THE USE OF POSITIVE REWARDS AND
PUNISHMENTS IN MANAGING CLASSROOM
BY AN ENGLISH TEACHER AT MTS JABAL
NOER GELURAN TAMAN-SIDOARJO
THESIS
Submitted in partial fulfillment of requirement for the degree of
Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd) in Teaching English
By:
Fitra Amaliya
NIM D05212010
ENGLISH TEACHER EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHER TRAINING
SUNAN AMPEL STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
SURABAYA
NIM. D05212010
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Sebagai sivitas akademika UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya, yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya:
Nama : Fitra Amaliya
NIM : D05212010
Fakultas/Jurusan : Fakultas Tarbiyah dan Keguruan/ Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris E-mail address : kurutafitra@gmail.com
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, menyetujui untuk memberikan kepada Perpustakaan UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya, Hak Bebas Royalti Non-Eksklusif atas English Teacher at Mts Jabal Noer Geluran Taman-Sidoarjo
beserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan Hak Bebas Royalti Non-Ekslusif ini Perpustakaan UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya berhak menyimpan, mengalih-media/format-kan, mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data (database), mendistribusikannya, dan menampilkan/mempublikasikannya di Internet atau media lain secara fulltext untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin dari saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis/pencipta dan atau penerbit yang bersangkutan.
Saya bersedia untuk menanggung secara pribadi, tanpa melibatkan pihak Perpustakaan UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya, segala bentuk tuntutan hukum yang timbul atas pelanggaran Hak Cipta dalam karya ilmiah saya ini.
Demikian pernyataan ini yang saya buat dengan sebenarnya.
Surabaya,
Penulis
(FITRA AMALIYA)
KEMENTERIAN AGAMA
UNIVERSITAS ISLAM NEGERI SUNAN AMPEL SURABAYA
PERPUSTAKAAN
ABSTRACT
Amaliya, Fitra. 2016. The Use of Positive Rewards and Punishments in Managing Classroom by An English Teacher at MTs Jabal Noer Geluran Taman-Sidoarjo. A Thesis. English Education Department, Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teacher Training, Sunan Ampel State Islamic University Surabaya. Advisor: M. Hanafi, M.Ag, MA.
Key Words: Positive Reward, Positive Punishment, Classroom Management This thesis is aimed to know the use of positive reward and punishment conducted by the teachers in managing English classroom. The research questions of the study are to find out what kind of positive reward and punishment used, how the implementations, and what the outcomes of positive reward and punisment used in managing english classroom. The subject of this study is a teacher and students of MTs Jabal Noer Geluran Taman-Sidoarjo.
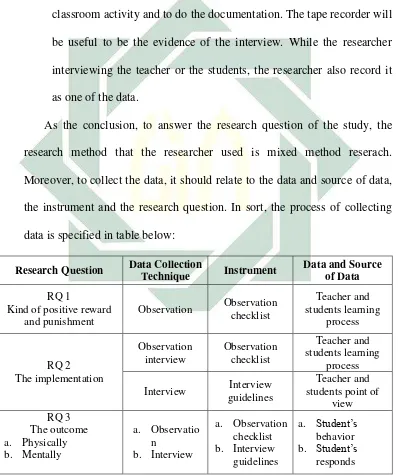
This study used mixed method research. To collect the data, the study used classroom observation, student teacher’s interview, and documentation. Classroom observation checklist and student teacher’s interview are the instruments to collect the data. Some steps used to analyze the data; those are data reduction, data display¸ data transformation, data correlation, data consolidation, data comparison and data integration.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ADVISOR APPROVAL SHEET ... i
APPROVAL SHEET ... ii
MOTTO ... iii
DEDICATION ... iv
ABSTRACT ... v
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... vi
PERNYATAAN KEASLIAN TULISAN ... viii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... ix
LIST OF CHART ... xii
LIST OF TABLE ... xiii
LIST OF APPENDIXES ... xiv
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Research Background ... 1
B. Research Question ... 6
C. Objective of the Study ... 6
D. Significance of the Study ... 7
E. Scope and Limits of the Study ... 7
F. Definition of Key Terms ... 8
G. Systematic of the Study ... 10
CHAPTER II REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ... 12
A. Classroom Management ... 12
1. Definition of Classroom Management ... 12
3. The Objective of Classroom Management ... 15
4. Controlling Students Behavior ... 16
B. Rewards and Punishments ... 18
1. Rewards and Punishments Theory ... 18
5. The Implementation of Rewards and Punishments ... 21
6. Use of Rewards and Punishments ... 25
8. Positive Punishments ... 33
C. Review of Previous Studies ... 35
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD ... 40
A. Approach and Research Design ... 40
B. Subject of the Study ... 41
G. Checking Validity of Findings ... 53
H. Research Stages ... 53
A. Research Findings ... 56
1. Kind of Positive Rewards and Punishments in Managing Classroom by the English Teacher at MTs Jabal Noer Geluran. ... 56
2. Implementation of Positive Rewards and Punishments in Managing Classroom by the English Teacher at MTs Jabal Noer Geluran ... 67
3. Outcome of Positive Reward and Punishments in Managing Classroom by the English Teacher at MTs Jabal Noer Geluran ... 81
B. Discussion ... 88
1. Common Positive Rewards and Punishments ... 88
2. Six Common Ways to Implement Positive Reward and Punishment ... 94
3. Five Outcomes In Students Behavior and Classroom Management ... 98
CHAPTER V CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 101
A. CONCLUSION ... 101
1. Kind of Positive Rewards and Punishments in Managing Classroom by the English Teacher at MTs Jabal Noer Geluran ... 101
2. Implementation of Positive Rewards and Punishments in Managing Classroom by the English Teacher at MTs Jabal Noer Geluran ... 103
3. Outcome of Positive Rewards and Punishments in Managing Classroom by the English Teacher at MTs Jabal Noer Geluran ... 104
B. SUGGESTION ... 105
REFFERENCES ... 107
LIST OF CHART
LIST OF TABLE
Table 2.1 Types of rewards and punishments theory...20
Table 2.2 Three basic of positive reinforce categories...30
Table 3.1 Techniques for Collecting Data Based on Research Questions...45
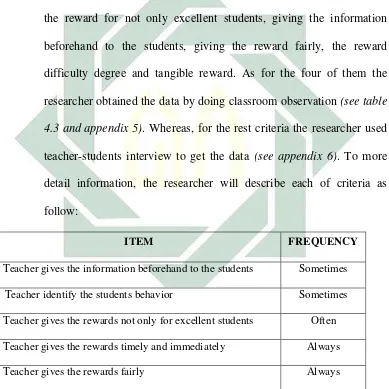
Table 4.3 The implementation of positive rewards by observation checklist ...64
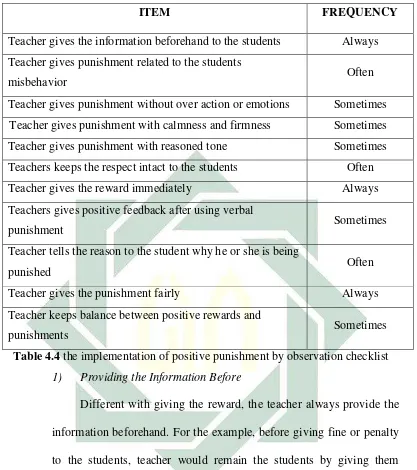
Table 4.4The implementation of positive punishments by observation Checklist...69
LIST OF APPENDIXES
Appendix 1
Observation Checklist Appendix 2
Teacher’s Interview Guidelines
Appendix 3
Student’s Interview Guidelines
Appendix 4
Surat Validasi Instrumen Appendix 5
Data Display: Observation Appendix 6
Data Display: Interview Appendix 7
Surat Tugas Dosen Pembimbing Appendix 8
Kartu Konsultasi Appendix 9
Surat Keterangan Penelitian Appendix 10
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
On this chapter as the introduction of the thesis, the researcher explains the background of the study as the reason of the research, the research question which the researcher will be answered by the study, research objective as the purpose of the study, scope and limitation, significance of the study and keywords definitions.
