AN ANALYSIS OF THE ENGLISH TEST TYPE FOR THE
FIRST YEAR STUDENTS OF SMAN 1 PAMULANG
TANGERANG BANTEN
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Margarita Noviani Budi Lestari Student Number: 011214108
ENGLISH EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAMME DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
iv
vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I would like to send my greatest praise to The Father and Jesus Christ to whom I put all of my hope, worries, cries, and happiness and who always guides where to go, and shines my life. To Saint Mary, Saint Joseph and my guardian Angel, I am really fortunate since they always pray for me.
I also would like to express my gratitude to Yohana Veniranda, S.Pd., M.Hum, as my sponsor. I really thank her for her guidance, critical opinion, and giving so much useful suggestion in her busy time. To all PBI lecturers, I thank them for sharing the knowledge and experiences with me. To all Sanata Dharma University staff, especially PBI staff, I thank them for helping me with the administration matter.
I am here because of my family. I would like to express my grateful to my beloved mother “Monyi” and father “Babe” who always give me never ending love, passion, prayers, and financial support. I thank my one and only sister Mbak Ririk, Mas Heri, and my niece Joan, who always support me to finish this thesis.
My appreciation also goes to Mbak Riri and the big family of Sanggar Galileo Yogyakarta, all lecturers of Industrial Engineering Study Program at Atmajaya University Yogyakarta, and the big family of SMP Panembahan Senopati Tirtomoyo Wonogiri Central Java. I thank them for inviting and allowing me to teach there, sharing the experiences and developing my talent.
I feel enjoyable in my life because of my special friend Ary “BG” who is always besides me in my cries and happiness. I also thank my truly friends who always brighten my life and gave me many special moments; Vanny, Flor, Jati, Dyah, Emil, Niken, Harin. I am really lucky to have them. I thank them for the happiness, sadness, laughter and cries that they shared to me. I thank all of my classmates in PBI, especially the 2001 academic year students for the cooperation during the study.
vii
Oscar “Crepo”, Seto, Wida, and the others. I will miss every moment that I once had with them.
Last, but not least, I would like to express my thanks to everyone around me that I cannot mention. I really appreciate their supports, prayers, and attentions. Every question and wonder about my study that was sent to me was the power to finish this thesis.
viii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE... i
APPROVAL PAGES ... ii
DEDICATION PAGE ... iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ... v
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS... vi
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... viii
LIST OF TABLES ... xi
ABSTRACT ... xii
ABSTRAK... xiii
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION ... 1
1.1 Background of the Study... 1
1.2 Research Problems ... 2
1.3 Problem Limitation ... 2
1.4 Benefits ... 3
1.5 Definition of Terms... 3
CHAPTER 2: THEORETICAL REVIEW ... 6
2.1Theoretical Description ... 6
ix
Page
2.1.2 Teacher-Made Tests ... 6
2.1.3 Types of Tests ... 7
2.1.4 The Function of Test ... 10
2.1.5 The Characteristics of a Good Test ... 12
2.1.6 English Competency Based Curriculum for SMA... 16
2.1.7 The Objectives of the English Competency Based Curriculum... 18
2.1.8 A Test Blueprint ... 20
2.1.8.1 The Purpose of Test Blueprint ... 20
2.1.8.2 Preparing the Test Blueprint ... 21
2.1.9 Language Skills and Language Elements being Tested... 22
2.1.9.1 Testing Language Skills ... 22
2.1.9.2 Testing the Language Elements ... 22
2.2 Theoretical Framework ... 23
CHAPTER 3: RESEARCH METHODOLGY ... 26
3.1 Method ... 26
3.2 Data Source ... 26
3.3 Data Collection ... 26
3.4 Data Analysis ... 28
x
Page
CHAPTER 4: ANALYSIS RESULT ... 29
4.1 The Description of the items in the teacher made test ... 29
4.2 Results ... 30
4.2.1 The test blueprints: Listening items ... 31
4.2.2 Speaking items ... 33
4.2.3 Reading items... 34
4.2.4 Writing items ... 36
4.3 The test types ... 37
4.3.1 The test types: Listening items... 39
4.3.2 Speaking items ... 40
4.3.3 Reading items... 41
4.3.4 Writing items ... 42
4.4 Implication to Language Teaching ... 43
CHAPTER 5: CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS ... 47
5.1 Conclusions ... 47
5.2 Suggestions ... 48
BIBLIOGRAPHY... 50
APPENDICES ... 51
Appendix A: The blueprints of teacher-made test for progress tests ... 52
xi
LIST OF TABLES
Page
Table 4.1: Frequency Distribution of Progress test items ... 30
Table 4.2: The Test Blueprints of the listening Test of Progress tests... 32
Table 4.3: The Test Blueprints of the speaking test of Progress test ... 33
Table 4.4: The Test Blueprints of the reading Test of Progress tests ... 35
Table 4.5: The Test Blueprints of the writing Test of Progress tests... 36
Table 4.1.1: Frequency Distribution of Test types in the Progress test items 38 Table 4.1.2: Frequency Distribution of Test types of the listening items in the Progress test ... 39
Table 4.1.3: Frequency Distribution of Test types of the speaking items in the Progress test ... 40
Table 4.1.4: Frequency Distribution of Test types of the reading items in the Progress test ... 41
xii
ABSTRACT
Lestari, Margarita Noviani Budi. 2008. An Analysis of the English Test Type for the First Year Students of SMAN 1 Pamulang Tangerang Banten. Yogyakarta: Faculty of Teachers Training and Education, Department of Language and Arts Education, English Language Education Study Program. Sanata Dharma University.
Testing is a very important part of the curriculum since the result of the test provides more objective information. To be accurate, a test should be evaluated based on the objectives stated in the curriculum, which is Competency based Curriculum as a guideline. The research aimed to investigate the blue prints of the progress test items for the first year students of SMAN 1 Pamulang and the English test type of the progress test items in obtaining the objectives stated in the Competency based Curriculum.
The research is a document analysis. There are five types of progress test papers for the first year students of SMAN 1 Pamulang. The results were put in tables and interpreted in words.
The result revealed that the progress tests did not cover all objectives stated in the Competency based Curriculum. They covered three out of six listening objectives; to complete the form, chart, and map based on the gathered information of the spoken text, to find out particular information in the simple spoken text, and to find out the general information of the short spoken text. They covered two out of nine reading objectives; to find out particular information, and to interpret the meaning of words, phrases, and statement based on context. They covered two out of four speaking objectives; to express the thought, opinion, feeling, and attitude in simple way, and to answer simple question in various thing. They also covered one out of three writing objectives; to demonstrate the basic competence.
