ABSTRACT
THE USE OF MIND MAPPING TECHNIQUE TO INCREASE STUDENT’S READING COMPREHENSION IN DESCRIPTIVE TEXT AT THE SECOND YEAR STUDENTS
OF SMP NEGERI 3 BANDAR LAMPUNG By
CHAIRUNNISA
Reading is one of the language skills that should be mastered by the students after following a set of English Instruction at school. One of the targets of national curriculum for English at junior high-school (SMP) level is students’ comprehension on various types of texts, such as recount, descriptive, and narrative. However, it is common that most students are observed being reluctant to read reading texts, even the short ones. Their lack of vocabulary mastery also limit their effort to achieve reading comprehension. Therefore, the teacher should be creative in selecting the techniques to be used in teaching reading activities in classroom, in order to boost students’ reading comprehension without stuck with such problems.
The objective of this research is to find out whether using Mind Mapping technique is an effective way to increase the students’ ability in reading comprehension. The population of this research was the second year students of SMP Negeri 3 Bandar Lampung that consists of seven classes and two classes were chosen as the experimental class and the try-out class. This research is quantative research. The research design was one group pretest posttest design. In collecting data, the reseacher administered pretest, treatments, and posttest. In analyzing the data, the T-Test was employed to reach the significant value.
LIST OF CONTENTS
Page
ABSTRACT...………... i
APPROVAL...………... ii
ADMISSION...………... iii
CURICULLUM VITAE....………... iv
MOTTO...………... v
DEDICATION...………... vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT.………... vii
LIST OF CONTENS...………... ix
LIST OF TABLES...………... x
LIST OF FIGURES...………... xi
LIST OF APPENDIXES...………... xii
I. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Background of the Problems...……….. 1
1.2. Formlated of the Problem ………...………... 5
1.3. Objectives of the Research ……….……… 5
1.4. Uses of the Research ………...…………..……….. 6
1.5. Scope of the Research……….……….. 6
1.6. Definition of Terms ……...………... 7
II. LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1. Concept of Reading Comprehension...……… 8
2.2. Concept of The Reading Aspects …………...……….. 11
2.3. Teaching Reading Comprehension ... ……… 12
2.4. Concept of Descriptive Text ………... 15
2.5. Concept of Mind Mapping Technique ………... 18
2.6. Advantages and Disadvantages of Mind Mapping ………... 21
2.7. Procedures of Teaching Reading Comprehension by Using Mind Mapping...………... 23
2.8. Theoretical Assumption ………... 25
3.2. Population and Sample ………..………... 28
3.3. Data Collecting Technique ..………..……….. 29
3.5. Procedures of Collecting Data ………...………...…. 32
3.5. Criteria of Good Test of Reading ………... 33
3.5.1. Validity…...……….. 33
3.5.2. Reliability...………....…... 35
3.5.3. Level of Difficulty ………... 37
3.5.4. Discrimination Power ……….. 38
3.5.5. Scoring System ……… 39
3.6. Data Analysis …...………. 40
3.7. Data Treatment………...…. . 40
3.8. Hypothesis Testing ………. 41
3.9. Statistical Testing ……….... 42
IV. RESULT AND DISCUSSION 4.1. Result of the Research ………...……...…...….. 44
4.1.1. Result of Pre-Test...…………..………... 45
4.1.2. Result of Post-Test………...………. 46
4.1.3. Normality Test ………. 47
4.1.4. Increase in Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement …... 48
4.2. Discussion of finding increase of each aspects of reading... 51
V. CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTIONS 5.1. Conclusion ……..…………...……...………...……. 62
5.2. Suggestions…...………..………... 63 REFERENCES
LIST OF APPENDIXES
Page
APPENDIX 1 – The Research Schedule ... 69
APPENDIX 2 – Tryout Test ... 71
APPENDIX 3 – Item Analysis on the Tryout Test ... 80
APPENDIX 4 – Pretest ... 86
APPENDIX 5 – Posttest ... 93
APPENDIX 6 – Comparison Between Pretest and Posttest ... 100
APPENDIX 7 – The Computation of Distribution Frequency ... 101
APPENDIX 8 – Descriptive Statistics of Pretest and Posttest ... 102
APPENDIX 9 – Increases of Students’ Reading Comprehension ... 104
APPENDIX 10 – The Distribution Answer of Reading Aspects ... 105
APPENDIX 11 – Normality Test ... 107
APPENDIX 12 – Critical Value of the t Distribution ... 109
APPENDIX 13 – Lesson Plan ... 110
Lesson Plan 1 ... 110
Lesson Plan 2 ... 116
LIST OF FIGURES
Page
LIST OF TABLES
Page
Table 1. Difficulty Level of the Tryout Items ... 30
Table 2. Discrimination Power of the Tryout Items ... 30
Table 3. Table of Specification of the Tryout Test ... 34
Table 4. The Distribution Frequency of Students’ PreTest Scores ... 46
Table 5. The Distribution Frequency of Students’ PostTest Scores ... 47
Table 6. Paired-Sample T-Test on the Means of Pretest and Posttest ... 49
Table 7. The Students’ Reading Comprehension Improvement ... 50
Table 8. The distribution of students’ pre-test achievement in each aspect reading Comprehension ... 56
Table 9. The distribution of students’ post-test achievement in each aspect reading Comprehension ... 57
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
This research contains a brief explanation of the introduction. It consists of the background, the formulation of problem, the objectives of the research, the uses of the research, the scope of the research, and the definition of terms.
1.1 Background
Language is a system of communication that enables humans to cooperate. In fact, humans use it to express themselves and manipulate objects in their enviroment. People use language to communicate with other people, express their personal reaction, and think something out. Peitro (1990:50 ) said that language is one of the most useful tools we have as human. It can be deduced that without language we could not express our feeling clearly to other people even engaging in their activities.
