Adeng Pustikaningsih, M.Si.
Dosen Jurusan Pendidikan Akuntansi
Fakultas Ekonomi
Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta
Operations
Management
Outline
Global Company Profile: Regal Marine
Goods and Services Selection
Product Strategy Options Support Competitive
Advantage
Generation of New Product Opportunities
Product Life Cycles
Life Cycle and Strategy
Product-by-value Analysis
Product Development
Product Development System
Quality Function Deployment (QFD)
Organizing for Product Development
Outline - continued
Issues for Product Design
Robust Design
Modular Design
Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
Value Analysis
Environmentally Friendly Design
Time-Based Competition
Purchase of Technology by Acquiring Firm
Joint Ventures
Outline - continued
Defining the Product
Make-or-buy Decisions
Group Technology
Documents for Production
Service Design
Documents for Service
Application of Decision Trees to Product
Design
Learning Objectives
When you complete this chapter, you should
be able to :
Identify or Define
:
Product life cycle
Product development team
Manufacturabililty and value engineering
Robust design
Time-based competition
Modular design
Computer aided design
Value analysis
Group technology
Learning Objectives
continued
When you complete this chapter, you should be
able to:
Explain
:
Alliances
Concurrent engineering
Product-by-value analysis
Regal Marine
Global market
3-dimensional CAD
reduced product development time
reduced problems with tooling
reduced problems in production
As
Engineering
designed it.
© 1984-1994 T/Maker Co.
As Operations made it.
© 1984-1994 T/Maker Co.
As Marketing
interpreted
it.
© 1984-1994 T/Maker Co.
As
the
customer
wanted it.
© 1984-1994 T/Maker Co.
Need-satisfying offering of an organization
Example
P&G does not sell laundry detergent
P&G sells the benefit of clean clothes
Customers buy satisfaction, not parts
May be a good or a service
Product Strategy Options
Product differentiation
Low cost
Generation of New Product
Opportunities
Economic change
Sociological and demographic change
Technological change
Political/legal change
Changes in
market practice
professional standards
Product
Product
Idea
Package
Physical
Good
Features
Quality
Level
Service
(Warranty)
Brand
(Name)
Product Life Cycle
Introduction
Growth
Product Life Cycle
Introduction
Fine tuning
research
product development
process modification and enhancement
Product Life Cycle
Growth
Product design begins to stabilize
Effective forecasting of capacity becomes
necessary
Adding or enhancing capacity may be
Product Life Cycle
Maturity
Competitors now established
High volume, innovative production may be
needed
Product Life Cycle
Decline
Product Life Cycle, Sales, Cost,
and Profit
S
ale
s,
C
os
t &
P
rof
it
.
Introduction
Growth
Maturity
Decline
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
Position of Firm in Its
Industry
Industry Leader
Top Third
Middle Third
Bottom Third
Products in Various Stages of Life
Cycle
Growth
Decline
Time
Sales
Virtual
Reality
Roller
Blades
Jet Ski
Boeing
727
Introduction
Product-by-Value Analysis
Lists products in descending order of their
individual dollar contribution to the firm.
Helps management evaluate alternative
Product Development Stages
Idea generation
Assessment of firm‟s ability to carry out
Customer Requirements
Functional Specification
Product Specifications
Design Review
Test Market
Introduction to Market
Evaluation
S
cop
e
of
pr
od
uc
t
de
ve
lopm
ent
t
ea
m
Quality Function Deployment
Identify customer wants
Identify how the good/service will satisfy
customer wants
Relate customer wants to product hows
Identify relationships between the firm‟s
hows
Develop importance ratings
Idea Generation Stage
Provides basis for entry into market
Sources of ideas
Market need (60-80%); engineering & operations (20%);
technology; competitors; inventions; employees
Follows from marketing strategy
House of Quality
Customer
Requirements
Product
Characteristics
Customer Requirements Stage
Identifies & positions
key
product benefits
Stated in core benefits proposition (CBP)
Example: Long lasting with more power
(Sears’ Die Hard Battery)
Identifies detailed list of product
attributes desired by customer
Focus groups or
House of Quality
Customer
Requirements
Product
Characteristics
Functional Specification Stage
Defines product in terms of how the
product would meet desired
attributes
Identifies product‟s engineering
characteristics
Example: printer noise (dB)
Prioritizes engineering
characteristics
May rate product compared
Determines how product will be made
Gives product‟s physical specifications
Example: Dimensions, material etc.
