iii
THE EFFECT OF COOPERATIVE LEARNING TYPE TGT USING CONCEPT MAPS TOWARDS STUDENTS’ LEARNING OUTCOMES ON FLUID
DYNAMICS TOPIC GRADE XI SMA NEGERI 5 BINJAI A.Y. 2012/2013
Debora Betty Sitanggang (Reg. Number 409322015)
ABSTRACT
vi
CONTENT
Page
Validation Sheet i
Biography ii
Abstract iii
Preface iv
Content vi
Figure List x
Table List xi
Appendix xii
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION 1
1.1. Background 1
1.2. Problem Identification 4
1.3. Problem Limitation 4
1.4. Problem Formulation 5
1.5. Research Objective 5
1.6. Research Benefit 5
CHAPTER II LITERATURE REVIEW 6
2.1. Theoretical Framework 6
2.1.1. Learning Definition 6
2.1.2. Learning Activity 7
2.1.3. Learning Outcomes 8
2.1.4. Definition of Learning Model 8
2.1.5. Cooperative Learning Model 9
2.1.5.1. Special Future of Cooperative Learning 11 2.1.5.2. Learner Outcomes for Cooperative Learning 11
vii
2.1.5.4. Theoretical and Empirical Support Cooperative Learning 12
2.1.6. Cooperative Learning Type TGT 13
2.1.7. Direct Instructional Learning Model 15
2.1.7.1. Learner Outcome for Direct Instruction 15
2.1.7.2. Syntax for Direct Instruction 15
2.1.8. Concept Maps 16
2.1.8.1. Definition of Concept Maps 16
2.1.8.2. Characteristic Concept Maps 16
2.1.8.3. Constructing Concept Maps 17
2.1.8.4. Benefit of Concept Maps 18
2.1.9. Fluid Dynamics 18
2.1.9.1. The Equation of Continuity 19
2.1.9.2. Bernoulli’s Equation 20
2.1.9.3. The Application of Bernoulli’s Equation 23
2.2. Literature Review 28
2.3. Conceptual Framework 28
2.4. Research Hypothesis 29
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD 30
3.1. Place and Time of Research 30
3.2. Population and Sample Research 30
3.2.1. Population of Research 30
3.2.2. Sample of Research 30
3.3. Research Variable 30
3.4. Types and Design Research 31
3.5. Research Instrument 31
3.5.1. Content Validity 31
3.5.2. Affective Domain Instrument 32
3.5.3. Psychomotor Domain Instrument 33
3.5.4. Student’s Activity Instrument 34
viii
3.7. Data Analysis Techniques 38
3.7.1. Determine Mean 38
3.7.2. Determine Deviation Standard 38
3.7.3. Determine Variance 38
3.7.4. Normality Test 39
3.7.5. Homogeneity Test 39
3.7.6. Hypothesis Test 40
CHAPTER IV Research Result and Discussion 43
4.1 Result of Research 43
4.1.1. Pretest Data of Experimental and Control Class 43 4.1.2. Post-test Data of Experimental and Control Class 44
4.2. Data Analysis 45
4.2.1. Normality Test 45
4.2.1.1. Normality Test of Pre-Test Data 45
4.2.1.2 Normality Test of Post-test Data 45
4.2.2. Homogeneity Test (Homogeneity Test) 46
4.2.3. Hypothesis Testing 46
4.2.4. Observation 50
4.3. Discussion 51
CHAPTER V Conclusion and Suggestion
5.1. Conclusion 57
5.2. Suggestion 58
x
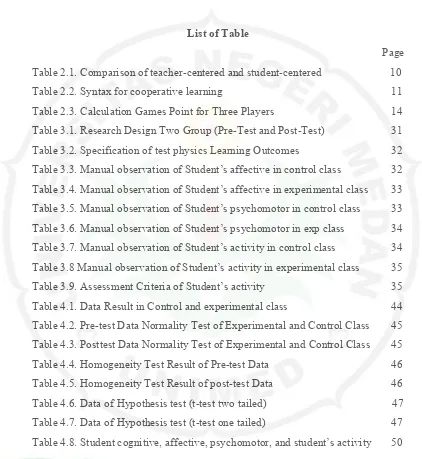
List of Table
[image:6.612.101.523.80.539.2]Page Table 2.1. Comparison of teacher-centered and student-centered 10
Table 2.2. Syntax for cooperative learning 11
xi
List of Appendix
Page
Appendix 1 Lesson Plan 61
Appendix 2 Student Worksheet I 81
Appendix 3 Student Worksheet II 82
Appendix 4 Specification Table Of Learning Outcomes Student Test 83
Appendix 5 Instrument Assessment 93
Appendix 6 Descriptor of Observation of Student’s Affective 97
Appendix 7 Descriptor of Observation of Student’s Psychomotor 99
Appendix 8 Descriptor of Observation of Student’s Activity 101
Appendix 9 Pretest Result 103
Appendix 10 Posttest Result 105
Appendix 11 Table Pre-test and Post-test of Experimental Class 107
Appendix 12 Calculation of Mean Value and Standard
Deviation of Pretest and Posttest 109
Appendix 13 Normality Test of Data 111
Appendix 14 Homogenity Test of Pre-test Data 113
Appendix 15 Hypothesis Testing 115
Appendix 16 Affective Assesment of Control Class 117
Appendix 17 Psychomotor Assesment of Control Class 129
Appendix 18 Activity Assesment of Control Class 141
Appendix 19 List of Critical Value for Liliefors 153
Appendix 20 Daftar NiIai Persentil Untuk Distribusi t 154
Appendix 21 Tabel Wilayah Luas di Bawah Kurva Normal 0 ke z 155
Appendix 22 Daftar Nilal Persentil Untuk Distribusi F 156