A. Research Background
In teaching and learning process, the role of teacher is very crucial in the class. One of the most important skills that teachers should have in teaching and learning process is the ability to manage the classroom. Marzano states that the most important role of teachers among the other roles is as a manager. Teachers should be able to manage classes well and provide conditions that enable students to learn in order to obtain the expected results.1 If teachers cannot properly manage the classrooms, teaching and learning process will not run effectively. An effective classroom teaching depend on the teachers role and responsible in managing classroom that involves goals, time spent, relationship, students choices and freedom, student misbehavior, etc.2 According to Colin and Robert, effective classroom management is considered through four aspects: management in the
1
Robert J. Marzano, Classroom Management that Works: Research-Based Strategies for Every Teacher (Virginia USA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development, 2003), p. 1. 2
classroom, mediation with individuals, modification of behavior, and monitoring school discipline.3 In the modification of behavior, the teacher should be able to manage the students’ interaction with other student and students with the teacher and controlling students’ behavior.
For some teachers, controlling and manage the students behavior in the class is quite hard. Especially for the class that has the variety of the students background that some of them is troublemaker and has problem behavior such as fighting, disrespect, defiance, hostility toward the teacher, damaging school property, refusing to accept sanctions or punishments and so on. Actually, the good learning environment for the students to study is important because an effective classroom teaching means that the learning environment should be orderly and quiet.4 In this kind of classrooms, the student can have more focus in learning and the teacher can teach the students comfortably.
Not only the teacher, should the students also feel comfortable with the situation of the class. Classes are convenient not only of how nice and neat the classrooms is, but also in terms of the condition and situation where the teacher can manage the students effectively. Classroom behavior problems are considered as one of the factor that determines how well the teacher delivers the lesson. As the evidence, there is a survey of public agenda where 75% of the teachers were able to teach effectively, if there were no disruptive behaviors in classrooms. As the result, the teacher strategy and technique in
3
Colin J. Smith and Robert Laslet, Effective Classroom Management, Second edition (London: Taylor and Francis e-Library, 2002), p. i.
4
managing classroom especially in managing student’s behavior is urgently needed.
As the teacher, it can be really tiresome and bothersome when to deal with the chaotic class with the misbehavior students. As the result, those behaviors must be minimized for learning to occur effectively. However, it needs to be remembering that not all the students are misbehavior. There are also appropriate and good student’s behaviors. For this kind of behavior the teacher also need to make the students maintaining those appropriate behavior. Since the teacher cannot appreciate the students good behavior, the students may feel disappointed and be unmotivated to do the same behavior again especially in following the learning process. In these circumstances the teacher not only need to minimize the student’s problem behavior, but also maintaining the appropriate behavior.
One of the techniques that can be used for the classroom management especially in managing student’s behavior is by giving the rewards and punishments. Rewards and punishments are two techniques used frequently by teachers in classrooms for controlling behaviors. A reward is used for getting a behavior to occur more often. On the contrary, punishment is a consequence that decreases the probability that a behavior will occur.5 Those techniques have the similar purpose in managing the students’ behavior to create the good environment for the students.
The theory of rewards and punishments was founds since hundreds years ago. However, in Indonesia and other country giving rewards and
5
punishments to the students become a culture in term of education. Actually, there is a stereotype of punishments in society that in some people opinion, punishments was related with corporal and strictness. For children in many countries, corporal punishment is a regular part of the school experience; it is also a form of child abuse.6 However, there are also positive punishments as the extrinsic motivation for the students to learn. Moreover, this kind of punishments might be helpful to educate the students.
Some teachers belief that positive rewards and punishments were used to discipline the students in having the English learning process effectively. One of them is the English teachers in MTs Jabal Noer Geluran. According to the researcher preliminary, research at PPL2, This school condition related to the students environment of Islamic boarding school where rewards and punishments are allowed. Although the students are studying in Islamic boarding school, they have some disruptive students that often make the class in chaos. Because of that, the teacher applies the positive rewards and punishment to manage the student’s behavior so that the learning process can run effectively.
To solve those problems and misconception about punishment, the researcher wants to discuss and analyze some kind of the positive rewards and positive punishments used by the English teacher to manage the English classroom at MTs Jabal Noer Geluran. This study also discuss about the right implementation and the way the teachers deliver the rewards and punishment and the impact of positive rewards and educative punishment to the students.
6
UNESCO Asia and Pacific Regional Bureau for Education, Positive Discipline in the Inclusive, Learning-Friendly Classroom: a Guide for Teachers and Teacher Educators (Bangkok:
Moreover, the researcher also is more specific in positive rewards and positive punishment as the alternative of corporal punishment. In addition, the students’ response toward the classroom management conducted by the teachers.
