THE EFFECT OF USING DESCRIPTIVE VIDEO IN
TEACHING LISTENING COMPREHENSION
(Quasi-Experiment Research at the First Year of SMK Islamiyah Ciputat)
A “Skripsi”
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyaand Teachers’ Training in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement for the Degree of Strata1(Bachelor of Art) in English
Language Education
By:
TEGUH FACHMI 1110014000020
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBIYAAND TEACHERS’ TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH
iii Abstract
FACHMI,TEGUH,2014, The Effect of Using Descriptive Video in Learning Listening (Quasi-Experiment Research at First Year of SMK Islamiyah Ciputat,Skripsi, Department of English Education, The Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training, State Islamic University SyarifHidayatullah Jakarta.
Advisor I :ZahrilAnasy, M.Hum. Advisor II :Ertin MA TESOL.
Key Word: Learning Listening, and Descriptive Video.
The purpose of the research is to investigate the effectiveness of using descriptive video in learning listening, specifically it is written on the title of this research, that is
“The Effect of Using Descriptive Video in Learning Listening, Quasi-Experiment Research at First Year of SMK Islamiyah Ciputat.” This research is aimed to determine the effectiveness of using descriptive video in learning listening and without using it, also to find out the student’s ability in learning listening at first year of SMK Islamiyah Ciputat. The method used in this research is the method of quasi-experiment with pretest posttest control group design. Instrument used is form of objective tests as multiple choices, and fill in the blanks.
The research was conducted at first year of SMK Islamiyah Ciputat on Augustus 1st until September 1st 2014 of the school year 2014/2015. The sample used was a student class X Accountancy 1 and X Accountancy 2 with the number of 35 students in each class, the experimental class of class X Accountancy 1 is taught by using null hypothesis (Ho) which says there is significant effect of using descriptive video in learning listening is rejected and the alternative Hypothesis (Ha) which says that there is significant effect of using descriptive video in learning listening is accepted.
iv Abstrak
FACHMI, TEGUH, The Effect of Using Descriptive Video in Learning Listening (Quasi-Experiment Research at First Year of SMK Islamiyah Ciputat). Skripsi, Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Ilmu Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah, Jakarta.
Advisor I :Zahril Anasy.,M.Hum Advisor II: Ertin.,MA TESOL
Kata kunci: Belajar Mendengar (Listening), dan Video Deskripsi.
Tujuan penelitian ini adalah untuk meneliti keefektifan penggunaan video deskripsi dalam pembelajaran listening. Penelitian ini berjudul “The Effect of Using Descriptive Video in Learning Listening, Quasi-Experiment di Kelas Sepuluh SMK
Islamiyah Ciputat”. Penelitian ini dilakukan untuk mengetahui tingkat ke-efektifan penggunaan video deskripsi dalam pengajaran listening dan tanpa menggunakan video deskripsi dalam pengajaran listening, penelitian ini juga dimaksudkan untuk mengetahui tingkat kemampuan listening siswa kelas 10 SMK Islamiyah. Metode yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini adalah Kuasi-Eksperimen menggunakan pre-test dan post-test, control grup desain, instrumen yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini adalah test yang berupa pilihan ganda dan melengkapi yang kosong.
Penelitian ini dilaksanakan di kelas sepuluh SMK Islamiyah pada tanggal 1 Agustus sampai dengan tanggal 1 September 2014 tahun akademik 2014/2015, sampel yang digunakan adalah kelas sepuluh Akuntansi satu dan sepuluh Akuntansi dua dengan jumlah 35 siswa pada masing-masing kelas. Kelas eksperimen adalah kelas x Akuntansi satu yang mendapatkan perlakuanya itu belajar listening
menggunakan video deskripsi dan kelas control adalah kelas x Akuntansi dua yang tidak mendapatkan perlakuan. Setelah diberikan perlakuan terhadap kelas eksperimen dan tanpa perlakuan di kelas control dan setelah dilakukan pre-test dan post-test maka data yang sudah di dapatkan kemudian di analisa menggunkan t-test. Berdasarkan hasil dari kalkulasi statistic, nilai to atau t-observasi adalah 5.758 dan nilai t-table (t-tabel) dengan derajat kebebasan 68 dalam signifikansi 5 persen adalah1.7 dan dalam signifikansi 1 persen adalah 2.4. maka diketahui bahwa to (observasi) lebih tinggi nilainya dari t-tabel, 1.7< 5.758 > 2.4berdasarkan data hasil penghitungan statistic diatas maka dapat disimpulkan bahwa Null Hipotesis (Ho) ditolak, sedangkan Alternatif Hipotesis (Ha) dapat diterima, yang berarti terdapat pengaruh yang sangat berarti dalam pembelajaran listening menggunakan video deskripsi.
v
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
In the name of Allah the Merciful, the Compassionate, all praises be to Allah
Subhanahu WaTa’ala, the almighty God, who has sent Muhammad, peace be upon
him, to be His prophet and messenger for people all over the world. The author
realizes and feels very sure that without His blessing, mercy, and guidance, it would
be impossible for me to finish this “skripsi”.
On this opportunity, the author herewith would like to express his profound
gratitude, more than he can express to Zahril Anasy M.Hum, his first advisor, who
has painstakingly spent his valuable time to guide and give excellent suggestions to
me in preparing this paper. His special thanks also go to Ertin MA TESOL., his
second advisor, for the correction and invaluable criticism and suggestions she has
rendered to me in the completion of the “skripsi”.
In addition, he is also very much indebted toDrs Syauki M.Pd, the present head of
English Education Department. His thanks also go to Didin Nuruddin Hidayat MA
TESOL as my academic advisor who always stimulates and encourages him to finish
the paper. Finally, his thanks go to Mulyono M.Pd the headmaster of SMK Islamiyah
who has permitted him to conduct observations and research at his school.
Last, but far from least, his very sincere thanks especially go to his own beloved
parents, (Mr. Abdul Halim S.Hi and Mrs Icih S.Pd.i) and all of those who have
helped him, who are not mentioned personally here, without their patience, guidance,
and cooperation this paper could have never been written.