[image:7.612.89.542.85.659.2]1
CHAPTER I
INTRDUCTION
1.1 Background
The level of prosperity of a nation is not just determined by the abundance of natural resources available, but it takes a human resources qualified so that they can manage those resources properly and to maintain the balance of the ecosystem that are around. Education has a significant role in the process of improving the quality of human resources. In fact the state of human resources that is less competitive because of the quality of our education is still relatively low. Therefore, education should be a very important concern by various stakeholders, especially the teachers and all those involved in the implementation of teaching and learning activities in order to produce a generation of intelligent and qualified in the future.
The Official rationales for formal education state that Education: gives people more and better life career opportunities
helps people make therapeutic use of their leisure time
develops peoples’ knowledge and understanding of themselves and the world
encourages people to work together in a spirit of tolerance and mutual kindness
produces more fulfilled, ’rounded’, law-abiding people gives youngsters a broader perspective on life and the world
2
In other words, education is seen as the path to human ethos and ethics, even the main clan towards the perfection of life. (Sinamo, 2010)
The quality of education in Indonesia at now very concern. It proved that Indonesia's human development index decline. The quality of education in Indonesia was ranked 12th out of 12 countries in Asia. Indonesia has a low competitiveness, and still according to a survey by the same institution predicated Indonesia as a follower and not just as a technology leader of the 53 countries in the world. (Ganis, 2010).
In an effort to improve the quality of education, the teaching and learning activities has to be planned and executed in such a way optimally. Implementation of the learning activity encompass teachers, students, the learning environment and learning model used become one unit. The relationship between teachers and students when the learning process takes place should occur in both directions, not just centered on the teacher, but the student should also be actively involved, so that students are able to construct their own knowledge, teachers act more as a facilitator, motivator and mediator.
Education must be transformed from the passive, technical, and apolitical orientation that is reflective of most students' school-based experiences to an active, critical, and politicized life-long endeavor that transcends (the boundaries of classrooms and schools).
3
Experienced researchers when implementing the Integrated Field Experience Program (IFEP) many students who say that physics is a difficult subject to understand because teachers often use conventional learning models and less actively engage students during the teaching and learning activities as such activities and interactions of students are less well thus causing saturation students during teaching takes place, students can only count but do not understand the concept of real physics and lead to results that are less optimal learning outcomes.
Based on preliminary studies conducted in SMA Negeri 5 Binjai by distributing questionnaires to 22 students, 54.54% said that physics lessons is ordinary, as 40.90% students like physics and 4.54% students stated that they do not like physics. The results of the interviews conducted for teachers of Physics SMA Negeri 5 Binjai obtained information that the physical value of the average of all students in grade XI, as much as 50% of students have not reached the KKM. This is due to the learning of teachers just use the conventional model of learning, where learning is a sequence of conventional lectures, discussion and assignment. The cooperative learning model requires student cooperation and interdependence in its task, goal, and reward structures (Arends, 2012).