The result revealed that the progress tests did not used all of the test types. The progress test only used matching, multiple choice, short answer and essay types.
xiii
ABSTRAK
Lestari, Margarita Noviani Budi. 2008. An Analysis of the English Test Type for the First Year Students of SMAN 1 Pamulang Tangerang Banten. Yogyakarta: Fakultas Keguruan dan Imu Pendidikan, Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa dan Seni, Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Tes merupakan bagian yang sangat penting dalam kurikulum karena hasil dari tes tersebut menyediakan informasi yang lebih obyektif. Untuk hasil yang lebih akurat, tes harus diukur berdasarkan tujuan yang terdapat dalam kurikulum yaitu kurikulum bahasa Inggris berbasis kompetensi sebagai pedoman. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui kisi-kisi dari soal tes kemajuan untuk siswa kelas satu SMAN 1 Pamulang dan tipe tes bahasa Inggris dari soal tes dengan Kurikulum berbasis Kompetensi.
Penelitian ini adalah analisa dokumen. Ada lima macam soal tes kemajuan untuk siswa kelas satu SMAN 1 Pamulang. Hasil dari analisa disajikan dalam bentuk table dan kemudian diinterpretasikan dalam kata-kata.
Dari hasil penelitian terungkap bahwa tes kemajuan tidak mencakup semua tujuan yang terdapat di dalam kurikulum berbasis kompetensi. Mereka hanya mencakup tiga dari enam tujuan mendengarkan; melengkapi bentuk, diagram, dann peta sesuai dengan kumpulan informasi dari teks berbicara, menemukan informasi khusus dari teks berbicara sederhana, dan menemukan informasi umum dari teks berbicara pendek. Mereka mencakup dua dari sembilan tujuan membaca; menemukan informasi khusus dan menginterpretasikan arti kata, frasa dan ungkapan sesuai konteks. Mereka mencakup dua dari empat tujuan berbicara; mengekspresikan pikiran, opini, perasaan dan sikap dengan cara sederhana dan menjawab pertanyaan sederhana yang beraneka macam. Mereka juga mencakup satu tujuan dari tiga tujuan menulis; mendemonstrasikan kompetensi dasar.
Dari hasil penelitian terungkap bahwa dalam tes kemajuan siswa tidak menggunakan semua tipe test yang ada. Tes kemajuan hanya menggunakan tipe menjodohkan, pilihan ganda, isian pendek dan esai.
1
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
This research was intended to investigate the English test type of the
teacher-made tests for the first year students of SMAN 1 Pamulang.
For the purpose of the research, this chapter presents background, research
problem, problem limitation, benefits of the study and definition of terms.
1.1. Background of the Study
Language, according to the English Competency based curriculum of SMA,
is a means to transfer ideas, thought, opinions, and feeling. English is the first
foreign language in Indonesia which is taught as a compulsory subject in
secondary (junior and senior) school.
In the Competency Based Curriculum, it is stated that this curriculum is
aimed to create the language competence of students. The competence that is
intended to be developed is discourse competence that is supported by linguistics
competence, socio cultural competence, and action competence.
In order to get the goal, the students’ progress should be monitored by doing
a test. The teacher –made test is one of the important test which is made to know
the students’ progress and the evaluation process.
There are many problem arise in the test making. A Teacher faces difficulties
in order to make a good test. Designing a good test is not easy. Hughes (1976)
states that a great deal of language testing is of very poor quality, they fail to
reflect an actual achievement of the teacher’s goals and objectives. The test will
not measure the objectives of the curriculum and it cannot be used for
determining the students’ achievement.
1.2. Research Problems
The research was intended to know the test type of SMAN 1 Pamulang. The
study can be focused on the question:
1. What are the blue prints of the progress test items for the first year students of
SMAN 1 Pamulang?
2. What are the English test types of progress test items for the first year
students of SMAN 1 Pamulang related to the objectives stated in Competency
based Curriculum?
1.3. Problem Limitation
This study is limited to the following areas of focus:
1. The objectives used as the basis analysis are the objectives listed in the
English Competency based Curriculum for SMA.
2. The research is limited to the English progress tests for the first year students
of SMAN 1 Pamulang. There are four sets of test used in this study. The
topics are friendship, school life, domestic tourism and favorite sport. The
tests are made by the teachers themselves to measure the students’ ability in
1.4. Benefits
The result can be useful for:
1. The English progress test makers
The English progress test makers can develop better test in the future with a
new curriculum.
2. The students
The next English progress test can be expected to take better tests which
contain the characteristics of good tests for students.
3. The future researchers
The future researchers are expected to carry out further study along this topic.
1.5. Definition of Terms
1. Test Types
In this study, the test types are classified into three: supply type (short answer) and select type (true-false, matching, and multiple choice), and essay type. Ebel (1979: 56) states that the most commonly used types of tests are the essay (or
discussion) type, the objective (or short-answer) type, the mathematical problem
type, and the oral examination type. Mehrens and Lehmann (1973: 245) states that
all objective item formats may be divided into two classes: supply type (short answer) and select type (true-false, matching, and multiple choice).
2. Blue print
Mehrens (1969: 197) states that a blueprint relates the course objectives to the
items. The blue print lists the major topics that will be included in the test (Bertrand,
1980: 80)
In this study, blue print is a detailed plan on making of the test items. Blue
print is used to answer the first research problem.
3. SMAN 1 Pamulang Tangerang Banten
SMAN 1 Pamulang Tangerang Banten is located inside the Pamulang Permai
2 housing complex. The address is Jl. Benda Timur XI Pamulang Permai 2 housing
complex Pamulang Tangerang Banten. There are only two private school at
Pamulang, and SMAN 1 Pamulang is the best of all. SMAN 1 Pamulang has 24
classes, they are 8 classes for the first-year students, 8 classes for the second-year
and 8 classes for the third-year. Each class consists of 40 students on average. For 24
classes there are 4 teachers who teach English subject. It means that one teacher
teaches about six classes. In the first-year, English subject is taught twice a week and
45 minutes in one meeting. SMAN 1 Pamulang has enough facilities to support the
English language teaching and learning process. There are language laboratory,
computer laboratory and library which contribute much for students in learning
English. All of the facilities are in a good condition.
4. The first-year students
In Senior High School there are three grades of students. The first-year
student is one of the three grades. The age range of the first year students is fifteen
until sixteen years old. The first year student is the students who are graduates from
had learned English about nine years on average. So that they are expected skillful
and mastering English in the intermediate level.
5. Construct
Hughes (1989: 26) states that construct is any underlying ability that is
hypothesized in a theory of language ability. In other words, it is the sub abilities that
6
CHAPTER 2
THEORETICAL REVIEW
This chapter consists of two sections. The first one is Theoretical Description
and the last part is Theoretical Framework.
