STRUCTURAL AMBIGUITY OF NEWS HEADLINES “YAHOO NEWS”
(THE STUDY OF X-BAR THEORY)
A Thesis
Submitted to Letters and Humanity Faculty
In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for
The Degree of Strata 1
SARAH LIZARA SEVIDA 1110026000056
ENGLISH LETTERS DEPARTMENT LETTERS AND HUMANITIES FACULTY
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH JAKARTA
ABSTRACT
Sarah Lizara Sevida, Structural Ambiguity of News Headlines "Yahoo News” (the
Study of X-bar Theory). Thesis: English Letters Department, Letters and
Humanities Faculty, State Islamic University Syarif Hidayatullah, Jakarta, 2015.
This thesis is purposed to depict the structural ambiguity in the headline of Yahoo News by using x-bar theory of syntax and also to find the cause of structural ambiguity in the headline of Yahoo News. The data are collected from the headlines of Yahoo News during 15–21 April 2014. There are 9 data found that possible be structural ambiguity. As the findings, the structural ambiguity occurs in the headlines of Yahoo News, which caused by modifier placement, such as prepositional phrase, relative clause, adjective phrase, and noun phrase, in which, it can be as an adjunct or as a complement in the headline. In conclusion, the headlines of Yahoo News are vulnerable have structural ambiguity, which make the readers have (at least) more than one interpretation meaning in their mind.
Key word: news headlines, structural ambiguity, and x-bar theory.
APPROVEMENT
STRUCTURAL AMBIGUITY OF NEWS HEADLINES “YAHOO NEWS”
(THE STUDY OF X-BAR THEORY)
A Thesis
Submitted to Letters and Humanities Faculty In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for
The Degree of Strata 1
Sarah Lizara Sevida 1110026000056
Approved by
Advisor I Advisor II
Dr. H. Muhammad Farkhan, M.Pd. Rima Muryantina, S.Hum., M.Ling.
19650919 200003 1 002
ENGLISH LETTERS DEPARTMENT LETTERS AND HUMANITIES FACULTY
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH JAKARTA
2015
LEGALIZATION
Name: Sarah Lizara Sevida
NIM: 1110026000056
Title: Structural Ambiguity of News Headlines “Yahoo News” (the Study of X-bar Theory)
The thesis entitled has been defended before the Letter and Humanities Faculty’s Examination Committee on February 6th
, 2015. It has already been
accepted as a partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Strata 1.
Jakarta, February 6th, 2015
Examination Committee
Signature Date
1. Drs. Saefudin, M.Pd. (Chair Person) _________ _________ 19640710 199303 1 006
2. Elve Oktafiyani, M.Hum. (Secretary) _________ _________ 19781003 200112 2 002
3. Dr. H. Muhammad Farkhan, M.Pd. (Advisor I) _________ _________ 19650919 200003 1 002
5. Rima Muryantina, S.Hum., M.Ling. (Advisor II) _________ _________
6. Drs. Saefudin, M.Pd. (Examiner I) _________ _________ 19640710 199303 1 006
7. Yenny Rahmawati, M.Ed. (Examiner II) _________ _________
DECLARATION
I hereby declare that this submission is my own work and that, to the best of my
knowledge and belief, it contains no material previously published or written by
another person nor material which to a substantial extent has been accepted for
award of any other degree or diploma of the university or other institute of higher
learning, except where due to acknowledgement has been made in the text.
Jakarta, February 6th, 2015
Sarah Lizara Sevida
ACKNOWLADGEMENT
In the name of Allah the Most Gracious, the Most Merciful
Alhamdulillahi robbil alaamiin, all praises to Allah SWT, Almighty and
especially her mother, for her every-time-prayers. It makes the writer realize that
she would have never finished her study without their support and prayers.
This work cannot be completed without a great deal of help from many
people, especially Dr. H. Muhammad Farkhan, M.Pd and Rima Muriantina, S.Hum, M.Ling, the writer’s thesis advisor on writing this thesis. The deepest gratitude for their guidance, helpful correction, patient, cooperation, time, and
kindness until this thesis finished.
The writer also would like to express her deepest gratitude to the
individuals for helping her finishing this thesis and for their contribution in the
process of writing until it had become a complete work. They are as follows:
1. Mr. Prof. Dr. Oman Faturahman, M.Hum, as the Dean of Letters and
Humanities Faculty, State Islamic University Syarif Hidayatullah, Jakarta.
2. Mr. Drs. Saefudin, M.Pd, as the Head of English Letters Department.
3. Mrs. Elve Oktafiyani, M.Hum, as the Secretary of English Letters
Department.
4. Dr. H. Muhammad Farkhan, M.Pd, the Vice Dean of Letters and
Humanities Faculty and also as the writer’s advisor for guiding and suggesting her in making a good thesis from the beginning until the end of
writing.
5. All of the lecturers in English Letters Department for teaching her many
things during study.
6. All the staff of library and academic of Adab and Humanities Faculty and
State Islamic University.
7. The writer’s dearest Muhammad Fikri Fauzan for always giving support, motivation, and accompanies her in bad and good time.
8. The writer’s ‘Big family’ friends.
9. All her closed and beloved friends in English Letters Department 2010,
who have been accompanying her from the first semester.
May Allah SWT, The Almighty and The Merciful, bless them all. The writer
realizes that this paper is not fully perfect. Therefore, the writer would like to
accept any constructive suggestion to make this paper better.