This study is the continuing research because there were also some previous study discuss about the rewards and punishment theory in the classroom. Most of the study is about the role of rewards and punishment, and the issue of corporal and the effectiveness of punishment.7 However, this study has different focus from those previous researches. This research is more specific in positive rewards and punishment, which has the main purpose to educate the students and make them to be more responsible and discipline. While the previous study take place for general subject. This research takes the new idea of investigating the classroom management especially in teaching English classroom. Therefore, that it also explain some rewards and punishment that suitable in English classroom. Hence, the researcher conducts this study to identify the form of positive rewards and positive punishments used by the teacher and to analyze the way the teacher use positive rewards and positive punishments in managing the English classroom at MTs Jabal Noer Geluran.
7John W. Maag, “R
B. Research Question
The leading research questions that the researcher proposes to pursue are:
1. What kinds of positive rewards and positive punishments does the teacher commonly use in managing the English classroom at MTs Jabal Noer Geluran?
2. How do the teacher uses positive rewards and positive punishments in managing the English classroom at MTs Jabal Noer Geluran?
3. What are the outcome of positive rewards and punishments in managing the English classroom at MTs Jabal Noer Geluran?
C. Objective of the Study
Based on the background of the study that has been explained above, the research objectives that the writer wants to achieve by this study are: 1. To identify the form of positive rewards and positive punishments
commonly used by the teacher in managing the English classroom at MTs Jabal Noer Geluran.
2. To analyze the way the teacher use positive rewards and positive punishments in managing the English classroom at MTs Jabal Noer Geluran.
D. Significance of the Study
Theoretically, the result of the study hopefully will show the function of the use positive rewards and positive punishments in classroom management in teaching English. It is expected that it will add to the education theory development. Especially for the students in English education department and English teacher for their references in managing the classroom while teaching English.
For the author, this study will be so valuable as the knowledge and sources in managing the classroom. Therefore, the author may apply this knowledge in the future when she becomes the English teacher.
For the students, this study will help them to increase their motivation in learning English and be more discipline in the classroom. So that they can learn English effectively and will be more responsible in their role as the students.
For the teacher, this study will give them the awareness about the significant of positive rewards and positive punishments. In addition, they can avoid the use of corporal punishments and negative rewards instead in order to manage the classroom.
E. Scope and Limits of the Study
by the English teacher at MTs Jabal Noer Geluran. To make the discussion specific, the researcher emphasize the research in the kind of positive rewards and positive punishments, the way to use and the outcome of positive rewards and positive punishments.
The limitation of this study will focused on the students in MTs Jabal Noer Geluran, especially for students in the VII grade year 2015/2016. Here, the researcher chooses this school because the teacher used this strategy as their reference for classroom management. Moreover, the environment of the school that most of the students is in the Islamic boarding school where rewards and punishments are common and allowed.
F. Definition of Key Terms
There are several important keywords to define in this study that help the researcher do the research and understand the concept of the study clearly.
1. Classroom management
The action teachers take to create an environment that is respectful, earning, orderly, and productive. Classroom management support and facilitates both academic and social-emotional learning.8 On the other words, classroom management is the way the teachers manage the classroom and the student’s behavior in order to create the effective
learning process.
2. Rewards and Punishments
Reward and punishment is one of the techniques in classroom management especially in controlling student’s behavior aspect.
8
Reward is a consequence that increases the probability for a behavior will occur. It refers to anything that follows a behavior and increases the likelihood of that behavior. In addition, it is assumed after giving the rewards the behavior’s of students will happen again.
On the other hand, punishment is a consequence that decreases the probability for a behavior will occur.9 The teacher may use punishments to educate and discipline the students and give them a moral lesson not to do the same mistake again.
3. Positive rewards
The frequency of a response increases because it is followed by a rewarding stimulus.10 For the example: the teacher gives the students praise for their excellent score in the test.
4. Positive punishments
A consequence that decreases the probability for a behavior will occur by adding an unpleasant stimulus.11 For the example is when the students cheat in the test the teacher will give the punishments additional assignment
5. The implementation of rewards and punishments
The implementation of reward and punishment is the way the teacher deliver rewards and punishment in order to have the best result such as provide the student with an alternative means of obtaining some
9
Santrock, Educational Psychology: Classroom Update: Preparing for Praxis and Practice, p. 216.
10
Susan Lamke et al., the Well-managed Classroom: Strategies to Create a Productive and Cooperative Social Climate in Your Learning Community, Illustrated edition (Boys Town Press, 2007), p. 45.
11
positive reinforcement, punish for being off-task, also reinforce for being on-task, and avoid physical punishment and so on. 12
6. Use of rewards and punishments
In general, the purpose of the rewards and punishments strategy in form of learning is to produce changes in the probability that some behavior will occur.13 It means that by giving the rewards and punishments can motivate the students to do better in their learning process by changes the misbehavior or maintaining the appropriate behavior.
G. Systematic of the Study
This thesis systematically consists of five chapters. Here are the short description of its contain:
Chapter one is introduction. On this chapter as the introduction of the thesis, the researcher explain about the background of the study as the reason of the research, the research question which the researcher will be answered by the study, research objective as the purpose of the study, scope and limitation, significance of the study and definitions of key term.
Chapter Two is review of related literature. The literature review chapter explains about some theory that support and review the previous study that has correlation with the topic chosen by the researcher. This chapter focuses on classroom management and its objective, rewards and punishments
12
Robert E. Slavin, Educational Psychology: Theory and Practice, Tenth edition (New Jearsey: Pearson, 2012), p. 337.
13
theory, the implementation and the use of rewards and punishments and about the positive rewards and positive punishments.
Chapter Three is research method. This chapter concern on the methodology and the procedure to develop the study. On the research method, the researcher tries to conduct the valid and reliable research by its method and its analysis. The subtitles of this chapter are approach and research design, subject of the study, data collection technique, data collection instrument and data analysis technique.
Chapter Four is research findings. This chapter concern about the finding and the discussion of the research. It consists of data display and research discussion.
Chapter Five or the last chapter is conclusion and suggestion. It is explain the conclusion about the research and some suggestion for the reader or the teacher.
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
The literature review chapter will explain about some theory that support and review the previous study that has correlation with the topic chosen by the researcher. This chapter will focus on the classroom management, rewards and punishments theory and review of previous study.
