammatical cohesion berdasarkan teori Halliday.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Inside Cover ... i
Inside Title ... ii
Declaration ... iv
Thesis Advisor’s Approval ... v
Thesis Examiner’s Approval ... vi
Motto ... vii
Dedication ... viii
Acknowledgement... ix
Table of Contents ... xi
Abstract ... xiv
Intisari ... xv
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION 1.1. Background of the Study ... 1
1.2. Statement of the Problem... 7
1.3. Objective of the Study ... 8
1.4. Significance of the Study ... 8
1.5. Scope and Limitation ... 9
1.6. Definition of Key Terms ... 10
CHAPTER II: LITERARY REVIEW 2.1. Theoretical Framework ... 11
2.1.1. Cohesion ... 11
2.1.2. Types of Cohesion ... 15
2.1.3. Grammatical Cohesion ... 16
2.1.3.1. Reference ... 18
2.1.3.2. Substitution ... 26
2.1.3.3. Ellipsis ... 31
3.4.1.1. Research Instrument ... 42
3.4.1.2. Data collection techniques ... 42
3.5. Techniques of Analysis Data ... 43
CHAPTER IV: FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION 4.1. Findings ... 44
4.1.1. Reference ... 44
a. Personal Reference ... 44
b. Demonstrative Reference ... 47
c. Definite Article Reference ... 50
d. Comparatives Reference ... 52
4.1.2. The Function of Grammatical Cohesion ... 74
4.2. Discussion ... 75
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION 5.1. Conclusion ... 77
5.2. Suggestions ... 79
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... 80
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
This chapter is going to describe some descriptions of the study which will
be discussed more as the following chapters. They are Background of study,
Statement of the Problem, Objective of the study, Significance of the study, Scope
& Limitation and Definition of the key terms. All of them will be described and
explained as the following below :
1.1 Background of the Study
The development of science and technology which is so fast in this world
that makes language development more widely improve. There are many things
can be provided as well as we want to do. Everything can be done as fast as
possible. All the things cannot be well-developed as now days without some
helping elements, one of them is a language.
Wardhaugh (1977:3) said that language is a system of arbitrary vocal
symbols used by human communication. Kreidler (1998: 19) defined language as
a utility that can be used for creating an interaction and allow us to communicate
with other people in our daily activity wherever we are, such as in public place, an
institution included education or not, tourism object, family, etc. Language is
what particular members of society speaks (Wardhaugh, 2006). Language is also a
system of communication in speech and written by people of a particular country
2
In addition, it can be concluded that language is the communication tool to
communicate. Moreover, language helps people to convey what to tell the other
people. People can express their mind using verbal or nonverbal language and
people are able to produce words to express what they mean (Hurford and
Heasley, 1983:3).
Language as communication tool in the discipline of language studies is
called linguistics; it is the study covering lexical, syntactical patterns, and
discourse level, (Chojimah, 2011:1). Linguistics divided into two kinds, they are:
micro linguistics (phonology, morphology, syntax and semantics), macro
linguistics (Discourse analysis and pragmatics). They are elements of language
that cannot be separated from each other.
This study deals with discourse analysis. Discourse analysis is academic
discipline which studies about how language is used in real condition or situation
and to analyze the discourse. The data of discouse analysis are text and context.
The purpose of the discourse analysis is to get information which has relation with
situation and condition in society. Discourse analysis also has many aspects to
consider. One of the aspects is cohesion which can be defined as interconnection
of some parts (sentence) in text, caused by internal factor.
There are two cohesive devices in the cohesion; grammatical and lexical
cohesive devices. First, grammatical cohesive devices deal with cohesion between
or among sentences because of grammatical factors. The grammatical factors
could be about cohesive devices covering reference (meaning expression which is
3
assumption which the context make the meaning clear), conjunction (a word
which connects word or phrases or clauses), substitution (replacement a word or a
group of word with other word which have same meaning), Hamida (2012: 03).
Second, lexical cohesive devices deal with cohesion between or among sentence
because of lexical choice, lexical cohesive devices covers; repetition (repetition
word or phrases to create cohesive interconnection), synonymy (two or more word
/expression which have similar meaning), hyponymy (word or phrase which have
general-specific meaning relation), metonymy (connection between part and
whole meaning relation), antonymy (word, phrase, expression which have
opposite meaning), Hamidah (2012:03). The importance of studying cohesion,
especially cohesive devices (grammatical and lexical) is to create a good and
systematic text and also to make us easily understand what information is
delivered on it.
From the explanation above, language is thing which cannot be separated
from our daily life, because of language we can interact with other people and
express anything. Language is used not only in direct interaction like in
conversation but also language can be used in direct interaction like in newspaper,
book, prose, poetry, novel and etc. Indirect interaction between the writer and the
reader. the researcher would like to conduct a research concern in grammatical
cohesion used in Nawal El-Saadawi’s Woman at Point Zero. The object that will
be analyzed in this research is novel, becaaause this novel is very important to be
4
of this research is” Grammatical Cohesion Used in Nawal El-Saadawi’s Woman at Point Zero”.
Woman at Point Zero is the popular novel by Nawal El- Saadawi in 1975,
but in 1983 this novel is translated by Sherief Hetata and it is published in
September 15th on 1997. This novel is 108 pages.
