THE STUDENTS’ PERCEPTIONS ON THE USE OF
THE GROUP PRESENTATION TECHNIQUE IN
LANGUAGE TEACHING METHODOLOGY COURSE
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By:
Arshinta Widya Hanani
Student Number: 021214072
English Language Education Study Program
Department of Language and Arts Education
Faculty of Teachers Training and Education
Sanata Dharma University
Yogyakarta
2007
“…Nothing seems real I’m starting to feel Lost in the haze of a dream
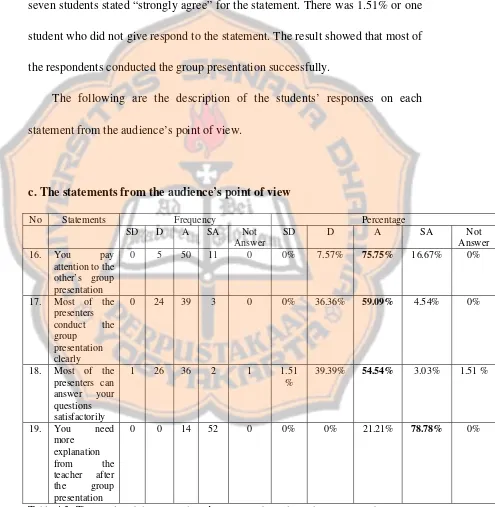
And as I draw near The scene becomes clear Like watching my life on a screen…”
Regression (Dream Theater)
“…I may never find all the answers I may never understand why
I may never prove What I know to be true
But I know that I still have to try…” The Spirit Carries on
(Dream Theater)
“…This feeling inside me Finally found my life, I’m finally free
No longer torn in two
Living my own life by learning from you We’ll meet again my friend someday soon…”
Finally Free (Dream Theater)
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, I would like to express my deepest gratitude to my Lord, Jesus
Christ for His guidance and blessings so I could accomplish this thesis.
I would like to address my deep gratitude to my sponsor, Ag. Hardi
Prasetyo, S.Pd., M.A. I thank him for his great patience, support (‘move on, be
brave’), and guidance so I could accomplish this thesis. I also thank him for
permitting me to do this research in his class. I really appreciate all his great
efforts to check my thesis.
I would also like to thank Laurentia Sumarnie, S.Pd for her advice and
support (“things are beautiful in its time”), so I feel confident to continue the
collaborative research. Without her advice I believe I could not finish this thesis.
I dedicate this thesis to Mom and Dad, who have given me their love,
care, and prayer in finishing this thesis. This thesis is also dedicated to my sister,
Nita, and my brothers, Rindra, Andhi, and Radit.
I would also like to thank the following people: my classmates of PBI
2002 Class B (Rinos, Ajeng, Uyak, Santi, Woro, Lisa, Rumi, Daru, and Gede). I
thank them for their support and for being good friends. Finally, I thank the
people whom I could not mention here.
Arshinta Widya Hanani
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE ... i
PAGE OF APPROVAL ... ii
BOARD OF EXAMINERS ... iii
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ... iv
DEDICATION PAGE ... v
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... vi
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... vii
LIST OF TABLES ... x
ABSTRACT ... xi
ABSTRAK ... xii
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION A. BACKGROUND ... 1
B. PROBLEM LIMITATION ... 3
C. PROBLEM FORMULATION ... 4
D. RESEARCH OBJECTIVES ... 5
E. RESEARCH BENEFITS ... 5
F. DEFINITION OF TERMS ... 7
CHAPTER II: THEORETICAL REVIEW A. THEORETICAL DISCUSSION ... 9
1. Presentation ... 9
a. Definition of Presentation ... 10
b. Characteristics of Presentation ... 11
2. Perception ... 15
a. Definitions of Perception ... 16
b. Perceptual Process ... 17
c. Factors Influencing Perception ... 19
3. Cooperative Learning ... 24
a. Definition of Cooperative Learning ... 24
b. Characteristics of Cooperative Learning ... 25
c. Benefits of Cooperative Learning ... 28
4. Constructivism ... 29
a. Characteristics of Constructivism ... 29
b. Principles of Constructivism ... 31
5. The Nature of Language Teaching Methodology ... 32
B. THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK ... 32
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY A. RESEARCH METHOD ... 35
B. RESEARCH PARTICIPANTS ... 35
C. RESEARCH INSTRUMENTS ... 36
D. DATA GATHERING ... 39
E. DATA ANALYSIS ... 39
CHAPTER IV: DATA ANALYSIS A. The Implementation of Group Presentation Technique in Language Teaching Methodology Course ... 41
1. Data Presentation and Analysis ... 41
2. Discussion ... 46
B. The Students’ Perceptions on the Group Presentation Technique Used in Language Teaching Methodology Course ... 47
1. Data Presentation and Analysis ... 48
2. Discussion ... 58
C. Some Possible Suggestions that can be Drawn for the Improvement of Group Presentation Technique in Language Teaching Methodology Course ... 59
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS A. CONCLUSIONS ... 62
B. SUGGESTIONS ... 64
1. For Students of English Language Education Study Program ... 64
2. For Lecturers of English Language Education Study Program ... 65
3. For Other Researchers ... 66
REFERENCES ... 67
APPENDICES ... 69
Appendix 1 : The raw data of the observations ... 70
Appendix 2 : The questionnaires result ... 87
Appendix 3 : The interview result with the lecturer of Language Teaching Methodology course ... 106
Appendix 4 : The interview result with the students ... 108
Appendix 5 : The observation sheet ... 119
Appendix 6 : The questionnaire ... 122
Appendix 7 : The interview questions ... 125
LIST OF TABLES
Table 4.1: The result of the respondents’ responses both as the
presenters and the audiences ... 48
Table 4.2: The results of the respondents’ responses from the
presenter’s point of view ... 52
Table 4.3: The results of the respondents’ responses from the
audience’s point of view ... 56
ABSTRACT
Hanani, A.W. (2007). The Students’ Perceptions on the Use of the Group Presentation Technique in Language Teaching Methodology Course. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
This study investigates the students’ perceptions on the use of the group presentation technique in Language Teaching Methodology courses. There are three problems formulated in the problem formulation: (1) How is the implementation of group presentation technique in Language Teaching Methodology course? (2) What are students’ perceptions on the group presentation technique used in Language Teaching Methodology course? (3) What are some possible suggestions that can be drawn from the students’ perceptions on the group presentation technique to improve its implementation?