2
insists on mastering the four skills of language that are; listening, speaking, reading and writing. Moreover, reading is very essential in learning English in order to get information from the written English. In reading activity, the reader should interpret the meaning of written text. According to Hornby A.S (1972:63) comprehension is the power of understanding fully. It means that comprehension determine the essence of reading process. And by reading with comprehension, the one will recognize the purpose and the important point of the text beside understanding the surface of the text. In other words, it can be said that there will be no reading without comprehension. In the process, the students will perform some tasks given, such as understanding the content. When student cannot get something from what they read, they will not get the knowledge, that is a part of learning.
In some situations, reading in the first languange is very different from foreign language. In fact, reading foreign language is more difficult from reading the first language. Cohen (1994) said that reading foreign language is often slower and less succesful because the reader must understand many unknown vocabularies and complicated sentence structure which make the reader difficult. In addition, it is found that Indonesian students encounter reading difficulties as foreign language learner such as, read slowly word by word, incompetence to apply reading strategy, easy frustated and dissatisfied particularly when they meet some difficult words, read the text aloud in which it may inhibit comprehension, and they confuse to read authentic text in foreign language (Nuttal, 1996 ).
Based on 2006 curriculum (SBC), the student is supposed to deal with many kind of text such as descriptive text, recount text, narrative text, report text, procedure text, and functional texts such as advertisement, brochure, schedule, message, notice, personal letter, invitation (Depdiknas, 2006). In this research, the researcher was only focus in descriptive text. Descriptive text is a simple text that use simple present tense that has been learned since in elementary school. In descriptive text, students have to read after describing something or someone related to material given.
4
technique is dominated by the teacher (teacher-centered). It is necessary for English teacher to make reading materials more interesting and motivating so that the students can progress in reading.
To overcome the problems above, the researcher assumes that there should be some suitable technique in teaching reading in order to motivate the students to read all the texts so they can get the information fully.There are many ways and techniques to increase students’s reading ability. One of them is by using mind mapping technique. In fact teaching reading by using mind mapping is not new issue in English language. Mind mapping technique has been applied in many studies. Buzan (2003) argues that the children can learn in interesting way using certain technique which is called Mind Mapping. In the use of mind mapping, students not only use their left side of their brain but also use the right side of their brain in the same time to identify words in learning language. In mind mapping, students were having occasion to make symbols, lines or signs to help them recognize the words or fact in their mind maps. Futhermore, in their own way, student can comprehend certain topic or material by using mind mapping. So, every student was not feeling depressed in understanding the material.
easily tell other people about their understanding of certain topic by using their own mind mapping.
Reffering to those explanation above, the research is aimed to investigate the effectiveness of mind mapping technique in descriptive text to increase student’s ability in reading comprehension. In details, the research entitle “ THE USE OF MIND MAPPING TECHNIQUE TO INCREASE STUDENTS’ READING COMPREHENSION IN DESCRIPTIVE TEXT AT THE SECOND YEAR STUDENTS OF SMP NEGERI 3 BANDAR LAMPUNG”.
1.2Formulation of the Problems
Based on the background above, the writer formulated the problem as follow :
Is there any significant increase students’ reading comprehension achievement after the implementation mind mapping technique in teaching reading descriptive text at the second year students of SMPN 3 Bandar Lampung ?
1.3Objective of the research
Based on the background above, the objective of this research is:
6
1.4Uses of the research
The uses of research are as follow :
1. Theoretically
The results of this research can be used as the reference for those who want to conduct a research in English teaching process.
2. Practically
This research can be used to English teachers to increase their students’ reading achievement.
1.5Scope of the Research
1.6 Definition of terms
There are some terms used by the writer and to make it clearly, the writer gives the definition as follow :
Reading
It refers to an active process which involves readers, material of reading and the readers’ previous knowledge in order to get meaning of the text they read.( Nuttal, 1987)
Reading comprehension
It refers an active thinking process in which a reader simultaneously extracting and constructing meaning through intercation and involvement with written language (Tankersley, 2005)
Mind mapping
It refers to a technique of making outline which is used the represent words, ideas, tasks, or another linked to arranged radically around a central key word or idea by lines and typically it contains words, ideas, shorts phrase or picture .(Buzan, 2006)
Descriptive text
CHAPTER II
LITERATURE REVIEW
This chapter reviews the theories that support the research. There are some theories that were described in framework. It consists of the concept of reading comprehension, the concept of reading aspects and the concept of teaching reading comprehension . This chapter also discusses about the concept of the descriptive text. Futhermore, this chapter is elaborates mind mapping technique, the advantages and disadvantages of mind mapping, procedures of mind mapping technique in reading descriptive Text, the theoretical assumption and the hypothesis.
2.1Concept of Reading Comprehension
process not a product”. Readers filter understanding through the lens of their knowledge and experience (Tankersley, 2005:108) because she /he is able to relate the information given which has been stored in her/his mind( Clark and Silberstein, 1987, cited in Brown, 2001:299-300).
Based on Howart (2006), reading is just as communicative as any other form of language. It means that reading is an interaction between the reader and the writer through texts where the writer tries to encode the message to the readers. So that the readers try to decode the messages that sent by the writer.
Basiclly, these concept said that reading always deal with printed materials, which stresses on the grasping meaning from printed language. It means that reading activity is the interaction between the perception of the graphic symbols that represent the language and the readers’ language skill, cognitive skill and the knowledge of the world. From this process, the reader tries to create meaning intended by the writer.
Brown stated that reading is comprehending. How much and how easily readers comprehend depends on variables within and outside them (Durkin, 1979 in McIntyre, Hulan, Layne, 2011). The variable include the reader, the activity of reading and the text. Actually, reading English as foreign language seems to be more complicated for the students since it is not their native language according to Brown (2011), but, if those three intersect, it will affect how well comprehension will occur.