The researcher decides to analyze this novel because of some factors. The
first is the researcher likes novel from Arabic and the author is Nawal El-Saadawi
because all of his works is talking about woman. Nawal El-Saadawi , born in the
village of Kafr Tahla, is Egyptian novelists, doctor and militant writer on Arabic
women’ problems and their struggle for liberation. Refusing to accept the
limitations imposed by both religious and colonial oppression on most women of
rural origin, she passed as a doctor in 1955 and become Egypt’s Director of Public
Health. She began to write since 25 years ago, her books focused on women. In
1972, her first work of non-fiction, women and sex, evoked the antagonism of
highly placed political and theological authorities, and the ministry of Health was
pressurized into dismissing her. Under similar pressures she lost her post as Chief
Editor of Health Journal and as Assistant General Secretary in the Medical
Association in Egypt. From 1973 to 1976 she worked on researching women and
neurosis in the Medicine Faculty of Ain Shams University; and from 1979 to 1980
she was the United Nations Advisor for the Women’s Programme in Africa
(ECA) and Middle East (ECWA). Later in 1980, as a culmination of the long war
she had fought for Egyptian women’s social and intellectual freedom – an activity
5
Sadat regime. She has since devoted her time to being a writer, journalist and
worldwide speaker on women issues. (Nawal: 1983: 109)
The second, this novel is the true story and the experience of the writer its
self who told about story of Firdaus’ life as first actress of the novel. The last, this
novel is inspirational story which inspires to the readers. It can be called as the
inspirational story because this novel told about a prostitute who defended herself
by passive attitude to everyone especially men. The passive attitude in this novel
means that the woman did not want to try looking for other ways for her future,
but she stayed by her mind and she receive whatever will be happened. She
received capital punishment as the real of free way. So, this story gave an
inspiration for women do not fall on negative ways. We have to brave to help our
self because now is woman emancipation. This novel also gave knowledge to men
to appreciate and command respect to women although they are prostitute or not.
In other hand, there are some novels which were giving inspiration for human, but
every novel has certain characteristic to give inspiration for some readers. Such as
this novel, this novel is full with intricacies life and physic pressure.
Further, the researcher wants to research this novel Woman at Point Zero
by Nawal El-Saadawi in sub-part of cohesion, especially in grammatical cohesion.
The descriptions of the types of grammatical cohesion are reference, substitution,
ellipsis and conjunction. This novel is from Arabic and translated into English by
Sherief Hetata, the writer is interested to analyze the grammatical cohesion. In
other hand, the novel is easy to understand and there are many grammatical
6
Having been aware of the previous studies is really important to get more
qualified in the research. There are some writers who wrote in the same field. Ulfi
Dina Hamida (2012), Grammatical And Lexical Cohesion in translated text of
Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono’s speech of Jakarta bomb attacks. In her thesis, she
analyzed grammatical and lexical cohesion with qualitative research approach in
content or document analysis method to analyze the speech. And her finding of
grammatical cohesion is conjunction mostly occur in her research and from
lexical cohesion is repetition, hyponymy, metonymy and antonymy.
In addition, Anik Suprianti (2013), The Grammatical Cohesion And Context
Of Situation In The Articles Of Hot English Magazine And Hello Bali Magazine.
She analyzed the types of grammatical cohesion and situational context which is
found in Hot English and Hello Bali, and she used qualitative method. Her result
of the analyzis said that the article of that magazine used 3 context situation types,
they are field, tenor and mood. And found the types of grammatical chesion, they
are referensi, substitusion and conjunction.
. Moreover, Jamilah (2009), Grammatical and Lexical Cohesion of
Jurnalistic Text and Fiction Text. Her thesis about cohesion in jurnalistic and
fiction texts. And she applied descriptive and comparative method. And her
finding is cohesion devices are more dominant in fiction text. Although they have
different intensity in using cohesion devices items, cohesion devices are the
important role in integrating the texts although they occur in the different type of
7
From three previous studies above, the researcher makes conclusion.
There is similarity between my thesis and previous study, it uses discourse
analysis as the study. The differencess of this thesis is the focus on the study, they
use grammatical and lexical cohesion in text but in my thesis only focus on
grammatical cohesion using descriptive qualitative method that is applied in
Novel. Because the data of this research are explained descriptively and
qualitative research so the truth can expressed with some way without number.
In this research, the researcher will analysis text in Nawal El-Saadawi’s Woman at point Zero that consist in grammatical cohesion and will explain detail
one by one of the function based on the types of grammatical cohesion with
Halliday’s theory. The importance of studying grammatical cohesion is to create a
good and systematic text and to understand what information was delivered on it
and it will be supported by other linguists such as Guy Cook, Hoey, etc.
1.2 Research Questions
Based on the background of the research, this study is conducted to answer
the problem formulated in the following question:
a. What are the types of grammatical cohesion found in Nawal
El-Saadawi Woman at Point Zero?
b. What are the functions of grammatical cohesion found in Nawal
8
1.3 Research Objectives
The objectives of study are:
a. To give description of the kinds of grammatical cohesion used in
Nawal El-Saadawi’s Woman at Point Zero.
b. To give description of the function of grammatical cohesion used
in Nawal El-Saadawi’s Woman at Point Zero.
1.4 Significance of the Research
The significance of this research is to enrich the understanding about
cohesion especially in grammatical cohesion through novel as Nawal
El-Saadawi’s Woman at Point Zero., by reading this novel and investigate
grammatical cohesive devices used in the novel. From this research we can
understand and know how cohesion used and applied in the text. To study
grammatical cohesion is very important not only to create a good and systematic
text but also to understand the novel.
Moreover, the writer hopes this study will contribute for:
1. English Department Student
The students can understand and know what is the types of
grammatical cohesion, this study also can improve their skill in English
especially in discourse analysis.
2. Other Researchers
This research can be used as reference for other researcher who try
9
1.5 Scope and Limitation
Scope and limitation is purposed to make a border of this research. So, the
researcher focuses on the important aspect and also deep conclusion for this
research. The scope and limitation include:
a. Novel
There are many novels that can be found by the different titles in
some books. But, the researcher focuses on one titles of novel,
Nawal El-Saadawi’s Woman at Point Zero, this novel is one of novel that discusses about woman, and the researcher is very
interested and loves this novel because it is from Arabic and the
author is Nawal El-Saadawi (Egyptian novelists, doctor and
militant writer on Arab women’s problems and their struggle for
liberation-was born in the village of Kafr Tahla).
b. Grammatical cohesion
Any variety of a language characterized by systematic differences
in pronunciation and vocabulary from other varieties of the same
language, especially in grammar, grammatical cohesion is limited
to investigate in Nawal El-Saadawi’s Woman at Point Zero. Because, the researcher can find the types of grammatical cohesion
which is applied in the novel. It is very important to analyze the
novel to create a good and systematic text and also to make it easy
10
1.6 Definition of the Key Terms
In order to give clear definition and as guidance for the readers to
understand the whole study, the definition of key term are given here.
