Directory UMM :Journals:Journal Of Policy Modeling:Vol22.Issue6.2000:
Teks penuh
Gambar
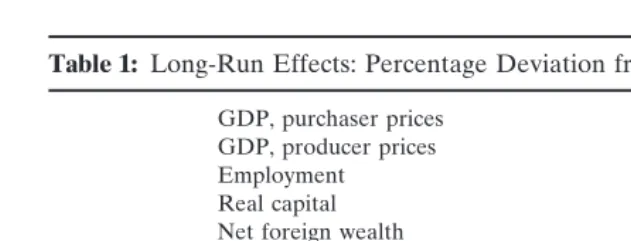
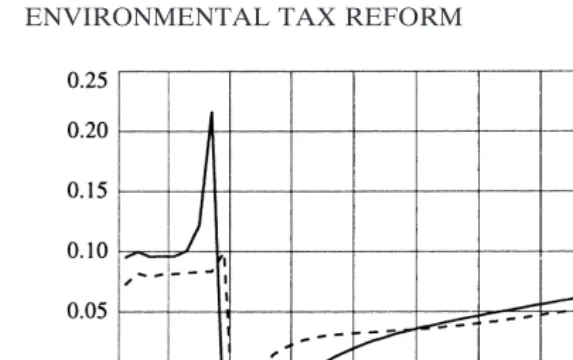
Dokumen terkait
The increase in the marginal capital income tax rate thus imposes a cost on a mimicker while a wealthy household revealing his true type is not affected, which means that
Indeed, reducing marginal tax rates is the most effective way to raise labor supply (in terms of hours), while increasing income differentials between low-skilled workers and
For women the relative difference in the number of QALYs between the highest and the lowest income decile increased from 7% in the youngest age-group to 37% in the oldest age-group
Farm wage employment contributes 22% to the average farm household income, nonfarm wage employment represents 6±12% (and is particularly important in the Northern region), and
While these conjectures are tantalizing, a full testing of the notions in the present paper would require that labour market equilibrium be derived under alternate assumptions about
This study examines the effect of minimum wage increases on teen hours of work and employment using both state- and individual-level panel data in the US. The state-level
Sections 2–4 explore, respectively, the case of zero, positive and negative income elasticity of leisure demand in a simple general equilibrium model with endogenous growth..
Here, tax structure refers to the mix of taxes on physical capital income, labor income and consumption which satisfy an exogenously given government budget constraint.. The