In science education in recent years, the increasing awareness of the
importance of learner-centre in the teaching–learning situation has generated a lot
of attention in relation to understanding how learners learn and how to help them
learn about concepts. Concept mapping serves as a strategy to help learners
organize their cognitive frameworks into more powerful integrated patterns. The
hierarchical attribute of a concept map also makes meaningful learning proceed
more easily as new concepts or concept meanings are subsumed under broader,
more inclusive concepts.
4
is 65.13 (on a scale of 10-100), then (Nasution, 2011) her research showed that t-test tcount > ttable (3.70 > 1.67), which mean that Ha is received and students’
activity in experimental class is appropriate with post-test. Also (Batubara, 2011) obtained the average value of student learning outcomes after implementing the cooperative learning type TGT in experiment class is 67.13 which in control class is 60.13. The weakness of they studies did not using concept maps.
Based on the above description of the problem, the authors is interested in doing research entitled: "The Effect of Cooperative Learning Type TGT using Concept Maps towards Students’ Learning Outcomes on Fluid Dynamics
Topic Grade XI SMA Negeri 5 Binjai A.Y 2012/2013".
1.2 Problem Identification
Based on the background of the issues outlined above, it can identify issues relevant to this study are
1. Students think physics is a difficult subject and less attractive.
2. The results of studying physics under the low minimum completeness criteria.
3. Learning that is dominated by the teacher (teacher-center).
1.3 Problems Limitation
Implemented research that can be optimized, then the scope of the material covered is limited,
1. Using Cooperative learning model type TGT using concept maps.
2. Subjects in this study were students grade XI semester SMA Negeri 5 Binjai Academic Year 2012/2013.
5
1.4 Problems Formulation
Based on the background of the problem and the extent of the problem above, the research questions in this study were:
1. How about student’s learning outcome of physics which use Cooperative Learning Type TGT using Concept Maps on Fluid Dynamic's Topic Grade XI Semester II SMA Negeri 5 Binjai.
2. How about student’s learning outcome of physics which use Direct Instruction Learning Models on Fluid Dynamic's Topic Grade XI Semester II SMA Negeri 5 Binjai.
3. Are the different caused the effect of Cooperative Learning Type TGT using Concept Maps towards learning outcome on Fluid Dynamic's Topic Grade XI Semester II SMA Negeri 5 Binjai.
1.5 Research Objectives
Base on the problems formulation, the objectives in this research were to: 1. Knowing the effect of Cooperative learning type TGT using concept maps
to the student’s learning outcomes on fluid dynamics topic.
2. Knowing the effect of Direct Instruction Learning Models to student’s learning outcomes on fluid dynamics topic.
3. Knowing the different caused effect of Cooperative Learning Type TGT using Concept Maps towards learning outcome on Fluid Dynamic's Topic Grade XI Semester II SMA Negeri 5 Binjai.
1.6 Research Benefits
The expected benefits of this research are
1. As information matter that student learning outcomes are effect by cooperative learning type TGT using concept maps.
57
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
5.1. Conclusion
Conclusion of this research based on data of research result, data analysis,
and discussion so can conclude that:
1. Student’s learning outcome of physics which use Cooperative Learning
Type TGT using Concept Maps on Fluid Dynamic's Topic Grade XI SMAN
5 Binjai AY. 2012/2013 before given treatment average of pretest as 38.33
and after given treatment is 75.63.
2. Student’s learning outcome of physics which use Direct Instruction Learning
Models on Fluid Dynamic's Topic Grade XI SMAN 5 Binjai AY. 2012/2013
before given treatment average of pretest is 37.4 and after given treatment is
65.4.
3. There are different caused the effect of Cooperative Learning Type TGT
using Concept Maps towards learning outcome on Fluid Dynamic's Topic
Grade XI SMAN 5 Binjai AY.2012/2013 with tcount > ttable= 3.263 > 2.013
at significant level ߙ= 0.05.
5.2. Suggestion
Based on research result and discussion before, researcher give suggestions as
follows:
1. To the next researcher who want to do research about cooperative learning
type TGT suggested more direct, or guide student to be more active while
work in group by ask to every student in group about what student already
do in group so student will be motivate to be active in solving group
58
2. To the next researcher suggested before start teaching learning process,
firstly should be explained to student how the implementation of
cooperative learning type TGT using concept maps, so at teaching learning
process is occur student already know what will do.