Cohesion: aptitude connection between one element with other elements
until become good arranged words to be listened and read.
Grammatical cohesion: Cohesion between or among sentence because of
grammatical factors.
Reference : Expression which the meaning referring other word.
Substitution: Replacement a word or a group of word with other word which
have same meaning
Ellipsis: Omission of parts of sentences under the assumption which the
context make the meaning clear.
Conjunction: A word which connects word or phrases or clauses.
Woman at Point Zero: The novel which is written by Nawal El-Sadawi and
CHAPTER II
LITERATURE REVIEW
This chapter reviews several theories related to this research. Those are
definion of cohesions, type of cohesion, definion of grammatical cohesions, types
of grammatical cohesion which consist of four kinds (references, subtitution,
ellipsis, and conjunction), definion of context and related studies to support the
analysis and studies.
2.1. Theoretical Framework
2.1.1. Cohesion
Cohesion is one of the elements of linguistic which has a function to
connect imperfect text become the perfect text, till the reader can understand what
is the mean of the text. In other words, cohesion is regarded as a semantic concept
that refers to relations of meaning that exist within the text (Halliday and Hasan,
1976: 4). Flowerdew and Mahlberg (2009: 103) introduced the notion of the
property of connectedness to refer to Cohesion. Connectedness is the flow of
information and is reflected by the choice of vocabulary words or grammatical
linking words that contribute to textual relations (Flowerdew and Mahlberg, 2009:
106). As Scott and Thompson (2001: 14) stated, cohesion depends on repetition
within the text. Hoey (1991: 4) described cohesive ties that require the reader to
12
the interpretation of some element in the discourse is dependent on that of another
(Halliday and Hasan, 1976: 4).
Stoddard defined cohesion as a mental construct (1991: 20). This
definition implies that cohesion must be interpreted and it requires mental effort
on the part of the reader. In other words, cohesion requires to search for certain
words or grammatical items that help to give meaning and purpose to clauses and
sentences, so that information is distributed in a logical way.
Cohesion is usually interpreted in contrast to coherence. Many scholars
pay attention to the fact that both of terms can be focused easily. And this research
is focused on cohesion. So, it is necessary to give differences between two terms.
Cohesion is one of elements of linguistic which connect between one text and
other text until good form of text and it can be understood by the reader what the
text about. While of coherence, it deals with meaning form of the text, it
correlates or not. But, it does not seem simple to define the unique characteristics
of cohesion and coherence. Both refer to text-forming mechanisms, but it does not
presuppose that they have same meaning or they are synonymous.
Some discourse analysts determined these concepts from context or
linguistic point of view. Thus, cohesion is defined either as an evaluative measure
of texts or as linguistic devices used for putting sentences together (Stoddard,
1991: 13). Halliday and Hasan (1976) in Anastasya Tsareva presented that
cohesion as linguistically determined. So, the description of sentence connectors
13
seems no point in denying that the basic concept of cohesion concentrates on
connections made by grammatical or lexical items, whereas coherence is a mental
phenomenon that refers to the mind of the writer and reader (Thompson, 2004:
179). Other linguists said that it is referring to other scholars, describes cohesion
in contrast to coherence. The first concept is defined as components of the surface
text that are mutually connected and the latter one is described as components of
the textual world that are mutually accessible and relevant (Hoey, 1991: 11).
The concept of cohesion comprises the interfaces between lexis and
grammar, as well as between grammar and text analysis (Scott and Thompson,
2001: 14). The role of cohesive ties in a text is to prompt the perception of
coherence. The concept of coherence can therefore be described from the
reader/hearer’s point of view as the unfolding perception of purpose within a
delimited area of meaning (Scott and Thompson, 2001: 6).
Coherence is not defined in the work of Halliday and Hasan (1976) in
Anastasya Tsareva who have been influential in the discussion of cohesion. They
described the concept of coherence under the term of texture.
The concept of texture is used to express the property of being a text
(Halliday and Hasan, 1976: 2). Cohesion is one part of what is said to be textual.
Various language resources used to express relationship to the environment fulfill
the function of the textual component which characterizes a text (Halliday and
14
Texts are formed by grammatical units; words, clauses, and sentences.
And, the unit link is the parts of a sentence or a clause and they are called to be
structural. “Structure is one means of expressing texture” (Halliday and Hasan,
1976: 7). From this statement, It shows whether a text is well-formed or not. In
contrast, cohesion is not seen as structural relations in the usual sense.
Halliday and Hasan (1976:9) use the term cohesion to refer to
non-structural text-forming relations. They use a special role in creating a text, but
they are not structure. Text-forming relations are properties of a text. They give to
link information within a text. This is achieved through relations in meaning. The
significant property of the cohesive relation is the fact that one item provides the
source for the interpretation of another (Halliday and Hasan, 1976: 19).
From readers’ perception, cohesion seems to be complicated. Many
differences of readers’ interpreted variously. Cohesion can be found and
interpreted across sentence boundaries, but readers who have different processing
abilities may or may be not able to be experienced to understanding of a text.
However, cohesion is important in the description of a text since it gives texture
that functions as a unity with respect to its environment (Halliday and Hasan,
1976: 2). Moreover texture or coherence includes the connection between the text
and the cognitive and experiential environment of the processor (Stoddard, 1991:
19). Flowerdew and Mahlberg (2009: 103) said that cohesion focuses on features
on the textual surface, whereas coherence describes underlying meaning
15
Halliday (1994: 309) said that the main idea of cohesion saying that we
need to establish relationships between sentences and clauses in order to construct
discourse. The number of grammatical items in a sentence determines its length.