2.1. Theoretical Description
2.1.1. Test
Grondlund (1968: 1) says that a test is a systematic procedure to determine
the amount a student has learned. He adds that the test includes quantitative and
qualitative descriptions of students’ behavior plus value judgments concerning the
desirability of the behavior. (Mehrens and Lehmans, 1973: 6) says that a test is the
presentations of a standard set of questions to be answered and the result of it is in
the form of numerical value. Funk and Wagnalls (1951) says that a test is subjection
to conditions that disclose the true character of a person or thing in relation to some
particular quality. Guralnik (1976) says that a test is a set of questions, problems, or
exercises to determine a person knowledge, abilities, aptitude, and qualification.
From the definition above, it can be concluded that a test is a systematic procedure
which is a set of questions, problems, or exercises to determine a student knowledge,
2.1.2. Teacher – Made Tests
A test designed by the teacher can provide the most important data which
consists of the students’ general achievement of the progress test and final test. In
order to get the data to determine the students’ progress, the teacher arranged a test
by looked at the specific goals and objectives of the units he teaches. Teacher also
had to look for the curriculum which is used.
The English progress test in SMAN 1 Pamulang is designed by the teacher
herself. A teacher –made test is arranged by the teacher who will use the test
according to her needs. The test is meant to measure how far students have mastered
the lesson materials that have been taught.
2.1.3. Types of Tests
There are several types of tests. Hughes (1976) categorized tests into four
groups. The first is “the proficiency tests” (p. 9). They are used to measure people’s
ability in language regardless of any training they may have had in that language.
The second is “the achievement test” (p. 10). They are made to establish how
successful individual students, group of students or the course themselves have been
in achieving objectives. The final achievement tests are those administered at the end of a course of study. Whereas, the progress achievement tests are intended to measure the progress that students are making.
The third category is “the diagnostic tests” (p. 10). They are made to identify
students’ strength and weaknesses. They are intended primarily to ascertain what
number of test items in each specific area, with slight variations from one item to the
next so that the course of specific learning errors can be identified. The diagnostic
test focuses on the common sources of error encountered by students, so that the
learning difficulties can be pinpointed and remedied. This test is designed to probe
deeper into the course of learning deficiencies that are left unresolved. The fourth is
“placement tests” (p. 11). They are used to provide information which will help to
place the students at the stage (or in the part) of the teaching program most
appropriate to their abilities. Placement testing is not always necessary. Teachers
who have worked with students for some time may know their past achievement,
well enough so that pre-test may not needed. Placement testing is most useful when
the teacher is unfamiliar with the students’ skills and abilities. The placement test
provides an invaluable aid for placing each student at the most beneficial position in
the instructional sequence.
Considering that categorization, English progress test falls into the progress
achievement test because the test emphasizes on measuring the students’ progress on
mastering the language materials given in the classroom within a period of time. One
way of measuring progress would be repeatedly to administer final achievement
tests, but this is not really feasible, particularly in the early stages of a course. The
low scores obtained would be discouraging for both students and teacher. The
alternative is to establish a series of well-defined short-term objectives.
Based on the tests administered, Lado (1964) explained that there are
“discrete tests” (p. 14) and “integrative tests” (p. 15). The discrete point test is one in
independent of each other, but it is usually related in its form to the next item. The
integrative one is testing combination of many language elements in the completion
of a task. It measures students’ ability to use the target language. The items are
dependent on one another, and are related in meaning.
Therefore, English progress test is included in the integrative test for it
consists of reading, vocabulary structure, and speaking component, and each of them
is related to one another. Without understanding the meaning of an item, an
individual may not do it correctly as far as he recognizes its form.
Arthur (1989) adds the categorization. Based on the method of scoring, if no
judgment is required on the past of scorer, then the scoring is objective. A
multiple-choice with the correct responses unambiguously identified, would be a case in point.
If judgment is called for, the scoring is said to be subjective. There are degrees of
subjectivity in testing. The impressionist scoring of a composition may be considered
more subjective than the scoring of short answers in response to questions. Then,
English progress test for the first year student of SMAN 1 Pamulang is an objective
test.
Ebel (1979: 56) states that the most commonly used types of tests are the
essay (or discussion) type, the objective (or short-answer) type, the mathematical
problem type, and the oral examination type. Mehrens and Lehmann (1973: 245)
states that all objective item formats may be divided into two classes: supply type (short answer) and select type (true-false, matching, and multiple choice). The supply
and select types of objective item formats are sometimes called recall and
free answer-type and the structured answer type of item. Lien (1971: 63) and
Grondlund (1971: 131) used essay and objective or supply type and selection type.
Carroll and Sapon (1958: 43) states that there are two types; language aptitude test
and language proficiency test. And three types: placement tetsts, diagnostic tests, and
achievement tests. Finnocharo (1969 : 337) puts forward the definition of test types
as a series of varied tests which measure receptive and productive abilities. Further
she adds that these types are also called as devices that permit the teacher to measure
the attainment of a particular skill.
In this study, test types are a series of varied tests which measure the
student’s progress in receptive abilities (listening and reading) and productive
abilities (speaking and writing). The English progress test for the first year students
of SMAN 1 Pamulang used supply type (short answer) and select type (true-false, matching, and multiple choice) and essay type.
2.1.4. The Function of Test
The result of the tests determine the success of a course. Therefore, tests are
needed to give information about “what individuals have achieved in a second or
foreign language” (Hudges, 1990 : 4)
Moreover, Lado (1969) states that there are six categories which indicate
different emphasis in measuring students’ ability and potential.
1. to determine the readiness of an instructional program.
2. to classify or place individual in appropriate language classes.
4. to measure aptitude for learning.
5. to measure the extent of students’ achievement of the instructional goals.
6. to evaluate the effectiveness of the instruction.
Arifin (1985) has his own opinion. The evaluation activities have the
objectives as follows:
1. to know how far the students master the materials that have been given.
2. to know how far the capability of the students in learning the lesson materials.
3. to know whether the students’ development level has been appropriate to the
development level of the work program.
4. to know the efficiency and affectivity degree of the teaching strategy that has
been used, both about the methods and techniques of teaching and learning.
Howard (1963) clarifies the need of the test. On his opinion tests are used as
tools in reaching decisions. It could be the decisions which are institutional; that is, the decision are made on the behalf of an institution (school, college, corporation,
etc) and such decisions are made frequently. The test can be extremely effective in
such situation because it help the institution to reach a higher percentage of good
decisions which will affect himself or, perhaps, a son or daughter.
All the opinion stated above explains the function of the test. Norman (1976)
lists some more important supplementary uses of the test as follows:
1. Use in reporting pupil progress to parents.
The systematic use of evaluation procedures in the classroom provides the
Teacher with an objective and comprehensive of each pupil’s learning progress.