Jakarta, February 6th, 2015
The writer
TABLE OF CONTENTS
4. Adverb and Adverbial Phrase………. 14
5. Adjective and Adjective Phrase………... 15
6. Prepositions and Prepositional Phrase……… 15
7. Coordinating Conjunctions………... 16
8. Complement Phrase………... 16
C. Surface and Deep Structure……… 17
D. Structural Ambiguity……….. 17
E. X-bar Theory……… 19
F. The Causes of Structural Ambiguity………. 27
CHAPTER III RESEARCH FINDINGS……… 32
A. Data Description……….. 32
B. Data analysis……… 33
CHAPTER IV CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS……….….. 72
A. Conclusions...……… 72
B. Suggestions..………. 73
BIBLIOGRAPHY……….. 75
APPENDICIES……….. 79
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Study
Language is the most important way of communication, and
communication always takes place in kinds of social context. It means that
when language is used, the people communicate their individual thought, the
cultural beliefs, and practices of the communities. In other words, language is
composed to the people’s idea or message both personal and the broader, and going into society level.1
The communication itself consists of spoken language and written
language. Both languages have difference in the way of uttering the message
or the idea. Spoken language utters the words straightly to hearer, while,
written language does not utter messages straightly to the readers. In brief,
written language is rather hard to understand than spoken language.2
Moreover in written language, in Eva Prášková’s Research Paper ‘Grammar in Newspaper Headline’ Crystal says that there are usual in some types of written language, such as notices, headlines, labels, advertisements,
subheadings, Web sites and other settings.3 Headlines of newspapers in web
1
Julie S. Amberg & Deborah J. Vause, American English: History, Structure, and Usage, (United State of America: Cambridge University Press, 2009), p.3
2M. Rayhan Bustam, “
The Analysis of Ambiguous Structures through the Structural Ambiguity Concept”, (Journal Linguistics Magister: Faculty of Arts – Padjajaran University,
Apollo Project, Vol.1 No.1, 2012), p.1 ; Silvia Rindika Puspita Andriani, “Structural Ambiguity in the Jakarta Post Newspaper’s Headline News”, (S-1 Thesis: English Department, Faculty of Letters, State University of Malang, 2012), p.1
3Eva Prášková, “
Grammar in Newspaper Headlines”, (Bachelor Paper: Faculty of Arts and Philosophy – University of Pardubice, 2009), p.3
sites have known as introducing news reports or as drawing the readers.4 But,
Alireza Bonyadi and Moses Samuel in his article ‘Headlines in Newspaper Editorials: A Contrastive Study’ states,“…, newspaper headlines not only have the function of indicating the topic and summarizing the main content of
the news text, but they also try to help the reader grasp the meaning of the
text.”5 It means that the aim of headlines is using a few short words as possible to deliver the idea.6
Yahoo News is one of electronic media, which provides local and
international news. Sometimes, in Yahoo News, the meaning of headlines can
be misinterpreted and the readers need to follow the news update itself. It is
caused by only minor sentences are used in headlines of Yahoo News, so the
meaning can be misleading.7 In short, the most problem of headlines is
meaning interpretations.
The message or the idea, which has several possible meaning
interpretations are known as ambiguity.8 According to Hurford’s statement in Rayhan’s Journal ‘The Analysis of Ambiguous Structures through the Structural Ambiguity Concepts’ defines, “Any ambiguity resulted from the
ambiguity of a word is a lexical ambiguity, and a sentence which is
ambiguous because its word relates to each other in different way even
4
Hye-Kyung Lee, “Linguistics Variations between English News Headlines in the U.S. and Those in Korea”, (Journal Linguistic Research: Ajou University, 2012), p.330
5
Alireza Bonyadi and Moses Samuel, “Headlines in Newspaper Editorials: A Contrastive
Study”, (Article: SAGE Open – Islamic Azad University and University of Malaya, 2013), p.1
6Eva Prášková,
op.cit.,p.3
7
Ibid., p.1
8
though none of the individual word are ambiguous is structurally
(grammatically) ambiguous”.9
Furthermore, ambiguity becomes one of fundamental language abilities of
speakers, particularly, structurally ambiguous sentences being more
challenging and more interested case. It includes as the criteria for the
assessment of theory of grammar.10 In syntax, the sentence pattern can make
a grammatical ambiguity, which, is caused by having more than one tree
diagrams in a sentence. In other words, it has two different deep structures
although it has same surface structure for each.11 Tree diagram represents
constituent structure in a sentence. The syntactic categories in constituent
structure have relationship between the head of its phrase and the other
members of the phrase, for instance: verb phrase, the head is verb of verb
phrase.12
In analyzing the structural ambiguity, X-bar theory is used because
every phrasal category has a head of its same syntactic structure. Generally,
ambiguity is analyzed by semantic view but in this research, the ambiguity
will be analyzed by syntax view, which is, how words can be combined into
sentences that affect to its meaning of words and sentences.13 Furthermore,
X-bar theory exposes words by deep structure in detail; articulated trees. In
9 M. Rayhan Bustam, op.cit., p.2
10
Danny D. Steinberg, dkk, Pscholinguistics: Language, Mind, and World 2nd Ed., (London: Longman Linguistics Library, 2001), p.345, 362
11
Ibid., p.364
12
Victoria Fromkin, dkk, An Introduction Language 7th Ed., (Boston: Heinle, 2003), p.130
13Diyah Elmawati, “Structural Ambiguity in the Headlines Compiled by Department of
other words, the primary of X-bar theory of phrase structure is how to
generate the correct constituent of the English sentence.14
In this case, the writer emphasizes the analysis only in headlines of
Yahoo News at https://news.yahoo.com. The writer chooses the structurally
ambiguous headlines as her corpus in order to represent the different
interpretation meaning of those headlines itself. The form of communication
that relies on the written language based electronic media on Yahoo News.
The writer is interested in analyzing the headlines because in the headlines of
news, the writer often finds structurally ambiguous meanings, which are able
to confuse the readers, so it can be generated into X-bar theory. The writer
chooses Yahoo News as media because Yahoo provides many features, in
which, the most people use to sign in daily. As we know that, news is written
language that vulnerable makes the meaning of headlines be ambiguous for
reader because it has uncompleted description about its news without reading
overall. In brief, the headlines are more fit as the data of structural ambiguity.
B. Focus of the Study
In this research, the writer would like to focus her study on syntax,
which relates to meaning of the sentence, especially uses X-bar theory on
structurally ambiguous headlines which derives from Yahoo News, in which,
the data is chosen by purposive sampling. The writer chooses the data by
purposive sampling because she prefers to choose structurally ambiguous
14
headlines, which are more fit and clearly can be generated to X-bar theory to
show, how the theory works in analyzing the structurally ambiguous
headlines.
C. Research Questions
To make convenient and simple, the writer tries to formulate the
question to get more specific purpose. The research questions are:
1. Why does the structural ambiguity occur in the headlines of Yahoo
News?
2. How is the structural ambiguity in the headlines of Yahoo News
explained by X-bar theory?
D. Objective of the Study
According to research questions, this research purpose to:
1. Explaining the structural ambiguity in the headline of Yahoo News by
X-bar theory.
2. Describing the causes of structural ambiguity in the headlines of
Yahoo News.
E. Significance of the Study
The writer expects this research will increase the science of the writer in
linguistics field especially syntax. Then, the writer hopes this research will be
people. Besides, this research also will show how X-bar theory can depict
and explain the structural ambiguity represented by the real-life in formal
context like headlines in Yahoo News or other similar contexts.
F. Research Methodology
1. Method of the Study
In this research, the writer uses the qualitative method. The
structurally ambiguous headlines of Yahoo News are intended as source.
The corpus was taken by purposive sampling of the headlines, which are
taken deliberately by the writer. Then, it will be analyzed with X-bar
theory of Noam Chomsky, to depict and to explain the structural
ambiguity of news headlines of Yahoo News during April 15th – 21th, 2014.