A. Classroom Management
1. Definition of Classroom Management
Classroom management is one of the crucial aspects in teaching and learning process. It is important to create effective teaching and learning process. Marzano states that the most important role of teachers among the other roles is as a manager. Teachers should be able to manage classes well and provide conditions that enable students to learn in order to obtain the expected results.1 The successful of teaching and learning process is depending on the ability of teachers to organize classrooms and manage the behavior of their students. James M. Cooper states that classroom management refers to the action teachers take to create an environment that is respectful, earning, orderly, and productive. Classroom
1
management support and facilitates both academic and social-emotional learning.2
Another definition of classroom management, by Jim Scrivener, is how the way the teacher manages their student’s learning by organizing and controlling what happens in the classroom. Jim also added that classroom management is ways of keeping order in class and specifically to discipline-related problems.3 It is supported by Wilford A. Weber definition of classroom management that it is a complex set of behaviors the teacher uses to establish and maintain classroom condition that will enable students to achieve their instructional objective efficiently that will enable them to learn.4 From the explanation above, it can be concluded that classroom management is the way the teacher manage the students, environment, and the class in order to have the effective teaching and learning process.
Furthermore, one of the teacher’s ability in managing classroom is to be able to controlling students behavior. Gordon Lyons also state that it is critical necessary of teachers’ ability in executing the student behavior
and classroom problems strategically.5 Thus, it needs to maintain effective classroom management that teachers are required to be able in organizing
2
James M. Cooper, Classroom Teaching skill, ninth edition edition (USA: Cengage Learning, 2011), p. 217.
3
Jim Scrivener, Classroom Management Techniques (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012), p. 1–2.
4
Cooper, Classroom Teaching skill, p. 230. 5
the classroom and managing behavior problems created by students to attain the educational outcome positively.6
According to Colin and Robert, effective classroom management is considered through four aspects:
a. Management in the classroom: It is related on analyzing classroom organization and reducing sources of friction in the class.
b. Mediation with individuals: It is refers to knowledge of how to provide the counseling and guidance which some students require, understanding their problems and avoiding damaging confrontations in the classroom.
c. Modification of behavior: It involves applying learning theory to shaping and changing behavior in ways which are practical and realistic within the routine of the normal classroom
d. Monitoring school discipline: It considers how schools evaluate the effectiveness of policies on discipline.7
From all the aspect above, it can be interpret that effective classroom management is about the teacher ability to manage the students’ interaction with other student and students with the teacher and controlling students’ behavior. And in modification of behavior aspect,
the teacher also should be able to modify the student’s behavior to be better in supporting learning process.
6
Regina M. Olive and Daniel J Reschy, Effective Classroom Management: Teacher Preparation and Professional Development" National Comprehensive Center for Teacher Quality (Washington DC: 2007), p. 1.
7
2. The Objective of Classroom Management
Classroom management is intended to create conducive learning environment for students so that the learning objectives are achieved effectively and efficiently. When the class is interrupted, the teacher must try to overcome them, so that the class condition can be conducive and teaching and learning process can run smoothly. According to Corrie as cited by Hue Ming-tak and Li Wai-Shing, classroom management is a necessary condition for the creation of a supportive, respectful learning environment. Effective teaching and learning can take place only if there is good order and positive learning climate in the classroom, the view that discipline is a crucial dimension of classroom management and is essentially a means to create the necessary condition for learning has been endorsed by various educationalist.8
Another objectives of classroom management was also proposed by Jim that good classroom management is the condition where teacher and learners can work together and talk or listen each other in respectful and supportive manner and also it is to do with creating the conditions where such an atmosphere likely to exist.9 Here, to create the condition of effective classroom management, the role of the teacher as the manager of the class is important.
From the classroom management objectives above, it can be concluded that the objective of classroom management is to create and maintain conditions of class so that the learning process can run well. It is
8 Hue Ming-tak and Li Wai-Shing, Classroom Management : Creating a Positive Learning Environment (Hongkong: Hongkong University Press, 2008), p. 5.
9
mean that the effort made by the teacher is to make the students spirit and enthusiasm in following the classroom activities and to make sure that the students is learning not only listening and following the activities is the class.
3. Controlling Students Behavior
As we know that students are often make trouble in the classroom and difficult to handle. A teacher who does everything to avoid trouble may still have problem because of students. Student misbehavior can be caused by many things, both from situations outside and inside the classroom.
Therefore, teachers should have good techniques to control the students’ behavior. Haddad states in his book that one of the techniques in managing students’ behavior is using positive discipline technique. In
addition, the great majority of behavior problems which a teacher must deal are relatively minor disruption, behavior that would be appropriate on the playing field but not in the classroom.10 Moreover, Edmund and Carolyn divided the student’s problem behavior into four categories and one special problem:
a. Non problem are common behavior that are not really problems for anyone because they are of brief duration and don’t interfere with learning process such as some talk during activities transition, brief inattention and a short pause while working on an assignment.
b. Minor problem are behaviors that run counter to class procedure or rules but do not disrupt class activities or seriously interfere the learning process such as students calling out, leaving seats without permission, doing unrelated work in class, eating candy and so on. c. Major problem included behavior that disrupt the learning process but
whose occurrence is limited to one or few students only. For the example are students chronically off test, cheating on a test, rarely complete the assignment etc.
d. Escalating or spreading problem are the minor and major problem that has become common place and constitutes treat to the learning environment such as continuously social talking even when the teacher repeatedly ask for quiet. Talking back and refusing to cooperate with the teacher and others.
e. Special problems is some problem occur commonly enough in the class and need to handle it although it is not frequently happened such as fighting, aggressive behavior, chronic avoidance of work, bullying, disrespect, defiance, or hostility towards the teacher and so on.11
As the teacher, its can be really tiresome and bothersome when they deal the chaos class with the misbehavior students. As the result, those behaviors must be minimized for learning to occur effectively. However, it needs to be remembering that not all the students are misbehavior. There are also appropriate and good student’s behaviors. According to Edmund T.
Emmer, there are two categories of students appropriate behavior.
11
a. Student involvement in learning process
Student involvement is indicated by many behaviors, including attention during presentation and discussion, progress on seatwork and other assignment etc.
b. Student’s compliance with classroom rules and procedures
It is for every student that does all the rule and procedure in the class. It is based on the contract that the teacher and students made before.12
In both of categories, the teacher should be able to keep maintaining the student’s appropriate behavior. So that they can always stand to be a good students and the learning process can run smoothly. As the result, there are some techniques for the teacher to maintaining the students appropriate behavior and minimalize their misbehavior. One of the techniques is by giving rewards and punishments.