In order to help the writer to answer those problems, some theories are employed. First are the definition of presentation and characteristics of an effective presentation. Second are the definition of perception, the perceptual process, and the factors influencing perception. Third are the definition, the characteristics, and the benefits of cooperative learning. Fourth is the characteristics and principles of constructivism. Fifth is the nature of Language Teaching Methodology course.
In order to answer those problems, the writer employed a survey research. The survey was done by gathering the empirical data through observing the classes, distributing questionnaires, and interviewing the lecturer and the students from class B and D of Language Teaching Methodology course.
The findings of this study showed that the implementation of group presentation technique in Language Teaching Methodology course already fulfilled most of the characteristics of a good presentation, although there were some characteristics of a good presentation that had not been implemented by the presenters. Most of the students in class B and D have positive responses on the technique. However, there are some problems in implementing the group presentation technique. There are some possible suggestions derived from the respondents in order to improve the implementation of group presentation technique. Those are for group dynamics, facilities, and the presentation technique.
There are some suggestions that can be proposed by the writer. The suggestions are for the students of English Language Education Study Program, the lecturers of English Language Education Study Program, and for the other researchers who would like to conduct further research.
ABSTRAK
Hanani, A.W. (2007). The Students’ Perceptions on the Use of the Group Presentation Technique in Language Teaching Methodology Course. Yogyakarta: Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Keguruan dan Ilmu Pendidikan, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui persepsi mahasiswa mengenai penggunaan presentasi dalam kelompok dalam mata kuliah Language Teaching Methodology. Ada tiga masalah yang dirumuskan dalam perumusan masalah: (1) Bagaimana penggunaan teknik presentasi kelompok dalam mata kuliah Language Teaching Methodology? (2) Bagaimana persepsi siswa-siswa terhadap penggunaan teknik presentasi kelompok dalam mata kuliah Language Teaching Methodology? (3) Saran-saran apa saja yang bisa disampaikan setelah mengetahui persepsi siswa-siswa terhadap penggunaan teknik presentasi kelompok untuk meningkatkan mutu teknik presentasi kelompok di kelas Language Teaching Methodology?
Untuk membantu menjawab masalah-masalah tersebut, penulis mencantumkan beberapa teori. Teori pertama tentang arti presentasi dan karakteristik dari teknik presentasi yang efektif. Teori kedua tentang arti persepsi, proses terbentuknya persepsi, dan faktor-faktor yang mempengaruhi perspsi seseorang. Teori ketiga tentang definisi, karakteristik, dan manfaat cooperative learning. Teori keempat tentang karakteristik constructivism. Teori kelima tentang arti Language Teaching Methodology.
Untuk menjawab masalah-masalah tersebut, penelitian ini menggunakan metode survey. Survei dilakukan dengan mengumpulkan data yang diperoleh dari observasi kelas, pembagian kuesioner, serta wawancara dengan dosen serta mahasiswa-mahasiswa dari kelas B dan D dalam mata kuliah Language Teaching Methodology.
Hasil penelitian ini menunjukkan bahwa penggunaan teknik presentasi kelompok sudah memenuhi sebagian besar dari kriteria suatu presentasi yang efektif, meskipun masih ditemui beberapa karakteristik dari presentasi yang efektif yang belum digunakan. Murid-murid di kelas B dan D memiliki persepsi yang positif terhadap penggunaan teknik presentasi kelompok. Akan tetapi, masih terdapat beberapa hambatan dalam penggunaan teknik presentasi kelompok. Ada beberapa saran dari para siswa untuk meningkatkan mutu teknik presentasi kelompok, yaitu dinamika kelompok, fasilitas, dan teknik presentasi.
Terdapat beberapa saran yang dapat diberikan oleh penulis. Saran-saran tersebut ditujukan kepada para mahasiswa Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, dosen-dosen Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, serta untuk peneliti yang ingin melaksanakan penelitian lebih lanjut.
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This study investigates the students’ perceptions on the implementation of
group presentation technique in Language Teaching Methodology course. This
chapter presents background of the study, problem limitation, problem
formulation, objectives of the study, benefits of the study, and definition of terms.
A. BACKGROUND
Traditionally, teaching-learning process is teacher-centered (English
Teaching Forum 1991: 31). It means that teacher is the only person who has to
explain the material. In other words, the students’ understanding on the material
depends solely on the teacher explanation. The students will only become
listeners. The students are also lack of interactions between the other students.
Nowadays, most lecturers apply teaching-learning technique which
emphasizes on increasing students’ autonomy. It means that the students are
required to become self-reliant learners and be more responsible for their own
learning. Besides, the students are also expected to be more cooperative with their
friends. In other words, most lecturers nowadays apply teaching-learning
techniques which emphasize not only the academic achievement, but also how
the students are able to cooperate with one another to achieve certain purpose.
One of the teaching-learning techniques that can be used to increase the
students’ interactions between the other students and the students’ autonomy in
learning is group presentation technique. Group presentation is defined as a
presentation conducted by a group which presents a method in language teaching
and then simulates the method. It is applied in Language Teaching Methodology
(KPE 264) courses, one of the compulsory courses taught in English Language
Education Study Program in Sanata Dharma University. This course aims to
equip the students with knowledge of well-established language teaching
approaches and methods and be able to apply the knowledge (Panduan
Akademik, 2002).
Group presentation technique used in the Language Teaching Methodology
course is expected to help the students become independent learners. Based on
the result of an interview, one of the lecturers of Language Teaching
Methodology course in Sanata Dharma University Yogyakarta has two
motivations in applying group presentation technique. First is that group
presentation technique can develop the students’ speaking skill. Students of
English Language Education Study Program are trained to be teachers. Group
presentation is aimed to train their speaking skill since as teachers, they have to
be able to explain things clearly and through presentation they can exercise their
explaining skills. The second motivation is that through group presentation, the
students can develop their social skill. Social skill in this study refers to how the
students help one another to understand the lesson and how the students learn to
respect others’ opinion. The students are also expected to be autonomous
learners. It means that the students’ understanding does not depend solely on the
teacher’s explanation. Moreover, group presentation can increase the students’
leadership skill and be responsible for their friends’ understanding of the lesson.
However, the students might perceive the use of group presentation
will train them to be self – reliant learners. However, some of them might find
that they could not master the material well because the presenters (their own
friends) could not explain the topic well.