2. Data Analysis
The data in this research will be analyzed qualitatively based on the
syntactic theory, which relates the meaning; that is, to analyze the
structurally ambiguous headlines of Yahoo News, which is applied to
X-bar theory of Noam Chomsky, by tree diagram representation is relevant
to the research.
3. Instrument of the Study
This research uses books, websites, dictionary, and software as
structurally ambiguous headlines of Yahoo News. Then the data
contained will be analyzed by X-bar theory of Noam Chomsky.
4. Units of Analysis
This research is qualitative research. It will be conducted by
explanatory descriptive analysis, used Chomsky’s X-bar theory. The unit
analysis in this research is the structurally ambiguous headlines of Yahoo
News, which are taken deliberately by the writer, during 15th – 21th April 2014 at https://news.yahoo.com. Data gained in this research are 9 corpus
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A. Previous Research
There are three relevant previous studies. The first study is by M. Rayhan
Bustam (2012) that entitled “The Analysis of Ambiguous Structures through the Structural Ambiguity Concept”. This research describes the ambiguous structure, such as in Noun Phrase, Prepositional Phrase, Relative Clause, Noun
Clause, and combination of those with conjunction (coordinating) in BNC
(British National Corpus) (1985-1994) and in The Structure of Modern
English: A Linguistic Introduction (2000). He analyzed the ambiguous
structure by using tree diagrams of syntax. He explained the causes of
ambiguous structure and also gave description about the purposed meaning for
each diagram. In the conclusion, he stated that the structural ambiguity can
happen in some structures.15
The second study is by Diyah Elmawati (2013) that entitled “Structural Ambiguity in the Headlines Compiled by Department of Languages, Cultures,
and Linguistics Bucknell University: A Study on the X-bar Theory”. This research describes the syntactically ambiguous headlines from Department of
Languages, Cultures, and Linguistics Bucknell University website, with its
URL (http://www.departments.bucknell.edu/linguistics/synhead.html.). She
depicted the structural ambiguity by using X-bar tree diagrams and also gave
15
M. Rayhan Bustam, “The Analysis of Ambiguous Structures through the Structural Ambiguity Concept”, (Journal Linguistics Magister: Faculty of Arts – Padjajaran University, Apollo Project, Vol.1 No.1, 2012), p.1-10
description about the purposed meaning for each diagram. In the conclusion,
she stated that structural ambiguity is caused by three causes, namely syntactic
category, placement of prepositional phrase that functions as an adjunct, and
subcategorization of verbs.16
The last study is by Silvia Rindika Puspita Andriani (2012) that entitled
“Structural Ambiguity in the Jakarta Post Newspaper’s Headline News”. This
research describes the structurally ambiguous phrases in the Jakarta Post
Newspaper’s headline news and how to resolve it. The data research are taken
during in month; October 2011. She depicted the structural ambiguity by using
X-bar tree diagrams and also gave description about the purposed meaning for
each diagram and the resolving. In the conclusion, she stated that structurally
ambiguous phrases happen in two types, namely Noun Phrase and
Prepositional Phrase. Those structurally ambiguous phrases are able to resolve
by attaching the hyphen or the preposition of, attaching the word; which is/are
and who is/are, and positing the prepositional phrase at the beginning of
sentence.17
Based on relevant previous researches above, position of this research
from the first previous research is to update the data by using electronic
media; Yahoo News (15 – 21 April 2014) while in Rayhan’s Research by using BNC (British National Corpus) (1985-1994) and in The Structure of
16
Diyah Elmawati, “Structural Ambiguity in the Headlines Compiled by Department of Languages, Cultures and Linguistics Bucknell University: A Study on the X-bar Theory”, (Lantern: Journal on English Language, Culture and Literature 2.3, 2013), p. 111-118
17Silvia Rindika Puspita Andriani, “
Modern English: A Linguistic Introduction (2000) and this research also to
complete the description of each diagram from previous research. This
research will explain more about what syntactic category that being the
complement or the adjunct is, in each diagram. Then, this research is not only
giving description about the purposed meaning for each diagram but also
showing to the readers about the meaning of headline which aimed.
Afterwards, position of this research from the second previous research is
to vary the data from Department of Languages, Cultures, and Linguistics
Bucknell University website to headline of electronic media; Yahoo News. As
same as with the first previous research, this research is not only giving
description about the purposed meaning for each diagram but also showing to
the readers about the meaning of headline which aimed.
Then, position of this research from the last previous research is to vary
the data from Jakarta Post (2011) to Yahoo News electronic media (2014) and
to complete the description of each diagram. This research will explain more
about what syntactic category that being the complement or the adjunct is, in
each diagram. And also, this research is not only giving description about the
purposed meaning for each diagram but also showing to the readers about the
meaning of headline which aimed.
B. Grammatical Category
Syntax determines the relevant component parts of a sentence and
grammatical function. In A Modern Course in English Syntax book, Herman
and Liliane state, “Constituents are like building blocks which pattern in certain ways to form larger and larger units, the largest units being the
sentence.” 18
In other words, constituents are all subparts of sentences.19 The
hierarchy of sentence constituents can be illustrated below:
Sentence clause phrase word morpheme20
Sentence is defined as a group of words, which contains two kinds of
phrases.21
(1) Noun (N) and noun phrase (NP)
The name of a person, place, or thing is called noun. Then, a noun
and an article or other modifiers, which are in a group of words is called
noun phrase.22 Norman and Ralph state, “A noun phrase consists of a noun and all the words and word groups that belong with noun and cluster
around it. The noun itself is called the ‘headword’ or ‘head’, and the other words and word groups are modifiers of the noun.” Some examples of
Herman Wekker & Liliane Haegeman, A Modern Course in English Syntax, (London: Routledge, 1989), p.5
19
Richard Veit, Discovering English Grammar, (Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company, 1986), p.9
20
Herman Wekker & Liliane Haegeman, op.cit., p.5
21
Richard Veit, op.cit., p.22
22
Ibid.