B. Rewards and Punishments
1. Rewards and Punishments Theory
It is a common belief that schools are not just responsible for imparting basic knowledge and skills, but also plays an important part in helping students develop responsible behaviors. Problems happen in everyday classroom life and should be handled by teachers. Rewards and punishments are two techniques used frequently by teachers in classrooms for controlling behaviors. A reward is used for getting a behavior to occur
12
more often. On the contrary, punishment is a consequence that decreases the probability that a behavior will occur.13
The theory of rewards or reinforcement and punishments were founded by BF Skinner cited by John W. Santrock. In Skinner theory responses are controlled by their consequences, Skinner found that a behavior is repeated when followed by a positive consequence and behavior is not repeated when followed by a neutral or negative consequence.14 Respond and stimulus in here is the rewards and punishments. In Skinner theory also explained about the positive and negative of rewards and only one kind of punishments. However, in Susan Lamke book there are some type of rewards and punishment:
a. Positive rewards or positive reinforcement is the frequency of a response increases because it is followed by a rewarding stimulus. For example: the teacher gives the students praise for their excellent score in the test.
b. Negative rewards or negative reinforcement, the frequency of a response increases because it is followed by the removal of unpleasant stimulus. For example: the teacher always nags at the students to do the task and keep nagging so that makes the students stressful.
c. Positive punishment is a consequence that decreases the probability that a behavior will occur by adding an unpleasant stimulus. For the example is when the students cheat in the test the teacher will give the punishments by giving additional assignment
13
Santrock, Educational Psychology: Classroom Update: Preparing for Praxis and Practice, p. 216.
14
d. Negative punishment is a consequence that decreases the probability that a behavior will occur by withdrawing an unpleasant stimulus. A student is losing part of his free time for not following the teacher’s instruction.15
Strength of Behavior
Consequences
Increases Decreases
Stimulus is Presented Positive Reinforcement Positive Punishment
Stimulus is Removed Negative Reinforcement Negative Punishment
Table 2.1 Types of rewards and punishment theory 16
In addition, ministry of education in Uganda differentiates the punishments between corporal punishments and positive discipline as the positive punishments to help the students decrease their misbehaving in the classroom.17 In the positive punishments, the teacher uses punishments to educate the students such as giving another assignment, time out and so on. While in the corporal punishments, it is like giving the students a harm and strictness. Moreover, this kind of punishments is likely to be avoided by the teacher.
15
Susan Lamke et al., the Well-managed Classroom: Strategies to Create a Productive and Cooperative Social Climate in Your Learning Community, p. 45–54.
16
Paul Chance, Learning and Behavior: Active Learning Edition (Cengage Learning, 2008), p. 128.
17
4. The Implementation of Rewards and Punishments
As the explanation above that, the main purpose in giving rewards and punishment technique is to maintaining the student’s good behavior and minimize the student’s misbehavior. However, to implement the rewards and punishment technique is not easy, as it seems. Because the result of the student’s behavior also depends on the way the teacher deliver those techniques effectively. Hence, in delivering the rewards and punishment, the teacher need to consider about some criteria and tips in implementing those technique.
In giving the rewards, the teacher should consider the target behavior that he/she would like to encourage. Because giving rewards too easily or too difficult can lose their motivational effect, and the teacher should be careful not to set up the rewards that only the most able students can achieve, but also for improvement, excellent effort, good conduct, and so on.18 Rewards should be given not only for excellent students, but also for students who usually do less well should be rewarded when they do better.19 In addition, the teacher should choose effective reinforces because not all reinforces are the same for every students, make rewards contingent and timely. The teacher must give rewards only after the students perform desirable behavior and it is more effective when they are given in a timely way, as soon as possible. Moreover, it has to be positively reinforcing and
18
Emmer and Carolyn M. Evertson, Classroom Management for Middle and High School Teachers, p. 139.
19
educate the students, and be sure to identify the student’s behavior.20 Giving the fair chance for every students and be selective in giving the rewards is the best choice for the teachers to make.
Robert E. Slavin gives some guideline for the use in implement the rewards to increase desired behavior in the classroom as follows:
a. Decide what behaviors you want from the students, and reinforce
these behaviors when they occur. For example, praise or rewards for a good work. Do not praise or rewards work that is not up to student’s capabilities. It is best to use positive rewards the least elaborate and tangible rewards that will work. In other words, if praise its self will work, don’t use small toys or materials incentives.
b. Tell the students the behavior you want and the reason. In giving the reason to the student for everything they accomplished is taught them to realize its value and make them to be more motivated.
c. Reinforce appropriate behavior as soon as possible after it occurs.
Delayed reinforcement is less effective than immediate reinforcement. It is important that students know how they are doing in class. So do not delay their grades, praise or feedback.21
On the other hand, there are also some criteria for the effective use of punishment. The punishment should not be given by the teacher arbitrarily, because the punishment is not a free action that has the attention
20
Santrock, Educational Psychology: Classroom Update: Preparing for Praxis and Practice, pp. 218–219.
21
and in control by the society and government.22 In those circumstances, O’Leary and O’Leary list some principles for the effective and human use of
punishment as follows:
a. Make it clear to the student why he or she is being punished
b. Provide the student with an alternative means of obtaining some positive reinforcement
c. punish for being off-task, also reinforce for being on-task d. Avoid physical punishment
e. Avoid punishing while in a very angry or emotional state f. Punish when a behavior starts than when it ends.23
In giving positive punishment, it should always in conjunction with providing the child information about appropriate and inappropriate behavior before. Punishment should be delivered immediately after unwanted behavior rather than later and when they are quick and to the giving verbal reminders, the teacher should avoid comparative evaluations
22
Ngalim Purwanto, Ilmu Pendidikan Teoretis dan Praktis, Second edition (Bandung: Remaja Rosdakarya, 2011), p. 191.
23
Slavin, Educational Psychology: Theory and Practice, p. 337. 24
Santrock, Educational Psychology: Classroom Update: Preparing for Praxis and Practice, pp. 222–225.
25
with other students especially of lower ability students with the higher one, because it can decrease their motivation in learning.26
It is better to give the students “task related” punishment. For the example if the students did not do the homework, they should do it three times. This punishment is positively can motivate the students to learn more. When giving the punishment, the teacher should consider the schools law and rules and keep the respect intact to the students. Moreover, it is better that the consequences emphasize fairness and justice in its implementation.27
The important principles according to Robert in delivering the positive rewards and punishment are contingency, specificity and credibility.28 The teacher also should select reinforces and criteria for rewards, select punishers and criteria for punishment if necessary.29 Keep the balance between positive rewards and punishment, behavior and its consequences is also crucial.30 As the conclusion, not only the form of the rewards and punishment given, but also how to deliver and implement those rewards and punishment, has the important role to make the rewards and punishment be more effective.
