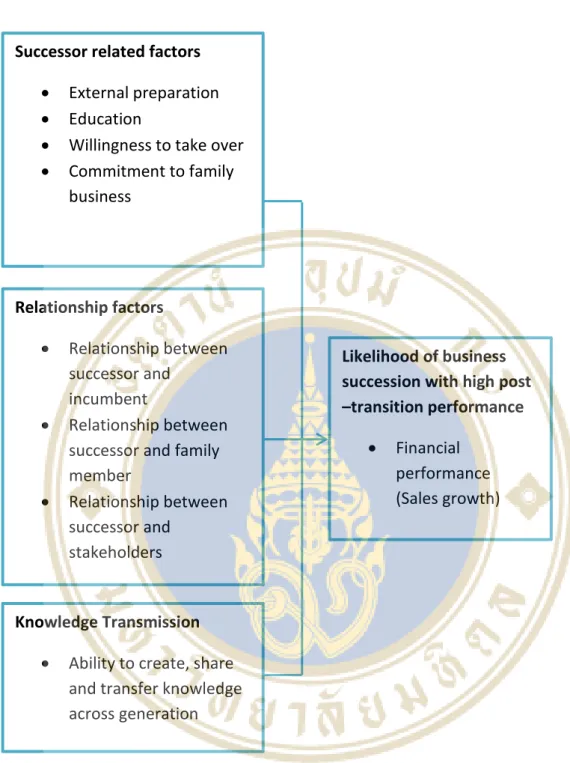
Determinants of family business succession are succession-related factors, relationship factors and knowledge transmission. This research was initially focused on the micro family business due to the doubt about the possibility of growth of this business sector. The case of Office Mate leads to a central question of this research “Which factors are most related to the success of a micro family business that achieves high performance after transition.

Statement of Problem
Dhanin Chearavanont & family, owns CP Group, the richest one in Thailand is a good example. The question is "What makes a micro family business successfully passed on to the next generation and transformed to be a medium or large business?" The obvious example that can answer this question is the Office Mate Plc., the catalog and e-commerce business model of office supplies distributor. Therefore, this paper aims to identify factors that influence micro-family business to achieve high post-transition performance in Thailand.
Research Questions
Research Objectives
Scope of the Study
Contribution of the Study
Organization of the Research
LITERATURE REVIEW
Definition of Micro Family Business
- Definition of Micro Enterprises
- Definition of Family Business
Researchers generally agreed that family involvement in business makes the family business unique (Miller and Rice, 1967). Previous research has attempted to define family business by its ownership and management, but enterprises that have the same level of family involvement in ownership and management may or may not consider themselves or behave as family businesses. From the review of the definition of micro businesses and family businesses, in this study a "micro family business" is defined as a business that employs less than 10 people and a business owner is self-managed in a personalized way, with the vision of the family firm or a small group of families and the intention of the dominant condition to form and follow this vision throughout the generations of the same family or small group of families.
Family Business Succession
It is considered a slow, multi-stage process that involves increasing participation of the successor and decreasing involvement of the incumbent until the real handover occurs. The phase in the succession process consists of phases in the process of transferring the leadership of a family business from the incumbent to the successor (Longenecker et al., 2009). So there is (1) the pre-business phase, in which the successor may only be passively aware of certain facets of the organization; (2) the introductory phase, during which the successor may be exposed to organizational jargon and members by family members, even though he or she has not even worked in the company on a part-time basis; (3) the introductory functional phase, in which the successor works as a part-time employee; (4) the functional phase, in which the successor enters the organization as a full-time member; 5) the advanced functional phase, in which the successor assumes management responsibilities; (6) the early succession phase, in which the successor assumes the presidency; and (7) mature succession, where the successor becomes the 'de facto leader' of the organization.

Success Factors
- Successor Related Factors
- Relationship Factors
- Knowledge Transmission
Stravrou (1999) showed that there is a positive correlation between firm size and the successor's intention to join the family firm. This normative commitment has a strong positive association with discretionary behavior that leads to effective family business performance. At the same time, the second generation must add new skills and offer new perspectives in the family business (Handler, 1992).