3. To the next researcher who will to do research about cooperative learning
ii
BIOGRAPHY
Debora Betty Sitanggang, was born in Medan on April 1st 1992. Father
named KR. Sitanggang, S.Sos and mother named Dra. ID. Sitorus, and she is the
first of three children. In 1997, the authors entered SD-2 HKBP Sidorame Medan.
In 1998, the authors moved to SD Negeri No. 95/95 Binjai and graduated in 2003.
In 2003, the authors continue her education in SMP Negeri 1 Binjai and graduated
in 2006. In 2006, the authors continue her education to SMA Negeri 3 Binjai and
graduated in 2009. In 2009, the author accepted in Physics Education Studies
Program in Department of Physics, Faculty of Mathematics and Science in State
59
REFERENCES
Arends, R. I., (2012), Learning How to Learn, 9th edition, Mc Graw-Hill, United State.
Batubara, M., (2011), Pengaruh Model Pembelajaran Kooperatif Tipe TGT (Teams Games Tournament) Terhadap Hasil Belajar Siswa Pada Materi Pokok Zat dan Wujudnya di kelas VII Semsester I SMPN 2 Medan T.P.
2010/2011., Skripsi, FMIPA, Unimed, Medan
Butar-Butar., (2011), Pengaruh Model Pembelajaran Kooperatif Tipe TGT (Teams Games Tournament) Terhadap Hasil Belajar Siswa Pada Pokok Bahasan Kinematika Gerak Lurus Semester I SMA Swasta Raksana
Medan X T.P. 2010/2011., Skripsi, FMIPA, Unimed, Medan.
Cohen, E. G., Brody, M.C., & Shevin, M.S., (2004), Teaching cooperative
learning: The Challenge For Teacher Education, State University of New
York Press, Albany, State University of New York.
Dahar, R. W., (1989), Teori-teori Belajar, Erlangga, Jakarta.
Djamarah, B.S., & Zain, A., (2006), Strategi Belajar Mengajar, Rhineka Cipta, Jakarta.
Ganis., (2010), Masalah Pendidikan di Indonesia,
http://ganis.student.umm.ac.id/2010/01/26/mahalnya-biaya-sekulah-di-masa-sekarang/(Accessed February 10th2013)
Hamalik, O., (2009), Kurikulum dan Pembelajaran, Bumi Aksara, Jakarta
Hodson, D., (1998), Teaching and Learning Science Towards a personalized
approach, Open University Press, Buckingham.
Joyce, B., (2003), Models of Teaching, Fifth Edition, Prentice-Hall of India, New Delhi.
Mintezes, J. J., Wandersee, J.H., & Novak D.J., (2005), Teaching Science for Understanding A Human Constructivist View, Elsevier Academic Press, United States of America.
Moore, A., (2000), Teaching and Learning: Pedagogy, Curriculum and Culture.
Rout ledge Falmer, London.
Moseley, D., Baumfield, V., Elliot, J., & Gregson, M., (2005), Frameworks for Thinking A Handbook for Teaching and Learning, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Nasution, F., (2011), Pengaruh Model Pembelajaran Kooperatif Tipe TGT
Terhadap Hasil Belajar Siswa Pada Materi Pokok Suhu dan
Pengukurannya di kelas VII Semester II MTS N 2 Medan T.P. 2010/2011.,
Skripsi, FMIPA, Unimed, Medan
Ollington, G. F., (2008), Teachers and Teaching Strategies, Innovations and
60
Purwoko, F., (2009), Bilingual Physics 2 for Senior High School Year XI, Yudhistira, Jakarta.
Rosyid., and Friends., (2008), Kajan Konsep Fisika 2 untuk Kelas XI SMA dan MA Tiga Serangkai Pustaka Mandiri, Solo.
Sanjaya,W., (2008), Strategi Pembelajaran Berorientasi Standart Proses Pendidikan, Kencana, Jakarta.
Schiering, M. S., Bogner, D., & Holmberg, J.B., (2011), Teaching and learning: a model for academic and social cognition, Rowman & Littlefield Education, United States of America.
Sinamo, J., (2010), 8 Etos Keguruan, Institut Darma Mahardika, Jakarta.
Slavin, E., R., (2005), Cooperative Learning, Nusa Media, Bandung.