Puji dan puji syukur kami panjatkan kehadirat Allah SWT yang senantiasa melimpahkan rahmat dan karunianya kepada peneliti sehingga dapat menyelesaikan skripsi ini yang berjudul “MENINGKATKAN KETERAMPILAN BERBICARA SISWA DENGAN MELAKUKAN DISKUSI KELOMPOK KECIL DI KELAS 8 SMPN 14 BINTAN”. Dewi Nopita, M.Sc. Pd, Ketua Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris Universitas Maritim Raja Ali Haji. Populasi dalam penelitian ini adalah seluruh siswa Kelas VIII C SMPN 14 Bintan tahun ajaran 2021/2022 yang berjumlah 28 siswa.
The purpose of this study was to describe how small group discussions improved the speaking skills of students in VIII. to class SMPN 14 Bintan. The population in this study was all students of Class VIII C of SMPN 14 Bintan in the academic year 2021/2022, consisting of 28 students. In conclusion, SGD has been excellent and effective in helping students speak English in the eighth grade of SMPN 14 Bintan.

INTRODUCTION
- The Background of The Study
- The Identification of the Problem
- The Limitation of the Problem
- The Research questions
- The Research Objectives
- The Significances of the Research
- Theoretically
- Practically
- The Definition of Key terms
Therefore, the researcher attempted to investigate through the development of speaking skills using Small Group Discussion (SGD) in 8th grade. The researcher identified several conditional factors related to classroom strategies that affect students' speaking skills. The previous study above confirms Orlich that small group discussions can improve students' speaking skills.
Based on the limitation of the problem, the research question could be formulated as; "How can students' speaking skills be improved by using small group discussions in class 8 SMP N 14 Bintan?". Regarding the research question, this study aims to describe how to improve students' speaking skills by conducting small group discussions in grade 8 of SMPN. The results of this study are expected to provide an alternative technique to attract students' interest, especially for speaking skills using SGD.
THE LITERATURE REVIEW
- Speaking Skill
- Aspects of Speaking
- Small Group Discussion
- The Characteristics of Small Group Discussion
- Steps How to Conduct SGD (Small Group Discussion)
- Review of Related Findings
- Conceptual Framework
Brown (2000) states that a small group discussion is a group of students working together to achieve certain goals. However, if used well, small group discussion can be one of the most effective techniques in teaching speaking that provides a real situation for students. Therefore, small group discussion can be a successful technique if it covers the characteristics of small group discussion.
The results of this study also show that the small group discussion strategy effectively increases students' activity and learning outcomes in speaking subjects, especially in English learning. This research was conducted by Bohari (2019) regarding the improvement of speaking skills through small group discussion in eleventh grade students of Sma Plus Munirul Arifin Nw Praya. In addition, small group discussions can improve students' speaking skills in class XI students of SMA Plus Munirul Arifin NW Praya.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
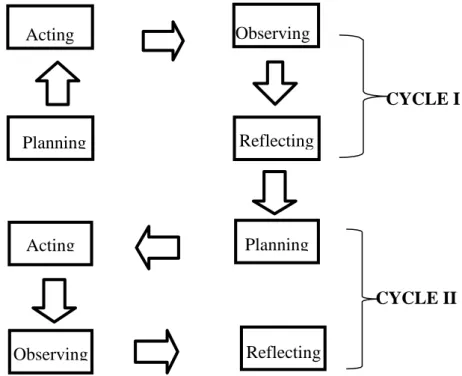
- Research Design
- Research Setting
- Setting At Place
- Setting At Time
- Research Procedure
- Research Instrument
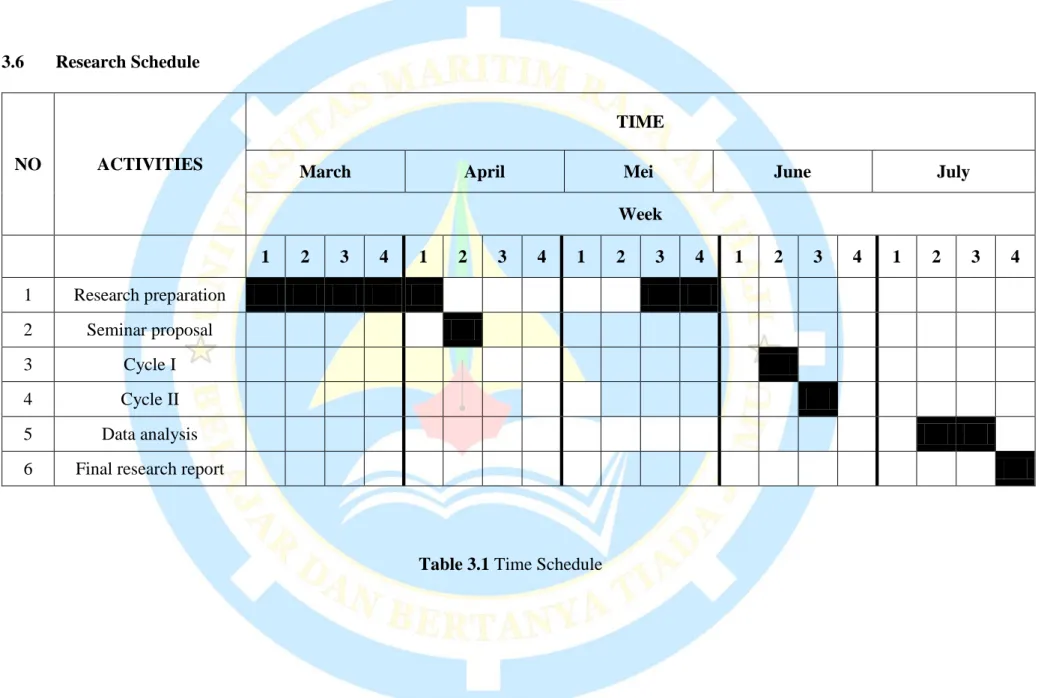
- Research Schedule
- The technique of Collecting Data
- The Quantitative Data
- The Qualitative Data
- Technique of Analyzing Data
To collect data, the researcher gave two tests to the students, namely pre-test and post-test. In the first cycle, the value the students obtained was not what the researcher wanted, far from enough. Next, the researcher asked the students to do the dialogue in front of the class.