10
the activity in their mind. In other words, reading comprehension is an activity to graps the meaning of written materials with full understanding.
Simanjuntak (1988: 4) added that the first point about reading process is reading comprehension. Knowledge is the basic element for comprehension. It means that knowledge related to what we do not know or new information that we have already known. For example, we already knew the word ‘stationary’, there are words denoting the kind of stationary like : pen, book, rules, eraser, etc. And we can imagine those pictures.
Moreover, Doyle (2004) stated that comprehension is a progressive skill in attaching meaning that begin at the same level and proceed to attach meaning to entire reading selection. All comprehension revolve around the reader’s ability in finding main idea and topic sentence from the text.
2.2 Concept of the Reading Aspects
Suparman (2012) stated that there are several aspects of reading comprehension skills that should be mastered by reader to comprehend the text : main idea, specific information, references, inference, and vocabulary. These aspects are explained below:
1) Main Idea
Finding the main idea of a paragraph is one of the most important reading comprehension skills. In some paragraphs, the main idea is not expilicitly stated in one sentence. Instead, it is left to the reader to infer or reason out. In other words, the main idea is the most important idea that the author develops throughout the paragraph. For example, in My family, the main idea of text is ‘ My family has four members’
2) Specific information
Supporting sentence or specific information develops the topic sentence by giving definition, examples, facts, comparison, analogy, cause, and effect statistics and quotation. For example of supporting sentence in the second paragraph of My family is’ My mother is 47 years old’.
3) Reference
12
phrases. It can give the readers signals to find the meaning of words elsewhere in the text. For instance, She in sentence ‘She's thin-faced and she's got long’ refer to his mother (from My family)
4) Inference
Inference is an educational guessing or prediction about something unknown based on available facts and information. It is the logical connection that the reader draws them between his observes or known and what he does not know. For exampel, question ‘ why the writer can not speak Sundanesse well? makes the reader a prediction based on the facts he find in the text.
5) Vocabulary
Vocabulary is the stock of word used by the people or even person. Concerning with those statements indeed vocabulary is fundamental for everyone who wants to speak or to produce utterances for reading. In the Elephant , for instance reader would know that ‘ a carnivore’ is the anwer to
the question ‘ what is the opposite meaning of a herbivore?’ after reading the sentence in the text that build the context for the word ’ a herbivore’.
2.3Teaching Reading Comprehension
1) The ability to read is a wide range of text English. This is language range goal for most teachers seek to develop through independent readers outside EFL/ESL classroom. It is supported by the knowledge of vocabulary that should be the ability to read text. For instance, if student are reading about animal, they should have known most words related to the topic of animal, such as cat, tiger, lion, etc.
2) Building knowledge of language will facilitate reading ability. Students can build their language competence, progress in their reading ability, become more indipendent in their studies, acquire cultural knowlege, and develop confindence and motivation to carry on learning. The teacher’s responsibility is to motivate reading by selecting appropriate materials.
3) The ability to adapt the reading technique according to reading purposes. In this case, teacher with EFL/ESL, learners can use a variety of adapted texts or authentic text that are suitable with the students’ level. These students are then taught to use different reading techniques for specific purposes. Such as, skimming may be sufficient in reading for finding specific information, but
would not serve well in reading for entertaiment.
14
5) Taking a critical stance to the contents of the texts. It can be implemented at advance level, in which students can check the authenticity of the text by looking at the following indicators: whether the article gives the name of the author or not, the date of publication, the aim of article, etc.
6) Developing an awareness of the structure of written text in English. In creative reading, students would be acquainted with writing mechanisms. For example, when they have to read other texts, they will have the knowlege of the text structure that is useful in their effort to achieve comprehension.
Woods (2005:63) classifies the activities in reading class into three a follow :
a) Pre- Reading Tasks
This task can be in form of vocabulary games,word searches, and matching synonyms. These activities can help students to approach a text in more confident way. Pre-reading stage helps the students activate the relevant schema.
b) While-Reading Tasks
c) Post-Reading Tasks
These tasks follow up the work covered and seek to extend candidates. Such as activities are directed writing activities, or role play and group discussion activities.
Principally, the aim of teaching reading is to develop students’ skill of reading English texts effectively and efficiently. Effective and efficient reading is always useful and tending to focus mainly on the purposes of the activity. This is realized when students are reading and interacting with various types of texts.
In short, in teaching reading, the teacher should provide a strategy to reach the purpose of reading to anticipate the different types of reading text in teaching reading. Therefore, in teaching reading, apropriate and possible technique should be applied based on the purpose of reading in order to get the most of classroom reading activities.
2.4 Concept of Descriptive text
16
to tell about the subject by describing its features without including person opinions. Futhermore, Mark and Anderson (2003) elaborate a factual description differs from a informational report because describes a specific subject rather than a general group. For example, the descriptions of a specific animal, the descriptions of a particular building or descriptions of a specific person.
As described by Gerot and Wigel (1994: 208), the generic structure in descriptive text are indentification used to identify phenomenon to be described and desription used to mentions parts, qualities, and characteristics of subject being described. According to Mark and Anderson (2006), in a paragraph of the descriptive text, it usually has an opening paragraph by introducing the subject of the description that give the readers brief details about when, where, who, or what. A series of paragraphs that describe one features of the subject, and a concluding section that signals the end of description (Gerot and Wigel 1994).
MY FAMILY
Identification My family has four members: those are I, my sister, and parents of course.