Jakarta, September 10th 2014
vi
TABLE OF CONTENT
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Study ……… 1
B. Identification of Problem ………... 3
C. Limitation of Problem ……… 3
D. The Formulation of Problem ………. 4
E. Purpose of Study………. 4
F. Significance of Study ………. 4
CHAPTER II: THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK A. Listening……… 5
1. The Nature of Listening ………. 5
2. Kinds of Listening…………..……….. 6
3. Technique in Teaching Listening………..……. 8
4. Difficulties in Teaching Listening………... 11
B. Video……….. 13
1. Definition of Video ………. 13
C. Descriptive Text………. 14
1. Nature of Text and Descriptive text………. 14
2. Purpose of Descriptive Text……….. 14
3. General Structure of Descriptive Text……….. 15
4. Function of Descriptive Text………. 15
D. Teaching Listening Using Video………. 16
E. Advantages of Using Video in Learning Listening………. 17
F. Research Hypothesis ………... 18
G. Previous Related Study……….. 19
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
vii
1. Research Design and Methodology……… 21
2. Objective of The Research………. 21
3. Time and Place ……….…. 21
4. Population and Sample ………. 22
5. Research Instrument ………. 22
6. Technique of Data Collection ……….. 23
7. Technique of Data Analysis ………. 23
8. Statistical Hypothesis ……… 24
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH FINDING A. RESEARCH FINDING ……… 25
1. Data Description and Data Analysis …………. 25
2. The Testing of The Hypothesis ………. 31
3. Data Interpretation ………. 32
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A. CONCLUSION ……… 34
B. SUGGESTION ………. 34
BIBLIOGRAPHY
viii
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1.1: The Score of pre-test and post-test experimental class………. 25
Table 1.2: The score of pre-test and post-test in control class………….… 27
1 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Study
In learning English there are four skills to be mastered namely
listening, speaking, reading and writing. Listening is receptive skill with
this skill student can get the information from the others, besides that
listening also a precursor skill to learn others English skills. Therefore,
listening is one that must be taught in order to improve student’s language
communication ability. This need is considered as the important thing to
be taught in vocational school due to their preparation to face the field of
work, according to BSNP Badan Standar Nasional Pendidikan states that
in listening skill student should be able to listen for information and
understand simple instructions.1
However, some Indonesian learners still face difficulty in learning
listening especially in getting and understanding the sound. It can be seen
when the writer did a pre-research in SMK Islamiyah Ciputat Tangerang
on Mei 2014. He found that some learners faced difficulty in getting and
understanding the information. They have low score on several listening
comprehension exercises on learners’ score book. The average score of
their listening comprehension exercises was 45. It categorized as low score
because it was below 70 as the English standard score at SMK Islamiyah
Ciputat Tangerang. The result of interview on Thursday, April 27th 2014
with the English teacher also showed that the learners faced difficulty in
understanding and getting the listening comprehension material, it might
occur due to their lack of vocabulary, less of practice on listening
comprehension material and then the availability of listening
comprehension tools such as sound and material are not easy to find.
According to M. Ngalim Purwanto, there are also some social factors
1
Badan Standar Nasional Pendidikan (BSNP) Silabus Bahasa Inggris SMK, Semua
2
which influence the learners’ learning and achievement.2
Those social
factors are family condition, teacher and teaching method, equipment
which used in teaching learning process, learning environment, and social
motivation. As one of factors which influence learners’ achievement, the
teaching methods are important factor because they can affect the learners’
motivation. If the methods are discouraging, the learners will probably
demotivate. On the other hand, if the methods are interesting, the learners
will be motivated.3 Based on the interview with the English teacher in
SMK Islamiyah Ciputat Tangerang, he said that he explained the theme of
listening comprehension material then student listen to the sound, after
listening to the sound then answer some listening comprehension exercises
on their exercise book. This method may not encourage learners’ activities
so that the learners tend not to pay attention and they do not get the
information and understand what the sound talking about, on the other
hand by using visual aids such as video can help them to get the
information and understand what the sound talk about, because audio and
visual are integrated each other to make language understandable.4 Hence,
teaching method is important in teaching learning process because it can
affect students’ motivation in teaching learning process.
Having a good teaching method is one of criteria of good teachers.
Harmer states that the teachers have to create interesting class.5 He or she
has to be able to prepare interesting class atmosphere by using variuos
Carla Meskill, Listening Skills Development Through Multimedia,(New York: University at Albany,1995),P.184
5
3
The English teacher can use a variation of method in teaching English
to make interesting class atmosphere. The teacher also can use various
sources in teaching language, for instance, teaching language by using
authentic visual materials, authentic printed materials, and realia.6 By
using various sources in teaching language, the learners may be more
motivated in learning English especially in learning listening
comprehension. They also would more understand and get more about the
sound while learning listening comprehension
Based on the description above, the researcher selects one of authentic
visual materials that are video because the video may be an effective and
helpful medium to motivate learners in language learning. According to
Carla Meskill she states that video is widely considered more powerful,
more salient, and more comprehensible input than other media for second
and foreign language students.7 In line with that, Susan Stempleski and
Barry Tomalin stated that video is the combination of moving picture and
sound which can present language comprehensively.8 Therefore, teaching
listening comprehension by using descriptive video will presumably affect
learners’ comprehension score because the video can improve learners’ understanding.
Furthermore, in learning language there are many various alternatives
techniques and media that teachers can apply for teaching language skills
especially for improving listening skill such as using, songs, podcasts,
movies or videos.9 Using descriptive video in teaching listening for
information might become an alternative ways because it is easy to
understand the information, motivating and help student to get information
6
Jerry G. Gebhard, Jerry G. Gebhard, Teaching English as a Foreign or Second Language, A Teacher Sel- Development and Methodology Guide: Second Edition, (United States of America: The University of Michigan Press, 2009),p.104
7
Carla Meskill, Listening Skills Development Through Multimedia,(New York:University at Albany,1995),P.184
8
Stempleski, Susan and Tomalin, Barryy,Video In Action Recipes For Using Video In Language Teaching,(Sydney: Prentice Hal,1990),p.3
9
4
correctly, besides that using movies or videos as media also helps student
to know the expression that is used in describing something directly from
authentic material such as video that also trigger students’ sensitivity sense
of hearing.