Altman, Valenzi, and Hodgetts (1985: 86) state that need is one of the
important factors which can affect someone to have perception towards
something. The students as the samples on this study may need to know the
knowledge of Language Teaching Methodology. Some other students need the
group presentation technique only for fulfilling the lecturer’s requirements. The
different situation may lead the students to have different perceptions. Altman et
al (1985: 80) state that motivation also affect someone in having his/her
perception. In this study, the students might be motivated to learn the methods of
language teaching because the students have positive perceptions on the
implementation of group presentation technique. The students’ motivation in
learning the methods of language teaching will affect the students’ achievement.
This study is then aimed to find out how the implementation of group
presentation technique used in the Language Teaching Methodology course is, to
reveal and dig out the students’ perceptions on group presentations technique
used in Language Teaching Methodology class, and to present suggestions which
can contribute to the improvement of the implementation of group presentation
technique in English Language Education Study Program Sanata Dharma
University.
B. PROBLEM LIMITATION
The use of group presentation technique in Language Teaching
technique since the use of group presentation gives various experiences to the
students. This research will be focused on three things, namely the
implementation of group presentation in Language Teaching Methodology class,
the students’ perceptions on group presentation used in Language Teaching
Methodology class, and finding out and presenting some suggestions for the
improvement of the implementation of group presentation technique in English
Language Education Study Program Sanata Dharma University.
The researcher chose the Language Teaching Methodology course because
this course uses group presentation technique. Group presentation is a
presentation conducted by a group which presents the theoretical review of a
method in language teaching and then simulates the method discussed in the
course references (Course Guidelines for presentation in Language Teaching
Methodology course).
C. PROBLEM FORMULATION
From the problem limitation, the problems can be formulated as follows:
1. How is the implementation of group presentation technique in Language
Teaching Methodology course?
2. What are students’ perceptions on the group presentation technique used in
Language Teaching Methodology course?
3. What are some possible suggestions that can be drawn from the students’
perceptions on the group presentation technique to improve its
D. RESEARCH OBJECTIVES
The objectives of this research are as follows:
1. To know the implementation of the group presentation technique used in the
Language Teaching Methodology course.
2. To know and dig out students’ perceptions on the group presentation technique
used in the Language Teaching Methodology course.
3. To draw some possible suggestions for the improvement of the implementation
of group presentation technique in Language Teaching Methodology course
in English Language Education Study Program Sanata Dharma University.
E. RESEARCH BENEFITS
The findings of the research hopefully will be beneficial for the students,
the lecturers, and English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma
University Yogyakarta.
1. Students of English Language Education Study Program
The research finding hopefully will make the students know how to make a
successful group presentation. A successful group presentation can be achieved
through the implementation of some characteristics of a good presentation as
mentioned in Chapter 2. The research finding will also make the students know
the benefits of their group presentation. Through group presentation technique,
the students experience cooperation between members of their group. The
students also experience learning the material autonomously. Hopefully by
positive perception on the technique. By having positive perception, the students’
motivation to learn the material through group presentation may increase. The
implementation of group presentation technique hopefully becomes more useful
and more interesting for the students. Furthermore, the students will realize that
they cannot only increase their academic achievement, but also develop their
teaching skill and social skill through group presentation technique.
2. Lecturers of English Language Education Study Program
The research finding hopefully will make the lecturers consider the
students’ perceptions on certain teaching technique used by the lecturers. The
students’ perceptions on the teaching technique implemented by the lecturer can
be used to improve the teaching-learning activity.
3. English Language Education
The research finding hopefully will be beneficial for English Language
Education in general, especially for English Language Education Study Program
Sanata Dharma University. In group presentation technique, the students are
required to be self-reliant and independent problem solver. It means that the
students do not depend solely on the lecturer’s explanation, but more on their
friends’ explanation and their own effort to master the material. Through group
presentation technique, the students have more chance to practice their English
ability and teaching skill. By providing the students with more opportunities in
practicing the teaching skill, hopefully English Language Education Study
Through this study, it is expected that English Language Education Study
Program Sanata Dharma University also pays attention to the suggestions given
by the students for the improvement of the quality of the teaching technique used
in English Language Education Study Program Sanata Dharma University. It is
also expected that the implementation of the group presentation technique will
develop the teaching materials used in English Language Education Study
Program Sanata Dharma University.
F. DEFINITIONS OF TERMS
1. Perception
In this study, perception is defined as “The process by which an organism
receives or extracts certain information about the environment” (Forgus, 1966).
In other words, perception in this study refers to how the students perceive on
receiving group presentation technique as the teaching-learning technique.
2. Group Presentations (Course Guidelines for presentation)
In this study, group presentation is defined as a presentation conducted by a
group which explains a method in language teaching and then simulate the
method. Group presentation is divided into two parts. The first part is the
theoretical review. In the theoretical review, the members of the group have to
explain the method. The second part is the method simulation. In the method
simulation, the group who has presented the theoretical review should simulate
how the method works. The members of the group should assign one of the
3. Language Teaching Methodology (KPE 264)
Based on “Panduan Akademik 2002”, Language Teaching Methodology is
one of the compulsory courses taught in English Education Study Program in
Sanata Dharma University Yogyakarta. In this study Language Teaching
Methodology refers to a course which has a goal to assist the students to have
adequate knowledge of well-established language teaching approaches and
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL REVIEW
The theoretical review is divided into two parts. The first part is the
theoretical discussion. The theoretical discussion is divided into five subtitles: (1)
The definition of presentation and some characteristics of presentation. (2)
Definitions of perception, the perceptual process, and factors influencing
someone in having his or her perception. (3) Definition of cooperative learning,
characteristics of cooperative learning, and benefits of cooperative learning. (4)
Characteristics and principles of constructivism. (5) The nature of Language
Teaching Methodology. The second part is the theoretical framework.
A. THEORETICAL DISCUSSION
In the theoretical discussion, the writer presents five points. First is the
definition and the characteristics of presentation, second is the definition of
perception, the perceptual process, and factors influencing someone in having his
or her perception, third is the definition, the characteristics, and benefits of
cooperative learning, fourth is the characteristics of constructivism model, and
fifth is the discussion of the nature of Language Teaching Methodology course.