However, these grammatical items or the number of sentences in a paragraph or
the whole text are only a characteristic feature of discourse structure, but they do
not determine whether a text is coherent or not. What helps to describe cohesion
in written discourse is the study of semantic resources used for linking across
sentences in order to see how the different parts of a text are connected. What can
be observed within sentences are structures which define the relations among the
parts (Halliday and Hasan, 1976: 10). In terms of cohesion, what can be observed
across sentences in written discourse are not structures but links that have
particular features that are to be interpreted on the part of a reader.
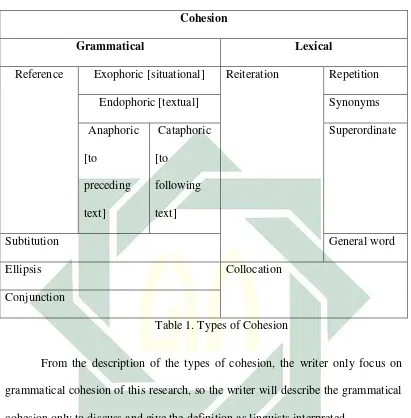
2.1.2 Types of Cohesion
There are two broad divisions of cohesion identified by Halliday and
Hasan (1976:6) grammatical and lexical. Reference, substitution, ellipsis and
conjunction are the various types of grammatical cohesion. Lexical cohesion is
realized through repetition of lexical items, synonyms, super ordinates and general
words. Table 1 (based on Halliday and Hasan, 1976) presented the division of the
16
Cohesion
Grammatical Lexical
Reference Exophoric [situational] Reiteration Repetition
Endophoric [textual] Synonyms
Anaphoric
[to
preceding
text]
Cataphoric
[to
following
text]
Superordinate
Subtitution General word
Ellipsis Collocation
Conjunction
Table 1. Types of Cohesion
From the description of the types of cohesion, the writer only focus on
grammatical cohesion of this research, so the writer will describe the grammatical
cohesion only to discuss and give the definition as linguists interpreted.
2.1.3. Grammatical Cohesion
Grammatical cohesion refers to the linguistic structure. The highest
structural unit in the grammar is the sentence (Halliday and Hasan 1976: 28). The
structure determines the order in which grammatical elements occur and the way
they are related within a sentence. Cohesive relationships with other sentences
17
on it. Various linguistic means to help identifying whether a text can function as a
single meaningful unit or not.
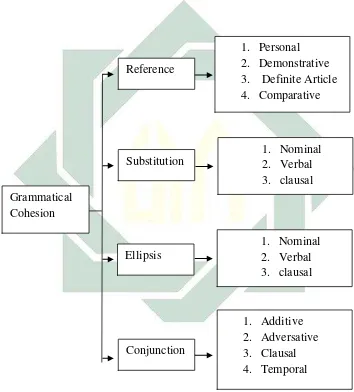
Based on Halliday and Hasan (1976) illustrated the types of grammatical
cohesion that will be discussed further:
Table II. Types of Grammatical Cohesion
The classification is taken from Halliday and Hasan (1976). It is not fully
exemplified. For details see Halliday and Hasan (1976: 333-338). Grammatical
Cohesion
Reference
Substitution
Ellipsis
Conjunction
1. Personal 2. Demonstrative 3. Definite Article 4. Comparative
1. Nominal 2. Verbal 3. clausal
1. Nominal 2. Verbal 3. clausal
18
2.1.3.1. Reference
Reference is one of the kinds of grammatical cohesion, it is linguistic unit
that refers to others linguistic which out run or come after. In other hand, some
linguists said, the principle of reference is based on the exploration of the
lexico-grammatical environment of a text to look elsewhere to get a full picture and to
make complete sense of a word or structure (Halliday and Hasan, 1976: 31).
Referential cohesion plays a special role in creating cohesive ties between the
elements that can be difficult or even impossible to interpret if a single sentence is
taken out of context (Nunan, 1993: 21). Gillian Brown and Yule (1983:204) said,
reference is one in which the relationship of reference is taken to hold between
expressions in a text and entities in the world, and that of reference between
expression in different part of text.
Reference is the specific nature of the information that signed from
retrieval. In this case of reference the information to be retrieved is the referential
meaning, the identity of the particular thing or class of things that is being referred
to; and cohesion lies in the continuity of reference, whereby the same thing enters
into the discourse a second time (Halliday and Hasan, 1976:32).
Based on Halliday and Hassan (1976:31) reference is divided into two
parts, they are; (1) exophoric (situation) and (2) endophoric. Endophoric
Reference is distinguished between two types;
a. Anaphoric : Anaphoric reference points listeners or readers backwards
19
b. Cataphoric : Cataphoric reference looks forward in the text in order to
identify the elements the reference items refer to.
So, that is meant that, anaphoric is the one instructing the hearer and the
readers to look backward and in contrast, cataphoric look to forward. And to make
clear this explanation, see the diagram below;
The kinds of Reference
Reference
Reference of exophoric is interpretation or pointing to word relation puts
on and depends on situational context. Whether the interpretation is on the text its
self, so the relation is called by endophoric reference. Reference of endophoric
anaphoric the unit relation and other between text. This relation refers to
something that is called before. Endophoric cataphoric reference refers to
something that will be mentioned after it. For the example;
… Two eyes to which I clung with all my night
Two eyes that alone seemed to hold me up. To Exophoric
(situation or kontextual)
Endophoric
(textual)
20
this very moment I do not know whether they
were wide or narrow, nor can I recall if they were
surrounded by lashes or not. (p.17)
The word “they” as element of cohesion which indicate to “two eyes” as element of reference and the piece of sentence above is grammatical cohesion that
refers to endophoric reference ( because, the reference is in the text ) and has
anaphoric character (because the reference is called before or previously
mentioned) by using the third person in plural free types.