Based on the authenticity of the material, in this research the
writer will use descriptive video which related to the topic or theme of
material that is taught in ten grade students of SMK Islamiyah, the writer’s
reason of applying this descriptive video is expected to help student in
understanding the information on listening for information. With this
descriptive video the listening material is expected to be easy to deliver
and help the comprehension of student on material and expression used in
describing something. The video is taken from several resources such as
you tube, or website that served a description of something, someone or
place which related to theme or topic in the textbook, for example the
descriptive video about visit Indonesia which describe about the tourism
place around Indonesia.
As the writer read the result from several previous related studies
that average students tend to prefer listening with visual aids rather than
just listen to an audio format. Hence, based on the assumption above it is
expected that teaching listening by using descriptive video can offer an
alternative way on providing the variation techniques in teaching listening.
Finally, the writer has intended to study more and selects his topic about
the “The Effect of Using Descriptive Video in Teaching Listening
Comprehension” (Quasi-Experimental Research at First Year of SMK
5
B. Identification of Problems
According the background study, the writer identifies some problems
relating to the teaching listening:
1. Although many factors that can affect leaners’ achievement,
teaching method is important in teaching learning process
because it can affect learners’ motivation in learning.
2. The teaching method used in SMK Islamiyah Ciputat Tangerang
Selatan may not encourage learners’ activities, especially
teaching method in teaching listening comprehension.
3. Some learners in SMK Islamiyah Ciputat Tangerang Selatan
have low score on several listening comprehension exercises.
4. Students’ lack of vocabulary in learning listening due to
students less of practice
5. Lack of media in teaching listening due to limited facility
6. Teachers have few varieties teaching methodology to make
more interactive listening activity in their class.
C. The Limitation of the Study
In conducting this research, the writer limits the problem to avoid
misunderstanding and only focuses on the effect of the use of descriptive
video in teaching listening comprehension to learners’ score in the ten
grade of SMK Islamiyah Tangerang in 2014/2015 academic year.
D. The Formulation of Problems
Based on identification of problems the writer formulates research
problems as follow:
6
E. Purpose of the study
The purpose of this study is to investigate the effect of the use of
descriptive video in teaching listening to learners’ score. Whether or not the
use of descriptive video can affect the learners’ score. Hopefully this
method becomes an alternative way on providing the variation techniques
in teaching listening.
F. Significance of the Study
The result of this research is expected to give information for:
1. The teachers
For the teachers, the result of this research is expected to give
them information about the effect of using descriptive video in
increasing students’ listening comprehension score, so the teachers can use this method in teaching listening.
2. The students
For the student the research result is expected to motivate them
in learning listening because by using descriptive video, the class
will be interesting. Hence, the students can improve their listening
skill.
3. The reader
For the reader, the research result is expected to give
information and knowledge about the effect of using descriptive
7
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A.Listening
1. The Nature of Listening
Students can understand and response the language by listening. Listening
is one of the most important elements in studying of foreign language.
Listening is needed for natural precursor to speaking EFL. Generally, there are
no a specific definitions of listening but there are consistent element that people
agree should be included in a listening definition. A content analysis of 50
definitions of listening found that the five most used elements were perception,
attention, remembering, and response.1
The author quoted the definition of listening due to not to be confused, as “The selective process of attending to hearing, understanding, and remembering aural symbols.”2
It means that listening not just attending to hearing but also
understanding and remembering information selectively. Hearing is dealing
with sense but listening deals with mind. Therefore, hearing and listening are
being as natural ability, but listening different from hearing. Hearing is simple
recognition of sound but listening implies some conscious attention to the
Glenn in janusik, listening pedagogy: Where Do We Go from Here? In Andrew D. Wolvin,(Ed.)
Listening and Human Communication in 21st Century ,(London: Blackwell Publishing Ltd, 2010),P.204
2
8
2. Kinds of Listening
According to Jeremy Harmer there are two kinds of listening namely
extensive and intensive listening. To improve students listening skill in
listening English Language it is important for them to increase their language
input by practicing extensive and intensive listening. The number of listening
skills practiced would depend on the nature of the listening passage, the level of
the learners, and the purpose of listening.3 Below are the kinds of listening
based on Jeremy Harmer:
a. Extensive listening
This type is where a teacher encourages students to choose for them
what they listen to and do it, for pleasure and general language
improvement, it is can also have a dramatic effect on a students‟ language
learning
Extensive listening has also a greater ease than other types as it is
concerned to promote overall comprehension of a text and never requires
learners to follow every word and understand them. Learners need to
comprehend the text as a whole which is called global understanding.
Activities in this section must be chosen in terms with the proficiency level
of the listeners.
At the lower level they may have problems to organize the
information, so some of non-verbal forms in responding might be given such
3
9
as putting pictures in a right sequence, following directions on a map,
checking of items in a photograph, completing a grid, chart or timetable etc.
At the developed stage, some language based tasks requiring
constructing meaning, inferring decisions, interpreting text and
understanding gist are usually recommended. Completing cloze exercises or
giving one or two word answers, multiple choices, predicting the next
utterances, forming connected sets of notes, inferring opinions, or
interpreting parts of the text are some samples.4
b. Intensive listening
Intensive listening or 'Hearing clearly' is also a prime aspect of
listening as it includes accurate perception without which the second phase
of processing meaning becomes very difficult. Listening intensively is quite
important to understand the language form of the text as we have to
understand both the lexical and grammatical units that lead to form meaning.