1. Presentation
In the following discussion, the writer presents the definition of presentation
and the characteristics of presentation.
a. Definition of Presentation
The writer will present some definitions of presentation. According to
Mackey (1965: 228), presentation is communicating something to somebody. It
means that presentation is a means of communication to convey a message from
one person to another. Cassie and Constantine (1977:121) state that presentation
is speaking in public (1977: 121). There are two elements in a presentation, they
are the presenter and the audience. A presenter is someone who is responsible for
presenting something to the audience. The presenter is also responsible for
making the audience understand what he or she is presenting. In a presentation
the situation is presenter – dominated. (Petrequin, 1968: 15). Cassie and
Constantine add that giving a lecture is included into a type of oral presentation.
Related with Cassie and Constantine’s statement, Burden and Byrd (1999:
91) state that a lecture is an instructional strategy – a method for delivering
instruction that is intended to help students to achieve a learning objective (1999:
85) – in which the teacher gives an oral presentation of facts and principles, with
the students frequently being responsible for note-taking. In a lecture, the
classroom activity is teacher-directed and the teacher presents the material to the
students. It is not always the teacher who can explain the topic. The teacher may
ask the students to explain the topic. When the students replace the teacher’s role
in explaining the topic, it can be defined as student’s presentation technique. In
this study, the student’s presentation is conducted in groups. It can be defined as
In the following discussion, the writer will present the elements of
presentation and some characteristics of presentation.
b. Characteristics of Presentation
A presentation must have two elements, they are the presenter and the
audience. There are some criteria of a presenter in a presentation. According to
Petrequin (1968: 21), the presenter must be prepared to show as well as talk to
gain students’ attention. It means that the presenter must have enough and good
preparation for the topic to be presented. The presenter must also be able to direct
audience’ attention to what he or she presents. The presenter is responsible for
making the audience understand what he or she is presenting. The job of the
speaker is to perform the task with clarity and efficiency so that the listeners
benefit from the experience (Petrequin, 1968: 17). Thus, the presenter must be
clear in presenting the topic. Unclear explanation in a presentation may lead the
audience to have wrong understanding of the topic.
A presenter can be called as the speaker of a presentation. Hasling (1988:
13) states that a speaker must use sufficient volume of voice so that the audience
is able to hear the speaker’s voice. Hasling adds that the speaker should have a
positive attitude toward the subject matter and toward the audience. What is
meant by positive attitude is that a speaker has to respect the audience and
presents the subject matter clearly and enthusiastic. It is important for a speaker
to develop and maintain a positive attitude toward what the speaker is doing in
the voice and the attitude, a presenter should also be confident in front of the
audience.
In a student’s presentation technique, the audiences are the students who
are not presenting the subject matter. Petrequin (1968: 15) states that the
students’ (the audiences) role is watching, hearing, and noting what happens
during the presentation. The audiences may also give response to the subject
matter which is being presented. The response may be in forms of questions or
suggestion, or critiques.
Rosenshine (1987), cited by Burden and Byrd (1999: 88) writes five
suggestions of how to present an effective presentation.
1) Organize the material
First is to organize the material. It means that the material which is going
to be presented should be well-organized. A well – organized material will help
the presenter master what he or she is presenting. The presenter may brainstorm
his or her idea so that the material can be explained in detail. The presenter may
start the topic with general idea down to the specific idea, so that the audience
can follow the flow of the material which is being presented.
2) State the lesson goal
Second is to state the lesson goal. In student’s presentation technique, the
presenter should state first the goal of his or her presentation. By stating the goal
of his or her presentation, the presenter will help the audience to have clear idea
3) Provide step-by step presentation
Third is to provide step-by-step presentation. The presenter should begin
the presentation with an opening or introduction, content, and closing or
summary of what has been presented. In the introduction part, the presenter
usually does the opening by greeting and mentioning the topic of the subject
matter. After introducing the topic, the presenter starts to elaborate the topic. The
presenter usually closes the presentation by summarizing what has been
presented.
4) Focus on one thought at a time
Fourth is to focus on one thought at a time. It means that the presenter
should focus on the point which is being presented. The presenter may also check
the audience understanding before continuing to the next point.
5) Model behaviors by going through the directions
Fifth is to model behaviors by going through the directions. The presenter
is the focus of the audience’s attention. Thus, a presenter must show proper
behavior. Rosenshine and Stevens (1986), cited by Burden and Byrd (1999: 92)
add that teaching behaviors (clarity, enthusiasm, smooth transition) are important
for a presentation. In student’s presentation technique, the presenter should show
the teaching behavior that can motivate the audience to learn the material.
According to Cassie and Constantine (1977: 121), there are four parts of a
good presentation; they are preparation, beginning, body, and peroration.
1) Preparation
First part of the presentation is the preparation. In preparing a
planning of the presentation. There are two steps in preparation part. The first
step is to collect as complete as possible all the material needed. Complete
material is important because the presenter will have enough preparation for
answering audience’s questions. The second step is to expand ideas by
determining the aim of the presentation. Presentation may be aimed for
informing, persuading, or entertaining.
2) Beginning
Second part of a presentation is the beginning. As stated by Cassie and
Constantine (1977: 123) that the most important part of a presentation is the
beginning. The beginning of a presentation will determine the next step of the
presentation. In the beginning of the presentation, the presenter should grasp the
audience’s attention on what the presenter will present. Cassie and Constantine
add that the beginning of a presentation may be in forms of a question or a
statement which relates to the audience or to the main topic of the subject matter.
3) The body
Third part of a presentation is the body. The body must contain the
arguments and main ideas. As a presenter, he/she must be able to develop the
main idea and have enough and accurate arguments to be presented. The
presenter must master the content of the subject matter he /she is presenting. The
body of a presentation may consist of some sections. The presenter must give
clear cut at the end of every section. The presenter should notice when he/she has
already come to the end of every section and give summary of it (Cassie and
4) Peroration
The fourth part of a presentation is the peroration. Peroration means the
conclusion of a speech, summing up the points, and enforcing the arguments
(Cassie and Constantine, 1977:125). In the peroration part, the presenter should
present the conclusion of the subject matter which has been presented. The
conclusion must be clear and show the cumulative meaning so that the audience
will leave the room without confusion or still have a big question mark of what
has been concluded by the presenter.
Based on the characteristics of a good presentation from some experts
presented above, it can be concluded that a good presentation should provide
presenter, audience, organization of the material, statement of the lesson goal,
step-by step presentation, focus on one thought at a time, and model behaviors by
going through the directions. Furthermore, a good presentation should consist of
preparation, beginning, the body, and peroration.