2. Use in guidance and counseling
The result is especially useful for guidance and counseling. It includes the process
of assisting a pupil with educational and vocational decisions, guiding him in the
selection of curricular and extracurricular activities, and helping him to solve
personal and social adjustment problems. All require an objective knowledge of the
pupil’s abilities, interests, attitudes, and other personal characteristics.
3. Use in school administration
In this role, the administrator is able to judge the extent to which the objectives of
the school are being achieved, to identify strength and weaknesses in the
curriculum, and to appraise special programs in the school.
4. Use in school research
Carefully controlled studies of such things as the comparative effectiveness of
different curricular, different teaching method and different organizational plans
require objectives measure of pupil performance.
There are many opinions about the role of evaluation in education. We can
divide it into two functions: evaluation provide feedback to improve the educational
system and process and evaluation help determining the result of a program in a
period of time. For example, students’ achievement of mastering the learning
materials.
Related to the function of tests explained above, the teacher-made test are
used to determine students’ achievement and the effectiveness of instruction of
2.1.5. The Characteristics of a Good Test
Lado, Harris (1969) states that all good test has three qualities: validity,
reliability, and practicality. Hatch and Farhady (1969) also says that a good test
should have three basic requirements, two of which are absolutely crucial. Those two
characteristics are validity and reliability, and the practicality as the third criteria is
not so important.
2.1.5.1. Reliability
Reliability is the degree of consistency among test scores. Hughes (1989: 36)
suggests how to make test more reliable. There are two components of test
reliability, that is the performance of candidates from occasion to occasion and the
reliability of scoring.
2.1.5.2. Validity
A test is said to be valid if it measures accurately what it is intended to measure
(Hughes, 1989: 22). The general concept of validity was traditionally defined as "the
degree to which a test measures what it claims, or purports, to be measuring"
(Brown, 1996, p. 231). There are three types of validity as follows.
1). Construct validity
Heaton (1975: 154) states that “if tests construct validity, it is capable of
measuring certain specific characteristics in accordance with a theory of language
behaviour and learning”. This assumes the existence of certain learning theories
or constructs underlying the acquisition of abilities and skills. Hughes (1989: 26)
adds that “a test, part of a test, or a testing technique is said to have construct
supposed to measure”. The word ‘construct’ refers to any underlying ability (or
trait) which is hypothesized in a theory of language ability. One might
hypothesis, for example, that the ability to read involves a number of
sub-abilities, such as the ability to guess the meaning of unknown words from the
context in which they are met. It would be a matter of empirical research to
establish whether or not such a distinct ability existed and could be measured. If
we attempted to measure that ability in a particular test, then that part of the test
would have construct validity only if we were able to demonstrate that we were
indeed measuring just that ability. Brown (1996) adds that a construct, or
psychological construct as it is also called, is an attribute, proficiency, ability, or
skill that happens in the human brain and is defined by established theories.
Construct validity has traditionally been defined as the experimental
demonstration that a test is measuring the construct it claims to be measuring.
Such an experiment could take the form of a differential-groups study, wherein
the performances on the test are compared for two groups: one that has the
construct and one that does not have the construct. If the group with the construct
performs better than the group without the construct, that result is said to provide
evidence of the construct validity of the test. This idea is also supported by
McNamara (2004), he said that construct mean the underlying ability or trait
being measured by the test. Campbell and Stanley (1966) states that construct
validity can be considered as labels that assign meanings to the test we are
2). Content validity
A test is said to have content validity if its content constitutes a representative
sample with which it is meant to be concerned (Hughes, 1989: 22). A test is
designed to measure mastery of a specific skill or the content of a particular
course of study, and we can expect the test to be based upon a careful analysis of
the skill or an outline of the course. Content validity includes any validity
strategies that focus on the content of the test. To demonstrate content validity,
testers investigate the degree to which a test is a representative sample of the
content of whatever objectives or specifications the test was originally designed
to measure. To investigate the degree of match, test developers often enlist
well-trained colleagues to make judgments about the degree to which the test items
matched the test objectives or specifications (Brown 1996: 231-249). Heaton
(1975: 154) adds another aspect to consider about content validity. He says “the
test should be so constructed as to contain a representative sample of the course,
the relationship between the test items and the course objectives always being
apparent”. In other words, content validity also measures how the test item meets
the course objectives.
3). Face validity
Hughes (1989: 27) states that a test is described as having face validity if it looks
right or as if it measures what it is supposed to measure. Face validity is hardly a
scientific concept, yet it is important. It is often useful to show the test to other
people so that possible absurdities and ambiguities can be discovered (Heaton,
Instead of validity and reliability as the essential characteristics of a good
test, usability also important. The usability of a test includes the ease and time
administration, the scoring, the interpretation and application, and the cost. Valette
(1967) says that the essential requirements of a good test are reliability and validity.
Since those two criteria are the most important.
2.1.6. English Competency based Curriculum for SMA
Nunan (1988) states that ‘curriculum’ is more widely than ‘syllabus’.
Curriculum refers to all aspects of planning, implementing, evaluating and managing
an educational programme. Whereas, ‘syllabus’ refers to the selecting and grading of
content. Then, we can conclude that syllabus is a smaller part of the curriculum.
Romberg says that ‘curriculum’ is a structural series of learning experiences
complete with goals, methods, and activities. Giant (1982) describes curriculum as
the planed and guided learning experiences and intended learning outcomes,
formulated through the systematic reconstruction of knowledge and experience,
under the auspices of the school, for the learner’s continuous and willful growth in
personal-social competence.
The English Competency based Curriculum for SMA belongs to this kind of
curriculum. The objectives stated in the curriculum are general objectives, that is, to
develop four language skills, while educational evaluation is based on specific
objectives made by each teacher herself. Mulyasa (2002: 39) states that the
Competency-Based Curriculum (CBC) means “a curriculum concept which
certain standards, so that the results can give beneficial things for student’s mastery
of certain competency”. The main competence that will be achieved is discourse
competence. In this competence, students are able to involve themselves in a text
when they are communicating. A text means a communication that is effected by the
topic being discusses interpersonal relationship among the speakers, and
communication way in the culture context. The achievement of this competence is
supported by Linguistic competence, Socio cultural competence and Strategic
competence. In addition, in the process of teaching learning, the Competency Based
Curriculum emphasizes three domains. They are cognitive, psychomotor, and
affective. There are some ponds of the CBC English Syllabuses as stated in the 2004
curriculum (2002: 6 -7):
1. Definition of the Competency Based Curriculum
English is a means of oral and written communication. In this term,
communication aims to understand and express the information, thought, feeling,
and developing science, technology, and culture using the language.