The kinds of grammatical of references are classified into four types, they
are: (1) Personal reference, (2) Demonstratives reference, (3) Definite article
reference, and (4) Comparatives reference.
(1) Personal Reference
Halliday and Hasan (1976: 37) said that personal reference is
reference by means of function in the speech of situation, through the
category of person. So, personal reference is indication that refers to
someone. All the types of pronoun, well it is singular or plural
pronoun, they are included in personal reference. The pronoun “it” is also included in personal reference.
Based on the grammatical conception, the personal pronoun
can be classified into three parts. They are; (1) speaker: I, We, (2)
listener: You, (3) spoken: He, She, It, They. As semantic conception
21
and Hasan (1976:44) called as speech roles and other roles. Speech
roles is speaker roles: ( I, we), addressee roles : (you). And, other roles
are (he, she, it, they, and one).
Personal reference that form a cohesion is declared in personal
pronoun as head (he/him, she/her, it, they/them), possessive
determiners as deixis (his, her, its, their), and possessive pronouns as
head (his, hers, its, theirs). For example:
1). One of my friends was called Day. She was a doctor.
2). He said these words, but his voice in my ear had a different
tone.
3). He thinks that I didn’t hear him.
In other words, other roles can include in personal reference of
cohesion by note, the word “one” is as exophoric. Speech roles (I, you,
we) deals with situational context, it is on speaker role or reference
roles, although I, you, we are included in exophoric reference. And
speech role can become endophoric reference if it is on quoted speech.
It will be found in narrative text or novel. For example;
“Are you crying, Miss Iqbal?”
Ffrom the data above, it is so clear that this sentence contains
cohesion that is characteristic of endophoric reference especially
included in cataphoric part. It can be seen by the word “you” deals
22
Personal pronoun “It”, it is not only thing or other object but
also “it” can deal with process. As grammatical concept, “It” can deals
with clause, as Halliday and Hassan said that “It” refers to extended
reference, and text reference. (Halliday dan Hasan, 1976: 52). For
example:
The next instant I was following him into
the street, and the door had already closed
behind us. But I continued to turn round
and look back at it for quite a while as if it
was about to swing open again, or as
though I had a feeling of certainty that
someone was standing behind it and
getting ready to push it open at any
moment.
The example above, there are three words “It”, all of them
explain that the word “It” refers to the word “door”.
(2) Demonstrative Reference
Based on Halliday and Hassan (1976:57), Demonstrative
reference is essentially a form of verbal pointing. Demonstrative
reference divided into two groups, they are nominal demonstrative
that consist of (this, these, that, those), adverbial demonstrative (here,
23
Nominal demonstrative reference is to indicate something that
is near or not is (this/these and that/those). “This and that” deal with
time. “This” refers to this time or future time. And the word “that”
refers to time in the past. For example:
“Firdaus, I beg of you. Don’t cry” “Let me cry,” I said
“ But, Ive never seen you cry before. What’s happened?” “ Nothing…. Nothing at all.”
“That’s not possible. Something must have happened.”
“Nothing at all has happened,” I repeated.
Nominal demonstrative reference for singular type is this and
that. This/that can refer to singular or plural thing. These or those
refers to plural thing. As the example above, the underline word “that”
refers to the word “nothing”.
Adverbial demonstrative reference, it is included in “there and
here”. They deals with place that is previous mentioned. And the word
“then and now” are also included in adverbial demonstrative
reference, they deal with the time. For example;
The time had come for me to shed the last grain of
virtue, the last drop of sanctity in my blood. Now I
was aware of the reality, of the truth. Now I knew
what I wanted. Now there was no room for
24
Now I realized that the least delude of all woman
was prostitute. That marriage was the system built
on the most cruel suffering for women.
(3) Definite Article Reference
Definite article “the” is classified together with demonstratives and
possessives. Historically, it is a reduced form of that (Halliday and Hasan,
1976: 58). It serves to identify a particular individual or sub class within
the class designed by the noun; but it does this only through dependence
on something else (Halliday and Hasan, 1976: 71). The definite article
creates a cohesive link between the sentence in which it occurs and the
referential information. It does not contain that information in itself, and it
does not say where the information is located; its only function is to signal
definiteness (Halliday and Hasan, 1976: 74). So, “The” is used as a mark to show that the information necessary for identifying the element is
recoverable.
(4) Comparatives Reference
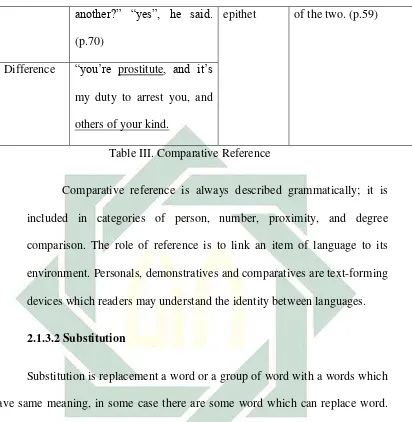
Basically, the comparative is divided into two groups, they are
general comparison and particular comparison. General comparative
declares about similarity and dissimilarity between something that is
compared. General comparative deals with the same thing; same, equal,
identical, identically, or similar things; such, similar, so, similarly,
likewise, and dissimilarity or dissimilar things, can use the word, other,
25
Based on Nunan (1993: 24) Comparative reference is expressed
through adjectives and adverbs and serves to compare items within a text
in terms of identity or similarity”. Halliday and Hasan (1976: 76)
distinguished between the two sub-types of comparative reference: general
and particular. General comparative reference expresses likeness between
things, in the form of identity, similarity and unlikeness or difference.
Halliday dan Hasan (1976: 80) ”particular comparison expresses
comparability between things in respect of a particular property. The
property in question may be a matter of quantity or of quality. It’s meant
that particular reference expresses comparability between things. This is
comparison in respect of quantity or quality. Particular comparison in
terms of quantity is expressed by a comparative quantifier or an adverb of
comparison sub-modifying a quantifier. Particular comparison in terms of
quality is expressed by comparative adjectives or adverbs sub-modifying
an adjective Halliday and Hasan (1976: 76-84).