In order to support this study, the writer will present the theory of
perception since one of this research aims is to dig out the students’ perception on
students’ presentation technique.
2. Perception
Since this study is aimed to know students’ perception on the student’s
presentation technique, thus the writer presents the discussion of some definitions
of perception according to some experts, the perceptual process, and factors
a. Definitions of Perception
The definition of perception can be derived from some sources. .
According to Kreitner and Kinicki (1992: 26), perception is a mental and
cognitive process that enables us to interpret and understand our surroundings. It
means that perception may exist as our responses to our surrounding. Another
definition of perception is stated by Leontiev (1981: 31). Leontiev defines
perception as the process in which the existence of the objects and phenomena is
reflected in a person’s consciousness. The process happens with the help of the
person’s sensory organs, namely: eyes, ears, tongue, nose, and skin. Leontiev’s
statement means that a person may perceive objects, surroundings, and events or
occurrence around him or her consciously by the help of sensory organs.
Haire (1956), cited by Leontiev (1981: 31) states that perception is a
process in which the individual recognizes information, fits the information, and
compares the information with the previous one which is stored in the person’s
memory. Haire’s statement means that a person, after receiving the stimuli, will
identify the stimuli. He or she then will recall his or her memory whether he or
she has already received the same stimuli or not. If he or she has already received
the stimuli before, he or she will recognize the stimuli. The stimuli may be in
form of information. The person then matches the information, and compares the
information with the previous information. Gibson, Ivancevich, and Donnelly
(1973: 216) state that perception is an activity which employs us in everyday of
our lives. The perception is a set of factors which influence the motivational state
of people in organization. The definition of perception stated by Gibson et. al
Another point of view about perception comes from Forgus (1966: 1).
Forgus defines perception as the process of information extraction. It means that
perception is the process where the information is filtered or selected. Altman,
Valenzi, and Hodgetts (1985: 85) add that perception is the way stimuli are
selected and grouped by a person in such a way that the stimuli can be
meaningfully interpreted (see figure 1). Furthermore, Altman et. al state that
perception is how a person views reality. The way a person views the reality
depends on how the information that is available organized.
After knowing some definitions of perception, in the following discussion
the writer will discuss how perception arise in someone’s mind.
b. The Perceptual Process
As stated by Altman et. al (1985: 85) perception is the way stimuli are
selected and grouped by a person in such a way that the stimuli can be
meaningfully interpreted. Below is the diagram showing how the perceptual
process happens.
The existence of perception begins from the stimuli. Warga (1983: 207)
defines stimuli as forms of physical energy that strikes our sensory receptors. The
physical energy is usually in forms of light, heat, and pressure. Sensory receptors
are the organs of our body (ears, nose, skin, eyes) whose duty is to convey
selected in the brain. The selected stimuli will result in the form of information.
The information will be organized and interpreted by the brain. The interpretation
of the information is called sensation (the translation of external energy). After
interpreting the information, the brain then translates the information into
meanings. The result of the meaningful translation of the information is called
perception. An example of this is when a person sees a smoked-jug, he or she
might interpret the jug contains either hot water or cold water. The person’s
seeing of the smoke is called the sensation. If the person decides to touch the jug,
thus the person translated the sensation into perception of a jug containing cold
water. The example above shows that sensation and perception is different.
People tend to consider sensation and perception the same. Sensation is the
translation of external energy, while perception is the sensation’s meaningful
translation. The interpretation process results in behavior response. Since
behavioral response is not included in this study; thus, the next discussions will
not present the behavioral response.
From the perceptual process discussed above, it is clearly seen that
perception comes from the stimuli. The stimuli then are selected in the brain. The
selected stimuli will result in the form of information. The information will be
organized and interpreted by the brain. After interpreting the information, the
brain then translates the information into meanings. The result of the meaningful
translation of the information is then called perception. Furthermore, perception
will create behavior response. Perception may arise from some factors. Thus, in
the following discussion, the writer will present some factors which can affect
c. Factors Influencing Perception
There are four important factors which can affect someone to have
perception towards something (Altman et al, 1985: 86), they are:
1) Selection of stimuli
Each person selects certain stimuli and may be different from one person
to another. The different selection of stimuli may be because of each person has
different interests towards something.
Orang-orang cenderung mengabaikan informasi atau petunjuk yang menyebabkan mereka merasa kurang nyaman.
(Winardi, 1992: 47)
(People tend to ignore information which makes them feel less comfortable.)
For example, a girl is listening to music. Meanwhile, she is surrounded by
so much noise, such as baby’s crying, neighbor’s lawnmower machine, and noise
of starting car machine. She may ignore all of the noise since she feels that it is
more interesting to hear the music.
2) Organization of stimuli
The selected stimuli should be organized in order to be meaningful.
Altman, et al (1985: 87) state that the perceptual organization of information can
help us categorize sensory inputs. The categorization will make the complexity of
the information become simpler until a person can interpret the stimuli as
meaningful information.
3) The situation
Each person has different expectation towards a situation happened
perceived (Altman et. al, 1985:89). Altman et. al add that familiarity with the
situation and a person’s past experience also affect what he or she perceived.
Student’s expectation of the situation happened during the group presentation
technique may influence their perceptions towards the technique. The students’
past experiences on the use of the technique will also influence students’
perceptions towards the technique. If the students had a bad experience on the use
of group presentation technique before, the students will have negative perception
towards the technique. On the contrary, if the students’ expectation towards the
situation happened during the group presentation technique is fulfilled, then the
students will have positive perception towards the technique.
Mendesaknya waktu, sikap orang-orang, dengan siapa seseorang bekerja, akan mempengaruhi ketepatan persepsi.
(Winardi, 1992: 48)
(Time constraint, people’s attitude and with whom someone will interact
will influence the accuracy of perception.)
4) Self – concept
The next factor which influences someone’s perception is self – concept.
Altman et. al (1985: 90) define self – concept as the way someone perceives his
or herself. The way we feel and see ourselves will affect our perception of our
surroundings. Altman et. al add that self – concept is very important because it
will determine what a person perceives and do. For example, a student who feels
that he or she is an independent person, will enjoy and like to be in the
presentation technique which also requires the student’s independence in learning
the material without explanation from the teacher. The students’ self–concepts
can shape their like or dislike towards the use of student’s presentation technique.