2. Functions and Aims
In the contexts of education, English is functioned as a communication tools to
access information. In the daily context, it is functioned as a means to build
interpersonal contact, change information and enjoy the esthetic of English
language culture.
2.1.Improve communication skill in the target language in the form oral and
written. The communication skill consists of listening, speaking, reading, and
writing.
2.2.Raise the awareness of the essential and the importance of English language
as one of the foreign language as the main tool of learning process.
2.3.Develop the understanding of the relationship between language and culture
and enlarge the knowledge of the culture. Therefore, the students will have
the knowledge across to culture and involve in the culture diversity.
3. Scope
The scopes of English subject are:
3.1.Language skills that consist of listening, speaking, reading, and writing.
3.2.Sub-competency that consists of language competence, linguistic
competence, strategy competence.
3.3.Development of positive attitude through English language as a means of
communication.
4. Approach
The process of learning language is directed to the achievement of competence
that can be seen in the students skill to do the steps of communication. They are
called speech act, speech function or language function. The approach is not
“let’s talk about something” but rather than “let’s to do something with
2.1.7. The objectives of the English Competency based Curriculum
The curriculum states that the aim of teaching English is to enable the students’
posses the skills in reading, writing, speaking, and listening. Those four language
skills should be presented integrative through themes, which have been selected
based on the students’ interest and students’ vocabulary mastery. In addition, the
emphasis of this curriculum in the language skills, the language elements such as
structure, vocabulary, and pronunciation are taught to support the mastery of the four
language skills.
The reading indicators stated in English Competency Based Curriculum
pages 16-29 can be formulated into nine objectives of reading. They are
1. to find out particular information.
2. to find general information of the text.
3. to find out the explicitly main idea.
4. to find out the implicit main idea.
5. to find out all the explicitly detailed information.
6. to find out the implicitly stated information.
7. to interpret the meaning of words, phrases, and statement based on context.
8. to find out the communicative purpose of the text.
9. to find out the organizational of the text.
The writing indicators stated in Competency Based Curriculum pages 16-29
can be formulated into three objectives. They are
1. to write daily communication text.
3. to demonstrate the basic competence of grammar and the rule of writing.
The speaking indicators stated in Competency Based Curriculum pages 16
-29 can be formulated into four objectives. They are
1. to ask and answer simple question in various thing.
2. to do short dialogue fluently.
3. to convey the description of things, people or place, a set of moment in simple
way.
4. to express the thought, opinion, feeling, and attitude in simple way.
In this study, all items in the progress test should relate to the objectives of
skills indicator in the Competency Based Curriculum for the first year students of
Senior High School.
2.1.8. A Test Blueprint
Ebel (1979: 69) states a test blueprint is one of the strategies that have been
used to outline the coverage of test, as part of specification. It is useful in guiding the
construction of a test and informing the students what they may expect to find on the
examination and how they can best prepare to do well on it. It means that test
blueprint is the framework of the test.
2.1.8.1 The Purpose of Test Blueprint
Mehrens and Lehmans (1973: 181) state that the purpose of test blueprint is
to define as clearly as possible the scope and emphasis of the test and relate the
test items in terms of both objectives and content. A completed blueprint describes
the number of test items needed to obtain a balanced measure of the instructional
objectives and the course content emphasized in the instruction.
In addition, teachers use the blueprints to plan a unit in the first place. The
blueprints become convenient checklists to help the teacher and the students keep
working toward their started objectives. It lists the activities a unit covered teachers
can more easily monitoring instrument of her teaching process.
In this research, the purpose of finding the test blueprints is to know the
construct of the test. The curriculum is the basis of finding the test blueprint. It is
analyzed based on the language skills and language elements. Teachers have to bring
students to achieve the requirements stated in the curriculum. To help teachers
prepare the test, the process of finding the blueprints is done after the test is
constructed. The last, this research is aimed to find out the English test type of the
progress test for the first year students in SMAN 1 Pamulang. It may be seen from
the blueprints that are found.
2.1.8.2 Preparing the Test Blueprint
Mehrens and Lehmans (1973: 181) states that the major areas of contents and
abilities to be covered by the test are assigned to the several rows or columns. He
adds that each item may the classified in one of the cells. Various numbers of items
are assigned to each of the rows and columns. Knowing the proportion of items
specified for a particular row and column, one can ideally determine the proportion
In addition, Bertrand (1979: 80) states blueprint as the setting levels of
category into a table and then listing the content, subject matter, skills, or other
learning activities which is designed to measure. Therefore, in this study, some
categorizations are made. Each item of the test is categorized into four skills. They
are listening, speaking, reading and writing. After that, the items are classified based
on objectives and indicators of the study. The items are also analyzed its topic or
subtopic that is applied in the test, and what material I used. To know the percentage
of the result clearly, the test blueprint are in the form of column and row.
2.1.9. Language Skills and Language Elements being Tested
There are two main components of language testing, they are language skills
and language elements. Heaton (1979) said that there are four major skills in
communicating language : listening, reading, speaking, writing and three language
elements, they are : phonology, vocabulary, and grammar.
2.1.9.1. Testing Language Skills
1) Listening Comprehension ; it is a test in which single utterances, dialogue, talks,
and lecturers are given to the tester.
2) Speaking ability ; it usually uses the form of an interview, a picture description,
and reading aloud.
3) Reading ; it is a test in which questions are set to the students’ understanding of
a written text, and
2.1.9.2. Testing the Language Elements
1) Phonology ; a test of phonology concerns pronunciation, stress, and intonation.
2) Vocabulary ; a test of vocabulary concerns word meaning and
arrangements. Vocabulary tests measure students’ knowledge of the meaning of
certain words and word groups.
3) Grammar ; a grammar test measure students’ ability to manipulate structures and
to distinguish appropriate grammatical forms from inappropriate ones.
On the other hand, Lado (1961) said that there are two variables in language
testing, they are: language skills and language components. Language skills can be
divided into four namely: listening, speaking, reading, and writing. Besides, there is
another skill, that is ability to translate. Language elements can be divided into four,
namely: pronunciation, grammatical structure, the lexicon, and cultural meaning.
Similar to Heaton, Harris (1969) describes that language included four
language skills and complexes of skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and
four language elements, namely: phonology, grammatical structure, vocabulary rate
and general fluency. Briefly, he classifies the language into the four skills and four
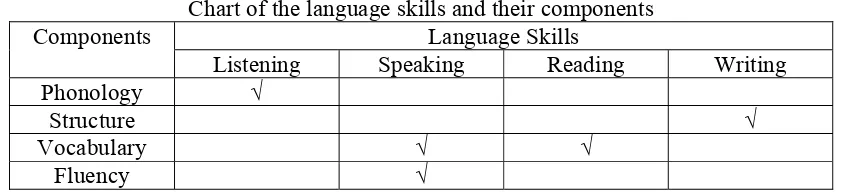
elements. He clarifies his idea to the following table.