So, intensive listening requires attention to specific items of language, sound
or factual detail such as words, phrase, grammatical units, pragmatic units,
sound changes (vowel reduction and consonant assimilation), stress,
intonation and pauses etc. Feedback on accuracy and repetition on the
teacher's part promote success here.5
Intensive listening refers to listening for precise sounds, words,
phrases, grammatical units and pragmatic units. Although listening
4
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English language Teaching Third Edition Completely Revised and Update,(London: Longman,200),P.228
5
10
intensively is not often called for in everyday situations, the ability to listen
intensively whenever required is an essential component of listening
proficiency.
3. Technique in Teaching Listening
Sometimes teacher confused to determine appropriate techniques in
teaching listening. This occurs that listening was traditionally seen as a passive
process by which the listener receives information sent by a speaker.6
Therefore, here by that should make teachers more creative and more
challenged to find the right technique. Here are some teaching techniques of
listening that the author uses in this research which taken from Nation &
Newton and Harmer as followed:
a. Oral cloze exercises
Oral cloze test is the listeners listen to a story and occasionally the
teacher pauses so that the learners can guess the next word in the story. The
word should be easy to guess and the guessing should not interrupt the story
too much. If the learners can produce very little English, a list of possible
words can be put on the board for them to choose from, or they can answer
in their first language. Immediately after the learners have guessed, the
teacher gives the answer7.
6
I.S.P. Nation & J. Newton, Teaching ESL/EFL Listening and Speaking, (New York: Routledge, 2009), p.38
7
I.S.P. Nation & J. Newton, Teaching ESL/EFL Listening and Speaking, (New York: Routledge,
11
b. Silent viewing (for language)
The teacher plays the video at normal speed but without the sound.
Students have to guess what the characters are saying. When they have done
this, the teacher plays the video with sound so that they can check to see if
they guessed correctly.8 This technique can be used either to stimulate
language activity about what is seen on the screen (rather than what is being
said) or to focus what is being said, by a variety of guessing / prediction
tasks.9
c. Freeze frame
Freeze frame at any stage during a video sequence we can „freeze‟ the
picture, stopping the participants dead in their tracks. This is extremely
useful for asking the students what they think will happen next or what the
character will say next.
By these video techniques is expected there is stimulation to remember
the language by guess the word, to stimulate language activity about what is
seen on the screen, and can build students creatively in interpreted the
language. From these techniques above, have the following features as
proposed Nation & Newton as followed:
a. The learners are interested in what they are listening to.
b. They are able to understand what they are listening to.
8
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English Language Teaching; Third Edition Completely Revised and Updated, (England: Longman, 2004), p.286.
9
12
c. The material is at the right level for the learners.
d. There are a few unfamiliar or partly unfamiliar items that they can understand through the help of context, or through the teacher‟s explanation. Some of these items occur several times in the input.
e. There is a little bit of deliberate attention given to language features
without too much interruption to the flow of the story.
f. There are possibilities for interaction during the listening as the teacher
occasionally asks questions or gets the learners to anticipate what will
happen, and as the learners ask the teacher to repeat, slow down, or
explain.
g. There is a large quantity of input.
h. Learners do not have to produce much output.10
From the following features above the teacher forbidden to choose the material or technique without look at the student‟s capacity in listening ability, see number one, the learners are interested in what they are listening
to,so the students will motivated to improve student‟s listening ability due to
the appropriate material and usually students easy to understand the meaning
language of the interesting material what they want.
10
13
4. Difficulties in Teaching Listening
There are many difficulties in teaching listening and become the problems
for teacher to solve it. While listening, usually learners need to hear things more
than once, this problem happen too many learners due to their concentrate or
their understanding.
Teaching listening, especially English has Foreign Language need to pay
special attention to some factor that they strongly influence the speech process,
and can usually prevent comprehension if they are not attended to and can make
its process difficult. These are the following characteristics of spoken language
that make listening process difficult and usually detectable in teaching listening
itself, quoted from Brown which is adopted from several sources.
1. Clustering: attending to appropriate “chunks” of language – phrases,
clauses, constituent.
2. Redundancy: recognizing the kinds of repetitions, rephrasing, elaborations,
and insertions that unrehearsed spoken language often contains, and
benefiting from that recognition.
3. Reduced Forms: understanding the reduced forms that may not have been a part of English learner‟s past learning experience in classes where only formal “textbook” language has been presented.
4. Performance Variables: being able to “weed out” hesitations, false starts,
pauses, and corrections in natural speech.
5. Colloquial Language: comprehending idioms, slang, reduced forms, shared
14
6. Rate of Delivery: keeping up with the speed of delivery, processing
automatically as the speaker continuous.
7. Stress, Rhythm and Intonation: correctly understanding prosodic elements
spoken language, which is almost always much more difficult than
understanding the smaller phonological bits and pieces.
8. Interaction: managing the interactive flow of language from listening to
speaking to listening, etc.11
After seeing the problem above it can be concluded that those problems
were caused by students‟ less of concentration in understanding and getting the
information from the sound. Further the use of video in teaching listening is
expected can ease those problems because video helps learner‟s comprehension
in learning listening.
According to Carla Meskill she states that audio and visual are integrated
each other to make language understandable. In line with that Carla also states
that the use of video in teaching listening can present language more powerful,
more salient, and more comprehensible input than other media for second and
foreign language students.12 Furthermore, Susan Stempleski and Barry Tomalin
stated that video is the combination of moving picture and sound which can
present language comprehensively.13 Therefore, teaching listening
11
H. Douglas Brown, Language Assessment: Principle and Classroom Practices, (New York: Longman, 2004), p. 122.
12
Carla Meskill, Listening Skills Development Through Multimedia,(New York: University at Albany,1995),P.184
13
15
comprehension by using descriptive video will presumably affect learners‟ comprehension score because the video can improve learners‟ understanding.
Besides that from those following above video materials can be a learning
alternative because they contain dialogues from highly proficient English
speakers, which could contribute to an easier understanding of their
pronunciation. Material is collected from English TV series, movies,
advertising, could increase student´s motivation, as Van Duzerin Lady Jhoana
Arteaga (1998) claims that students listen to relevant and interesting things for
them which keep their motivation and attention high.