To make clear, the example is provided in the table in the
following below;
Comparative reference
General Particular
Identity The same shape, the same
colour, in the same
condition.
quantity/
numerative
My husband ate twice as
much food as I did. (p.48)
26
another?” “yes”, he said.
(p.70)
epithet of the two. (p.59)
Difference “you’re prostitute, and it’s
my duty to arrest you, and
others of your kind.
Table III. Comparative Reference
Comparative reference is always described grammatically; it is
included in categories of person, number, proximity, and degree
comparison. The role of reference is to link an item of language to its
environment. Personals, demonstratives and comparatives are text-forming
devices which readers may understand the identity between languages.
2.1.3.2 Substitution
Substitution is replacement a word or a group of word with a words which
have same meaning, in some case there are some word which can replace word.
Halliday (1976:89) described substitution as a sort of counter which is used in a
place of the repetition of the particular item. Halliday (1976:89) said that
substitution is a relation between linguistics item such as word or phrase or a
27
He said;
“Every prostitute has a pimp to protect her
from other pimps, and from the police. That’s what I’m going to do”.
The word “do” in second sentence of conversation replaces the word
“protect”. So, the word “do” substitute the word “protect”.
In other hand, Halliday (1976:31) also distinguishes between substitution
and reference, he said: “By contrast to substitution, which is a grammatical
cohesion, reference is a semantic relation. One of the consequences of this
distinction, as we shall see, is that substitution is subject to a very strong
grammatical condition: the substitution must be of the same grammatical class as
the item for which it substitutes. This restriction does not apply to reference. Since
the relationship is on a semantic level, the reference item is in no way constrained
to match the grammatical class of the item it refers to. What must macth are the
semantic properties”.
From the explanation above the differences between substitution and
reference is, for substitution, something which is substituted must be in same
grammatical class while of reference, the grammatical class can distinguish by
note the meaning which is referred is same.
In English, substitution has a function to replace noun or verb or clause.
28
grammatical relation in the wording. They introduce three types of substitution:
nominal, verbal and clausal.
(1) Nominal substitution
Nominal substitution is one of kinds of substitution. The part which
is substituted is nominal class. Substitute of this substitution is one/ones,
same, and so. (Halliday, 1980: 112)
The function of substitution one/ones as head of a noun phrase and
it will be able to substitute the part to head in noun phrase as Halliday
(1976: 91) said that the substitution one/ones always functioned as head a
nominal group, and can substitute only for an item which it is Head of a
nominal group.
I knew that all of them were cows which are
sold by farmers at varying prices, and that an
expensive cows was better than a cheap one.
From the example above explains that the word “one” always
function as head, and it substitutes the word “cows” that function as a head
in “expensive cows”. And the function of the word “one” is as head in a
phrase “a cheap one”which substitutes the word “cow”.
it is not only “one/ones”, but “so” is also included in nominal
substitution. It is not like substitute “one” that function as head of phrase,
29
He asked in a quiet voice, “Firdaus, do you remember the first time we met?”
“yes”.
“Ever since that day I have been thinking about you.”
“ And I, too, have been thinking about you.” “I have been trying to hide my feelings, but
it’s no longer possible.” “Sohave I.”
For the example above, the function of the word “so” as mentioned
above is as substitution that substitutes all nominal phrase “my feelings.”
(2) Verbal substitution
Nominal substitution is one kinds of substitution. The part which is
substituted is verbal class. The substitutes is “do and do so” (Halliday,
1976:122).
Substitution “do” always function as head of verb phrase, and the
position is always in the end of phrase. Based on Halliday (1980: 112) said
that the verbal substitute in English is “do”. This operates as head of a
verbal group, in the place that is occupied by the lexical verb; and its
position is always final in the group.
Substitution “do so” is always used than substitution “do” if the
30
wherever the focus of information is required to fall on the Head of the
verbal group-the lexical verb its self, as opposed to an auxiliary in the
substitute takes the form do so (1976: 122).
…
“what do you want of me?” I asked
“I want to protect you from other men.” He replied.
“but no one elsebesides you is menacing me.”
“if it isn’t me, it will be someone else. There are pimps running around everywhere. If you
want me to marry you, I’m perfectly willing to
do so.”
“ I don’t see the need for you to marry me as well. It’s enough that you take what I earn. My body at least is mine.”
The function of the word “so” is a substitution. It substitutes the verb phrase “to protect you from other men”.
(3) Clausal substitution
Clausal substitution is the last types of substitution. The function of
clausal substitution to substitute entire clause, it is not only on parts of
elements of clause. The word which is used to substitute is “so and not”.
There are three environments in which clausal substitution take place, they
are; report, condition, and modality. In each environments, there are two
31
substitution “so”, and negative form can be expressed by using substitution
“not” (Halliday and Hassan: 130-131).
2.1.3.3 Ellipsis
Ellipsis is omission of parts of sentences under the assumption which the
context make the meaning clear, in some cases sometime we think that do not
need some replacer to replace the word or phrases because without that phrase or
word we can understood the meaning or mean or phrase or word, and then the
word or phrase which already understood is omitted.
There are some definitions of ellipsis from some linguists. According
Hoey (1983: 110) treats ellipsis as deletion that occurs “when the structure of one
sentence is incomplete and the missing element(s) can be recovered from a
previous sentence unambiguously”. Thompson (2004: 180) defines ellipsis as “the
set of resources by which full repetition of a clause or clause element can be
avoided”. He distinguishes between substitution and ellipsis. That ellipsis omits
the last part of elements in sentence that has same meaning and clear
understanding, and this element occurs with incomplete sentence but it can be
understood, because the incomplete elements in the sentence has covered all of the
elements in sentence from the previous message. For example:
“ Did life teachyou to kill?”
“Of course it did.”