The researcher also gave the students feedback related to the students' performance before the class. The researcher therefore concluded that the research result showed that the implementation of the SGD can improve the students' speaking ability. As stated in the discussion in the previous chapter, the researcher can conclude that the SGD successfully improves the students' speaking skills.
The researcher suggested that they should participate in the activity to improve their English speaking skills. The Researcher explained in each group how to make a conversational dialogue Expression of Like and Dislike;.
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
Data Description
- The Quantitative Data
- The Qualitative Data
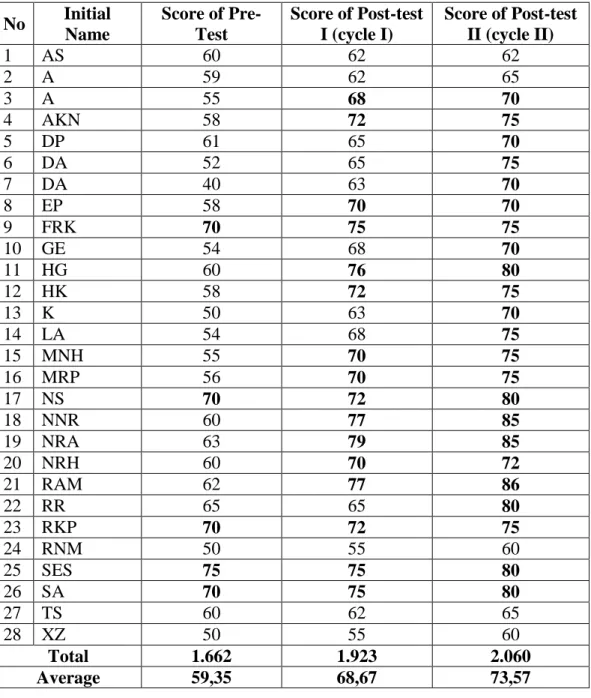
The tests given to students are in the form of pre-test, post-test cycle I and cycle II. In cycle I, the researcher found unsatisfactory results; Although students are enthusiastic about learning, results are still low. In cycle II, the researcher changed the topic of learning from expressing congratulations to expressing likes and dislikes; changing different topics in these two cycles was useful to gauge students' skills without repeating the same material.
The results of the student scores from the speaking test can be seen in the following table. Thus, the researcher can conclude that this method is successful in improving students' speaking skills using the SGD technique. The researcher uses observation to see the activities of students and researcher during the teaching and learning process.
Based on the observations from the checklist, the students were more excited to learn, as shown by their happy faces and excitement when asked by the researcher if there were any difficult words in the learning process using SGD. The smartphone was used to take photos and record the students' performance in the teaching and learning process. The first interview was conducted in the first cycle, when the students took the pre-test, and the second at the end of the second cycle.
In the interview transcript above, it can be concluded that both teacher and students like this technique. The use of two cycles and two meetings in each cycle consists of pre-test and post-test. In the first cycle, the students experienced an increase in scores from pre-test to post-test.
Some students were afraid to practice a conversation in front of the class; Some students were not serious about learning, and the value obtained did not achieve the goal desired by the researcher. Therefore, cycle two was conducted during the second week the researcher was at school.