In line with that as a good teacher we have to make a good selection of
video materials to expose learners to the suitable materials that facilitate their
learning. In addition, by using authentic material as watching video, students
can reduce these difficulties because usually visual and audio are integrated
each other to make language understandable. So that, by using descriptive video
as teaching media in teaching listening, hopefully students can improve their
listening ability.
B.VIDEO
1. Definition of Video
Video according to Oxford Learner‟s Pocket Dictionary video is type of magnetic tape used for recording moving pictures and sound.14 Susan
Stempleski and Barry Tomalin argued that video is the combination of moving
14
16
picture and sound which can present language comprehensively15. Video is the
technology of electronically capturing, recording, processing, storing,
transmitting, and reconstructing a sequence of still images representing scenes
in motion. From the descriptive above, the author defines descriptive video as
several storage formats for moving pictures that contain description of people,
place or historical building. Briefly, also define as the videos that contain
description things.
As multimedia technology video becomes more accessible to teachers and
learners of other languages, its potential as a tool to enhance listening,
hopefully becomes new strategy in teaching listening. Video allows integration
of text, graphics, audio, and motion video in a range of combinations. According to Carla Meskill “video is widely considered more powerful, more salient, and more comprehensible than other media for second and foreign language students”.16
In line with that Brooks said “multimedia systems with video under
learner control are also preferred other instructional activities”.17In short,
multimedia input such as video as an authentic material apparently motivates
learners and engages their attention to aural input.
15
Stempleski, Susan and Tomalin, Barryy,Video In Action Recipes For Using Video In Language Teaching,(Sydney: Prentice Hal,1990),p.3
16
Carla Meskill,Listening Skills Development Through Multimedia,(New York:University at Albany,1995),P.184
17
17
C.Descriptive Video
1. Nature of Descriptive Video
Descriptive video is the video which is used to describe something,
someone or place, one of the characteristic of descriptive video is the narrator
who describes what is happening on the screen. From the definition above it
can be concluded that descriptive video is the video which contain description
of something, someone or place which the narrator is main characteristic of
descriptive video who distinguish with others kind of video. The function of
descriptive video is to provide viewer a deep information of something,
someone or place.
D.Teaching Listening Using Video
Today listening is considered as the importance material in foreign language
classroom. There are several reasons for this growth, emphasizing the role of
comprehensible input, second language acquisition research has given a major
concern to listening. As Rost (1994, pp 141-142) point out, listening is vital in the
language classroom because it provides input for learner. Without understanding
input at the right level, any learning simply cannot begin. Listening is thus
fundamental to speaking.18
Today there are many ways in teaching language, one of them is teaching
listening by using video. Video have become more and more popular in language
teaching for decades. All skills, such as speaking, listening, reading and writing
18
18
can be instructed with videos. Videos are not only used for entertainment, but they
also can provide a great approach for language teaching and learning. The
availability of video materials for teaching listening is high, the choice of videos is
the key which can make videos useful or useless in a lesson plan. In line with that
Susan Stempleski and Barry Tomalin argued that video is a combination of
moving pictures and sound that can present language more comprehensively than
any other teaching medium.
Most video materials show people with objects in a setting particularly if it is
a real setting, when learners watch the video programs; they are exercising their
listening skills. With video the students have the additional clues the visuals give
them while they watch and listen. Therefore, teaching listening by using authentic
material such as video can reduce these difficulties because usually visual and
audio are integrated each other to make language understandable. So that, teaching
listening using video could be new variation way in learning listening.
E.Advantages of Using Video in Learning Listening
According to Joe Hambrook there are several advantages of using video in
classroom language learning:
1. Authenticity
One of the main benefits often claimed for video is that it can show language in
use in the real world. This is very important for learners to know about how
language is used in the real world in order to show them the use of language in
daily life. Hopefully it can help them to have ability for using language
contextually.
19
The increasingly discriminating uses of video have substantially confirmed that
cultural aspects of language and language use are often conveyed with
considerable force on the screen. It is therefore natural that course designers
and others should want video to be a powerful instrument in developing
language learners' awareness of important features of culture and
culture-specific language use.
3. Interactivity
Video is a powerful medium, and it is not surprising that people who use it to
teach languages would like to see their students reacting and responding to
what they see on the screen.19
4. Contexts of use
Careful consideration of the contexts in which materials might be used is
essential for effective course design in interactive video. What are the
constraints of the physical environment (in the learner's living room, in the
classroom, and so on), it will help student to be more comprehension about
using the context of the word.
19
20
F. Research Hypothesis
Ho : Using descriptive video in teaching listening comprehension does not
affect the learners‟ score positively at ten grade student of SMK Islamiyah
Ha : Using descriptive video in teaching listening comprehension affects
the learners‟ score positively at ten grade student of SMK Islamiyah.
G.Previous Related Study
Some related studies conducted by:
1. Fajri Rohman the title of his research is “Using Short Story Video in
Teaching Listening”. The purpose of his research is to find out the effectiveness
of using short story video in teaching listening. He conducted the research at
second grade of SMP Islam Assa‟adah, the sample of his research was 70 students of second grade SMP Assa‟adah divided into two groups, he uses quasi-experiment research control and quasi-experiment group with pre-test and post-test as
an instrument. The result of his research showed that there is significant effect of using short story video in increasing students‟ score in learning listening, it can be seen from the to is higher than tt. on critical signification 5% and 1%
(2.00<9.91>2.65). It means that Ha is accepted and Ho is rejected. This is
provesthat there is an effect of using short story video in teaching listening.
21
used 40 students of premier school as her sample divided into two groups first 20
students as control group and second 20 students as experiment group with
pre-test and post-pre-test as an instrument. The result of her research showed that there
is significant effect of using flash video in increasing students‟ score in learning
listening it can be seen from the to is higher than tt. on critical signification 5%
and 1% (2.00<8.91>2.65). It means that Ha is accepted and Ho is rejected. This is
proves that there is an effect of using flash video in teaching listening.