23
pronoun: I, you, he, she, it, we, you, they, me, him, her, us, them; (2)
possessive determiner: my, your, his, her, its, our, your, their; (3)
possessive pronoun: mine, yours, his, hers, ours, yours, theirs, and by
adding -‘s (or apostrophe), for example: Sarah’s book, the famous singer’s new album, and etc.; (4) reflexive pronoun: myself, yourself, himself,
herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves; (5) demonstrative
pronoun: this, that, these, those; (6) indefinite pronoun: everybody,
everyone, everything, somebody, someone, something, anybody, anyone,
anything, nobody, no one, none, nothing; and (7) interrogative & relative
pronoun: who, what, whom, which, that.24
(2) Determiner (Det)
There are some categories that include as determiners, which
precede the NP or used to specify the reference of a noun, such as all,
both, half, one, double, twice, a, an, the, that, these, my, your, his, same,
other, latter, last, and next, cardinal numerals, and etc.25
(3) Verb (V) and verb phrase (VP)
Lone word appears after subject (noun phrase) or action that is
expressed by word is called verb phrase.26 Norman and Ralph state, “Verb phrase consists of a verb and all the words and word groups that long with
the verb and cluster around it. The verb itself is called the ‘headword’ or ‘head’, and the other words and word groups are the auxiliaries,
24
Douglas Biber, dkk, Grammar of Spoken and Written English, (London: Longman, 1999), p. 328, 347, 351, 108, 70
25
Ibid., p.258
26
modifiers, and complements of the verb.”27
Verb consists of intransitive
verb and transitive verb. Intransitive verb is a verb that is not followed by
an NP, for example: the game ended. While, transitive verb is a verb that is
followed by NP, for example: A riot ended the game.28
On the other hand, verbs are not always action words. The others
are ‘express being’ that include as form of the linking verb or verb be; am,
is, are, was, and were. Moreover, there are some verbs, which act as
linking verb, such as appear, become, feel, look, remain, seem, smell,
sound, and taste.29 Clearly, verbs can be illustrated as in chart below:30
Active Voice
Norman C. Stageberg & Ralph M. Goodman, op.cit., p.187
28
Richard Veit, op.cit., p.25
29
Ibid, p.31-32
30
had offered offering offered
Moreover, auxiliaries (Aux) are also used with verbs to form verb
phrases, such as (1) present auxiliaries: can/may/must (offer); (2) past
auxiliaries: could/might/should/would (offer); (3) perfect auxiliaries:
could/may—might/should/would (offer); (4) progressive auxiliaries: can— could/ may—might/should/ would (be offering); (5) passive auxiliaries: can—could/ may—might/should/ would (be offered). In addition, auxiliaries of be able to / ought to / have to / had better + simple form of
verb (V1).31
(4) Adverb (Adv) and adverbial phrase (AdvP)
A word that modifies a verb is called adverb. Generally, adverb is
formed by adding the inflection –ly, –wise or –wards, such as quickly, rapidly, angrily, happily, kindly, piecewise, homewards, seawards,
onward, afterwards here, there, eastward, skyward, away, outside, left,
straight, west, soon, late, often, yesterday, now, then, today, tomorrow,
recently, later, always, fast, slowly, early, and etc.32 Furthermore, adverb
is head of adverb phrase. Adverb phrase can occur in a VP or in an AdjP.
As modifiers (adverb modifies verbs while adjective modifies nouns),
adverb can be similar form with adjective, in the way of expressions of
31
Ibid., p.483-485
32
degree comparison; comparative and superlative degree. For example: fast,
faster, fastest; hard, harder, hardest.33
(5) Adjective (Adj) and adjective phrase (AdjP)
Words that can be attached optionally besides article in noun
phrase are called adjective. In other words, adjective is used for describing
or modifying a noun.34 To identify a word that includes as adjective, it can
be seen by derivational endings of its word, such as –ous, -ic(al), -al, -ant or -ent, -ible or –able, -ful, -less, -y, -ish, -some, etc.35 Furthermore,
(6) Prepositions (P) and prepositional phrase (PP)
A word such as of, in, over; past or with, at, by, for, to, from, on,
about, above, after, against, among, before, behind, below, beneath,
between, beyond, despite, except, inside, into, outside, under, upon, by
means of, with reference to, on account of, in regard to, and etc., is called
Douglas Biber, dkk, op.cit., p.531-532
36
Ibid., p.521-522
37
preposition. Norman & Ralph state “Prepositions which are usually
followed by a noun, noun phrase, personal pronoun, or noun-substitute
(object of preposition) called prepositional phrase”.38
(7) Coordinating Conjunctions (Cjc)
Conjunctions provide to connect sentences/clause, or phrases. It
consists of coordinators; and, but, or, for, etc., and subordinators; that, if,
although, so that, as soon as, etc, as in examples: (1) Coordinating
conjunctions that connect to the noun phrase, by words and and or.39 For
example: the man and the woman greeted Donald, they struggled without
food or a reliable supply of water, and etc.40 Furthermore, (2) other
conjoined words can also happen both verb phrase and prepositional
phrase.41 For example: James dated Susan but married Phyllis and
Stephanie stepped off the pier and into the lake.
(8) Complement Phrase (CP)
The word that that precedes the complement clause in the two
sentences is called complementizer (C) or complementizing conjunctions
(Cjcl). Such as in sentence: John believed that Cathy knew that Marry
helped George. 42
38
Norman C. Stageberg & Ralph M. Goodman, op.cit., p.242-234 ; Douglas Biber, dkk, op.cit., p.75
39
Herman Wekker & Liliane Haegeman, Ibid, p.61; Richard Veit, op.cit., p.53
C. Surface and Deep Structure
According to An Introductory English Grammar book, each sentence has
deep structure and surface structure. Deep structure is an abstract grammatical
structure that relates to its meaning. Meanwhile, surface structure relates to the
pronunciation of the sentence.43 For example: the shooting of Oswald was
terrible. Its sentence is able to have two different interpretation meanings. It
means that, the sentence the shooting of Oswald was terrible has different
deep structure but having same surface structure.44
The shooting of Oswald was terrible (Surface structure)
Possible meanings:
The 1st meaning: Someone (not specified) shot Oswald (Deep structure)
The 2nd meaning: Oswald shot someone (not specified) (Deep structure)
D. Structural Ambiguity
Structural ambiguity appears when the words can be grouped in more than
one way. A result of different structure is called structural ambiguity or
syntactic ambiguity or grammatical ambiguity. Having more than one
interpretation meanings are possible because the rules of syntax allow
different structure for the same linear order of words. For instance: old man
and woman. This phrase has two interpretation meanings, as in:
43
Norman C. Stageberg & Ralph M. Goodman, op.cit., p.308, 311
44
Diagram 1 Diagram 2
Based on diagrams above, (1) old modifies man and (2) old modifies both of
man and woman.45 In other words, Structural ambiguity is also known when
the sentence has two different underlying interpretations, which is represented
differently in deep structure. For instance: Annie bumped into a man with an
umbrella. This sentence has two underlying interpretation meanings, as
illustrated in diagrams below.