From the example above, it can be understood that the short answer of this
32
because it is the result of omitting of the question “did life teach you to kill?”. “it
did” shows that the answer has covered all the elements of sentence and has clear
meaning. Like the last sentence that just with “I have” answer, all can use ellipsis
theory if the purpose or mind is same.
Fawcett (2000: 190) introduced the definition of ellipsis as recoverability
at the level of form. He also told about co-ordination that occurs when clauses
form a single element of structure. Ellipsis often occurs in co-ordinative clauses
when there are semantic and syntactic similarities between two units (Fawcett
2000: 264), for example;
She could not read or write and know nothing about psychology,
(She could not read or write and she could not know nothing about
psychology)
If see from the differences of both of them, the first sentence is ellipsis
sentence, because it has same point, it is “she could not”. And second sentence,
there is no ellipsis. It’s only to give understanding about ellipsis. This ellipsis is
only omitting subject and auxiliary.
Eggins (2004: 147) said about minor clauses and explores the
connection between clause structure and contextual dimensions. She notes that in
a dialogue there is a correlation between the different structure of an initiating
move and the structure of a responding move (Eggins, 2004: 147). Minor clauses
33
“And have you eaten yet?
“Yes, I have.”
“I have” is a ellipsis. The complete answer of this ellipsis is “yes, I have
eaten yet”. The answer can use ellipsis by omitting all of elements after subject
and auxiliary. Because of ellipsis (I have) has covered all the elements that same
point.
As Halliday (1976:142), there are three types of ellipsis, they are; nominal
ellipsis, verbal ellipsis, and clausal ellipsis.
(1).Nominal Ellipsis
Halliday and Hasan (1976: 148) said that: any nominal group
having the function of head filled by a word that normally functions
within the modifiers is an elliptical one.
It is meant that the omitting is one part in nominal phrase. This
ellipsis is marked by omitting head of nominal phrase. The omitting
head is replaced by a word that has a function as modifier in nominal
phrase. In other words, nominal ellipsis is marked by shift modifier
position to head position in nominal phrase.
(2). Verbal ellipsis
It is omitting a part of element in verbal group. It forms
34
mentioned before. Halliday and Hasan (1976) distinguish two types of
verbal ellipsis: lexical and operator ellipsis.
Lexical ellipsis is omitting verb in verbal group. The element
of verbal group which is ellipted can be begun of right composing part
to left. Although, the exist element is only operator element. This
operator element can come from verbal group which is reference, or it
is new operator, example;
“And have you eaten rice yet?
“Yes, I have.”
And have you eaten rice yet?.-. Yes, I have (eaten rice yet)
(3).Clausal ellipsis
Clausal ellipsis is always used for sentence question that is
only need the answer yes/no. it is marked by the losing all the
sentence that is referenced, for example:
“Do you want to eat?”
“Yes.”
From the example above, it can be mentioned that all the
component of sentence is omitted except “yes”. the component of
sentence that is replaced by the word “yes” is subject, verbal group,
35
2.1.3.4. Conjunction
Conjunction is a word which connecting word or phrases or clauses. But in
our daily life we found conjunction also connecting two or more idea in a
sentence. As Halliday (1976:226) said that conjunction can be classified into four
parts, they consist of additive, adversative, clausal, and temporal.
(1). Additive
The coordination which is put in front of a new sentence is
additive. The conjunction that is included in additive kinds is; and,
and also, or, nor, furthermore, by the way, in other words, thus,
likewise, on the other hand, else, etc. Example:
When I cooked fish I used to give it all to him,
and just take the head or the tail for myself. Or if
it was rabbit I cooked, I gave him the whole
rabbit and nibbled at the head. (p. 48)
(2). Adversative
Adversative is the relation which abstain the perception before.
As according Halliday and Hasan (1976: 250) said that: “The basic
meaning of the adversative relation is ‘contrary of expectation’.” And
the conjunction that is included in adversative is; yet, but, though,
only, however, actually, on the contrary, instead, at least, anyhow, etc.
36
The same touch, the same consistency, the
same naked cold. Yet the cold did not touch me,
did not reach me. (p.7)
(3). Clausal
Clausal conjunction is consisted of; so, therefore, for, because,
in that case, otherwise, under the circumstance, etc. Example:
I could not understand where this girl had
sprung from, nor realize that she could only be
me. For I was always dressed in a long
gallabeya which trailed along the ground, and
no matter where I went it was always barefoot.
(p.20)
(4). Temporal
It explains about correlation that deals with time ordered.
Temporal conjunction is consisted of; then, next, soon, at once, in the
end, meanwhile, just then, etc. Example:
I could hear his bed creak as he lay down,
followed after some time by the sound of his
regular snoring. Then, only, was I assured that
37
2.2. Previous Studies
As the other writers have done in doing the research, having been aware of
the previous studies is really important to get more qualify in research. There are
some writers who writing in same field.
The first is according Ulfi Dina Hamida (2012), “Grammatical And Lexical
Cohesion in translated text of Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono’s speech of Jakarta
bomb attacks”. In her study, the researcher conducts a research with qualitative research approach in content or document analysis method to analyze the speech.
There are two result of study, they are findings of grammatical and lexical
cohesive devices are used in translated text of Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono’s
speech of Jakarta bomb attacks. And her data analysis reveals that grammatical
cohesive devices occurring in translated text of Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono’s speech are conjunction, reference and substitution. In her findings, she also found
grammatical cohesive devices which is often occur and rarely occur in translated
text Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono’s speech of Jakarta bomb attacks, and she rank
or staged from grammatical cohesive devices which frequently occur until
grammatical cohesive devices which is rarely occur. First, the most frequently
occurring cohesive devices is conjunction, in translated text of Susilo Bambang
Yudhoyono’s speech of Jakarta bomb attacks conjunction is grammatical cohesive
devices which often occur. Second is references, in translated text of Susilo
Bambang Yudhoyono’s speech of Jakarta bomb attacks references is grammatical
cohesive devices which frequently occur after conjunction and the last is
38
cohesive devices often occur and rarely occur in translated text of Susilo
Bambang Yudhoyono’s speech of Jakarta bomb attacks. lexical cohesive devices
occurring in translated text of Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono’s speech are
repetition, hyponymy, metonymy and antonymy.