3. Lady Jhoana Arteaga Potosí, Edwin Andrés Guarín Loaiza and Ana
Catalina López Garcia their tittle of research is “Using Video Materials As A Teaching Strategy For Listening Comprehension”. The purpose of their research is to find out the the effectiveness of using video material as a teaching strategy
for listening comprehension. Their research is focused on analyzing the impact
that videos on listening skill for a group of 5 students of first semester in a
TEFL program of a public university in Colombia. The result of their research
showed that video activities as teaching strategies in a TEFL class have a
positive effect on English listening comprehension. This effect was reflected
mainly in the comparative analysis on listening comprehension tests practiced
during the whole process. It can be evidenced how students obtained better
results in the final test after implementing the video sessions. Consequently,
those results let us to conclude that using video as strategies for teaching
listening comprehension were positively impacted in their listening
comprehension skill.
22
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Research Methodology
1. Time and Place
The research is held at SMK Islamiyah, which is located on Jl. Ki
Hajar Dewantara Ciputat Tangerang Selatan. The research is held from
Augustus until September 2014.
2. Research Design and Methodology
This research uses quantitative method, the design of research is
experiment research, John W. Best defined experimental research as the
description and analysis of what will be or what will occur, under carefully
controlled condition.1 In this research the writer uses quasi-experimental
research. Quasi-experimental research is applied because the writer is able
to control at least one of the most dominant variable of the research2, in
this case the ability of student listening’s skill. The experimental research is chosen to determine influences an outcome or dependent variable3
,
which is the effect of using descriptive video in learning listening to the
students of ten grades SMK Islamiyah Ciputat. In investigating the effect
of using descriptive video in learning listening, two classes of ten grades
are selected. The first class is used as a control group which does not
receive any treatment and the other class as an experimental group which
is taught by using descriptive video the first step the writer explain the
topic of video then ask the students some question related to the topic,
1
Yogesh Kumar Singh, Fundamental of Research Methodology and Statistic,(New Delhi, new Age International Publisher,2006),p134
2
Syaodih,Nana, Sukmadinata,
MetodepenelitianPendidikan(Bandung:PTRemajaRosdakarya,2012),p220.
3
23
after that they watch the video and answer the question related to the
information of the video.
3. Population and Sample
The population of this research is all students of ten grades of SMK
Islamiyah Ciputat which consists of four classes, namely class X TKJ
(Teknik Komputer dan Jaringan)1, X TKJ II, X Tata Boga (TB)1, X
AP(Administrasi Perkantoran), X Accountancy 1, X Accountancy 2. The
writer uses purposive sampling, purposive sampling technique according
to Husaini Usman and R. Purnomo Setiady is used when the researcher
only take the sample which is suitable with the purpose of the research4. In
this case because the researcher uses descriptive video and limits the
content video only about famous historical building and tourism place of
Indonesia as mentioned in core material of descriptive text in curriculum
2013 so that, the sample that is used by the researcher are two classes of
ten class of accountancy SMK Islamiyah, the first class is 35 students as
experimental class consist of 10 male, 25 female and 35 students of the
second one as controlled class consist of 9 men and 26 women .
4. Technique of Data Collection
Collecting data is an important thing, in this research the technique
of data collection which is used by the writer are:
a. Pre–test
The pre-test is given in the beginning of attending class (pre-test is
given before doing the experiment) in order to know students’
knowledge and achievement of the listening material. The instrument
consists of 24 items test consisting of two types:
1. Multiple choices, there are 9 items and each items is scored 5.5 so
the total score of this type is 49.5
4
24
2. Gap filling, completing 15questions and each item is scored 3,3 so
the total score of this type is 49.5
b. Post-test
The post-test is given in the end of the treatment, in order to know
students’ ability and students’ achievement in mastering listening. The
instrument consists of 24 item test consisting of two types:
1. Multiple choice, there are 9 items and each items is scored 5.5 so the
total score of this type is 49.5
2. Gap filling, completing 15 questions and each item is scored 3.3 so
the total score of this type is 49.5
5. Objective of the Research
The objective of this study is to investigate the effect of the use of
descriptive video in teaching listening to learners’ score. Whether or not
the use of descriptive video can affect the learners’ score, compared with
learning listening without using descriptive video at SMK Islamiyah
Ciputat Tangerang Selatan.
6. Research Instrument
a. Pilot Study of Instrument
The pilot test aims to check validity and reliability of the
instrument. It was conducted before doing pre-test and post-test. It
applied out of class control and experimental class, if the respondents
were able to understand the given instruction it was concluded that
instrument can be used as pre-test and post-test.
b. Validity and Reliability Test
After conducting pilot study, validity test and reliability test is
25
what is intended to be measured.5 Meanwhile reliability test is
conducted to know how representative, how consistent, and how
replicable is the measurement, means if we administer the test in the
other class and in the other time we still have the same score’s average.
7. Technique of Data Analysis
In analyzing the data, the writer uses statistical calculating of t-test to
find out the difference score of students’ achievement in learning listening
by using descriptive video. Data processing is the step to know the result
of both experimental class which is using descriptive video in learning
listening as variable X and controlled class without using descriptive video
as variable Y, and their differences.
The writer uses comparative technique. The comparative technique
is an analysis technique to evaluate hypothesis concerning the differences
between two variable examined statistically.
In comparative technique, the variables are compared to recognize
whether or not the differences are significant. The writer uses t-test
formula that adapted from Sudjiono before using t-test formula; the writer
has sought some formula below 6:
a. Determining Mean Variable I (X) with formula:
M1 = the average of variables score
Arthur,Hughes,Testing For Language Teachers Second Edition,( Cambridge : Cambridge University press,2003) p.26.