5. Use of Rewards and Punishments
In the classroom management, when the teacher use the rewards and punishment, they should know and aware of the function or the
26
Emmer and Carolyn M. Evertson, Classroom Management for Middle and High School Teachers, pp. 135–137.
27
Rogers, Classroom Behaviour, Third: 146–148. 28
Slavin, Educational Psychology: Theory and Practice, p. 309. 29
Ibid., p. 335. 30
purpose of those strategy. It is intended to give the awareness for the teacher, when giving some treatment; it has the specific purpose or function why the teacher chooses the strategy. Because every choice the teachers make, it has a meaning behind it. In general, the purpose of the rewards and punishment strategy in form of learning is to produce changes in the probability that some behaviors will occur.31 As well as the Santroct statement, Robert also said that positive reinforces or reward is the way to strengthen a behavior while positive punishment is the way to weaken behavior, escape from unpleasant situation or preventing something unpleasant from occurring.32 It means that by giving the rewards and punishment can motivate the students to do better in their learning process by changes the misbehavior or maintaining the appropriate behavior.
Although the main purpose of the rewards and punishment is similar. There are also some different in each concept of purpose or function. Reinforcement means to strengthen or increasing the students desirable behavior in hope that those behavior will occur again.33 Larson states that by recognizing and rewarding good behavior, teachers provide motivation for the students to improve their social skills.34 As in rewards, Santrock and Edmund also clarify about some uses of rewards.
a. Rewards uses as incentive to engage in task and learning, in which case the goal is to control the student’s behavior. For the example the
31
Santrock, Educational Psychology: Classroom Update: Preparing for Praxis and Practice, p. 215.
32
Slavin, Educational Psychology: Theory and Practice, pp. 120–121. 33
Santrock, Educational Psychology: Classroom Update: Preparing for Praxis and Practice, p. 216.
34
teacher gives the students some rewards if the get the best score on test. This function lead to perception, that the students behavior was caused by external rewards, and not by the students own motivation to be competent.
b. Rewards used to convey information about students mastery that can increase the students intrinsic motivation by increasing their sense of competence. For the example, the teacher puts a reward system in which the more work students accomplish, the more points the will earn. Here, the students will be motivated and feel competent in their work.35
c. Reward as an extra motivational tool to encourage students to practice appropriate behavior or to improve participation to under motivated students such as recognition, positive feedback and the satisfaction that accompanies learning and goal attainment.
d. Convey confident in the student’s ability to do well in the classroom. For the example by displaying an encouraging “can do” attitude, that generates student’s excitement and self-confidence.36
Positive rewards given by the teacher will be able to improve positive class climate and add interest and excitement to the class. Class climate here means that the students will respond positively to the teacher, and contributing to a mutually supportive pattern of interaction.37 It also can help teacher manage their classroom effectively and can improve some
35
Santrock, Educational Psychology: Classroom Update: Preparing for Praxis and Practice, p. 421.
36
Edmud T. Emmer and Carolyn M. Evertson, Classroom Management for Middle and High School Teachers, eight edition (New Jearsey: Pearson, 2009), p. 124–125.
37
students conduct.38 In group rewards, it can make the students be more cooperative and cohesive to each other in the class.39 Giving positive rewards for appropriate behavior allows the students who lack skills to observe others being praised for positive behavior.40
On the other hand, the purpose of the punishment, there are two kinds, namely in short term and long term goals. The goal in the short term is to stop the misbehavior, whereas in long term goal is to teach and encourage students to be able to stop their own misbehavior. In a pedagogical perspective, punishment is used with the aim to facilitate the way for the achievement of educational goals to be easier.41
According to Santrock, positive punishment main objective is to decrease the students undesirable behaviors.42 Prompt and time out as the example of positive punishment can help the teacher to prevent the inappropriate behavior or its escalation and to teach the students learn self-control and rethink about their misbehavior in the class.43 Giving feedback or verbal punishment can change the student’s mindset about the connection between behavior and consequences. It also can increase the
38
Santrock, Educational Psychology: Classroom Update: Preparing for Praxis and Practice, p. 225.
39
Emmer and Carolyn M. Evertson, Classroom Management for Middle and High School Teachers, p. 141.
40
Slavin, Educational Psychology: Theory and Practice, p. 67. 41
Ngalim Purwanto, Ilmu Pendidikan Teoretis dan Praktis, Second edition (Bandung: Remaja Rosdakarya, 2011), p. 187–188.
42
Santrock, Educational Psychology: Classroom Update: Preparing for Praxis and Practice, p. 222.
43
informational value of the feedback by catching them in the act of being good.44
The principle of positive rewards and punishment is that the students should be reinforced for not only within their current capabilities but also stretch and teach them towards new skill and knowledge.45 giving the consequences of the students behavior or positive punishment are an attempt by the teacher to link the wrong behavior of the students to an outcome that hopefully, will emphasize fairness and justice, and may even teach the students about accountability and responsibility. As the result, the students will experience the consequences of their own behavior about what they do and how they treat others.46 However, Paul chance recommended a combination of positive punishment and positive rewards in order to gain the best result of those techniques in managing classroom.47
From the description above, we can draw the conclusion that any theory is not complete yet, because it is only one aspect. Each theory needs each to be the complete theory. In addition, the main use of rewards and punishment is to maintaining the students appropriate behavior and minimize the student’s misbehavior.
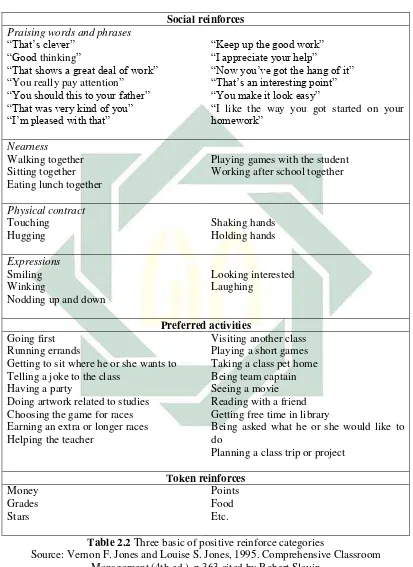
6. Positive Rewards
One type of rewards is the positive rewards. Positive rewards is the frequency of a response increases because it is followed by a rewarding
44
Slavin, Educational Psychology: Theory and Practice, p. 126. 45
Ibid., p. 127. 46
Rogers, Classroom Behaviour, Third: 146. 47
stimulus, as in the example in which the teacher’s positive comments increased the students writing behavior.48 In addition, it is assumed after giving the positive rewards the behaviors of students will happen again. Edmud and Carolyn explained some example of positive rewards that can be used for the teacher in managing classroom.