Description My mother is 47 years old. Her name's Anisa. She's thin-faced and she's got long, blond hair and beautiful green eyes. She is still slim because she always tries to stay in shape. She is very good-looking, always well-dressed and elegant. My father, Lukman, is 5 years older than my mother. He is 52. In spite of his age he's still black-haired, with several grey hairs. He has bright blue eyes. He is quite tall, but a bit shorter than me. He's very hard-working. Besides that he is working in a travel company. He can even make a dinner when my mother is outside. His cooking and his meals are always very tasty as well as my mothers'.
Finally, my sister Nadina. She is 22. She is also red-haired and green-eyed. She has long wavy hair and freckles. She is definitely shorter than me. She is rather introverted. But she is very sensible, smart and co-operative. Right now she is studying English and also knows Arabic and Mandarin. I want to be so smart as she is. They all, except me, speak Sundanese very well, because we were living in Bandung for 5 years. My sister have been going to primary school there. Unfortunately I was only 3 when we were leaving to Jakarta, so I can't speak Sundanese. Now we are happily living in Jakarta.
18
has charateristic in the form of generic structure and language feature which make the text has certain characteristics that will be different from the other text genres.
2.5 Concept of Mind Mapping Technique
Mind mapping is popularized by Tony Buzan who claims that it is an enourmous superior note taking method. Buzan (2006) argued that mind mapping is a diagram which created as a way to organize ideas and to represent words, tasks, or another linked to an arranged radically around a central keywords by lines and typically it contains words, colors, short phrase, or picture.
Moreover, mind mapping is a technique which enhances creativity used to generate, visualize, structure, and classify idea, and as an aid in studying, organizing, problem solving, decision making, and writting (Buzan, 2006). In line with that, Margulies (1991) states that mind mapping is an analytical process that involves creativity integrating a combination of visual, colour, codes, words, and connectors. It can be employed as a method to takes notes, to study before an exam, to brainstrom, or make connections between ideas.
1) The central topic is the starting point for mind map that gives a brief description of a story (Eppler, 2006:2);
2) The main themes of the subject radiate from the central image a branches. The first level of branches is called basic ordering ideas that can be organized into different sections or topic. (Eppler, 2006:2 & Margulies, 1991);
3) The topic of lesser importance are represent as ‘twigs’ of the relevant branch (Margulies, 1991);
4) Keywords are the words given to each of branches to convey meaning of the topic(Eppler, 2006:2);
5) Images are widely seen as the best way to describe a mind mapping because it can give better meaning than words. It can be used anywhere, as a subtitute for central topic, the branch or instead of a keyword on the branch(Eppler, 2006:2).
Mind mapping can help someone to maximizes the potential ability of the brain to memorize and organize ideas (Wycoff, 2003, cited in Kusumaningsih, 2008) because mind map help enhance the brain’s capacity to recall information (Beare, 2009). It also motivating way for students to summirize a unit, because it assists in digesting information, retaining it and exploring new concepts and topics in our own unique way (Margulies, 1991).
20
information in mind map. In line with that, the usage of visual and colors can provides an interesting way to make sense of something the student is learning (Margulies, 1991) and maximize the brain’s ability in associating number with visual qualities (image and color) and as a result, the memory will able to store more facts (Beare, 2009). The following example of mind mapping :
(prafulla.net)
2.6. Advantages and Disadvantages of Mind Mapping
Mind mapping has some advantages and disadvantages for teaching. Althought mind mapping is good technique for teaching reading, but mind mapping also has disadvantages.
2.6.1 The advantages of Mind Mapping
Buzan (2007) proposes to use mind mapping technique because it makes students to be imaginative, to find new idea, to save time, to be creative, to keep note, to develop a concept, and to perform a presentation. Moreover, Plotnik (1997 cited in Dolehanty, 2008) states that “ the main advantages to concept mapping are the use of the visual symbols which are easily recognized. It also easy to scan for specific word or general ideas and it allows for a more holistic understanding of a concept”.
In addition, Hofland (2007) argues that mind mapping can contributes to learner’ motivation because of its creative aspects. This statements is supported by Bono (1969 cited in Hofland) who states that “creativity” is a great motivator because it makes people interested in what they are doing. Creativity gives hope that can be a worthwhile idea. Creativity gives the possibility of some sort of achievement everyone. Creativity makes life more fun and more intersting.
22
information in mind mapping. When the students are making their mind mapping, they feel challenge to draw appropriate symbols or pictures because each student wants their mind mapping be the most interesting one. Therefore, it can motivate them to be more creative in the learning process because unconciously they need to increase their imagination.
Additionally, Porter (1999, cited in Kusumaningsih, 2003) states that mind mapping could increase the freedom of expression and instructs the innovative and comprehensive approach in ideas arrangement. It is also supported by Stanley (2004, cited in Kusumaningsih, 2003) who affirms that mind mapping techniques can help students generate their ideas more easily
Based on theories above, it can be concluded that the use of mind mapping technique in classroom is effective because it could increase student’s motivation and make the teachers easier to explain the learning material.
2.6.2 The Disadvantages Of Mind Mapping
2.7 Procedures of Teaching Reading Comprehension by Using Mind Mapping Technique in Descriptive Text
Based on the theory, the researcher gives treatment to the students by understanding the teaching reading descriptive text through mind mapping technique using descritive text as the materials. The teaching procedures are described based on the steps implemented for mind mapping technique
Pre reading activity
In pre reading activity, it is as an opening act in order to lead the teacher to the core of teaching and learning. Pre-activity facilities students to build up their schemata before coming to the topic of the lesson.
The main purpose of giving pre-reading activities is to lead students’ attention to the topic. According to Markstein and Hirasawa (1981: 183), if the teacher spends more time in introducing the reading, the result will be better. Careful reading preparation really helps the intermediate level students which give them benefit to be more receptive to the content. In general, pre-reading activities that will do in class as follows: brainstroming, showing picture, and asking question based on the topic.