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
The Relation of Success Factors to Micro Family Business in Thailand Thailand
- External preparation
- Educational Level
- Willingness to Take Over
- Successor’s Commitment
- Relationship between Successor and Incumbent
- Relationship between Successor and Family Member
- Relationship between Successor and Stakeholder
- Ability to Create and Transfer Knowledge
Stravrou (Stavrou, 1999) indicated that there is a positive correlation between business size and successor intentions to join the family business. In this way, successors willing to take over micro family business must have the spirit of entrepreneurship. Even they have to work hard, but they realize the rewards of family business; the opportunity to create financial security, the authority to design their lifestyle.
This type of person usually knows how to achieve their business goals and has great confidence in their ability to grow the family business. Different from successors with affective and normative commitment, successors who have calculative and imperative commitment are likely to devote minimal effort to business, which is negatively related to discretionary behavior that leads to the effective functioning of the family business. The key person in the micro-family business is an established company that takes overall responsibility for the business and owns knowledge, which is the family business's key competence.
The family business transition process is first and foremost about managing relationships and expectations among family members. Conflicts/rivalries/competition between family members, risks related to the high sensitivity of family business consensus such as For example, the founder of the family business may be supported by few suppliers, customers, employees and financial institutions in the initial stage of the business.
Successors should acquire especially tacit knowledge about the incumbent, as this knowledge will create the competitive advantage for their family business.
Framework
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- Research Method
- Case study
- Case study Criteria
- Measurement Items
- Small Survey
- Survey Sample
Only existing family businesses in Bangkok and surrounding provinces that have undergone a management transition and meet these criteria are considered. First, there must be an example of family businesses that consist of a business vision held by a family or a small group of families and the intentions of the dominant condition that this vision is formed and followed through the generations of the same family or small group of families. Second, management of family businesses must have been successfully transferred to the second generation at least two years prior to the study with no assessment of post-transition performance.