Diagram 1
Diagram 2
45
Based on diagram above, (1) [Annie bumped [into a man] with an umbrella]
and (2)[Annie bumped into] [a man with an umbrella].46
E. X-bar Theory
The base of X-bar theory determines the characteristic and kind of
syntactic relationship in articulated tree that requires the lexicon.47 The name
of X-bar theory derives from a system for identifying intermediate categories;
X’ and any category (Noun, Adjective, Verb, Preposition, etc.) is represented by X, such as NP for phrasal level, N’ for intermediate level, and N for word
or head level in x-bar notion.48
In other words, each of lexical categories such as Noun, Verb, Preposition,
Adjective is as a ’head’ in the notion of x-bar theory or ‘head’ is as the central
46
George Yule, The Study of language 4th Ed., (New York: Cambridge University Press, 2010), p.98
47
Kristen Malmkjaer, The Linguistics Encyclopedia Second Edition, (London and New York: Roudlege, 2002), p.184
48
core of x-bar theory. Then, it will project to phrasal node of the same category
itself such as noun: noun phrase, verb: verb phrase, and etc. It means that the
‘maximal projection’ of the head is the phrasal category. The figure of x-bar
theory schemata as in:
Based on schemata above, (1) lexical categories project all phrases as in
phrase structure rules; ‘the mother’ with two daughters places the top node on left side and the daughter places on right side. The daughters at the same level
are known as sisters, (2) a head (X0 or X) subcategorizes complements that are
always phrases and, (3) specifiers are optional; it may be words or phrases. In
brief, the first way of X-bar theory works, finding the type of phrase for
determining its ‘head’. The next step, find its specifiers, complements,
adjuncts, and conjunctions.49 Furthermore, Specifiers are represented as sister
to X’ or as daughter of XP. In other words, specifiers are as a modifier, such
as determiner or demonstratives pronoun specifies a NP; adverb never, often,
away, down specifies a VP; a degree word very, quite, so, too, or as specifies
an AdjP. Then, adjuncts are daughters of an intermediate category (X’; N’, V’, A’, P’) and sisters to another intermediate category (X’; N’, V’, A’, P’).
Complements of x-bar trees are represented as sisters of the head (N, V, A, or
49Cheryl A Black, “
P) or a daughter of an intermediate category (X’; N’, V’, A’, P’). Complements are used to complete the meaning of phrase or to provide more
information about the head. As in following examples: (1) His belief that
justice will prevail (CP complement to noun), (2) Happy to be here (Infinite
complement to adjective), (3) Wrote a long letter to his only sister (NP—PP complement to verb), (4) Tell John that his mother is coming to dinner (NP— CP complement to verb).50 It is shown in diagrams as in:51
Another example of diagram, as in:
According to the diagram above, adjunct rules is X’ X’ (ZP) and complement rule is X’ X (WP).52It means that an X’ level category is taken
by adjuncts rule and creates another X’. Whereas an X’ level category is taken
by complements rule and creates an X. So, complement is always being lower
50
Kristen Malamkjaer, op.cit., p.185; Victoria Fromkin 9th Ed., op.cit., p.102-103 and 106
51
Andrew Radford, Transformational Grammar, (New York: Cambridge University Press, 1988), p.177; Andrew Carnie, op.cit., p.163
52
than adjunct or adjunct is always higher than complement in x-bar tree and it
is being closer to the head than adjuncts.53 Such as in diagram below:54
More clearly, there are three examples of sentences: a student of Physics with
a long hair, the book of linguistics and the book with a blue cover. Those
phrases have different x-bar tree although their determiner is followed by noun
and prepositional phrase. The diagram can be illustrated as: Diagram 1 a
student of Physics with a long hair
The rules are (1) determiners are sisters of N’ and daughters of NP, (2) adjuncts are sisters and daughters of N’; with long hair, (3) complements are sisters of N and daughters of N’; student of Physics.55
Diagram 2 the book of linguistics
53
Ibid., p.165
54
Andrew Radford, op.cit., p.178
55
The PP of linguistics above is a complement because it is a sister to N.
Diagram 3 the book with a blue cover
This PP with a blue cover is also a sister to N but it is as adjunct. The
difference of both diagrams is the PP of the first diagram refers to complete
the meaning of the noun, while the PP of the second diagram refers to more
optional and does not fix relating to the NP. In A Generative Introduction
book, to differ a complements from adjunct PP inside NP, is by looking the
preposition taken. Complement in English is almost always using the
preposition of, while adjunct is using other prepositions such as at, under,
from, on, with, to, etc.56 In addition, the characteristic of adjunct rule is
repetitive rule. In other words, adjuncts can create infinite sequence of X’ node, which is, X’ category posits on the left side while another X’ right side
of x-bar tree. In contrast to adjuncts, in complement rule, an X’ category
56
posits on the left side and only X category posits the right side, which means,
it always closer to the head than adjuncts. The characteristic of complement
rule is only once can arrange with XP. So, one N category is for one
complement.57 As in sentence: the book of linguistics with a blue cover from
Heinle by Victoria Fromkin in x-bar tree as follows:
Complements and adjuncts are not only in NP but also they are in VP, AdjP,
AdvP, and PP. To see a complement in VP, the easy way is finding the direct
object of a verb (NP). It means that the object of a verb is a complement.
Then, the prepositional and adverbial of verbs are as adjuncts. For instance:58
I sing [the song] [loudly] [with all my heart]
V direct object adverbial PP
57
Ibid., p.165
58
Moreover, for looking specifiers, the clue is its position will always be the
left-most element. According to the earlier explanation, specifiers are
represented as sister to X’ or as daughter of XP. It shows that the rule has to
arrange at the top of the structure. In NP, the specifier is its determiner and it
can only be joined with other specifiers.59
On the other hand, the phrase structure rule as in S: NP VP cannot fit to
X-bar schemata for explaining a sentence because sentence (S) cannot be the
head of any phrase of x-bar theory. So, to fit a sentence in x-bar rule, there
are two ways to know what the head in a sentence is, (1) creating inflectional
phrase (IP), which is I as the head of this phrase. In other words, tense marker
is as the head because I or Infl is characterized as an inflection of some kinds
on the first verb in the verb group because not all sentences have auxiliary
verb including modals, such as will, has, is, may, might, could, would, can,
and several others. In How to Study Linguistics book, Geoffrey Finch states,
“This forms an I bar by merging with a verb phrase and then it is raised to
59
full IP (or I) by merging with subject elements acting as specifiers.” Clearly, it can be illustrated as in both tree bars below:
In addition to IP, the subject of the sentence; NP is as the specifier of the IP
while the verb phrase acts as the complement of the head.60
(2) By complementizer phrase (CP), in previous sub-chapter A; constituent
structure, CP is indicated as subordinating conjunctions because they provide
to subordinate one sentence or clause to another. Whereas, a complementizer
phrase (CP) in x-bar theory has a complement as its head word and an IP as
its own complement. Moreover, complementizer that, whether, and wh-word
seem to be a marker of complementizer phrase. For instance as in both tree
bars below:61
60
Kristen Malamkjaer, op.cit., p.185; Geoffrey Finch, How to Study Linguistics 2nd Ed., (New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2003), p.187-188; Victoria Fromkin 9th Ed., op.cit., p.107
61
F. The Causes of Structural Ambiguity
In structural ambiguity, attachment ambiguity is being the mostly problem
of modifier placement.62According to Graeme Hirst’s book, there are seven of attachment ambiguities in English, namely:
(1) Prepositional Phrase (PP) attachment, which modifies a verb or a Noun
Phrase (NP). For example: Ross wanted to phone the man with the limp.