1) Greeting
2) The teacher checks the students’ attendance list.
24
4) The teacher brainstroms students knowledge of the text by asking several questions related to the theme they just have already heard.
5) The students are informed the material they are going to learn, the goals of learning to achieve and reading technique the students use.
While reading activity
6) The students competitively complete the provided cluster related to the question from the teacher.
7) Based on the students’ answer, the teacher make mind mapping as the example in the white board, to make the students understand when they make their own mind map.
8) The teacher started make mind mapping in the center of blank page in the whiteboard and use image in the central idea. After that, the teacher connect to each branches to central image and in each branches, the teacher give the keywords to make the student understand when they are fill in the branches.
9) The students get the text from the teacher after that the students read the text and the students make their own mind map.
10) Some students explain their mind mapping.
11) Asks the students to answer the question that relates with the text which have given by the teacher.
Post reading activity
13) The teacher arises the students’ reflection by asking them, what they have got and what they have learnt.
14) The teacher closes the meeting while greeting the learners.
By implement this technique, it is expected that there was a significant difference of students’s achievement in understanding reading descriptive text through mind mapping technique and there is an increase of learners’ reading achivement before and after being taught through mind mapping technique.
2.8Theoretical Assumption
Students’ reading ability can be developed through various techniques. The same technique might be better to be applied in reading comprehension ability. One of reading ability for the students is identifying main idea, references, inference, finding detail information, and vocabulary. The students have to be able to identify main idea in various types of texts
26
understanding and memorizing. When the students interpret the texts visually, it reflects their understanding of what they have read in a unique way.
Transferring these visuals into words, phrases, and sentences make it easier as the ideas and comprehension of the texts has become much clearer to them. In line with this process above, the students will be more active in the class after using mind mapping technique. It helps the students to create meaningfull reading experiences in the classroom and it is an effective technique in understanding reading skill for students’ achievement because there will be significant differences of their understanding toward the reading text and finally toward their achivement.
2.9 Hypothesis
Based on the theoretical assumption above, the researcher formulated the hypothesis as follows:
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD
This chapter discusses the methods of research used in this study, those are: the research design, population and sample, data collecting technique, proceures of collecting data, criteria of good test of reading, the data analysis, data treatment, hypotesis testing, and statistical testing.
3.1 Research Design
28
In this study, reading test was conducted to find out whether there was significant changes in experimental group after being given mind mapping technique or not by comparing the average score (mean) of the pre-test with the average score (mean) of the post-test. The researcher was conducted pretest, three treatments, and posttest. In this design, pretest and posttest was administered to see whether mind mapping technique can be used to increase students’ reading comprehension achievement. According to Setiyadi (2006: 132), the design of the study as follows
T1 X T2
Where :
T1 = Pretest
X = Treatments
T2 = Posttest
3.2. Population and Sample
priority class. It was applied based on the consideration that every student in population has the same chance to be chosen in order to avoid the subjectivity in the research (Setiyadi, 2006:39). The steps in determining experimental group and try out group were the writer provides seven pieces of paper printed the name of class of population. Then, the writer takes two classes randomly and get the first classes as try out group and the second as experimental class. The experimental class has pretest, posttest, three treatments.
3.3 Data Collecting Technique
In collecting the data, the research uses some technique as follows:
1) Try Out Test
The try out test was administered to Class VIII F that considered of 34 students.
This test was given to identify the quality of the test before it was used to obtain
the data for the research. The test included multiple choices that consist of 40
items with four alternative options A, B, C, and D: one correct response and three
distractors. The try out test was conducted for 90 minutes. In determining the
quality of the test the researcher see in these aspects such as validity, reliability,
level of difficulty, and the discrimination power. From the computation of level of
30
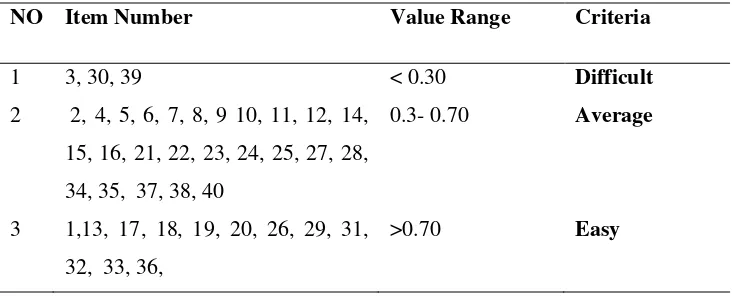
[image:40.612.135.501.297.446.2]were 25 items which categorized as the moderate difficulty items (in the range of 0.30-0.70) 12 items in easy category which had less than 0.20 indexes. In short, the researcher had 20 test items that had a good discrimination power and positive value since a large acknowledgeable the students that poor students got the items correct. The result is shown in table belows, which summarize the difficulty level and the discrimination power:
Table 1. Difficulty Level of the Tryout items
NO Item Number Value Range Criteria
1 3, 30, 39 < 0.30 Difficult
2 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 10, 11, 12, 14, 15, 16, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 27, 28, 34, 35, 37, 38, 40
0.3- 0.70 Average
3 1,13, 17, 18, 19, 20, 26, 29, 31, 32, 33, 36,
>0.70 Easy
Table 2. Discrimination Power of the Tryout items
NO Item Number Value Range Criteria
1 1, 3, 13, 17, 18, 19, 20, 26, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 36, 39
<0.20 Poor
2 2, 4, 5,6, 7,8 9, 10, 11, 12, 14, 15,16, 21,22, 23, 24,25, 27,28, 34, 35, 37, 38, 40
2) Pre-test
For the pretest, the reseacher took Class VIII D that consisted of 34 students. This
test was administered to find out the students’ basic reading comprehension
before treatments. The test included multiple choices that consist of 25 items with
four alternative options A, B, C, and D: one correct response and three distractors.