Table 1
Chart of the language skills and their components Language Skills
Components
Listening Speaking Reading Writing Phonology √
Structure √
Vocabulary √ √
2.2. Theoretical Framework
From the theories of language testing, the teachers need some requirements to
construct a good test. A test is said to be good if it is valid, reliable, and has
practicality. The test maker is faced with the matter of how to make a test with good
characteristics. They also should think deeply how to construct the test with
appropriate requirements of detailed course syllabus or on the books and other
materials used.
This study is aimed to find out the framework of the progress test. In order to
know the framework of the progress achievement test, the test blueprint is needed. It
shows how a test is constructed and how far it reflects the curriculum as the
evaluation. It will indicate in which area of skills and language elements that the test
works. From that value, the test blueprints help the teacher in guiding the students to
prepare the next exam since it will inform the students what they may expect to find
on the examination.
Two questions are formulated as research problems. The first problem was:
what are the blueprints of the progress test for the first year students of SMAN 1
Pamulang. The second research problem was: what are the English test types of
progress test items for the first year students of SMAN 1 Pamulang related to the
objectives stated in Competency Based Curriculum. In order to answer the first
research problem, the progress achievement test will be analyzed based on the
Competency Based Curriculum. Each item of the progress test will be categorized
based on the four skills; they are listening, speaking, reading, and writing. Next, each
test, each item will be classified based on the objectives or indicators of the material
of each skill that are stated in the curriculum. The result of the classification will be
put into tables which contain of some criteria. They are objectives of the study, topic
or subtopic, material, and indicators. The results are counted into percentage. The
percentage is described in words. The test blueprints will show the construct of the
test. In order to answer the second research problem, the each item of the progress
26
CHAPTER 3
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1. Method
To conduct this study, the researcher employed a descriptive research. This
kind of research according to Gay (1992: 217), involves collecting data in order to
test hypotheses or to answer question concerning the current status of the subject of
the study. This research is meant to describe the English test types that used in the
progress test for the first year students of SMAN 1 Pamulang. Considering the above
problems, this research was a document analysis. Document analysis known as
content analysis, deals with the systematic examination of current records or
documents as sources of data (Best, 1970: 133).This research was carried out without
disturbing or influencing the subjects.
3.2. Data Source
The subject of this research was teacher-made test papers for the first year
students of SMAN 1 Pamulang. The teacher-made test papers were designed for
progress test in the first semester. There were four sets of progress tests used in this
study. The topics were friendship, school life, domestic tourism and favorite sport.
3.3. Data Collection
In order to answer the first problem, the data collected were evaluated based
students of SMA. The data were divided into categories and listed in tables based on
the objectives that were measured. The table used is as follows:
Table 1 : The blue prints of the progress test items based on the objectives measured.
Total No Objectives
∑ %
Total
The first column was used to write the numbers of the objectives. The second
column was filled with the objectives statements. The third column was used to write
the numbers of the items measuring one of the objectives stated. The last column was
used to write the total frequencies of the items and their percentage.
Table 4 : The list of test types used on each objectives.
Total
No Test types
∑ %
Total
The first column was used to write the numbers of the test types. The second
column was filled with the test type statements. The last column was used to write
the total frequencies of the items and their percentage.
To answer the second problem, this research applied the use of words to
sentences. The words interpretations are used as the basis in answering the second
problem.
3.4. Data Analysis
In order to find out the English test type which is used of the progress test
items for the first year students in SMAN 1 Pamulang, the data collected were
analyzed by classifying the data into qualitative data. Qualitative data included the
written description of the subjects. In other words, the data were described using
words or sentences.
The data were analyzed based on the measured objectives. The results were
put into tables. The total frequencies of each category were calculated and changed
into percentage. The figures written in table were described and interpreted in words.
The progress test items were analyzed based on the objectives in the
Competency Based Curriculum. Moreover, the progress test items were analyzed
based on the English test types which were used conducted to a library study.
3.5. Research Procedure
There were some steps in conducting the research. First, the writer gathered
the progress test papers for the first year students of SMAN 1 Pamulang especially
on the first semester. Then, the writer evaluated each of the progress test items based
on the Competency Based Curriculum. Next, the writer conducted a library study to
analyze the English test types which were used of each progress test items. The last
29
CHAPTER 4
ANALYSIS RESULT
This chapter presents the results which answer the questions previously
formulated in the research problem. The first question concerns what the blue prints
are. The second question concern what is the English test type of progress test items
for the first year students of SMAN 1 Pamulang related to the objectives stated in
Competency based Curriculum.
4.1. The Description of the items in the teacher-made test.
This reseacrh analyzed the teacher-made test. The data was taken from the
English progress test for the first-year students of SMAN 1 Pamulang, academic year
2006-2007, and first semester. The total items of the four paper tests are 104 items.
Based on the test content, the test consisted of language skills tests and language
elements tests. The progress test covered listening, reading, speaking, and writing
objectives for English language skills, and vocabulary and grammar for English
language elements. Each paper test contains 26 test items. They are divided into two
types; multiple-choice and non multiple choice test type. The non multiple choice
test type also divided into many types, there are matching items, short answer items,
and essay. Each types of test consist of five until fifteen numbers from all. The
progress test for the first year students of SMAN 1 Pamulang also consists of
listening question item. It is the short-answer items. It consists of five until ten
Table 4.1: The Frequency Distribution of Progress test items
4. 2. Results
This research deals with what the blue prints are and what the English test
type of the progress test items related to the objectives stated in the Competency
based Curriculum. To answer those two problems, this research employed a
document analysis on the progress test items. The two problems are analyzed below
in detail. The Competency based Curriculum; language is a vehicle of
communication. The curriculum is meant to help students using language in the
process of interaction in the society. Students do not learn the language merely, but
they use the language as a means of learning something (Depdikbud, 2003). In the
process of learning activities, it includes then four skills.
After a period of time of learning activities, there are some tests that are
given to the students. One of the tests discusses in this research is progress test. It is
viewed that progress test is a kind of test which is used to evaluate the performance
of the students after a certain period of time in learning English. By conducting these
tests, the teachers may evaluate the teaching-learning process that happens in the
Distribution of the Progress test items
class, the curriculum designers may get input for such an improvement in the
curriculum, the government can also achieve the result to get a description of its
human resources for sake the country’s development (Pakpahan, 2004).
The test blueprint of test is very important since it is the framework of the
test. It may contribute the test makers a wider view of test blueprint. Considering the
test blueprint, next, they may construct a text with appropriate requirement so that
they may produce a test with good characteristics.