This sentence has two underlying interpretation meanings, namely (1)
[Ross wanted to [phone the man] with the limp] means the PP the limp
modifies to verb wanted to or as adjunct of the VPand (2) [Ross wanted to
phone] [the man with the limp] means the PP the limp is attached to the NP
the man as adjunct.63
(2) PP attachment, which may able to attached in more than one NP.64 For
example: The book near the bag with red color is mine. This sentence has
two underlying interpretation meanings, namely (1) [The book [near the
62
Graeme Hirst, Semantic Interpretation and the Resolution of Ambiguity, (New York: Cambridge University Press, 1987), p.131 and p.135
63
Ibid., p.132 and p.135
64
bag] with red color] [is mine] means the PP with red color modifies to the
NP the book or as adjunct of the NP the book and (2) [the book near] [the
bag with red color] [is mine] means the PP with red color is attached to
the NP the bag or as adjunct of the NP the bag.
(3) Relative clauses attachment, which may able to attached in more than one
NP.65 For example: The book near the bag that had red color is mine. This
sentence has two underlying interpretation meanings. To explain the
structural ambiguity, there are two x-bar diagrams will be represented, as
in diagram (1) [the book [near the bag] that had red color] [is mine]
65
Diagram (2) [the book near] [the bag that had red color] [is mine]
In diagram (1), the relative clause that had red color modifies to the NP
the book or as adjunct of the NP the book, while in diagram (2), the
relative clause that had red color is attached to the NP the bag as adjunct.
(4) PP attachment, which modifies Verb Phrase (VP) or Adjective Phrase
underlying interpretation meanings, namely (1) [He seemed nice] [to her]
means he seemed to her to be nice or as adjunct of the VP seemed and (2)
[he seemed] [nice to her] means he seemed to act nicely towards her or as
adjunct of the AdjP nice.66
(5) PP attachment, which may able to attached in more than one VP. For
example: Ross said that Nadia had taken the cleaning out on Tuesday.
This sentence has two underlying interpretation meanings, namely (1)
[Ross said [that Nadia had takenthe cleaning out] on Tuesday] means the
PP on Tuesday modifies to verb said …, which is, on Tuesday and (2)
[Ross said] [that Nadia had taken the cleaning out on Tuesday] means the
PP on Tuesday is attached to the verb had taken ….
(6) Adverb Phrase (AdvP) attachment, which modifies the sentence verb or
the whole sentence. For example: Happily, Nadia cleaned up the mess
Ross had left. This sentence has two underlying interpretation meanings,
namely (1) [Nadia cleaned up the mess Ross had left] [happily]] means the
adverb happily means a fortunate occurrence and (2) [Nadia cleaned up
happily] [the mess Ross had left] means that Nadia feel happy when clean
up the mess.67
(7) Adverb attachments, which placed to two verbs between clauses, such as
deserve and (b) [The friends of you praise sometimes] [deserve it] means
the adverb sometimes is attached to the verb praise.
(2) A good secretary can type quickly written reports. This sentence has
two underlying interpretation meanings, namely (a) [A good secretary can
type quickly] [written reports] means the adverb quickly modifies to verb
type and (b) [A good secretary can type] [quickly written reports] means
the adverb quickly is attached to the NP written reports.68
68
CHAPTER III
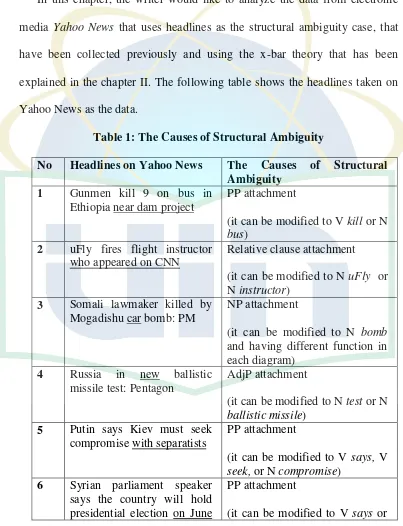
explained in the chapter II. The following table shows the headlines taken on
Yahoo News as the data.
Table 1: The Causes of Structural Ambiguity
No Headlines on Yahoo News The Causes of Structural Ambiguity
6 Syrian parliament speaker says the country will hold presidential election on June
PP attachment
(it can be modified to V says or
3 V hold)
1. The headline “Gunmen kill 9 on bus in Ethiopia near dam project” has two underlying interpretation meanings, which caused by PP attachment. It
means the headline has two deep structures and one surface structure. The
surface structure of this headline is Gunmen kill 9 on bus in Ethiopia near
dam project. Then, the deep structure of this headline (possible meanings);
on diagram (a): Gunmen do kill near dam project to 9 people on bus in
Ethiopia (it does not know surely the position or the location of the bus).
Meanwhile, on diagram (b): Gunmen do kill 9 people on bus, in which the
(a) [Gunmen kill [9 on bus in Ethiopia] near dam project]
The diagram above shows that the NP Gunmen is as the specifier
of the IP, then it has five complements and three adjuncts. They are begun
by the VP kill 9 on bus in Ethiopia near dam project which acts as the
complement of the head of the IP. Afterwards, the V kill that actually can
be transitive or intransitive verb but in this diagram, the V kill is as
transitive verb because it has the object, which is as complement, namely
the NP 9 on bus in Ethiopia. Furthermore, in the NP 9 on bus in Ethiopia,
it has two adjuncts and two complements, which is, the PP on bus and in
Ethiopia is as adjuncts of the N 9 (nine people) whereas the NP bus and
Ethiopia is as complement in each the PP on and in. Then, the V kill is
dam project, it also has object of preposition, which as complement,
namely the NP dam project. Moreover, the head of this diagram is the
tense marker of the V kill; present tense and the meaning of this diagram is
Gunmen do kill near dam project to 9 people on bus in Ethiopia (it does
not know surely the position or the location of the bus).