The try out test was conducted for 45 minutes.
3) Treatment
After the pretest, the researcher were conducted the treatment for three meetings,
which took 90 minutes in every meeting. The researcher was teach reading
comprehension of descriptive text by using mind mapping technique to the
students experimental class.
4) Posttest.
The posttest was conducted after the treatment. It was to evaluate the students’
reading comprehension achievement after giving the treatments. The items for the
posttest were similiar to those of the pretest, only the order of the texts and their
corresponding items were rearranged. The test were multiple choices that consist
32
3.4 Procedures of Collecting Data
In collecting the data, the researcher used the following steps:
1) Determining the population and sample : there were seven classes of the second year students of SMPN 3 Bandar Lampung. The researcher chose two classes, VIII F as a try out class and VIII D as the sample class by lottery. 2) Selecting the instrument materials : the reseacher selected the material was
chosen from text book. The selecting process considered materials that has been taught to the students and the students interest.
3) Administering the try out test : the test was done in order to measure the level of difficulty (LD) and discrimination power (DP) as well as find out the reliability and validity of the test.
4) Administering the pretest: pretest was conducted before the treatments. It is aimed to check students’ reading ability in determining main idea, references, inference, finding detail information, and vocabulary in texts. Pretest is administered for about 45 minutes.
5) Giving treatment: three treatments by using mind mapping are given in two weeks. The treatment was conducted in three meetings and 90 minutes for each. The treatments was classroom activity, which uses an apply mind mapping technique in reading.
vocabulary after the treatments. It was administered for 45 minutes in experimental group.
7) Analyzing the data and testing hypothesis : after scoring students’ work was finished, the reseacher compared the result of pretes and posttest to see
whether the score of posttest is higher than pretest.
3.5 Criteria of Good Test of Reading
The two reading tests were given to the students to check their reading
comprehension achievement. They are pretest and posttest. The researcher was used
objective test. It was multiple choice tests consists of four options (A, B, C, D), to
make it easy to check and to give score. The material was descriptive text. The
researcher were given 25 items for pretest and 25 items for posttest. The purpose of
pretest was to know the students’ reading comprehension achievement before
treatments. The purpose of posttest was to know the students’ increase of reading
comprehension achievement after treatments. To know whether the test was good or
not, some criteria should be conseidered. The criteria of good test were : validity
(content validity and construct validity), reliability, level of difficulty and
discrimiination power.
3.5.1 Validity
34
validity according to the different purpose of the tests. In this research, the researcher were use content validity and construct validity.
3.5.1.1 Content Validity
Content validity is the extent to which a test measures a representative sample of the subject matter content, the focus of content validity is adequancy of the sample and simply on the appearance of the test (Hatch and Farhady,1982:251).
In this research, the researcher was formulated table specification, so every test item
can be matched with the goal and the materials have been taught. The content of the
[image:44.612.120.489.408.550.2]item is presenteds in the table of specification below:
Table 3. The table of specification of Data Collecting Instrument
No Reading Skills Item Numbers Percentage
(%)
1 Determining main idea 6, 10, 13, 19, 26, 30, 37 17.5%
2 Finding detailed
information
4, 5, 8, 9, 17, 28, 29, 31, 34, 36, 38
27.5%
3 References 2, 12, 23, 25, 32, 39 15%
4 Inferences 1, 7, 14, 16, 18, 21, 24, 27 20%
5 Vocabularies 3, 11, 15, 20, 22 , 33, 35, 40 20%
Total 40 100%
spesific informaton of the text that was why the determaining main idea, finding specific information, inference and vocabulary took bigger part than finding reference
3.5.1.2 Construct Validity
Construct validity is concerned with whether the test is actually in line with the theory of what it means to know the language (Shohamy. 1985; 74). Knowing the test is true reflection of the theory in reading comprehension, the researcher was examined whether the test questions actually reflect the means of reading comprehension or not. The test consist of some reading skills namely, determining the main idea, supporting details, reference, inference, vocabulary and specific information.
3.5.2 Reliability
Reliability is defined as the extent to which a questionnaire, test, observation or any
measurement procedure produces the same results on repeated trials. In short, it is
the stability or consistency of scores over time or across ratters. It is a measure of
accuracy, consistency, dependability, or fairness of scores resulting from the
administration of particular examination. According to Heaton (1988:162) reliability
is a necessary characteristic of any good test.
To measure the coefficient of the reliability between odd and even number (reliability
36
Note
= total score of odd number
= the correlation of odd group and even group
= square of X
= square of Y
total number of students
(Henning, 1987:60)
After getting the reliability of half test, the researcher then uses “ Spearmean Brown’s
Prophency Formula” to determine the reliability of the whole test as follows:
Note:
= The reliability of the whole test
= The reliability of half test
(Hatch and Farhady, 1982: 246)
The criteria of reliability are:
0.90 – 1.00 = High
0.50 – 0.89 = Moderate
0.0 – 0.49 = Low
In this research, the result of reliability of the try-out test is 0.79 (see appendix 3). It could be inferred that the test had moderate of reliability, in the range 0.50-0.89. It indicated that this instrument would produce consistent result when it was administered under similar condition and participants but in different time (Hatch and Farhady, 1882: 286). So, it can be concluded that the test was reliable.
3.5.3 Level of dificulty
Arikunto (1993:209) in his book says that the test item are good if they are not too
difficult and not too easy or in the other word the difficulty level is average.