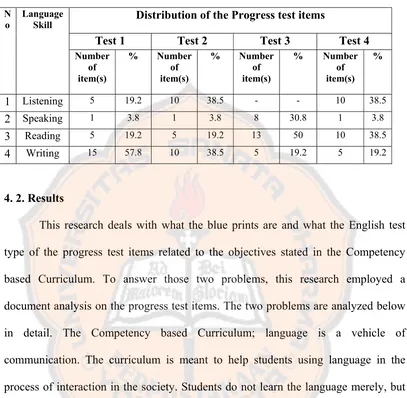
4.2.1. The test blueprints: Listening items
In order to find out the test blueprints, the progress tests were analyzed based
on Competency based Curriculum as the basis of test construction. There are six
listening objectives in the Competency based Curriculum. They are (1) to find out the
general information of the short spoken text, (2) to interpret the meaning of a
statement, (3) to find out the communicative purpose of the short spoken text, (4) to
complete the form, chart, and map based on the gathered information of the spoken
text, (5) to give response to the expression of the spoken question or statement, (6) to
predict the further story of the spoken text. The listening test of the Progress test was
analyzed based on those objectives, and the results are presented in Table 4.2.on the
Table 4.2: The Test Blueprints of the listening Test of Progress Tests
Distribution of the Progress test items
Test 1 Test 2 Test 3 Test 4
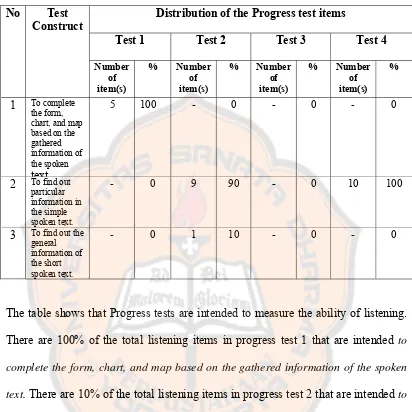
The table shows that Progress tests are intended to measure the ability of listening.
There are 100% of the total listening items in progress test 1 that are intended to complete the form, chart, and map based on the gathered information of the spoken text. There are 10% of the total listening items in progress test 2 that are intended to find out the general information of the short spoken text while there are 90% of the total listening items in progress test 2 that are intended to find out particular information in the simple spoken text. There are 100% of the total listening items in progress test 3 that are intended to find out particular information in the simple spoken text.
In the listening test of Progress tests three objectives were not tested. They
spoken question or statement, and to predict the further story of the spoken text.
According to Hughes (1989: 23), the more likely it is to be inaccurate measure of
what is supposed to be measured. Therefore in the future, the test writer should
concern about the absence of those objectives to build with good content validity.
4.2.2. Speaking items
The speaking indicators stated in English Competency Based Curriculum
pages 16-29 can be formulated into four objectives of speaking. They are (1) to ask and answer simple question in various thing. (2) to do short dialogue fluently. (3) to convey the description of things, people or place, a set of moment in simple way. (4)
to express the thought, opinion, feeling, and attitude in simple way.
The speaking test on the Progress test was analyzed based on the formulation
objectives states above. The results are presented in the Table 4.4 :
Table 4.4: The Test Blueprints of the speaking test of Progress Tests
Distribution of the Progress test items
The table shows that Progress tests are intended to measure the ability of speaking.
There are 100% of the total speaking items in progress test 1 that are intended to express the thought, opinion, feeling, and attitude in simple way. There are 100% of the total speaking items in progress test 2 that are intended to express the thought, opinion, feeling, and attitude in simple way. There are 12.5% of the total speaking items in progress test 3 that are intended to express the thought, opinion, feeling, and attitude in simple way while there are 87.5% of the total speaking items in progress test 3 that are intended to answer simple question in various thing. There are 100% of the total speaking items in progress test 4 that are intended to express the thought, opinion, feeling, and attitude in simple way.
In the speaking test of Progress Tests two objectives were not tested. They
are to do short dialogue fluently and to convey the description of things, people or place, a set of moment in simple way. According to Hughes (1989: 23), the more likely it is to be inaccurate measure of what is supposed to be measured. Therefore in
the future, the test writer should concern about the absence of those objectives to
build with good content validity.
4.2.3. Reading items
The reading indicators stated in English Competency Based Curriculum
interpret the meaning of words, phrases, and statement based on context. (8) to find out the communicative purpose of the text. (9) to find out the organizational of the text.
The reading test on the Progress test was analyzed based on the formulation
objectives states above. The results are presented in the Table 4.3.
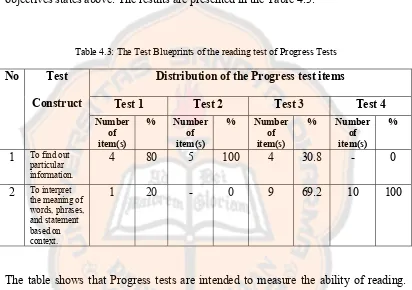
Table 4.3: The Test Blueprints of the reading test of Progress Tests
Distribution of the Progress test items
Test 1 Test 2 Test 3 Test 4
The table shows that Progress tests are intended to measure the ability of reading.
There are 80% of the total reading items in progress test 1 that are intended to find out particular information while there are 20% of the total reading items in progress test 1 that are intended to interpret the meaning of words, phrases, and sentences..
words, phrases, and sentences. There are 100% of the total reading items in progress test 4 that are intended to interpret the meaning of words, phrases, and sentences.
In the reading test of Progress Tests six objectives were not tested. They are
to find general information of the text, to find out the explicitly main idea, to find out the implicit main idea, to find out all the explicitly detailed information, to find out the implicitly stated information, to find out the communicative purpose of the text,
and to find out the organizational of the text. According to Hughes (1989: 23), the more likely it is to be inaccurate measure of what is supposed to be measured.
Therefore in the future, the test writer should concern about the absence of those
objectives to build with good content validity.
4.2.4. Writing items
The writing indicators stated in English Competency Based Curriculum pages
16-29 can be formulated into three objectives of writing. They are (1) to write daily communication text. (2) to write a text in various forms (3) to demonstrate the basic competence of grammar and the rule of writing.
The writing test on the Progress test was analyzed based on the formulation
objectives states above. The results are presented in the Table 4.5 on the next page:
Table 4.5: The Test Blueprints of the writing test of Progress Tests
Distribution of the Progress test items
1 To demonstrate the basic competence.
15 100 10 100 5 100 5 100
The table shows that Progress tests are intended to measure the ability of writing.
There are 100% of the total writing items in progress test 1 that are intended to
demonstrate the basic competence of grammar and the rule of writing. There are
100% of the total writing items in progress test 2 that are intended to demonstrate the
basic competence of grammar and the rule of writing. There are 100% of the total
writing items in progress test 3 that are intended to demonstrate the basic
competence of grammar and the rule of writing. There are 100% of the total writing
items in progress test 4 that are intended to demonstrate the basic competence of
grammar and the rule of writing.