Third, before the transition, the family business must be a microfamily business, according to the definition used in this study. The results of case studies will provide a basis for developing measurement items that will be useful for further empirical research. The research questions and measurement scales will be developed to assess validity and reliability through questionnaire research.
The questionnaire will be developed with the validity and reliability of measurement items in mind. The questionnaire will be tested through pilot interviews with ten micro-enterprise successors and a survey will be conducted among 100 micro-enterprise owners/successors who are members of two entrepreneurial business clubs in Thailand. As mentioned, the database of micro family businesses in Thailand is in a blank, the selection of respondents was purposive sampling and snowball sampling method.
These potential respondents were then also asked to identify other family businesses that met the following criteria; The successor to the family business is the 2nd generation. Before the successor came in, the family business was a micro-company with no more than 20 employees. The successor has successfully transferred management.
CASE STUDIES OF MICRO FAMILY BUSINESSES
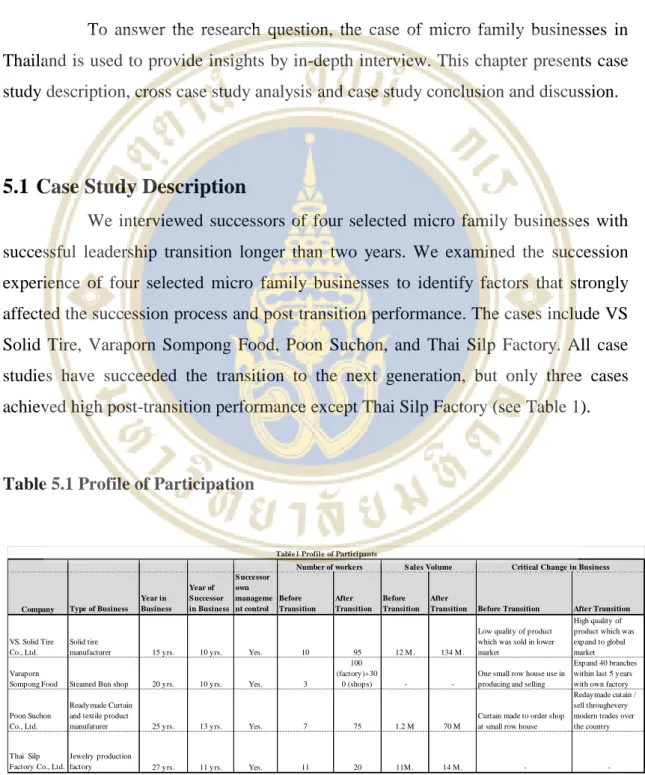
- Case Study Description
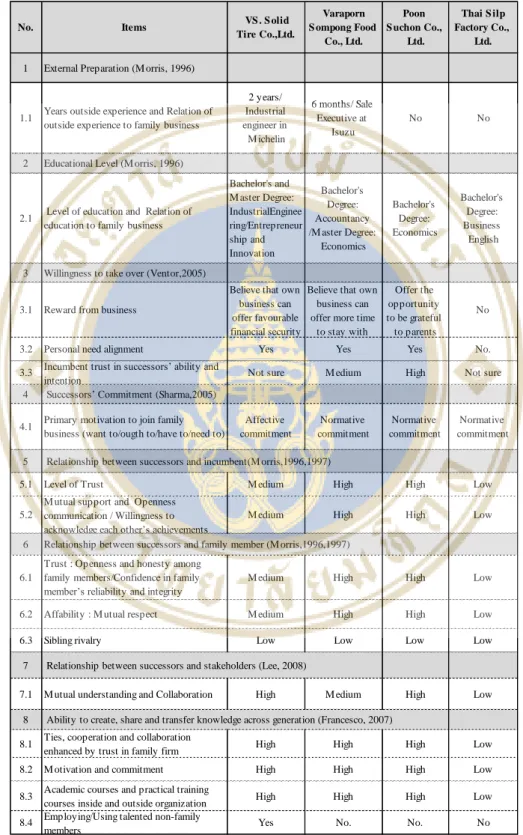
- VS Solid tire
- Varaporn Sompong Food
- Poon Suchon
- Thai Silp Factory Co., Ltd
- Cross Case Studies Analysis
- Case Study Discussion
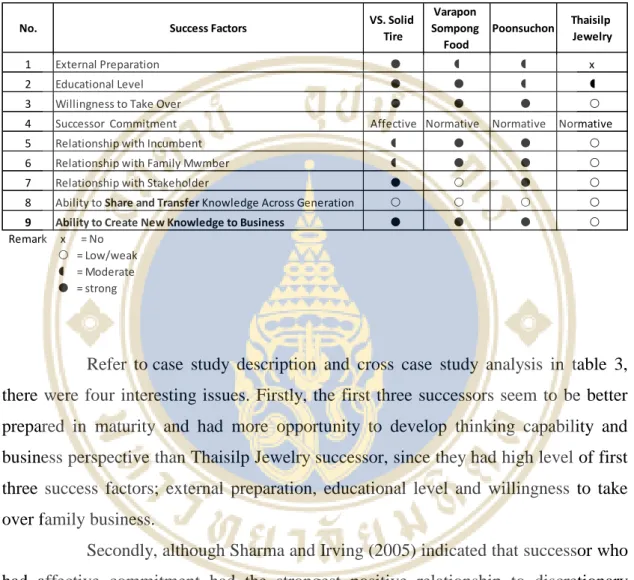
- Successors of micro family business who have high external preparation and educational level are likely to create a successful transition with
- Successors of micro family business who have willingness to take over business and have affective or normative commitment are more patient
- Relationship between successor and incumbent and family members of micro family business has influence on successful transition but to
- Finding 4: Relationship between the successor and stakeholders are important to support the successful transition and the first step of successor in
- Finding 5: In order to make high post-transition performance, the ability to create, share, and transfer knowledge across generation is less
In order to advance the business, the successor decided to quit his job and start working in the family business. The reason he joined the family business is a belief in career potential and financial returns, not an obligation to do so. He believed that the success of his family business was the result of his willingness to change.