Defined by engineering
drawing
Done often on computer
Computer-Aided
Design (CAD)
House of Quality
Product
Characteristics
Quality Function Deployment
Product design process using
cross-functional teams
Marketing, engineering, manufacturing
Translates customer preferences into specific
product characteristics
Involves creating 4 tabular „Matrices‟ or
„Houses‟
To Build House of Quality
Identify customer
wants
Identify
how
the good/service will satisfy
customer wants
.
Relate the customer‟s
wants
to the product‟s
how
s
.
Identify relationships between the firm‟s
how
s
.
Develop importance ratings
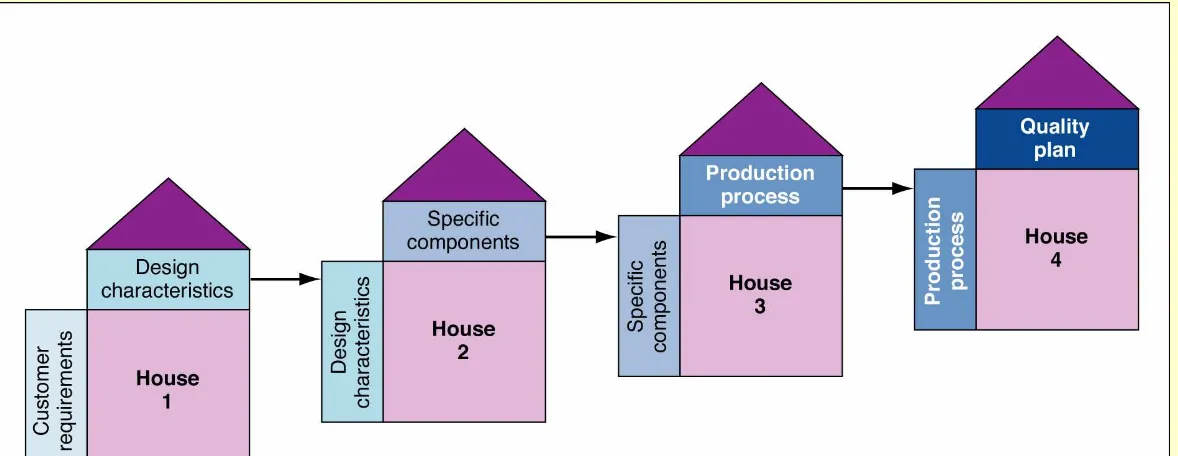
House of Quality Sequence
Design Characteristics Quality Plan Production Process Specific Components D es ig n C ha ra cte ris tics Speci
fic
C
om
po
ne
nts Produ
You‟ve been assigned
temporarily to a QFD team.
The goal of the team is to
develop a new camera
design. Build a House of
Quality.
© 1984-1994 T/Maker Co.
High relationship
Medium relationship
Low Relationship
Customer
Requirements
Importance
Customer
Target Values
House of Quality Example
Customer
Requirements
Importance
Customer
Target Values
Light weight
Easy to use
Reliable
What the customer desires
House of Quality Example
High relationship
Medium relationship
Low Relationship
Customer
Requirements
Importance
Customer
Target Values
House of Quality Example
High relationship
Medium relationship
Low Relationship
Customer
Requirements
Importance
Customer
Target Values
Light weight
Easy to use
Reliable
Aluminum
Parts
Auto
Focus
Auto
Exposure
3
2
1
Relationship between
customer attributes &
engineering characteristics
House of Quality Example
High relationship
Medium relationship
Low Relationship
Customer
Requirements
Importance
Customer
Target Values
Light weight
Easy to use
Reliable
Aluminum
Parts
Auto
Focus
Auto
Exposure
3
2
1
5
1
1
Target values for engineering
characteristics (‘basement’);
key output
House of Quality Example
High relationship
Medium relationship
Low Relationship
Customer
Requirements
Importance
Customer
Target Values
Light weight
Easy to use
Reliable
Aluminum
Parts
Auto
Focus
Auto
Exposure
3
2
1
5
1
1
Manufacturability and
Value Engineering
Benefits:
reduced complexity of products
additional standardization of products
improved functional aspects of product
improved job design and job safety
improved maintainability of the product
Issues for Product Development
Robust design
Time-based competition
Modular design
Computer-aided design
Value analysis
Robust Design
Modular Design
Products designed in easily segmented
components.
Designing products at
a computer terminal or
work station
Design engineer
develops rough
sketch of product
Uses computer to
draw product
Often used with CAM
Shorter design time
Database availability
New capabilities
Example: Focus more on product ideas
Improved product quality
Reduced production costs
Value Analysis
Focuses on design improvement during
production
Environmentally Sound
Strategy
Benefits
Safe and environmentally sound products
Minimum raw material and energy waste
Product differentiation
Environmental liability reduction
Cost effective compliance with environmental
regulations
Environmentally Friendly Design
Make products recyclable
Use recycled materials
Use less harmful ingredients
Use lighter components
Time-based Competition
Product life cycles are becoming shorter.