a. Grades and other symbols, In this strategy, the teachers use some grade such as A+, excellent, 100 etc., and other symbols such as star, table marking, sticker, etc. to appreciate the student’s behavior or achievement in the class.
b. Recognition, Recognition in here means of giving attention to the student. For the example: by praising them in fronts of the class, awarding a certificate for achievement, or displaying the students work or project.
c. Competition, The teacher held a competition for the student and chooses the best students of the class are one way to create the rewards activity. It can make the students have a high motivation to do the assignment.
d. Activities as rewards, The example of activities as rewards are work with a friend, free computer or reading time, visit the school library, watch an English movie in the class or another activity that support the students learning process.
e. Material incentives, it includes the awarding of objects of value to the students. For the example are food, pen, books, games and other
48
“That shows a great deal of work” “You really pay attention”
“Now you’ve got the hang of it” “That’s an interesting point”
Getting to sit where he or she wants to Telling a joke to the class
Having a party
Doing artwork related to studies Choosing the game for races Earning an extra or longer races Helping the teacher
Planning a class trip or project
Token reinforces Table 2.2 Three basic of positive reinforce categories
Source: Vernon F. Jones and Louise S. Jones, 1995. Comprehensive Classroom Management (4th ed.), p.363 cited by Robert Slavin
49
Robert proposes three basic of categories of positive reinforce or positive rewards as follows: Social reinforces such as praise, smiles, hugs, recognition or attention. Activity reinforces such as access games, watching movie, field trip and other fun activity. And the last is token or symbolic reinforces such as money, grades, stars, or points. Besides those three basic categories, there are also other example of positive rewards such as call home and privileges. Call home is calling or sending a note to the parents to tell their children excellent behavior. While the example of privileges are games, special roles, allowed to line up first or to have other small privileges.50
In increasing desirable behaviors, Santrock also give some kind of rewards. There are contracting, prompts and shaping. Contracting is giving the rewards by write a contract with the students beforehand. Prompt is the promise or an added stimulus or cue that the teacher give just before a response and increases the likehood the response will occur. While, shaping is the rewards that involves teaching new behaviors by reinforcing successive approximations to desirable behavior. In addition, shaping used only when contracting and prompts is not working because it needs patient and period. Group rewards is also one of the examples of positive rewards. This reward can be used for entire class. For the example: if the main score of this class increased in the test, we will watch English movie next 2 week. This reward also has the benefit to teach the
50
students class cooperation and togetherness.51 In addition, there are also verbal rewards such as praise and giving feedback to enhance students motivation.52
As the summary, there are many kinds or form of the positive rewards. As three basic categories of rewards there are social reinforces, preferred activities and token reinforces. Group rewards, recognition, competition, contracting, prompts, shaping also some of their form of positive rewards.
7. Positive Punishments
In Indonesia society there is a stereotype of punishments that in some people opinion, punishments was related to corporal and strictness. However, there are also positive punishments as the extrinsic motivation for the students to learn and the alternative of corporal punishment in classroom. The Ministry of Education and Sports in Uganda define the positive discipline or positive punishment is a different way of guiding students by paying attention to their emotional and psychological needs and it is includes nonviolent consequences for misbehavior.53 Moreover, this kind of punishments might be helpful to educate the students because it helps students learn self-discipline without fear.
In the positive punishments, the teacher uses punishments to educate the students such as giving another assignment, time out and so on. In the book of classroom management for middle and high school teachers by
51
Santrock, Educational Psychology: Classroom Update: Preparing for Praxis and Practice, pp. 219–222.
52
Ibid., p. 421. 53
Edmund and Carolyn examine some example of positive punishments that did not harm the students.
a. Use nonverbal cues. This punishment is for the minor intervention problems. The teacher can punish the students by giving a signal such as a finger to the lips, a headshake (no-no!), and making eye contact to the students, slightly touching a student and so on.
b. Use a fine or penalty. For teaching English this punishment is the most suitable for the students. By giving a fine or penalty, it also can improve the English student’s skill. For the example write verb conjunction, memorize some English vocabulary, multiplying the English task, etc.
c. Use proximity. Move closer to the students and combine proximity and nonverbal cues to stop inappropriate behavior without interrupting instruction.
d. Assign detention or time out. Time out and assign detention is used for the students to help the students learn self-control and rethink about their misbehavior in the class. The student should move out the class and permitted to enter the class only after making a commitment to change the behavior.
again. For the example, if i (john) did not do the homework, i will have to do it again twice.54
In decreasing undesirable behaviors, Santrock has two techniques of punishment, there are times out and respond cost. As the same of Edmund theory, time out is giving some time for the students to rethink about their mistake while respond cost is the same as fine or penalty. Santrock also suggest some reprimand or verbal punishment as the positive punishment to decrease the student’s undesirable behaviors.55 Robert also purposes some example of positive punishment that can be used such as verbal reminders, repeated reminders and applying consequences for decreasing the student misbehavior.56
As the summary, there are many kinds or form of the positive punishment such as nonverbal punishment, verbal punishment/ reminders, repeated reminders, fine or penalty, detention or time out, individual contract, applying consequences and task-based punishment.
C. Review of Previous Studies
Many researchers have carried out the study related to this topic. In this part, the researcher reviews some of previous study for other researcher that has similar focus with this study. There are some researchers that have similar focus on rewards and punishment topic such as, “Rewarded by Punishment: Reflections on the Disuse of Positive Reinforcement in Schools” by John W. Maag University of
54
Ibid., p. 174–184. 55
Santrock, Educational Psychology: Classroom Update: Preparing for Praxis and Practice, pp. 222–224.
56
Lincoln. This study is about the positive rewards and their reflection of the effectiveness and the misprejudice of the punishments in school. In addition, it examines the reason why some school chooses punishments rather than the positive rewards. This article also argues for educators to plan the occurrence of positive reinforcement to increase appropriate behaviors rather than running the risk of it. Theory that found from this research can be additional resources for the writer.57 His research is only focus on the punishment that has the opinion that punishment is better than rewards. However, this research has the same balance between rewards and punishment in the class.
Another research was conducted by Ilegbusi under the title of An Analysis of The Role of Rewards and Punishment in Motivating School Learning. This research also study about the rewards and punishment used for motivating the students in the class. To be more specific it is answered some question about whether rewards and punishment facilitate or hinder learning and to what extent, how they operate to increase.58 In addition, his study also different with the researcher study because the term of punishment in here is indicating the harmful punishment and it is focus only on the role of rewards and punishment. Whereas this study in not only focus on the role but also the impact and some kind of positive rewards and positive punishment that not harmful for the students.