The classification of the difficulty level is as follow (Arikunto, 1993:212):
0,0 – 0,3 = too difficult
0,3 – 0,7 = average
0,7 – 1,0 = too easy
The formula that was used to determine the difficulty level of each test item is as
follow:
LD = R/N
In which:
LD = level of difficulty
R = the number of correct answers
38
Based on the criteria above, there were 6 easy items in the try-out test (1, 4, 6, 8, 30, and 33). There were 7 difficult items (14, 18, 21, 27, 32, 33, and 39). And, there were 27 average items. (see appendix 3).
3.5.4 Discrimination Power
According to Arikunto (1993:213), discrimination power is the ability of the item to
differentiate between the students who have high ability and those who have low
ability. The discrimination power of an indication item the extent, to which the item
discriminates between test taker from the less able. The formula of the discriminate
power is:
! "
In which :
DP : discrimination power
U : the number of students from the upper who answer correctly
L : the number of students from the lower who answer correctly
N : the number of students
(Shohamy, 1985:82)
The criteria of discrimination power are:
a) If the value positive, it has positive discrimination because large number
or more knowledge students than poor students get the item correct. If the
b) If the value negative, it has negative discrimination power because lower
and higher level of students gets the item correct.
c) In general, the higher discrimination index is better. In the classroom
situation most items should be higher than 0.20 indexes.
(Shohamy, 1985:82)
Based on the criteria above, there were 15 items in the try-out test which did not fulfill the standard of discrimination power, since those items had discrimination index under 0.20 which meant that the items had bad and poor discrimination power. By looking discrimination power and level of difficulty, the total items that were administered were 25 items (2, 4, 5,6, 7,8 9, 10, 11, 12, 14, 15,16, 21,22, 23, 24,25, 27,28, 34, 35, 37, 38, and 40). Tose items had discrimination power above 0.21 with the criteria from satisfactory to excellent items. (see appendix 3)
3.5.5 Scoring System
In scoring the students’ results of the test, Arikunto’s formula was be used. The ideal highest score is 100. The score of pretest and posttest was calculated by using this formula:
S = # $ x 100
Where:
S = the final score of the test
R = the total number of the right answers
40
3.6 Data Analysis
Analysis means categorizing, ordering, manipulating, and summarizing of data obtain
answer to research questions (Kerlinger, 1988:125). The purpose of analysis is to
reduce data to be intelligible and interpretable so that the relation of research problem
can be studied.
In order to find out how significant the increasing of the students’ reading
comprehension in descriptive text through mind mapping techinque, the data was
analyzed by these following procedures:
a) Scoring the pretest and posttest
b) Tabulating the results of the tests and calculating the scores of the pretest
and posttest
c) Drawing conclusion from the tabulated result of the pretest and posttest
which statistically analyzed using Repaeted Measuares T-Test computer
through SPSS version 16.0.
3.7 Data Treatment
According to Setiyadi (2006:168-169), using t-test for hypothesis testing has 3 basic assumptions, namely:
1. The data is interval or ratio
3.8 Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing was used to prove whether hypothesis that the proposes by the researcher was accepted or not by using t-test. The researcher used SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Science) version 16.0 for Windows. The researcher used Paired Samples T-test in order to know the significance of the treatments’ effect by comparing the mean of the pre-test and the post-test. The hypothesis was analyzed at significant level of 0.05 in which the hypothesis was approved if sig.< .
The criteria are:
Ho (null hypothesis) is accepted if t-ratio is lower than t-table (t-ratio<t-table). It means that there is no significant increase of students’ reading comprehension achievement of descriptive text after they are taught through Mind Mapping technique.
H1 (alternative hypothesis) is accepted if t-ratio is higher than t-table (t-ratio>t-table). It means that there is a significant increase of students’ reading comprehension achievement of descriptive text after they are taught through Mind Mapping technique .
42
3.9 Statistical Testing
Match t-test is use to analyze the data statistically. It is used since match t-test is probably the most widely used statistical test for the comparison of two means. It can be uses with very small sample sizes. It is uses as the data coming from the sample or known as paired data (Hatch & Farhady, 1982: 108). This research only uses one class for the experimental class and there is no control group. Therefore, match the t-test is used. Match t-t-test is used to analize the data of the increase the students’ reading ability in identify main idea. It compares two kinds of data or mean (average score of the students) prom similar sample (Setiyadi, 2006: 170).
First, scoring the pretest and posttest, then the scores of pretest and posttest are analyzed and compared to find out whether there is a significant increase in students’ ability by calculating the means of both pretest and posttest using match T-test. To find the means of pretest and posttest, a following simple statistic formula is uses:
%
where,
% = mean (average score)
= total number of the students’ score
N = total number of the students
Then after calculating the means of pretest and posttest, the data is analyze by using match t-test. It is used as the data come from the same sample or known as pairing the data (Hatch and Farhady, 1982: 114). The formula is as follows:
& % ' %(
)*+ ,- ./,0/ )*+
)*
1-Where,
%1 = mean of pretest
%2 = mean of posttest
)*+ = standard error of differences between two means (denominator)
)* = standard deviation
n = number of students
(Hatch and Farhady, 1982: 116)
The hypothesis is analyzed at the significant level of .01 in which the hypothese are approved if sig. < .:
Ho : t-ratio t-table accepted
H1 : t-ratio t-table rejected
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
This chapter presents the conclusion of the study and suggestions for future research in related topic. The conclusions of the study are based on the finding and the discussions in the previous chapter.
5.1 Conclusion
In general, the aims of the research were to find out the effectiveness of the use of mind mapping technique in teaching descriptive text to increase students’ reading comprehension. Some conclusions are drawn as follows :
inference, and 12.58% for finding vocabulary. It also can be seen from the result of the hypothesis testing which showed that the Sig. < (p<0.05, p=0.000).