(b) [Gunmen kill] [9 on bus [in Ethiopia] near dam project]
According to diagram above, it can be drawn that the specifier of
the IP is the NP Gunmen and then, there are five complements and three
adjuncts. In this diagram, the VP kill 9 on bus in Ethiopia near dam
as in previous diagram that becomes the transitive verb because the V kill
is followed by the object of verb; the NP 9 on bus in Ethiopia near dam
project. So, the NP on bus in Ethiopia near dam project is as complement
of the V kill. Furthermore, the NP 9 on bus in Ethiopia near dam project is
followed by three NPs as complement, which is, the NP Ethiopia modifies
the PP in; the NP dam project modifies the PP near; and the NP bus
modifies the PP on and also it is followed by three PPs as adjunct, which
is, the PP on bus near dam project in Ethiopia modifies its NP 9 (9
people); the PP in Ethiopia modifies the PP on bus near dam project; and
the PP near dam project modifies the NP bus. Moreover, the head of this
diagram is the tense marker of the V kill; present tense and the meaning of
this diagram is Gunmen do kill 9 people on bus, in which the location of
bus is near dam project, in Ethiopia. But in this case, it does not know
surely where gunmen do kill is, it is possible if gunmen do kill in
somewhere and they leave the bus near dam project.
Based on both diagrams, the head is the tense marker of the V kill;
characteristic of adjuncts are by seeing the preposition taken, such as from,
at, with, on, etc. While the characteristic of complements is by seeing the
preposition taken, it almost always uses of (Andrew carnie, 2006; 164).
Last but not least, the aimed meaning of the headline actually is diagram
(b). Additionally, Yahoo News reported that attackers fired a public bus
that was carrying 28 citizens on Wednesday, which took place at
Banishangul Gumuz region. In Gumuz region, there is a dam construction.
That attack resulted in death of nine people and wounding seven people
(Yahoo News, April 16, 2014).”
2. The headline “uFly fires flight instructor who appeared on CNN” has two underlying interpretation meanings, which caused by relative clause
attachment. It means the headline has two deep structures and one surface
structure. The surface structure of this headline is uFly fires flight
instructor who appeared on CNN. Then, the deep structure of this headline
(possible meanings); on diagram (a): the person who appeared on CNN is
(a) [uFly [fires flight instructor] who appeared on CNN]
As in diagram above, it consists of three complements and one
adjunct, and the NP uFly acts as the specifier of the NP. After that, the VP
fires flight instructor follows the head of the IP. It means that the VP fires
flight instructor is as the complement of the head. Furthermore, the V fires
can be transitive or intransitive verb but in this diagram, the V fires
becomes transitive verb because the V fires has object of the verb, namely
the NP flight instructor, which as complement of the V fires. Next, in this
diagram, the relative clause who appeared on CNN is attached to the NP
uFly, which is, as the complement of the NP uFly. Meanwhile, the AdjP
flight becomes the adjunct of the NP instructor. Moreover, the head of this
of this diagram is the person who appeared on CNN is uFly’s owner (not
the flight instructor).
(b) [uFly fires] [flight instructor who appeared on CNN]
The diagram above can be drawn that the NP uFly becomes the
specifier of the IP, because the NP uFly is the subject of the sentence and
having one adjunct and three complements, namely the AdjP flight which
attached to the NP instructor acts as the adjunct of the NP instructor; the
relative clause who appeared on CNN is as complement of the NP flight
instructor meanwhile the NP flight instructor who appeared on CNN is as
complement of the transitive verb fires; and the VP fires flight instructor
who appeared on CNN becomes the complement of the head of the IP.
present tense and the meaning of the diagram is the person who appeared
on CNN is flight instructor (not uFly’s owner).
According to both diagrams above, it can be assumed that the head
is the tense marker of the V fires; present tense. Then, the relative clause
who appeared on CNN is as complement in both diagrams but it has
different phrasal category that preceded. In diagram (a), the relative clause
who appeared on CNN is as complement of the NP uFly (Fly’s owner)
while in diagram (b) the relative clause who appeared on CNN is as
complement of the NP flight instructor because it completes the meaning
of both phrases that preceded. So, the relative clause who appeared on
CNN becomes the cause of the structural ambiguity in this headline. In
addition to relative clause, in some cases wh-word can be as marker of CP
(complementizer phrase; interrogative marker) (Kristen Malmkjaer, 2002;
185). However, in this case the wh-word; who is as relative clause. Lastly,
the aimed meaning of the headline refers to diagram (b). According to
Yahoo News, the news was about firing a flight instructor, Mitchell
Sasado, who worked at uFly business. He was fired because of according
to uFly’s owner, Claudio Teixeira, Mitchell often skipped his work and “shamed Canadian” by the way of his dressing. When Sasado appeared on
CNN, he wore jeans and plaid shirt, which made Teixeira, got many
complaints by his email. So, Teixeira considered that Sasado shamed his
3. The headline “Somali lawmaker killed by Mogadishu car bomb: PM” has two underlying interpretation meanings, which happens in NP attachment.
It means the headline has two deep structures and one surface structure.
The surface structure of this headline is uFly fires flight instructor who
appeared on CNN. Then, the deep structure of this headline (possible
meanings); on diagram (a): the person who appeared on CNN is uFly’s owner (not the flight instructor). Meanwhile, on diagram (b): the person
who appeared on CNN is flight instructor (not uFly’s owner).
(a) [Somali lawmaker killed by Mogadishu [car] [bomb]: PM]
By seeing the diagram above, it can be assumed that this diagram
NP Somali lawmaker and having two complements and four adjuncts,
which are the Adj Somali is adjunct of the NP lawmaker. Then, the PP by
car bomb Mogadishu becomes as adjunct of the V killed. Actually, the
verb killed can be transitive or intransitive verb. However, the V killed in
this diagram is as intransitive verb because it is followed directly by the
PP by car bomb Mogadishu (not the NP). After that, the word Mogadishu
is mentioned as the PP (not as the NP) because it shows the location or the
area; in Mogadishu of this headline. Clearly, the PP in Mogadishu is as
adjunct of the NP car bomb. Then, the NP bomb acts as adjunct of the N
car. Furthermore, the NP car bomb Mogadishu becomes as complement of
the PP by. It means the NP car bomb Mogadishu becomes as object of the
PP by. Next, the VP killed by car bomb Mogadishu acts as complement of
the head of the IP. Afterwards, the head of this diagram is the tense marker
of the V killed; passive voice and the meaning of this diagram is Somali
lawmaker killed by car, which is, Somali lawmaker’s car. It is possible if
(b) [Somali lawmaker killed by Mogadishu [car bomb]: PM]
The diagram above shows that the NP Somali lawmaker becomes
the specifier of the IP and also it consists of three complements and three
adjuncts. Actually, the verb killed can be transitive or intransitive verb.