6
Anas Sudijono.Pengantar Statistik Pendidikan, (Jakarta: PT GrafindoPersada, 2008), p.315
26
c. Determining Standard Deviation Score of Variable X:
d. Determining Standard Deviation Score of Variable Y:
e. Determining of standard Error mean variable X with formula:
√
SE M1 = standard error mean of gained score
SD1 = standard deviation of gained score
N = number of students
f. Determining of standard Error mean variable Y with formula:
√
SE M1 = standard error mean of gained score
SD1 = standard deviation of gained score
N = number of students
g. Determining standard error from mean of variable X and variable Y,
with the formula:
√
∑
√∑
27
h. Determining t- observation (t0) with the formula:
i. Determining t- table (tt) in significant level 5% and 1% with the degree
of freedom (df), with formula:
df = degree of freedom
n = number of student
8. Statistical Hypothesis
To prove the hypothesis, the data obtains from experiment class and
control class was calculated by using t-test formula with assumption as
follow:
H0: µ1 = µ2, or
HA: µ1 ≠ µ2
The criteria for the hypothesis testing are: if tois higher than “t” table
so the null hypothesis (HO) is rejected, this mean that there is difference
score in learning listening achievement between using descriptive video
and without using descriptive video, it can be concluded that video has
28
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDING
A. Data Description and Data Analysis
As described in previous pages that the writer held the field research at
SMK Islamiyah Ciputat, Tangerang Selatan. He held the field research by
taking students’ score of test (Pre-test and post-test). The pre-test is given before the treatment is begun and the post-test is given after the treatment is
finished.
To find out the result of test(pre-test and post-test) the writer makes the
table of the students’ score is as follow:
Table 4.1
The score of pre-test and post-test experimental class
Student Pre-test Post-test Gained Score
1 65 72 7
2 78 80 2
3 67 85 18
4 72 80 8
5 80 85 5
6 82 85 3
7 68 75 7
8 59 75 7
9 60 78 18
10 64 80 16
11 45 60 15
12 52 70 18
13 39 50 11
14 64 84 20
29
16 82 89 7
17 36 64 28
18 60 80 20
19 40 75 35
20 48 64 16
21 72 80 8
22 54 68 14
23 72 90 13
24 49 75 26
25 72 85 13
26 64 80 16
27 70 94 24
28 48 76 28
29 56 72 16
30 34 56 22
31 64 80 16
32 52 72 20
33 48 70 22
34 80 95 15
35 73 85 12
Total 2137 2693 556
Average 61.05 76.94 15.88
Based on table 1.1, we can see that the experimental class highest
pre-test score was 82 while the lowest pre-pre-test score was 34 and the highest
post-test score of experimental class was 95 and the lowest of post-post-test score was
50, from the table above it can be concluded that the ability of student
listening was increased.Moreover, it can be seen from the experimental class’
average score was 15.88compare with the control class’ average score was
30
learning listening. From the student’s post-test score above it can be assumed
that the experiment class has higher score than control class’ post-test score.
Table 4.2
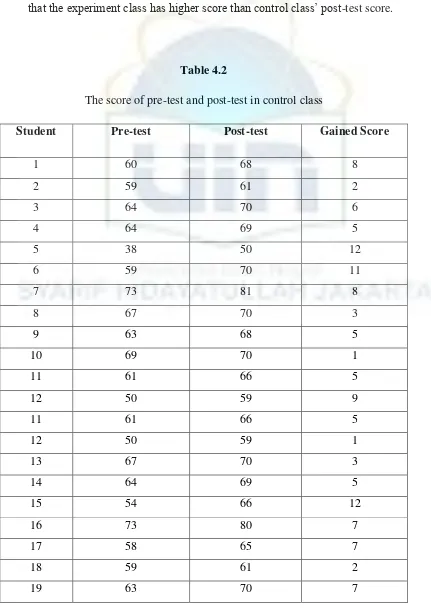
The score of pre-test and post-test in control class
Student Pre-test Post-test Gained Score
1 60 68 8
2 59 61 2
3 64 70 6
4 64 69 5
5 38 50 12
6 59 70 11
7 73 81 8
8 67 70 3
9 63 68 5
10 69 70 1
11 61 66 5
12 50 59 9
11 61 66 5
12 50 59 1
13 67 70 3
14 64 69 5
15 54 66 12
16 73 80 7
17 58 65 7
18 59 61 2
31
20 64 73 9
21 70 79 9
22 56 79 23
23 60 75 15
24 68 68 0
25 59 71 12
26 67 70 3
27 61 66 5
28 73 82 9
29 57 70 13
30 59 60 1
31 60 68 8
32 71 77 6
33 50 55 5
34 67 71 4
35 58 75 17
Total 2165 2422 257
Average 61.85 69.2 7.34
Based on the table 1.2, we can see that the highest pre-test of control
class was 72 while the lowest score was 50. And the highest score of post-test
in control class was 82 while the lowest score of post-test in control class was
55. Moreover, the average score of control class was 7.34 if we compare with
the average score of experiment class was 15.88, from the data above it can
be concluded that the control class has lower score than experiment class, it
means that there is no significant improvement of students’ listening ability
32
Table 4.3
The result of gained score in
Both experimental class and control class
Student X Y X Y X2 Y2
1 7 8 -8.88 0.66 78.85 0.43
2 2 2 -13.88 -5.34 192.65 28.51
3 18 6 2.12 -1.34 4.49 1.79
4 8 5 -7.55 -2.34 57.00 5.47
5 5 12 -10.88 4.66 118.37 21.71
6 3 11 -12.88 3.66 165.89 13.39
7 7 8 -8.88 0.66 78.85 0.44
8 16 3 0.12 -4.34 0.01 18.83
9 18 5 2.12 -2.34 4.49 5.47
10 16 1 0.12 -6.34 0.01 40.19
11 15 5 -0.88 -2.34 0.77 5.47
12 18 9 2.12 -1.66 4.49 2.75
13 11 3 -4.88 -4.34 23.81 18.83
14 20 5 4.12 -2.34 16.97 5.47
15 16 12 0.12 4.66 0.01 21.71
16 7 7 -8.88 -0.34 78.85 0.11
17 28 7 12.12 -0.34 46.89 0.11
18 20 2 4.12 -5.34 16.97 28.51
19 35 7 19.12 -0.34 365.57 0.11
20 16 9 0.12 1.66 0.01 2.75
21 8 9 -7.88 1.66 62.09 2.75
22 14 23 -1.88 15.66 3.53 245.23
23 18 15 2.12 7.66 4.49 58.67
33
25 13 12 -2.88 4.63 8.29 21.43
26 16 3 0.12 -4.34 0.01 18.83
27 24 5 8.12 -2.34 65.93 5.47
28 28 9 12.12 1.66 146.89 2.75
29 16 13 0.12 5.66 0.01 32.03
30 22 1 6.12 -6.34 37.45 40.19
31 16 8 0.12 0.66 0.01 0.43
32 20 6 4.12 -1.34 16.97 1.79
33 22 5 6.12 -2.34 37.45 5.47
34 15 4 -0.88 -3.34 0.77 11.15
35 12 17 -3.88 6.66 15.05 44.35
Total ∑ =556 ∑Y=257 ∑=0 ∑Y= 0 ∑X2=1856.3 ∑Y2=766.46