5.2 Suggestions
Based on the basis of the research findings, some suggestions are proposed for teacher, students, and future research. The suggestions are as follows:
1) It is suggested to English teachers to apply mind mapping technique in descriptive text to make the students well prepared with the ability to identify the language feature and generic structure from the text. The teachers also suggested to give brainstroming before asking the student to make mind mapping. It is important to make students know what they have to do with the text, what kind of information that they need to find from the text.
2) Teachers are also suggested not too much do intervention to the students when they make mind mapping. It is because if the teachers do too much intervention, it is make the student can lose their confidence and they may not enjoy the reading process anymore.
64
REFERENCES
Arikunto, Suharsimi. 2010. Prosedur Penelitian Suatu Pendekatan Praktek. Jakarta: Rineka cipta.
Beare, Kenneth. 2009. Reading-Identifying Skill Requirement. [Online]. Available at About.com Guide. Accessed on October 12th 2012.
Brown. 1982. Reading diagnosis and remediation. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice- hall, Inc.
Brown, H. Douglas. 2001. Language Assessment: Principle and Classroom Practices. New York: Addison Wesley Longman, Inc.
Buzan, Tony. 2000. The Power of Mind Mapping: “How to Use Mind Maps to Boost Your Creativity, Achive Faster Success, Greater Results, and Develop Winning Ideas aat the Speed of Thought”. (online). Available at
www.FortuneWell.com. Accessed on October 12th 2012
Buzan, Tony. 2003. Mind Maps for Kids (the shortcut to success as school). English: Thorson.
Buzan, Tony. 2006. Learning Skills: Mind Mapping: Mind mapping, whole
brain note taking, uses both sides of your brain to study subjects usually only studied with your left brain. (online). Available at www.FortuneWell.com. Accessed on October 12th 2012.
Cohen, L. Manion, L. 1994. Research Method in Education: Fourth Edition. New Fetter Lane: Rout ledge 11.
Depdiknas. 2006. Materi Sosialisasi dan Penelitian Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP). Jakarta: Depdiknas.
Dolehanty, C. 2008. Concept Mind Mapping and Reading Comprehension. [Online] Available at http://www.paec.org/david/reading/general.pdf. Accessed on October 18th 2012.
Eppler, Martin J. 2006. A Comparison Between Concept Maps, Mind Maps, Concepptual Diagram, and Visual Methapor as Complementary Tools for Knowledge Construction and Sharing. [Online]. Available at
http://liquidbriefing.com/twiki/pub/Dev/RedEppler2006/comparison between_concept_maps_and other_visualization.pdf. Accessed on October 14th 2012.
Gerot, Linda and Wignell, Peter. 1994. Making Sense of Functional Grammar. Sydney: Antipodean Educational Enterprises (AEE).
Harmer, Jeremy. 1998. How to Teach English. United states: Longman. Hatch, E & Farhady, H. 1982. Research Design and Statisticfor Aplied
Linguistics. Massachusets: Newbury House Publisher.
Heaton, J. B. 1975. Writing English Language Test. New York. Longman Inc. Hedge, Tricia. 2003. Teaching and Learning in the Language Classroom. UK:
OUP.
Henning, G. 1987. A Guide to Language Testing. Cambridge: Newbury House Publishers.
Hobartswan. 2010. Mind Mapping: Learning and Teaching with Both Sides of the Brain. [Online]. Available at
http://www.thefacilitator.com/htdocs/Mind%20Mapping.pdf. Accessed on October 12th 2012.
Hofland, C. 2007. Mind Mapping in the EFL classroom. Fontys Teacher Training College Sittard.
Hornby, A.S. 1972. Oxford Advance Learners Dictionary of Current English. Oxford University Press. New York
Howart, P. 2006. Making Reading Communication. http://academic.cuesta.edu.Html. Accessed on Monday, October 13, 2012, 10 : 05: 25: 30 pm.
Kerlinger, Fred N. and Elazar J. Pedhazur. 1998. Multiple Regression in Behavgioral Research. New York: Rinehaert and Winstion, Inc.
Kusumaningsih, Litani. W. 2008. The Effectiveness of Mind Mapping
Mark, Anderson. Anderson Kathy. 2003. Text Types in English. Malaysia: Original Library.
Markstein, L., & Hirasawa, L. 1981. Developing reading skills. Cambridge: Newbury House Publishers.
McIntyre. Ellen, Hulan. Nancy & Layne, Vucky. 2011. Reading Instructions for Diverse Classroom: Research Based, Culturally Practice. New York: The Guildford Press.
Murley, Diane. 2007. Mind Mapping Complex Information. Retrieved from Acrobat Reader- (2007-11.pdf). Accessed on 14th October 2012. Nuttal, C. 1987. Teaching Reading Skills and Study Skills. Boston. London. Oxforf, R.L. 1990. Language Learniing Strategies: What Every Teacher Should
Know. New York: Heinle & Heinle Publisher, A Division Of Wadsworht. Inc.
Pietro. 1990, Strategies in Communication.Logman group.ltd
Setiyadi, Bambang Ag. 2006. Metode Penelitian Untuk Pengajaran Bahasa Asing: Pendekatan Kuantitatif and Kualitatif. Bandar Lampung: UNILA
Shohamy, E. 1985. A Practical Handbook in Language Testing for The Second Language Teacher. Tel Aviv: Tel Aviv University.
Simanjuntak, E.G. 1988. Developing Reading Skills ELF Students. P2LPTK. Jakarta: Depdikbud.
Suparman, U. 2012. Developing Reading Comprehension Skills and Strategies. Bandung: Arfido Raya.
Tankersley, Karen. 2005. Literacy Strategies for Grades 4-12, Reinforcing the Threads of Reading. Alexandria, Virginia Utara: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development.
Wood, David. 1998. How Children Think and Learn. Oxford, UK: Brasil Black Ltd.
Zahrowi, Ahmad. 2009. Descriptive Text. [Online]. Available at