In the writing test of Progress Tests two objectives were not tested. They are
to write daily communication text and to write a text in various forms. According to
Hughes (1989: 23), the more likely it is to be inaccurate measure of what is supposed
to be measured. Therefore in the future, the test writer should concern about the
absence of those objectives to build with good content validity.
4.3. The test types
the English test types; supply type (short answer), select type (true-false, matching,
and multiple choice) and essay (or discussion) type.
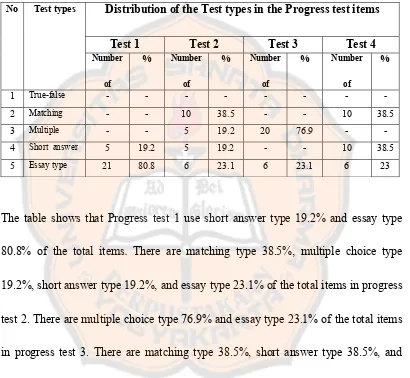
Table 4.1.1: The Frequency Distribution of Test types in the Progress test items
The table shows that Progress test 1 use short answer type 19.2% and essay type
80.8% of the total items. There are matching type 38.5%, multiple choice type
19.2%, short answer type 19.2%, and essay type 23.1% of the total items in progress
test 2.There are multiple choice type 76.9% and essay type 23.1% of the total items
in progress test 3. There are matching type 38.5%, short answer type 38.5%, and
essay type 23% of the total items in progress test 4.
In the progress test 1 there are true-false type, matching type, and multiple
choice type were not used. In the progress test 2 only true-false type which was not
used. In the progress test 3 there are true-false type, matching type, and short answer
Distribution of the Test types in the Progress test items
Test 1 Test 2 Test 3 Test 4
No Test types
Number of
% Number of
% Number of
% Number of
%
1 True-false - - - - -
2 Matching - - 10 38.5 - - 10 38.5
3 Multiple - - 5 19.2 20 76.9 - -
4 Short answer 5 19.2 5 19.2 - - 10 38.5
type were not used. In progress test 4 there are true-false type and multiple choice
type which were not used.
4.3.1. The test types: Listening items
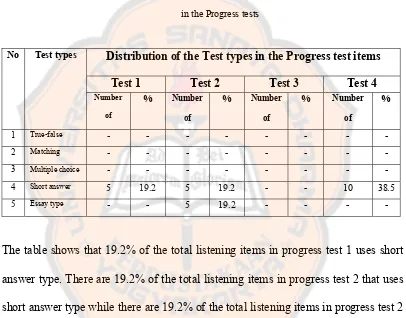
Table 4.1.2: The Frequency Distribution of Test types of the listening items
in the Progress tests
The table shows that 19.2% of the total listening items in progress test 1 uses short
answer type.There are 19.2% of the total listening items in progress test 2 that uses
short answer type whilethere are 19.2% of the total listening items in progress test 2
that uses essay type. There are 19.2% of the total listening items in progress test 4
that uses short answer type.
In the listening test of Progress Test 1, there are four test types (true-false
type, matching type, multiple choice type, and essay type) were not used. In the
listening test of Progress Test 2, three test types (true-false type, matching type, and
multiple choice type) were not used. In the listening test of Progress Test 3, all of the
Distribution of the Test types in the Progress test items
Test 1 Test 2 Test 3 Test 4
No Test types
Number of
% Number of
% Number of
% Number of
%
1 True-false - - - - -
2 Matching - - - - -
3 Multiple choice - - - - -
4 Short answer 5 19.2 5 19.2 - - 10 38.5
test types (true-false type, matching type, multiple choice type, short answer type,
and essay type) were not used. In the listening test of Progress Test 4, four test types
(true-false type, matching type, multiple choice type, and essay type) were not used.
4.3.2. Speaking items
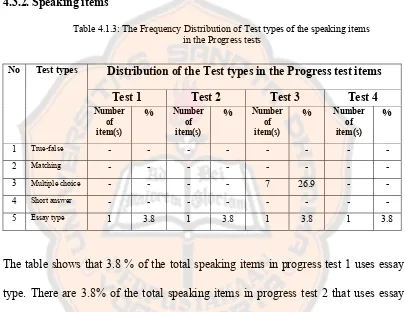
Table 4.1.3: The Frequency Distribution of Test types of the speaking items in the Progress tests
The table shows that 3.8 % of the total speaking items in progress test 1 uses essay
type. There are 3.8% of the total speaking items in progress test 2 that uses essay
type. There are 26.9% of the total speaking items in progress test 3 that uses multiple
choice type while there are 3.8% of the total speaking items in progress test 3 that
uses essay type. There are 3.8% of the total speaking items in progress test 4 that
uses essay type.
In the speaking test of Progress Test 1, four test types (true-false type,
matching type, multiple choice type, and short answer type) were not used. In the
speaking test of Progress Test 2, four test types (true-false type, matching type,
Distribution of the Test types in the Progress test items
multiple choice type, and short answer type) were not used. In the speaking test of
Progress Test 3, three test types (true-false type, matching type, and short answer
type) were not used. In the speaking test of Progress Test 4, four test types were not
used.
4.3.3. Reading items
Table 4.1.4: The Frequency Distribution of Test types of the reading items in the Progress tests
The table shows that there are 19.2% of the total reading items in progress test 1 uses
essay type. There are 19.2% of the total reading items in progress test 2 that uses
multiple choice type. There are 50% of the total reading items in progress test 3 that
uses multiple choice type while there are 38.5% of the total reading items in progress
test 4 that uses matching type.
In the reading test of Progress Test 1, four test types (true-false type,
matching type, multiple choice type, and short answer type) were not used. In the
speaking test of Progress Test 2, four test types (true-false type, matching type, short
Distribution of the Test types in the Progress test items
answer type, and essay type) were not used. In the speaking test of Progress Test 3,
four test types were not used. In the speaking test of Progress Test 4, four test types
(true-false type, multiple choice type, short answer type, and essay type) were not
used.
4.3.4. Writing items
Table 4.1.5: The Frequency Distribution of Test types of the writing items in the Progress tests
The table shows that there are 57.7% of the total writing items in progress test 1 uses
essay type. There are 38.5% of the total writing items in progress test 2 that uses
matching type. There are 19.2% of the total writing items in progress test 3 that uses
multiple choice type. There are 19,2% of the total writing items in progress test 4
that uses essay type.
In the writing test of Progress Tests 1, four test types (true-false type,
matching type, multiple choice type, and short answer type) were not used. In the
Distribution of the Test types in the Progress test items