Engineering drawing
Shows dimensions, tolerances, &
materials
Shows codes for
Group Technology
Bill of Material
Lists components, quantities &
where used
Shows product structure
Monterey Jack
(a)
U.S. grade AA.
Monterey cheese shall conform to the following
requirements:
(1)Flavor.
Is fine and highly pleasing, free from undesirable flavors and
odors. May possess a very slight acid or feed flavor.
(2)Body and texture.
A plug drawn from the cheese shall be reasonably
firm. It shall have numerous small mechanical openings evenly
distributed throughout the plug. It shall not possess sweet holes,
yeast holes, or other gas holes
(3)Color.
Shall have a natural, uniform, bright and attractive
appearance.
(4)Finish and appearance - bandaged and paraffin-dipped.
The rind
shall be sound, firm, and smooth providing a good protection to the
cheese
Code of Federal Regulation, Parts
53 to 109,. Revised as of Jan. 1,
1985, General Service
1-5/8
13/16
3/8
13/16
13/16
diameter
13/32
diameter
1/4 R
1
2-1/2
5/16
2-1/4
45°
Bracket
Scale: FULL
Drawn: J. Thomas
A- 435-038
Bill of Material
P/N:
1000
Name:
Bicycle
P/N
Desc
Qty
Units Level
1001
Handle Bars
1
Each
1
1002
Frame Assy
1
Each
1
1003
Wheels
2
Each
2
1004
Frame
1
Each
2
© 1995 Corel Corp.
Make-or-Buy Decisions
Decide whether or not you want (or need) to
produce an item
May be able to purchase the item as a
Parts grouped into families
Similar, more standardized parts
Uses coding system
Describes processing & physical
characteristics
Part families produced
in manufacturing cells
Mini-assembly lines
112mm
60mm
4mm x 45° chamfer
80mm
Product Code:
1 5 3 1
Part function (round rod)
Material (steel)
Max. length (50 < L < 150)
Primary machine (lathe)
Round Rod
Improved product design
Reduced purchases
Reduced work-in-process inventory
Improved routing & machine loading
Reduced setup & production times
Simplified production planning & control
Simplified maintenance
Production Documents
Assembly Drawings
Assembly chart
Shows exploded view of product
Head
Neck
Handle
End
Cap
1
2
3
SA1
A1
A2
Tuna Fish
Mayonaise
Bread
Tuna
Assy
FG
Sandwich
Route Sheet
Lists all operations
Route Sheet for Bracket
Sequence
Machine
Operation
Setup
Time
Operation
Time/Unit
1
Shear # 3
Shear to
length
5
.030
2
Shear # 3
Shear 45°
corners
8
.050
3
Drill
press
Drill both
holes
15
3.000
4
Brake
press
Work Order
© 1984-1994 T/Maker Co.
Engineering Change Notice (ECN)
A correction or modification of an
Configuration Management
A system by which a product‟s planned and
changing components are accurately
identified and for which control and
Service Design -
Improving Customer Relations at
a Drive-up Window
Be especially discreet when talking with customer through the
microphone
Provide written instructions for customers who must fill out
forms you provide
Mark lines to be completed or attach a note with instructions
Always say ”please” and “thank you”
Establish eye contact with the customer if the distance allows it
If the transaction requires that the customer park the car and
Moment-of-Truth at GTE
Experience Detractors
I had to call more than once to
get through.
A recording spoke to me rather
than a person
While on hold, I get silence,and
wonder if I am disconnected.
The operator sounded like he
was reading a form routine
questions.
The operator sounded
uninterested
I felt the operator rushed me.
Standard Expectations
Only one local number needs to
be dialed
I never get a busy signal
I get a human being to answer
my call quickly and he or she is
pleasant and responsive to my
problem
A timely resolution to my
problem is offered
The operator is able to explain
to me what I can expect to take
place
Experience Enhancers
The operator was
sincerely concerned and
apologetic about my
problem
He asked intelligent
questions that allowed
me to feel confident in
his abilities
The operator offered
various times to have
work done, to suit my
schedule
Application of Decision Trees to
Product Design
Particularly useful when there are a series of
decisions and outcomes which lead to other
decisions and outcomes.
Considerations:
Include all possible alternatives and states of nature -
including “doing nothing”
Enter payoffs at end of branch
Approach determining expected values by “pruning”
Transition to Production
First issue: knowing when to move to
production!
Second: must view product development as
evolutionary, not responsibility of single
individual/department
Third: expect to need a trial production
period to work the bugs out