Those four factors mentioned above describe the factors which can
influence someone in having his or her perceptions on something. Those factors
also describe the factors that can influence student’s perceptions toward group
presentation technique.
The selection of the technique based on the students’ like or dislike will
affect students’ perceptions towards the use of the technique. When the students
like the technique, they will have good perception toward the technique. The
organization of the group presentation will affect the students’ perceptions
towards the use of the technique. When the group presentation is well-organized,
the students will have good perceptions towards the technique. The students can
interpret the use of the group presentation technique as meaningful information.
Students’ familiarity and expectation of the situation in the use of group
presentation technique will affect students’ perceptions on the technique. When
the students are familiar with the technique and the situation of the technique is
appropriate with the students’ expectation, the students will have good
perceptions on the use of the technique. The students’ self-concepts will affect
the students’ perceptions on the use of the group presentation technique too. If the
students perceive that they are motivated in using the group presentation
Furthermore, Winardi (1992: 47) discusses seven factors that can
influence someone in having his or her perception on something. Some of those
factors are similar to the statement from Altman et al. The same factors are
organization of stimuli, selective perception which is similar to selection of
stimuli, and situational factor. Then, Winardi adds that stereotype, needs,
emotion, and attitude are the factors that can influence someone in perceiving
something too.
1) Stereotype
People tend to have their stereotype on a particular thing. Stereotype is the
process of categorizing people or things based on a limited amount of information
(Altman et al, 1985: 91). In other words, people make their own classification on
a thing or a person based on their expectation. People tend to pay attention to
things which are appropriate to their stereotype and ignore others that do not
match with their perception.
2) Needs
People work or do something to fulfill their needs. Every person has
different needs. For example, in arranging a wedding party, people may have
many considerations in decorating a party room. The decorations are arranged to
satisfy their needs and expectations. They will choose the decorations which they
feel the best for the party room. People tend to perceive something positively if
they feel that thing can satisfy their needs and expectation. If the students feel
that the use of group presentation technique can fulfill their needs in learning the
3) Emotion
Kreitner and Kinicki (1992: 212) state that emotions have a significant
effect on our perceptions. A person’s emotion can affect his or her perception on
something. Negative emotions, such as anger, jealousy, envy, disappointment and
so on toward something may lead someone to have bad perceptions on that thing.
On the contrary, when someone has positive emotions, such as happiness,
contentment, gladness, and so on toward something, he or she will have good
perceptions on that thing. For example, a student always greets and smiles at her
teacher when they are passing each other. However, the teacher often ignores her
greeting. The student feels disappointed by the teacher, thus, she considers her
teacher as a self-assertive person and will have bad perception toward the teacher.
4) Attitude
Attitude may affect someone to have perceptions toward something.
Sikap merupakan suatu keadaan siap mental, yang dipelajari dan diorganisasi menurut pengalaman, dan yang menyebabkan timbulnya pengaruh khusus atas reaksi seseorang terhadap orang-orang, objek-objek, dan situasi-situasi dengan siapa ia berhubungan
(Winardi, 1992: 48)
(Attitude is a mental-prepared condition, which is learned and organized based on the experiences and causes the existence of a specific influence on someone’s reaction toward people, objects, and situations with whom the person make relation.)
From the discussion, we know that many factors can influence students’
perception on the use of the group presentation technique. Selection of stimuli,
organization of stimuli, the situation, self – concept, stereotype, needs, emotion,
and attitude are some factors which may influence the students in having their
During preparing the presentation, the students need to work together in
groups which can be categorized into cooperative learning since the students need
to cooperate with one another in order to achieve certain goal, thus, in the
following discussion, the writer will present the theory of cooperative learning.
3. Cooperative Learning
In order to support this study, the writer also includes the discussion of the
cooperative learning approach since in the process of preparing the group
presentation technique, the students need to cooperate with one another in order
to achieve certain goal, which is in accordance with the characteristic of
cooperative learning approach. The discussion of the cooperative learning
approach is divided into three parts, definition, characteristics, and benefits that
the students have got in the cooperative learning.
a. Definition of Cooperative Learning
Johnson, Johnson, and Holubec (1994), cited by Richards and Rodgers
(2001: 195) write the definition of cooperative learning as the instructional use of
small groups through which students work together to maximize their own and
each other’s learning. It means that in cooperative learning approach, the learning
activities are mostly done in groups and every student is responsible not only for
their own learning but also for each other’s learning.
Another definition of the cooperative learning approach is also presented
by Slavin. According to Slavin, cooperative learning refers to the variety of
teaching methods in which students work in small groups to help one another
learn academic content (1995: 2). In the cooperative learning approach, the
materials. Following the two definitions of the cooperative learning approach
mentioned above, Olsen and Kagan (1992) cited by Richards and Rodgers (2001:
192) define the cooperative learning approach as follows:
Cooperative learning is group learning activity organized so that learning is dependent on the socially structured exchange of information between learners in groups and in which each learner is held accountable for his or her own learning and is motivated to increase the learning of others.
Based on those definitions it can be concluded that in implementing the
cooperative learning approach, the teacher allows the students to cooperate with
each other and to share knowledge or information to achieve the learning goals.
Each student is also expected to be active in helping the other students and be
responsible not only for their own learning but also for other’s learning.
In order to support the discussion of cooperative learning, in the next
discussion the writer will present some characteristics of cooperative learning.
b. Characteristics of Cooperative Learning
One of the main characteristics of the cooperative learning approach can
be identified from the word cooperative. Richards and Rodgers (2001: 195) state
that the word cooperative in cooperative learning refers to cooperation in
learning. Cooperation is working together to accomplish shared goals. In
cooperative learning situation, the students work together to achieve certain
purpose.
Olsen and Kagan (1992) cited by Richards and Rodgers (2001: 196) write
five key elements of the cooperative learning approach. First is positive
success in learning depends on the other student. On the other words, what helps
one member helps all. The second element is group formation. The existence of
positive interdependence between students implies that grouping has occurred. It
means that teacher may make the group based on certain criteria or by chance.