Data Analysis
- Quantitative Data
- Qualitative Data
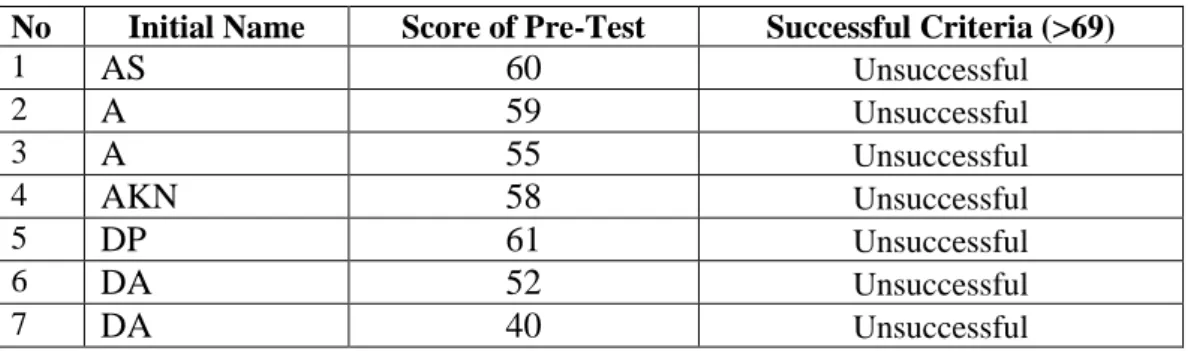
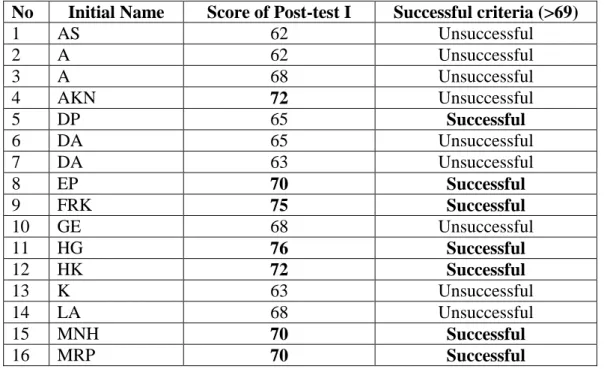
According to the above calculations, students' speaking skills in English classes were still lacking. After conducting the SGD in the classroom, the students were given a post-test I to determine the result of cycle I. The following are the results of the students' post-test speaking in cycle I in the second meeting.
According to the students' speaking skill score in the 1st cycle, there was an increase in the students' average scores from the students' speaking skills in the previous study (pre-test) to the students' speaking skills in the first cycle (post-test). ME). According to the students' speaking skill score in the 2nd cycle, there was an increase in the students' average scores from the students' speaking skills in the previous study (pre-test) to the students' speaking skills in the second cycle (post-test). II). The researcher also designed a post-test to collect data to determine if there was an increase in the scores of some students from the pre-test to the post-test I. 43.
The researcher acts as a teacher in the class based on the previous lesson plans, so that the students do not get excited and feel pressured. First, the researcher opened the class by greeting, taking attendance and getting to know each student. At the second meeting, the researcher opened the class by greeting and attending to the students while getting to know each student.
After the SGD was implemented, the researcher discussed the process of Cycle I and the result of post-test I with the teacher. So, to increase the number of students who can exceed the minimum completeness criteria, the researcher and teacher try to modify the Action. The researcher tried their best to teach and motivate the students to increase their speaking ability using SGD.
The researcher also tried to highlight some aspects that had not yet been done in the first cycle.
Discussion
However, most students failed to pass the minimum mastery criterion in this cycle. In the second cycle, the researcher gave the topic "Like and dislike expressions". The researcher changes a different topic from cycle I, because, with the same topic, it will be called repetition, while the researcher aims to improve the students' skills. However, after the second cycle, all students confidently told the researcher that they could speak English fluently.
Qualitative data showed that students are confident and motivated to speak English without fear of making mistakes. In SGD, students were more active and participated in speaking teaching. Based on the above conclusions, the researcher can make some suggestions to the English teacher, students and other researchers.
The researcher presented the learning material, namely Congratulation using speaking skills;. The researcher went around each pair to confirm and check the work of each pair of students. Finally, before the researcher finishes the class, give the researcher time to discuss or ask questions about the learning.
The researcher reviewed the previous meeting and explained that the second meeting had a test (post-test) using the group formed in the first meeting. The researcher asked the students to choose the type of greeting expression and make a dialogue based on the chosen type; the researcher went around to check the group work;. Finally, before the researcher closed the class, the researcher gave them time to discuss or ask questions about the learning.
The researcher reviewed the previous meeting and explained that the second meeting had a test (post-test) used by the group formed in the first meeting.
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
Conclusions
SGD activities can improve students' English speaking ability, which can be seen from their scores and responses to CAR's teaching activities. For that reason, the SGD can be used as an alternative strategy for teachers' speaking instruction, improving and maintaining English speaking.
Suggestions
Improving Students' Speaking Ability Through Practice Rehearse Pairs of The Tenth Grade of Man Malang 1. OBSERVATION CHECKLIST Students: SMPN 14 Bintan. At the end of the lesson, students are expected to be able to: Use the term Like and Dislike to someone in vocabulary, fluency, comprehension and pronunciation. The exercises are as follows: 1. conversation about Like and Dislike, including the answers. do it with your partner).
The exercise is as follows: Make a conversation about the Expression of Like and Dislike, including the answers.
Observation Checklist
Lesson Plan (Cycle I)
Lesson Plan (Cycle II)
Assessment Instrument
Interview Guidelines
Pre-test
Post-test (Cycle I)
Pre-test
Post-test (Cycle II)
Documentation