However, the V killed in this diagram is as intransitive verb because it is
straightly followed by the PP by car bomb Mogadishu (not NP). It means
that the PP by car bomb Mogadishu is as adjunct of the V killed. Then, as
same as the description in previous diagram of the word Mogadishu, it is
mentioned as the PP (not as the NP) because it shows the location or the
adjunct of the NP car bomb. Next, the Adj Somali can be optional to the
bomb Mogadishu acts as complement of the head of the IP. After that, the
head of this diagram is the tense marker of the V killed; passive voice and
the meaning of this diagram is Somali lawmaker was killed by someone’s car with the bomb in Mogadishu. It is possible if someone’s car with the bomb is near on Somali lawmaker’s car or on street side or someone throws the bomb form his/her car to Somali lawmaker’s car. In this case,
the bomb NOT posits in Somali lawmaker’s car.
Above all, the head of both diagrams are the tense marker of the V
killed; passive voice. The N bomb has different function in each diagram.
In diagram (a), the N bomb is as adjunct of N car whereas diagram (b) the
N bomb is as complement of N car. So, this N bomb can be the trigger of
the structural ambiguity of this headline. Lastly, according to Yahoo
News, the aimed meaning of the headline actually is diagram (a). The
main point of Yahoo News is Mohamed, the Somali lawmaker, was killed
when a bomb stuck to a vehicle he was in exploded in Mogadishu's
government district (Yahoo News & Digital Journal, April 21, 2014)”.
4. The headline “Russia in new ballistic missile test: Pentagon” has two underlying interpretation meanings, which happens in NP (caused by
adjective). It means the headline has two deep structures and one surface
structure. The surface structure of this headline is Russia in new ballistic
missile test: Pentagon. Then, the deep structure of this headline (possible
meanings); on diagram (a): Russia has new test of ballistic missile (at
Pentagon). Meanwhile, on diagram (b): Russia has test of new ballistic
missile (at Pentagon).
As reflected in the diagram above, this diagram consists of three
complements, two adjuncts and having no specifier. For complements,
they are the NP new ballistic missile test (at) Pentagon, which as the
object of preposition in and the NP ballistic missile, which completes the
NP test. Then, the PP in new ballistic missile test (at) Pentagon is attached
to the NP Russia, which known as further information of the NP Russia
itself. Meanwhile, the AdjP new is attached to NP test acts as adjunct of
the N test. Then, the word Pentagon is mentioned as the PP (not as the
NP) because it shows the location or the area; at Pentagon of this headline.
Clearly, the PP at Pentagon is as adjunct of the NP new ballistic missile
test. Afterwards, the head of this diagram is the N Russia and the meaning
of the diagram is Russia has new test of ballistic missile (at Pentagon).
Based on diagram above, there are three complements and two
adjuncts, namely the NP new ballistic missile test (at) Pentagon is as
complement of the PP in. In other words, the NP new ballistic missile test
(at) Pentagon is as the object of the preposition in. Afterwards, the NP
new ballistic missile becomes complement of the N test because the NP
new ballistic missile gives further information about what the test is. Then,
the PP in new ballistic missile test (at) Pentagon is attached to the NP
Russia, which is, also known as more information of the NP Russia. In
other words, the PP in new ballistic missile test (at) Pentagon is as
complement of the NP Russia. Meanwhile, the AdjP new modifies the NP
ballistic missile, which mentioned as adjunct of the NP ballistic missile.
However, this Adj new can be optional to the NP ballistic missile. Then,
the PP at Pentagon is as adjunct of the NP new ballistic missile test.
Clearly, the word Pentagon is mentioned as the PP (not as the NP) because
it shows the location or the area; at Pentagon of this headline. Moreover,
the head of this diagram is the N Russia and the meaning of this diagram is
Russia has test of new ballistic missile (at Pentagon).
To sum up, the head of both diagrams is the N Russia. The AdjP
new is as adjunct for both diagrams but it has different phrasal category
that preceded. In diagram (a), the Adj new is as adjunct of the N test while
in diagram (b), the Adj new is adjunct of the N ballistic missile. So, the
Adj new can be as the cause of the structural ambiguity in this headline. In
NP (1986:28). According to Yahoo News report, the aimed meaning of the
headline actually is diagram (a). The report tells that Russia performed a
new test-launch of a large-scale ballistic missile (ICBM) as tensions over
Ukraine increased, the Pentagon confirmed on Tuesday (Yahoo News,
April 15, 2014 & Space Daily, April 15, 2014).”
5. The headline “Putin says Kiev must seek compromise with separatists” has three underlying interpretation meanings, which caused by PP attachment.
It means the headline has three deep structures and one surface structure.
The surface structure of this headline is Putin says Kiev must seek
compromise with separatists. Then, the deep structure of this headline
(possible meanings); on diagram (a): Putin together with the separatists
says to Kiev that he must seek compromise. Then, on diagram (b): Putin
says that Kiev must seek together with the separatists about compromise.
Meanwhile, on diagram (c): Putin says that Kiev must seek a compromise
(a) [Putin says [Kiev must seek compromise] with separatists]
By seeing the diagram above, it can be drawn that the NP Putin
which is as the subject of sentence becomes the specifier of the IP and
there is one adjunct and five complements, such as the PP with separatists
modifies the transitive verb says. It means the PP with separatists becomes
adjunct of the transitive verb says. After that, the VP says Kiev must seek
compromise with separatists acts as complement of the head of the IP.
Furthermore, the NP separatists in the PP with separatists becomes
its preposition with. Next, the CP Kiev must seek compromise being the
object of the transitive verb says. In other words, the CP Kiev must seek
compromise is as complement of the transitive verb says. Afterwards, the
VP seek compromise becomes complement of the head of CP. Then, the
NP compromise is as the complement of the V seek. Actually, the verb
seek can be transitive or intransitive verb. However, the V seek in this
diagram is as transitive verb because the NP compromise is the object of
the verb seek. Then, the head of this diagram is the tense marker of the V
says; present tense and the meaning of this diagram is Putin together with
the separatists says to Kiev that he must seek compromise.
The diagram above consists of one adjunct, five complements and
the NP Putin acts as the specifier of the IP. The PP with separatists
becomes adjunct of the V seek in this headline because it can be optional
to the V seek. In addition, the verb seek can be transitive or intransitive
verb. However, the V seek in this diagram is as transitive verb.
Furthermore, the NP compromise is object of the transitive verb seek. So,
the complement of the V seek is the NP compromise. Meanwhile, the NP
separatists in the PP with separatists is the object of preposition with. In
other words, the NP separatists being complement of the Preposition with.
Next, the NP Kiev becomes specifier of the CP. The VP seek compromise
with separatists becomes complement of the head of the CP. Then, the CP
Kiev must seek compromise with separatists is determined as complement
of the transitive verb says because the CP provides further information of
the transitive verb says. The VP says Kiev must seek compromise with
separatists which follows the head of the IP, is known as the complement
of the head of the IP. Moreover, the head of this diagram is the tense
marker of the V says; present tense and the meaning of this diagram is
Putin says that Kiev must seek together with the separatists about