From the table above the writer got ∑X = 556 by summing all scores in
variable X, while ∑Y = 257 by summing all scores in variable Y, after the
amount is known, T-test formula is used as follow:
1. Determining Mean I with formula:
Mean Variable X = ∑X = 556 = 15.88
n 35
2. Determining Mean II Y = ∑ Y = 257 = 7.34
n 35
3. Determining of Standard Deviation of variable X:
SDx = √∑X
2 =
√ √ = 7.28
n 35
4. Determining of standard Deviation of variable Y:
SDy= √∑ Y2 = √ = √ = 4.6796367380385 = 4.67
34
5. Determining standard of error mean of variable X:
SEMX = SDX =7.28 = 7.28= 7.28=1.2487135506003=1.248
√ √ √ √
6. Determining standard of error mean of variable Y:
SEMy = SDx= 4.67 = 4.67 = 4.67 = 0.8010291595197 = 0.801
√ √ √ √
7. Determining standard of error mean difference of Mxand My :
SEMy–My =√ 0 = √
= √
= √
= 1.483 8. Determining towith formula:
to= Mx- My =15.88-7.34
SEMx-My 1.483
= 5.7585974376 =5.758
9. Determining t-table in significant level 5% and 1% with df
df= (n1 + n2-2) = (35+35-2)=68
the writer gained t-table
= (S.L 5% = 1.7
= (S.L 1% = 2.4
10.The comparison between t-score with t-table
t-score = 1.7<5.758>2.4
B. The Testing of the Hypothesis
The research was held to answer the question whether using descriptive
35
grade students SMK Islamiyah Ciputat. In order to provide answer for the
question above, the Alternative Hypothesis (Ha) and Null Hypothesis (Ho)
were proposed as follows:
1. Null hypothesis (Ho): there is no significant effect of using descriptive
video in learning listening
accepted and the Hypothesis Alternative is rejected. It means that there is
no significant effect of using descriptive video in learning listening.
2. If to ≥ ttable, in significant degree of 1%, the Null Hypothesis (Ho) is
rejected and the Hypothesis Alternative (Ha) is accepted. It means that
there is a significance effect of using descriptive video in learning
listening.
The hypothesis criterion above states that; if to>tt = Hais accepted and
Hoisrejected, and if to<tt= Ha is rejected and Hois accepted. Ha is the
alternative hypothesis, Ho null hypothesis, to is t observation, and ttis t test.
The result of the statistic calculation indicates that the value of
tois5.758 which is higher than ttable(tt) at significance level 5% =1.7 and
ttable(tt) at significance level 1% = 2.4 it means that the null hypothesis (Ho)
is rejected and the alternative Hypothesis (Ha) is accepted.
C. Data Interpretation
From the data result in the table above, the average score of
experimental class is knownwas15.88.Meanwhile in control class that is
taught without using descriptive video the average scores is known 7.34
Based on calculation above, it showed that there is obvious difference
36
by df(n) as 68, at the significant 5% = 1.7 although at the significant 1% =
2.4. Based on calculation and average scores, the last score togot 5.758. As
known “to” is higher than “t” table as 1.7<5.758>2.4.
Because to is higher than “t” table so the null hypothesis (HO) is rejected, this mean that there is difference score in learning listening
achievement between using descriptive video and without using descriptive
video has difference significant. The conclusion is that learning listening by
37 CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
A.Conclusion
After collecting and analyzing the data of this research about the effect of the
use of descriptive video in teaching listening comprehension to learners’ score,
the researcher concludes some points related to this research as following:
1. The use of descriptive video as one of media used in teaching listening
comprehension affected the learners’ score positively. It can be seen from
the analysis of quantitative data The result of the statistic calculation
indicates that the value of to is 5.758 which is higher than ttable (tt) at
significance level 5% =1.7 and ttable(tt) at significance level 1% = 2.4 it
means that the null hypothesis (Ho) is rejected and the alternative
Hypothesis (Ha) is accepted.
2. The students’ ability in learning listening comprehension at ten grade of
SMK Islamiyah are relatively same as showed on the calculation at the
previous chapter, it can be seen from the mean value of control and
experiment class before receiving the treatment, the mean value of control
class was 61.85 while the experiment class 61.05. It means that their ability
relatively equal due to their little differences. But after giving the treatment
there are positive difference between experiment and control group, the
experiment group got higher mean value than control. The mean value of
experiment class was 76.94 while the mean value of control class was 69.2.
3. Interesting media and interesting activities could encourage learners’
motivation in teaching and learning process.
B.Suggestion
As closing of this research, the researcher provides some suggestions as
following:
1. Teachers can use descriptive video as media in teaching listening
38
2. Teachers have to create interesting activities by using interesting media in
order to encourage learners’ motivation in teaching and learning process. 3. For further research, different genders can be investigated to know whether
or not the genders, boy and girl, had different effect toward the use of
descriptive video in teaching listening comprehension which can affect the