The third element is individual accountability. Accountability refers to
responsibility. It means that each student or each group is responsible not only for
their own learning, but also for other student’s or group’s learning. The fourth
element is social skills. Social skills determine how the students interact with
each other to achieve activity or task objectively. Students’ social skills may
develop through cooperative learning approach. The students will learn how to
communicate with each other and to respect other’s opinion. The fifth element of
the cooperative learning approach is structuring and structures. Structuring and
structures of the cooperative learning approach refer to ways of organizing
student interaction and how the students interact.
The teacher’s role in the cooperative learning approach is not only as
source of learning, but also as the facilitator of learning. Harel (1992) cited by
Richards and Rodgers (2001: 199) states that as a facilitator of learning, the
teacher interacts, teaches, refocuses, asks questions, clarifies, and supports the
students during the teaching learning activity. Still according to Harel, as a
facilitator, the teacher may give feedback, redirect the groups with questions,
encourage the groups to solve its own problem, encourage thinking, extend
Furthermore, the teacher of the cooperative learning approach usually helps the
students with learning tasks and gives few commands. The cooperative learning
approach also requires the teacher to give more freedom to the students to explore
the topic being discussed and evaluate their performance together with their
friends.
Besides the teacher - student interaction, the interaction between the
students in the cooperative learning approach is aimed to enable the students help
each other. The role of the students in the cooperative learning approach is as the
director of their own learning. The students are also expected to plan, monitor,
and evaluate their own learning. The cooperative learning approach requires the
students to involve and participate during the teaching learning activity.
From the explanation presented before, it can be concluded that there are
five important components in the cooperative learning, they are: positive
interdependence, group formation, individual responsibility, social skills,
structuring and structures. The teacher of the cooperative learning is not dominant
in the learning process. The teacher’s role is as a facilitator of the learning
process. The success of the learning process depends on the students by
encouraging each other to achieve the goals.
Cooperative learning approach also gives some advantages for the
students in developing not only their language skill but also their social skills. In
the following discussion, the writer will present some advantages of applying
cooperative learning approach which can be beneficial for the teacher, the
c. Benefits of Cooperative Learning
Based on the characteristics of the cooperative learning approach, this
approach gives benefits for the students especially in developing the students’
social skills. Mc Groarty (1989), cited in Kessler (1992: 2) writes six primary
benefits of the cooperative learning approach. First, by using the cooperative
learning approach, the students will increase the frequency and variety of second
language practice through different types of interaction. Second, cooperative
learning approach gives possibility for the students to develop or use the language
in ways that can support their ability to think and increase their language skills.
Third, the students have opportunities to integrate the language with
content-based instruction. Fourth, the cooperative learning approach gives opportunities
to include a greater variety of curricular materials to stimulate language as well as
concept learning. Fifth, this approach gives freedom for the teacher to master new
professional skills especially in communication. Sixth, this approach can give the
students opportunities to act as resources for each other and give more active role
in learning.
Based on the benefits of the cooperative learning approach which are
presented before, the writer concludes that the cooperative learning approach
gives advantages for the students, the teacher, and for the material developers.
The students have more opportunities to develop their language skill as well as
their social skills by doing various interactions and being the source of the
information. The cooperative learning approach also gives the teacher chance to
master new skills especially in facilitating the interaction and communication
material developer since it provides variety of curricular materials to stimulate
language as well as concept learning. However, cooperative learning approach is
not merely discussion groups or group works of students. Richards and Rodgers
(2001: 201) state that in cooperative learning, the group activities should be
carefully planned to maximize students’ interaction and to facilitate students’
contributions to each other’s learning.
The writer also includes the discussion of constructivism since by
applying group presentations technique, the students should not depend on the
teacher’s explanation. The students are required to be self-reliant learners. Thus,
in the following discussion, the writer will present theory of constructivism.
4. Constructivism
In order to support this study, the writer also includes the discussion of the
constructivism since in the group presentation technique the students are expected
to be reliant and independent problem solver. The students become
self-reliant since the success of learning of the students rely on each other.
Independent problem solver means the students do not depend on the teacher’s
explanation in solving some problems which may arise during the learning
process.
a. Characteristics of constructivism
The students may help each other solve the problems. Self-reliant and
independent problem solver are two of the characteristics of constructivism.
Gavelek. (1986), Smagorinski. (1995), Vygotsky. (1978), Wertsch, Mc-Namee,
helping students develop evolving knowledge bases through interactions is best
achieved by using the social constructivist model.
Brooks and Brooks (1993: x) write five conditions for applying
constructivism in learning process. First, the teacher must provide a learning
environment where students are able to search for meaning, appreciate
uncertainty, and inquire responsibly. It means that the teacher must give the
students opportunity to be responsible for their own learning. Second, in the
constructivist classroom, student-student interaction is emphasized, and students
must understand that they are responsible for their own learning in the learning
situation. It means that in the constructivist classroom, the students are expected
to cooperate with each other to achieve certain purpose of learning. Third,
educators must begin to make important pattern which modify the
implementation practices that encourage students to think and rethink, and
demonstrate. It means that the lecturers have responsibility to modify the teaching
technique so that the students can be more actively involved in the class activity
and directly practice the theory of the lesson. Fourth, in the constructivist
classroom, it is important for the teacher to focus on and value students’ points of
view. It means that the lecturers need to pay attention to the students’ way of
think. Fifth, in the constructivist classroom, the assessment processes must
connect the learner with the teacher and provide feedback. It means that there
should be an interactions between the lecturers and the students through the
assessment processes so that the lecturers can give feedback to the students.
Hogan and Pressley (1997: 8) state that learning occurs in a context of
social interactions leading to understanding. The above statement means that the
In the constructivist classroom, the students experience active problem-solving
activities with others, but progressively become independent problem solvers. It
means that the students solve the problems which emerge by themselves.
Constructivist classroom emphasizes also on the interaction between the teacher
and the students. The teacher maintains to guide the learners’ rising
understanding, providing assistance as needed. Finally, the teacher gives the
responsibilities to the learners.
b. Principles of the constructivism
There are four principles of the constructivism stated by Brooks and
Brooks (1993: 35). First, posing problems of emerging relevance to students. It
means that students’ lack of interest in the material given by the teacher can be
lessened by helping the students to construct understandings of the importance of
the topic. The relevance can arise through teacher mediation by proposing the
students with a good problem. Second, structuring learning around primary
concepts. It means that the teacher organizes information around conceptual
cluster of problems, questions, and inconsistent situations because students are
most engaged when problems and ideas are presented holistically rather than in
separate parts. Third, seeking and valuing students’ points of view. Fourth,
adapting curriculum to address students’ suppositions.