What the scion learned from helping her parents in the business since childhood contributes to her business outlook. Her role in the business is to manage skilled workers to deliver products on time. Stavrou (Stavrou, 1999) has proven that there is a positive correlation between the size of the business and the successor's intention to join the family business.
In other words, the micro family business is normally unable to attract the successor in terms of monetary matters. However, creating a high performance after the transition in the micro family business depends much more on the competence of the successors and the perspective of the business. Since the business characteristics of the family micro-business are simple, the raw materials needed for production are generally supplied.
Because the case studies show the difference between the context of micro family businesses in Thailand and literature review.
MEASUREMENT ITEMS
- Measurement Items
- Questionnaire Design
- Pilot Test
- Data collection
- Descriptive Analysis
- Open-End Question
- Reliability Test
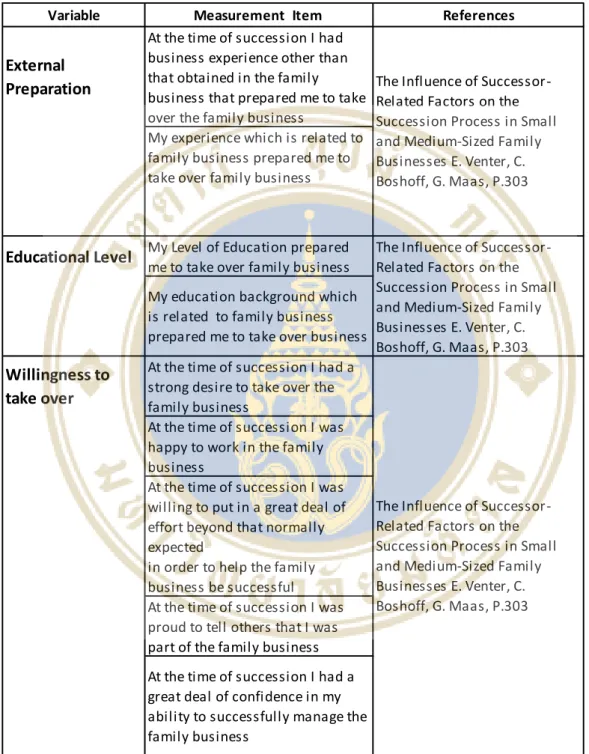
At the time of the inheritance, I had different business experience than that gained in the family business that prepared me to take over the family business. Education Level My education level prepared me to take over the family business My education history related to the family business prepared me to take over the business. At the time of inheritance I was proud to tell others that I was part of the family business. At the time of the inheritance I had great confidence in my ability to successfully manage the family business.
My experience related to family business prepared me to take over family business. The former employees and non-family manager in family business are the essential obstacle for me to develop business. The last part is a reflection of the perception of the respondents in various aspects regarding the family business transition.
My level of education prepared me to take over the family business My educational background related to the family business. At the time of inheritance I was proud to tell others that I was part of the family business. At the time of the inheritance I had great confidence in my ability to successfully manage the family business.
The former employees and non-family manager in family business are the essential obstacle for me to develop business.
CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
Conclusion
It may be difficult for a micro family business to definitely increase sales volume in a few years, while other aspects such as management system, product quality can be improved and lead to higher turnover later. Third, whether the growth of the company's industry and the economic situation during the period of operation of the successor affect the growth of the micro family business. It is possible that the growth of a micro family business will depend on economic growth.
Limitation and Recommendation for Future Research
Nonmarket-Based Transfers of Wealth and Power: A Family Business Research Framework. American Journal of Small Business, 11(3), pp. An Empirical Investigation of Pre-Entry Socialization of Successors for Leadership in Family-Controlled Businesses, Management Perspectives on Organizational Effectiveness . Succession in small and medium-sized family firms: Towards a typology of predecessor roles during and after the induction of the successor.
Determinants of primary stakeholders' satisfaction with the succession process in family businesses. Succession in family firms: Exploring the effects of demographic factors on offspring's intentions to join and take over the firm. The influence of successor-related factors on the succession process in small and medium-sized family businesses.