The second is Anik Suprianti (2013), “The Grammatical Cohesion and
Context of Situation in the Articles of Hot English Magazine and Hello Bali
Magazine”. In her thesis, she analyzed the types of grammatical cohesion and
situational context which is found in Hot English and Hello Bali. She also used
the context theory and cohesion as Halliday and Hasan (1985 and 1976). The
method of this thesis is qualitative method. The data analysis that is used by the
writer is, the writer read, understanding, give a mark and write it down as related
to the topic. The result of this analyzis show that the article of this magazine
which is used has 3 context situation types, they are field, tenor and mood. And
found the types of grammatical chesion, they are reference, substitusion, and
conjunction.
And the last is Jamilah (2009), “Grammatical and Lexical Cohesion of
Jurnalistic Text and Fiction Text”. In her thesis, she explained that her thesis is
about cohesion in jurnalistic and fiction texts. The main object of the research is
to know the cohesion devices (grammatical and lexical cohesion) integrate the
sentences in both jurnalist text and fiction text and also she want to know about
the dominant cohesion devices which are used in both texts as distinguish between
them. In her thesis, to analysis her study, she applied descriptive and comparative
39
Halliday and Hasan. She also concluded that the dominant cohesion devices are
more dominant in fiction text. However, although they have different intensity in
using cohesion devices items, cohesion devices are the important role in
integrating the texts although they occur in the different type of the text.
There are three previous studies in my thesis, the first previous study of its
analysis used translated text of speech and the method is qualitative approach.
This study of this previous study focus on grammatical and lexical cohesion in
term of discourse analysis. While of second previous study is The Grammatical
Cohesion And Context Of Situation In The Articles Of Hot English Magazine
And Hello Bali Magazine. The method that is used is qualitative method. This
analysis is studied by using discourse Analysis. And the third is Grammatical and
Lexical Cohesion of Jurnalistic Text and Fiction Text by used the descriptive and
comparative method and it used discourse analysis as its study.
From three previous studies above, the writer can make conclusion. There is
similarity with my thesis. And, it uses discourse analysis as the study. And the
differencess of this thesis is the focus of the study, they use grammatical and
lexical cohesion in text but in my thesis only focus on grammatical cohesion and
function of grammatical cohesion with descriptive qualitative method.
So, in this study, the writer focuses on sentences in Nawal El-Saadawi’s
Woman at point Zero that is included in grammatical cohesion and it will be
described detail one by one the function based on the types of grammatical
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHOD
This chapter discusses the method that the researcher used in this research
including research approach, data source, data research instruments, techniques
of data collection and techniques of data analysis. They will be discussed below :
3.1 Research Approach
Research is any activities to collect the data, analyze it, and presents the
result. It is done in systematic and scientific steps to answer a certain problem.
The kind of research is descriptive qualitative research (Ary, 2006:32). This study
is called descriptive because the data of this study are explained descriptively, the
qualitative research is a research which is analyzed qualitatively, because the truth
can be expressed with some ways without number. Qualitative have some types
based on collecting data, one of them is descriptive qualitative approach in
document or content analysis, this analysis focuses on analyzing grammatical
cohesin and giving explanation in each point of grammatical cohesion that applied
in Nawal El-Saadawi’s Woman at Point Zero. In addition, Creswell (1994:1)
stated that the qualitative research is an inquiring the process of understanding a
social or a human problem based on the building a complex, holistic picture,
formed of the words, reporting the detail view of informants and conducted in a
natural setting. Bogdan and Biklen (1998:77) stated that in qualitative research,
the human investigator is the primary instrument for the gathering and analyzing
41
Therefore, the researcher used descriptive qualitative, because this method
is suitable to analyze grammatical cohesion that applied in Nawal El-Saadawi’s
Woman at Point Zero. In this study, the researcher conducted a research with
descriptive qualitative research in analyzing content of grammatical cohesion that
applied in Nawal El-Saadawi’s Woman at Point Zero. According to the researcher this method also simple and easy to use in some of reasons like in method of data
collecting, data analysis. So the researcher used descriptive qualitative and content
analysis to analyze grammatical cohesion that applied in Nawal El-Saadawi’s Woman at Point Zero.
And the researcher tried to describe every types of grammatical cohesion in
the Novel that is included in; reference, substitution, ellipsis, and conjunction.
And the analysis will be explained clearly in the paragraph form.
3.2 Data Source
The data sources of this research is the novel of Nawal El-Saadawi’s
Woman at Point Zero.
3.3 Data
The data of this research is focused on words, phrases, clauses, sentences
used in the novel that shows reference, substitution, ellipsis, and conjunction that
is included in grammatical cohesion in the novel of Nawal El-Saadawi’s Woman
42
3.4 Data Collections
To collect the data of data sources, there are several ways, the researcher
has done these several ways on this study:
3.4.1 Research Instruments
Based on the early of this chapter, this study uses qualitative
approach, the instrument of this study will be human. So, the main
instrument is I as the reseacher who gathers and analyzes the data. the
supporting instruments are like personal computer to download some sources
of the research, it is to make an easier in analyzing the data of the research.
3.4.2 Data Collection Techniques
To collect the data from the data sources, the researcher has the steps
as follows:
a. First, the researcher downloads a novel, Woman at Point Zero of
Nawal El-Saadawi on computer and it is printed.
b. Second, the researcher reads the novel, Woman at Point Zero of
Nawal El-Saadawi.
c. Third, the researcher identifies, underlines a word, phrase, clause, and
coding some types of grammatical cohesion and function. The type of
grammatical cohesion consists of reference, substitution, ellipsis, and