In this study, the writer conducts the research in the Language Teaching
Methodology course since Language Teaching Methodology is one of the
content-based courses which apply group presentation technique. Hence, the
5. Nature of Language Teaching Methodology (KPE 264)
In this study, the writer also includes the discussion of Language
Teaching Methodology since it is one of the content - based courses which apply
the group presentation technique.
English Language Education graduates are expected to be competent not
only in understanding the theory of the English language, but also in
implementing the methods of teaching English Language. Based on the course
guidelines of the Language Teaching Methodology, the subject of Language
Teaching Methodology is designed to incorporate both of the theoretical review
and foundation of English Language Teaching methods and the practical
application, simulation, and demonstration of how each of the ELT methods
works in the design and implementation of English language programs. Based on
the “Panduan Akademik, 2002”, the goal of Language Teaching Methodology is
that the students have adequate knowledge of well-established language teaching
approaches and methods and are able to apply them.
B. THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
Different motivation, expectation, and needs on the group presentation
technique may lead the students to have perceptions on the technique. The use of
group presentations technique gives various experiences to the students. Students
might find that the group presentations technique will train them to be self –
reliant learners. But some of them might find that they could not master the
material well because the presenters (their own friends) could not explain the
In this study, the writer attempts to answer three questions. First is to find
out the implementation of the group presentation technique in Language
Teaching Methodology course. Second is to find out the students’ perceptions on
the implementation of group presentation technique in Language Teaching
Methodology course. Third is to find out some possible suggestions that can be
contributed for the improvement of the implementation of group presentation
technique after knowing the students’ perceptions on the technique used in the
Language Teaching Methodology course.
The writer needs to know the implementation of the group presentation
technique because the writer needs to know the cause of the students’ perceptions
on the technique. In order to find out the answer of the first research questions,
the writer employs observations, which were conducted twice. The writer also
employs the characteristics of an effective presentation and an effective method
simulation. It is employed in order to help the writer finds out some
characteristics of an effective presentation and method simulation. The writer
also employs the definition of presentation and group presentation. The writer
also includes the definition, the characteristics, and the benefits of cooperative
learning approach and characteristics of constructivism theory. The writer
employs cooperative learning approach and constructivism theory because in the
process of conducting the group presentation, the students are expected to
cooperate with each other. The students are also required to independent
explanation. The result of the observations will be written in paragraphs, then
analyzed, and interpreted.
In answering the second problem, the writer employs the definitions of
perceptions, the perceptual process, and factors that can affect someone in having
his/her perception. The writer needs to know the definitions of perceptions since
it helps the writer to know what perception is. The perceptual process will help
the writer to know how perception is formed. Factors influencing perception is
also needed by the writer because it helps the writer to find out factors that can
cause a student to have certain perception. In order to find out the answer of this
research question, the writer distributed questionnaires. The result of the
questionnaires will be coded, analyzed, interpreted, and written in paragraphs.
The third research questions concerns with some possible suggestions that
can be drawn to improve the implementation of group presentation technique. In
order to answer this problem, the writer conducted interviews and interpreting the
result of the open-ended questionnaires.
The next chapter will discuss methodologies that are used to find out the
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The purpose of Chapter 3 is to present the method used to answer the three
questions stated in Chapter 1. The discussion is presented into five major parts,
namely research methodology, description of research participants, instruments,
data gathering technique, and data analysis procedure.
A. RESEARCH METHOD
This research was a survey research. According to Ary, Jacobs, and
Razavieh (2002: 374), survey research is a technique in research which data are
gathered by asking questions to a group of individuals. There are two instruments
that are usually used in a survey research, those are interview and questionnaire.
In obtaining the data, the writer used qualitative method. Ary, et al (2002: 421)
states that qualitative method employs words to answer research questions. A
qualitative method usually presents the data in the form of description. Thus, in
this research, the researcher would interpret the data in form of numbers into
verbal statements.
B. RESEARCH PARTICIPANTS
The participants of this research were the students of Language Teaching
Methodology course from class B and D in English Education Study Program
Sanata Dharma University from year 2004/2005. The writer chose the students of
class B and D of Language Teaching Methodology course as the research
participants because the students from class B and D experienced the
implementation of group presentation technique. The total of the research
participants from those two classes were seventy two students. There were four
students for the interview and seventy two students should fill in the
questionnaires.
C. RESEARCH INSTRUMENTS
The writer used three instruments in obtaining the data, namely, observation
sheet, questionnaires, and interview sheet.
1. Observation sheet
The first instrument used in this study was observation. According to
Fraenkel and Wallen, observation is used in order to know how people act or how
things look (1993: 384). Thus, in order to know the implementation of group
presentation technique, the writer conducted observation. In the observation
sheet, the writer already wrote some characteristics of a good presentation, a good
simulation, and a good model of a teacher. The writer, then, would observe
whether the presenters were already implemented the characteristics of a good
presentation, a good method simulation, and a good model of a teacher. The
writer did not only record the characteristics that were shown by the presenters,
but also the audience’s behaviors and the condition during the presentation. The
observation sheet consisted of three parts. The first part consisted of nineteen
items as can be seen in Appendix 6 on page 119. In the first part, the writer
focused the observation on the theoretical review and question and answer
focused on the method simulation. In the last part the writer focused on the
student who acted as the teacher in the method simulation. The third part
consisted of sixteen items. The result of the observation would be interpreted in
the form of paragraphs.
Among the four observation models given by Fraenkel and Wallen (1993:
384), the writer chose to be a complete observer. As a complete observer, the
writer would observe the activities of a group without becoming a participant in
those activities.
2. Questionnaire
The second problem identified in this research was answered using
questionnaires. On the questionnaires, the writer would record the perceptions of
the students of Language Teaching Methodology course class B and D, students’
opinion of a good group presentation, and some suggestions to the
implementation of the group presentation technique.
Ary, Jacobs, and Razavieh (1990: 418) state that a questionnaire was an
instrument of the study to gather information through the respondents’ written
responses to a list of questions. In order to gather the students’ perceptions on the
implementation of group presentation technique, the writer employed a
combination between closed-ended and opened-ended questionnaires. Ary, et al
(ibid 418) stated that closed-ended questions allow individual to pick the
response that best represented his/her belief or opinion. While, open-ended
questions let a free response from the participants rather than limit the response to