57John W. Maag, “Rewarded by Punishment: Reflections on the Disuse of Positive Reinforcement in Schools”, The Council for Exceptional Children, vol. Vol. 67, No. 2, (2001), p.173–186. 58Ilegbusi, “An Analysis of Th
Other past research comes from Gregory S Ching under the title looking into the issues of rewards and punishment in students. This study is concerned with the way in which rewards and penalties, may or may not, motivate students to engage in learning and change their behavior. And as the result the his research that the positive discipline approach by rewards and punishment in practice often appeared to be on penalties for bad behavior rather than enhancing engagement and motivation.59 Unbalancing between rewards and punishment in his study makes the students often afraid to the teacher and the difference with this study is that it did not tell the way to deliver the rewards and punishment in the class. The research by Pamela Oliver under the title Rewards and Punishments as Selective Incentives for Collective Action: Theoretical Investigations is about positive and negative selective incentives. To be more specific it is discuss about the importance of selective incentives, the difference between individual and collective incentive and the dynamics of positive and negative selective.60 However, it is difference with this study because his study only focus on the giving selective as reward and punishment rather that delivering and the impact of the reward and punishment.
Other study is from Claudia Langa, with the title Rewards and Punishments Role in Teacher-Student Relationship from the Mentor’s Perspective. The purpose of his study is to identify the most efficient
59Ching, “Looking into the issues of rewards and punishment in students”.
modalities of intervening on the child’s disturbing behavior applying the punishment-reward duet. There are also some suggestions for improving pupils’ conduct by applying the most adequate modalities of reducing their
undesirable actions in the school environment.61 In managing classroom, behavior between children and teenager is different. Moreover, this study subject is in secondary high school so that the student’s behavior is different with the children.
Another research was conducted by Lutfiana from UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya under the title of “Problem Implementasi Educative Punishment Untuk Anak Didik Usia Dini dan Upaya Solusinya di TK Zainul Hasan Probolinggo”. This research also studies the educative punishment for the children in kindergarten and its solution.62 In addition, it is also different with the researcher study because educative punishment for children and high school students is different. In addition, it is for the English classroom management that might be able to improve their English skill.
From the previous study above, the researcher concludes that those all previous study have the similarities and the difference with this research. However, this research focuses on analyzing some kind of positive reward and positive punishment, the implementation and the way the teachers deliver the reward and punishment and the impact of positive
61Langa, “Rewards and Punishments Role in Teacher
-Student Relationship from the Mentor’s Perspective”.
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD
This chapter concern on the methodology and the procedure to develop the study. On the research method, the researcher tries to conduct the validity and reliability research by its method and its analysis. The subtitles of this chapter are research design, subject of the study, data collection technique, data analysis technique and research validity.
A. Approach and Research Design
The research will be designed to analyze how the positive rewards and positive punishments manage the English classroom effectively. In addition, it has the correlation with the teacher’s classroom management in teaching English in the class. The researcher also will conduct the research method to find out what kind of positive rewards and positive punishments that commonly used as part of classroom management technique in teaching English and how the teacher use it to the students. Based on the purpose of the study, the researcher will held the research in MTs Jabal Noer Geluran Taman where some of the students have special problem behavior in the class.
quantitative and qualitative research methods in different ways, with each approach adding something to the understanding of the phenomenon.1 Moreover, multimethod research employs different types of data collecting methods for example, both survey and archival data and both number and written data. Multimethod research occurs when the research questions are investigated by using two different data collection procedures (e.g., observations and focus groups.2 On the other word, mixed method research is the research based on the qualitative and quantitative data in spoken or written and number data by the subject of the study.
The data taken also has the characteristic that shown the data is authentic, reliable, valid, systematic, practice. Hence, the researcher will analyze the students in MTs Jabal Noer Geluran Taman to get the qualitative and quantitaive data. Thus, in mixed method research, the research will develop some basic question about what and how the research happened and how to solve it, who are involved in the research and where the research will be held.
B. Subject of the Study
The study will concern on the teacher’s classroom management that used positive rewards and the positive punishments in teaching English. The researcher will choose MTs Jabal Noer Geluran Taman as the participants and the subject of the study. MTs Jabal Noer Geluran Taman is an Islamic junior high school that has the special condition than other school. In this
1
Donald Ary, Lucy Cheser Jacobs, and Chris Sorensen, Introduction to Research in Education, Eight edition (Wadsworth: Cengage Learning, 2010), p. 559.
2
school, most of the students are also the students in Islamic boarding school of Jabal Noer. As the Islamic boarding school, the rewards and punishments system is normally occurred as the rule. Because of this condition, this school is the most suitable one to have the research.
There are many teachers in this school, but the researcher interested in how Fitria Ulfa S. Pd teaching English that she usually use the rewards and punishments technique. It is because when the researcher doing preliminary research in PPL 2, Mrs. Fitria has a good performance and ability in managing the student’s behavior and classroom. Thus, the researcher will have to interview and observe the teacher to collect the data. Besides the teacher as the subject of the study, the students in seven classes also included as well as the subject of the study. There are two class of female and male class in the seven classes, each class has 40-45 students. The students will be needed for the interview as the other reference of the data.
C. Data and Source of the Data
1. Type of Data
a. Primary data
Primary data is the main data that the researcher from the subject of the study. The primary data was collected by doing some observation and interview. The researcher will observe the teacher in teaching English and her classroom management technique. In addition, the researcher does the interview to the teacher as well as to the students.
The secondary data is the supporting data obtained from sources, such as document related to classroom management and reward and punishment. Some of document that the researcher needs are the student’s notebook, the teacher’s behavior report, and the student’s attendance report and so on. Furthermore, the researcher takes pictures and video records as proof of behavior problems occurred in classroom. Some theories were also taken by the researcher to support the data obtained.
2. Source of Data
The sources of both primary and secondary data are from teachers, students, and the document as the supporting data at MTs Jabal Noer Geluran. The primary data was taken from class observation and interview to teacher and students. On the other hand, the secondary data was obtained by the copies of documents that related to classroom management and students behavior.
D. Data Collection Technique
The data collection or the procedure of development is by some steps, the researcher follow the theory of Cressweell to conduct the mixed method reserach. The most common sources of the data include interviews, observations, and documents.3
3